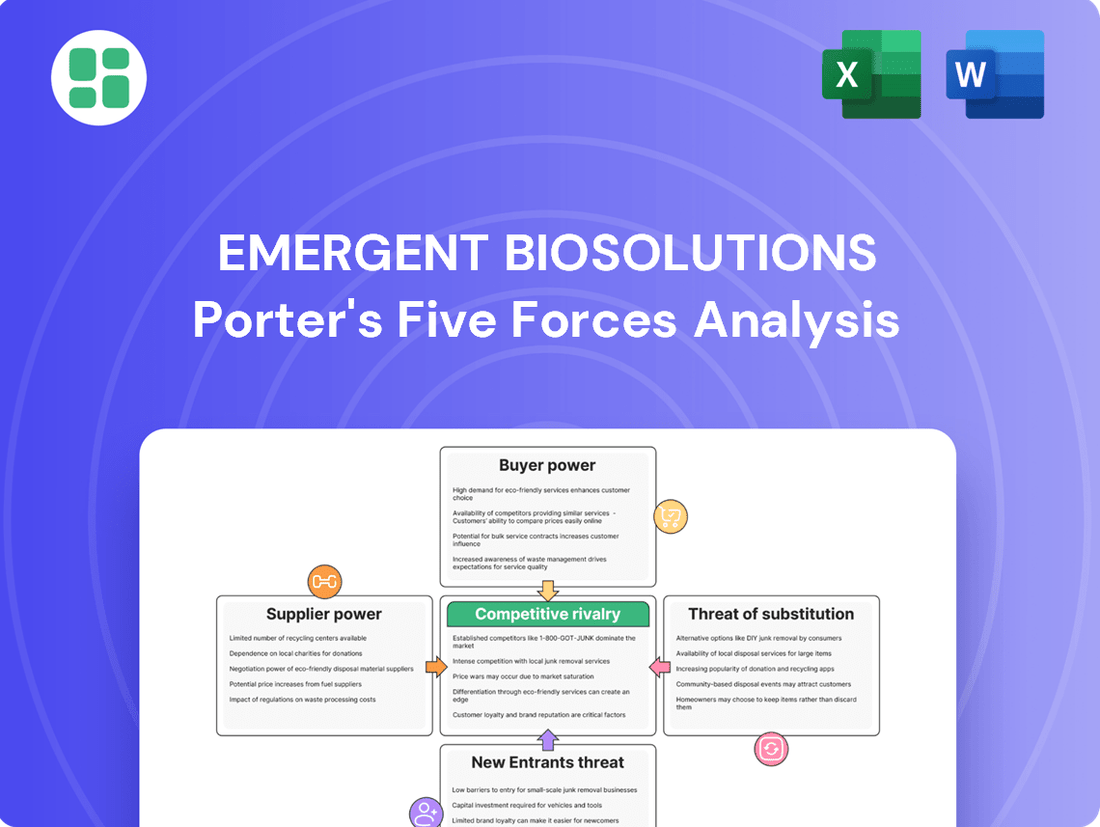
Emergent BioSolutions Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Emergent BioSolutions Bundle
Emergent BioSolutions operates in a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry and significant buyer power, particularly from government entities. The threat of substitutes, while perhaps less direct, looms as alternative public health solutions emerge.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Emergent BioSolutions’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Emergent BioSolutions' reliance on highly specialized raw materials for its critical medical countermeasures, like vaccines against biological threats, places significant bargaining power in the hands of a few key suppliers. The unique nature and limited availability of these essential components mean that these suppliers can dictate terms, potentially increasing costs for Emergent.
This concentration of specialized suppliers, especially for inputs like cell culture media or specific viral vector components, can create a dependency that emboldens suppliers. For instance, in 2023, the global demand for certain biopharmaceutical raw materials saw price increases due to supply chain disruptions, a trend that could directly impact companies like Emergent if their key suppliers are few.
Suppliers possessing proprietary technology or intellectual property for essential components, such as specialized cell lines or unique manufacturing processes, wield significant bargaining power. Emergent BioSolutions' reliance on these patented inputs can limit its ability to source alternatives, directly impacting production costs and supply chain flexibility.
