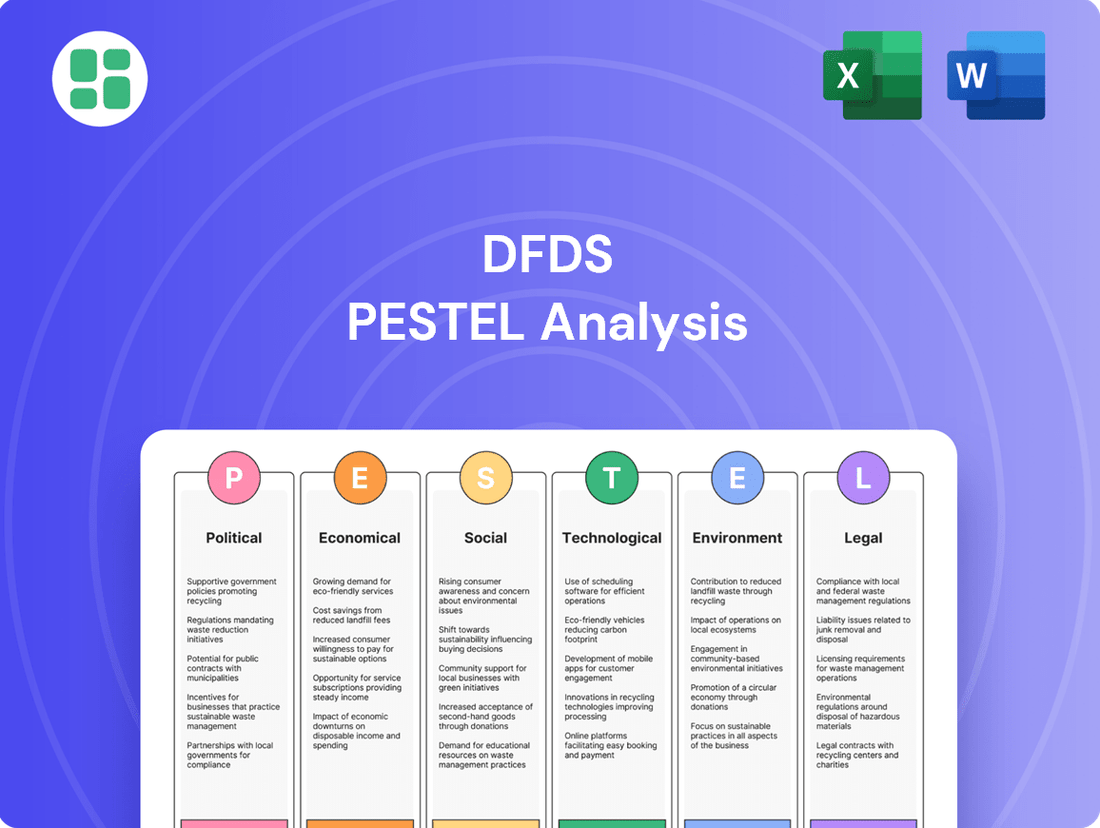
DFDS PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
DFDS Bundle
Navigate the complex external forces shaping DFDS's future with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that present both opportunities and challenges for the company. Equip yourself with actionable intelligence to refine your own strategic planning and investment decisions. Download the full PESTLE analysis now and gain a critical competitive advantage.
Political factors
DFDS's extensive operations across Northern Europe and the Baltic Sea mean it's significantly influenced by regulatory changes in both the EU and the UK. For instance, the ongoing implementation of the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) and the upcoming FuelEU Maritime Regulation, set to begin in 2025, will directly affect DFDS's operational expenses and the need for compliance measures.
Furthermore, the UK's post-Brexit trade agreements and evolving border policies introduce complexities for freight volumes and customs processing. This necessitates continuous adaptation of DFDS's services and logistics to ensure efficiency on its key routes, impacting its ability to manage costs and maintain service levels.
Geopolitical stability in Northern Europe and the Baltic Sea is paramount for DFDS, directly influencing its ferry and logistics services. For instance, ongoing tensions in Eastern Europe could lead to increased transit times and costs for freight moving through the region, impacting DFDS's €2.1 billion revenue in 2023 which relies heavily on these routes.
