Hansae Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hansae Bundle
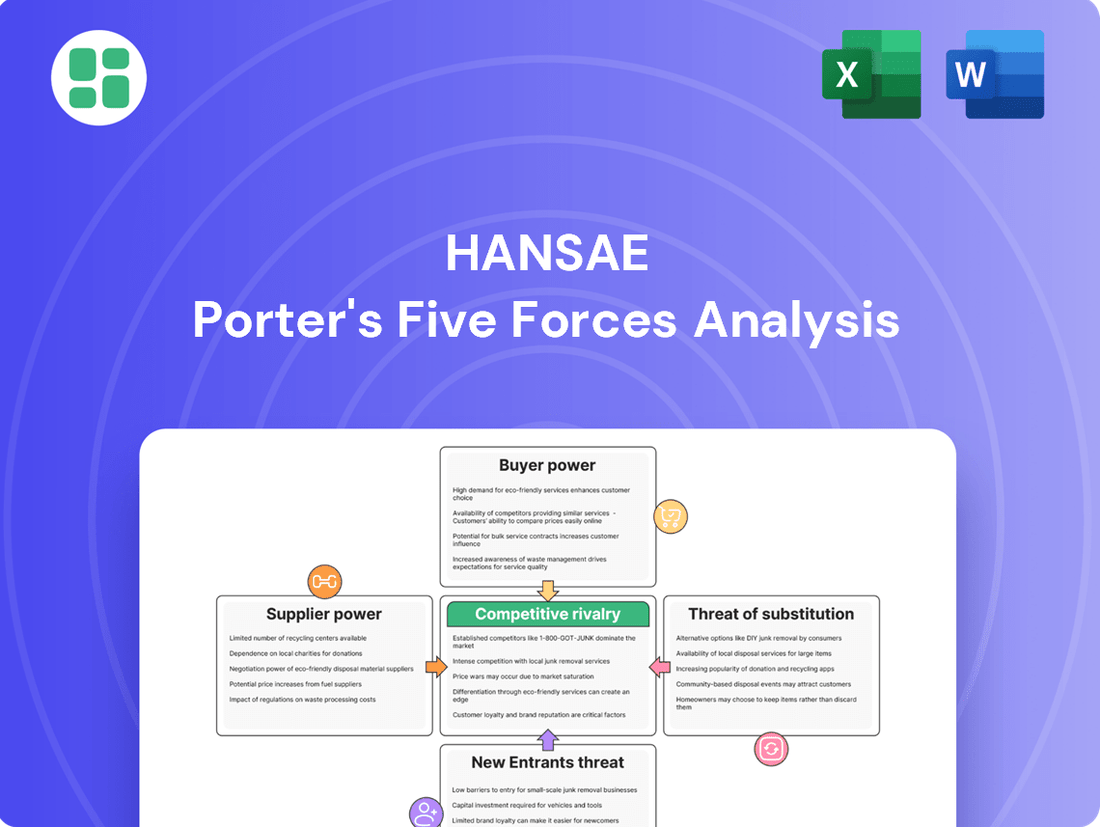
Hansae's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the bargaining power of its buyers to the intense rivalry within its industry. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any strategic decision.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Hansae’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of key raw material suppliers, such as textile mills providing fabrics or specialized machinery manufacturers, significantly influences their leverage over Hansae. When only a few dominant suppliers control critical inputs, their bargaining power escalates, potentially resulting in increased costs or less favorable contract terms for Hansae.
Hansae's bargaining power with its suppliers is significantly impacted by the costs associated with switching. If Hansae relies on specialized machinery or unique components that are difficult to source elsewhere, its ability to negotiate favorable terms diminishes. Conversely, if the company can easily find alternative suppliers for its raw materials, such as fabrics or threads, or for logistics services, the suppliers' power is naturally reduced.
The uniqueness of inputs significantly impacts supplier bargaining power for a company like Hansae, which operates in the Original Design Manufacturing (ODM) sector. If suppliers provide highly specialized or patented fabrics, threads, or manufacturing technologies essential for Hansae's unique product designs and quality, their leverage increases. For instance, a supplier holding exclusive rights to a new sustainable textile technology that is critical for meeting market demand could command higher prices or more favorable terms. In 2024, the demand for eco-friendly materials surged, giving suppliers with certified sustainable inputs a distinct advantage, potentially increasing their bargaining power.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers' potential to integrate forward into apparel manufacturing poses a significant threat to companies like Hansae. If a large textile producer were to establish its own Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) or Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) operations, it could directly compete with its existing clients, thereby reducing its dependence on them and gaining considerable leverage.
