Hancock Whitney Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hancock Whitney Bundle
Hancock Whitney navigates a banking landscape shaped by intense rivalry, evolving customer demands, and the ever-present threat of new digital entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any strategic decision.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hancock Whitney’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hancock Whitney's reliance on specialized technology providers for core banking, online platforms, and cybersecurity means these suppliers can wield significant influence. The bargaining power of these tech vendors is often moderate to high, particularly when banks are locked into proprietary systems with substantial switching costs and deep customization.
The financial services industry, including institutions like Hancock Whitney, frequently grapples with the inertia of legacy systems. This often necessitates ongoing investment with existing suppliers, which can curtail flexibility and strengthen the suppliers' negotiating position. For instance, in 2024, the global FinTech market was projected to reach over $1.5 trillion, highlighting the scale and importance of these technology partners.
Skilled financial professionals, especially in wealth management, data analytics, and cybersecurity, are crucial suppliers for institutions like Hancock Whitney. The high demand for this expertise grants these employees considerable bargaining power, directly impacting compensation packages.
In 2024, the competition for top-tier financial talent intensified. Regional banks such as Hancock Whitney find themselves in direct competition with larger national banks and agile fintech companies, often leading to increased labor costs as they strive to attract and retain specialized skills.
While individual depositors typically hold minimal sway, large corporate clients and high-net-worth individuals can leverage their significant balances to negotiate more favorable interest rates and premium services from Hancock Whitney. This segment of the funding market is crucial for managing overall funding costs.
Hancock Whitney benefits from a robust and diversified deposit base, which generally provides stability and helps mitigate funding cost volatility. However, the broader banking sector, particularly midsize and regional institutions like Hancock Whitney, has contended with elevated interest expenses on their interest-bearing deposits throughout 2024.
Data and Analytics Providers
Data and analytics providers wield significant bargaining power, especially as financial institutions increasingly rely on data for strategic advantage. Banks require precise and up-to-the-minute information for everything from planning their next moves to catching fraudulent activities and tailoring customer interactions. This reliance elevates the importance of these providers.
The market for financial data is substantial. For instance, the global big data and business analytics market was projected to reach over $300 billion in 2024, a testament to the critical role data plays across industries, including banking.
- High Demand for Specialized Data: Banks need granular market data, customer behavior analytics, and sophisticated risk assessment tools that only specialized providers can offer.
- Switching Costs: Integrating new data systems can be costly and time-consuming, making banks hesitant to switch providers, thereby strengthening the existing suppliers' position.
- Data Quality and Timeliness: The accuracy and speed of data delivery are paramount for competitive decision-making, giving providers with superior offerings more leverage.
- Consolidation in the Provider Market: As the data analytics sector matures, consolidation can lead to fewer, larger players, further concentrating bargaining power.
Payment Network Providers
Payment network providers like Visa and Mastercard hold significant sway over financial institutions such as Hancock Whitney. Their near-monopolistic status in processing transactions grants them considerable leverage in setting fees and dictating service agreements, impacting Hancock Whitney's revenue streams from payment services.
These networks are critical infrastructure for any bank offering debit and credit card services. The increasing trend of embedded finance, where payment functionalities are integrated directly into non-financial platforms, further solidifies the dependence of banks on these established payment gateways.
- Visa and Mastercard dominate global payment networks.
- Their oligopolistic structure allows for strong pricing power.
- Hancock Whitney relies on these networks for its transaction processing services.
- Embedded payments increase reliance on these infrastructure providers.
