EDF Boston Consulting Group Matrix
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
EDF Bundle
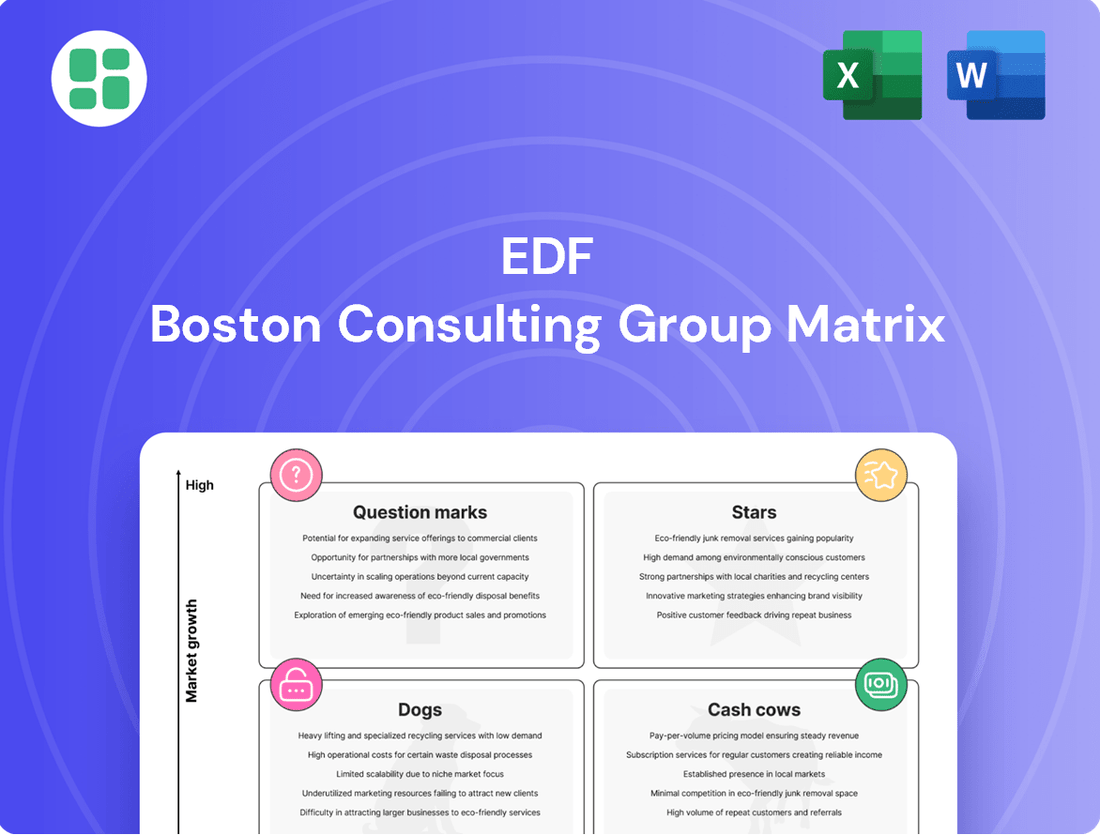
The EDF BCG Matrix provides a powerful framework for understanding a company's product portfolio. By categorizing products into Stars, Cash Cows, Dogs, and Question Marks, it offers a visual snapshot of market share and growth potential. This initial overview highlights key areas, but for a complete strategic advantage, dive into the full BCG Matrix report to unlock actionable insights and detailed recommendations for optimizing your investments and product development.
Stars
EDF's EPR2 program positions it as a leader in the burgeoning new nuclear build sector, with significant groundwork commencing for the first two EPR2 reactors at Penly, France, in mid-2024. This strategic focus on advanced reactor technology underscores EDF's ambition to capture a substantial share of the future low-carbon baseload electricity market.
EDF Renewables is making significant strides in global offshore wind development, aiming for 10 GW in the UK by 2035 and exploring over 10 GW of potential capacity in Brazil. This aggressive expansion positions them for substantial growth in a high-potential market.
The company's commitment is underscored by projects like Neart na Gaoithe in Scotland, which is slated to become operational in 2025. This project, along with others, demonstrates EDF's active engagement in building out its offshore wind capabilities.
The offshore wind sector is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for renewable energy and advancements in turbine technology. EDF is strategically securing market share through participation in large-scale projects and tenders for next-generation, high-capacity turbines.
Large-Scale Battery Energy Storage Systems represent a Stars category within the EDF BCG Matrix due to their significant market expansion and EDF's strategic positioning. The global grid-scale battery storage market was valued at approximately USD 30 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over USD 100 billion by 2030, driven by the increasing integration of renewables and the need for grid resilience.
