Ford Motor PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ford Motor Bundle
Navigate the complex external forces shaping Ford Motor's destiny. Our PESTLE analysis delves into the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the automotive giant. Gain critical insights to inform your investment decisions and strategic planning.
Unlock a deeper understanding of Ford Motor's operating environment. From evolving consumer preferences to stringent environmental regulations, this analysis provides the crucial context you need. Download the full PESTLE analysis now to gain a competitive advantage.
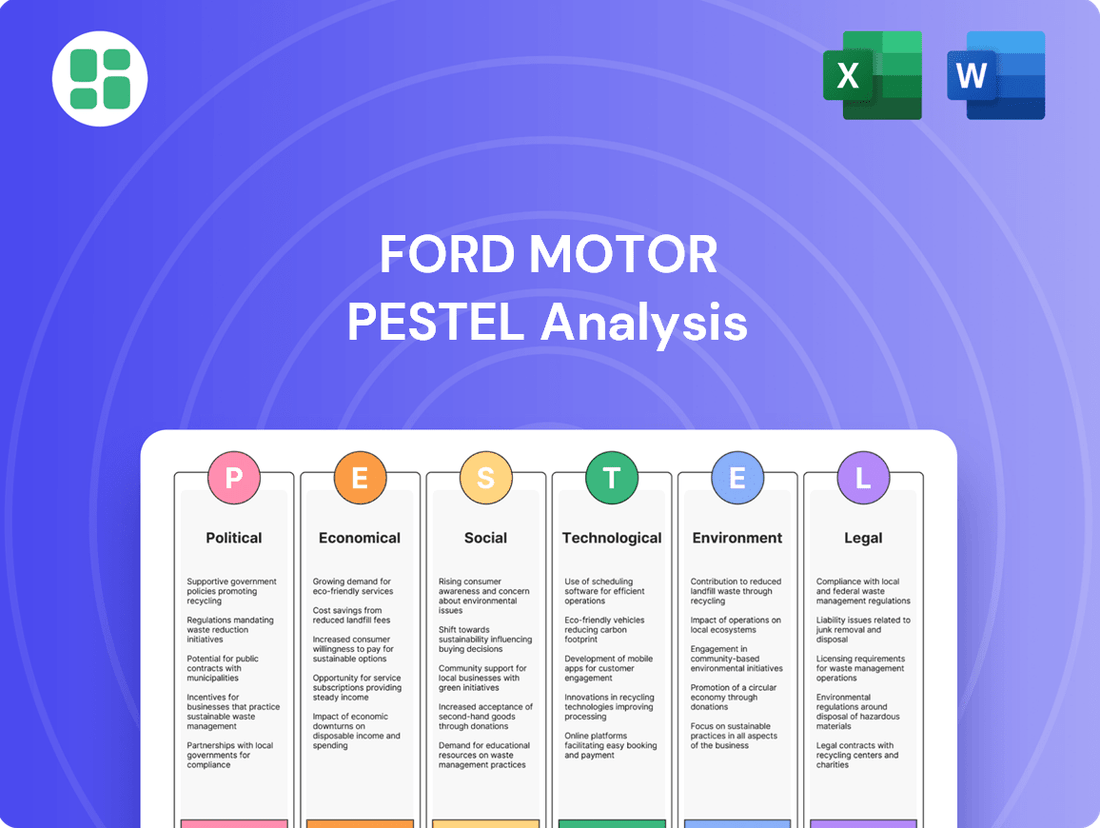
Political factors
Government policies, such as tax credits and incentives for electric vehicles (EVs), are a major driver for consumer adoption and directly shape Ford's production plans. For instance, the federal EV tax credit, which can reach up to $7,500, can now be applied at the point of sale, making EVs more affordable upfront. This, combined with various state and local initiatives designed to encourage greener transportation, creates a more favorable market for Ford's growing EV lineup.
Fluctuating trade policies and tariffs, especially those implemented by the U.S. government on imported vehicles and parts, present a considerable hurdle for Ford. These shifts create uncertainty in production costs and market access.
Ford anticipates a significant financial impact from these tariffs, projecting a hit between $1.5 billion and $2 billion in 2025. This figure underscores the direct financial strain these policies can impose on the automotive giant.
In response, Ford is proactively adjusting its operations. Strategies include optimizing its global supply chains, increasing the proportion of components sourced within the United States, and actively engaging with government officials to find ways to lessen the negative effects of these trade measures.
Global emissions regulations and fuel efficiency standards, like those stemming from the Paris Climate Agreement and California's stringent vehicle greenhouse gas standards, are fundamentally reshaping the automotive industry. These mandates are compelling companies like Ford to accelerate their transition towards electric and zero-emission vehicles, a strategic pivot critical for future market access and compliance.
Ford has publicly committed to ambitious environmental targets, aiming to reduce its Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions by 76% from 2017 levels by the year 2035. This commitment underscores the significant pressure from regulatory bodies and public demand for more sustainable automotive solutions.
