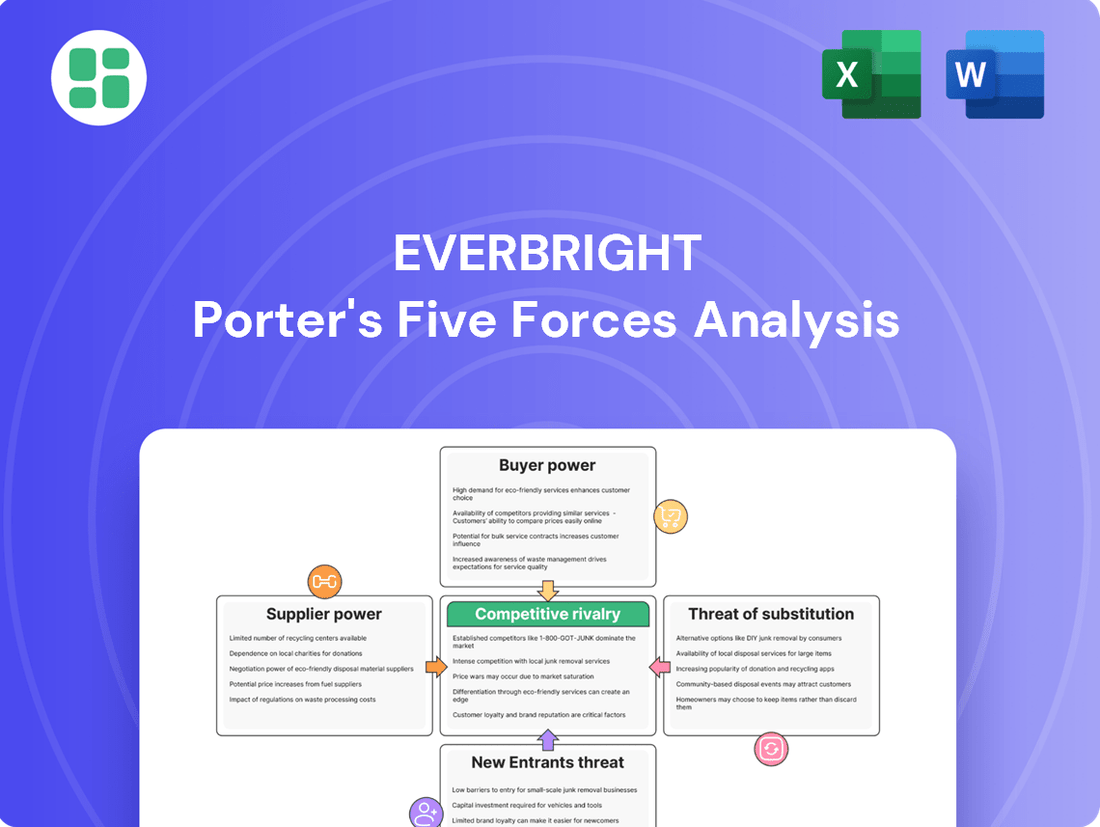
Everbright Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Everbright Bundle
Everbright faces moderate bargaining power from its suppliers, as raw material costs can fluctuate. The threat of new entrants is also a significant factor, requiring continuous innovation and cost management. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Everbright’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for China Everbright Group is notably influenced by providers of sophisticated financial technology and software. These specialized vendors possess considerable leverage due to the unique and intricate nature of their solutions, which are indispensable for Everbright's diverse financial services, including banking, securities, and asset management.
The high switching costs associated with integrating and customizing these advanced technological systems significantly amplify the power of these suppliers. For instance, the implementation of new core banking systems or advanced trading platforms can require substantial investment and time, making it difficult and costly for Everbright to change providers quickly.
In 2024, the financial technology sector saw continued consolidation and innovation, with a few key players dominating specialized areas like AI-driven analytics and cybersecurity for financial institutions. This concentration means that Everbright, like many large financial conglomerates, relies on a limited number of highly capable tech partners, thereby strengthening their bargaining position.
