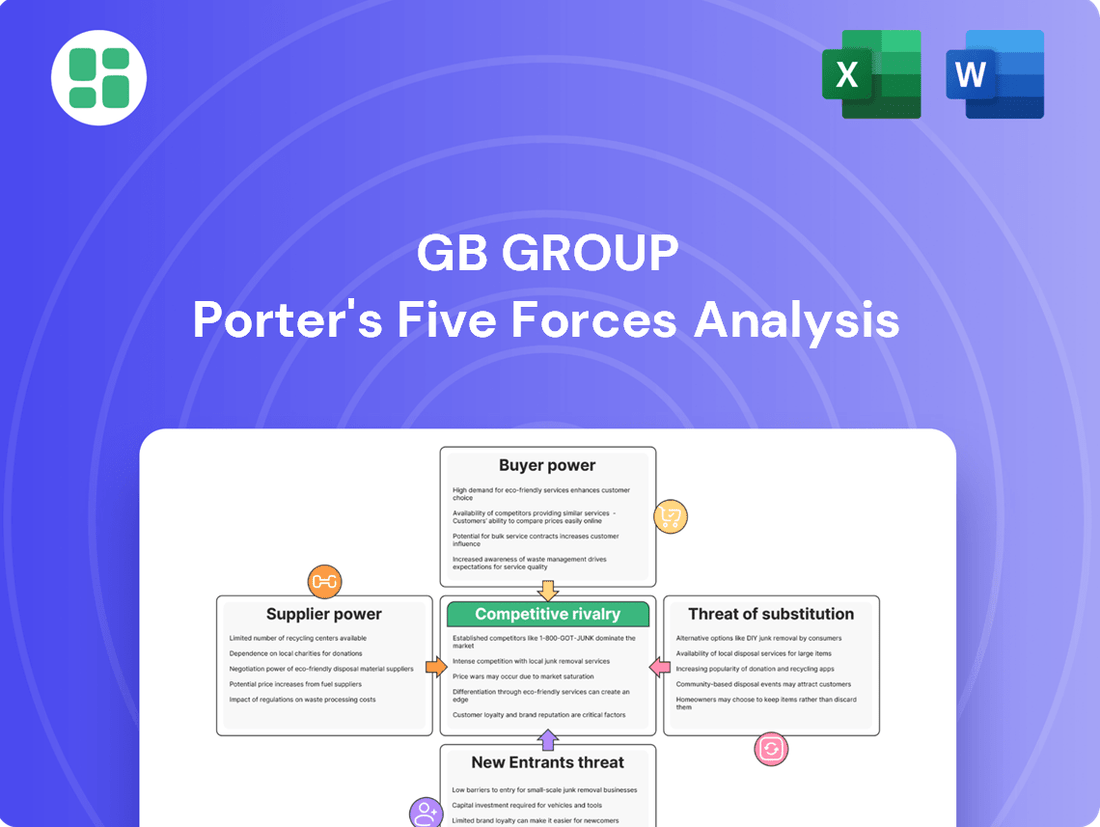
GB Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
GB Group Bundle
GB Group's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the bargaining power of its buyers to the intense rivalry within its industry. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any strategic decision.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping GB Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
GB Group's reliance on external data providers, including credit bureaus and government registries, highlights a significant supplier power dynamic. The unique and essential nature of this data, coupled with potential market concentration among providers, grants them considerable leverage.
The cost and availability of this critical data directly influence GB Group's operational expenditures and the quality of services offered to its clients. For instance, in 2024, the global data analytics market, which includes data providers, was projected to reach over $300 billion, indicating substantial market value and potential pricing power for key suppliers.
Technology and software vendors can hold significant bargaining power over GB Group, especially if they provide specialized, proprietary solutions. For instance, if GB Group relies on a unique AI algorithm or a highly integrated cybersecurity framework that is difficult to replicate or replace, the supplier can dictate terms. High switching costs, such as the expense and time involved in migrating data or retraining staff on new systems, further amplify this power. In 2024, the increasing reliance on sophisticated cloud-based software and data analytics tools means that vendors in these niches can command premium pricing.