Meeting these evolving emissions standards necessitates substantial, ongoing investment from Ford in research and development for new vehicle technologies, particularly in electrification and battery advancements. Furthermore, the company must invest in sustainable manufacturing practices across its global operations to minimize its environmental footprint.
Geopolitical Stability and Supply Chain Resilience
Geopolitical stability is a critical concern for Ford, directly influencing its intricate global supply chain. Trade tensions and regional conflicts can create significant disruptions, impacting everything from raw material availability to the cost of components. For instance, ongoing trade disputes or the emergence of new tariffs can quickly alter the economics of vehicle production. Ford's strategy involves actively diversifying its sourcing to mitigate risks associated with any single region. This includes a notable push to increase investment in North American manufacturing facilities, aiming to bolster resilience against unforeseen global events and align with evolving trade pacts.
Ford's commitment to supply chain resilience is evident in its strategic investments. By 2025, the company plans to invest billions in its North American operations, with a significant portion dedicated to battery production and electric vehicle manufacturing. This localization effort helps reduce reliance on overseas suppliers, particularly for critical components like semiconductors and battery cells, which have been subject to significant global shortages and price volatility in recent years. This strategic shift is designed to create a more robust and adaptable supply network.
- Diversification: Ford is actively reducing its dependence on single-region sourcing for key automotive components.
- Localization: Significant investment is being channeled into North American manufacturing, including battery plants, to enhance supply chain security.
- Resilience: These moves aim to protect against disruptions caused by geopolitical events, trade policy changes, and global supply shortages.
- Trade Compliance: Increased domestic production also supports adherence to regional trade agreements and potential future regulatory shifts.
Government Procurement and Fleet Policies
Government procurement policies and ambitious fleet electrification targets are shaping a significant demand landscape for Ford's commercial electric vehicles. As nations increasingly prioritize sustainability, large-scale government purchases of vehicles like the Ford E-Transit are becoming a key revenue driver. For instance, by the end of 2024, many countries aim to have a substantial portion of their public fleets transition to zero-emission vehicles, directly benefiting manufacturers like Ford.
These government mandates not only drive direct sales but also indirectly foster the necessary charging infrastructure crucial for the widespread adoption of electric commercial fleets. This supportive ecosystem is vital for Ford's long-term EV strategy, ensuring that its commercial offerings are practical and economically viable for a broader range of clients.
- Fleet Electrification Targets: Many national governments, including those in the European Union and the United States, have set targets for public fleets to reach 100% zero-emission by 2030 or earlier, creating a substantial potential market for Ford's E-Transit.
- Government Procurement Power: The sheer volume of vehicles purchased by government agencies represents a significant opportunity for manufacturers, potentially securing large, multi-year contracts for electric commercial vehicles.
- Infrastructure Influence: Government investment in public charging networks, often spurred by fleet electrification goals, directly supports the usability and economic feasibility of electric commercial vehicles for businesses and public services.
Government incentives, such as the Inflation Reduction Act's EV tax credits, directly influence consumer demand for Ford's electric vehicles. These policies, coupled with evolving emissions standards globally, compel Ford to accelerate its electrification strategy. The company's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 76% from 2017 levels by 2035 highlights the significant pressure from regulatory bodies and public expectations for sustainable automotive solutions.
Trade policies and tariffs, particularly those impacting imported components, create cost uncertainties for Ford. The company projects these tariffs could impact its financials by $1.5 billion to $2 billion in 2025, driving strategic decisions like increased North American sourcing and supply chain diversification.
Geopolitical stability directly affects Ford's global supply chain. Trade tensions and regional conflicts can disrupt raw material availability and component costs, prompting Ford to invest billions in North American manufacturing, including battery plants, by 2025 to enhance resilience.
Government procurement policies and fleet electrification mandates are creating substantial demand for Ford's commercial electric vehicles, like the E-Transit. Many governments aim for significant portions of their public fleets to be zero-emission by 2030, presenting a key revenue opportunity for Ford.
| Factor | Impact on Ford | Supporting Data/Examples |
| Government Incentives (EVs) | Boosts consumer demand for EVs, influencing production. | Federal EV tax credit up to $7,500, applicable at point of sale. |
| Emissions Regulations | Drives investment in electrification and R&D. | Ford aims for 76% reduction in Scope 1 & 2 GHG emissions by 2035 (from 2017 levels). |
| Trade Policies & Tariffs | Increases production costs and creates market uncertainty. | Projected financial impact of $1.5-$2 billion in 2025 due to tariffs. |
| Geopolitical Stability | Affects supply chain reliability and raw material costs. | Ford investing billions in North American manufacturing by 2025 for supply chain resilience. |
| Fleet Electrification Targets | Creates demand for commercial EVs like the E-Transit. | Many governments targeting zero-emission public fleets by 2030. |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal forces impacting Ford Motor, offering a comprehensive view of its operating landscape.
