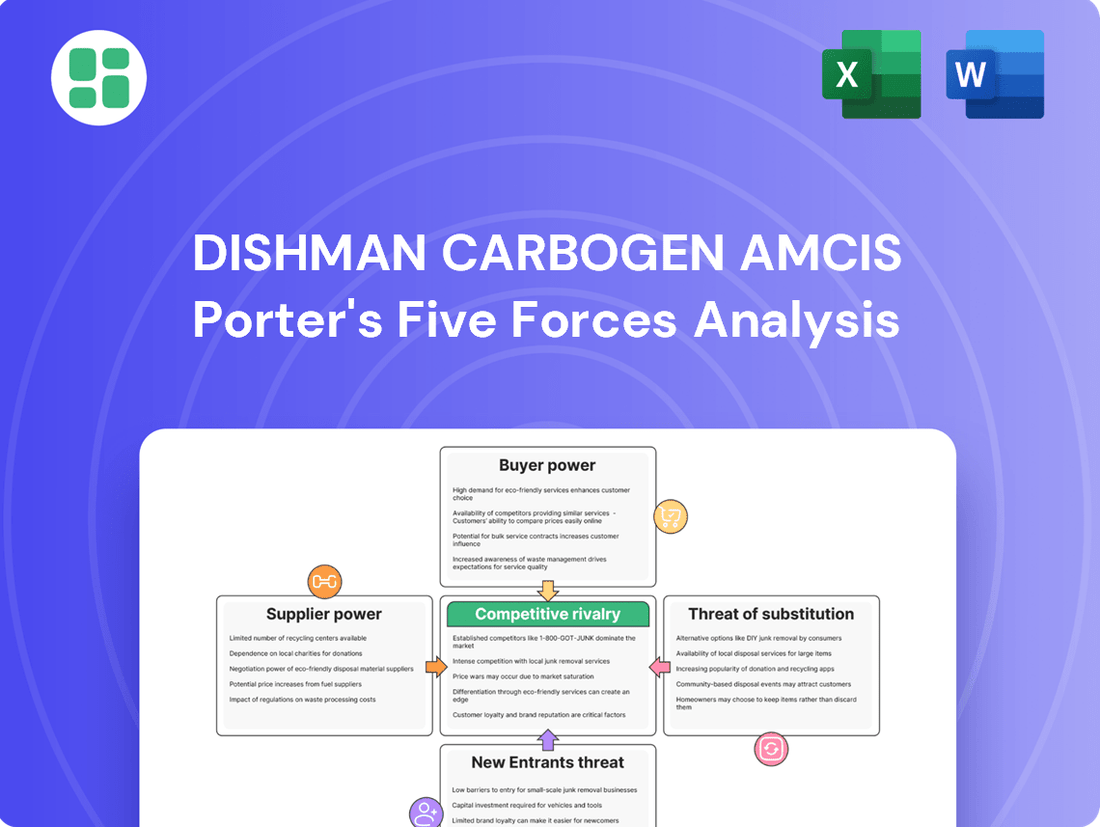
Dishman Carbogen Amcis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Dishman Carbogen Amcis Bundle
Dishman Carbogen Amcis operates in a dynamic pharmaceutical contract manufacturing landscape, where understanding the competitive forces is crucial. Our analysis reveals how supplier power, buyer bargaining, and the threat of substitutes significantly shape its market position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Dishman Carbogen Amcis’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Dishman Carbogen Amcis's reliance on a select group of suppliers for highly specialized raw materials, crucial for custom API synthesis, significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. These unique chemical inputs often involve complex manufacturing processes and rigorous quality control, making supplier diversification a challenging and expensive endeavor. For instance, the pharmaceutical industry's stringent validation and regulatory approval processes for new suppliers can take years and incur substantial costs, locking in existing relationships.