Suppliers of specialized technology, skilled financial talent, and critical data analytics tools can exert considerable bargaining power over Hancock Whitney. This influence is amplified by high switching costs associated with legacy systems and the intense competition for specialized expertise in the evolving FinTech landscape of 2024. The reliance on dominant payment networks like Visa and Mastercard further concentrates supplier leverage, impacting fee structures and service agreements.
| Supplier Type | Hancock Whitney Reliance | Bargaining Power Factors | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers | Core banking, online platforms, cybersecurity | Proprietary systems, switching costs, customization | FinTech market projected over $1.5 trillion |
| Skilled Financial Professionals | Wealth management, data analytics, cybersecurity | High demand, competition from national banks & fintechs | Intensified competition for talent |
| Data & Analytics Providers | Strategic planning, fraud detection, customer interaction | Need for granular data, integration costs, data quality | Big data & business analytics market projected over $300 billion |
| Payment Networks (Visa, Mastercard) | Transaction processing for card services | Dominant market share, oligopolistic structure | Growth of embedded finance increasing dependence |
What is included in the product
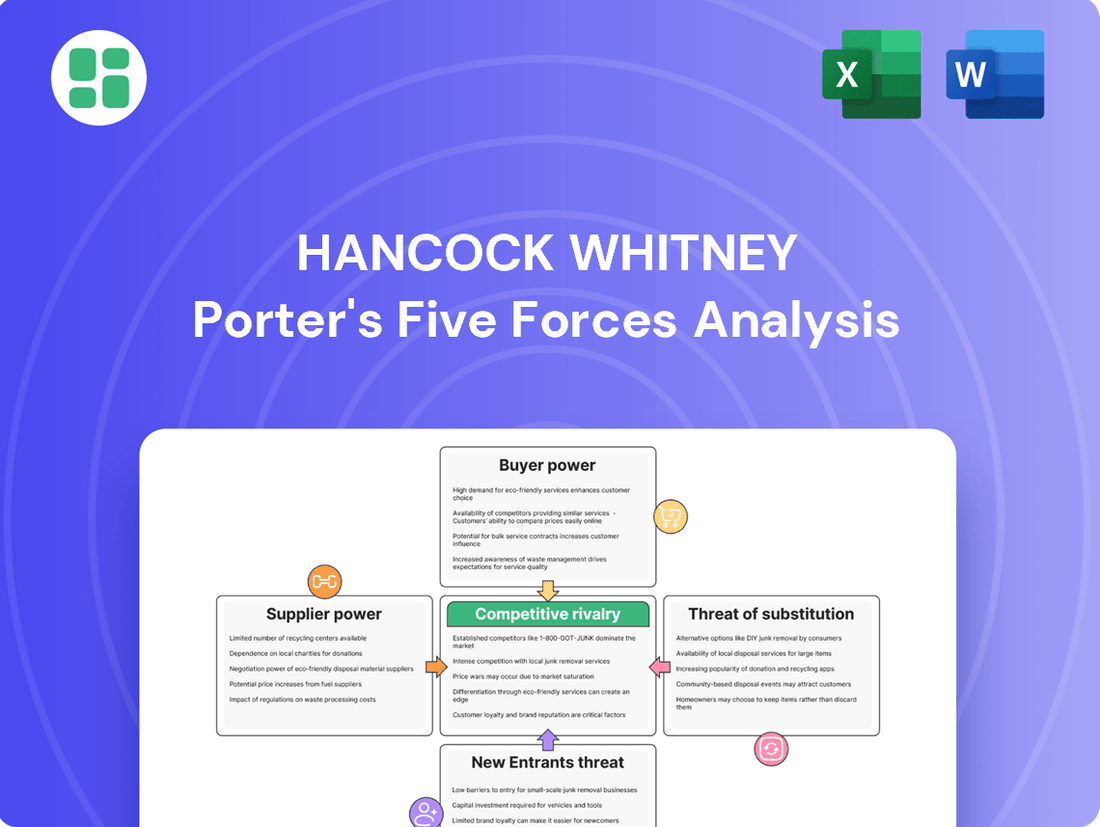
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Hancock Whitney, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces chart, simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic clarity.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual retail customers, like those who deposit money or take out small loans, typically don't have a lot of sway. This is because many banking products are pretty standard, and there are tons of banks to choose from. In 2023, the average savings account interest rate remained relatively low, often below 1%, giving customers little leverage to negotiate better terms.