The Ford Motor PESTLE analysis serves as a pain point reliever by offering a clear, summarized version of the full analysis for easy referencing during meetings or presentations, streamlining complex external factors into actionable insights.
Economic factors
Global economic growth and consumer spending are critical drivers for Ford's performance, especially concerning its vehicle sales. In 2024, the International Monetary Fund projected global growth at 3.2%, a figure expected to hold steady into 2025, providing a generally supportive environment. However, consumer disposable income directly impacts demand for new vehicles, particularly higher-priced segments like electric vehicles (EVs) where Ford is investing heavily.
Economic slowdowns or recessions pose a significant risk, as seen in past downturns. A dip in consumer confidence can lead to postponed or canceled vehicle purchases, directly affecting Ford's revenue and profitability. For instance, during periods of economic uncertainty, consumers often defer major purchases, impacting sales volumes for both traditional and electric models.
Ford's financial outlook for 2025 remains intertwined with these macroeconomic uncertainties. While the company aims for robust sales, persistent inflation or unexpected geopolitical events could dampen consumer spending power and thus vehicle demand. Analysts are closely monitoring consumer sentiment surveys and inflation rates as key indicators for Ford's sales trajectory.
Rising inflation significantly impacts Ford by increasing the cost of essential inputs like steel, semiconductors, and labor. For instance, the Producer Price Index for manufactured goods saw a notable increase in late 2023 and early 2024, directly affecting Ford's manufacturing expenses and potentially squeezing profit margins on its vehicle sales.
Higher interest rates, a tool used to combat inflation, present a dual challenge for Ford. For consumers, elevated rates make auto loans more expensive, which can dampen demand for new vehicles, particularly higher-priced models. Simultaneously, Ford's own borrowing costs for crucial investments, such as its ambitious EV and autonomous driving initiatives, also rise, impacting the financial viability of these long-term strategic projects.
The fluctuating costs and availability of key materials like lithium, nickel, cobalt, steel, and semiconductors present a significant economic challenge for Ford, particularly as it ramps up electric vehicle (EV) production. For instance, lithium prices, after reaching highs in late 2022, saw considerable volatility throughout 2023 and into early 2024, impacting battery manufacturing costs.
Supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by geopolitical events and increased demand, continue to create price volatility for these essential components. This can directly translate to higher production expenses and potential delays in manufacturing schedules for Ford's new EV models and traditional vehicles alike.
In response, Ford is actively working to mitigate these economic risks by diversifying its battery material suppliers and investing in localized production facilities. This strategy aims to create a more resilient supply chain and gain better control over input costs, a crucial element for profitability in the competitive automotive market of 2024 and beyond.
Currency Exchange Rates
Fluctuations in currency exchange rates significantly influence Ford's financial performance, especially concerning its global sales and the sourcing of international components. For instance, a strengthening U.S. dollar can make Ford vehicles less competitive in foreign markets, potentially dampening sales volumes. Conversely, a weaker dollar can escalate the costs associated with importing essential parts and raw materials, squeezing profit margins.
Consider the impact on Ford's 2024 outlook. As of early 2024, the U.S. dollar has shown some volatility against major currencies like the Euro and the British Pound. If the dollar strengthens considerably against these currencies throughout the year, Ford could face headwinds in its European and UK operations, impacting revenue generated from those regions. This dynamic directly affects the translation of foreign earnings back into U.S. dollars.
- Impact on International Sales: A stronger USD makes exports pricier, potentially reducing demand in key overseas markets.
- Cost of Imported Components: A weaker USD increases the cost of parts sourced internationally, affecting production expenses.
- Currency Hedging Strategies: Ford employs hedging strategies to mitigate currency risks, but significant unexpected movements can still affect profitability.
Investment in Electrification and Technology
Ford is channeling significant capital into electrifying its fleet and advancing autonomous driving capabilities. This economic commitment, exceeding $22 billion through 2025 for connected and electric vehicles, is crucial for its long-term competitive standing. However, these substantial upfront investments in technology and battery manufacturing inherently involve considerable financial risk and can pressure immediate profitability.
The economic implications of this strategic shift are multifaceted:
- Significant Capital Outlay: Ford's commitment to electrification and technology represents billions in investment, impacting cash flow and requiring careful financial management.
- Future Growth Driver: These investments are designed to secure Ford's position in the evolving automotive market, anticipating future demand for EVs and advanced driver-assistance systems.
- Short-Term Profitability Impact: The high costs associated with R&D, new manufacturing processes, and battery supply chains can lead to reduced earnings in the interim period.
- Economic Sensitivity: The success of these investments is tied to broader economic conditions, including consumer spending power and government incentives for EV adoption.
Ford's financial health is intricately linked to global economic trends, with consumer spending on vehicles being a primary indicator. Projections for 2024 and 2025 suggest steady global growth, but this can be easily disrupted by inflation and interest rate hikes, which directly impact consumer purchasing power and Ford's borrowing costs.
