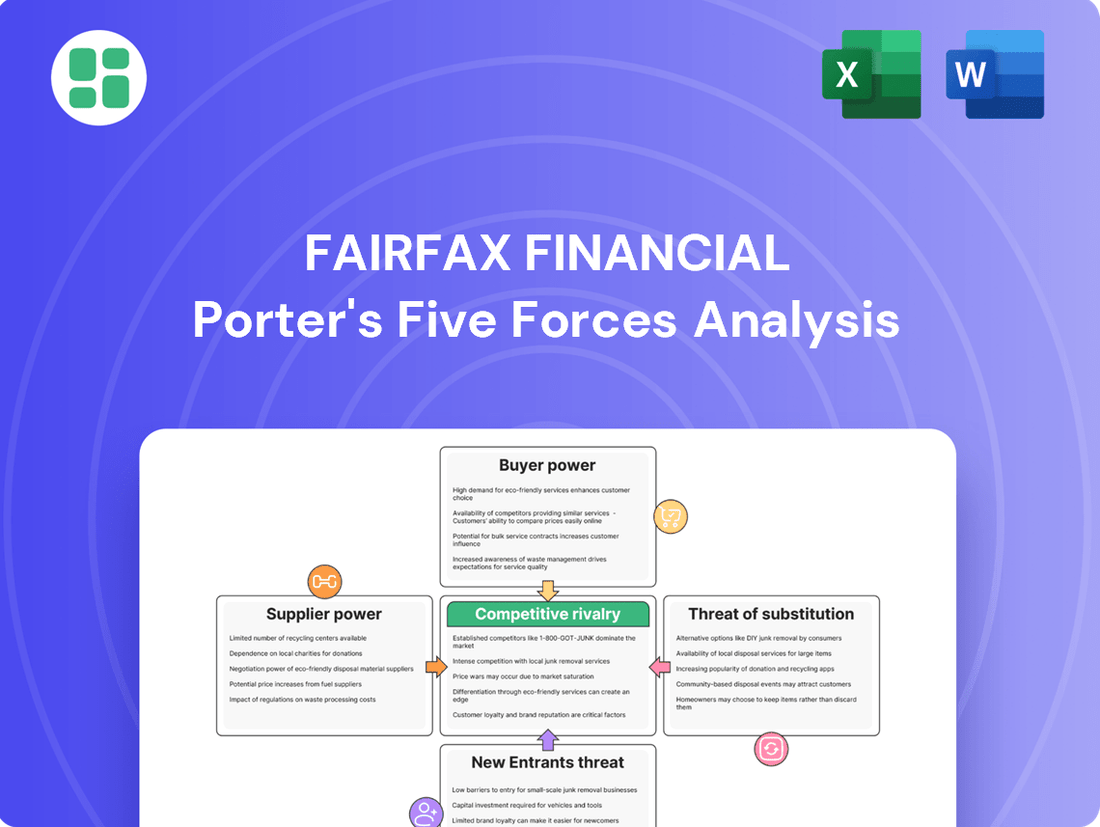
Fairfax Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fairfax Financial Bundle
Fairfax Financial operates in a dynamic insurance and financial services landscape, where understanding the competitive forces is crucial. Our analysis reveals how the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry shape Fairfax's strategic landscape.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Fairfax Financial’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fairfax Financial, a major insurance and reinsurance entity, depends heavily on access to global capital and retrocessionaires to cover substantial risks. The cost and availability of this capital, influenced by interest rates and investor risk tolerance, directly affect Fairfax's underwriting capacity and financial performance.
In 2024, the global reinsurance market is expected to maintain strong capitalization and profitability. This generally translates to a more favorable supply of capital for companies like Fairfax, potentially moderating the bargaining power of capital providers.
The insurance sector's reliance on sophisticated technology and data analytics for underwriting, claims, and risk assessment is growing. Suppliers of specialized software, AI, and extensive datasets wield significant influence, particularly as digital transformation accelerates. Deloitte's 2024 insights show insurers are adopting AI for better customer experiences and loss prevention, underscoring the power of these tech providers.
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly those with specialized human capital, is a significant factor for Fairfax Financial. Actuaries, expert underwriters, and seasoned risk managers are indispensable for Fairfax's core property and casualty insurance and reinsurance businesses. The limited availability of individuals possessing these niche skills can translate into substantial leverage for them, potentially driving up compensation expectations and complicating talent acquisition efforts.