However, the rise of online and mobile banking has changed things a bit. These platforms make it much easier for customers to compare offerings and switch banks if they find a better deal. This increased accessibility to information and simplified switching process has given individual customers a slightly stronger voice in the market.
Small businesses, though individually less influential than large corporations, exert moderate bargaining power. They often prioritize personalized service and local market understanding, areas where regional banks like Hancock Whitney can excel. This focus on tailored relationships can give them a degree of leverage.
The availability of alternative financing options further shapes their power. With numerous online lenders and credit unions offering competitive rates and faster approvals, small businesses have more choices. For instance, in 2023, the Small Business Administration (SBA) reported approving over $40 billion in loans, indicating a robust alternative lending landscape that empowers borrowers.
Large commercial and corporate clients wield considerable influence over Hancock Whitney. Their substantial transaction volumes allow them to negotiate favorable terms, and their access to a wide array of financial institutions and capital markets means they can easily switch providers if unsatisfied. This puts pressure on Hancock Whitney to offer competitive pricing and services.
Hancock Whitney's strategy to counter this involves cultivating deep relationships through full-service offerings, particularly in relationship lending. By becoming an indispensable partner, the bank aims to increase customer loyalty and reduce the likelihood of clients seeking alternatives. This focus on integrated financial solutions is crucial for retaining these high-value customers.
In 2024, the banking sector saw continued competition for corporate deposits, with average savings account rates hovering around 4.00% to 4.50% for high-yield options, reflecting the bargaining power of large depositors. Hancock Whitney's ability to secure and retain these clients hinges on its capacity to offer more than just competitive rates, emphasizing value-added services and personalized banking relationships.
Wealth Management Clients
Wealth management clients, especially high-net-worth individuals, wield significant bargaining power. Their demand for bespoke services, competitive investment performance, and the ability to switch between multiple providers, including non-bank financial institutions, amplifies this influence.
These clients often have substantial assets, making them highly sought after. For instance, in 2024, the average net worth of clients served by top-tier wealth management firms continued to climb, with many managing portfolios exceeding $1 million. This financial clout allows them to negotiate fees and demand tailored solutions, putting pressure on firms to offer superior value.
- High-Net-Worth Client Influence: Clients with substantial assets can dictate terms due to their financial capacity.
- Demand for Customization: Personalized investment strategies and service offerings are expected, not optional.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of numerous wealth management providers, including fintech alternatives, intensifies client choice and bargaining power.
- Performance Expectations: Clients demand consistent, competitive returns, holding firms accountable for investment outcomes.
Digital-First Customers
Digital-first customers wield significant bargaining power. Their ability to easily compare offerings from neobanks and fintechs, coupled with reduced switching costs, amplifies their influence. Hancock Whitney's strategic investments in robust digital platforms are therefore essential for customer retention in this segment.
This trend is evident in the increasing adoption of digital banking. For instance, by the end of 2023, over 70% of U.S. bank customers reported using mobile banking for at least some of their transactions, a figure expected to climb further. This digital engagement directly translates to heightened customer expectations and a greater willingness to explore alternative providers if their needs aren't met.
- Digital-first customers can easily switch to competitors offering better rates or user experiences.
- The proliferation of fintech and neobank solutions provides readily available alternatives.
- Hancock Whitney's digital investments are critical to maintaining loyalty and competitive standing.
- Customer retention hinges on providing seamless and superior digital banking services.
Customers' bargaining power at Hancock Whitney is influenced by their size, the availability of alternatives, and their digital sophistication. While individual retail customers have limited leverage, large corporate clients can negotiate favorable terms due to their substantial transaction volumes and access to broader capital markets. In 2024, competition for corporate deposits pushed average savings account rates for high-yield options to around 4.00% to 4.50%, directly reflecting this client power.