Rising material costs, particularly for battery components like lithium, present a significant challenge, affecting production expenses. Ford's substantial investments in electrification, totaling over $22 billion through 2025, are vital for future competitiveness but also introduce financial risks and can strain short-term profitability.
Currency fluctuations also play a crucial role, with a strong U.S. dollar potentially hindering international sales and increasing the cost of imported parts. Ford's strategic responses, including diversifying suppliers and investing in local production, aim to build resilience against these economic volatilities.
| Economic Factor | 2024/2025 Projection/Impact | Ford's Exposure/Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Global Economic Growth | Projected steady at 3.2% (IMF) | Supports vehicle demand, but sensitive to downturns. |
| Inflation & Interest Rates | Persistent inflation, higher rates expected | Increases input costs, raises borrowing costs for investment, dampens consumer demand. Ford monitors consumer sentiment and inflation. |
| Material Costs (e.g., Lithium) | Volatile, impacting battery production | Affects EV manufacturing costs. Ford diversifies suppliers and invests in localized production. |
| Currency Exchange Rates | USD volatility against EUR, GBP | Stronger USD hurts international sales; weaker USD increases import costs. Ford uses hedging strategies. |
| Capital Investment (EV/Autonomous) | >$22 billion through 2025 | Secures future market position but strains short-term profitability and requires careful financial management. |
Same Document Delivered
Ford Motor PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive Ford Motor PESTLE analysis delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the automotive giant. Understand the external forces shaping Ford's strategy and future.
Sociological factors
Consumers are increasingly favoring electric and hybrid vehicles, a trend fueled by growing environmental awareness and the volatility of gasoline prices. This shift is a significant sociological factor impacting the automotive industry.
Ford is actively addressing this by broadening its electric and hybrid vehicle offerings, with a stated goal of having fully electric vehicles represent 50% of its global sales by 2030. This strategic pivot reflects a direct response to evolving consumer preferences.
To capitalize on this trend, Ford must adapt its product development and marketing approaches to align with these changing customer demands, ensuring its offerings resonate with an environmentally conscious and tech-savvy consumer base.
Consumer tastes are evolving, with a clear move away from traditional sedans towards utility vehicles, vans, and trucks, and importantly, their electric counterparts. This shift is driven by changing lifestyles and a demand for greater versatility.
Ford is strategically positioning itself to capitalize on this trend. For example, the F-150 Lightning, an electric version of America's best-selling truck, saw its sales increase by over 120% in the first quarter of 2024 compared to the same period in 2023, demonstrating strong market acceptance. Similarly, the Mustang Mach-E continues to attract buyers looking for electric performance and utility.
Beyond vehicle type, there's a growing expectation for integrated technology and connected services. Consumers now value features like advanced infotainment systems, over-the-air software updates, and seamless smartphone integration, influencing how vehicles are designed and marketed by companies like Ford.
As cities grow, so does the need for different ways to get around. Think ride-sharing services, car-sharing programs, and even self-driving buses. These are all part of the new mobility solutions that urban dwellers are looking for. In 2024, major cities globally are seeing continued population growth, with projections indicating that over 68% of the world's population will live in urban areas by 2050, according to UN data.
Ford is actively investing in these areas, recognizing the shift away from traditional car ownership in some segments. Their focus on connected services and exploring autonomous vehicle technology is a direct response to this trend. By 2025, it's anticipated that the global mobility-as-a-service market, which includes ride-sharing and car-sharing, could reach hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting the significant market opportunity.
Autonomous vehicles, in particular, hold the promise of making urban transportation safer and more efficient. Imagine fewer traffic jams and reduced accident rates. Ford's commitment to developing these technologies positions them to capitalize on the evolving urban landscape and changing consumer preferences for mobility.
Aging Population and Younger Buyer Preferences
Demographic shifts are reshaping the automotive market. Ford must navigate an aging population alongside the distinct preferences of younger consumers. This duality impacts everything from vehicle design to how Ford markets its cars.
Younger buyers, often Gen Z and Millennials, are signaling a strong demand for advanced technology, seamless connectivity, and environmentally sustainable options. For instance, a 2024 study indicated that over 60% of Gen Z consumers consider a vehicle's tech features a primary purchasing factor. This pushes manufacturers like Ford to integrate cutting-edge infotainment systems and explore electrification more aggressively.
Conversely, an aging demographic typically places a higher premium on user-friendliness and robust safety features. Ease of entry and exit, clear dashboard displays, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are becoming increasingly important. By 2025, the 65+ population in the US is projected to reach nearly 58 million, representing a significant market segment that Ford needs to address with tailored vehicle attributes.
- Younger Consumer Priorities: Focus on advanced tech, connectivity, and sustainability.
- Aging Consumer Priorities: Emphasis on ease of use, safety features, and accessibility.
- Market Impact: Ford needs a diverse product portfolio to appeal to both demographic groups.
- Data Point: Over 60% of Gen Z consumers cite tech features as a key purchase driver (2024 data).