Trade disputes or shifts in international relations can disrupt established DFDS routes, affecting freight volumes and potentially requiring costly rerouting or enhanced security measures. The company's extensive network, vital for connecting markets like the UK and Scandinavia, depends on predictable trade corridors, which were tested by evolving trade agreements in 2024.
Governments across the EU and UK are actively channeling funds and offering incentives to drive the decarbonization of the maritime industry. This political landscape presents a significant opportunity for DFDS.
Initiatives like the UK's green shipping corridors program and the Nordic Council of Ministers' projects are specifically designed to speed up the adoption of alternative fuels and cutting-edge technologies. These programs can provide crucial financial backing for DFDS's transition to greener operations.
The substantial capital needed for investing in new, environmentally friendly vessels and upgrading port infrastructure can be partially mitigated by this governmental support. For instance, the EU's Innovation Fund has allocated billions of euros for climate-neutral solutions, including those in the maritime sector, with several projects involving alternative fuels receiving significant backing in recent years.
International Maritime Organization (IMO) Policies
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) sets global rules impacting shipping companies like DFDS. Current policies focus heavily on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing safety. These regulations directly shape DFDS's fleet modernization plans and how it operates its ships.
The IMO's updated strategy targets net-zero emissions by 2050, with crucial interim goals for 2030 and 2040. This means DFDS needs to invest in newer, more efficient vessels and explore alternative fuels. For instance, the IMO 2020 sulfur cap already required significant adjustments to fuel choices and exhaust gas cleaning systems.
DFDS must align its long-term strategy with these evolving international maritime standards. This includes:
- Investing in advanced hull coatings and energy-saving technologies to reduce fuel consumption.
- Exploring and adopting alternative low-carbon and zero-carbon fuels like LNG, methanol, or ammonia.
- Ensuring all vessels meet stringent safety and environmental compliance standards, avoiding potential fines and operational disruptions.
- Adapting operational practices, such as slow steaming, to meet emission reduction targets.
Port Policies and Infrastructure Development
National and local port authorities wield significant influence through their policies on access, fees, and infrastructure upgrades. These regulations directly shape DFDS's operational costs and strategic planning.
Investments in critical infrastructure like shore power, alternative fuel bunkering, and advanced digital port systems are paramount. For instance, the development of LNG bunkering facilities at key European ports enables DFDS to utilize more environmentally friendly fuels, supporting its sustainability goals.
DFDS's active collaboration with ports, such as the ongoing feasibility study for a green shipping corridor between the UK and the Netherlands, highlights the importance of these partnerships. This initiative aims to reduce emissions by up to 70% by 2030, demonstrating the tangible impact of political will and infrastructure investment on future growth.
- Port Authority Policies: Regulations set by authorities like Port of Rotterdam or Port of Dover impact operational efficiency and cost.
- Infrastructure Investment: Government and port authority funding for shore power and alternative fuel facilities directly supports DFDS's green transition.
- Green Corridor Initiatives: Collaborative projects, like the UK-Netherlands green corridor, signal future regulatory and infrastructure support for sustainable shipping.
Political factors significantly shape DFDS's operational landscape, particularly through evolving environmental regulations and governmental support for green initiatives. The EU's Emissions Trading System and the upcoming FuelEU Maritime Regulation starting in 2025 will directly impact costs, while UK post-Brexit trade policies add complexity to freight operations.
Geopolitical stability in Northern Europe is crucial, as tensions can increase transit times and costs, affecting DFDS's revenue streams. Trade disputes can also disrupt key routes, necessitating costly adaptations. However, governments are providing incentives for decarbonization, such as the UK's green shipping corridors and EU's Innovation Fund, which can offset investments in new, eco-friendly vessels and infrastructure.
International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations, like the net-zero target by 2050 and interim goals for 2030 and 2040, are driving DFDS's fleet modernization. National and local port authorities also play a vital role through their policies and infrastructure investments, such as shore power and alternative fuel bunkering, exemplified by the UK-Netherlands green corridor project.
What is included in the product
This DFDS PESTLE analysis examines the impact of Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors on the company's operations and strategic planning.