Switching suppliers in the biopharmaceutical sector is a costly and time-consuming endeavor. Emergent BioSolutions, like others in the industry, faces significant hurdles due to rigorous regulatory demands, extensive validation protocols, and the potential for supply chain interruptions. These factors contribute to elevated switching costs, giving existing suppliers considerable leverage.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by the availability of substitute inputs. When alternative materials or components are easily accessible, a company can switch suppliers to negotiate more favorable terms, thus reducing supplier leverage. This principle generally holds true across many industries, providing a degree of control for buyers.
However, for Emergent BioSolutions, operating in the specialized field of medical countermeasures and biodefense, the landscape shifts considerably. The critical raw materials and specialized components necessary for producing vaccines, therapeutics, and other biodefense products often lack readily available direct substitutes. This scarcity inherently strengthens the bargaining power of the few suppliers who can provide these essential inputs, limiting Emergent's options for price negotiation and supply chain flexibility.
- Limited Substitutes: The unique nature of biopharmaceutical ingredients means few, if any, direct alternatives exist for critical components used in Emergent's products.
- Supplier Concentration: The market for specialized biological inputs is often concentrated among a small number of manufacturers, further enhancing their bargaining power.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Even if theoretical substitutes exist, regulatory approval processes for changes in raw materials for biopharmaceutical products are lengthy and costly, discouraging Emergent from seeking alternatives.
- Impact on Costs: This lack of substitutes directly translates into higher input costs for Emergent, impacting its overall cost of goods sold and profitability.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
Suppliers with the capability or incentive to forward integrate, meaning they could start manufacturing or distributing products themselves, represent a potential competitive threat to Emergent BioSolutions. While direct raw material suppliers engaging in this is rare, specialized Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) that provide crucial services could potentially transition into becoming direct competitors. This leverage underscores the importance for Emergent to cultivate robust supplier relationships.
For example, if a key CDMO partner, which might have been a significant supplier to Emergent in 2024, decided to invest heavily in its own finished product lines, it could directly compete for market share. This scenario highlights the strategic imperative for Emergent to ensure supplier loyalty and collaboration.
- Supplier Forward Integration Capability: The potential for suppliers, particularly specialized CDMOs, to move into manufacturing or distribution of finished products.
- Competitive Threat: This capability can transform a supplier into a direct competitor, impacting Emergent's market position.
- Strategic Importance of Relationships: Maintaining strong supplier partnerships is crucial to mitigate this risk and ensure continued access to critical services.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Emergent BioSolutions is substantial due to the highly specialized nature of its inputs and the limited number of qualified providers. For instance, the production of certain vaccines and therapeutics relies on proprietary cell lines or unique manufacturing processes, granting significant leverage to the few entities possessing this expertise. This concentration is evident in the biopharmaceutical sector where a handful of companies may control critical raw materials, as seen in the 2023 global demand surge for bioprocessing components, which saw price increases impacting companies with fewer sourcing options.
Switching suppliers in this regulated industry involves extensive validation and potential delays, effectively locking Emergent into existing relationships and bolstering supplier power. The potential for these suppliers, particularly Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs), to integrate forward and compete directly with Emergent also adds to their leverage, making strong supplier relationships a strategic necessity.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Emergent BioSolutions | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Substitutes for Specialized Inputs | Increases supplier leverage and input costs | Proprietary cell lines or unique viral vectors are often irreplaceable. |
| Supplier Concentration | Reduces Emergent's negotiation power | A small number of CDMOs may dominate specific biopharmaceutical manufacturing services. |
| High Switching Costs | Entrenches existing supplier relationships | Regulatory approval for new raw material suppliers can take years. |
| Potential for Forward Integration | Creates a risk of direct competition | CDMOs investing in finished product lines could compete with Emergent's offerings. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Emergent BioSolutions, focusing on the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes within the biopharmaceutical sector.
Instantly visualize Emergent BioSolutions' competitive landscape to pinpoint and address key strategic vulnerabilities.
