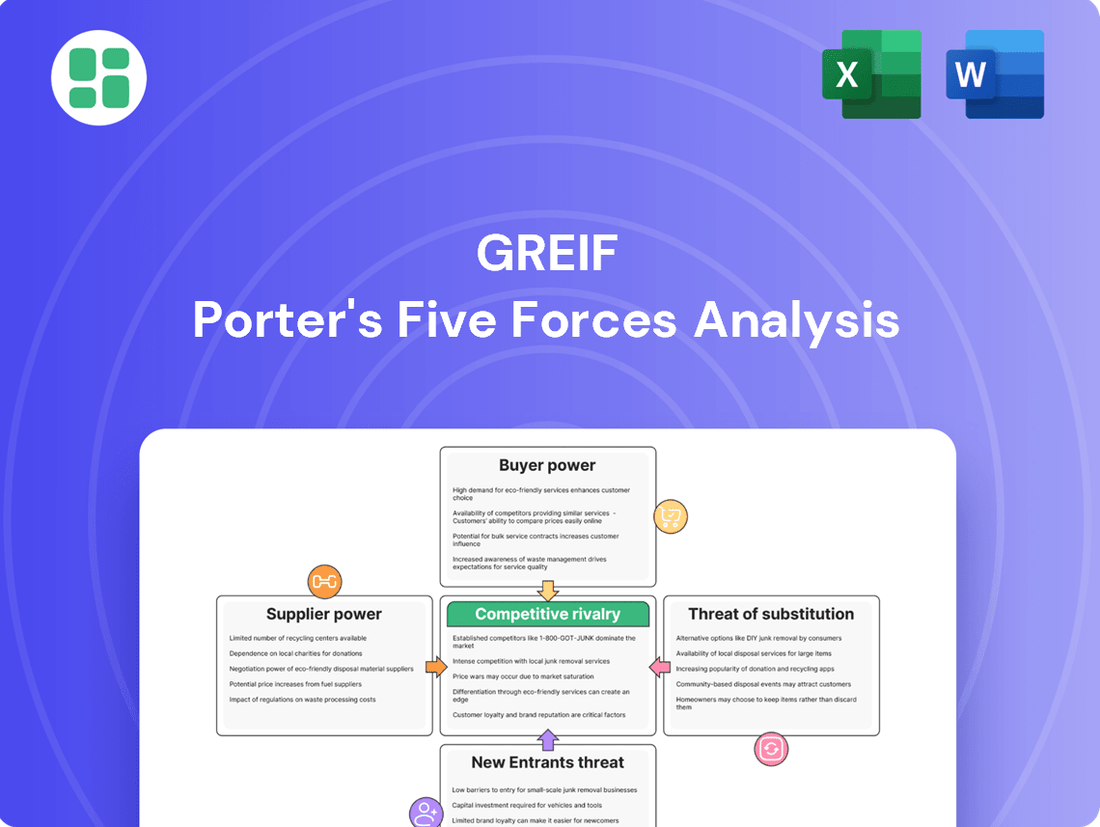
Greif Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Greif Bundle
Greif's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, the threat of new entrants, substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the industrial packaging market.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Greif’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Greif's reliance on a concentrated supplier base for critical raw materials like steel, plastic resins, and fiber significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. When few suppliers control essential inputs, they can dictate terms, especially if Greif requires specialized components with limited alternatives.
The period leading up to and including 2024 has seen considerable supply chain volatility. For instance, steel prices, a key input for Greif's rigid packaging, experienced significant fluctuations. In early 2024, global steel prices saw upward pressure due to production issues and strong demand in certain sectors, potentially increasing Greif's procurement costs.
The costs Greif incurs when switching raw material suppliers can be substantial. These include expenses for retooling machinery, re-qualifying new materials to ensure they meet quality standards, and adapting existing production processes. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a manufacturing company to switch a key supplier was estimated to be between 5% and 20% of the annual supply contract value, a significant figure that limits Greif's agility in seeking alternative providers.