Talent, especially in finance, tech, and real estate, is a key supplier for Everbright. In China's competitive landscape, skilled professionals wield significant influence over their compensation and work environments. For instance, in 2024, average salaries for experienced financial analysts in major Chinese cities saw an upward trend, reflecting this demand.
Providers of market data and financial information services hold significant sway over Everbright. Access to precise, up-to-the-minute data is absolutely critical for making sound investment choices, managing risks effectively, and ensuring compliance with regulations across all of Everbright's various business areas.
The fact that there are only a few providers offering comprehensive, top-tier data means they can command higher prices for their services. For instance, in 2024, the global financial data market was valued at approximately $33 billion, with a significant portion of this attributed to subscription-based services for market data and analytics, reflecting the essential nature and concentrated supply of these resources for firms like Everbright.
Supplier Power 4
Everbright's bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by its operating environment, particularly in China. Given its state-owned nature, there's a tendency for large infrastructure and essential service providers, often also state-owned, to hold significant sway. This can translate into less flexibility for Everbright when negotiating pricing and terms for critical utilities or major projects.
This dynamic can lead to more stable, albeit potentially less cost-advantageous, supplier relationships. For instance, in 2024, state-owned enterprises in sectors like energy and telecommunications often maintained pricing structures that reflected strategic national interests rather than pure market competition, potentially impacting Everbright's operational costs.
- State-Owned Supplier Influence: Many key infrastructure and service providers in China are state-owned, granting them considerable bargaining power.
- Limited Negotiation Flexibility: Everbright may face constraints in negotiating prices and terms with these strategic suppliers.
- Impact on Operational Costs: The pricing of essential utilities and large-scale services from state-owned entities can directly affect Everbright's cost structure.
- Strategic Importance vs. Cost Savings: The government's strategic priorities can sometimes outweigh pure cost-efficiency in supplier relationships.
Supplier Power 5
Capital suppliers, including major institutional investors and the state, wield considerable influence over large financial conglomerates like China Everbright Group. For instance, in 2023, the total assets of China's banking sector, a key source of capital, reached approximately $65 trillion, highlighting the sheer scale of these suppliers.
While Everbright itself is a significant capital provider, it also relies on external funding for its growth and investment strategies. The cost and accessibility of this capital are directly tied to broader market conditions and evolving state policies, which can significantly affect Everbright's operational profitability and its ability to pursue strategic objectives.
- Capital Dependency: Everbright requires substantial capital for its diverse operations and investments, making it reliant on external sources.
- Market and Policy Influence: The availability and cost of capital are shaped by macroeconomic factors and government regulations, impacting Everbright's financial flexibility.
- State as a Key Supplier: The Chinese state, as a major shareholder and regulator, holds significant power in influencing capital allocation and financial sector policies.
The bargaining power of suppliers for China Everbright Group is a complex interplay of technological dependence, market concentration, and the unique structure of the Chinese economy. Specialized technology providers and data vendors hold significant leverage due to high switching costs and the critical nature of their services for Everbright's operations.
In 2024, the consolidation within the fintech sector meant Everbright, like many financial institutions, had to rely on a limited number of advanced technology partners, thereby strengthening these suppliers' negotiating positions. Similarly, providers of essential market data, a market valued at approximately $33 billion in 2024, can command premium pricing due to the concentrated supply of comprehensive, high-quality information.