Quickly identify and mitigate threats from competitors and suppliers, enabling more proactive and effective business strategy.
Customers Bargaining Power
Emergent BioSolutions' customer base for critical medical countermeasures is heavily concentrated among government agencies, notably the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the Department of Defense (DoD). This consolidation of buyers, particularly the U.S. government, grants them substantial bargaining leverage. Their ability to purchase in massive quantities and their crucial role in national health security amplifies this power.
The significant purchasing volume by these government entities means they can negotiate favorable terms. For instance, in 2024 and 2025, Emergent BioSolutions reported approximately $400 million in orders from the U.S. government specifically for its smallpox and mpox product portfolio. This reliance on a few large government customers underscores their considerable influence over pricing and contract conditions.
Government procurement processes are inherently structured and competitive, often subject to political shifts and budgetary constraints. This dynamic can significantly impact pricing and the terms of contracts for companies like Emergent BioSolutions, limiting their negotiating power.
For Emergent BioSolutions, the timing of U.S. government purchases, particularly the exercise of annual purchase options within existing contracts, directly influences revenue streams. These government-dependent revenue cycles can create leverage for the customer in price discussions.
In 2023, Emergent BioSolutions reported total revenues of $728.6 million, with a substantial portion tied to government contracts, highlighting the importance of these procurement policies and their influence on the company's financial performance and bargaining position.
Government customers, while needing critical medical countermeasures, are highly sensitive to price and operate within strict budget limitations. This often leads them to seek the most cost-effective options available, directly impacting Emergent BioSolutions' pricing power.
The ability of these government entities to issue tenders and negotiate long-term contracts further intensifies this downward pressure on pricing. For instance, Emergent BioSolutions reported that revenues from key products like NARCAN® and its Anthrax MCM saw a decrease in Q4 2024, partly attributed to lower sales volumes and the timing of those sales, reflecting this price sensitivity.
Availability of Alternative Suppliers for Customers
The bargaining power of customers for Emergent BioSolutions is significantly shaped by the availability of alternative suppliers for critical medical countermeasures and contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) services. Governments, a primary customer base, are increasingly focused on supply chain resilience and may actively seek to diversify their sources, thereby reducing dependence on any single provider.
Emergent operates in specialized biodefense markets where its capabilities are notable, yet competition exists. This competitive landscape includes large pharmaceutical corporations with established vaccine and biologics divisions, as well as other biodefense-focused companies. For instance, in 2024, the global biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market was valued at approximately $200 billion, indicating a substantial and competitive sector.
- Diversification efforts by governments can increase customer bargaining power.
- Competition from large pharmaceutical companies and specialized biodefense firms provides alternatives.
- The broad biopharmaceutical CDMO market, valued around $200 billion in 2024, highlights the competitive environment.
Customer's Ability to Backward Integrate (In-House Production)
Customers, particularly large governmental entities or significant pharmaceutical clients utilizing Emergent BioSolutions' contract development and manufacturing (CDMO) services, possess a degree of bargaining power through their potential to develop or produce certain products internally. While the complexity and cost associated with in-house manufacturing of advanced biologics present a substantial hurdle, the mere theoretical possibility of backward integration serves as a latent negotiation leverage. This capability, though financially demanding, can pressure Emergent BioSolutions to present more favorable terms and pricing to retain these crucial clients.
Emergent BioSolutions faces considerable customer bargaining power, primarily from its major government clients like the U.S. HHS and DoD. These entities, by purchasing in large volumes for national security needs, can negotiate favorable terms. For example, in 2024, Emergent secured approximately $400 million in orders from the U.S. government for its smallpox and mpox products, demonstrating the scale of these transactions and the leverage they provide to buyers.
The company's reliance on a concentrated customer base, particularly the U.S. government which accounted for a significant portion of its $728.6 million in 2023 revenue, amplifies this power. Government procurement processes, often driven by budget constraints and political considerations, further empower customers to demand competitive pricing, as seen with price sensitivities impacting sales of products like NARCAN® and Anthrax MCM in late 2024.