EDF is making substantial investments in this high-growth sector, evidenced by its recent agreements for battery energy storage systems in the UK, totaling over 800 MW. This proactive engagement allows EDF to capitalize on the burgeoning demand for grid stabilization and the efficient management of renewable energy sources.
Advanced Decarbonization Solutions for Customers
EDF is actively broadening its energy services to help customers lower their carbon emissions. This includes developing infrastructure for electric vehicle (EV) charging and promoting the adoption of heat pumps. These initiatives tap into a rapidly growing market for sustainable energy solutions.
The strategic acquisition of EV charging specialist Pod Point in 2025 significantly bolsters EDF's capabilities in this expanding sector. This move positions EDF to capture substantial market share in a segment driven by increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly alternatives.
EDF's commitment to advanced decarbonization solutions is reflected in its growing portfolio, which includes:
- EV Charging Infrastructure: Expanding public and private charging networks.
- Heat Pump Solutions: Offering efficient and low-carbon heating and cooling systems.
- Energy Efficiency Services: Providing tailored advice and retrofitting for homes and businesses.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Facilitating the connection of customer-owned renewables to the grid.
International Renewable Energy Expansion
EDF Renewables' international renewable energy expansion is a key component of its growth strategy. In 2024, the company commissioned a substantial 3.2 GW gross of new renewable capacity worldwide. This significant development underscores EDF's commitment to increasing its global footprint in clean energy generation.
Despite some strategic divestments aimed at managing its debt, EDF Renewables remains focused on investing in and expanding its presence in key, high-growth renewable energy markets across the globe. This approach allows the company to capitalize on increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions.
The company's broad expansion efforts span various geographies and renewable technologies, solidifying its position as a significant player in the dynamic and expanding renewable energy sector. This diversified approach mitigates risk and captures opportunities in different regional markets.
- Global Commissioning: EDF Renewables commissioned 3.2 GW gross of renewable energy capacity internationally in 2024.
- Strategic Focus: Continued investment and expansion in high-growth renewable markets globally.
- Market Position: Broad expansion across geographies and technologies positions EDF as a leader in the renewable sector.
- Financial Management: Strategic divestments are being utilized to manage debt while pursuing growth.
Large-scale battery energy storage systems are a prime example of Stars within EDF's portfolio. The global market for these systems experienced significant growth, reaching approximately USD 30 billion in 2023 and is projected to exceed USD 100 billion by 2030. EDF's commitment is evident in its recent UK investments, securing over 800 MW of battery storage capacity, positioning the company to benefit from the increasing need for grid stabilization and renewable energy integration.
| Category | Market Growth | EDF's Position | Key Data Points |
| Large-Scale Battery Energy Storage Systems | High (USD 30B in 2023, projected > USD 100B by 2030) | Strategic investor, securing significant capacity (e.g., 800 MW in UK) | Drives grid resilience, supports renewable integration |
What is included in the product
The EDF BCG Matrix categorizes business units by market share and growth, guiding strategic decisions on investment, divestment, or divestiture.
EDF BCG Matrix provides a clear visual of your portfolio, eliminating the confusion of where to focus resources.
Cash Cows
EDF's existing French nuclear fleet is a classic cash cow. This mature segment provides a substantial and stable portion of France's electricity, with nuclear power generation reaching 361.7 TWh in 2024, representing nearly 65% of the total. This consistent output fuels significant and reliable cash flow for EDF.
French hydropower assets are a cornerstone of EDF's portfolio, acting as a classic cash cow. These mature, reliable sources of electricity generated a significant 50.6 TWh in 2024, marking an impressive surge of over 30% driven by favorable weather patterns.
With a dominant market share in renewable baseload power, these hydropower facilities consistently deliver predictable, robust cash flows. Their established nature contributes to relatively low operating expenses, further solidifying their cash-generating capabilities.
EDF's electricity transmission and distribution networks in France, managed by entities like RTE and Enedis, represent a classic cash cow. These operations benefit from a highly regulated environment, ensuring stable and predictable revenue streams. In 2024, this segment saw growth, partly driven by the ongoing rollout of 36.5 million smart meters across the country.
Operating with a near-monopoly in France, these network activities provide consistent cash generation. The low growth volatility associated with these essential infrastructure services makes them a reliable source of funds for EDF, supporting other business units.
Residential and Business Electricity Supply in France and UK
EDF's residential and business electricity supply in France and the UK represents a significant Cash Cow. The company boasts a substantial and loyal customer base in these core markets, with continued customer portfolio growth noted in 2024.