Wealth management clients, particularly high-net-worth individuals, also exert considerable influence. Their demand for bespoke services and competitive investment performance, coupled with the ability to switch providers, amplifies their bargaining power. By the end of 2023, the average net worth of clients managed by top wealth firms exceeded $1 million, underscoring their financial clout.
Digital-first customers are increasingly powerful due to the ease of comparing offerings from neobanks and fintechs. By the end of 2023, over 70% of U.S. bank customers used mobile banking, a trend that heightens expectations and encourages exploration of alternatives if needs aren't met.
What You See Is What You Get
Hancock Whitney Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Hancock Whitney Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, providing a comprehensive overview of the competitive landscape. You're looking at the actual document, meaning the detailed examination of industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes is precisely what you'll get. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Hancock Whitney operates in a highly competitive landscape, particularly against large national banks. These behemoths, such as JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America, benefit from significant advantages. For instance, in 2023, JPMorgan Chase reported total assets of $3.9 trillion, dwarfing Hancock Whitney's approximately $35 billion. This vast resource base allows national banks to invest heavily in technology, expand their branch networks, and offer a more comprehensive suite of financial products and services, often at more competitive pricing.
The competitive edge of national banks is further amplified by their extensive marketing reach. They can afford broad advertising campaigns across multiple platforms, building brand recognition and customer loyalty on a scale that regional banks struggle to match. This allows them to attract a wider customer base, from individual depositors to large corporate clients, and to absorb the costs associated with innovation and regulatory compliance more readily than smaller institutions.
Hancock Whitney faces substantial competition from other regional and community banks across its Gulf Coast operating states. These local institutions often leverage deep-rooted community ties and personalized customer service to attract and retain clients, creating a highly competitive environment for both deposits and loans.
For instance, in 2024, the banking landscape in states like Texas and Florida, key markets for Hancock Whitney, continues to feature a multitude of community banks actively vying for market share. These banks frequently differentiate themselves through tailored product offerings and a strong local presence, making it challenging for larger institutions to gain a significant edge solely on scale.
Credit unions present a notable competitive rivalry for banks like Hancock Whitney. Their not-for-profit structure often allows them to offer more attractive rates and lower fees, particularly appealing to individual consumers and small businesses. In 2023, the credit union sector in the U.S. saw continued growth, with total assets reaching over $2.3 trillion, indicating their significant market presence and ability to draw customers seeking community-centric financial services.
Fintech Companies and Neobanks
Fintech companies and neobanks are intensifying competition within financial services, offering specialized, tech-forward solutions. These nimble players are rapidly innovating in areas such as payments, lending, and digital banking, often outperforming traditional institutions in customer experience and operational efficiency.
The competitive landscape is marked by fintechs and neobanks that can quickly adapt and capture market share. For instance, the global fintech market was valued at approximately $110.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, highlighting the disruptive force these companies represent. Hancock Whitney, like other traditional banks, faces pressure to enhance its digital offerings and customer-centricity to remain competitive.
- Rapid Innovation: Fintechs and neobanks introduce new products and services at a faster pace than many legacy banks.
- Customer Experience Focus: These digital-first entities often prioritize user-friendly interfaces and seamless digital journeys.
- Specialized Offerings: Many fintechs focus on niche areas like peer-to-peer lending or international money transfers, carving out distinct market segments.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower overhead costs associated with digital-only operations allow them to offer competitive pricing.
Non-Bank Financial Institutions
Competition for Hancock Whitney also arises from non-bank financial institutions. These include independent mortgage lenders, specialized commercial finance companies, and various investment firms.
These entities often concentrate on particular financial products, frequently offering more streamlined application and approval processes. This focus can attract customers away from the broader service offerings of traditional banks like Hancock Whitney, particularly for specific needs such as mortgages or specialized business financing.