Furthermore, the competitive landscape within the biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing organization (CDMO) sector, valued at roughly $200 billion in 2024, means customers have alternatives. Governments actively seek supply chain diversification, and other large pharmaceutical companies or specialized biodefense firms can offer competing services, thereby increasing customer leverage over Emergent BioSolutions.
What You See Is What You Get
Emergent BioSolutions Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Emergent BioSolutions, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the biopharmaceutical industry. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, providing an in-depth examination of buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Emergent BioSolutions operates in a dynamic environment with a broad spectrum of competitors. This includes major pharmaceutical corporations like Johnson & Johnson, which has significant R&D capabilities and market reach, alongside specialized biotechnology firms such as Novavax and GSK, known for their vaccine development expertise. Bavarian Nordic also represents a key player in the biodefense sector.
The competitive landscape is further populated by Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) that offer similar manufacturing services. This diversity, spanning global pharmaceutical behemoths to focused biotech innovators and manufacturing service providers, means Emergent BioSolutions faces rivalry on multiple fronts, from product innovation to manufacturing capacity and government contract bidding.
The biodefense market is currently experiencing robust growth, which is a key factor influencing competitive rivalry. This expansion signals a healthy industry, but also a magnet for new entrants and existing players looking to capitalize on increasing demand.
Projections show the global biodefense market was valued at approximately $17.8 billion in 2024. This sector is anticipated to reach $29.6 billion by 2033, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.52%.
Such significant growth naturally attracts more competitors, intensifying the rivalry among companies. It also fuels investment in research and development, leading to a continuous stream of new products and technologies, further sharpening the competitive landscape.
Emergent BioSolutions' competitive standing hinges on the distinctiveness of its medical countermeasures and contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) services. Certain products, such as its anthrax and smallpox vaccines, hold critical positions within national strategic stockpiles, offering a degree of insulation from direct competition.
However, in other market segments, like its opioid overdose reversal agent NARCAN®, the company encounters significant competitive pressures. The degree of product differentiation directly impacts the intensity of rivalry; greater uniqueness can dampen direct competition, while a shift towards commoditization naturally escalates it.
High Exit Barriers
Emergent BioSolutions, like many in the biopharmaceutical sector, faces high exit barriers. These are significant hurdles that make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the industry. This means that even when profitability dips, competitors often remain, intensifying rivalry.
The biopharmaceutical industry is characterized by substantial investments in specialized manufacturing facilities and ongoing, capital-intensive research and development. For instance, the cost of building and maintaining FDA-compliant manufacturing sites, crucial for producing biologics, can run into hundreds of millions of dollars. Furthermore, the lengthy and complex regulatory approval processes, often spanning many years and requiring extensive clinical trials, represent a sunk cost that cannot be easily recouped.
- Specialized Assets: Biopharma companies invest heavily in unique manufacturing equipment and technologies that have limited alternative uses, making divestment difficult.
- R&D Investment: Billions are spent annually on drug discovery and development, creating substantial unrecoverable costs if a company exits. In 2023, global biopharmaceutical R&D spending was estimated to exceed $200 billion.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The lengthy drug approval pathways, which can take over a decade and cost billions, create a commitment to the market that is hard to abandon.
- Brand and Reputation: A company's reputation for innovation and product quality is built over time and is difficult to transfer or sell if exiting the market.
Strategic Importance of Biodefense Market
The biodefense market holds significant strategic importance for national security, prompting governments to cultivate relationships with multiple suppliers and invest in robust domestic capabilities. This strategic imperative means that competition isn't solely driven by commercial factors but also by government mandates and national priorities.
This strategic importance shapes the competitive landscape by fostering government R&D funding and potentially offering preferential treatment to domestic firms. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services continued its investments in biodefense preparedness, aiming to secure diverse supply chains for critical medical countermeasures.
- National Security Focus: Governments prioritize biodefense for public health and national security, influencing supplier choices and market dynamics.
- Government Support: Public funding for research and development, and procurement contracts significantly shape competitive advantages.