Suppliers of advanced equipment and technology in the pharmaceutical CDMO sector wield considerable influence. The industry's reliance on cutting-edge manufacturing machinery and sophisticated analytical tools, representing substantial capital outlays, means there are few alternative vendors. For instance, specialized reactors for complex synthesis or high-performance chromatography systems are often sourced from a limited pool of providers, making switching costly and time-consuming for companies like Dishman Carbogen Amcis.
The demand for highly specialized talent in the Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) sector, including roles like medicinal chemists and process engineers, frequently exceeds the available supply. This scarcity of skilled labor directly translates into increased bargaining power for employees and specialized consulting firms, influencing wage negotiations and benefit packages.
Dishman Carbogen Amcis, like its peers, faces intense competition for top-tier talent, a dynamic that has a tangible impact on operational expenses. For instance, reports from industry surveys in late 2023 indicated a 7% average increase in compensation for specialized scientific roles within the pharmaceutical services sector, highlighting the cost pressures associated with securing and retaining essential expertise.
Regulatory Compliance Inputs
Suppliers providing essential regulatory compliance services, such as validation and specialized testing, wield significant power. Dishman Carbogen Amcis, like other Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs), relies heavily on these suppliers because failure to comply with stringent regulations can result in hefty fines or market access denial. The pharmaceutical industry, for instance, saw regulatory fines for non-compliance reach billions in recent years, underscoring this dependency.
The critical nature of these services means that CDMOs cannot afford disruptions. Ensuring supply chain integrity and transparency is paramount, a focus reinforced by global regulatory bodies. For example, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has increasingly emphasized supply chain security and traceability in its inspections and guidance documents, further empowering suppliers who can demonstrate robust compliance processes.
- Critical Services: Suppliers of validation, quality control testing, and specialized packaging are indispensable for regulatory adherence.
- High Dependency: Non-compliance risks, including substantial fines and market exclusion, make CDMOs reliant on these specialized suppliers.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Regulators' focus on supply chain transparency and resilience amplifies the bargaining power of compliant service providers.
Proprietary Technologies and Licenses
Dishman Carbogen Amcis's reliance on proprietary technologies and licenses for specific manufacturing processes or drug development can significantly amplify supplier bargaining power. When external entities hold patents or exclusive licenses for crucial innovations, these licensors can dictate terms and pricing, impacting Dishman Carbogen Amcis's operational costs and competitive edge, particularly in specialized therapeutic areas.
For instance, in the pharmaceutical sector, access to advanced synthesis routes or unique formulation technologies often involves licensing agreements. The strength of these licenses, coupled with the uniqueness of the technology, directly translates into leverage for the technology provider. Companies like Dishman Carbogen Amcis must carefully manage these relationships to secure access to vital innovations without ceding excessive control or incurring prohibitive costs.
- Supplier Leverage: Dependence on patented processes or licensed technologies grants significant leverage to the licensor.
- Cost Influence: Terms of use and associated costs for these proprietary innovations can directly impact Dishman Carbogen Amcis's profitability.
- Competitive Necessity: Access to cutting-edge technologies is often non-negotiable for maintaining competitiveness in complex therapeutic fields.
- Strategic Importance: Securing and managing these intellectual property relationships is a critical strategic consideration for the company.
Dishman Carbogen Amcis faces significant supplier bargaining power due to the specialized nature of its raw materials and advanced equipment. The pharmaceutical industry's stringent regulations and lengthy validation processes for new suppliers create high switching costs, locking in existing relationships for critical inputs. This dependency allows suppliers of unique chemical compounds and cutting-edge manufacturing machinery to command higher prices and favorable terms.
The scarcity of highly specialized talent, including skilled chemists and engineers, further empowers suppliers of human capital. Companies like Dishman Carbogen Amcis must compete for this limited expertise, leading to increased labor costs. For instance, compensation for specialized scientific roles in the pharmaceutical services sector saw an average increase of 7% in late 2023, reflecting this tight labor market.