Health, Safety, and Trust in Technology
Public perception and trust in vehicle safety, particularly with the rise of autonomous driving, significantly influence consumer adoption of new technologies. Ford's commitment to safety is evident in its advanced driver-assist systems like Ford Co-Pilot360™, which aims to build consumer confidence.
The company's BlueCruise hands-free driving technology further underscores this focus, seeking to alleviate driver concerns about advanced vehicle capabilities. However, maintaining this trust is paramount, especially in light of past safety-related recalls that can erode public faith.
For instance, in 2023, Ford issued several recalls, including one affecting over 100,000 vehicles due to potential braking system issues, highlighting the ongoing need for rigorous safety validation and transparent communication to uphold public trust in their technological advancements.
- Public Trust: Consumer willingness to adopt advanced vehicle safety features, including autonomous driving, hinges on perceived reliability and safety.
- Ford's Safety Features: Technologies like Ford Co-Pilot360™ and BlueCruise are designed to proactively enhance safety and build user confidence.
- Impact of Recalls: Safety recalls, such as those in 2023 affecting hundreds of thousands of vehicles, directly impact public perception and trust in automotive technology.
Sociological factors are significantly influencing the automotive landscape, with a pronounced shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles driven by environmental concerns and fluctuating fuel prices. Ford's strategic response includes a goal for electric vehicles to comprise 50% of global sales by 2030, directly aligning with these evolving consumer preferences.
Consumer tastes are also evolving beyond powertrain, favoring utility vehicles, vans, and trucks, especially their electric variants, reflecting changing lifestyles and a demand for versatility. Ford's F-150 Lightning, for example, saw a 120% sales increase in Q1 2024 over Q1 2023, demonstrating strong market acceptance for electric trucks.
Demographic shifts present a dual challenge, with younger consumers prioritizing technology and sustainability, while an aging population values ease of use and safety features. By 2025, the US population aged 65+ is projected to reach nearly 58 million, a segment requiring tailored vehicle attributes.
Public trust in vehicle safety, particularly with autonomous driving, remains a critical factor. Ford's safety technologies like Co-Pilot360™ aim to build confidence, though past recalls, such as one in 2023 affecting over 100,000 vehicles due to braking issues, underscore the need for ongoing rigorous safety validation and transparent communication.
| Sociological Factor | Consumer Trend | Ford's Response/Data |
| Environmental Awareness | Preference for EVs/Hybrids | 50% EV sales goal by 2030 |
| Lifestyle Changes | Demand for Utility Vehicles | F-150 Lightning Q1 2024 sales +120% YoY |
| Demographic Shifts | Younger: Tech/Sustainability; Older: Ease/Safety | US 65+ population ~58M by 2025 |
| Trust in Technology | Safety Concerns (Autonomous Driving) | 2023 recall impacting >100K vehicles |
Technological factors
Ford is heavily investing in battery technology, exploring new chemistries like Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) and Lithium Manganese Rich (LMR). These advancements aim to lower production costs, extend driving ranges, and enhance safety, crucial steps for making electric vehicles (EVs) more competitive with traditional gasoline cars. Ford's dedicated Ion Park facility is at the forefront of these developments.
Ford is heavily investing in autonomous driving technology, with its BlueCruise system already enabling hands-free driving on over 130,000 miles of pre-mapped highways in North America. The company is pushing towards Level 4 autonomy, which would allow vehicles to operate without human intervention in defined operational domains.
This development involves significant investment in advanced sensor suites, including LiDAR and high-definition cameras, alongside sophisticated AI and machine learning algorithms. Ford's strategic partnerships and internal R&D efforts are focused on creating a robust and safe autonomous driving experience, with plans to integrate these capabilities into more urban settings and a wider range of vehicles in the coming years.
The automotive industry's technological evolution is heavily influenced by the rise of software-defined vehicles (SDVs) and enhanced connectivity. Ford is actively embracing this shift, integrating its FordPass™ Connect system across its lineup. This allows for remote vehicle access, diagnostics, and real-time data, fundamentally changing how owners interact with their cars.
A key aspect of this technological push is the implementation of over-the-air (OTA) updates. Ford utilizes OTA technology to continuously improve vehicle software, introduce new features, and even boost performance without requiring a dealership visit. This capability is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and customer satisfaction in a rapidly advancing technological landscape.
Manufacturing Process Innovations
Ford is actively integrating cutting-edge manufacturing processes to boost efficiency and sustainability. The company is leveraging artificial intelligence within its production lines, aiming to optimize operations and reduce waste. For instance, Ford's '3-Wet' paint system is a key innovation designed to significantly cut CO2 emissions during the painting process.
Furthermore, Ford demonstrates a strong commitment to circular economy principles by prioritizing aluminum recycling and the incorporation of recycled or renewable materials in vehicle plastics. This focus on sustainable sourcing and manufacturing aligns with broader industry trends and regulatory pressures, positioning Ford to meet evolving environmental standards and consumer expectations.