A clear, actionable breakdown of the external factors impacting DFDS, transforming complex market dynamics into manageable insights for strategic decision-making.
Economic factors
DFDS's core freight and logistics operations are intrinsically tied to the economic pulse of Europe and the wider world. As such, any slowdown in global economic expansion directly translates to reduced demand for shipping and transportation services, impacting DFDS's top line.
Looking ahead to 2025, forecasts suggest a generally subdued economic growth environment in Europe. For instance, the European Commission's Spring 2024 forecast projected a modest GDP growth of 1.7% for the Eurozone in 2025, a figure that, while positive, signals a potentially challenging landscape for freight volume expansion.
A decline in manufacturing output or a dip in consumer spending across key European markets would inevitably dampen the need for goods movement. This directly affects DFDS's ability to fill its vessels and trucks, potentially leading to lower utilization rates and impacting overall profitability.
Fluctuations in global fuel prices pose a significant economic hurdle for DFDS, with fuel costs representing a substantial segment of their operational expenditures. While some projections indicate a possible decrease in fuel prices by 2025, the persistent volatility remains a critical factor impacting freight rates and overall profitability.
The ongoing shift towards alternative fuels, which may carry higher initial costs, further complicates DFDS's approach to managing expenses effectively in the coming years.
As a Danish company with extensive operations across Europe, DFDS is significantly exposed to currency exchange rate fluctuations. For instance, in 2024, the Danish Krone (DKK) has shown some volatility against the Euro (EUR). A stronger DKK could reduce the value of revenues earned in Euros when translated back into Danish Kroner, while a weaker DKK would have the opposite effect, potentially increasing reported revenue from Eurozone countries.
These movements also affect DFDS's costs. If the DKK weakens against the British Pound (GBP), for example, the cost of procuring goods or services in the UK, or even maintaining operations there, would increase in Krone terms. This directly impacts DFDS's bottom line, as seen in the financial reports where currency impacts are often highlighted as a key risk factor affecting profitability and the competitiveness of its services across different markets.
Inflation and Operating Costs
High inflation rates across Europe, particularly in the 2024-2025 period, directly impact DFDS's operating expenses. This includes increased costs for fuel, essential maintenance, crew wages, and onboard supplies, all of which can squeeze profit margins. For instance, if average inflation in key European markets hovers around 3-4% in 2024, as projected by many economic forecasts, DFDS will face significant cost pressures.
While DFDS actively pursues operational efficiencies and fleet modernization to mitigate these effects, persistent inflation poses a substantial challenge. If the company cannot fully pass on these rising costs through fare adjustments or implement sufficiently aggressive cost-saving initiatives, its profitability could be negatively affected.
- Increased Fuel Costs: Fuel is a major operating expense for DFDS, and sustained high oil prices, potentially linked to geopolitical instability in 2024, directly inflate these costs.
- Wage Inflation: Rising living costs in Europe necessitate higher wages for employees, impacting labor expenses across crewing, port operations, and administrative functions.
- Maintenance and Repair Expenses: The cost of spare parts, materials, and specialized labor for vessel maintenance is also subject to inflationary pressures, increasing the overall upkeep budget.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Broader inflationary trends can be exacerbated by supply chain issues, leading to higher prices for all procured goods and services, from catering supplies to IT equipment.
Competitive Environment and Market Dynamics
DFDS operates in highly competitive markets, facing significant pressure from established players and emerging entrants across both its ferry and logistics segments. For instance, in the North Sea ferry routes, competition remains robust with operators like Stena Line and P&O Ferries. Similarly, the logistics sector sees constant rivalry from global giants and specialized regional providers, impacting pricing power.
This heightened competition directly translates into downward pressure on freight rates and passenger fares. In 2024, industry reports indicated a general trend of rate stabilization or slight declines in certain key European freight corridors due to overcapacity in some areas, affecting DFDS's revenue potential. Maintaining market share and profitability hinges on DFDS's agility in adjusting its service offerings and network to meet evolving customer demands and competitive landscapes.