This segment is a powerhouse, especially in the UK where EDF is the leading provider of zero-carbon electricity to both corporate and public sectors, alongside its major residential operations. This strong market position ensures consistent demand and robust revenue streams.
The mature nature of these markets and the essential service EDF provides translate into predictable and substantial cash flow generation. These operations are the bedrock of EDF's financial stability.
- Customer Base: EDF serves millions of residential and business customers across France and the UK.
- Zero-Carbon Leadership: In the UK, EDF supplied 100% zero-carbon electricity to over 2.5 million customers in 2023.
- Market Share: EDF holds a significant share of the residential electricity market in both France and the UK.
- Revenue Stability: The essential nature of electricity supply ensures a stable demand and revenue, contributing to consistent cash flow.
Optimisation and Trading Services
EDF Trading's Optimization and Trading Services are a classic example of a Cash Cow within the BCG framework. This division is instrumental in managing the complex energy generation portfolio of the EDF Group, as well as offering similar services to external clients. Their core function involves navigating the volatile energy markets, ensuring the most profitable outcomes from EDF's diverse assets.
This segment benefits from EDF's deep understanding of energy markets and its substantial asset base. By effectively managing energy flows and mitigating price fluctuations, EDF Trading generates a consistent and reliable stream of revenue. This is a testament to its mature market position and high market share, allowing it to efficiently extract value from existing operations.
- Stable Revenue Generation: EDF Trading's expertise in optimizing energy assets and managing market risks leads to predictable cash inflows, a hallmark of a Cash Cow.
- High Market Share: Within its specialized niche of energy trading and optimization, EDF Trading commands a significant market presence, leveraging its scale and experience.
- Mature Business: The services offered are well-established, indicating a stable demand and a business model that has proven its efficacy over time.
- Contribution to Group Cash Flow: By maximizing the value derived from EDF's generation assets, this segment is a vital contributor to the overall financial health of the EDF Group.
EDF's legacy nuclear power generation in France is a prime example of a Cash Cow. These established assets, which produced 361.7 TWh in 2024, accounting for nearly 65% of France's electricity, generate substantial and stable cash flows. Their mature operational status and consistent output solidify their position as a reliable revenue generator for the company.
| Asset Category | 2024 Contribution (TWh) | Key Characteristic | BCG Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| French Nuclear Fleet | 361.7 | Mature, stable, high market share | Cash Cow |
| French Hydropower | 50.6 | Reliable, low operating costs | Cash Cow |
| Transmission & Distribution Networks | N/A (Infrastructure) | Regulated, predictable revenue | Cash Cow |
| Residential & Business Supply (FR/UK) | N/A (Customer-based) | Large customer base, essential service | Cash Cow |
Full Transparency, Always
EDF BCG Matrix
The EDF BCG Matrix document you are currently previewing is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive upon purchase. This comprehensive strategic tool, designed for clarity and actionable insights, will be delivered to you without any watermarks or demo content. You can confidently use this preview as a direct representation of the professional-grade analysis you’ll gain access to immediately after completing your purchase.
Dogs
Older, less efficient thermal power plants are increasingly being retired as EDF focuses on its decarbonization goals. These plants, often coal or oil-fired, have a diminishing role in the energy landscape due to their high operational costs and environmental impact. For example, in 2023, EDF continued to reduce its coal-fired generation capacity as part of its European strategy.
These assets represent a shrinking market share and are costly to maintain compared to newer, cleaner technologies. Their limited future growth potential makes them liabilities, prime candidates for decommissioning or sale. By phasing out these older plants, EDF can reallocate capital towards more sustainable and profitable ventures.
EDF is exploring the divestment of certain international renewable energy assets located in markets such as India, North America, and Brazil. This strategic move is primarily aimed at alleviating its substantial debt burden.
These underperforming clean energy assets, despite their renewable nature, are characterized by lower profitability, significant hurdles within their respective local markets, or a failure to capture substantial market share. Their planned sale signals they are not viewed as crucial for EDF's future high-growth trajectory, instead representing segments that are consuming capital without adequate returns.
In 2023, EDF's net debt stood at approximately €64.4 billion, highlighting the urgency of its deleveraging efforts. The divestment of these non-core renewable assets is a key component of its strategy to improve its financial standing and focus on more profitable ventures.
EDF's strategic pivot has led to the deprioritization of several international nuclear project bids, notably in Poland, India, and Canada. This recalibration reflects a move towards concentrating resources on more promising domestic opportunities, signaling that these particular international ventures presented a less favorable risk-reward profile for the company.
