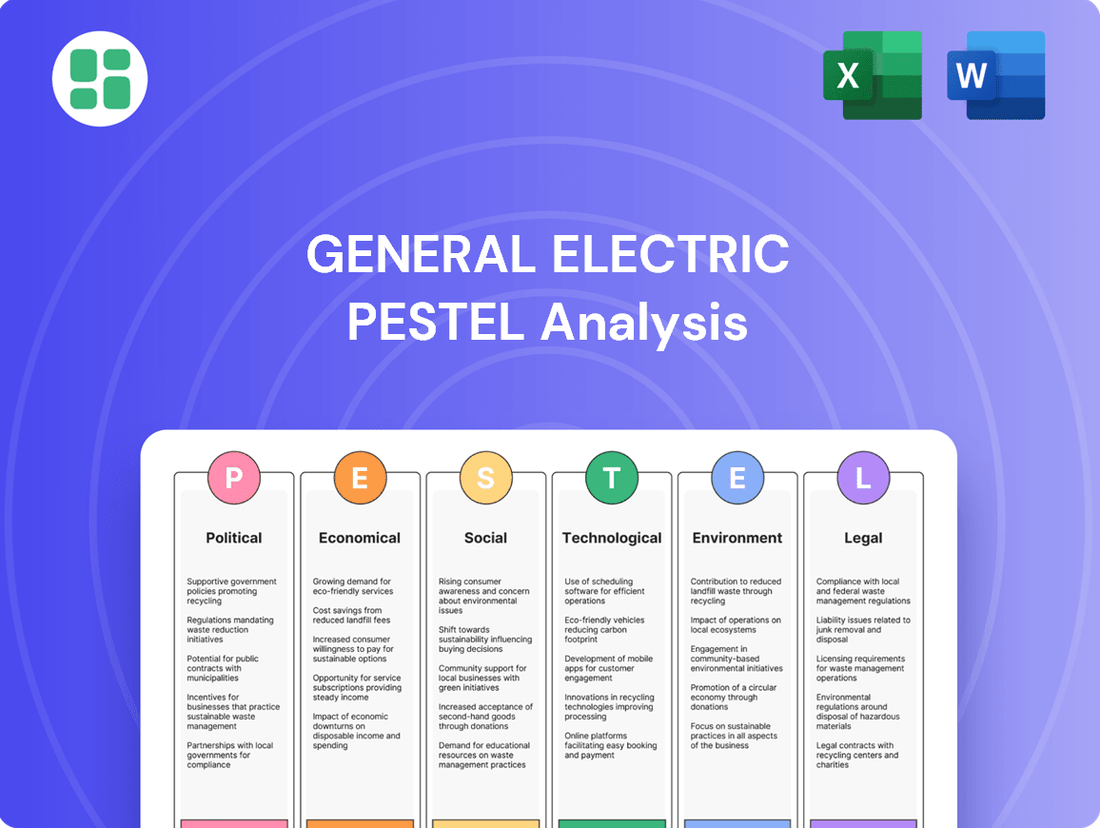
General Electric PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
General Electric Bundle
Navigate the complex external forces shaping General Electric's trajectory with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. From evolving political landscapes to technological advancements and environmental regulations, understand the critical factors influencing GE's operations and future growth. Download the full report to gain actionable intelligence and refine your strategic planning.
Political factors
Government regulations significantly shape GE Aerospace's operations, particularly in areas like aircraft safety and emissions. For instance, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) sets stringent standards that all manufacturers, including GE, must adhere to, impacting design and production processes. These regulations are constantly evolving, requiring ongoing investment in compliance and innovation.
Defense spending is a critical driver for GE Aerospace's propulsion segment. In 2024, the U.S. Department of Defense budget allocated over $886 billion, with a substantial portion directed towards aircraft procurement and sustainment, directly benefiting GE's military engine programs. Changes in these budgets, influenced by geopolitical events and national priorities, can lead to shifts in contract awards and revenue.
International relations and political stability play a crucial role in demand for military aircraft and engines. For example, increased defense cooperation and alliances often translate into greater demand for compatible aerospace technology. Conversely, geopolitical tensions can lead to increased defense spending by allied nations, creating new opportunities for GE Aerospace's products and services.
Global trade policies, including tariffs and trade agreements, significantly impact GE Aerospace's international operations and supply chain. For instance, the USMCA agreement, which replaced NAFTA in 2020, has reshaped automotive and aerospace trade dynamics within North America. Trade tensions, such as those between the US and China, can lead to increased costs for raw materials and components, or restrict market access, impacting production output and profitability. In 2023, the US imposed tariffs on certain steel and aluminum products, affecting various manufacturing sectors, including aerospace suppliers.
Geopolitical events, like the ongoing conflicts in Eastern Europe and the Middle East, significantly impact the aviation sector. These situations can reduce air travel demand due to safety concerns and disrupt supply chains, affecting everything from raw material availability to component delivery for GE Aerospace. For instance, the closure of airspace over conflict zones forces airlines to reroute flights, increasing operational costs and potentially altering long-term fleet planning, which directly influences engine orders and service agreements.