The company's strategic responses are vital. DFDS's investment in new, larger ferries and its expansion into new logistics markets, such as its acquisition of the logistics company DSV's former road freight business in the Nordics in late 2023, demonstrate efforts to adapt. These moves aim to leverage economies of scale and broaden its service portfolio, crucial for navigating dynamic market conditions and preserving its competitive advantage.
- Intense Competition: DFDS faces rivals like Stena Line and P&O Ferries on key ferry routes, and global logistics players in its transport division.
- Rate Pressure: Increased competition in 2024 has contributed to pressure on freight rates and passenger fares across several European markets.
- Adaptability is Key: DFDS's ability to adjust its network, such as through strategic acquisitions like the DSV road freight business, is critical for staying competitive.
- Market Share Focus: Navigating these dynamics requires a constant focus on optimizing services to retain and grow market share in both ferry and logistics operations.
Economic factors significantly shape DFDS's performance, with European economic growth being a primary driver of freight demand. Projections for 2025 indicate modest GDP growth in the Eurozone, suggesting a potentially constrained environment for volume expansion. This means that shifts in manufacturing output or consumer spending directly influence how much goods need to be transported, impacting vessel and truck utilization for DFDS.
Fuel price volatility remains a critical economic concern for DFDS, as it constitutes a substantial operational cost. While some forecasts suggest potential price moderation by 2025, ongoing price instability directly affects freight rates and overall profitability. Furthermore, the transition to alternative fuels may introduce higher upfront expenses, adding another layer to cost management strategies.
Currency exchange rate fluctuations present another economic challenge for DFDS, given its extensive European operations. For instance, movements between the Danish Krone and the Euro in 2024 can impact the reported value of revenues and the cost of operations in different markets, affecting the company's profitability and competitive positioning.
High inflation rates across Europe, particularly in the 2024-2025 period, are increasing DFDS's operating expenses. This includes higher costs for fuel, maintenance, and wages, potentially squeezing profit margins if these increases cannot be fully passed on to customers. For example, if inflation averages 3-4% in key European markets during 2024, DFDS will face considerable cost pressures.
| Economic Factor | Impact on DFDS | 2024/2025 Data/Projections |
|---|---|---|
| European GDP Growth | Influences freight demand and transport volumes. | Eurozone GDP projected at 1.7% for 2025 (European Commission Spring 2024 Forecast). |
| Fuel Prices | Major operational expense, impacting profitability and freight rates. | Volatility persists, with potential for moderation but ongoing risk. |
| Inflation Rates | Increases operating expenses (fuel, wages, maintenance). | Key European markets may see average inflation around 3-4% in 2024. |
| Currency Exchange Rates | Affects reported revenue and operational costs across different markets. | DKK volatility against EUR noted in 2024; impacts cross-border costings. |
Preview Before You Purchase
DFDS PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact DFDS PESTLE Analysis you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use.
This is a real screenshot of the product you’re buying—delivered exactly as shown, no surprises. It offers a comprehensive look at the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting DFDS.
The content and structure shown in the preview is the same DFDS PESTLE Analysis document you’ll download after payment, providing actionable insights for strategic planning.
Sociological factors
Consumer preferences for travel are increasingly shaped by a desire for sustainable options and a growing demand for leisure experiences. DFDS's recognition as the 'World's Leading Ferry Operator' underscores its success in aligning with these evolving passenger expectations, demonstrating a commitment to passenger satisfaction and community involvement.
The convenience of sea routes also plays a significant role, especially when contrasted with other transportation methods. To remain competitive, DFDS must continually adapt its services to align with shifting tourism trends and enhance onboard offerings to meet passenger desires for engaging experiences.
Societal attitudes toward environmental responsibility and ethical business practices are increasingly shaping consumer and business decisions. DFDS's proactive stance on sustainability, demonstrated by its commitment to reducing carbon emissions and minimizing food waste, directly bolsters its public perception and brand reputation. For instance, DFDS aims to have a fully fossil-free fleet by 2040, a significant undertaking that resonates with environmentally conscious travelers and cargo clients.
The availability of skilled workers for maritime, road, and logistics operations is a significant sociological consideration for DFDS. In 2024, the European Union faces ongoing challenges in securing qualified personnel, particularly in specialized maritime roles, with reports indicating a shortage of certified seafarers in certain sectors.