The availability of highly skilled talent, like data scientists and AI engineers, acts as a significant supplier power for GB Group. A constrained supply of these specialized professionals can escalate recruitment and retention expenses, directly affecting GB Group's capacity for innovation and delivering advanced solutions.
Infrastructure Providers
GB Group's reliance on infrastructure providers like cloud computing services, data centers, and network infrastructure is significant for its operations. While the market has several large providers, specialized or customized solutions can increase supplier leverage. For instance, in 2024, the global cloud computing market was valued at approximately $600 billion, with major players like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud dominating a substantial share. A switch to a different provider for deeply integrated or custom-built infrastructure can be costly and time-consuming, giving these suppliers considerable bargaining power.
The bargaining power of these infrastructure providers is amplified when GB Group requires highly specific configurations or substantial data storage capacity that is not easily replicated by competitors. Any price hikes or service disruptions from these critical suppliers can directly impact GB Group's ability to deliver its services efficiently and maintain its profitability.
- Significant Market Share: Major cloud providers hold substantial market share, potentially limiting alternatives for specialized needs.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with migrating data and reconfiguring custom infrastructure can lock GB Group into existing relationships.
- Service Interruption Impact: Downtime or performance degradation from infrastructure providers can directly affect GB Group's revenue and customer satisfaction.
- Technological Dependence: Reliance on proprietary technologies or unique service offerings from a provider can further strengthen their negotiating position.
Regulatory Data Access Entities
Regulatory Data Access Entities, such as government bodies that manage official databases or financial regulators that license data, wield considerable influence. Their control over essential information for compliance and identity verification directly impacts GB Group's operational capabilities and growth strategies. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, effective since 2018, has significantly shaped how data can be accessed and processed, indirectly affecting the cost and complexity of data acquisition for companies like GB Group.
These entities can exert bargaining power through their pricing structures for data access and the specific terms and conditions they impose. GB Group's reliance on these sources for crucial identity verification and compliance services means that changes in these entities' policies or fees can have a direct financial impact. In 2024, the ongoing evolution of data privacy laws globally continues to place a premium on compliant data access, potentially increasing the leverage of these gatekeepers.
- Data Access Fees: The cost charged by regulatory bodies for accessing official databases.
- Compliance Requirements: The stringency of regulations that dictate data usage and access protocols.
- Licensing Agreements: The terms and conditions under which GB Group can utilize data from these entities.
- Data Availability and Quality: The reliability and accuracy of the data provided by these authoritative sources.
GB Group faces significant bargaining power from its data and technology suppliers. The essential nature of data from credit bureaus and government registries, coupled with potential market concentration, grants these providers leverage. Similarly, specialized software vendors offering proprietary solutions or integrated frameworks can dictate terms due to high switching costs.
The increasing reliance on sophisticated cloud services and AI talent in 2024 further amplifies supplier power. For instance, the global cloud computing market, valued around $600 billion in 2024, is dominated by a few major players, giving them considerable influence. A shortage of specialized data scientists also escalates recruitment costs, impacting GB Group's innovation capabilities.
| Supplier Type | Key Leverage Factors | Impact on GB Group | 2024 Market Data/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Providers (Credit Bureaus, Registries) | Unique/Essential Data, Market Concentration | Influences operational costs, service quality | Global Data Analytics Market projected >$300 billion |
| Technology Vendors (Software, AI) | Proprietary Solutions, High Switching Costs | Dictates terms, potential for premium pricing | Increasing reliance on cloud/AI tools |
| Infrastructure Providers (Cloud, Data Centers) | Specialized Configurations, High Switching Costs | Affects service efficiency, profitability | Global Cloud Market ~$600 billion; major players dominate |
| Skilled Talent (Data Scientists, AI Engineers) | Limited Supply, High Demand | Increases recruitment/retention expenses, impacts innovation | Growing demand for AI/data expertise |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting GB Group, examining industry rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the availability of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive threats with a dynamic, visual representation of Porter's Five Forces.