- Domestic Capability Emphasis: Nations often encourage or mandate domestic production and innovation to ensure supply chain resilience.
The competitive rivalry for Emergent BioSolutions is intense, fueled by a growing biodefense market valued at approximately $17.8 billion in 2024 and projected to reach $29.6 billion by 2033. This expansion attracts both established pharmaceutical giants like Johnson & Johnson and specialized firms such as Novavax and GSK, alongside numerous Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs).
Emergent's competitive edge relies on the distinctiveness of its medical countermeasures, like its anthrax and smallpox vaccines, which are critical components of national stockpiles. However, in areas like its opioid overdose reversal agent NARCAN®, the company faces more direct competition, highlighting how product differentiation impacts rivalry intensity.
High exit barriers, including substantial investments in specialized manufacturing facilities and lengthy regulatory approval processes, keep competitors engaged even during periods of lower profitability. For instance, global biopharmaceutical R&D spending exceeded $200 billion in 2023, underscoring the significant capital commitment within the sector.
Government mandates and national security priorities also shape competition, with nations often favoring domestic suppliers and investing in diverse capabilities, as seen in continued U.S. Department of Health and Human Services biodefense preparedness funding in 2024.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Emergent BioSolutions' public health products is significant. Alternative medical countermeasures, such as broad-spectrum antivirals or entirely different preventative strategies, can directly compete with Emergent's specialized vaccines and therapeutics for diseases like anthrax and smallpox. The market for biodefense products is diverse, with governments often exploring multiple approaches to national security and public health preparedness.
For example, while Emergent BioSolutions is a key supplier of anthrax vaccines (like BioThrax) and smallpox vaccines (like ACAM2000) to the U.S. government, the existence of other vaccine candidates or even non-pharmaceutical interventions could dilute demand. The efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility of these substitutes play a crucial role in their adoption, potentially impacting Emergent's market share for its specific countermeasures.
Emergent BioSolutions faces a significant threat from generic and biosimilar versions of its products, particularly as patents expire or manufacturing processes become less complex. This is a common challenge across the pharmaceutical industry, impacting revenue streams and profitability.
The market for NARCAN® (naloxone HCl nasal spray), a key product for Emergent, exemplifies this threat. Intense competition exists from other companies offering similar opioid overdose reversal products, putting pressure on Emergent's market share and pricing power. For instance, in 2023, the FDA approved multiple generic versions of naloxone nasal spray, directly impacting the competitive landscape for NARCAN®.
The introduction of biosimilars, which are highly similar to biologic medicines, can also erode market share and force price reductions. For Emergent, this means that as their proprietary products face off-patent competition, their financial performance could be substantially affected by the availability and adoption of these lower-cost alternatives.
A significant threat to Emergent BioSolutions' contract development and manufacturing (CDMO) business comes from clients choosing to develop or expand their own in-house manufacturing capabilities. This alternative allows pharmaceutical and biotech companies to bypass the need for external CDMO partners.
While building or expanding internal facilities demands substantial capital and specialized knowledge, it offers clients greater control over their production processes. This option remains a persistent consideration for potential CDMO clients, regardless of the broader market growth.
The global biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market was projected to reach over $200 billion by 2024, highlighting its expansion. However, this growth doesn't negate the fundamental choice clients face: leverage external CDMO expertise or invest in their own manufacturing infrastructure.
Advancements in Public Health Preparedness
Innovations in public health infrastructure, such as improved surveillance systems and rapid diagnostics, can reduce the demand for specific medical countermeasures offered by companies like Emergent BioSolutions. These advancements, while bolstering overall public health, can act as indirect substitutes for certain product lines.
Governments are significantly increasing investments in biodefense research and early warning systems. For instance, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has been a major funder of biosecurity initiatives. In 2024, continued emphasis on these areas signals a growing capacity for non-product-based public health solutions.
- Enhanced Surveillance: Better tracking of disease outbreaks can mitigate the need for immediate, large-scale deployment of specific countermeasures.