Demographic trends, such as an aging workforce across Europe and increased competition for skilled labor from other industries, directly affect DFDS's operational capacity and can drive up labor expenses. This trend is exacerbated by a general decline in younger individuals entering vocational trades essential for logistics and transport.
DFDS's commitment to being a 'caring employer' and prioritizing employee well-being is a strategic imperative. By fostering a positive work environment and investing in employee development, the company aims to attract and retain a diverse and skilled workforce, which is crucial for maintaining high standards of service and operational efficiency in the face of these demographic shifts.
Societal Demand for Sustainable Logistics
Societal and business expectations are increasingly leaning towards logistics operations that are not only efficient but also environmentally responsible. This growing demand for greener supply chains is a significant driver for companies like DFDS to actively pursue and invest in cleaner technologies, such as alternative fuels and more fuel-efficient vessels. For instance, by 2024, DFDS has been actively exploring and implementing solutions to reduce its carbon footprint, aiming to align with the EU's ambitious climate targets.
This shift in demand directly influences DFDS's strategic decisions, pushing the company to optimize its supply chain networks to minimize emissions and enhance overall sustainability. Offering integrated logistics services that actively support customers in achieving their own sustainability objectives is becoming a key differentiator. In 2025, the market is seeing a clear trend where businesses are selecting logistics partners based on their environmental performance, making sustainability a crucial competitive advantage.
- Growing Environmental Awareness: Consumers and businesses alike are more conscious of the environmental impact of transportation, leading to a preference for eco-friendly logistics.
- Regulatory Pressures: Governments worldwide are implementing stricter environmental regulations, compelling logistics firms to adopt sustainable practices.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Many companies are integrating sustainability into their core business strategies, demanding the same from their logistics partners.
- Competitive Differentiation: Companies that demonstrate a strong commitment to sustainability can gain a significant edge in attracting and retaining environmentally-conscious clients.
Impact of Digitalization on Daily Life and Commerce
The pervasive digitalization of daily life and commerce has fundamentally reshaped customer expectations, particularly within the logistics sector. Consumers and businesses alike now anticipate effortless online booking processes, immediate real-time tracking for shipments, and highly efficient digital communication channels. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 70% of B2B buyers prefer digital self-service options for procurement, highlighting this demand for seamless online interactions.
DFDS's strategic response to this societal evolution is evident in its ongoing commitment to digital innovation. The company is actively investing in technologies designed to elevate the customer experience and streamline operational efficiencies. This includes enhancements to their online platforms and the development of integrated digital solutions for freight management. By prioritizing these digital advancements, DFDS aims to meet and exceed the evolving demands of a digitally-native marketplace.
This societal shift also profoundly influences how businesses engage with logistics providers. There's a growing expectation for integrated logistics services that are managed and communicated through unified digital platforms. Companies are looking for partners who can offer end-to-end visibility and control over their supply chains, facilitated by robust digital infrastructure. This trend is further underscored by projections suggesting that the global digital logistics market could reach over $40 billion by 2027, driven by the need for greater transparency and efficiency.
- Customer Expectations: Increased demand for online booking, real-time freight tracking, and efficient digital communication.
- DFDS Investment: Continued focus on digital innovation to improve customer experience and operational efficiency.
- Business Demands: Expectation for integrated logistics services managed through digital platforms.
- Market Trend: Digital logistics market growth driven by the need for transparency and efficiency.
Societal expectations are increasingly prioritizing sustainable and ethical business practices, directly impacting consumer choices in travel and logistics. DFDS's commitment to environmental responsibility, aiming for a fossil-free fleet by 2040, resonates with this trend, enhancing its brand reputation. The company's focus on employee well-being also addresses demographic challenges like an aging workforce and competition for skilled labor, crucial for operational continuity.