Gain immediate clarity on market dynamics and potential disruptions, allowing for proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
GB Group's large enterprise customers, particularly those in financial services, e-commerce, and government, wield considerable bargaining power. These clients represent a substantial portion of GBG's revenue, giving them leverage to negotiate favorable terms. For instance, a major financial institution might account for a significant percentage of GBG's recurring income, making their demands difficult to ignore.
Customers hold sway if switching to a competitor isn't too difficult or costly, even with integrated identity verification and fraud prevention. For instance, if a company's core systems require significant overhaul to adopt a new provider, the switching costs are high, reducing customer power. GB Group aims to mitigate this by making its solutions integral to client operations, thereby raising these barriers.
When solutions become commoditized, like basic identity verification, customers see less difference between providers. This means they'll shop around more based on price, giving them more power. For instance, in 2024, the identity verification market saw numerous new entrants offering similar core services, intensifying price competition.
GB Group needs to keep innovating to stand out. If its offerings are seen as just another commodity, customers can easily switch to a cheaper alternative. This pressure forces GB Group to focus on unique features or superior service to maintain its customer base and pricing power.
Customer Concentration
Customer concentration significantly amplifies the bargaining power of buyers. If GB Group relies heavily on a small number of key clients, these customers gain leverage. For instance, if a few large enterprises account for over 60% of GB Group's revenue, they can dictate terms, potentially forcing price reductions or demanding customized services that strain profitability.
The impact of losing a major customer can be severe. A single client representing 15% of GB Group's annual turnover, if lost, could necessitate a substantial revenue recovery effort. This dependency makes the company vulnerable to demands for concessions, as the cost of losing such a client outweighs the benefit of resisting. Diversification is key to reducing this vulnerability.
- High Customer Concentration: If a few large clients generate a disproportionate share of GB Group's revenue, their bargaining power increases.
- Financial Impact of Client Loss: Losing a significant customer can materially harm GB Group's financial performance.
- Leverage for Better Terms: Concentrated customers can demand lower prices or more favorable contract terms.
- Mitigation Strategy: Diversifying the customer base is crucial to dilute the bargaining power of individual clients.
Regulatory Compliance Demands
Customers in highly regulated sectors, such as financial services, often impose strict compliance mandates on their suppliers. These requirements, particularly around identity verification and fraud prevention, can significantly empower these customers. For instance, a bank might demand specific audit trails or data residency features, making it difficult for a provider like GB Group to serve multiple clients without extensive customization.
These stringent demands translate into tangible power for customers. They can dictate specific functionalities, reporting standards, or even the technology stack GB Group must utilize to meet regulatory obligations. Failure to align with these compliance needs can directly impact GB Group's ability to secure and retain business, as customers may switch to competitors who can more readily adapt.
In 2024, the global regulatory technology (RegTech) market was valued at approximately $11.5 billion, demonstrating the significant investment and focus on compliance. For companies like GB Group, which operates within this space, meeting diverse and evolving regulatory demands is paramount. The bargaining power of customers is amplified when they represent large segments of GB Group's revenue and possess the leverage to enforce their specific compliance requirements.
- Customer Leverage: In regulated industries, customers can dictate specific compliance features, enhancing their bargaining power.
- Market Influence: The growing RegTech market, valued at $11.5 billion in 2024, underscores the importance of meeting regulatory demands.
- Risk of Churn: Non-compliance with customer-specific regulations can lead to significant customer attrition for GB Group.
- Operational Impact: Meeting diverse compliance needs can require substantial investment in product development and customization.
GB Group's customers, particularly large enterprises in finance and e-commerce, possess significant bargaining power due to their substantial revenue contribution and the relatively low switching costs for certain services. This leverage allows them to negotiate favorable terms and pricing, especially as identity verification solutions become more commoditized, as seen in the competitive landscape of 2024.
Customer concentration further amplifies this power; if a few major clients account for a large portion of GBG's revenue, they can dictate terms, potentially impacting profitability. For instance, losing a client representing 15% of annual turnover necessitates significant recovery efforts, making GBG vulnerable to concessions.