- Rapid Diagnostics: Quick identification of threats allows for more targeted responses, potentially reducing reliance on broad-spectrum treatments.
- Non-Pharmacological Interventions: Robust quarantine protocols and public health messaging can slow disease spread, lessening the immediate pressure on medical supply chains.
Price-Performance Trade-off of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Emergent BioSolutions' products hinges significantly on the price-performance trade-off offered by alternative solutions. If a new technology or treatment emerges that is demonstrably more effective or substantially cheaper than Emergent's current offerings, particularly for cost-sensitive government clients, a shift towards these substitutes becomes a real possibility.
This dynamic creates continuous pressure for Emergent to innovate and maintain competitive pricing. For instance, in the biodefense sector, the emergence of novel vaccine platforms offering faster development cycles or broader protection could challenge existing countermeasures. In 2024, the global vaccine market, valued at over $150 billion, is characterized by rapid technological advancements, meaning substitute threats are ever-present.
- Price-Performance Advantage: Substitutes offering superior efficacy at a lower cost pose a significant threat.
- Customer Sensitivity: Government agencies, a key customer base for Emergent, are often price-sensitive.
- Innovation Imperative: The threat of substitutes necessitates ongoing investment in research and development to stay ahead.
- Market Dynamics: The broader biopharmaceutical market, with its rapid technological evolution, constantly introduces potential substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Emergent BioSolutions' core products, particularly in public health and biodefense, remains a significant factor. Alternative medical countermeasures, including different vaccine types or entirely new preventative strategies, directly compete with Emergent's specialized offerings like anthrax and smallpox vaccines. The U.S. government, a primary customer, actively explores multiple approaches to national security and public health preparedness, meaning other companies' products or even non-pharmaceutical interventions can reduce demand for Emergent's specific solutions.
For instance, while Emergent is a key supplier of vaccines like BioThrax and ACAM2000, the market constantly sees new vaccine candidates and potential non-pharmacological interventions emerge. The overall global vaccine market was valued at over $150 billion in 2024, a figure that reflects ongoing innovation and the continuous introduction of potential substitutes. Factors like efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility of these alternatives directly influence their adoption and can impact Emergent's market share and pricing power.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Emergent | Key Factors |
| Alternative Vaccines/Therapeutics | Reduces demand for specific Emergent products | Efficacy, cost, speed of development |
| Generic/Biosimilar Products | Erodes market share and pricing power | Patent expiry, manufacturing complexity |
| In-house CDMO Capabilities | Loss of contract manufacturing revenue | Client control, capital investment |
| Public Health Infrastructure | Decreases reliance on specific countermeasures | Surveillance, diagnostics, non-pharmacological methods |
Entrants Threaten
Developing and manufacturing biopharmaceutical products, particularly vaccines and intricate therapeutics, demands immense capital for research, clinical trials, and specialized production facilities. For instance, Emergent BioSolutions reported capital expenditures of $204.7 million in 2023, highlighting the significant financial commitment required to operate in this sector.
These substantial upfront costs act as a significant deterrent, effectively raising the barrier to entry for potential new competitors looking to challenge established players like Emergent BioSolutions.
The biopharmaceutical sector, including companies like Emergent BioSolutions, is characterized by exceptionally stringent regulatory oversight. New entrants must navigate a labyrinth of complex and costly clinical trials and secure approvals from bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) before any product can reach the market.
For instance, the development of a new vaccine or therapeutic can take over a decade and cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars, presenting a formidable financial and temporal barrier. This extensive process, particularly for critical medical countermeasures, acts as a significant deterrent to potential new competitors.
Established companies like Emergent BioSolutions have cultivated deep regulatory expertise and built crucial relationships with these agencies over years of operation. This existing infrastructure and knowledge base provide a substantial advantage, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to penetrate the market effectively.
Existing patents and proprietary technologies represent a significant hurdle for new companies looking to enter the biopharmaceutical space. For instance, Emergent BioSolutions holds patents on its Narcan nasal spray, a critical opioid overdose reversal medication, and its ACAM2000 smallpox vaccine. These established intellectual property rights make it challenging for newcomers to develop competing products without infringing, necessitating costly licensing or the creation of entirely novel, non-infringing technologies.