Digitalization is fundamentally altering customer expectations, with a demand for seamless online interactions, real-time tracking, and efficient digital communication. DFDS is investing in digital innovation to meet these demands, aiming to provide integrated logistics services through unified digital platforms. This aligns with market trends showing significant growth in digital logistics, driven by the need for transparency and efficiency.
| Sociological Factor | Impact on DFDS | Supporting Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Consciousness | Increased demand for sustainable transport solutions. | DFDS aims for a fossil-free fleet by 2040. Over 70% of B2B buyers prefer digital self-service options (2024). |
| Digitalization | Expectation for seamless online booking, real-time tracking, and digital communication. | Global digital logistics market projected to exceed $40 billion by 2027. |
| Demographics | Challenges in securing skilled maritime and logistics personnel. | Shortage of certified seafarers in certain EU sectors (2024). Aging workforce across Europe. |
Technological factors
The maritime industry is rapidly embracing new fuels like methanol, ammonia, LNG, and hydrogen to achieve its decarbonization goals. DFDS is a key player in this transition, investing in technologies such as ammonia-powered ships and researching green methanol for its operations. For instance, DFDS announced in late 2023 plans to operate the world's first large-scale container ship powered by green ammonia, aiming for delivery in 2027.
The successful widespread adoption of these alternative fuels hinges on the development and accessibility of bunkering infrastructure. Without sufficient availability and scalability of these new fuel supply points, the transition will face significant hurdles. The International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) 2023 GHG Strategy aims for net-zero emissions by or around 2050, driving this technological evolution.
Advancements in automation and digitalization are significantly reshaping port operations and vessel management. This includes the adoption of automated cargo handling systems, sophisticated intelligent navigation, and the use of data analytics for optimizing routes and enabling predictive maintenance. For instance, by 2024, many major ports are implementing AI-driven solutions to streamline logistics, with some reporting up to a 20% increase in throughput efficiency.
DFDS is actively pursuing the standardization and digitalization of its extensive network to boost customer service and operational efficiency. This strategic move is crucial for enhancing safety protocols and achieving substantial cost reductions across its fleet and terminals. The company's ongoing digital transformation initiatives are expected to yield a 10-15% improvement in operational cost savings by the end of 2025.
DFDS's increasing reliance on digital platforms for operations, from ship navigation to customer bookings, exposes it to escalating cybersecurity threats like ransomware and data breaches. The maritime sector experienced a significant rise in cyber incidents in 2023, with reports indicating a 400% increase in ransomware attacks targeting shipping companies compared to previous years, underscoring the vulnerability of connected systems.
To counter these risks, DFDS must implement stringent cybersecurity measures and adhere to evolving industry standards, such as the IMO Cyber Risk Management Framework, which became mandatory for shipping companies from January 1, 2024. Proactive defense strategies are crucial for safeguarding critical infrastructure, sensitive customer data, and operational continuity against increasingly sophisticated cyber adversaries.
Advanced Data Analytics and AI for Logistics Optimization
Advanced data analytics and AI are revolutionizing logistics, enabling DFDS to fine-tune operations. By analyzing vast datasets, DFDS can optimize route planning, reducing transit times and fuel consumption. For instance, in 2024, AI-powered route optimization in the shipping industry has shown potential to cut fuel costs by up to 10%.
These technologies also enhance capacity utilization by predicting demand more accurately. This means DFDS can better match its fleet capacity to customer needs, minimizing empty space and maximizing revenue. In 2024, companies adopting AI for demand forecasting reported an average improvement in forecast accuracy of 15-20%.
Furthermore, improved supply chain visibility through AI and analytics allows DFDS to track shipments in real-time, anticipate disruptions, and respond proactively. This leads to more reliable delivery schedules and elevated customer satisfaction, especially crucial for integrated logistics networks.
- Route Optimization: AI algorithms can process real-time traffic, weather, and vessel performance data to suggest the most efficient routes, potentially saving significant fuel costs.
- Demand Forecasting: Predictive analytics help anticipate cargo volumes and passenger numbers, enabling better resource allocation and service planning.
- Capacity Utilization: AI can optimize the loading of vessels and trailers, ensuring maximum use of available space and reducing operational inefficiencies.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Real-time tracking and data integration provide end-to-end visibility, allowing for quicker responses to potential delays or issues.