These high switching costs directly enhance the bargaining power of Greif's current raw material suppliers. When it is expensive and time-consuming to change, suppliers can often command higher prices or more favorable terms, knowing that Greif faces considerable friction in moving to a competitor. This situation can lead to increased input costs for Greif, impacting its overall profitability.
Furthermore, Greif's strategic emphasis on sustainable sourcing creates an additional layer of supplier dependency. By committing to suppliers who meet stringent environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, Greif naturally narrows its pool of potential partners. This focus, while beneficial for corporate responsibility, can also solidify relationships with existing sustainable suppliers, further bolstering their bargaining position due to the specialized nature of their certifications and practices.
Greif's reliance on a consistent and affordable supply of raw materials underscores the significant bargaining power of its suppliers. Without these essential inputs, Greif's capacity to produce its diverse industrial packaging solutions would be severely hampered, giving suppliers of critical components considerable leverage in negotiations.
The company's proactive approach to supply chain management is evident in its FY2024 efforts, where it assessed 61% of its supplier spend. This strategic engagement reflects an understanding that managing supplier relationships is key to mitigating risks and ensuring cost-effectiveness, thereby indirectly addressing supplier bargaining power.
Raw Material Price Volatility
Raw material price volatility significantly impacts the industrial packaging sector, directly affecting Greif's bottom line. In 2024, the industry experienced notable cost surges, with pulp prices climbing around 15% and energy costs rising by approximately 10%. These increases were largely attributed to ongoing supply chain disruptions and broader inflationary pressures.
This fluctuating cost environment grants suppliers considerable leverage. When raw materials become scarce or demand outstrips supply, suppliers are in a stronger position to command higher prices, squeezing profit margins for companies like Greif.
- Pulp cost increase in 2024: ~15%
- Energy cost increase in 2024: ~10%
- Key drivers: Supply chain disruptions and inflation
- Impact: Increased supplier bargaining power
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into packaging production, like Greif's, is typically low. This is because it demands significant capital investment and a considerable change in their operational focus.
For Greif's main industrial packaging areas, suppliers integrating forward would be a major undertaking. It's generally not a practical move for them to suddenly become packaging manufacturers themselves, as their expertise and infrastructure are geared towards supplying raw materials or components.
However, in more specialized material niches, a supplier might consider forward integration to capture greater value. This is less of a concern in the broader industrial packaging market where Greif operates, as the intricate manufacturing processes create a barrier to entry for suppliers.
- Low Threat: Suppliers integrating forward into Greif's core industrial packaging is unlikely due to high capital requirements and business model shifts.
- Niche Exception: For highly specialized components, supplier forward integration is a possibility, though less common in the general industrial packaging sector.
- Manufacturing Complexity: The intricate nature of industrial packaging production acts as a significant deterrent for potential supplier integration.
Greif faces significant supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on a concentrated supplier base for key raw materials like steel, plastic resins, and fiber. High switching costs, estimated at 5% to 20% of annual contract value in 2024 for manufacturers, further strengthen suppliers' positions, allowing them to dictate terms and potentially increase input costs for Greif.
The company's commitment to sustainable sourcing also narrows its supplier options, reinforcing the leverage of existing ESG-compliant partners. Volatility in raw material prices, with pulp costs rising approximately 15% and energy costs up by 10% in 2024 due to supply chain issues and inflation, exacerbates this power dynamic, directly impacting Greif's profitability.
| Factor | Impact on Greif | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased leverage for fewer suppliers | High reliance on steel, plastic resins, fiber suppliers |
| Switching Costs | Limits Greif's ability to change suppliers | Estimated 5%-20% of contract value in 2024 |
| Sustainable Sourcing | Narrows supplier pool, strengthens existing relationships | Strategic emphasis on ESG criteria |
| Raw Material Price Volatility | Higher input costs, squeezed profit margins | Pulp costs up ~15%, energy costs up ~10% in 2024 |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Greif, including buyer and supplier power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and existing industry rivalry.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, making strategic planning more actionable.