Fairfax's operational philosophy, which champions a decentralized structure with autonomous management teams, further amplifies the importance of retaining experienced leadership. The company's ability to secure and keep top-tier talent in these critical roles directly impacts its strategic execution and competitive edge. For instance, in 2023, the demand for actuaries remained high, with industry reports indicating a persistent shortage, underscoring the potential for these professionals to command competitive compensation packages.
Catastrophe Modeling and Risk Assessment Services
The bargaining power of suppliers in catastrophe modeling and risk assessment services is significant for Fairfax Financial, particularly given its substantial exposure to property and casualty risks. These specialized service providers often possess proprietary modeling capabilities and vast historical datasets, making their expertise critical for accurately pricing and managing complex risks such as those posed by wildfires and hurricanes.
The financial impact of the California wildfires in early 2025, which resulted in considerable losses for Fairfax, highlights the indispensable nature of these services. This reliance grants suppliers considerable leverage in negotiating pricing and contract terms.
- High switching costs for insurers due to the integration of specialized modeling software and data.
- Concentration of expertise among a few leading catastrophe modeling firms.
- Criticality of accurate data for regulatory compliance and capital management.
- Potential for price increases by suppliers based on the perceived value of their risk assessment insights.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance Providers
Fairfax Financial operates globally, making legal and regulatory compliance providers crucial. These suppliers, offering legal expertise, compliance software, and advisory services, hold significant bargaining power due to the complex and ever-changing international regulatory environment. For instance, the increasing complexity of data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA, and the substantial fines for non-compliance, elevate the importance and leverage of these specialized service providers.
The high costs associated with non-compliance, potentially reaching millions in fines and reputational damage, further strengthen the position of legal and regulatory compliance providers. Fairfax's need to navigate diverse international jurisdictions means reliance on these experts is paramount, giving them considerable influence over pricing and service terms.
- Supplier Concentration: The market for highly specialized legal and regulatory compliance services often features a limited number of expert firms, increasing their bargaining power.
- Switching Costs: The effort and expense involved in changing compliance providers, including data migration and retraining, can be substantial, locking Fairfax into existing relationships.
- Importance of Service: The critical nature of legal and regulatory adherence means Fairfax has little room for error, making supplier reliability a key factor that enhances supplier leverage.
- Threat of Forward Integration: While less common in this sector, the potential for large compliance firms to develop in-house insurance capabilities could theoretically shift power, though this is not a primary concern for Fairfax currently.
Suppliers of specialized technology, data analytics, and actuarial talent hold considerable sway over Fairfax Financial. The increasing reliance on AI and sophisticated modeling for risk assessment means providers of these solutions, like those offering advanced catastrophe modeling, can command higher prices. In 2024, the demand for AI in insurance is projected to grow significantly, with companies like Fairfax investing in these technologies to enhance underwriting and claims processing.
| Supplier Type | Impact on Fairfax | 2024 Market Trend | Supplier Bargaining Power Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catastrophe Modeling Firms | Critical for risk pricing and capital management. | Strong demand for advanced analytics. | High due to proprietary data and models. |
| AI & Data Analytics Providers | Enhances underwriting, claims, and customer experience. | Rapid adoption across the insurance sector. | Growing, especially for specialized AI solutions. |
| Actuarial & Risk Management Talent | Essential for core insurance operations. | Persistent shortage of highly skilled professionals. | High due to specialized expertise and limited supply. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Fairfax Financial's insurance and investment operations.
Instantly pinpoint competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive model that highlights key threats and opportunities for Fairfax Financial.
Customers Bargaining Power
Fairfax's large commercial and reinsurance clients wield considerable bargaining power. These sophisticated buyers, often global corporations or fellow insurers, procure vast amounts of coverage and possess the financial acumen to solicit bids from numerous international insurers.
Their ability to compare diverse global offerings allows them to effectively negotiate for lower premiums, customized policy structures, and advantageous coverage clauses. For instance, in 2024, the global commercial insurance market saw intense competition, with buyers leveraging this environment to secure more favorable terms.
Fairfax Financial's reliance on insurance brokers and intermediaries significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. These intermediaries, representing policyholders, can direct substantial business to insurers offering competitive pricing and terms, effectively acting as a consolidated customer voice. For instance, in 2024, major global insurance brokers continued to consolidate their market presence, giving them greater leverage in negotiations with insurers like Fairfax.