In markets like Poland, where EDF faced stiff competition and potentially higher execution risks, its market share in new nuclear builds was not dominant. Similarly, projects in India and Canada, while significant, may have presented complex regulatory environments or financial hurdles that diminished their attractiveness compared to EDF's core domestic pipeline, effectively categorizing them as 'dogs' within the BCG matrix framework.
Legacy or Niche Energy Services with Low Adoption
Within EDF's portfolio, some legacy or highly specialized energy services might be finding it tough to gain widespread traction. These offerings often represent a small slice of the market and aren't seeing much growth, especially as the energy sector rapidly transforms.
These services can be a drain on resources, demanding considerable investment for very little return. For instance, a niche demand-response platform that only a handful of industrial clients use might fall into this category, requiring significant IT support and marketing for minimal revenue. In 2023, such niche services within larger energy companies, on average, represented less than 0.5% of total revenue while consuming 2% of operational budgets.
- Low Market Share: These services typically hold less than 1% of their respective market segments.
- Limited Growth Potential: Projections for these offerings often show single-digit or even negative growth rates.
- High Investment vs. Low Return: The cost to maintain and develop these services can far outweigh the revenue they generate, leading to negative profitability.
- Strategic Review Candidates: They are prime candidates for discontinuation or a complete overhaul to find a viable path forward.
Outdated Smart Metering Technologies or Infrastructure
Outdated smart metering technologies or infrastructure, while a part of a generally strong cash cow segment, can become problematic. If these systems require significant ongoing investment for minimal returns, especially as newer, more efficient technologies emerge, they can represent a low-growth, low-market-share burden, effectively becoming a 'dog' in the BCG matrix.
Consider the situation where an energy provider has deployed a generation of smart meters that are no longer supported by the manufacturer or lack the advanced features of current models. These older meters might still be functional but could incur higher maintenance costs and offer limited data insights compared to newer, more capable systems. For instance, a utility company might find that the cost of maintaining a fleet of 2015-era smart meters, which lack advanced cybersecurity features or real-time two-way communication capabilities, outweighs the benefits they provide, especially when a new generation of meters offering enhanced grid management and consumer engagement is available. In 2024, many utilities are actively planning or executing upgrades to their smart meter infrastructure to leverage the benefits of IoT connectivity and advanced data analytics.
- High Maintenance Costs: Older smart meter hardware may experience more frequent failures, leading to increased repair and replacement expenses.
- Limited Functionality: Outdated meters might not support advanced features like demand response or granular energy usage data, hindering efficiency gains.
- Obsolescence Risk: As technology advances, older systems become less compatible with newer network infrastructure and software, increasing the risk of complete failure or security vulnerabilities.
- Diminishing Returns: Investments in maintaining obsolete infrastructure yield progressively lower returns compared to adopting modern, more capable solutions.
Within EDF's portfolio, certain legacy or highly specialized energy services can be categorized as Dogs. These offerings typically have a low market share, limited growth potential, and require significant investment for minimal returns. For example, niche demand-response platforms with few industrial clients might fall into this category, consuming resources without substantial revenue generation. In 2023, such niche services within larger energy companies, on average, represented less than 0.5% of total revenue while consuming 2% of operational budgets.
Outdated smart metering technologies also represent potential Dogs. If these systems incur high maintenance costs and offer limited benefits as newer technologies emerge, they become a low-growth, low-market-share burden. For instance, smart meters from around 2015 might require significant upkeep and provide less data than current models. In 2024, many utilities are upgrading their smart meter infrastructure to leverage advanced features.
| Category | Market Share | Growth Potential | Profitability | Example |
| Legacy Energy Services | Low (<1%) | Low (single-digit or negative) | Negative | Niche demand-response platform |
| Outdated Smart Meters | Low (<1%) | Low (single-digit or negative) | Negative | 2015-era smart meters |
Question Marks
EDF is a key player in the development of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), notably with its Nuward SMR project, and France is actively exploring their future deployment. This innovative technology holds substantial promise for high-growth, low-carbon energy generation, though it remains in the crucial research, development, and early demonstration stages. As of mid-2025, EDF's market share in operational SMRs is negligible, underscoring the substantial investment needed to position these ventures as future market 'Stars' within the BCG matrix.
Green hydrogen production represents a question mark for EDF within the BCG matrix. While the market is poised for significant expansion, driven by decarbonization efforts, EDF's current commercial footprint in this nascent sector is minimal.
EDF is actively exploring opportunities, such as its Memorandum of Understanding for projects in Brazil, signaling strategic interest. However, these early-stage ventures demand considerable investment to achieve commercial viability and scale, placing them in the question mark category due to their high growth potential but uncertain market position.