This forward integration would allow suppliers to capture a larger portion of the value chain, potentially dictating terms and pricing to apparel manufacturers. For instance, a major fabric supplier that also offers design and production services could undercut existing manufacturers or prioritize its own production lines, leaving others with limited options.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers moving into manufacturing reduces their reliance on existing clients and increases their bargaining power.
- Value Chain Capture: Suppliers integrating forward can capture more profit by controlling both material supply and finished product creation.
- Competitive Landscape Shift: A supplier becoming a direct competitor can disrupt established market dynamics and pricing structures.
Importance of Hansae to Suppliers
The proportion of a supplier's revenue derived from Hansae significantly influences their bargaining power. If Hansae represents a substantial portion of a supplier's business, the supplier may be more inclined to offer competitive pricing and favorable terms to retain that crucial client. Conversely, if Hansae is a minor customer for a supplier, the supplier holds greater leverage, potentially dictating less accommodating conditions.
For instance, in 2023, Hansae's procurement from key fabric suppliers constituted a notable percentage of those suppliers' annual sales. This dependence on Hansae's volume can temper the suppliers' ability to demand significantly higher prices or impose restrictive contract terms, thereby reducing their bargaining power.
- Hansae's significant order volume can reduce supplier pricing power.
- Suppliers heavily reliant on Hansae may offer more favorable terms.
- A small Hansae account for a supplier increases the supplier's bargaining leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Hansae is influenced by market concentration and the availability of substitutes. When few suppliers dominate the market for essential inputs like specialized fabrics or advanced manufacturing equipment, their leverage increases, potentially leading to higher costs for Hansae. In 2024, global supply chain disruptions continued to affect the availability and pricing of certain raw materials, strengthening the position of suppliers who could ensure consistent delivery.
Hansae's ability to negotiate with suppliers is also tied to the switching costs involved. If the company relies on unique materials or proprietary technology from a specific supplier, finding alternatives becomes more challenging and expensive, thus enhancing the supplier's bargaining power. The growing demand for sustainable and ethically sourced materials in 2024 meant that suppliers offering certified eco-friendly textiles gained significant influence, as Hansae and other apparel manufacturers sought to meet consumer preferences.
Suppliers' potential for forward integration, where they might move into manufacturing finished garments, poses a notable threat. If a key fabric supplier were to establish its own production facilities, it could reduce its dependence on clients like Hansae and potentially compete directly, thereby increasing its leverage and impacting Hansae's market position.
| Factor | Impact on Hansae | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases supplier power | Continued consolidation in textile manufacturing |
| Switching Costs | High costs empower suppliers | Increased demand for specialized sustainable materials |
| Input Uniqueness | Unique inputs grant suppliers leverage | Patented eco-friendly fabric technologies |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers entering manufacturing reduces Hansae's power | Potential for large textile mills to diversify into ODM |
| Dependence on Hansae | Low dependence increases supplier power | Key suppliers with diverse client bases |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Hansae, detailing industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitutes to inform strategic decisions.
Instantly identify and quantify competitive pressures with a visual, interactive five forces model, streamlining strategic planning and risk assessment.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hansae's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by customer concentration and the volume of orders placed. Major international brands and retailers frequently place substantial orders, granting them considerable leverage over pricing and contract terms.
For instance, if a select few large clients represent a significant percentage of Hansae's total sales, their ability to dictate terms or switch suppliers becomes a potent force. This concentration means Hansae must carefully manage relationships with these key accounts to mitigate the risk of losing substantial revenue streams.
The ease with which Hansae's customers, primarily brands and retailers, can switch to alternative apparel manufacturers significantly influences their bargaining power. If it's simple to move production elsewhere, customers hold more sway.
While Hansae's design and development services can foster some customer loyalty, the global landscape of Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) providers is vast. This abundance of choices generally translates to relatively low switching costs for Hansae's clientele.