For instance, in 2024, the non-bank mortgage origination market continued to be a significant competitor. While overall mortgage volumes fluctuated, non-bank lenders, known for their agility, captured a substantial share of originations, sometimes exceeding 50% of the market depending on interest rate environments and regulatory shifts.
- Non-Bank Lenders: Focus on specific products like mortgages, often with faster processing.
- Specialized Finance Companies: Cater to niche commercial financing needs, bypassing traditional bank structures.
- Investment Firms: Offer alternative investment and financing solutions that can compete for capital.
- Agility Advantage: Non-banks can adapt more quickly to market changes and customer demands in their specialized areas.
Hancock Whitney faces intense competition from large national banks, regional players, credit unions, fintechs, and non-bank financial institutions. National banks like JPMorgan Chase, with $3.9 trillion in assets in 2023, leverage scale for technology and pricing. Regional banks in key markets like Texas and Florida compete on personalized service and local ties. Credit unions, exceeding $2.3 trillion in assets nationally in 2023, offer attractive rates due to their non-profit status. Fintechs, representing a $110.8 billion market in 2023, drive rapid innovation and superior customer experiences.
| Competitor Type | Key Strengths | 2023/2024 Data Point |
| National Banks | Scale, Technology Investment, Brand Recognition | JPMorgan Chase Total Assets: $3.9 Trillion |
| Regional/Community Banks | Local Presence, Personalized Service | Active competition in Texas and Florida markets |
| Credit Unions | Attractive Rates, Lower Fees, Community Focus | U.S. Credit Union Sector Assets: Over $2.3 Trillion |
| Fintechs/Neobanks | Innovation, Customer Experience, Specialization | Global Fintech Market Value: ~$110.8 Billion |
| Non-Bank Financial Institutions | Product Specialization, Streamlined Processes | Non-bank mortgage lenders captured significant origination share |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Online lending platforms, encompassing peer-to-peer (P2P) and direct online lenders, present a significant threat by offering faster and often more convenient alternatives to traditional bank loans. These platforms cater to both individuals and small businesses seeking quick capital, directly challenging Hancock Whitney's traditional lending operations.
The digital-first approach of these competitors, characterized by streamlined online applications and rapid fund disbursement, appeals to a growing segment of borrowers who prioritize speed and ease of access. For instance, the online lending market saw substantial growth, with some estimates suggesting it could reach hundreds of billions of dollars globally by 2024, indicating a strong and expanding substitute market.
Customers seeking investment, wealth management, and trust services have numerous alternatives to a bank's integrated offerings. Dedicated investment firms, mutual funds, and independent brokerage houses present a significant threat of substitution.
These specialized entities often boast a broader selection of investment products and can project a perception of superior expertise within particular asset classes. For instance, the global assets under management in ETFs and mutual funds reached an estimated $54 trillion in 2024, highlighting the substantial market presence of these substitutes.
The growing prevalence of non-bank Payment Service Providers (PSPs) and digital wallets presents a substantial threat of substitutes for traditional banking services. These platforms, including PayPal, Square, and Venmo, enable seamless peer-to-peer and business-to-consumer transactions, often bypassing traditional bank accounts and credit cards. By 2024, the global digital payments market is projected to reach over $10 trillion, highlighting the significant shift in how consumers and businesses manage their money.
Embedded finance solutions, which integrate financial services directly into non-financial platforms like e-commerce sites or ride-sharing apps, further diminish reliance on core banking functionalities. This trend means that everyday payment needs can be met without direct engagement with a bank. For instance, in 2023, the value of transactions processed through embedded finance in the US alone was estimated to be in the hundreds of billions of dollars.
Direct Corporate Finance
Large corporate clients increasingly bypass traditional bank lending by accessing capital markets directly. This trend is fueled by the availability of alternative funding sources like bond issuance and equity offerings, reducing reliance on banks for substantial financing needs. For instance, in 2024, U.S. non-financial corporations issued over $1.5 trillion in corporate bonds, a significant portion of which would have previously been bank loans.