- AI Integration: Ford is deploying AI for predictive maintenance and quality control, aiming to minimize downtime and enhance product consistency.
- '3-Wet' Paint System: This technology reduces the number of paint application steps, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced VOC emissions.
- Recycling Initiatives: Ford aims to maximize aluminum recycling rates and increase the use of recycled content in vehicle components, contributing to a lower carbon footprint.
- Sustainable Materials: The company is exploring and implementing the use of renewable materials in plastics and other interior components.
Charging Infrastructure and Energy Management
The expansion of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure remains a critical technological factor for widespread adoption, directly impacting Ford's market penetration. By the end of 2024, the U.S. had over 170,000 public charging ports, a number projected to grow significantly. Ford's strategy includes bolstering its Blue Oval Charge Network, which by early 2025 offers access to over 100,000 charging points across North America, and importantly, integrating access to Tesla's Supercharger network, adding tens of thousands more locations. This move is crucial for alleviating range anxiety and making EV ownership more practical.
Furthermore, advancements in energy management technologies are reshaping the EV landscape. Smart charging solutions, which optimize charging times based on grid load and electricity prices, are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Ford is exploring these capabilities to enhance customer experience and potentially reduce charging costs. Concurrently, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, allowing EVs to send power back to the grid, is gaining traction. While still in early deployment phases, V2G offers potential revenue streams for EV owners and grid stability benefits, areas Ford is monitoring and developing for future integration.
- Charging Network Expansion: Ford's Blue Oval Charge Network aims for over 100,000 charging points in North America by early 2025, augmented by Tesla Supercharger access.
- Public Charging Growth: The U.S. is projected to surpass 200,000 public charging ports by the end of 2025, indicating a rapidly growing ecosystem.
- Smart Charging Adoption: Ford is investing in smart charging to optimize EV energy consumption and costs for consumers.
- V2G Technology Development: The company is exploring vehicle-to-grid capabilities, which could offer new value propositions for EV owners and grid operators.
Ford's commitment to electric vehicle (EV) technology is evident in its significant investments in battery innovation, including exploring new chemistries like LFP and LMR to reduce costs and improve range. The company's BlueCruise system, enabling hands-free driving on over 130,000 miles of highways by late 2024, highlights its push towards advanced driver-assistance systems and eventual Level 4 autonomy.
The automotive industry's shift towards software-defined vehicles is a key technological driver, with Ford integrating its FordPass Connect system for enhanced connectivity and over-the-air updates to continuously improve vehicle functionality. These technological advancements are crucial for Ford's competitiveness and customer engagement in the evolving automotive market.
Ford is also leveraging AI in manufacturing for efficiency and sustainability, exemplified by its '3-Wet' paint system that reduces CO2 emissions. The company's focus on recycling and using recycled materials in vehicle components further underscores its commitment to environmentally conscious production methods.
| Technology Area | Ford's Focus/Investment | Key Data/Milestones (2024-2025) |
| Battery Technology | LFP, LMR chemistries; Ion Park facility | Cost reduction, range extension, safety improvements |
| Autonomous Driving | BlueCruise; Level 4 autonomy | Hands-free driving on 130,000+ miles (late 2024); advanced sensor integration |
| Software-Defined Vehicles | FordPass Connect; Over-the-Air (OTA) updates | Remote access, diagnostics, continuous software improvement |
| Manufacturing | AI integration; '3-Wet' paint system | Optimized operations, reduced waste, lower CO2 emissions in painting |
| EV Charging | Blue Oval Charge Network; Tesla Supercharger access | 100,000+ charging points (early 2025); U.S. public ports >200,000 (end 2025) |
Legal factors
Ford must adhere to rigorous global vehicle safety regulations, exemplified by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States. These standards are constantly evolving, with recent updates in 2024 focusing on enhanced driver-assistance systems and cybersecurity for connected vehicles. Failure to comply can lead to significant fines and reputational damage.
Ongoing advancements in safety, such as improved pedestrian detection systems and stricter requirements for electronic stability control, demand continuous engineering investment from Ford. These updates can necessitate costly recalls; for instance, Ford issued a recall for over 400,000 vehicles in early 2024 due to issues with rearview camera systems, highlighting the financial impact of safety compliance.
Ford operates under a stringent global framework of environmental and emissions laws, including evolving greenhouse gas regulations and mandates pushing for zero-emission vehicles. For instance, the European Union's CO2 emission standards for new passenger cars and vans set targets for fleet average emissions, with significant penalties for non-compliance. California's Advanced Clean Cars II regulation, adopted by several US states, requires an increasing percentage of zero-emission vehicle sales, directly impacting Ford's product development and sales strategies.
Compliance with these diverse regulations, such as those enforced by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and various international bodies, necessitates substantial investment in research and development for cleaner powertrain technologies and manufacturing processes. In 2023, Ford announced plans to invest over $50 billion through 2026 in electric vehicles and battery technology, a direct response to these regulatory pressures and market shifts.