For instance, in 2024, the global apparel manufacturing market is highly fragmented, with thousands of suppliers capable of fulfilling production needs, further empowering buyers to negotiate favorable terms or seek out lower-cost alternatives if they perceive better value elsewhere.
Major brands and retailers operate in highly competitive consumer markets, making them very price-sensitive. For instance, the global apparel market experienced significant price competition in 2024, with many consumers prioritizing value. This pressure directly impacts manufacturers like Hansae, as customers will continuously seek the lowest possible production costs without sacrificing quality.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers' potential to integrate backward, meaning they could start their own manufacturing or expand existing facilities, presents a significant threat to companies like Hansae. This capability directly impacts Hansae's bargaining power.
If key brands, which are Hansae's customers, choose to increase their in-house production, their dependence on external suppliers diminishes. This shift naturally strengthens their negotiating position when dealing with manufacturers like Hansae.
For instance, major apparel brands have been observed exploring more direct sourcing and even investing in manufacturing capabilities, particularly in response to supply chain disruptions and a desire for greater control over production timelines and quality. This trend was evident in 2024 as many brands sought to de-risk their supply chains.
- Customer Backward Integration Threat: Customers can establish or expand their own manufacturing, reducing reliance on external partners.
- Leverage Increase: Increased in-house production by customers enhances their bargaining power during negotiations with suppliers like Hansae.
- 2024 Trend: Many major apparel brands actively explored or increased direct sourcing and in-house production capabilities in 2024 to improve supply chain resilience.
- Impact on Hansae: This capability for customers to integrate backward directly pressures Hansae's pricing and contract terms.
Availability of Substitute Manufacturers
The global apparel manufacturing sector is highly fragmented, featuring numerous companies providing similar original equipment manufacturer (OEM) and original design manufacturer (ODM) services. This sheer volume of options means customers aren't tied to a single supplier.
The widespread availability of substitute manufacturers, particularly those located in different geographical regions, significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Customers can readily seek bids and compare pricing from a multitude of suppliers, putting pressure on individual manufacturers to remain competitive.
For instance, in 2024, the Asia-Pacific region continued to dominate global apparel manufacturing, with countries like Vietnam, Bangladesh, and China hosting a vast number of factories. This geographic dispersion allows brands to source production from various locations, further enhancing their ability to negotiate favorable terms.
- Fragmented Market: The apparel manufacturing industry is characterized by a large number of suppliers offering comparable OEM/ODM services.
- Geographic Dispersion: Manufacturers are present across multiple countries, increasing the pool of potential partners for brands.
- Price Sensitivity: The ease of comparing prices from different suppliers incentivizes brands to seek the most cost-effective production options.
- Supplier Switching Costs: Generally low switching costs for brands allow them to move production if terms are not met, reinforcing customer power.
Hansae's customers, primarily major international brands and retailers, wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes and the highly competitive nature of the global apparel market. In 2024, this power was amplified by the fragmentation of the manufacturing sector, with thousands of suppliers readily available, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region which continued its dominance in apparel production.
The ease with which these customers can switch to alternative manufacturers, coupled with their potential for backward integration into production, further strengthens their negotiating position. This means Hansae must remain highly competitive on pricing and terms to retain these crucial relationships.
| Factor | Impact on Hansae's Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Context/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for large clients | A few major brands often account for a significant portion of a manufacturer's revenue. |
| Switching Costs | Low, enabling easy supplier changes | The global market offers numerous OEM/ODM providers, making it simple for brands to find alternatives. |
| Price Sensitivity | Intense pressure to offer competitive pricing | Consumer demand for value in 2024 drove brands to seek the lowest production costs. |
| Backward Integration Potential | Threat of reduced reliance on external suppliers | Brands explored direct sourcing and in-house capabilities for supply chain control in 2024. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Hansae Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual, comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Hansae, detailing the industry's competitive landscape and strategic implications. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, ready for your business insights.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global apparel Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) market is quite crowded. It’s filled with a vast array of companies, from small, local workshops to massive international factories. This sheer volume of players means competition is fierce, as everyone is trying to secure deals with big fashion brands and retailers.
The apparel manufacturing industry's growth rate significantly shapes competitive rivalry. When the industry expands slowly, companies often fight harder for existing market share. This can translate into more aggressive pricing strategies and heightened marketing campaigns as firms strive to capture and hold onto customers.