Furthermore, the influence of state-owned enterprises as suppliers of essential services and infrastructure, coupled with the state's role as a capital supplier, adds another layer of complexity. This often results in less negotiation flexibility for Everbright, with pricing structures sometimes reflecting strategic national interests over pure market competition, as seen in sectors like energy and telecommunications in 2024.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Example Impact on Everbright | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Technology & Software Providers | High switching costs, specialized solutions, market concentration | Increased reliance on a few key tech partners, potentially higher costs for system upgrades | Fintech sector consolidation, AI/cybersecurity dominance by few players |
| Market Data & Financial Information Services | Criticality of data, limited number of comprehensive providers | Higher subscription costs for essential market intelligence | Global financial data market valued at ~$33 billion, driven by subscription services |
| Skilled Talent (Finance, Tech, Real Estate) | High demand in competitive Chinese market | Upward pressure on compensation and benefits for key personnel | Rising average salaries for experienced financial analysts in major Chinese cities |
| State-Owned Infrastructure/Service Providers | State ownership, strategic importance, limited competition | Less negotiation flexibility on pricing and terms for utilities and major projects | State-owned energy/telecom pricing reflecting national interests |
| Capital Suppliers (Institutional Investors, State) | Everbright's reliance on external funding, market conditions, state policies | Cost and accessibility of capital influenced by macroeconomic factors and regulations | China's banking sector assets ~$65 trillion (2023), indicating scale of capital sources |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Everbright's financial services sector.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visually intuitive breakdown of industry forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
China Everbright Group's customer base is broad, encompassing individual consumers, major corporations, and institutional investors. Large corporate and institutional clients often wield greater bargaining power due to the substantial volume of business they generate and their financial expertise. These sophisticated clients can negotiate for more favorable pricing, bespoke services, and elevated service standards.
In retail banking and wealth management, individual customers typically wield limited direct bargaining power. However, this dynamic is shifting as digital platforms and readily available financial information empower them collectively.
The ease with which customers can switch between Everbright's digital offerings and those of competitors, coupled with a wider array of financial products, amplifies their collective leverage. For instance, by mid-2024, the global digital banking user base surpassed 2.5 billion, highlighting the scale of this empowered customer base.
To counter this growing buyer power, Everbright must prioritize exceptional service quality, seamless digital experiences, and consistently competitive product pricing. Maintaining customer loyalty in this environment demands a proactive approach to meeting evolving customer expectations.
Everbright's real estate development segment experiences significant buyer power, especially when market conditions are unfavorable. In 2024 and extending into 2025, the Chinese property market has seen a notable downturn, characterized by falling prices and a surplus of available housing. This situation directly empowers homebuyers, granting them greater choice and a stronger hand in negotiations.
Buyer Power 4
Customers in the securities and asset management sectors, particularly large institutional investors, wield significant bargaining power. They can readily compare fees, performance metrics, and service offerings from numerous asset managers. This ease of comparison, coupled with a keen sensitivity to investment returns and prevailing market conditions, puts pressure on firms like Everbright to consistently deliver value and differentiate their services.
Everbright faces this buyer power directly. For instance, in 2024, institutional investors often negotiated lower management fees, especially for larger mandates. A study by Cerulli Associates in early 2024 indicated that average fees for large-cap equity mandates had seen a slight downward trend due to intense competition and investor scrutiny on costs.
- Sophisticated clients can easily switch providers based on performance and fees.
- High sensitivity to investment returns drives fee pressure.
- Everbright must innovate and demonstrate superior performance to retain clients.
- Institutional investors' ability to negotiate fees impacts Everbright's revenue.
Buyer Power 5
The bargaining power of customers for Everbright is significantly shaped by the state's multifaceted role. As both an owner and a major client, the government's influence can lead to unique negotiation terms, often tied to national strategic objectives.
Government-backed projects and state-owned enterprises represent a substantial client base for Everbright. For instance, in 2024, state-owned enterprises were projected to account for a significant portion of infrastructure spending, a key sector for Everbright. This dual position can sometimes constrain Everbright's commercial flexibility, but it concurrently offers a degree of client stability.
- State as Owner: The government's ownership stake in Everbright can influence pricing and service demands.
- State as Client: Government projects often come with specific procurement regulations and long-term commitments.
- Regulatory Influence: As a regulator, the state can set standards that impact service offerings and customer expectations.
- Strategic Priorities: Client relationships may be influenced by national development plans, potentially overriding purely commercial considerations.