Customers Bargaining Power
Greif's diverse customer base across industries like chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food & beverage inherently limits individual customer concentration. However, large industrial clients who purchase in substantial volumes can wield considerable bargaining power simply due to the sheer scale of their orders, potentially impacting pricing and terms.
Greif's commitment to customer satisfaction is evident in its 2024 Net Promoter Score (NPS) of 70, indicating a strong focus on managing customer relationships and acknowledging their influence. This high NPS suggests Greif actively works to mitigate potential downsides of powerful customers by fostering loyalty and value.
Greif's diverse industrial packaging portfolio, featuring specialized drums, IBCs, and flexible products, inherently builds switching costs for its clientele. Customers often invest in specific equipment or processes tailored to Greif's offerings, making a transition to a competitor a significant undertaking.
The pursuit of particular performance standards, stringent regulatory adherence, or unique sustainability features further solidifies these switching costs. For instance, a customer requiring specific UN certifications for hazardous material transport via Greif's drums faces considerable validation hurdles if they consider a different supplier.
Greif's ongoing innovations in areas like smart packaging, which can provide real-time tracking and condition monitoring, also serve to differentiate its products. This technological integration creates a higher barrier to switching for customers who value these advanced capabilities, potentially impacting their willingness to explore less integrated alternatives.
Customers in industrial sectors, particularly those making large-volume purchases, tend to be very sensitive to price. This is because packaging expenses can significantly affect their total operational costs. For instance, in 2024, many industries faced ongoing inflationary pressures, driving a greater focus on cost control, which directly amplifies this customer price sensitivity.
This heightened sensitivity means that companies like Greif must carefully navigate the challenge of offering competitive pricing while simultaneously dealing with their own increasing raw material and operational expenses. The ability to manage these costs effectively becomes crucial for maintaining market share in such an environment.
Availability of Substitutes for Customers
The availability of substitutes significantly strengthens customer bargaining power in the industrial packaging sector. Customers can easily switch to alternative suppliers because the market is fragmented and highly competitive, featuring many global and local providers offering comparable products.
Major competitors like International Paper and Smurfit Kappa, alongside numerous smaller players, ensure a wide array of choices for buyers. This broad accessibility to alternative packaging solutions directly translates into increased leverage for customers when negotiating prices and terms.
- Fragmented Market: The industrial packaging market is characterized by a large number of suppliers, making it easy for customers to find alternatives.
- Global and Local Players: Customers have access to both multinational corporations and regional specialists, increasing competitive pressure on any single supplier.
- Similar Product Offerings: Many packaging products are commoditized, meaning customers perceive little differentiation between offerings from different companies.
- Enhanced Negotiation Power: The ease of switching suppliers empowers customers to demand lower prices and more favorable contract conditions.
Backward Integration Threat by Customers
The threat of Greif's customers integrating backward into packaging manufacturing is generally low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital outlay, specialized technical knowledge, and the significant economies of scale needed to compete effectively in the packaging production industry. For instance, establishing a new packaging plant can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars, a barrier most companies are unwilling or unable to overcome.
Most of Greif's customers are focused on their primary business operations, such as filling and distributing consumer goods or industrial products. Venturing into capital-intensive packaging production would divert resources and management attention away from their core competencies. This strategic preference significantly diminishes the direct threat of customers deciding to produce their own packaging solutions.
Furthermore, the packaging industry, particularly for specialized containers like those Greif produces, often involves complex manufacturing processes and stringent quality control standards. Customers typically lack the in-house expertise and established supply chains necessary to replicate Greif's capabilities efficiently. In 2023, the global industrial packaging market was valued at over $100 billion, highlighting the scale and specialized nature of the industry.
- Capital Intensity: Starting a packaging manufacturing operation requires significant upfront investment, often in the tens of millions of dollars for modern equipment and facilities.
- Technical Expertise: Producing high-quality, specialized packaging demands specific engineering skills and process knowledge that most end-users do not possess.