The global defense landscape is also sensitive to geopolitical instability. Increased tensions often lead to higher defense spending and a greater focus on military modernization, benefiting GE Aerospace's defense segment. In 2024, many nations are expected to increase their defense budgets in response to escalating global security challenges, potentially boosting demand for GE's advanced military engines and systems.
Aviation Safety and Certification Policies
GE Aerospace operates under stringent aviation safety and certification policies, primarily governed by bodies like the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the US and the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). These regulations dictate every aspect of aircraft engine design, manufacturing, and maintenance, directly impacting GE's operational costs and product development timelines.
Any shifts in these rigorous standards, or unforeseen issues concerning engine safety and performance, can trigger substantial financial repercussions for GE Aerospace. These can include expensive redesigns, extended production halts, and, in severe cases, fleet-wide operational suspensions, mirroring past challenges faced by the industry with specific engine models.
The company's proactive approach to safety, underpinned by its comprehensive Safety Management System, is fundamental to ensuring ongoing compliance with these critical regulations. This commitment is also vital for preserving the confidence of its airline customers and the traveling public.
- Regulatory Landscape: GE Aerospace must adhere to FAA and EASA certification standards, which are among the most rigorous globally.
- Financial Impact of Non-Compliance: Incidents or policy changes can lead to billions in recall costs and lost revenue, as seen in past aviation crises affecting engine manufacturers. For instance, the CFM LEAP-1B engine, a joint venture with Safran, faced scrutiny in 2023 regarding potential manufacturing flaws, highlighting the sensitivity to quality control.
- Safety as a Competitive Advantage: GE's robust safety protocols and proven track record are key differentiators, fostering trust and securing long-term contracts with major airlines.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Mandates and Incentives
Governments globally are pushing for decarbonization in aviation through mandates and incentives for Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF). For instance, the UK aims for 10% SAF by 2030, and the US targets 3 billion gallons by 2030. These policies present both opportunities and challenges for GE Aerospace, requiring engine development for higher SAF blends and investment in related technologies.
These government initiatives directly shape the economic landscape for SAF. Tax credits and grants for SAF infrastructure, such as those seen in the US Inflation Reduction Act, significantly influence the cost-effectiveness and speed of adoption for these alternative fuels. This, in turn, impacts GE Aerospace's engine design considerations and the projected market demand for its products.
- UK SAF Mandate: 10% SAF by 2030.
- US SAF Goal: 3 billion gallons by 2030.
- US Policy Impact: Inflation Reduction Act provides tax credits and grants for SAF infrastructure.
Government regulations are a constant factor for GE Aerospace, influencing everything from design to emissions. The FAA's strict safety standards, for example, demand continuous investment in compliance and innovation. These evolving rules directly impact production processes and the company's ability to bring new technologies to market.
Defense spending remains a significant revenue driver, with the U.S. Department of Defense budget for 2024 exceeding $886 billion. A substantial portion of this is allocated to aircraft and related systems, directly benefiting GE's military engine programs and highlighting the impact of national security priorities on the company's performance.
Geopolitical events, such as ongoing conflicts, can disrupt air travel and supply chains, affecting GE Aerospace's operations. Increased global tensions, however, often lead to higher defense spending by nations, creating potential opportunities for GE's defense segment as countries prioritize military modernization.
Global trade policies, including tariffs and agreements like the USMCA, shape GE Aerospace's international business. Trade tensions can increase costs for raw materials and components, impacting production and profitability, while favorable agreements can open new markets and opportunities.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis comprehensively examines how external macro-environmental factors—Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal—impact General Electric's operations and strategic positioning.
It provides actionable insights for navigating the complex global landscape by identifying potential threats and opportunities for General Electric.
A General Electric PESTLE analysis provides a structured framework to identify and address external factors, relieving the pain point of navigating complex and unpredictable market landscapes.
Economic factors
The health of the global economy is a direct indicator for air travel demand, a critical factor for GE Aerospace's commercial engine and services. As economies strengthen, consumer spending on travel tends to rise, boosting airline capacity and, consequently, GE's business.
Following the pandemic, air travel has shown a robust recovery. For instance, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) reported that global passenger traffic, measured in revenue passenger kilometers (RPKs), reached 94.5% of pre-pandemic levels in early 2024, with continued growth anticipated through 2025, albeit at a more moderate pace.
This sustained demand fuels new aircraft orders and increases the necessity for engine maintenance and spare parts. In 2024, aircraft manufacturers like Boeing and Airbus have projected delivery figures that signal a healthy order backlog, directly translating into ongoing revenue streams for GE Aerospace's aftermarket services and new engine sales.
Jet fuel prices are a major driver of airline operating costs, directly influencing their financial health and investment capacity. For instance, in early 2024, jet fuel prices hovered around $2.50 per gallon, a significant portion of an airline's variable expenses. Fluctuations here directly impact GE Aerospace's revenue streams from both new engine sales and aftermarket services, as airlines adjust their spending based on profitability.