Ship Design and Energy Efficiency Innovations
Technological advancements in ship design are significantly boosting energy efficiency and cutting fuel usage. Innovations like advanced hull coatings that reduce drag, air lubrication systems that create a cushion of air under the hull, and optimized engine technologies are key. For instance, by 2024, DFDS has been actively investing in upgrading its fleet with more fuel-efficient vessels and exploring cleaner propulsion methods, aligning with its sustainability targets and aiming to control operational expenses.
DFDS's strategic focus on technological integration is evident in its ongoing efforts to enhance operational performance. The company's commitment to adopting innovations that reduce its environmental footprint is directly linked to managing the rising costs associated with fuel. In 2024, the maritime industry saw a continued push towards digitalization and automation in ship operations, which DFDS is also leveraging to improve efficiency and safety.
Key technological factors impacting DFDS include:
- Hull Optimization: Implementing advanced hull coatings and designs to minimize water resistance, leading to lower fuel consumption.
- Propulsion Systems: Investing in more efficient engine technologies and exploring alternative fuels and hybrid systems.
- Digitalization: Utilizing data analytics and smart technologies for route optimization, predictive maintenance, and overall operational efficiency.
Technological advancements are central to DFDS's strategy for decarbonization and efficiency. The company is actively investing in new fuels like green ammonia and methanol, with plans for the world's first large-scale ammonia-powered container ship by 2027. This aligns with the IMO's 2050 net-zero goal.
Digitalization and automation are transforming operations, with AI-driven solutions improving port throughput by up to 20% by 2024. DFDS aims for 10-15% operational cost savings by the end of 2025 through these initiatives. Cybersecurity is a growing concern, with a 400% rise in ransomware attacks on shipping companies in 2023, necessitating adherence to the IMO Cyber Risk Management Framework from January 2024.
AI is also optimizing routes, potentially cutting fuel costs by 10% in 2024, and enhancing demand forecasting accuracy by 15-20%. These technologies improve supply chain visibility and customer satisfaction.
Innovations in ship design, such as advanced hull coatings and more efficient propulsion systems, are crucial for reducing fuel consumption. DFDS's fleet upgrades in 2024 reflect this focus on sustainability and cost control.
Legal factors
The EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) now includes maritime transport, creating a new legal compliance layer for DFDS starting in January 2024. This means DFDS must account for and purchase allowances for a growing percentage of its CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide emissions from voyages connected to EU ports. For 2025, the surrender obligation for emissions is set to increase, directly impacting operational costs.
The FuelEU Maritime Regulation, effective January 1, 2025, will impose limits on the greenhouse gas intensity of fuels used by ships calling at EU ports. This means DFDS must adapt its fuel sourcing and fleet technology to meet these new standards, encouraging a shift towards renewable and lower-emission alternatives to avoid potential financial penalties.
DFDS navigates a complex international maritime legal landscape, adhering to conventions established by the International Maritime Organization (IMO). These include critical regulations like MARPOL, which sets stringent standards for preventing pollution from ships, and SOLAS, ensuring vessel safety. In 2023, the IMO continued to drive discussions on decarbonization, with potential new regulations impacting fuel choices and operational efficiencies for companies like DFDS.
Competition Law and Market Dominance Regulations
As a significant operator in Northern European shipping and logistics, DFDS is subject to rigorous EU and national competition laws. These regulations govern mergers, acquisitions, pricing strategies, and overall market conduct to foster fair competition and prevent monopolistic practices within the sector.
For instance, the European Commission actively monitors market concentration. In 2024, the Commission approved several mergers within the transport sector after thorough reviews, ensuring that these combinations did not unduly restrict competition. DFDS must navigate these oversight mechanisms, particularly concerning its market share in key ferry routes, such as those connecting the UK and mainland Europe.
- Merger Control: DFDS must notify and seek approval for significant acquisitions or mergers that could impact market competition, adhering to thresholds set by competition authorities.
- Anti-Competitive Practices: Regulations prohibit practices like price-fixing, market sharing, and abuse of dominant market positions to ensure a level playing field.
- Market Dominance: Authorities monitor companies with substantial market share to prevent them from leveraging their position to stifle smaller competitors or harm consumers.