Everbright's customers, especially large institutional investors and sophisticated corporate clients, wield considerable bargaining power. This is driven by their ability to compare services, negotiate fees, and switch providers based on performance and cost. The digital age has amplified this, with over 2.5 billion global digital banking users by mid-2024, readily accessing information and alternative options.
In the real estate sector, homebuyers in 2024 and early 2025 found themselves in a strong position due to a downturn in the Chinese property market, characterized by falling prices and ample inventory, empowering them with greater negotiation leverage.
The state, as both owner and a major client, exerts a unique form of bargaining power over Everbright. Government projects and state-owned enterprises, which represented a significant portion of infrastructure spending in 2024, can influence terms and pricing, sometimes prioritizing national strategic objectives over purely commercial considerations.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Everbright's Response/Impact |
| Institutional Investors | Fee sensitivity, performance comparison, large mandates | Pressure on management fees; need for superior performance |
| Corporate Clients | Volume of business, financial expertise, bespoke service demands | Negotiation for favorable pricing and tailored services |
| Individual Consumers (Digital) | Ease of switching, access to information, collective power | Need for competitive pricing and seamless digital experience |
| Real Estate Buyers | Market downturn, surplus inventory, choice | Increased negotiation leverage in property transactions |
| Government/SOEs | Ownership, large project scale, strategic alignment | Potential for negotiated terms, but also client stability |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Everbright Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Everbright Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You are looking at the actual, professionally written document detailing the competitive landscape for Everbright, ready for your strategic planning. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, fully formatted file, enabling immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
China Everbright Group faces fierce competition from established state-owned and joint-stock commercial banks, as well as rapidly evolving fintech firms. This intense market pressure, particularly evident in the banking sector's shrinking net interest margins, directly impacts profitability.
Everbright’s diverse operations mean it contends with a wide array of competitors. In the lending and deposit sector, it faces traditional banking giants. Securities firms vie for market share in brokerage and investment banking services, while asset managers compete for wealth management clients. Furthermore, property developers present a competitive challenge in the real estate arena, collectively amplifying the competitive intensity Everbright experiences across its various business segments.
Government policies and regulatory directives heavily influence the competitive landscape in China's financial sector. State ownership offers advantages and support, but also mandates alignment with national strategies, impacting expansion, product development, and pricing, which in turn shapes competitive intensity.
In 2024, China's financial sector continued to navigate evolving regulations, with a focus on risk management and digital transformation. For instance, the People's Bank of China's ongoing efforts to manage systemic financial risks and promote financial stability directly affect how institutions compete, particularly in areas like fintech and cross-border transactions.
Competitive Rivalry 4
The competitive rivalry within the financial services sector, particularly impacting Everbright, is intensifying due to the rapid evolution of financial technology and digital banking. Fintech firms are actively reshaping the industry by introducing innovative and often more accessible or affordable services, directly challenging established institutions.
To maintain its competitive edge, Everbright faces the imperative of consistent investment in digital transformation. This proactive approach is crucial to counter the agility and disruptive potential of these newer, digitally native players. For instance, in 2023, global fintech investment reached over $100 billion, highlighting the significant capital flowing into this disruptive space.
- Fintech Disruption: Companies like Ant Group and Square continue to expand their service offerings, from payments to lending, often with lower overheads than traditional banks.
- Digital Transformation Investment: Banks globally are allocating substantial resources to upgrade their digital infrastructure; for example, many large banks have earmarked billions for technology upgrades annually.
- Customer Expectations: Consumers increasingly expect seamless, mobile-first banking experiences, pushing all players to enhance their digital channels.
Competitive Rivalry 5
The real estate sector, a key component of Everbright's operations, faces a highly competitive landscape. Oversupply and falling property prices in 2024 are forcing developers to vie aggressively for market share, putting pressure on profit margins. This intense rivalry within real estate directly impacts Everbright's overall competitive standing.