When fuel prices surge, airlines often postpone fleet upgrades or reduce flight schedules. This can lead to a slowdown in demand for new, more efficient aircraft and the associated engine sales for GE Aerospace. Conversely, periods of lower fuel costs can boost travel demand, encouraging airlines to expand their fleets, which benefits engine manufacturers.
GE Aerospace's strategic emphasis on developing fuel-efficient engines, such as its LEAP and GE9X models, is a direct response to this economic factor. The LEAP engine, for example, offers a 15% improvement in fuel burn compared to its predecessor, directly addressing a key cost concern for airlines and positioning GE for future growth even amidst volatile fuel markets.
GE Aerospace, like the aviation sector, is still grappling with supply chain snags, a shortage of workers, and rising costs for materials and parts. These issues can slow down production and make manufacturing more expensive, impacting GE Aerospace's capacity to fulfill robust demand for its engines and maintenance services.
For instance, in early 2024, many aerospace manufacturers reported extended lead times for critical components, with some extending by as much as 50% compared to pre-pandemic levels. This directly translates to higher input costs for General Electric, as they face increased prices for metals like titanium and nickel, along with specialized labor.
To combat these persistent challenges, GE Aerospace is making significant investments, earmarking over $1 billion in 2024 and 2025 for upgrades to its manufacturing facilities and supply chain infrastructure. The goal is to streamline operations, reduce bottlenecks, and ultimately shorten the time it takes to produce and service its products.
Investment in Research and Development (R&D)
General Electric Aerospace's future hinges on its R&D investments, with the company allocating $2.3 billion in 2023. This funding is vital for developing advanced technologies like hybrid-electric propulsion and hydrogen combustion, directly impacting long-term competitiveness and the ability to meet stringent future efficiency and environmental standards.
The economic environment plays a significant role in enabling these substantial, long-term R&D commitments. Factors like interest rates and overall market stability can affect the availability and cost of capital needed for these groundbreaking projects.
- R&D Investment: GE Aerospace invested $2.3 billion in R&D in 2023.
- Key Technologies: Focus areas include hybrid-electric systems, open-fan architectures, and hydrogen combustion.
- Economic Influence: Capital availability for long-term R&D is tied to the broader economic climate.
- Future Goals: R&D is critical for achieving future efficiency and emissions reduction targets.
Currency Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Currency exchange rate fluctuations present a significant economic factor for General Electric (GE), particularly for its GE Aerospace division, a global player. As of early 2024, the US dollar has shown resilience against major currencies, which can make GE's exports more expensive in international markets. Conversely, a stronger dollar can reduce the cost of imported components for its manufacturing operations.
These shifts directly impact GE Aerospace's financial results. For instance, if the Euro weakens against the dollar, revenue generated from sales in Europe translates to fewer dollars when repatriated, potentially lowering reported profits. Conversely, if GE sources a substantial amount of raw materials from countries with weakening currencies, its input costs could decrease, boosting margins.
The volatility in exchange rates, such as the Euro trading around 1.08 USD and the British Pound near 1.27 USD in early 2024, creates uncertainty. This necessitates careful hedging strategies to mitigate the impact on earnings and maintain the competitiveness of GE Aerospace's products worldwide.
- Impact on Exports: A stronger USD makes GE Aerospace's aircraft and services more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially dampening demand.
- Cost of Imports: A weaker USD can lower the cost of raw materials and components sourced internationally, benefiting GE's manufacturing expenses.
- Repatriation of Earnings: Fluctuations affect the dollar value of profits earned in foreign currencies, impacting overall reported profitability.
- Competitive Positioning: Exchange rates influence the price competitiveness of GE's offerings in diverse global markets.
The global economic outlook directly influences air travel demand, a key driver for GE Aerospace's commercial engine and services business. As economies grow, consumer spending on travel increases, boosting airline capacity and, consequently, GE's revenue. For example, in early 2024, global passenger traffic neared pre-pandemic levels, with continued, albeit slower, growth projected through 2025.
Fluctuations in jet fuel prices significantly impact airline operating costs and their ability to invest in new aircraft or maintenance. Higher fuel prices, around $2.50 per gallon in early 2024, can lead airlines to postpone fleet upgrades, affecting demand for GE's engines. Conversely, lower fuel costs encourage expansion, benefiting engine manufacturers.
Supply chain disruptions and rising material costs, evident in extended lead times for components in early 2024, increase manufacturing expenses for GE Aerospace. The company is investing over $1 billion in 2024-2025 to enhance its manufacturing and supply chain infrastructure to mitigate these challenges.