The threat of substitutes for direct corporate finance, specifically bank lending, is substantial. Companies can tap into bond markets, issue equity, or utilize commercial paper to secure funds. This direct access diminishes their dependence on banks, particularly for larger capital requirements. In the first half of 2024, U.S. companies raised approximately $750 billion through equity offerings, showcasing a robust alternative to bank financing.
- Bond Issuance: Corporations can issue corporate bonds to raise capital, offering investors fixed or floating interest rates.
- Equity Offerings: Selling shares of stock to the public or private investors provides another avenue for corporate funding.
- Commercial Paper: Short-term, unsecured promissory notes issued by corporations are used for financing payroll, inventory, and other short-term liabilities.
Cryptocurrency and Blockchain-based Solutions
Emerging technologies like cryptocurrency and blockchain are presenting themselves as potential substitutes for traditional financial services. These innovations offer alternative ways to transfer value, send money across borders, and even engage in lending, potentially sidestepping established banking systems.
While widespread adoption is still developing, the capacity of these decentralized solutions to disintermediate existing financial processes poses a significant long-term threat. For instance, the global remittance market, a key area for banks, saw over $800 billion transferred in 2023, a market ripe for disruption by more efficient blockchain-based platforms.
- Blockchain's potential for faster, cheaper cross-border payments threatens traditional wire transfer fees, which can average 5-10% of the transaction value.
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms offer lending and borrowing services, potentially capturing market share from banks' interest income.
- The total value locked in DeFi protocols reached over $100 billion in early 2024, indicating growing user confidence and activity.
The threat of substitutes for Hancock Whitney's services is multifaceted, encompassing digital lending platforms, specialized investment firms, and emerging payment technologies. These alternatives often provide greater speed, convenience, or specialized expertise, directly challenging traditional banking models.
Online lenders offer faster loan processing, while investment firms provide diverse product selections, and payment providers like PayPal facilitate seamless transactions. These substitutes are capturing market share, particularly among younger demographics and businesses seeking agile financial solutions.
The increasing adoption of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology also presents a long-term substitution threat, potentially disintermediating core banking functions like cross-border payments and lending.
| Substitute Area | Key Competitors/Examples | Market Size/Growth Indicator (2024) | Impact on Hancock Whitney |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Lending | LendingClub, Prosper, SoFi | Global market projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars. | Direct competition for personal and business loans. |
| Investment & Wealth Management | Vanguard, Fidelity, Charles Schwab | Global assets under management in ETFs/mutual funds estimated at $54 trillion. | Loss of fee-based income and client assets. |
| Payments & Digital Wallets | PayPal, Square, Venmo, Apple Pay | Global digital payments market projected to exceed $10 trillion. | Reduced reliance on traditional bank accounts for transactions. |
| Corporate Finance | Bond Markets, Equity Markets | U.S. non-financial corporate bond issuance over $1.5 trillion (H1 2024). | Reduced demand for traditional corporate lending. |
| Emerging Technologies | Cryptocurrencies, DeFi Platforms | Total value locked in DeFi protocols exceeded $100 billion (early 2024). | Potential disruption of cross-border payments and lending. |
Entrants Threaten
Fintech startups pose a significant threat to traditional financial institutions like Hancock Whitney. The barriers to entry for digital-only financial services are considerably lower than those for brick-and-mortar banks, enabling nimble fintech companies to emerge and scale quickly. These new players often target specific customer segments or unmet needs, utilizing advanced technology to deliver innovative and personalized experiences that can attract customers away from established players.
Large tech companies like Apple and Google possess immense capital and vast customer bases, enabling them to easily enter the financial services sector. In 2024, for instance, Apple Pay continued its expansion, processing billions of transactions, demonstrating their established infrastructure and user trust. Their ability to leverage existing ecosystems and brand loyalty presents a formidable challenge to traditional financial institutions.