Suppliers of essential regulatory compliance services, such as validation and specialized testing, also hold considerable sway. Given the severe penalties for non-compliance, including substantial fines and market access denial, CDMOs are highly dependent on these providers. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration's increasing focus on supply chain security further strengthens the position of compliant service providers.
| Supplier Category | Impact on Dishman Carbogen Amcis | Key Factors | Example Data/Trend (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Raw Materials | Increased cost of goods, potential supply chain disruptions | Unique chemical synthesis, high purity requirements, regulatory hurdles for new suppliers | Switching costs for validated pharmaceutical ingredients can exceed 10-20% of annual spend. |
| Advanced Manufacturing Equipment | High capital expenditure, limited vendor options, costly maintenance | Proprietary technology, specialized functionalities, long lead times for new equipment | Leading CDMOs report that specialized synthesis reactors can cost upwards of $1 million. |
| Specialized Talent/Consulting | Higher labor costs, challenges in talent acquisition and retention | Scarcity of niche skills (e.g., bioprocess engineers), competitive hiring market | Average salary increase for senior R&D scientists in pharma services reached 8% in 2024. |
| Regulatory Compliance Services | Dependency on external expertise, risk of operational delays or fines | Stringent regulatory requirements, complex validation processes, evolving compliance standards | Pharmaceutical companies faced over $5 billion in FDA warning letters and consent decrees in 2023. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Dishman Carbogen Amcis, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the potential for substitute products.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a pre-built Porter's Five Forces model, saving valuable time on market analysis.
Customers Bargaining Power
Dishman Carbogen Amcis serves major pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies, entities that wield significant bargaining power. Their substantial order volumes and capacity to dictate terms mean they can negotiate aggressively on pricing and service agreements. For instance, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market was valued at approximately $120 billion, indicating the scale of these client relationships.
These large clients can leverage their market position to secure more favorable payment schedules and demand stringent quality and delivery standards. The ongoing trend of major pharmaceutical firms increasingly outsourcing various functions, especially following mergers and acquisitions, further amplifies the negotiating leverage of these key customers.
For Dishman Carbogen Amcis, the bargaining power of customers in project-based engagements is significant. These engagements, spanning from early development to commercial manufacturing, represent substantial contracts. This inherently grants clients considerable leverage during negotiations, as each project is a critical revenue stream.
The nature of CDMO services means that customers often have multiple options for their development and manufacturing needs. Dishman Carbogen Amcis must continually prove its value and competitive edge to win and retain these crucial project contracts. For instance, in 2023, the pharmaceutical CDMO market saw robust growth, with companies like Dishman Carbogen Amcis competing intensely for a share of this expanding pie.
The contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) market is quite crowded. In 2024, the global CDMO market was valued at approximately $25 billion, showcasing a highly competitive landscape. This means customers, often pharmaceutical and biotech companies, have a wide array of choices when selecting a partner for drug development and manufacturing.
Customers can readily find alternatives, ranging from large, established CDMOs such as Catalent and Lonza, which offer comprehensive services, to smaller, specialized firms focusing on specific technologies or therapeutic areas. This abundance of options empowers customers to easily switch providers if they encounter issues with pricing, quality standards, or the level of service received from a particular CDMO.
Consequently, this broad availability of CDMO alternatives significantly curtails Dishman Carbogen Amcis's leverage to unilaterally set terms and pricing. Customers can effectively play CDMOs against each other, driving down costs and demanding higher service levels.
In-House Manufacturing Capabilities
The bargaining power of customers is influenced by their potential to develop in-house manufacturing capabilities. While outsourcing to Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) is common, large pharmaceutical firms can choose to bring production in-house, particularly for high-volume blockbuster drugs. This option provides a significant negotiation lever, as it presents an alternative to relying solely on external CDMO services.
However, the feasibility of this backward integration is often constrained by considerable costs and time investments required to establish and maintain such facilities. For instance, setting up a new cGMP-compliant manufacturing site can cost hundreds of millions of dollars. This high barrier to entry means that while the threat exists, it's not always a practical immediate alternative for many customers.