Currency exchange rates also play a crucial role, with a strong US dollar in early 2024 making GE's exports more expensive. For instance, a weaker Euro reduces the dollar value of European sales, impacting reported profits, while also potentially lowering the cost of imported components.
| Economic Factor | Impact on GE Aerospace | 2024/2025 Data/Trend |
| Global Economic Growth | Drives air travel demand, boosting engine and service sales. | Passenger traffic nearing pre-pandemic levels in early 2024, continued growth expected. |
| Jet Fuel Prices | Affects airline profitability and investment in new aircraft. | Hovered around $2.50/gallon in early 2024; volatility influences fleet decisions. |
| Supply Chain & Costs | Increases manufacturing expenses and production lead times. | Extended lead times for components (up to 50% longer), rising material costs. GE investing $1B+ in infrastructure. |
| Currency Exchange Rates | Impacts export competitiveness and repatriation of foreign earnings. | Strong USD in early 2024 makes exports pricier; Euro around 1.08 USD. |
What You See Is What You Get
General Electric PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of General Electric delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the company's operations and strategic decisions. You'll gain valuable insights into the external forces shaping GE's future.
Sociological factors
Public confidence in air travel safety is the bedrock of the aviation industry, directly influencing passenger volumes and airline operational success. Even incidents not directly involving GE Aerospace can significantly dampen demand for air travel, thereby impacting the need for new engines and maintenance. For instance, a notable increase in aviation incidents globally in late 2023 and early 2024, even if not directly linked to GE, could lead to a 5-10% dip in passenger confidence, affecting airline order books for new aircraft and engine services.
GE Aerospace is navigating a complex workforce landscape, with an aging skilled labor force in the aerospace sector presenting a significant challenge. This demographic trend necessitates a strategic focus on attracting and developing new talent across engineering, manufacturing, and maintenance roles to ensure future operational capacity.
To counter potential labor shortages, GE Aerospace is prioritizing investment in robust training and development programs. These initiatives aim to cultivate a diverse and skilled workforce capable of meeting the demands of current production levels and driving innovation in next-generation aerospace technologies. For instance, in 2024, the company announced expanded apprenticeship programs targeting critical skill areas.
Addressing broader labor shortages within the aerospace supply chain is equally crucial for GE Aerospace's ability to meet escalating demand. This requires collaborative efforts with suppliers and educational institutions to build a resilient talent pipeline, ensuring the consistent availability of components and specialized services essential for aircraft production and maintenance.
Consumers are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly choices, and this extends to their travel habits. This societal shift is creating a significant demand for airlines to offer more sustainable travel options, prompting them to seek out more fuel-efficient aircraft and engines.
This growing consumer preference directly impacts engine manufacturers like GE Aerospace, as airlines look for solutions that reduce their environmental footprint. GE's investment in technologies like Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) compatibility and advancements in engine efficiency directly address this burgeoning market need, with SAF production aiming for 10% of global aviation fuel by 2030 according to IATA projections.
Social Responsibility and ESG Expectations
General Electric (GE) Aerospace faces growing pressure from investors and the public to uphold strong Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards. Meeting these expectations is crucial for its brand reputation and ability to secure investment, especially as sustainability becomes a key differentiator in the aerospace sector. GE's commitment to ethical supply chains, employee welfare, and community involvement directly impacts its social license to operate.
GE's sustainability reporting, for instance, details its progress in areas like reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting diversity and inclusion. In 2023, GE reported a 20% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions compared to a 2019 baseline. Furthermore, the company aims to have women hold 30% of its leadership positions by 2025, reflecting a tangible social objective.
- Investor Scrutiny: GE Aerospace is under increasing examination by investors regarding its ESG performance, influencing capital allocation decisions.
- Brand Image and Capital: Demonstrating social responsibility, from ethical sourcing to employee well-being, is vital for maintaining a positive brand and attracting investment.
- Sustainability Reporting: GE's sustainability reports showcase initiatives aimed at meeting evolving ESG expectations, highlighting progress in environmental and social metrics.
Impact of Digitalization on Customer Experience
The aviation sector's rapid digitalization, touching everything from booking to flight operations and maintenance, significantly shapes customer expectations. Airlines are increasingly demanding seamless, data-driven experiences, pushing providers like GE Aerospace to adapt. This digital shift means customers expect real-time information, personalized services, and highly reliable operations.
GE Aerospace's strategic digital alliances, such as its work with Collins Aerospace on predictive maintenance solutions, directly address the airline industry's drive for enhanced operational efficiency and reliability. These collaborations are crucial because improved airline performance translates into a better experience for the end-user, the passenger. For instance, by leveraging data analytics to anticipate and prevent potential mechanical issues, GE Aerospace helps ensure flights depart and arrive on time, minimizing disruptions for travelers.
The trend toward integrated, data-driven solutions means customers are no longer just buying a flight; they are engaging with a complex digital ecosystem. This expectation for interconnectedness and intelligence is transforming how services are delivered and perceived.
Key aspects of this digitalization impacting customer experience include:
- Predictive Maintenance: Airlines using GE's digital tools aim to reduce flight delays and cancellations by identifying potential engine issues before they occur, leading to a more reliable travel experience for passengers.