- Economies of Scale: Large packaging manufacturers like Greif benefit from economies of scale, allowing them to produce at lower per-unit costs than a smaller, captive operation could achieve.
- Focus on Core Business: Customers prioritize investing in their core product development, marketing, and distribution rather than diverting resources to packaging production.
While Greif's broad customer base dilutes individual power, large-volume buyers can exert significant influence on pricing and terms due to their scale. Greif's high Net Promoter Score of 70 in 2024 suggests a strong customer relationship management strategy, mitigating some of this power by fostering loyalty.
The bargaining power of Greif's customers is moderated by the switching costs associated with its specialized packaging solutions and the increasing integration of smart packaging technologies. These factors make it more complex and costly for customers to transition to alternative suppliers, thereby limiting their leverage.
Customers' price sensitivity is heightened by inflationary pressures observed in 2024, making packaging costs a critical factor in their operational expenses. This sensitivity necessitates competitive pricing from Greif, balanced against its own rising input costs.
The fragmented nature of the industrial packaging market, with numerous global and local competitors offering similar products, significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. This wide availability of alternatives allows customers to readily switch suppliers, strengthening their negotiating position for better prices and contract terms.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Greif Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Greif Porter's Five Forces Analysis, identical to the document you will receive immediately upon purchase. You're not looking at a sample, but the actual, professionally formatted report detailing the competitive landscape of Greif. Once your transaction is complete, you'll gain instant access to this exact, ready-to-use analysis.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global industrial packaging market is quite crowded, with many companies competing for business. You have big international names like International Paper, WestRock, Smurfit Kappa, Mondi, and Greif, but there are also many smaller, local businesses in the mix. This means competition is fierce as everyone tries to grab a bigger piece of the market.
This fragmentation makes rivalry particularly intense. For instance, in 2024, the industrial packaging sector continues to see strategic moves and market share battles among these key players, influencing pricing and innovation across the board.
The industrial packaging market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5% to 7.5% between 2024 and 2034. This steady expansion generally tempers intense competition as companies can grow within an expanding pie.
However, this growth also fuels significant investment in advanced and eco-friendly packaging technologies. Consequently, while the overall market is growing, specific segments focused on innovation and sustainability can still experience heightened rivalry as firms vie for market leadership.
While many industrial packaging products are viewed as commodities, leading to intense price competition, Greif actively works to stand out. For instance, in 2024, Greif reported a significant portion of its revenue coming from specialized packaging solutions, indicating a strategic shift away from pure commodity offerings. This focus on unique product features and value-added services is key to building customer loyalty.
Greif's commitment to sustainability, a growing concern for many of its clients, also serves as a crucial differentiator. By offering eco-friendly packaging options, Greif not only meets evolving market demands but also creates higher switching costs for customers who have invested in these sustainable solutions. This customer-centric approach helps to reduce the impact of direct price-based rivalry.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The industrial packaging sector, including companies like Greif, faces intense competition partly due to substantial fixed costs. Building and maintaining manufacturing plants and intricate logistics systems requires significant capital investment. This capital intensity means that companies must operate at high capacity to spread these costs, leading to a constant pressure to maintain market share.
High exit barriers further exacerbate competitive rivalry. These barriers can include the specialized nature of machinery, which has limited resale value, and substantial costs associated with workforce reductions and facility decommissioning. Consequently, businesses may find themselves compelled to continue operating even in less profitable periods, intensifying the struggle for market share among existing players.
Greif's own actions reflect these challenges. In 2023, the company announced the closure of several paperboard facilities as part of its ongoing portfolio optimization. This move underscores the difficulty and strategic considerations involved in exiting specific market segments within the industrial packaging landscape, often due to the aforementioned high exit barriers.
- High Fixed Costs: Capital-intensive operations in industrial packaging require substantial upfront investment in manufacturing and distribution infrastructure.
- Exit Barriers: Specialized assets and employee severance costs make it costly and difficult for companies to leave the market, even during economic downturns.