Several factors exacerbate this competitive rivalry:
- Developer Overstock: Many developers are holding significant unsold inventory, leading to price wars and promotional activities to move properties.
- Economic Headwinds: A slower economic growth forecast for 2024 in key markets can dampen buyer demand, further intensifying competition for the remaining buyers.
- Increased Marketing Spend: To stand out, developers are increasing marketing and sales expenditures, adding to operational costs and reducing profitability.
Everbright faces intense rivalry across its diverse financial services and real estate operations. The banking sector sees pressure from established players and agile fintechs, impacting margins. Similarly, the property market is characterized by oversupply and price competition, squeezing developer profitability.
Fintech disruption is a major driver of this rivalry, with new entrants offering innovative, often lower-cost services. This forces traditional institutions like Everbright to invest heavily in digital transformation to remain competitive, as evidenced by global fintech investments exceeding $100 billion in 2023.
In 2024, China's financial sector is shaped by regulatory focus on risk and digital advancement, influencing how institutions like Everbright compete. For example, the People's Bank of China's efforts to ensure financial stability directly impact competitive dynamics, especially in emerging areas like digital payments and cross-border finance.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Actions | Impact on Everbright |
| Established Banks | Aggressive pricing, expanded digital services | Margin pressure, need for service differentiation |
| Fintech Firms | Innovative product launches, lower cost structures | Customer attrition, pressure to accelerate digital adoption |
| Securities Firms | Enhanced research, specialized advisory | Competition for investment banking and brokerage mandates |
| Property Developers | Price discounts, increased marketing spend | Reduced profitability in real estate ventures |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The banking sector faces a significant threat from substitutes that allow companies to secure funding outside of traditional bank loans. Direct financing methods like issuing corporate bonds and equity are increasingly accessible, enabling businesses to bypass intermediaries. For instance, in 2023, global corporate bond issuance reached substantial figures, demonstrating a strong alternative for capital raising.
Furthermore, peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms, while subject to evolving regulations in markets like China, present another avenue for businesses to obtain financing. Informal financing channels also exist, offering alternative, albeit often less regulated, sources of capital. These substitutes can erode a bank's market share by offering potentially faster or more flexible financing solutions.
For investment and asset management services, individuals and corporations can directly invest in securities or utilize alternative investment vehicles. The proliferation of online brokerage platforms also enables self-managed portfolios, directly substituting traditional advisory services.
The growth of robo-advisors and low-cost exchange-traded funds (ETFs) poses a significant threat. For instance, by the end of 2023, the global ETF market reached over $11 trillion in assets under management, demonstrating their accessibility and cost-effectiveness as substitutes for actively managed funds.
Digital payment platforms, especially those from tech giants like Alipay and WeChat Pay, present a significant threat to Everbright's traditional banking payment services. These platforms provide a highly convenient and integrated user experience, often with lower transaction fees, directly impacting Everbright's retail banking revenue streams. In 2023, mobile payments in China, dominated by these platforms, saw continued robust growth, with transaction volumes reaching trillions of yuan, underscoring their substantial market penetration.
Threat of Substitution 4
In the real estate sector, the threat of substitutes is significant, particularly for new property purchases. Renting remains a primary alternative, offering flexibility without the long-term commitment and capital outlay of ownership. For instance, in 2024, rental yields in many major cities continued to provide competitive returns for investors, making renting an attractive option for many consumers.
Investing in existing, second-hand properties also serves as a substitute for new builds. These often come with lower entry prices and can be renovated to meet specific needs. Furthermore, the rise of alternative housing solutions, such as co-living spaces and modular homes, provides more affordable and adaptable options, especially in markets experiencing price stagnation or decline, a trend observed in several regions throughout 2024.
Government initiatives further amplify this threat. Subsidized housing programs and urban regeneration projects directly offer more accessible and affordable housing alternatives to the open market. These developments can absorb demand that might otherwise flow to new property sales, impacting developers’ market share.