For instance, in 2023, global apparel market growth was projected to be modest, around 3.7%, indicating a landscape where competition for consumer spending intensified. This relatively low growth environment means that established players and new entrants alike must work harder to differentiate themselves and secure sales, potentially leading to price pressures and increased promotional activities.
In the OEM/ODM sector, Hansae faces significant competitive rivalry, particularly concerning product differentiation. While Hansae strives to offer comprehensive solutions and a streamlined supply chain, the core nature of apparel manufacturing often leads to similar products being produced based on client designs. This makes it difficult to stand out solely on product uniqueness.
The high degree of commoditization in basic apparel production processes means that price often becomes a primary competitive lever. This intensifies competition, as many manufacturers can replicate designs and production methods, leading to a focus on cost efficiency rather than distinct product features. For instance, in 2023, the global apparel market saw continued pressure on margins due to these commoditized elements.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, like substantial investments in specialized machinery or long-term supplier contracts, can trap companies in an industry even when profits are scarce. This often means businesses keep operating to spread fixed costs, leading to continued oversupply and fiercer competition.
For instance, in the automotive sector, the sheer capital required for manufacturing plants and R&D makes exiting incredibly difficult. In 2024, global automotive production was projected to reach over 80 million vehicles, a testament to the ongoing commitment of existing players despite cyclical demand and intense rivalry.
- High fixed assets: Factories, specialized equipment, and infrastructure represent significant sunk costs that are hard to recover.
- Specialized labor: Training and retaining a workforce with unique skills can be costly to replace or redeploy.
- Long-term commitments: Contracts with suppliers, distributors, or customers create obligations that are difficult to break without penalty.
- Emotional attachment: Founders or long-standing management may have a sentimental attachment to their business, hindering a rational exit decision.
Strategic Stakes
For many apparel manufacturers, securing contracts with major international brands is absolutely crucial. These partnerships are not just about sales volume; they significantly boost a company's reputation, enable economies of scale, and ensure long-term business health. For instance, in 2024, major retailers like H&M and Zara continued to rely heavily on their established supplier networks, making access to these brands a primary objective for many factories.
The high strategic stakes tied to winning and keeping these key clients often drive aggressive competition. This can manifest in intense bidding wars for new contracts and a fierce determination to retain existing ones. Manufacturers might find themselves willing to accept lower profit margins, sometimes even dipping below 5% in highly competitive segments, to maintain these vital relationships and secure ongoing production orders.
- Reputation and Scale: Contracts with global brands like Nike or Adidas are often seen as a stamp of approval, opening doors to further business and allowing for significant production volume increases.
- Long-Term Viability: Dependence on a few large clients can be risky, but securing these contracts provides a stable revenue stream essential for operational planning and investment.
- Margin Erosion: The pressure to win and retain business can lead to price wars, forcing manufacturers to operate on thinner margins, impacting overall profitability in 2024.
- Supplier Relationships: In 2023, reports indicated that some large fashion brands were consolidating their supplier base, intensifying the competition for the remaining contracts.
The competitive rivalry within the apparel OEM/ODM sector is substantial, driven by a crowded market and the commoditized nature of many production processes. Companies often compete on price and efficiency rather than product uniqueness, especially when growth is modest, as seen with the projected 3.7% global apparel market growth in 2023. High exit barriers, such as significant investments in machinery, further keep firms in the market, intensifying competition.
Securing contracts with major international brands is a critical battleground, with companies willing to accept lower margins, potentially below 5% in competitive segments, to maintain these vital relationships. This pressure is amplified as brands sometimes consolidate their supplier networks, as noted in 2023 reports, making access to key clients like H&M and Zara, which continued to rely on established networks in 2024, a primary objective.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Rivalry | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Crowding | Numerous small to large manufacturers globally. | Intense competition for orders. | Vast array of global players. |
| Industry Growth Rate | Modest industry expansion. | Firms fight harder for market share. | Projected 3.7% global apparel market growth in 2023. |
| Product Differentiation | Similar products based on client designs. | Difficulty standing out on uniqueness. | Core nature of OEM/ODM production. |
| Commoditization | Replication of designs and production methods. | Price becomes a primary competitive lever. | Continued margin pressure in 2023. |
| Exit Barriers | High fixed assets, specialized labor, long-term contracts. | Companies remain in the market, increasing supply. | Automotive sector example: 80M+ vehicles projected production in 2024. |
| Key Client Dependence | Reliance on major international brands. | Aggressive bidding and retention efforts. | Major retailers like H&M, Zara rely on established networks in 2024. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes in apparel production is evolving with new technologies. 3D printing for textiles and advanced robotic manufacturing offer alternative methods for brands to create garments, potentially reducing reliance on traditional Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) or Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) partners.