Moreover, customers in regulated sectors like financial services can impose strict compliance mandates, enhancing their influence. The global RegTech market, valued at approximately $11.5 billion in 2024, highlights the critical need for providers like GBG to meet diverse regulatory demands, which can lead to customer churn if not addressed.
| Factor | Impact on GB Group | Customer Leverage | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High revenue dependence on few clients | Ability to dictate terms and pricing | Customer base diversification |
| Switching Costs | Varies by solution integration | Lower for commoditized services | Enhancing solution integration and value-add |
| Market Commoditization | Increased price sensitivity | Focus on price comparison | Innovation and differentiation in offerings |
| Regulatory Compliance | Demand for specific features | Dictating functionalities and standards | Proactive compliance management and customization |
What You See Is What You Get
GB Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for the GB Group, detailing each force with expert insights. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The identity data intelligence market, a space crucial for identity verification and fraud prevention, is teeming with a wide array of competitors. This includes established global tech giants as well as agile, specialized startups, all vying for dominance.
This crowded field, featuring both broad-spectrum technology providers and highly focused niche players, fuels intense rivalry. Companies are constantly battling to capture market share and secure customer loyalty across different market segments.
The competitive dynamic is further complicated by the presence of both direct rivals offering similar solutions and indirect competitors who address the same customer needs through alternative means, adding layers of complexity to strategic planning.
The digital identity and fraud prevention market is indeed growing robustly, with projections indicating continued expansion. However, this rapid growth doesn't eliminate competitive rivalry. As specific niches within this broad market mature, or if certain solutions become commoditized, companies may engage in more aggressive tactics. This could manifest as price wars, accelerated product innovation, or heightened marketing spend to secure market share.
For instance, while the overall market is expanding, a sub-segment like biometric authentication for mobile devices might see fiercer competition as more players enter and existing ones refine their offerings. This competitive intensity can drive down prices or necessitate substantial investment in R&D to stay ahead. Even with a healthy market growth rate, companies must remain vigilant about competitive pressures, as high growth can sometimes obscure underlying struggles for dominance in particular areas.
The degree to which competitors distinguish their products plays a crucial role in shaping competitive rivalry. When offerings are seen as largely interchangeable, price wars often erupt, intensifying competition. GB Group strives to stand out by emphasizing exceptional accuracy, extensive global reach, sophisticated AI and machine learning functionalities, and effortless integration into client systems.
However, the intensity of rivalry persists if these differentiating features can be readily copied by competitors. For instance, in the data verification sector, while GB Group highlights its advanced AI, if competitors quickly adopt similar technologies, the perceived uniqueness diminishes, leading back to price-sensitive competition. In 2024, the market for identity verification solutions, a key area for GB Group, continued to see significant investment, with companies like Onfido and Trulioo also enhancing their AI capabilities, indicating a constant need for GB Group to innovate and maintain its unique selling propositions.
Switching Costs for Customers
GB Group benefits from high switching costs, which inherently dampen competitive rivalry. When customers are deeply embedded within GB Group's systems, the effort and expense required to migrate to a competitor become significant deterrents. This integration often involves not just technical challenges but also the potential disruption of critical business operations.
GB Group actively cultivates these sticky customer relationships by providing mission-critical services that are integral to their clients' daily functions. This deep integration means that switching providers isn't a simple transactional decision; it involves substantial re-engineering and potential downtime. For instance, in the identity verification sector where GB Group operates, the complexity of integrating new data sources and compliance protocols can make switching a multi-month, high-cost endeavor.
Conversely, if switching costs were low, customers would be more inclined to shop around, comparing features and pricing more frequently. This would inevitably lead to intensified competition as providers would need to constantly attract new clients rather than retain existing ones through established relationships. The ease with which customers can switch directly correlates to the pressure on existing players to maintain competitive pricing and service levels.
- High switching costs reduce the ease with which customers can change providers.
- GB Group's strategy focuses on deep system integration and essential services to increase customer stickiness.
- The cost and complexity of migrating critical business functions act as a barrier to switching.
- Low switching costs typically result in greater price sensitivity and a higher propensity for customers to change suppliers.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity
GB Group operates in a sector characterized by high fixed costs. Developing and maintaining advanced identity data intelligence platforms requires significant investment in technology infrastructure, data sourcing, and ongoing research and development. These substantial upfront and ongoing expenses create a barrier to entry for new players.