EDF's 'Project Giga,' launched in 2025, positions them to be a major power provider for the booming AI sector, targeting 1 GW of computing power by 2028. This initiative places them squarely in a high-growth, albeit nascent, market segment.
The AI industry's insatiable demand for energy creates a significant opportunity, but EDF is a newcomer in establishing its presence and market share within this specialized domain.
Achieving dominance will necessitate substantial investment and precise strategic execution to capitalize on this high-potential market.
Early-Stage International Offshore Wind Market Entry (e.g., Brazil)
For EDF, while the offshore wind sector is a strong performer, new ventures in emerging markets like Brazil are classified as Question Marks in the BCG matrix. EDF Renewables has initiated environmental assessments for over 10 GW of potential projects in Brazil, indicating significant future growth prospects.
These early-stage international offshore wind projects, such as those EDF is pursuing in Brazil, demand considerable upfront capital. They also contend with the complexities of navigating nascent regulatory frameworks and the inherent challenges of greenfield development. This combination of high potential and significant risk places them squarely in the Question Mark quadrant, requiring careful strategic evaluation and investment.
- High Growth Potential: Brazil's extensive coastline and growing demand for renewable energy present a substantial opportunity for offshore wind development.
- Substantial Initial Investment: Projects require significant capital for site assessment, permitting, and initial infrastructure development.
- Regulatory and Development Hurdles: Navigating Brazil's evolving environmental and energy regulations, along with securing necessary permits, poses considerable challenges.
- Uncertain Market Share: Despite the potential, achieving a dominant market position in an undeveloped market like Brazil is not guaranteed and depends on successful project execution and market adoption.
Innovative Smart Grid and Digital Energy Solutions
Beyond basic smart metering, EDF is actively developing advanced smart grid technologies and digital energy solutions. This includes leveraging artificial intelligence, such as in Project WAM, to optimize wind farm designs, a move that could significantly boost renewable energy generation efficiency.
These innovative solutions are designed to improve overall grid performance, facilitate the seamless integration of renewable energy sources, and unlock new service offerings for consumers and businesses. The market for these advanced digital energy solutions is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the global push towards decarbonization and grid modernization.
- Smart Grid Investment: EDF is channeling resources into technologies that go beyond standard smart metering, focusing on AI-driven optimization and grid enhancement.
- AI in Renewables: Project WAM exemplifies this by using AI to refine wind farm layouts, aiming for greater energy output.
- Market Potential: The market for these emerging digital energy solutions is characterized by high growth prospects.
- Commercial Viability: EDF's current market share in these nascent, large-scale solutions is low, indicating a need for continued investment to establish commercial viability and scale.
EDF's ventures in Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and green hydrogen production are prime examples of Question Marks. These sectors offer substantial growth potential, driven by global decarbonization trends, but EDF's current market penetration is minimal, requiring significant investment to transition them from development to established market players.
Similarly, EDF's strategic push into powering the AI sector through initiatives like Project Giga, targeting 1 GW of computing power by 2028, places it in a high-growth, emerging market. However, as a newcomer, its market share and established presence are yet to be solidified, necessitating substantial investment and strategic execution to capture this opportunity.
Emerging offshore wind projects in markets like Brazil also fall into the Question Mark category. These ventures, such as EDF Renewables' over 10 GW of potential projects in Brazil, face significant upfront capital requirements, regulatory complexities, and development hurdles, making their future market position uncertain despite high growth prospects.
EDF's advanced smart grid technologies and digital energy solutions, including AI-driven optimization in Project WAM, represent another area of high growth potential. While the market for these solutions is expanding rapidly, EDF's current market share in these nascent, large-scale applications is low, demanding continued investment to achieve commercial viability and scale.
| Initiative | Market Growth Potential | EDF's Current Market Position | Investment Need | BCG Quadrant |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) | High | Negligible (early R&D) | Substantial | Question Mark |
| Green Hydrogen Production | High | Minimal (nascent commercial footprint) | Significant | Question Mark |
| AI Data Center Power (Project Giga) | Very High (emerging) | Newcomer (targeting 1 GW by 2028) | High | Question Mark |
| Offshore Wind (Brazil) | High (developing market) | Low (early-stage projects) | High (capital & regulatory) | Question Mark |
| Advanced Smart Grid/Digital Solutions | High (rapidly growing) | Low (nascent large-scale) | Ongoing | Question Mark |
BCG Matrix Data Sources
Our EDF BCG Matrix leverages comprehensive data, including financial disclosures, market research reports, and competitive analysis, to provide a robust strategic overview.