With vehicles becoming increasingly connected, Ford faces significant legal obligations related to data privacy and cybersecurity. Regulations like the GDPR in Europe and various state-level privacy laws in the U.S. dictate how Ford must handle the vast amounts of data generated by its vehicles, from driving habits to personal preferences. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines; for instance, under GDPR, penalties can reach up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher.
Protecting this data from cyber threats is paramount. The automotive industry is a growing target for cyberattacks, and a breach could compromise vehicle safety and customer trust. Ford must invest heavily in robust cybersecurity measures to prevent unauthorized access and data theft, as a significant data breach could lead to substantial legal liabilities and reputational damage, impacting future sales and customer loyalty.
Labor Laws and Union Relations
Labor laws and union relations are critical for Ford, especially in its major manufacturing hubs like the United States. These regulations and agreements directly influence operational costs, wage structures, and the overall stability of production. For instance, the United Auto Workers (UAW) union plays a significant role in shaping Ford’s labor landscape.
Collective bargaining agreements, such as the one ratified in late 2023, set the terms for wages, benefits, and working conditions for tens of thousands of Ford employees. These agreements, while aiming for stability, also carry the potential for significant financial implications and, in cases of disputes, can lead to costly production stoppages. The UAW secured significant wage increases and improved benefits for its members in the 2023 contract, reflecting the ongoing negotiation dynamics.
- Impact of UAW Contract: The 2023 UAW contract with Ford included substantial wage hikes, cost-of-living adjustments, and improved retirement benefits, directly increasing Ford's labor expenses.
- Production Stability: Historically, labor disputes have caused significant production disruptions for Ford, affecting vehicle output and supply chain continuity.
- Labor Cost Management: Ford's ability to manage labor costs through efficient negotiation and operational strategies is crucial for maintaining its competitive edge in the automotive market.
International Trade and Intellectual Property Laws
Ford operates within a complex web of international trade agreements, constantly adapting to shifting tariffs and import/export regulations that impact its global supply chain and vehicle pricing. For instance, trade tensions between major economic blocs can directly affect the cost of components and finished vehicles, influencing profitability.
Protecting its vast intellectual property portfolio, especially in cutting-edge areas like electric vehicle (EV) battery technology and autonomous driving systems, is paramount for Ford's competitive standing. The company invests heavily in legal resources to secure patents and defend against infringement, a critical expenditure in the rapidly evolving automotive landscape.
- Intellectual Property Protection Costs: In 2024, Ford's R&D spending on new technologies, which includes significant legal costs for patent filings and defense, is projected to exceed USD 10 billion.
- Trade Agreement Impact: The USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement) continues to shape North American auto manufacturing, with specific rules of origin impacting component sourcing and vehicle production costs for Ford.
- Global Tariffs: Fluctuations in tariffs, such as those potentially imposed on vehicles or parts between the EU and the UK post-Brexit, directly influence Ford's European market strategy and profitability.
- EV Technology Patents: As of early 2025, Ford holds over 500 active patents related to EV powertrain and battery management systems, underscoring the legal investments required to safeguard its technological advancements.
Ford navigates a complex legal landscape, facing stringent global safety standards, such as those from NHTSA, with evolving requirements for driver assistance and cybersecurity. Environmental regulations, including greenhouse gas mandates and zero-emission vehicle targets like California's Advanced Clean Cars II, necessitate significant investment in cleaner technologies, with Ford planning over $50 billion investment in EVs through 2026. Data privacy and cybersecurity laws like GDPR impose substantial obligations for handling vehicle-generated data, with potential fines reaching up to 4% of global turnover.
| Legal Area | Key Regulations/Factors | Impact on Ford | Example Data/Figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Safety | NHTSA regulations, Cybersecurity standards | Mandatory engineering investment, potential fines for non-compliance | Recall of over 400,000 vehicles in early 2024 for rearview camera issues |
| Environmental | Emissions standards (EU CO2, US EPA), ZEV mandates | Investment in EV technology, compliance costs | $50 billion+ planned EV/battery investment through 2026; California ACC II |
| Data Privacy & Cybersecurity | GDPR, US state privacy laws | Robust data protection measures, potential for large fines | GDPR fines up to 4% of global turnover; growing cyber threat to automotive data |
| Labor Law | UAW agreements, wage regulations | Influences labor costs, production stability | 2023 UAW contract included significant wage increases and benefit improvements |
| Trade & IP | Trade agreements (USMCA), patent law | Impacts supply chain costs, protects R&D investments | Over 500 EV technology patents held by Ford as of early 2025; USMCA rules of origin |
Environmental factors
Ford has committed to ambitious carbon emission reduction targets, aiming for carbon neutrality across its entire value chain by 2050. This includes significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, with a goal to cut Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 76% compared to 2017 levels by 2035.