The necessity to recoup these high fixed costs often drives companies to operate at or near full capacity. This can lead to aggressive strategies aimed at capturing market share, as underutilized capacity represents a direct drag on profitability. Consequently, intense competition, sometimes manifesting as price wars or aggressive sales efforts, is a common feature of this market.
In 2024, the identity verification market saw continued investment in AI and machine learning, further increasing the R&D component of fixed costs. For instance, major players are investing heavily in fraud detection algorithms and data enrichment services, pushing the technological frontier and the associated capital expenditure. This environment necessitates efficient operations and a strong market position to effectively manage cost structures.
- High R&D Investment: Companies in identity data intelligence must continually invest in R&D to stay competitive, with significant portions of budgets allocated to developing new algorithms and data processing capabilities.
- Infrastructure Costs: Maintaining robust and scalable data infrastructure, including cloud services and data storage, represents a substantial and ongoing fixed cost.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: The need to spread high fixed costs incentivizes companies to maximize capacity utilization, potentially leading to price competition as firms vie for volume.
The competitive rivalry within the identity data intelligence market is fierce, driven by a crowded landscape of global tech giants and specialized startups. Companies like GB Group, Onfido, and Trulioo are locked in a continuous battle for market share, often employing aggressive strategies such as price wars and accelerated product innovation to gain an edge.
GB Group differentiates itself through superior accuracy, extensive global reach, advanced AI capabilities, and seamless integration. However, the rapid adoption of similar technologies by competitors, as seen with enhanced AI in 2024 by players like Onfido and Trulioo, means GB Group must constantly innovate to maintain its unique selling propositions and avoid commoditization.
| Competitor | Key Differentiators | 2024 Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| GB Group | Accuracy, Global Reach, AI, Integration | AI Advancement, Data Enrichment |
| Onfido | AI-powered Identity Verification | Biometric Authentication, Fraud Detection |
| Trulioo | Global Identity Verification Network | Compliance Solutions, Data Security |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While digital identity verification solutions are becoming the norm, traditional manual processes, like in-person checks or postal verification, still linger as basic substitutes. These older methods, though inefficient and error-prone, might be used by smaller businesses or in areas with limited digital infrastructure. For instance, a small local shop might still rely on checking a physical ID at the point of sale.
These manual methods lack the speed, scalability, and robust security that advanced digital platforms offer. They are also more susceptible to human error and fraud. In 2024, the global digital identity verification market was valued at approximately USD 20.5 billion, showcasing a strong preference for more sophisticated solutions over manual ones.
Large enterprises with substantial IT budgets and unique security mandates may opt to build their own identity verification and fraud prevention systems. This approach serves as a direct substitute, allowing them to bypass external providers like GB Group, especially if off-the-shelf solutions don't fully align with their specific needs or if they prioritize retaining complete control over their sensitive data and operational workflows.
For less critical identity verification needs, basic background checks and standard credit reporting agencies can act as substitutes. These services offer a foundational level of identity assurance, but they don't possess the sophisticated, real-time data analysis and fraud detection capabilities that advanced identity intelligence platforms provide. For instance, while a credit report might confirm basic identity details, it's unlikely to flag sophisticated synthetic identity fraud, a growing concern in 2024.
Traditional Rule-Based Fraud Detection
The threat of substitutes for advanced fraud detection solutions, particularly those leveraging AI and machine learning, comes from simpler, traditional rule-based systems. These older methods, while less effective against evolving fraud tactics, remain a viable alternative for organizations with budget constraints or less complex fraud scenarios. For instance, a significant portion of small to medium-sized businesses might still rely on basic transaction monitoring rules due to cost-effectiveness, even if it means a higher rate of false positives.
These substitutes offer a lower barrier to entry and can be perceived as more transparent by some decision-makers. While not as sophisticated, they fulfill a basic need for fraud prevention. In 2024, it's estimated that many financial institutions still maintain legacy rule-based systems alongside newer technologies, indicating their continued, albeit limited, relevance.