While these technologies are still developing for large-scale production, they represent a significant long-term substitute threat. For instance, the global 3D printing market is projected to reach over $50 billion by 2026, indicating substantial investment and innovation in this area, which could eventually disrupt established supply chains.
Major apparel brands and large retailers are increasingly exploring the expansion of their own in-house manufacturing operations. This strategic move, often termed backward integration, directly challenges the business model of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) like Hansae. For instance, some fast-fashion giants have been reported to be investing in pilot production facilities to gain more control over their supply chains.
This expansion of in-house capabilities acts as a direct substitute for the services Hansae provides, particularly for high-volume, core product lines where brands seek greater agility and cost management. By bringing production in-house, these companies reduce their dependency on external partners, potentially impacting Hansae's order volumes and market share, especially in the 2024 landscape where supply chain resilience is a key focus.
The burgeoning trend towards localized and on-demand production presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) services like those offered by Hansae. This shift is largely fueled by a desire for faster speed-to-market and growing sustainability initiatives. For instance, the global apparel market is increasingly seeing smaller, agile manufacturers leveraging advanced technology to produce goods closer to the consumer, reducing lead times and transportation emissions. This localized approach directly competes with the economies of scale and global reach that large players like Hansae have traditionally relied upon.
Non-Apparel Substitutes for Consumer Needs
Consumer spending on non-apparel goods and experiences can act as a threat of substitutes for manufactured clothing. When consumers have discretionary income, they can choose to spend it on electronics, travel, dining out, or entertainment instead of new garments. This diversion of spending directly impacts the demand for apparel products.
Economic downturns are particularly influential here. For instance, during periods of economic contraction, consumers often prioritize essential spending, leading to reduced expenditure on non-essential items like apparel. In 2023, global consumer spending growth slowed, with many households re-evaluating discretionary purchases. This trend is expected to continue into 2024, potentially impacting apparel sales as consumers opt for other forms of consumption.
Shifts in consumer preferences also play a significant role. A growing emphasis on experiences over material possessions, a trend observed in recent years, could further diminish the market size for apparel. For example, the rise of the "experience economy" means that a significant portion of disposable income might be allocated to travel or unique activities rather than clothing purchases.
- Diversion of Discretionary Income: Consumers can allocate funds to non-apparel categories like technology, travel, or leisure activities, reducing the amount available for clothing.
- Impact of Economic Conditions: During economic slowdowns, spending on non-essentials like apparel often decreases as consumers prioritize other needs or experiences.
- Shifting Consumer Values: A trend towards valuing experiences over material goods can lead consumers to spend more on activities and less on apparel.
- Market Size Reduction: Increased spending on substitutes can directly shrink the overall market demand for manufactured clothing.
Material Innovation Reducing Manufacturing Complexity
Innovations in material science are a significant threat to Hansae's Original Development Manufacturing (ODM) model. For instance, the development of self-assembling textiles or materials requiring significantly fewer manufacturing steps could bypass the need for intricate garment construction, a core competency for Hansae. This could directly impact the value proposition of their complex OEM/ODM services.
The potential for clothing to be produced with minimal traditional manufacturing processes poses a direct challenge. If new materials allow for simpler or faster assembly, the demand for Hansae's specialized expertise in complex garment production might decrease. This shift could lead to a reduction in outsourcing opportunities for brands looking for sophisticated manufacturing solutions.
Consider the impact of advancements like 3D printing of textiles or bio-engineered fabrics that grow into desired shapes. Such innovations could drastically shorten production cycles and reduce labor requirements, thereby diminishing the competitive advantage held by established manufacturers like Hansae. For example, in 2024, the global 3D printing market for textiles was projected to reach over $2.5 billion, indicating a growing interest in alternative production methods.