Specialized Expertise and Talent Pool
The creation and production of medical countermeasures demand exceptionally specialized scientific, technical, and manufacturing skills. For instance, the complex biologics manufacturing processes utilized by companies like Emergent BioSolutions require deep knowledge in areas such as cell culture, purification, and sterile filling. Building a proficient workforce and fostering institutional knowledge is a protracted and arduous undertaking, presenting a formidable hurdle for newcomers aiming to swiftly establish a competitive footing in this highly regulated sector.
This specialized knowledge acts as a significant barrier to entry.
- Specialized Expertise: Developing and manufacturing medical countermeasures, like vaccines and therapeutics, requires highly specialized scientific and technical knowledge, often involving advanced biotechnology and pharmaceutical processes.
- Talent Acquisition Challenges: Companies such as Emergent BioSolutions invest heavily in attracting and retaining talent with expertise in areas like virology, immunology, and complex manufacturing operations, making it difficult for new entrants to build a comparable team quickly.
- Long Development Cycles: The lengthy and rigorous development and approval processes for medical countermeasures, often spanning many years and requiring extensive clinical trials, deter potential new entrants who may lack the necessary capital and patience.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating stringent regulatory requirements from bodies like the FDA is a significant barrier. Companies must demonstrate robust quality control, manufacturing consistency, and product safety, which demands established systems and deep regulatory understanding.
Established Government Relationships and Contracts
Emergent BioSolutions benefits from deeply entrenched relationships with government agencies, particularly for national preparedness initiatives. These long-standing ties translate into multi-year contracts that are challenging for new competitors to replicate. The company's proven track record, stringent regulatory compliance, and substantial manufacturing capabilities act as significant barriers to entry.
Securing these government contracts demands a substantial investment in infrastructure and a history of successful delivery, making it difficult for newcomers to compete. Emergent BioSolutions has notably secured significant government orders extending through 2024 and into 2025, underscoring the strength of these established relationships.
- Established Government Relationships: Long-standing ties with agencies like BARDA create a competitive moat.
- Multi-Year Contracts: These agreements provide revenue stability and deter new entrants lacking similar commitments.
- High Entry Barriers: Proven track record, regulatory hurdles, and manufacturing capacity are difficult for new firms to overcome quickly.
- Recent Contract Wins: Substantial orders secured for 2024 and 2025 highlight continued government reliance on Emergent.
The threat of new entrants into the biopharmaceutical sector, particularly for companies like Emergent BioSolutions, is generally low due to several formidable barriers. These include the substantial capital required for research and development, the complex and lengthy regulatory approval processes, and the need for specialized scientific and manufacturing expertise.
For instance, Emergent BioSolutions' 2023 capital expenditures reached $204.7 million, illustrating the significant financial commitment necessary. Furthermore, the company holds key patents, such as those for Narcan nasal spray, which protect its market position.
Established relationships with government agencies, like those for national preparedness, also create a significant advantage, with Emergent securing contracts extending through 2024 and 2025. These factors collectively make it exceedingly difficult for new companies to establish a competitive presence.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for R&D, clinical trials, and specialized manufacturing facilities. | Deters new entrants lacking substantial funding. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Stringent FDA approvals, lengthy clinical trial processes (often over a decade). | Requires deep regulatory expertise and significant time investment. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents on key products like Narcan and ACAM2000 vaccine. | Limits ability of new entrants to develop competing products without infringement. |
| Specialized Expertise | Need for advanced knowledge in virology, immunology, and complex biologics manufacturing. | Difficult for newcomers to build a proficient workforce quickly. |
| Government Relationships | Established contracts and proven track record with agencies like BARDA. | New entrants struggle to replicate multi-year commitments and secure similar orders. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Emergent BioSolutions is built upon a foundation of robust data, including SEC filings, annual reports, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms. We also leverage insights from trade publications and government regulatory databases to capture the full competitive landscape.