- Legacy Systems: Organizations with limited budgets may opt for older, rule-based fraud detection systems instead of investing in advanced AI/ML solutions.
- Simpler Analytics: Basic statistical models or manual review processes can act as substitutes for more complex fraud prevention technologies.
- Cost-Benefit Trade-off: While less effective, these simpler methods can be appealing for businesses with less sophisticated fraud threats or a preference for lower upfront costs.
- Transparency Preference: Some entities may favor the perceived transparency of rule-based systems over the "black box" nature of certain advanced AI models.
Alternative Security Measures
The threat of substitutes for GB Group's identity data intelligence services is present from alternative security measures that don't directly leverage identity data. For instance, organizations might invest more heavily in enhanced physical security, such as advanced surveillance systems or access control, to deter threats.
Robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) that relies on device possession or biometric factors, rather than solely on identity verification, can also serve as a substitute. These methods aim to secure access and mitigate risks without the deep dive into identity data that GB Group specializes in.
Furthermore, implementing stricter internal controls and employee training programs can bolster an organization's security posture, reducing reliance on external identity intelligence. For example, a company might implement mandatory data handling protocols and regular security audits to prevent breaches, thereby reducing the perceived need for GB Group's specific offerings.
- Physical Security Enhancements: Increased investment in CCTV, biometric scanners at entry points, and secure data centers can reduce the need for identity verification services.
- Device-Centric MFA: Solutions requiring a physical token or a registered device for authentication bypass the need for extensive identity data checks.
- Internal Controls & Training: Robust compliance programs and employee education on data security can act as a preventative measure, lessening the demand for identity intelligence.
- Network Segmentation: Isolating critical data assets within a network can limit the impact of a breach, making comprehensive identity intelligence less of a primary defense.
The threat of substitutes for GB Group's offerings is mainly from simpler, less sophisticated methods that fulfill a basic need for identity verification or fraud prevention. These include traditional manual checks and basic background screening services. While these substitutes are less effective and secure, they can appeal to businesses with budget constraints or less complex risk profiles.
In 2024, the global digital identity verification market reached approximately USD 20.5 billion, indicating a strong market preference for advanced solutions. However, legacy systems and simpler analytics, like rule-based fraud detection, continue to be used by some organizations, particularly SMEs, due to cost considerations. These methods, while not as robust against evolving threats, represent a lower-cost alternative.
Other substitutes involve enhancing physical security or relying more on device-centric multi-factor authentication (MFA) rather than deep identity data analysis. Strengthening internal controls and employee training also reduces the perceived need for external identity intelligence services. These alternative security measures aim to mitigate risks through different means, bypassing the core identity verification expertise.
| Substitute Type | Description | 2024 Market Relevance | GB Group's Competitive Edge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Verification | In-person checks, postal verification | Low, but present in niche markets | Speed, scalability, automation |
| Basic Background Checks | Standard credit reporting | Moderate, for foundational checks | Advanced fraud detection, real-time data |
| Legacy Rule-Based Systems | Older fraud detection logic | Significant in SMEs, cost-driven | AI/ML capabilities, adaptability |
| Physical Security | CCTV, access control | High, as a complementary measure | Digital identity assurance |
| Device-Centric MFA | Token-based or biometrics | High, for access control | Comprehensive identity intelligence |
Entrants Threaten
The identity data intelligence and fraud prevention sector, where GB Group operates, requires immense upfront capital. Developing and maintaining sophisticated platforms necessitates significant investment in cutting-edge technology, extensive data acquisition, and the hiring of highly specialized talent. For instance, building a robust fraud detection system can cost millions in R&D and infrastructure alone.
These substantial capital requirements act as a formidable barrier to entry. Potential new competitors must secure considerable funding to even begin developing a competitive offering, let alone scale it. This financial hurdle effectively discourages many smaller or less-funded entities from entering the market, thereby protecting established players like GB Group from a deluge of new rivals.
A significant hurdle for new companies entering GB Group's market is securing access to high-quality, global data. Established firms have cultivated deep relationships with data vendors, often possessing proprietary datasets that give them a distinct advantage in areas like identity verification and fraud prevention.