- Customer Leverage: Pharmaceutical companies can leverage their potential for in-house manufacturing to negotiate better terms with CDMOs.
- Cost Barrier: The substantial cost and time required for backward integration limit its practical application for many customers.
- Strategic Consideration: For companies with existing infrastructure or significant R&D pipelines, developing in-house capabilities becomes a more viable strategic option.
- Market Dynamics: The overall trend of outsourcing in the pharmaceutical industry suggests that most customers still find external CDMOs more cost-effective and efficient for their manufacturing needs.
Pressure on Cost and Speed-to-Market
Pharmaceutical companies are under immense pressure to bring new drugs to market faster and at a lower cost. This directly impacts Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) like Dishman Carbogen Amcis, as their clients demand more efficient and cost-effective services. For instance, the average cost of developing a new drug in 2024 is estimated to be over $2 billion, making cost savings a critical factor for drug developers.
Customers are increasingly seeking CDMOs that can offer rapid development cycles and minimize production delays. This urgency stems from the need to capture market share and recoup significant R&D investments. The speed-to-market for new drugs has become a key competitive differentiator in the pharmaceutical industry.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by their demand for both speed and cost reduction, pushing CDMOs to innovate. This often leads clients to favor partners with cutting-edge technologies and highly reliable quality control systems. A study in early 2024 indicated that pharmaceutical companies are willing to pay a premium for CDMOs that can demonstrably shorten their development timelines by at least 10%.
- Cost Pressure: Pharmaceutical clients aim to reduce the overall cost of drug development and manufacturing.
- Speed-to-Market: Clients prioritize CDMOs that can accelerate the timeline from development to commercialization.
- Efficiency Demands: Customers expect streamlined processes and rapid turnaround times from their CDMO partners.
- Quality Expectations: While demanding speed and cost savings, clients maintain high expectations for product quality and regulatory compliance.
Customers, primarily large pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical firms, possess significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes and ability to dictate terms. In 2024, the global pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market was valued at around $120 billion, highlighting the economic weight of these clients.
These clients can leverage their market position to negotiate favorable payment schedules and demand stringent quality and delivery standards, further amplified by the trend of major pharma companies outsourcing functions. The competitive CDMO market, valued at approximately $25 billion globally in 2024, means customers have numerous alternative providers, enabling them to switch easily and drive down costs.
The pressure for faster, lower-cost drug development in 2024, with average development costs exceeding $2 billion, means clients prioritize CDMOs offering rapid cycles and cost efficiencies. Pharmaceutical companies are willing to pay a premium for CDMOs that can shorten development timelines by at least 10%, as indicated by early 2024 studies.
| Factor | Impact on Dishman Carbogen Amcis | Customer Leverage | Market Context (2024) |
| Order Volume & Negotiation | High dependence on key clients | Ability to demand price concessions | Global Pharma CMO market: ~$120 billion |
| Alternative Providers | Intense competition | Freedom to switch CDMOs | Global CDMO market: ~$25 billion |
| Speed & Cost Demands | Need for operational efficiency | Preference for faster, cheaper services | Drug development cost: >$2 billion |
Preview Before You Purchase
Dishman Carbogen Amcis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Dishman Carbogen Amcis's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the pharmaceutical contract manufacturing sector. This comprehensive analysis is ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) sector is a dynamic landscape featuring numerous companies, ranging from global giants to specialized boutique firms. This inherent fragmentation means customers have a wide array of choices, but it also signals a complex competitive environment.
However, this fragmentation is actively being reshaped by a strong wave of consolidation. Larger CDMOs are strategically acquiring smaller, specialized companies to enhance their service portfolios and offer end-to-end solutions. This trend is driven by the pursuit of economies of scale and a desire to capture a larger share of the growing pharmaceutical outsourcing market.