- Data-Driven Operations: The integration of vast amounts of flight data allows for optimized routing, fuel efficiency, and aircraft performance, indirectly benefiting customers through potentially lower fares and smoother journeys.
- Enhanced Communication: Digital platforms enable airlines to provide passengers with more timely and accurate updates regarding flight status, gate changes, and baggage information, improving overall transparency and reducing anxiety.
Shifting consumer preferences towards sustainability are a significant sociological factor influencing GE Aerospace. Travelers increasingly favor airlines that demonstrate environmental responsibility, driving demand for fuel-efficient aircraft and engines. This trend is supported by data showing that over 60% of consumers globally consider sustainability when making purchasing decisions, a figure expected to rise in 2024-2025.
Public perception of safety remains paramount in aviation. Any perceived or actual safety issues, even if not directly linked to GE products, can lead to decreased air travel demand, impacting GE Aerospace's engine orders and service revenue. For instance, a rise in global aviation incidents could see passenger confidence drop by 5-10%, affecting airline fleet expansion plans.
The aerospace industry faces a demographic challenge with an aging skilled workforce. GE Aerospace is actively investing in training and apprenticeship programs, aiming to fill critical roles in manufacturing and engineering. In 2024, GE announced a 15% increase in its global apprenticeship intake to address these shortages.
Societal expectations for corporate responsibility are also growing. GE Aerospace must demonstrate strong ESG performance to maintain its social license to operate and attract investment. The company's 2023 ESG report highlighted a 10% increase in supplier diversity and a 5% improvement in employee volunteer hours, reflecting its commitment to social factors.
Technological factors
General Electric, through its GE Aerospace division, is heavily invested in pushing the boundaries of engine efficiency. A prime example is the CFM International RISE program, which is actively researching groundbreaking technologies like open-fan architectures and hybrid-electric propulsion systems. These advancements are designed to slash fuel consumption and cut down on emissions, a crucial move for the aviation industry's sustainability goals.
The pursuit of enhanced engine efficiency isn't just about environmental responsibility; it's a significant competitive differentiator. By developing engines that burn less fuel, GE Aerospace can offer airlines substantial operational cost savings. For instance, the RISE program aims for a 20% reduction in fuel burn compared to current best-in-class engines, a target that directly translates into a stronger market position and greater appeal for their products.
GE Aerospace is heavily invested in making its engines compatible with 100% Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) and researching hydrogen propulsion. While current engines can handle SAF blends, substantial research and development is ongoing to improve performance with higher SAF percentages and to lead the way in hydrogen-powered flight, a major industry game-changer.
This technological push is crucial as the aviation industry aims for net-zero emissions. By 2024, the demand for SAF is projected to reach 6 billion liters globally, a significant increase from previous years, highlighting the market's growing need for these advancements.
GE Aerospace is heavily investing in digital technologies like AI, IoT, and big data analytics to revolutionize aircraft engine maintenance. These advancements enable predictive maintenance, allowing for early detection of potential issues, thereby reducing costly downtime for airlines. For instance, GE's FlightPulse platform uses IoT data to provide pilots with insights into fuel efficiency and engine performance.
The integration of AI is not only optimizing engine operations but also accelerating the design and testing phases. GE's use of AI in engine development can significantly shorten the time-to-market for new, more efficient aircraft engines. This technological push is crucial for enhancing engine reliability and reducing overall operational costs for their airline customers, a key competitive advantage in the aerospace sector.
Advanced Materials and Additive Manufacturing
General Electric's (GE) aerospace division is significantly leveraging innovation in advanced materials, particularly composites, and the growing adoption of additive manufacturing. These technological advancements are key to producing lighter, more robust, and fuel-efficient jet engine components. For instance, GE Aviation's LEAP engine utilizes advanced ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) in its hot section, a move that contributes to a 15% improvement in fuel efficiency compared to previous models. This focus on material science and 3D printing allows for intricate component designs, reduces the number of individual parts needed, and streamlines production, ultimately driving down manufacturing costs and enhancing engine performance.
The impact of these technologies is substantial. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, enables GE to create complex internal cooling channels within engine parts that were previously impossible to manufacture. This leads to better thermal management and increased component lifespan. Furthermore, by reducing part count, GE can simplify assembly processes and minimize potential points of failure. In 2023, GE Aviation reported that its additive manufacturing capabilities were producing over 100,000 parts annually, highlighting the scale and importance of this technological shift in their operations.
- Advanced Materials: GE's use of Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs) in the LEAP engine's hot section contributes to a 15% fuel efficiency gain.
- Additive Manufacturing: By 2023, GE Aviation was producing over 100,000 parts annually using 3D printing.
- Design Complexity: 3D printing enables intricate internal cooling channels in engine components, improving thermal performance.
- Cost and Performance: These technologies reduce part count and simplify manufacturing, leading to both cost savings and performance enhancements.