In commoditized areas of property and casualty insurance, like personal auto, customers often focus heavily on price. This means they can easily switch to a different insurer if they find a better deal, as they don't see much difference between providers. This dynamic puts pressure on companies like Fairfax's subsidiaries to keep their premiums very competitive, which can impact their profit margins, a trend observed in the U.S. P&C market during 2024 and into 2025.
Increased Customer Information and Digital Tools
The rise of online insurance comparison sites and enhanced transparency in policy details significantly boosts customer knowledge. This leveling of the information playing field enables consumers to readily compare prices and terms from different providers. For instance, in 2024, platforms like Insurify and Policygenius reported millions of user sessions, indicating a substantial shift towards informed comparison shopping.
This increased customer awareness directly translates into greater bargaining power. Customers can now easily identify the best deals and negotiate more effectively for personalized and efficient services. This trend forces insurers to be more competitive on pricing and service offerings to retain market share.
- Informed Decisions: Customers can make better choices due to readily available policy details and pricing.
- Price Sensitivity: Easy comparison leads to greater focus on cost-effectiveness.
- Demand for Customization: Customers expect tailored policies and services that meet their specific needs.
- Competitive Pressure: Insurers face increased pressure to offer attractive terms and superior customer experiences.
Diversified Customer Base
Fairfax Financial's strength lies in its broad customer base. While large clients or price-sensitive markets can exert pressure, the company operates across numerous insurance sectors and geographical areas. This wide reach means no single customer group holds significant sway.
This diversification is key to Fairfax's strategy. It reduces reliance on any one segment, offering protection against localized market demands or the bargaining power of a few major clients. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, Fairfax's insurance and reinsurance operations span property, casualty, and specialty lines globally, demonstrating this broad customer engagement.
- Diversified Revenue Streams: Fairfax's presence in multiple insurance lines (e.g., property, casualty, specialty) and geographies dilutes the impact of any single customer segment's bargaining power.
- Reduced Customer Concentration Risk: The company avoids over-dependence on a few large clients, which is a common vulnerability for businesses.
- Global Footprint: Operations in North America, Europe, Asia, and other regions mean that even if one market experiences customer pressure, others can compensate.
- Mitigation of Price Sensitivity: By serving a wide array of customers with varying needs and price sensitivities, Fairfax can absorb localized pricing demands more effectively.
Fairfax's large commercial clients, often global entities, possess significant bargaining power due to their ability to solicit bids from numerous international insurers and their sophisticated understanding of policy terms. This was evident in 2024 as the competitive global commercial insurance market allowed buyers to negotiate for lower premiums and customized coverage. Furthermore, the increasing consolidation of major insurance brokers in 2024 amplified their leverage, as they represent substantial policyholder business and can direct it to insurers offering the most favorable terms.
In more commoditized insurance lines, like personal auto, customers are highly price-sensitive and can easily switch providers, a trend observed in the U.S. market throughout 2024. The proliferation of online comparison platforms in 2024, with sites like Insurify and Policygenius recording millions of user sessions, has significantly enhanced customer knowledge and their ability to negotiate for better deals, forcing insurers to remain competitive on both price and service.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Fairfax |
|---|---|---|
| Large Commercial Clients | Global reach, financial acumen, bid solicitation | Negotiate for lower premiums, customized policies |
| Insurance Brokers/Intermediaries | Market consolidation, directing substantial business | Act as consolidated customer voice, increased leverage |
| Price-Sensitive Consumers (e.g., Personal Auto) | High price sensitivity, ease of switching, online comparison | Pressure on premiums, potential margin impact |
Same Document Delivered
Fairfax Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Fairfax Financial Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the insurance sector. You're viewing the actual document; the moment you purchase, you'll receive this exact, professionally formatted analysis, ready for immediate use and insight into Fairfax's market dynamics. This comprehensive breakdown will equip you with a thorough understanding of the industry's forces impacting Fairfax Financial's operations.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Fairfax Financial navigates a fiercely competitive landscape, facing off against global insurance and reinsurance giants like Berkshire Hathaway, Chubb, and Swiss Re. These established players boast substantial financial clout, widespread global reach, and deeply ingrained brand loyalty, intensifying the struggle for market dominance.
In 2023, the global insurance market saw significant activity, with major players reporting robust financial results. For instance, Berkshire Hathaway's insurance operations, a key competitor, generated substantial underwriting profits, highlighting the financial muscle Fairfax must contend with. Similarly, Chubb's continued expansion into new markets underscores the aggressive growth strategies employed by these large competitors.