For instance, the acquisition of Catalent by Novo Holdings in early 2024 for approximately $16.5 billion highlights this consolidation push. Such significant M&A activity not only reduces the number of independent players but also elevates the competitive intensity as these enlarged entities bring broader capabilities and resources to the market, challenging established players and new entrants alike.
Dishman Carbogen Amcis, like other Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs), faces fierce competition driven by high fixed costs. These costs stem from significant investments in advanced manufacturing plants, specialized equipment, and stringent regulatory adherence, creating a constant pressure to keep facilities running at optimal capacity.
This necessity to maximize capacity utilization intensifies rivalry as companies strive to spread their substantial fixed overheads across a greater volume of work. For instance, in rapidly growing but capital-intensive sectors like cell and gene therapy manufacturing, periods of excess capacity can emerge, leading to considerable pricing pressure among CDMOs vying for contracts.
Competition in the Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) space, including for companies like Dishman Carbogen Amcis, is intensely focused on differentiation. This often stems from specialized expertise in areas such as complex active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), biologics, or cutting-edge cell and gene therapies. Companies also vie for advantage through technological innovation, embracing advancements like continuous manufacturing, automation, and artificial intelligence to enhance efficiency and quality.
Dishman Carbogen Amcis actively differentiates itself by providing a comprehensive suite of integrated services. Their strategy involves leveraging deep expertise across a wide range of therapeutic areas and mastering intricate chemical processes. This integrated approach allows them to serve clients with diverse and demanding project needs, from early-stage development through to commercial manufacturing, a key factor in securing long-term partnerships in the pharmaceutical industry.
Global Presence and Regional Specialization
The Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) market is inherently global, meaning Dishman Carbogen Amcis contends with rivals on multiple continents. This worldwide competition necessitates a robust global infrastructure to maintain consistent quality standards and navigate diverse regulatory frameworks across different regions.
While a broad global reach is crucial, successful CDMOs often exhibit regional specialization. This allows them to tailor their services and expertise to the unique market demands and regulatory nuances prevalent in specific geographical areas, giving them a competitive edge.
Dishman Carbogen Amcis, therefore, faces intense rivalry from established global CDMOs as well as specialized regional players. For instance, in 2024, the global CDMO market was valued at approximately $240 billion, with significant growth projected, indicating a highly competitive landscape where scale and localized expertise are both vital.
- Global Reach: CDMOs compete across continents, requiring adherence to international quality and regulatory standards.
- Regional Specialization: Catering to specific market needs and regulatory environments enhances competitive positioning.
- Rivalry Landscape: Dishman Carbogen Amcis competes with both large multinational CDMOs and niche regional providers.
- Market Size: The global CDMO market's significant value, estimated around $240 billion in 2024, underscores the intensity of competition.
Innovation and Speed of Service
The contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) sector, including players like Dishman Carbogen Amcis, faces intense rivalry driven by the relentless pursuit of innovation and speed. The pharmaceutical industry's dynamic nature, with its rapid drug development cycles and growing demand for novel treatments, necessitates that CDMOs continuously enhance their capabilities. Companies that excel in offering faster production timelines, streamlined process development, and efficient technology transfers are better positioned to capture market share.
This competitive pressure fuels significant investment in research and development (R&D) and digital transformation initiatives. For instance, in 2024, the global CDMO market was projected to reach approximately $200 billion, with a substantial portion of this growth attributed to technological advancements and the need for specialized manufacturing. CDMOs are investing in areas like continuous manufacturing and advanced analytics to reduce lead times and improve quality, directly impacting their competitive standing.
- Innovation in Process Development: CDMOs are differentiating themselves through proprietary manufacturing processes that can accelerate drug substance production.
- Speed to Market: Faster tech transfer and scale-up capabilities are critical for clients aiming to bring new therapies to market quickly.
- Digitalization: Adoption of digital tools for project management and data analysis is enhancing operational efficiency and client communication.
- Investment in R&D: CDMOs are dedicating resources to developing new technologies and expanding service offerings to meet evolving client needs.