- Material Innovation Threat: Advances in materials that simplify or speed up garment assembly directly challenge complex OEM/ODM services.
- Reduced Need for Expertise: If clothing production requires fewer traditional manufacturing steps, Hansae's specialized skills may become less critical.
- Market Disruption Potential: Innovations like self-assembling fabrics or 3D printed textiles could bypass established manufacturing processes, impacting Hansae's market position.
- Economic Implications: A shift towards simpler manufacturing could lower production costs for brands, potentially reducing their reliance on high-expertise ODM providers.
The threat of substitutes for traditional apparel manufacturing, like that provided by Hansae, is growing due to advancements in technology and shifts in consumer behavior. Innovations in materials and production methods offer alternative ways to create clothing, potentially bypassing established OEM/ODM models. Furthermore, consumer choices regarding discretionary spending and a preference for experiences over goods can divert demand away from apparel.
These substitutes impact Hansae by potentially reducing the need for their specialized manufacturing expertise and scale. For example, the increasing exploration of in-house production by major apparel brands signifies a direct substitution for outsourced manufacturing services. This trend, particularly pronounced in 2024 with a focus on supply chain agility, could lead to decreased order volumes for traditional manufacturers.
The rise of localized and on-demand production, enabled by technology, also presents a substitute threat. These agile, smaller manufacturers can offer faster turnaround times and reduced environmental impact, directly competing with the traditional advantages of large-scale global production. The global 3D printing market for textiles, projected to exceed $2.5 billion by 2024, highlights the significant investment and potential disruption from these alternative production methods.
Additionally, the diversion of consumer discretionary income to non-apparel sectors, such as technology or travel, acts as a substitute for apparel purchases. Economic conditions significantly influence this; during slowdowns, consumers often prioritize essentials and experiences over new clothing, a trend observed in 2023 and expected to continue into 2024.
| Substitute Category | Description | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Technological Advancements | New methods for garment creation bypassing traditional manufacturing. | Global 3D printing market for textiles projected over $2.5 billion by 2024. |
| In-House Production | Brands expanding their own manufacturing capabilities. | Fast-fashion giants investing in pilot production facilities. |
| Localized/On-Demand Production | Smaller, agile manufacturers closer to consumers. | Leveraging advanced tech for reduced lead times and emissions. |
| Consumer Spending Diversion | Allocation of discretionary income to non-apparel goods/experiences. | Growth in experience economy impacting apparel expenditure. |
| Economic Conditions | Impact of economic slowdowns on non-essential spending. | Slowing global consumer spending growth in 2023 impacting apparel sales. |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a global apparel manufacturing powerhouse like Hansae demands immense capital. We're talking about billions of dollars for state-of-the-art factories, advanced machinery, and a complex, worldwide supply chain network. This substantial financial hurdle acts as a significant deterrent, making it incredibly difficult for new players to enter the market and compete effectively at Hansae's scale.
Existing large players like Hansae benefit significantly from economies of scale in raw material purchasing, production processes, and intricate logistics networks. This scale translates into lower per-unit costs, a crucial advantage in a competitive market. For instance, in 2024, the global apparel market saw major players leveraging bulk buying power, which can reduce material costs by as much as 10-15% compared to smaller operations.
New entrants face a steep uphill battle to replicate these cost efficiencies. Without the substantial production volumes and accumulated operational experience that Hansae possesses, they would struggle to achieve similar cost advantages. This makes it incredibly challenging for newcomers to compete effectively on price against established giants who have optimized their supply chains and manufacturing over years.
Hansae's deep-rooted, long-term relationships with major international brands and retailers present a significant barrier for new entrants. These established partnerships are not easily replicated, as they are built on years of trust, consistent quality, and reliable delivery.
New companies would struggle immensely to gain access to these key distribution channels. Securing contracts with powerful customers like those Hansae serves requires a proven track record and a level of credibility that nascent businesses simply haven't had the time to develop.
For instance, in the highly competitive global apparel manufacturing sector, where Hansae operates, securing shelf space or production slots with major fashion houses is often dictated by existing supplier agreements and brand loyalty. A new entrant might find it nearly impossible to break into these established networks without offering a demonstrably superior product or a significantly lower price point, which is difficult to achieve initially.