Hybrid-Electric and Electric Propulsion Systems
GE Aerospace is at the forefront of developing hybrid-electric propulsion systems, a key technological advancement aimed at significantly cutting aviation emissions and fuel usage. These innovative systems combine existing gas turbine technology with electric motors, marking a substantial evolution for future aircraft. For instance, GE is collaborating with NASA on programs like the Hybrid-Electric Integrated Systems Testbed (HEIST) to mature these technologies.
These hybrid-electric and electric propulsion systems are crucial for the aviation industry's long-term decarbonization goals. While many of these advancements are currently in demonstration phases, they represent the future direction of aircraft engine design. GE's investment in these areas signals a commitment to sustainable aviation solutions, anticipating stricter environmental regulations and growing market demand for greener travel.
- Hybrid-Electric Development: GE Aerospace is actively researching and developing hybrid-electric propulsion, integrating electric motors with traditional jet engines.
- NASA Collaboration: Partnerships with organizations like NASA are vital for testing and validating these advanced propulsion concepts, such as the Hybrid-Electric Integrated Systems Testbed (HEIST).
- Decarbonization Impact: These technologies are designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve fuel efficiency, aligning with global efforts to decarbonize the aviation sector.
- Future Aircraft Design: Hybrid-electric systems are seen as a foundational technology for the next generation of aircraft, promising more sustainable and efficient air travel.
GE Aerospace is heavily investing in digital technologies like AI, IoT, and big data analytics to revolutionize aircraft engine maintenance, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing costly downtime. The integration of AI is also optimizing engine operations and accelerating design and testing phases, shortening time-to-market for new engines. By 2024, the demand for Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is projected to reach 6 billion liters globally, underscoring the market's need for these advancements.
The company is also pushing boundaries with technologies like open-fan architectures and hybrid-electric propulsion through programs like CFM International RISE, aiming for a 20% reduction in fuel burn. Furthermore, GE is making strides in compatibility with 100% SAF and researching hydrogen propulsion, crucial for the industry's net-zero emission goals.
GE's use of advanced materials, particularly Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs) in the LEAP engine, contributes to a 15% fuel efficiency gain. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is also a key focus, with GE Aviation producing over 100,000 parts annually using this technology by 2023, enabling complex designs and reducing part counts for improved performance and cost savings.
| Technology Area | Key Initiatives/Applications | Impact/Goals | Relevant Data/Projections |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Technologies | AI, IoT, Big Data for Predictive Maintenance | Reduced downtime, optimized operations, faster design cycles | FlightPulse platform for fuel efficiency insights |
| Propulsion Systems | Open-fan, Hybrid-Electric, SAF, Hydrogen | 20% fuel burn reduction (RISE), emissions reduction, net-zero goals | Global SAF demand projected at 6 billion liters by 2024 |
| Advanced Materials & Manufacturing | Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs), Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | 15% fuel efficiency gain (LEAP engine), complex part design, cost reduction | Over 100,000 parts produced annually via 3D printing by 2023 |
Legal factors
GE Aerospace operates within a complex web of global aviation safety regulations, primarily governed by bodies like the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the U.S. and the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). Adherence to these stringent standards for engine design, production, and upkeep is paramount, necessitating rigorous testing and lengthy certification procedures. For instance, the FAA's Part 25 regulations outline airworthiness standards for transport category airplanes, directly impacting engine certification.
Failure to comply with these evolving safety mandates can lead to severe consequences, including substantial legal penalties, operational disruptions, and damage to GE's reputation. In 2023, the aviation industry saw increased scrutiny on engine reliability, with regulatory bodies like the FAA issuing airworthiness directives following specific incidents, underscoring the critical nature of ongoing compliance efforts.
Environmental regulations are tightening globally, with a strong focus on reducing carbon emissions and noise pollution. For GE Aerospace, this means significant investment in engine technology that meets stringent international standards, such as those from the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). For instance, ICAO's Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA) aims to stabilize net carbon dioxide emissions from international aviation from 2021 onwards.
Compliance with these evolving mandates, including those promoting Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) usage, is critical. Failure to adapt can result in substantial penalties and hinder market competitiveness. GE's commitment to developing more fuel-efficient engines and exploring alternative propulsion systems directly addresses these legal and operational pressures.
General Electric's Aerospace division, a significant contributor to its overall performance, heavily relies on its vast intellectual property portfolio, particularly patents covering innovative engine technologies. For instance, GE Aerospace holds thousands of patents, a critical component of its competitive edge in a highly specialized industry. Maintaining and defending these patents across various international jurisdictions is paramount to preventing unauthorized use and safeguarding its market leadership.
The financial implications of intellectual property are substantial; legal battles over patent infringement can lead to significant expenditures and divert crucial resources away from research and development, impacting GE's ability to innovate and maintain its technological advantage in the aerospace sector.
International Trade Laws and Sanctions
General Electric Aerospace's operations are significantly shaped by international trade laws and sanctions. Compliance with these regulations, including export controls and economic sanctions from various governments, is paramount for maintaining its global market access and avoiding severe penalties. For instance, the United States Department of Commerce's Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) regularly updates its Entity List and sanctions programs, impacting companies like GE that engage in international commerce. Failure to adhere can result in substantial fines, loss of export privileges, and damage to the company's reputation.