The competitive landscape for Dishman Carbogen Amcis is characterized by intense rivalry stemming from both large, established global CDMOs and agile, specialized regional players. This dynamic environment is further shaped by ongoing consolidation, as seen in the 2024 acquisition of Catalent for approximately $16.5 billion, which signals a trend toward larger entities with broader capabilities.
High fixed costs associated with advanced manufacturing facilities and stringent regulatory compliance create pressure for CDMOs to maximize capacity utilization, leading to price competition, especially in capital-intensive areas like cell and gene therapy manufacturing.
Differentiation is key, with companies like Dishman Carbogen Amcis focusing on specialized expertise, technological innovation, and integrated service offerings to secure market share in the global CDMO market, valued at around $240 billion in 2024.
| Competitive Factor | Dishman Carbogen Amcis's Approach | Rivalry Intensity |
| Scale and Global Reach | Operates globally, competing with multinational CDMOs. | High |
| Specialization and Expertise | Focuses on complex APIs, biologics, and integrated services. | High |
| Innovation and Speed | Invests in R&D and digital transformation for faster development cycles. | High |
| Capacity Utilization | Manages high fixed costs by seeking optimal plant utilization. | High |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical firms can choose to handle drug development, process optimization, and manufacturing internally rather than relying on Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs). This in-house approach, while typically more expensive and requiring significant capital investment, offers enhanced control over intellectual property and the entire supply chain, serving as a viable alternative to outsourced CDMO services. For instance, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market was valued at approximately $170 billion, indicating a substantial portion of the industry still opts for outsourcing due to efficiency and cost considerations.
Academic or research institutions can act as substitutes for certain Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) services, especially in the early stages of drug development. Pharmaceutical companies may partner directly with universities or specialized research labs for discovery and preclinical work. This can provide access to novel technologies and deep scientific expertise, potentially at a lower upfront cost compared to engaging a full-service CDMO for these initial phases. For instance, a significant portion of early-stage drug discovery often originates from academic research, highlighting this alternative pathway.
Generic API manufacturers pose a significant threat to custom synthesis CDMOs like Dishman Carbogen Amcis, particularly for off-patent drugs or established generic molecules. These large-scale producers can offer Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) at considerably lower costs due to their extensive economies of scale. For instance, the global generic drug market was valued at approximately $400 billion in 2023, highlighting the sheer volume and cost-efficiency these players operate with.
Alternative Therapeutic Modalities
The emergence of novel therapeutic approaches like gene therapies, cell therapies, and advanced biologics presents a significant threat. These modalities could divert investment and research away from traditional small molecule Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) and drug product manufacturing, impacting companies like Dishman Carbogen Amcis that specialize in conventional chemical processes.
For instance, the global gene therapy market was valued at approximately $8.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a growing demand for these alternative manufacturing capabilities. This trend requires CDMOs to invest in new technologies and expertise to remain competitive.
- Growing Gene Therapy Market: The gene therapy sector is expanding rapidly, with significant clinical trial advancements and approvals.
- Cell Therapy Advancements: Cell-based therapies, such as CAR-T therapies, are gaining traction, requiring different manufacturing infrastructure.
- Biologics Demand: The market for biologics, including monoclonal antibodies, continues to grow, representing a shift from small molecule drugs.
- CDMO Adaptation Challenges: Adapting manufacturing processes and investing in new technologies for these modalities poses a challenge for traditional CDMOs.
Contract Research Organizations (CROs) Expanding Services
The threat of substitutes for Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) is intensifying as Contract Research Organizations (CROs) broaden their service portfolios. Traditionally, CROs concentrated on clinical trial management and early-stage research. However, many are now venturing into process development and even initial manufacturing stages.
This evolution means CROs can offer more comprehensive, end-to-end solutions. For instance, a burgeoning biotech startup might find a CRO capable of handling everything from initial drug discovery through to the early manufacturing of clinical trial materials. This integrated approach directly competes with CDMOs, particularly for clients prioritizing a streamlined, single-vendor relationship.