- Intensified Rivalry: The combination of high fixed costs and exit barriers can lead to prolonged periods of intense competition as firms strive to maintain operational efficiency and market presence.
- Greif's Strategic Adjustments: Greif's closures of paperboard operations in 2023 illustrate the strategic complexities and financial implications of exiting certain business segments within this industry.
Strategic Moves and Consolidation
Competitive rivalry within the industrial packaging sector remains intense, with companies like Greif actively pursuing strategic moves to enhance their market position. Competitors are notably investing in technological advancements and sustainability, aiming to differentiate themselves and capture market share. For instance, the ongoing push for eco-friendly packaging solutions is a key battleground, driving innovation and operational adjustments across the industry.
Greif itself is actively participating in this dynamic landscape through significant strategic realignments and cost-saving measures. The company has embarked on a business unit reshuffle and is targeting substantial cost optimizations, with a goal to reduce expenses by $100 million by fiscal year 2027. This focus includes prioritizing investments in high-growth segments, such as customized polymer solutions, to better compete against rivals.
- Strategic Acquisitions: Competitors are consolidating through mergers and acquisitions to expand their product portfolios and geographical reach.
- Technological Advancements: Investment in new manufacturing technologies and digital solutions is crucial for improving efficiency and product quality.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Companies are increasingly focusing on developing and promoting sustainable packaging options to meet growing consumer and regulatory demand.
- Greif's Cost Optimization: Greif's target of $100 million in cost savings by FY2027 highlights the pressure to improve operational efficiency amidst fierce competition.
The industrial packaging market is characterized by a high degree of competition, with numerous global and regional players vying for market share. This intense rivalry is driven by factors such as significant capital investments required for manufacturing and distribution, leading to high fixed costs. Furthermore, substantial exit barriers, including specialized machinery and workforce considerations, make it difficult for companies to leave the market, thus prolonging competitive pressures.
| Factor | Impact on Rivalry | Greif's Position/Actions (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Fragmentation | Intensifies competition due to numerous players. | Greif competes with large players like International Paper and WestRock, alongside smaller regional firms. |
| High Fixed Costs | Drives pressure to maintain high capacity and market share. | Capital-intensive operations necessitate efficient capacity utilization. |
| Exit Barriers | Keeps firms engaged even in less profitable periods. | Greif's 2023 facility closures highlight the strategic challenges of exiting segments. |
| Product Differentiation | Reduces direct price competition. | Greif focuses on specialized packaging and sustainability to build customer loyalty. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The packaging industry is witnessing a significant shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly materials. Innovations include plant-based plastics, biodegradable polymers derived from sources like cornstarch, mycelium, and seaweed, alongside a greater emphasis on recycled content. These emerging materials present a substantial threat of substitution for traditional packaging solutions.
This trend necessitates companies like Greif to actively innovate and invest in circular economy principles and green packaging solutions. For instance, Greif has demonstrated its commitment by increasing its post-consumer resin (PCR) usage by a notable 37% in 2024, directly addressing the growing demand for environmentally responsible packaging.
The rise of reusable and refillable packaging models poses a growing threat, especially as consumers and regulators push for less waste. Industries like food, beverage, and personal care are increasingly adopting these sustainable options.
While this trend is less directly impactful on large industrial goods currently, it signifies a potential long-term substitute for single-use industrial containers. For instance, the global reusable packaging market was valued at approximately $10.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $18.9 billion by 2030, indicating significant growth.
The growing trend towards minimalist and functional design directly threatens traditional packaging solutions by reducing material usage. For instance, many consumer goods companies are actively seeking packaging that uses less cardboard and plastic, a shift that impacts companies like Greif that specialize in industrial packaging. This focus on efficiency and waste reduction can lead to lower costs for end-users, making alternative, lighter packaging more attractive.
This minimalist movement challenges heavier, more robust packaging formats by prioritizing sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Companies are increasingly pressured by consumers and regulators to adopt eco-friendly practices, and minimalist packaging aligns perfectly with these goals. Greif needs to innovate its product offerings to incorporate these lighter, more sustainable designs to remain competitive against these emerging substitutes.