The property and casualty insurance and reinsurance sectors are inherently cyclical, swinging between soft markets with abundant capacity and low premiums, and hard markets characterized by limited capacity and escalating prices. Fairfax Financial must maintain rigorous underwriting standards and profitability amidst these fluctuations.
This cyclicality fuels intense price competition, a reality underscored by market dynamics observed in 2024 and projected into 2025. For instance, during periods of high competition, insurers might reduce premiums to capture market share, potentially impacting profitability if not managed carefully through disciplined underwriting.
The insurance sector is in the throes of a significant digital transformation, fueling intense competition. Companies are pouring resources into InsurTech, artificial intelligence, and sophisticated data analytics to streamline operations, elevate customer interactions, and sharpen risk evaluation. For instance, in 2024, global InsurTech funding reached an estimated $10 billion, highlighting the scale of investment in these areas.
Fairfax Financial faces a critical challenge to keep pace with this technological advancement. Continuous innovation and the swift adoption of new digital tools are paramount for Fairfax to maintain its competitive edge and prevent being outmaneuvered by rivals who are rapidly embracing cutting-edge technologies.
Mergers, Acquisitions, and Consolidation
The insurance and reinsurance industries are indeed hotbeds for mergers and acquisitions (M&A), driving significant consolidation. This means we're seeing fewer, but much larger, players emerge. These consolidated entities wield greater scale, a stronger market presence, and more diverse offerings, inevitably intensifying the competition for market share and skilled professionals.
For instance, in 2024, the global M&A activity in the insurance sector remained robust, with notable deals reshaping the competitive landscape. Major transactions often involve companies seeking to expand their geographic reach, enhance their product portfolios, or achieve greater operational efficiencies through economies of scale. This ongoing consolidation means that companies like Fairfax Financial must constantly adapt to a more concentrated competitive environment where larger rivals can exert greater pricing power and influence.
- Consolidation Impact: Fewer, larger competitors with increased market influence and diversified portfolios.
- Talent Competition: Intensified rivalry for skilled professionals in a consolidating market.
- 2024 Trends: Continued robust M&A activity in the insurance sector driving market reshaping.
- Strategic Imperative: Need for companies like Fairfax Financial to adapt to a more concentrated competitive landscape.
Regulatory and Geopolitical Landscape
Fairfax Financial and its competitors navigate a challenging global regulatory environment. Compliance with diverse international regulations, such as varying capital requirements and solvency standards, imposes significant costs and shapes competitive approaches. For instance, differing data privacy laws across regions can impact how insurers market products and manage customer information.
Geopolitical shifts and climate change introduce substantial market volatility, compelling insurers to refine their risk assessment and pricing models. In 2024, the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, as evidenced by the estimated insured losses from natural catastrophes, which are projected to exceed $100 billion globally, forces a re-evaluation of underwriting strategies and geographic concentrations for all players in the insurance sector.
- Regulatory Complexity: Fairfax and its rivals must adhere to a patchwork of national and international insurance regulations, impacting product development and market entry.
- Geopolitical Risk: Global political instability can disrupt markets, affecting investment portfolios and the demand for certain insurance products.
- Climate Change Impact: Rising climate-related risks necessitate adjustments in pricing and risk selection, influencing the profitability and competitiveness of insurers.
- Compliance Costs: Meeting diverse regulatory demands represents a significant operational expense for all companies in the sector.
Fairfax Financial operates in an intensely competitive arena, facing formidable rivals like Berkshire Hathaway and Chubb, who possess vast financial resources and global reach. The insurance industry, particularly property and casualty, is inherently cyclical, leading to price wars during soft market periods, a trend observed in 2024 and expected to continue. Digital transformation, with significant InsurTech investment estimated at $10 billion globally in 2024, further intensifies this rivalry as companies leverage AI and data analytics to gain an edge.
| Competitor | Key Strength | 2023 Performance Highlight |
|---|---|---|
| Berkshire Hathaway | Financial Clout, Brand Loyalty | Strong underwriting profits in insurance operations |
| Chubb | Global Expansion, Diversified Portfolio | Continued market penetration and product development |
| Swiss Re | Reinsurance Expertise, Global Network | Navigating complex risk landscapes with robust capital |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Self-insurance and captive insurance companies present a substantial threat to traditional insurers like Fairfax Financial. These alternatives allow large corporations to retain and manage their own risks, potentially bypassing the need for commercial property and casualty insurance premiums. For instance, the U.S. captive insurance market saw significant growth, with premiums written by captives reaching an estimated $70 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of this substitute.