Key substitutes impacting new property purchases include:
- Rental Market: Offering flexibility and lower upfront costs, with rental yields remaining competitive in 2024.
- Second-hand Properties: Providing lower purchase prices and renovation potential.
- Alternative Housing: Such as co-living and modular homes, catering to affordability and changing lifestyle needs.
- Government-Subsidized Housing: Directly competing by offering more affordable entry points into the housing market.
Threat of Substitution 5
The increasing trend of financial disintermediation presents a significant long-term threat to Everbright. Technology is enabling direct connections between those who have capital and those who need it, bypassing traditional financial institutions. This disintermediation is particularly impactful in areas like lending and investment, where platforms can facilitate more efficient and direct transactions.
This shift reduces the reliance on intermediaries like Everbright, potentially eroding their market share and profitability. For instance, the rise of peer-to-peer lending platforms and robo-advisors exemplifies this trend. By 2024, the global fintech market was valued at over $1.1 trillion, with a substantial portion driven by disintermediation technologies.
Everbright faces competition from:
- Digital lending platforms: These platforms connect borrowers directly with investors, often offering faster approvals and competitive rates.
- Robo-advisors: Automated investment platforms provide portfolio management services at lower costs than traditional human advisors.
- Crowdfunding sites: These allow businesses and individuals to raise capital directly from a large number of people.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Emerging blockchain-based financial systems aim to remove intermediaries entirely, offering a radical form of disintermediation.
The threat of substitutes for Everbright's core banking services is multifaceted, encompassing alternative financing methods and investment vehicles. Direct financing through corporate bonds and equity offerings bypasses traditional lending, with global corporate bond issuance remaining robust in 2023. Similarly, digital payment platforms, like Alipay and WeChat Pay, offer convenient alternatives to traditional banking services, experiencing significant transaction volume growth in China during 2023.
In investment services, robo-advisors and low-cost ETFs present accessible substitutes for managed funds. The global ETF market exceeded $11 trillion in assets under management by the end of 2023, highlighting their widespread adoption. These substitutes offer cost-effectiveness and ease of access, directly challenging traditional advisory models.
The financial sector is also experiencing disintermediation, with fintech platforms connecting capital providers and seekers directly. By 2024, the global fintech market was valued at over $1.1 trillion, driven by technologies that reduce reliance on intermediaries like Everbright.
| Substitute Type | Everbright Service | Example/Trend | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Financing | Bank Loans | Corporate Bonds, Equity Issuance | Global corporate bond issuance substantial in 2023 |
| Digital Payments | Traditional Payment Processing | Alipay, WeChat Pay | Trillions of yuan in mobile payment transactions in China (2023) |
| Investment Alternatives | Managed Funds, Advisory | Robo-advisors, ETFs | Global ETF market > $11 trillion AUM (end of 2023) |
| Fintech Disintermediation | Intermediated Financial Services | P2P Lending, Crowdfunding | Global fintech market > $1.1 trillion (2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants into China's financial sector, including for firms like Everbright, remains relatively low. This is primarily due to significant hurdles such as stringent regulatory requirements and the substantial capital needed to establish a presence.
Entities like the People's Bank of China (PBOC) and the National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) enforce rigorous licensing, compliance, and capital adequacy rules. These regulations create a formidable barrier, making it challenging for new domestic and international players to enter the market and compete effectively.
China Everbright Group's status as a state-owned financial conglomerate is a formidable barrier to new entrants. This backing provides access to capital, regulatory favor, and a vast domestic network that newcomers would find exceptionally difficult to replicate.
For instance, in 2024, state-owned enterprises (SOEs) in China continued to receive significant policy support and preferential treatment, often translating into lower borrowing costs and privileged access to markets. This inherent advantage makes it challenging for private or foreign entities to establish a competitive foothold in the Chinese financial services sector.