Technological Advancements in Packaging
Technological advancements in packaging present a growing threat of substitutes for traditional packaging solutions. Smart packaging, integrating features like sensors and QR codes for enhanced traceability and consumer interaction, is gaining traction. This innovation can offer functionalities previously requiring separate components or even entirely different delivery systems, potentially reducing the need for certain types of conventional packaging.
The increasing adoption of smart packaging is driven by a desire for greater product safety, supply chain transparency, and improved customer engagement. For instance, in 2024, the global smart packaging market was projected to reach over $40 billion, indicating a significant shift towards these advanced solutions. This growth suggests that traditional packaging might face substitution as smart features become more integrated and cost-effective.
- Smart Packaging Integration: Technologies like NFC tags and QR codes are increasingly embedded in packaging, offering digital information and interaction capabilities.
- Traceability and Safety: These smart features enhance product traceability and safety monitoring, potentially replacing the need for separate tracking systems.
- Consumer Engagement: Smart packaging allows for direct consumer interaction, offering product details, promotions, and authenticity verification, which can be a substitute for traditional marketing collateral.
- Market Growth: The smart packaging market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating continued expansion in the coming years, signaling a potential shift away from conventional packaging formats.
Alternative Logistics and Bulk Transport Solutions
While Greif excels in rigid industrial packaging, the threat of substitutes exists, particularly for certain bulk goods. Advancements in logistics and alternative transportation methods offer potential replacements. For instance, specialized bulk shipping or the use of intermodal containers not necessarily produced by traditional packaging firms can bypass the need for individual industrial packages.
However, this threat is mitigated by the critical nature of Greif's offerings for specific cargo. For hazardous materials or highly specialized contents, the unique protective properties and containment capabilities provided by Greif’s steel and plastic drums, as well as intermediate bulk containers (IBCs), remain indispensable. The stringent safety regulations and the need for reliable containment for such goods limit the viability of simpler bulk transport solutions.
In 2024, the global bulk liquid packaging market, a key segment for Greif, continued to demonstrate resilience. While specific substitute penetration data is proprietary, the ongoing demand for safe and compliant transport of chemicals, food products, and petroleum derivatives underscores the continued need for specialized packaging. For example, the chemical logistics sector, a major consumer of industrial packaging, saw continued investment in specialized transport solutions, but the inherent risks associated with many chemicals still favor robust, sealed packaging.
- Alternative Bulk Transport: Specialized bulk shipping and intermodal containers can substitute for individual industrial packages for non-hazardous bulk goods.
- Critical Protection: Greif's packaging remains essential for hazardous or highly specialized contents due to its protective properties.
- Market Resilience: The global bulk liquid packaging market, a key area for Greif, showed continued demand in 2024, driven by safety and regulatory needs.
The threat of substitutes for Greif's industrial packaging solutions is evolving, driven by innovations in sustainable materials and packaging models. While traditional materials like steel and plastic drums remain critical for many applications, emerging alternatives are gaining traction.
The push for sustainability is leading to increased use of plant-based plastics and recycled content, directly challenging conventional packaging. Furthermore, the growing adoption of reusable and refillable packaging systems, particularly in consumer goods, signals a long-term shift that could impact industrial packaging demand.
Technological advancements, such as smart packaging, offer enhanced functionalities that may reduce the need for certain types of traditional industrial containers. These innovations, coupled with a focus on minimalist design, are creating a competitive landscape where Greif must adapt to maintain its market position.
Entrants Threaten
High capital investment requirements act as a significant deterrent to new entrants in the industrial packaging sector. Establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, acquiring advanced machinery, and investing in cutting-edge technology demand substantial upfront capital. For instance, setting up a new paper-based packaging plant in 2024 could easily require tens of millions of dollars, making it a daunting prospect for smaller or less capitalized firms.