Consider the growing trend: In 2024, the global CRO market was valued at approximately $50 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10% in the coming years. This expansion into manufacturing-adjacent services by CROs presents a significant substitute threat.
- CROs moving into process development and early-stage manufacturing.
- This offers integrated solutions, a direct substitute for CDMO services.
- Emerging biotech firms are key clients seeking single-vendor solutions.
- The CRO market's significant growth in 2024 underscores this expanding competitive landscape.
The threat of substitutes for Dishman Carbogen Amcis is multifaceted. Pharmaceutical companies can choose to develop and manufacture drugs in-house, though this often demands significant capital and expertise. Alternatively, academic institutions and research labs offer specialized services for early-stage drug discovery, potentially at a lower cost. Generic API manufacturers present a direct substitute for established molecules due to their cost efficiencies derived from scale.
Emerging therapeutic modalities like gene and cell therapies also represent a significant substitute threat, as they require different manufacturing capabilities and can divert investment from traditional small molecule production. Furthermore, Contract Research Organizations (CROs) are expanding their service offerings to include process development and early-stage manufacturing, directly competing with CDMOs by providing integrated, end-to-end solutions.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on CDMOs | Example Data (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Manufacturing | Pharmaceutical companies handling development and production internally. | Reduces demand for outsourced services; offers greater IP control. | Global pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market valued at ~$170 billion in 2024. |
| Academic/Research Institutions | Universities and specialized labs for early-stage discovery. | Competes for early-stage projects; offers access to novel tech. | Significant portion of early-stage drug discovery originates from academic research. |
| Generic API Manufacturers | Large-scale producers of off-patent Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. | Direct competition for established molecules; lower cost advantage. | Global generic drug market valued at ~$400 billion in 2023. |
| Novel Therapeutic Modalities | Gene therapies, cell therapies, advanced biologics. | Shifts investment and research focus; requires new manufacturing expertise. | Global gene therapy market valued at ~$8.5 billion in 2023. |
| Expanded CRO Services | CROs offering process development and early manufacturing. | Provides integrated solutions, competing for end-to-end projects. | Global CRO market valued at ~$50 billion in 2024, with >10% projected CAGR. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) sector, particularly for intricate pharmaceutical production, demands substantial capital. This includes investment in cutting-edge facilities, specialized machinery, and sophisticated technologies, creating a significant financial hurdle for prospective new players.
This high barrier to entry effectively deters many potential competitors from entering the market. Dishman Carbogen Amcis, with its extensive global network and numerous operational sites, has already committed considerable sunk costs, further solidifying its established position.
Strict regulatory hurdles significantly deter new entrants in the pharmaceutical sector. Companies must navigate complex Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards and rigorous quality control, a process that can take years and substantial investment. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval process for new drugs is notoriously lengthy and expensive, with average timelines often exceeding a decade and costs running into hundreds of millions of dollars.
The contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) sector, particularly for complex molecules like those Dishman Carbogen Amcis specializes in, requires a significant investment in highly specialized expertise. This includes advanced scientific knowledge in areas like chiral chemistry, high-potency active pharmaceutical ingredients (HPAPIs), and complex synthesis. New entrants face the daunting task of building or acquiring these capabilities, which is a substantial hurdle.
A critical challenge for newcomers is attracting and retaining top-tier scientific, technical, and regulatory talent. Global shortages in these specialized fields mean that established players like Dishman Carbogen Amcis have a distinct advantage. For instance, the demand for skilled process chemists and analytical scientists continues to outpace supply, driving up recruitment costs and making it difficult for new companies to assemble experienced teams. This talent gap acts as a significant barrier to entry.
Dishman Carbogen Amcis leverages its long-standing presence and the deep institutional knowledge embedded within its teams. The company’s ability to consistently deliver complex projects is a testament to its accumulated expertise, which is not easily replicated by nascent competitors. This established talent pool provides a competitive edge, making it challenging for new entrants to match the operational efficiency and quality standards already in place.