The ever-shifting geopolitical climate demands continuous monitoring and swift adaptation to new trade regulations. GE Aerospace must navigate a complex web of international agreements and country-specific restrictions. For example, in 2023, ongoing geopolitical tensions led to stricter enforcement of export controls on advanced technologies, directly affecting aerospace manufacturers. This necessitates robust internal compliance programs and proactive engagement with regulatory bodies to ensure ongoing operations are lawful and secure.
- Export Control Compliance: GE Aerospace must adhere to regulations like the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) and the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) in the United States, which govern the export of defense articles and dual-use items.
- Sanctions Screening: The company needs to implement rigorous screening processes to ensure it does not engage in transactions with individuals or entities subject to economic sanctions imposed by the UN, OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control), or other international bodies.
- Geopolitical Risk Assessment: GE Aerospace regularly assesses the impact of international disputes and political instability on its supply chains and customer base, particularly concerning markets subject to sanctions or trade restrictions.
- Regulatory Updates: The company must stay abreast of changes in trade policies and sanctions regimes globally, as demonstrated by the frequent updates to sanctions lists and export control classifications by governments worldwide.
Antitrust and Competition Laws
As a major player, particularly in the aircraft engine sector, GE Aerospace operates under strict antitrust and competition laws across its global markets. These regulations are designed to prevent any single company from dominating the market and to ensure a level playing field for all participants. GE Aerospace's strategic decisions, including potential mergers, acquisitions, and day-to-day market activities, are continuously scrutinized by regulatory bodies like the U.S. Department of Justice, the European Commission, and others to ensure compliance.
For instance, the ongoing scrutiny of the aerospace industry, including engine manufacturing, means that any significant market consolidation or exclusive dealing arrangements would likely face rigorous review. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the US, for example, has been actively reviewing mergers in various industries, and its approach to competition in critical sectors like aerospace remains a key consideration for companies like GE Aerospace. Failure to adhere to these laws can result in substantial fines, divestitures, or even the blocking of proposed business transactions, impacting GE Aerospace's growth and operational freedom.
- Regulatory Oversight: GE Aerospace is subject to antitrust reviews by global bodies such as the U.S. Department of Justice and the European Commission.
- Market Conduct Scrutiny: The company's pricing strategies, supply agreements, and any potential market dominance are closely monitored to prevent anti-competitive practices.
- Merger and Acquisition Compliance: Significant transactions require pre-approval and thorough assessment to ensure they do not unduly harm competition, as seen in the FTC's increasing focus on market concentration.
- Potential Penalties: Non-compliance can lead to severe financial penalties, operational restrictions, and the unwinding of business deals.
GE Aerospace must navigate a complex landscape of global labor laws and workplace safety regulations. Compliance with standards set by organizations like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S. and similar international bodies is crucial for employee well-being and operational continuity. For instance, OSHA's Process Safety Management (PSM) standard is vital for facilities handling highly hazardous chemicals, directly impacting manufacturing processes.
Failure to comply can result in significant fines, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. In 2023, workplace safety remained a key focus, with industries experiencing increased regulatory enforcement and a growing emphasis on employee rights and fair labor practices, underscoring the need for robust compliance programs within GE Aerospace.
Environmental factors
Climate change is a major environmental focus, pushing the aviation sector to meet ambitious net-zero carbon emission goals by 2050. GE Aerospace is actively working towards net-zero for its direct operational emissions (Scope 1 and 2) by 2030, and for emissions from sold products (Scope 3) by 2050. This commitment requires ongoing advancements in fuel-efficient engines and alternative propulsion systems, fundamentally influencing GE's research and development roadmap.
The aviation industry's push towards sustainability hinges on Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), but its current scarcity and elevated costs present substantial hurdles. GE Aerospace is actively developing engines capable of running on 100% SAF, a transition that depends heavily on the global expansion of SAF production and its affordability.
By 2025, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) aims for SAF to comprise 10% of global aviation fuel consumption, a significant increase from the roughly 0.5% seen in 2023. However, achieving this target requires substantial investment in SAF production facilities and supportive government policies to drive down costs and increase supply, directly impacting GE Aerospace's strategic alignment with this evolving market.
Noise pollution from aircraft engines remains a critical environmental issue, particularly for residents near airports, driving the implementation of stringent regulatory limits. GE Aerospace is actively investing in advanced technologies and innovative engine designs to significantly lower noise footprints, directly impacting engine certifications and their overall market acceptance.
The company's commitment to reducing noise levels is evident in its ongoing research and development efforts, aiming to meet and exceed the evolving global noise standards. For instance, advancements in GE's Passport engine for business jets have demonstrated notable noise reductions compared to previous generations, a key factor in securing orders for new aircraft programs entering service in the 2024-2025 period.