For instance, in 2024, the global data management market was valued at over $100 billion, with a substantial portion dedicated to identity verification and compliance data. New entrants struggle to replicate the sheer breadth and depth of data that companies like GB Group have accumulated over years of operation, making it difficult to compete on accuracy and efficiency.
The identity verification and fraud prevention sector faces significant regulatory hurdles, acting as a potent deterrent for new entrants. Compliance with a patchwork of global data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA, alongside stringent anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) mandates, demands substantial legal and operational investment. Navigating these complex and frequently updated regulations requires specialized expertise, making it difficult for newcomers to establish a compliant and trustworthy footing.
Brand Reputation and Trust
In the critical sectors of identity verification and fraud prevention, a company's brand reputation is a significant barrier to entry. GB Group, for instance, has cultivated a strong reputation for trust, accuracy, and reliability over many years, which is essential for attracting and retaining large enterprise clients who cannot afford compromises in these areas. This established trust is not easily replicated by newcomers.
New entrants face a substantial challenge in rapidly building the same level of credibility and demonstrating a proven track record. For example, in 2024, enterprise clients often conduct extensive due diligence, prioritizing vendors with a history of consistent performance and robust security measures. This makes it difficult for new players to displace incumbents like GB Group, who have already secured significant market share through their established brand equity.
- Established Trust: GB Group's long-standing reputation for accuracy and reliability in identity solutions is a key differentiator.
- Enterprise Client Demands: Major businesses prioritize proven effectiveness and security, making it hard for new entrants to gain traction.
- Credibility Gap: New companies struggle to quickly build the necessary trust and track record to compete with established players.
Technological Complexity & Expertise
The significant technological complexity inherent in developing advanced identity verification and fraud prevention solutions acts as a substantial barrier to entry. Companies like GB Group need deep expertise in artificial intelligence, machine learning, big data analytics, and robust cybersecurity measures. This specialized knowledge is crucial for building platforms that are not only scalable and accurate but also highly secure.
The continuous innovation required in this field further elevates the threat of new entrants. Potential competitors without substantial investment in research and development and a team possessing this niche expertise will find it exceedingly difficult to compete. For instance, GB Group's 2024 annual report highlighted their ongoing investment in AI-driven fraud detection, underscoring the capital and talent commitment needed to maintain a competitive edge.
- High R&D Investment: Companies must commit significant resources to stay ahead in AI and machine learning for fraud prevention.
- Specialized Talent Pool: Access to experts in data science, AI, and cybersecurity is a critical and often scarce resource.
- Intellectual Property: Proprietary algorithms and data sets developed over time create a strong competitive moat.
The threat of new entrants for GB Group is relatively low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for technology and data acquisition, estimated in the millions for robust systems, deter smaller players. Furthermore, the need for specialized talent in AI and data science, coupled with significant R&D investment, creates a steep learning curve.
Securing access to comprehensive, global data is another major hurdle, as established firms like GB Group have cultivated extensive proprietary datasets. Regulatory compliance, including GDPR and CCPA, demands significant legal and operational expertise, further complicating market entry. In 2024, the global data management market exceeded $100 billion, highlighting the scale of data resources required.
Finally, GB Group's strong reputation for trust and reliability, built over years, is difficult for newcomers to replicate. Enterprise clients in 2024 prioritize proven track records, making it challenging for new entrants to gain the necessary credibility and displace established players.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in technology, data, and talent. | Significant financial hurdle. | System development costs can reach millions. |
| Data Access | Need for extensive, high-quality global data. | Difficult to match established players' datasets. | Global data management market > $100B. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex global data privacy and AML/KYC laws. | Requires specialized legal and operational expertise. | GDPR, CCPA compliance is critical. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Established credibility with enterprise clients. | New entrants struggle to build trust and track record. | Enterprise clients demand proven performance. |
| Technological Complexity | Expertise in AI, ML, big data, and cybersecurity. | Requires substantial R&D and specialized talent. | Ongoing investment in AI-driven solutions. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive mix of data sources, including financial statements, market research reports from firms like Gartner and Forrester, and regulatory filings from government agencies. This ensures a robust understanding of industry structure and competitive dynamics.