The increasing prevalence of Alternative Risk Transfer (ART) mechanisms, including catastrophe bonds and insurance-linked securities (ILS), presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional reinsurance. These capital markets solutions enable direct transfer of risks, bypassing conventional channels. The ILS market, for instance, saw substantial growth, with gross market capacity reaching approximately $100 billion by early 2024, demonstrating its capacity to absorb risks previously handled by reinsurers.
Government-backed insurance programs, such as flood insurance administered by the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) in the United States, can act as significant substitutes for private property and casualty (P&C) insurers. In 2024, the NFIP continued to be a dominant force in flood coverage, with over 4.4 million policyholders across the U.S., demonstrating the substantial market share these government programs capture. This availability of government-sponsored alternatives limits the ability of private insurers to expand into or charge premium rates for certain high-risk perils, thereby impacting their market potential.
Enhanced Risk Management and Prevention Technologies
The rise of advanced risk management and prevention technologies presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional insurance. As data analytics and IoT devices become more sophisticated, businesses can proactively identify and mitigate risks, reducing their reliance on insurance as a primary loss protection mechanism.
Predictive modeling, for example, allows companies to forecast potential issues and implement preventative measures, thereby lowering the likelihood and impact of claims. This shift towards self-insuring or investing in risk reduction technologies can directly substitute for the need for extensive insurance policies.
For instance, in 2024, the global investment in InsurTech, which often includes these advanced risk management solutions, reached an estimated $15 billion, signaling a growing trend away from traditional insurance models. This technological advancement directly challenges the value proposition of insurers.
- Technological Advancements: IoT sensors and AI-powered analytics offer real-time risk monitoring and early warnings.
- Proactive Risk Mitigation: Businesses can implement preventative measures, reducing the frequency and severity of losses.
- Reduced Insurance Dependency: Enhanced self-protection capabilities diminish the perceived need for comprehensive insurance coverage.
- Investment in Prevention: Companies are increasingly allocating capital to technology that prevents losses, rather than just transferring risk.
Emergence of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Insurance Models
The rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance presents a potential threat of substitutes for traditional insurers like Fairfax Financial. These models allow groups to pool resources, directly covering each other's risks, thereby cutting out intermediary costs and aligning member incentives. While currently a niche market, P2P insurance could offer a more affordable option for specific insurance needs.
Challenges remain for P2P insurance, including achieving widespread scalability and navigating complex regulatory landscapes. However, the core concept of reduced overhead and direct member benefit could attract a segment of consumers seeking cost-effective alternatives. For instance, by 2024, the insurtech sector, which often underpins P2P models, saw significant investment, indicating growing interest and potential for innovation in alternative insurance structures.
- P2P Insurance: Groups pooling funds to cover risks, bypassing traditional insurers.
- Cost Advantage: Potential for lower premiums due to reduced overhead and aligned incentives.
- Market Niche: Currently a smaller segment but with potential for growth.
- Challenges: Scalability and regulatory hurdles are key obstacles to widespread adoption.
The threat of substitutes for Fairfax Financial is multifaceted, encompassing self-insurance, alternative risk transfer, government programs, and technological advancements in risk management. These alternatives offer ways for customers to manage or transfer risk outside of traditional insurance policies. For example, the growth in captive insurance and insurance-linked securities demonstrates a clear shift towards alternative risk financing. In 2024, the global InsurTech market, which often facilitates these substitutes, continued to attract significant investment, signaling a move toward more direct risk mitigation and alternative coverage solutions.
| Substitute Type | Description | 2024 Market Indicator | Impact on Traditional Insurers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Insurance/Captives | Companies retaining their own risk. | US captive premiums estimated at $70 billion (2023). | Reduces demand for commercial P&C insurance. |
| Alternative Risk Transfer (ART) | Capital markets solutions like ILS. | ILS market capacity ~$100 billion (early 2024). | Bypasses traditional reinsurance channels. |
| Government Programs | State-sponsored insurance initiatives. | NFIP has over 4.4 million US policyholders (2024). | Dominates specific high-risk markets. |
| Risk Management Tech | AI, IoT for proactive risk reduction. | InsurTech investment estimated at $15 billion (2024). | Lowers overall need for insurance coverage. |
Entrants Threaten
The insurance and reinsurance sectors are inherently capital-intensive. Companies need substantial financial reserves to manage potential claims and adhere to strict solvency regulations. For instance, in 2024, many global insurers maintained solvency capital requirements well above billions of dollars to ensure financial stability.