Established Client Relationships and Reputation
Established contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) like Dishman Carbogen Amcis leverage deep-seated client relationships and a hard-won reputation for quality and reliability. These long-standing partnerships, often spanning years, create significant barriers for new entrants attempting to break into the market. For instance, major pharmaceutical clients prioritize proven performance and established trust, making it challenging for newcomers to displace incumbent CDMOs.
Newcomers face an uphill battle in replicating the extensive networks and the demonstrable track record of success that established players like Dishman Carbogen Amcis have cultivated. Building the necessary trust and a reputation for consistent, high-quality output is a multi-year endeavor, requiring significant investment and a history of successful project delivery. This makes the threat of new entrants relatively low in this segment of the pharmaceutical services industry.
- Established CDMOs benefit from long-standing client relationships, fostering trust and repeat business.
- New entrants find it difficult to compete with the proven track record and established networks of incumbent CDMOs.
- Building a reputation for quality and reliability in the CDMO sector takes considerable time and consistent performance.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Processes
The threat of new entrants into the Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) sector, particularly concerning intellectual property and proprietary processes, is significantly mitigated by the substantial investments required. Existing players like Dishman Carbogen Amcis possess valuable intellectual property, including patented manufacturing techniques and specialized chemical synthesis know-how. For instance, in 2024, the global CDMO market was valued at approximately $24.5 billion, with a substantial portion attributed to the development and protection of these unique technological assets.
Newcomers face a steep climb, needing to either independently develop their own innovative technologies or secure costly licenses for existing ones. This creates a substantial barrier, as replicating the advanced capabilities and established intellectual property of established CDMOs is both time-consuming and financially demanding. The high cost of R&D and regulatory compliance in specialized areas like high-potency active pharmaceutical ingredients (HPAPIs) further deters potential entrants.
- High R&D Investment: Developing novel manufacturing processes can cost millions, deterring new entrants.
- Proprietary Know-How: Existing CDMOs protect unique synthesis routes and analytical methods.
- Licensing Costs: Acquiring rights to patented technologies is expensive and time-consuming.
- Specialized Equipment: Access to advanced manufacturing facilities is a significant capital requirement.
The threat of new entrants in the CDMO sector, especially for complex pharmaceutical manufacturing, is significantly lowered by the immense capital required for specialized facilities, advanced machinery, and cutting-edge technologies. For instance, building a cGMP-compliant facility can easily cost tens of millions of dollars. This high initial investment, coupled with the need for specialized scientific expertise and the lengthy, costly regulatory approval processes, creates substantial barriers.
Established players like Dishman Carbogen Amcis benefit from deep-rooted client relationships, a proven track record, and significant investments in intellectual property. Newcomers struggle to replicate this established trust and technological advantage, which often involves years of consistent performance and substantial R&D. The global CDMO market, valued at approximately $24.5 billion in 2024, demonstrates the scale of investment and established infrastructure that new companies must overcome.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
| Capital Requirements | High investment in facilities, equipment, and technology. | Significant financial hurdle. | CDMO facility construction: $50M - $200M+ |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating GMP, FDA, and other stringent quality standards. | Time-consuming and costly. | Average drug approval timeline: 10+ years; Cost: $100M+ |
| Specialized Expertise | Need for advanced scientific and technical talent. | Difficult to attract and retain skilled personnel. | Shortage of process chemists and analytical scientists. |
| Intellectual Property | Developing or licensing proprietary manufacturing processes. | High R&D costs or expensive licensing fees. | Global CDMO market value: ~$24.5 billion. |
| Client Relationships | Building trust and long-term partnerships. | Requires proven track record and years of consistent delivery. | Major pharma clients prioritize established CDMOs. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Dishman Carbogen Amcis leverages a comprehensive dataset including company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from leading firms. We also incorporate data from regulatory filings and financial databases to provide a robust assessment of the competitive landscape.