To achieve these environmental goals, Ford is heavily investing in electrification, targeting 50% of its global vehicle sales to be fully electric by 2030. This strategic shift is crucial for meeting regulatory demands and consumer preferences for sustainable transportation solutions.
Ford is prioritizing sustainable sourcing, aiming to incorporate more recycled and renewable materials into its vehicles. This commitment extends to reducing waste, with a goal to divert 90% of manufacturing waste from landfills by 2030. The company is also expanding its battery recycling initiatives, recognizing the critical role of a circular economy in its environmental strategy.
Ford is actively pursuing a significant shift towards renewable energy sources for its manufacturing operations. A core environmental initiative is the ambitious goal of powering all its facilities with 100% carbon-free electricity by 2035, aiming for 100% locally sourced renewable energy.
This strategic pivot necessitates substantial capital allocation towards developing and integrating solar, wind, and hydroelectric power generation. By doing so, Ford aims to substantially decrease its dependence on traditional fossil fuels, aligning with global sustainability trends and regulatory pressures.
Water Stewardship and Waste Management
Ford is actively pursuing ambitious goals in water stewardship and waste management, aiming for zero water withdrawals in manufacturing and significant waste reduction globally. These efforts underscore a commitment to environmental sustainability throughout their operations.
Key initiatives include a target to eliminate single-use plastics by 2030 and a broader aspiration for zero waste to landfill across all facilities. This focus on resource efficiency is becoming increasingly critical for automotive manufacturers navigating evolving environmental regulations and consumer expectations.
- Water Conservation: Ford aims for zero water withdrawals in its manufacturing processes.
- Waste Reduction: The company is working to minimize waste generation across its global operations.
- Plastic Elimination: A target is set to eliminate single-use plastics from operations by 2030.
- Zero Waste Aspiration: Ford is striving to achieve true zero waste to landfill.
Environmental Impact of EV Battery Production and Disposal
While electric vehicles (EVs) offer significant advantages in reducing tailpipe emissions, the environmental footprint of battery production and disposal presents a notable challenge. Mining essential materials like lithium and cobalt can have localized environmental impacts, and managing end-of-life batteries requires careful consideration to prevent pollution. Ford is actively working to address these concerns by exploring more sustainable battery chemistries and investing in localized battery manufacturing to reduce transportation-related emissions.
Ford's strategy includes developing robust battery recycling programs, aiming to recover valuable materials and minimize waste. For instance, the company is collaborating on initiatives to establish a circular economy for EV batteries. By 2025, projections suggest that the global demand for lithium-ion batteries could reach hundreds of gigawatt-hours, underscoring the importance of sustainable production and recycling practices.
- Sustainable Battery Chemistries: Ford is researching and developing batteries that utilize more readily available and ethically sourced materials, reducing reliance on conflict minerals and minimizing environmental disruption during extraction.
- Localized Battery Production: Establishing battery manufacturing facilities closer to vehicle assembly plants, such as Ford's BlueOval City in Tennessee, aims to cut down on transportation emissions and improve supply chain efficiency.
- Battery Recycling Programs: Ford is investing in and partnering with recycling companies to ensure that used EV batteries are processed responsibly, recovering valuable metals like nickel, cobalt, and lithium for reuse in new batteries.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: The company is exploring second-life applications for EV batteries, such as energy storage systems, before they are ultimately recycled, further extending their useful lifespan and reducing overall waste.
Ford is actively addressing environmental concerns by setting ambitious emission reduction targets and investing heavily in electric vehicle (EV) technology. The company aims for carbon neutrality by 2050 and a 76% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 2035 compared to 2017. By 2030, Ford plans for 50% of its global sales to be fully electric, underscoring a significant shift towards sustainable transportation.
Ford's environmental strategy extends to sustainable material sourcing and waste reduction, with a goal to divert 90% of manufacturing waste from landfills by 2030 and eliminate single-use plastics by 2030. Furthermore, the company is committed to powering all its facilities with 100% carbon-free electricity by 2035, actively pursuing renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
Challenges remain, particularly concerning the environmental impact of battery production and disposal. Ford is investing in sustainable battery chemistries, localized production, and robust recycling programs to manage these issues effectively. By 2025, the projected global demand for lithium-ion batteries highlights the critical need for these sustainable practices.
| Environmental Target | Metric | Year |
| Carbon Neutrality | Across entire value chain | 2050 |
| Scope 1 & 2 Emissions Reduction | 76% reduction | 2035 (vs. 2017) |
| Electric Vehicle Sales | 50% of global sales | 2030 |
| Manufacturing Waste Diversion | 90% diversion from landfills | 2030 |
| Single-Use Plastics Elimination | Elimination | 2030 |
| Renewable Energy for Facilities | 100% carbon-free electricity | 2035 |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Ford Motor PESTLE Analysis is built on a robust foundation of data from official government publications, leading economic institutions like the IMF and World Bank, and reputable industry research firms. This ensures comprehensive coverage of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the automotive sector.