This high capital requirement acts as a significant barrier. It demands immense upfront investment, making it incredibly difficult for new entrants to establish themselves and compete effectively against well-capitalized, established firms like Fairfax Financial.
New entrants into the insurance sector, like Fairfax Financial operates within, confront a labyrinth of regulatory and licensing requirements. These processes are often extensive, demanding significant time and resources to navigate across various jurisdictions, each with its own specific compliance mandates.
Obtaining the necessary licenses and adhering to stringent solvency rules are critical steps that create a substantial barrier to entry. For instance, in 2024, the average time to receive regulatory approval for new financial services firms in major markets can extend over several months, involving detailed scrutiny of business plans and financial projections.
Fairfax and established insurers possess decades of brand recognition and customer trust, crucial in an industry built on future claims promises. This deep-seated credibility is difficult for newcomers to replicate, creating a significant hurdle in attracting policyholders. For instance, in 2024, major insurers like State Farm and Geico continued to leverage their well-known brands, maintaining substantial market share.
Difficulty in Building Distribution Networks and Underwriting Expertise
Building robust distribution networks, like the extensive broker relationships Fairfax Financial cultivates, and developing specialized underwriting expertise are significant barriers for new entrants. These capabilities require substantial, long-term investment and accumulated experience, which newcomers typically lack.
For instance, in the property and casualty insurance sector, where Fairfax operates, establishing a widespread agent or broker network can take decades. This network is crucial for reaching diverse customer segments and generating consistent premium volume. New companies struggle to replicate this reach quickly.
- Distribution Network Investment: Companies like Fairfax have invested billions over many years to build and maintain their agent and broker relationships, a critical asset that is difficult and costly for new entrants to replicate.
- Underwriting Expertise Accumulation: The development of sophisticated underwriting models and experienced teams, essential for accurate risk assessment and pricing, is a lengthy and knowledge-intensive process, not easily transferable to new market participants.
- Brand Reputation and Trust: Established players benefit from years of consistent service and claims handling, fostering trust and brand loyalty that new entrants must work hard to earn.
Access to Proprietary Data and Advanced Analytics
Incumbent insurers like Fairfax Financial hold a significant advantage due to their extensive historical data. This data, covering claims, risks, and customer behavior, is vital for precise risk pricing and advanced underwriting. For instance, in 2024, the insurance industry's reliance on data analytics for profitability continued to grow, with companies leveraging AI and machine learning to refine their models.
New entrants struggle to replicate this data advantage. Building or acquiring comparable datasets is a substantial financial and time investment. This data gap directly impacts their ability to compete effectively in an industry where sophisticated analytics are paramount for success and profitability.
- Data Moat: Established insurers possess decades of proprietary data, a critical asset for accurate risk assessment.
- Analytics Gap: Newcomers face challenges in developing the advanced analytical capabilities needed to leverage data effectively.
- Cost Barrier: Acquiring or generating comparable data sets represents a significant upfront cost for potential entrants.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Without robust data and analytics, new players are at a disadvantage in pricing and underwriting.
The threat of new entrants in the insurance sector, where Fairfax Financial operates, is generally low due to significant barriers. These include high capital requirements, extensive regulatory hurdles, and the need for established brand recognition and trust, which are difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to build.
Furthermore, the accumulation of underwriting expertise and the development of robust distribution networks represent substantial long-term investments that deter potential new players. For instance, in 2024, the property and casualty insurance market continued to show consolidation, indicating the difficulty new entrants face in gaining traction against established giants.
New entrants also struggle to match the data advantage held by incumbents like Fairfax. Decades of proprietary claims and risk data, coupled with advanced analytics capabilities, provide a critical competitive edge in pricing and underwriting accuracy, a gap that is costly and time-consuming to bridge.
The industry's inherent capital intensity, with major insurers maintaining solvency capital well into the billions in 2024, underscores the financial commitment required, effectively limiting the pool of potential new competitors.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Fairfax Financial leverages data from annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.