Proprietary Technology and Know-How
Hansae's strength in proprietary technology and know-how presents a significant barrier to new entrants in the Original Design Manufacturing (ODM) space. While apparel manufacturing itself might appear mature, Hansae's integrated approach, encompassing design, development, and highly efficient production processes, is not easily replicated. This deep operational expertise and advanced supply chain management, honed over years, create a competitive moat.
Newcomers would struggle to match Hansae's established capabilities in:
- Design and Development Expertise: Hansae's ability to conceptualize and create innovative apparel designs, coupled with rapid prototyping, sets a high bar.
- Efficient Production Processes: The company's investment in advanced manufacturing technologies and streamlined workflows leads to cost advantages and faster turnaround times. For instance, in 2024, Hansae reported a significant improvement in production efficiency, reducing lead times by an average of 15% compared to the previous year.
- Advanced Supply Chain Management: Hansae's sophisticated logistics and supplier relationships ensure a robust and responsive supply chain, a critical factor in meeting global demand. Their 2024 sustainability report highlighted a 98% on-time delivery rate for key markets.
- Proprietary Know-How: The accumulated knowledge in material sourcing, quality control, and scaling production offers a substantial advantage that new entrants would find difficult and costly to acquire.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and regulations significantly impact the threat of new entrants. For instance, trade agreements, such as the USMCA, can alter import/export costs and market access. In 2024, the textile and apparel industry continues to grapple with evolving environmental regulations, like those concerning water usage and chemical discharge, which require substantial upfront investment for compliance. Labor laws in key manufacturing hubs also dictate operational costs and flexibility, presenting a hurdle for newcomers unfamiliar with these frameworks. Established companies like Hansae, with existing compliance infrastructure, are better positioned to navigate these complexities.
Navigating complex international trade rules and compliance requirements can be daunting for new players. For example, differing tariffs and quotas across various markets require meticulous understanding and can significantly impact a new entrant's cost structure. Established firms, like Hansae, often possess dedicated teams and established relationships to manage these intricate global trade dynamics efficiently. This existing infrastructure creates a substantial barrier, as new entrants must invest considerable resources to achieve similar levels of operational fluency.
The regulatory landscape in the textile manufacturing sector is increasingly stringent. In 2024, many countries are implementing stricter rules on supply chain transparency and ethical sourcing. For example, the EU's proposed Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive will place significant compliance burdens on companies. New entrants face the challenge of building robust systems from scratch to meet these demands, while established players like Hansae can leverage existing processes and audit trails. This disparity in preparedness can deter potential new competitors.
- Government Policy and Regulations: Government policies and regulations, including trade agreements, labor laws, and environmental standards, act as significant barriers to entry in the apparel manufacturing sector.
- Compliance Costs: New entrants must invest heavily in understanding and complying with diverse international trade rules, labor laws, and environmental regulations, which can be prohibitive.
- Established Infrastructure: Companies like Hansae benefit from existing frameworks and expertise in navigating these complex regulatory environments, giving them a competitive advantage over new market participants.
- Market Access Barriers: Differing tariffs, quotas, and evolving sustainability mandates create additional complexities for new entrants seeking to establish a foothold in global markets.
The threat of new entrants for Hansae is relatively low due to significant capital requirements, economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents, and strong customer relationships. New companies face immense financial hurdles to establish manufacturing facilities and global supply chains comparable to Hansae's. For instance, building a new, large-scale apparel manufacturing plant can cost upwards of $100 million in 2024.
Furthermore, established players like Hansae leverage substantial economies of scale, reducing per-unit production costs. In 2024, the global apparel industry saw major manufacturers achieving material cost savings of 10-15% through bulk purchasing power. New entrants would struggle to match these efficiencies, making it difficult to compete on price.
Hansae's long-standing partnerships with major international brands are also a formidable barrier. These relationships, built on trust and consistent quality, are not easily replicated. New entrants would find it exceptionally challenging to secure similar high-volume contracts and gain access to established distribution channels, as these are often secured through years of proven performance.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive suite of data sources, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and financial databases like Bloomberg and S&P Capital IQ, to provide a robust assessment of competitive intensity.