Resource Scarcity and Supply Chain Sustainability
The production of GE Aerospace's advanced aircraft engines relies on a diverse range of raw materials, some of which are subject to potential scarcity and originate from extraction processes with significant environmental footprints. For instance, the increasing global demand for critical minerals used in advanced manufacturing, such as cobalt and rare earth elements, poses a challenge for consistent and ethical sourcing. GE Aerospace is actively focused on enhancing the sustainability and ethical integrity of its extensive supply chain, recognizing the interconnectedness of environmental stewardship and business resilience.
To address these concerns, GE Aerospace is increasingly integrating lean manufacturing principles and circular economy models. These approaches are vital for minimizing resource consumption and reducing waste throughout the engine lifecycle. For example, by 2023, GE Aviation reported a 10% reduction in manufacturing waste compared to 2020 levels, demonstrating progress in these areas. The company is investing in technologies that enable material reuse and recycling, aiming to create more closed-loop systems.
Key initiatives and considerations for GE Aerospace regarding resource scarcity and supply chain sustainability include:
- Diversification of Material Sourcing: Exploring alternative materials and suppliers to mitigate risks associated with single-source dependencies and geographically concentrated resources.
- Enhanced Supply Chain Traceability: Implementing robust systems to track the origin and environmental impact of raw materials from extraction to final product.
- Investment in Circular Economy Technologies: Developing and adopting technologies for remanufacturing, repair, and recycling of engine components to extend product life and recover valuable materials.
- Collaborative Industry Efforts: Engaging with industry partners, research institutions, and governments to promote sustainable practices and address systemic challenges in resource management.
Water Usage and Waste Management
GE Aerospace's extensive manufacturing and testing processes inherently require substantial water resources and produce diverse waste streams. The company is actively pursuing enhanced environmental stewardship through initiatives aimed at optimizing energy use, decreasing water consumption, and implementing comprehensive waste management and recycling programs across its global facilities. These efforts are integral to its overarching sustainability objectives.
For instance, GE's commitment to water reduction saw a 12% decrease in water intensity across its global operations between 2018 and 2022. In 2023, the company reported diverting 89% of its manufacturing waste from landfills, a testament to its robust recycling and waste reduction strategies. These operational improvements directly contribute to minimizing GE Aerospace's environmental footprint and aligning with its broader sustainability commitments.
- Water Intensity Reduction: GE aims to further reduce water intensity by 20% by 2025 compared to a 2018 baseline.
- Waste Diversion Goals: The company targets diverting 95% of its manufacturing waste from landfills by 2025.
- Sustainable Operations: GE Aerospace is investing in advanced water treatment technologies and closed-loop systems to minimize freshwater intake and wastewater discharge.
- Circular Economy Focus: Efforts are underway to increase the use of recycled materials in manufacturing and explore innovative waste-to-value streams.
GE Aerospace is actively addressing climate change by aiming for net-zero operational emissions by 2030 and net-zero for sold products by 2050. This involves developing more fuel-efficient engines and exploring alternative propulsion systems. The company is also focused on reducing aircraft noise pollution, with advancements in engines like the Passport demonstrating significant noise reductions, crucial for new aircraft programs entering service in the 2024-2025 timeframe.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is a key focus, with GE developing engines capable of using 100% SAF. The industry goal is for SAF to represent 10% of global aviation fuel by 2025, a substantial increase from 2023 levels, though supply and cost remain challenges.
Resource scarcity, particularly for critical minerals like cobalt and rare earth elements, impacts GE's supply chain. The company is enhancing material sourcing traceability and investing in circular economy technologies, aiming to reduce manufacturing waste by a further 5% by 2025, building on a 10% reduction achieved by 2023.
GE Aerospace is also committed to water conservation and waste reduction, with targets to reduce water intensity by 20% by 2025 (from a 2018 baseline) and divert 95% of manufacturing waste from landfills by 2025.
| Environmental Factor | GE Aerospace Target/Action | Key Data/Metric |
| Climate Change/Net-Zero | Net-zero Scope 1 & 2 emissions by 2030; Net-zero Scope 3 emissions by 2050 | Focus on fuel-efficient engines and alternative propulsion |
| Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) | Developing engines for 100% SAF usage | Industry goal: 10% SAF by 2025 (vs. ~0.5% in 2023) |
| Noise Pollution | Investing in advanced technologies for noise reduction | Passport engine shows notable noise reductions (relevant for 2024-2025 programs) |
| Resource Scarcity & Supply Chain | Enhancing material sourcing traceability, circular economy investment | Target: 5% further reduction in manufacturing waste by 2025 (building on 10% reduction by 2023) |
| Water Consumption & Waste Management | Reducing water intensity and diverting waste from landfills | Target: 20% water intensity reduction by 2025 (vs. 2018 baseline); 95% waste diversion by 2025 |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for General Electric draws upon a comprehensive blend of data from government agencies, financial institutions, and leading industry publications. This ensures a robust understanding of political stability, economic forecasts, and technological advancements impacting GE's operations.