Regulatory changes, like the ongoing evolution of open banking frameworks, can significantly alter the threat of new entrants. These shifts can democratize access to financial infrastructure and customer data, provided consent is obtained, thereby lowering traditional barriers to entry for non-traditional players.
For instance, in 2024, the continued push for open finance in various global markets means that fintechs and other technology-driven companies can more readily integrate with existing banking systems. This reduces the capital and licensing hurdles previously faced, allowing them to offer specialized, competitive financial services.
Niche Banks or Specialized Lenders
New entrants, particularly niche banks or specialized lenders, pose a threat by targeting underserved market segments or offering highly specialized lending services. These players can gain a foothold by providing customized products and personalized customer experiences that larger, more generalized institutions may not prioritize.
For instance, in 2024, the continued growth of fintech lenders specializing in small business loans or specific consumer demographics highlights this trend. These entities often leverage technology to streamline operations and offer competitive rates, directly challenging traditional banking models.
- Targeted Market Segments: Niche lenders can focus on industries like agriculture, healthcare, or technology, offering tailored financial solutions.
- Specialized Lending Products: Offerings might include equipment financing, inventory loans, or specific types of personal loans catering to unique needs.
- Competitive Advantage: Personalized service and deep industry expertise allow these new entrants to build strong customer relationships.
Foreign Banks Expanding Presence
Foreign banks might increase their footprint in the U.S., especially in economically vibrant areas where Hancock Whitney is active. These institutions could enter the market via acquisitions or by setting up new branches, introducing new capital and competitive approaches that could challenge existing players.
For instance, in 2023, foreign direct investment in the U.S. financial services sector saw significant activity, with European banks, in particular, showing renewed interest in U.S. markets following periods of consolidation and regulatory adjustments. This trend suggests a potential for increased competition for regional banks like Hancock Whitney.
- Increased Competition: Foreign banks can bring substantial capital and advanced technological capabilities, intensifying competition for deposits and loans.
- Acquisition Opportunities: While a threat, foreign bank expansion can also present acquisition opportunities for domestic banks looking to grow or divest.
- Regulatory Landscape: The U.S. regulatory environment for foreign banks is robust, but changes could facilitate or hinder new market entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Hancock Whitney is moderate but growing, driven by fintech innovation and evolving regulations. While traditional banking requires significant capital and licensing, digital platforms and open banking initiatives are lowering these barriers. For example, in 2024, the U.S. saw continued growth in digital-only banks and specialized lending platforms, which can attract customers with lower fees and more agile services.
Large technology firms also represent a substantial threat, leveraging their existing user bases and financial resources to offer payment and financial management services. Companies like Apple, with Apple Pay processing billions in transactions in 2023, demonstrate the potential for non-traditional players to capture market share. Their ability to integrate financial services into existing ecosystems creates a significant competitive advantage.
Foreign banks, particularly those with strong digital capabilities and capital reserves, could also increase their presence in the U.S. market. In 2023, there was continued interest from European financial institutions in U.S. markets, suggesting a potential for increased competition through acquisitions or new branch openings. This influx of capital and expertise can challenge regional banks by offering new products and services.
| Threat Factor | Description | 2024 Impact/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Fintech Startups | Lower barriers to entry, agile operations, niche focus. | Continued rise of digital lenders and payment platforms. |
| Big Tech Entry | Vast capital, existing customer bases, ecosystem integration. | Apple Pay's ongoing expansion and transaction volume growth. |
| Regulatory Changes | Open banking, data sharing mandates reducing entry hurdles. | Increased opportunities for fintechs to access banking infrastructure. |
| Foreign Bank Expansion | Capital infusion, advanced technology, potential acquisitions. | Renewed interest from European banks in U.S. financial services. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hancock Whitney leverages insights from their annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We supplement this with data from industry-specific publications and market research reports to capture the broader competitive landscape.