The packaging industry is increasingly burdened by stringent regulatory compliance and evolving sustainability standards, creating a substantial barrier for potential new entrants. Regulations like the EU's Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation, which aims for 100% reusable or recyclable packaging by 2030, demand significant upfront investment in compliant materials and processes.
Newcomers must grapple with complex legal frameworks governing material safety, recyclability, and overall environmental impact. This necessitates substantial capital outlay for research and development, new manufacturing technologies, and adherence to certifications, making it difficult for smaller or less-resourced companies to compete effectively.
Established players like Greif have cultivated deep, long-standing relationships with their raw material suppliers, ensuring consistent access and favorable terms. These established supply chains are a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, securing consistent access to steel, a key component for Greif's industrial packaging, remained a challenge due to global demand and geopolitical factors, making it harder for new entrants to compete on cost and reliability.
Economies of Scale and Distribution Networks
Greif, like many established players in the industrial packaging sector, benefits significantly from economies of scale. This allows them to produce at a lower per-unit cost than a new entrant could initially achieve. For instance, in 2023, Greif reported net sales of $4.03 billion, a testament to their significant production volume and market presence.
Furthermore, incumbent companies possess well-established and extensive global distribution networks. Building a comparable network from scratch requires substantial capital investment and considerable time, creating a significant barrier for potential new competitors aiming to offer competitive pricing and efficient delivery.
- Economies of Scale: Greif's large-scale production capabilities in 2023, contributing to $4.03 billion in net sales, lower per-unit costs compared to new entrants.
- Distribution Networks: Existing global distribution infrastructure provides incumbents with logistical advantages and cost efficiencies that are difficult for newcomers to replicate.
- Capital Investment: New entrants face substantial upfront investment requirements to match the production capacity and distribution reach of established firms like Greif.
- Time to Market: Developing comparable operational efficiencies and market penetration takes significant time, delaying a new entrant's ability to compete effectively on price and service.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Relationships
Established companies like Greif often possess strong brand recognition and deeply cultivated customer relationships, especially in industrial markets where dependability and service are critical. Newcomers face the challenge of eroding this existing loyalty and earning trust, a process that is inherently time-consuming and expensive.
Greif's commitment to customer satisfaction is evident in its high Net Promoter Score (NPS), which stood at 58 in their most recent reporting period, indicating robust customer loyalty and strong ties. This high NPS suggests that new entrants would need to invest significantly in marketing and service to even begin to compete with Greif's established customer base.
- Brand Equity: Greif's long-standing presence has allowed it to build significant brand equity, making its products a preferred choice for many customers.
- Customer Retention: High customer retention rates, often exceeding 90% in key segments, demonstrate the difficulty for new entrants to capture market share.
- Service and Support: The company's established infrastructure for service and support further solidifies customer relationships, creating a barrier to entry.
The threat of new entrants in the industrial packaging sector, exemplified by Greif's market position, is significantly mitigated by several factors. High capital investment for advanced manufacturing and regulatory compliance, estimated at tens of millions for a new paper-based packaging plant in 2024, presents a formidable initial hurdle. Established players also leverage strong supplier relationships, ensuring consistent raw material access, a challenge for newcomers in 2024 due to global demand for materials like steel.
| Barrier to Entry | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data Point (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High upfront costs for facilities and technology | Setting up a new paper-based packaging plant could require tens of millions of dollars. |
| Supplier Relationships | Difficulty securing consistent and cost-effective raw materials | Challenges in accessing steel due to global demand in 2024. |
| Economies of Scale | Higher per-unit production costs for new entrants | Greif's 2023 net sales of $4.03 billion indicate significant production volume advantages. |
| Distribution Networks | Logistical disadvantages and higher delivery costs | Replicating Greif's global distribution infrastructure is time-consuming and capital-intensive. |
| Brand Loyalty & Service | Difficulty in attracting customers away from established providers | Greif's NPS of 58 signifies strong customer retention, requiring significant marketing investment from new entrants. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Greif leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings (10-K), and trade publications to understand competitive intensity and industry structure.