The threat of new entrants for Everbright is significantly mitigated by the substantial capital required to establish robust distribution networks and cultivate customer trust. Everbright’s extensive branch network and decades of operation translate into a deep well of customer loyalty. For instance, as of the end of 2023, Everbright Securities boasted over 300 physical branches across China, a physical footprint that new competitors would find incredibly costly and time-consuming to replicate.
Threat of New Entrants 4
Technological innovation, especially in fintech, creates a dynamic environment for Everbright. While new technologies can democratize access and lower some entry barriers, the substantial capital needed for advanced tech, robust cybersecurity, and sophisticated data analytics remains a significant hurdle for many aspiring competitors looking to challenge established firms like Everbright.
The sheer investment required to match the technological capabilities of incumbents like Everbright, particularly in areas like AI-driven trading platforms and secure cloud infrastructure, acts as a powerful deterrent. For instance, the global fintech market was valued at over $11.2 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow, demanding significant R&D budgets to stay competitive.
Consider these factors impacting new entrants:
- High Capital Requirements: Developing and maintaining cutting-edge technology, including AI and blockchain solutions, demands substantial upfront investment, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars for advanced capabilities.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex financial regulations and compliance requirements, which can vary significantly by jurisdiction and are constantly evolving, adds considerable cost and complexity for new players.
- Brand Recognition and Trust: Established institutions like Everbright benefit from decades of building customer trust and brand loyalty, which is difficult and time-consuming for new entrants to replicate.
Threat of New Entrants 5
The threat of new entrants into China's financial services sector, particularly for Everbright, is currently moderate. The current economic climate in China, marked by challenges in the real estate sector and a broader economic slowdown, increases perceived risks and can reduce potential profitability, thus acting as a deterrent for new players. For instance, China's GDP growth slowed to 5.2% in 2023, a figure that, while seemingly robust, reflects underlying economic pressures that can impact investment appetite.
Furthermore, the regulatory environment has become more stringent following the fintech boom. This tightened oversight, including stricter capital requirements and compliance measures, makes the market less attractive for disruptive new entrants aiming for rapid, less regulated growth. Examples include increased scrutiny on data privacy and anti-monopoly regulations that have reshaped the competitive landscape for technology-driven financial firms.
- Deterrents: China's economic slowdown and real estate sector woes raise the risk profile for new financial firms.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Post-fintech boom regulations, including stricter compliance and capital requirements, create significant barriers.
- Market Attractiveness: The combination of economic uncertainty and regulatory tightening reduces the allure for rapid, disruptive market entry.
The threat of new entrants for Everbright in China's financial sector remains relatively contained due to substantial barriers. Stringent regulations from bodies like the PBOC and NFRA, coupled with high capital requirements for technology and infrastructure, deter many potential competitors. For example, in 2024, the ongoing focus on financial stability and consumer protection has led to even more rigorous licensing and operational standards, making market entry exceptionally challenging.
Everbright's established network, brand recognition, and state-backed advantages further solidify its position. Newcomers would struggle to match the extensive physical presence, like Everbright Securities' over 300 branches by the end of 2023, and the deep customer trust built over decades. The significant investment needed to replicate these foundational elements, alongside navigating evolving fintech regulations, presents a formidable challenge.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory | Strict licensing, capital adequacy, and compliance rules enforced by PBOC and NFRA. | Increases cost and time to market, limits operational flexibility. |
| Capital Requirements | Substantial investment needed for technology (AI, cybersecurity), distribution networks, and brand building. | Limits the pool of potential entrants, favors well-funded entities. |
| Brand & Network | Decades of customer trust and extensive physical branch networks (e.g., 300+ for Everbright Securities). | Difficult and costly for new entrants to replicate, leading to slower customer acquisition. |
| State-Owned Advantage | Policy support, preferential access to capital and markets for state-owned enterprises like Everbright. | Creates an uneven playing field, making it harder for private or foreign firms to compete on cost and access. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Everbright Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research, and economic indicators. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough understanding of competitive dynamics.