Labor Laws and Seafarer Regulations
DFDS, a major employer, navigates a complex web of labor laws across its operational countries and international seafarer regulations. These regulations dictate crucial aspects like maximum working hours, stringent safety protocols, equitable wage structures, and the handling of collective bargaining agreements. For instance, the Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) 2006, ratified by many of DFDS's operating nations, sets global standards for seafarer employment conditions, impacting crewing costs and operational planning.
Compliance with these diverse legal frameworks directly influences DFDS's operational flexibility and its approach to human resource management. Failure to adhere to these laws can result in significant penalties, reputational damage, and disruptions to service. In 2024, the ongoing review and potential updates to EU working time directives, for example, could further shape crew scheduling and rostering practices for DFDS's European fleet.
- Seafarer Working Hours: Adherence to regulations like the MLC 2006, which sets limits on maximum working hours and minimum rest periods for seafarers, is paramount for DFDS's crew management.
- Safety Standards: Compliance with international safety conventions, such as SOLAS (Safety of Life at Sea), directly impacts the design, maintenance, and operation of DFDS vessels and crew training.
- Fair Wages and Benefits: Ensuring fair wages and benefits, often influenced by national minimum wage laws and collective bargaining agreements with maritime unions, affects DFDS's labor costs and employee retention.
- Collective Bargaining: DFDS engages with various seafarer unions across its operating regions, requiring negotiation and adherence to collective bargaining agreements that cover terms of employment.
The EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) and FuelEU Maritime Regulation are key legal drivers for DFDS, impacting emissions and fuel choices from 2024 and 2025 onwards. These regulations necessitate investment in cleaner fuels and technologies to meet increasingly stringent greenhouse gas intensity limits, with compliance costs directly tied to emission levels.
DFDS must also adhere to international maritime laws like MARPOL and SOLAS, alongside evolving decarbonization discussions within the IMO, influencing fleet operations and fuel strategies. Competition laws, particularly EU regulations, require careful management of market share and potential mergers to prevent anti-competitive practices.
Labor laws, including the Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) 2006, govern seafarer working hours, safety, and wages, directly affecting DFDS's crewing costs and operational planning. Compliance with these diverse legal frameworks is critical for avoiding penalties and maintaining operational continuity.
Environmental factors
DFDS is actively pursuing ambitious decarbonization targets, aiming to cut Tank-to-Wake CO2 emissions intensity by 45% by 2030. This commitment extends to achieving net-zero emissions for its vessel operations by 2050, with parallel goals for road, land transport, and warehousing operations.
These environmental objectives necessitate substantial investment in green technologies, such as the development and adoption of alternative fuels like biogas and the ongoing retrofitting of vessels with more efficient systems. For instance, DFDS is exploring the use of battery-electric and hybrid solutions for shorter routes, reflecting a broader industry shift towards sustainable maritime transport.
DFDS is prioritizing the development of green shipping corridors, especially in Northern Europe and the Baltic Sea, as a crucial environmental strategy. This initiative focuses on creating routes that can accommodate alternative fuels, significantly reducing the company's carbon footprint.
The company is actively engaged in feasibility studies and collaborations to pioneer these corridors. A key objective is the adoption of fuels such as green methanol and ammonia, which are projected to cut annual CO2 emissions by substantial amounts, aligning with global decarbonization goals.
DFDS is actively working to reduce pollution beyond just carbon emissions. This includes a strong focus on minimizing food waste on its ferries and cutting down on single-use plastics. For example, in 2023, DFDS reported a 15% reduction in food waste across its fleet compared to 2022, a tangible step in their sustainability journey.
Managing waste and noise pollution in port communities is also a key environmental consideration for DFDS. These initiatives are crucial for maintaining good relationships with local residents and protecting the marine ecosystems where their operations take place. The company aims to be a responsible neighbor, contributing positively to the environments it serves.
Biodiversity and Marine Ecosystem Protection
DFDS operates extensively in sensitive marine environments, particularly the Baltic Sea, necessitating a keen focus on biodiversity and marine ecosystem protection. The company must adhere to stringent regulations aimed at preventing pollution, such as those governing emissions and waste disposal, to minimize its ecological footprint.
Managing ballast water is crucial to prevent the introduction of invasive species, a significant threat to native marine life. For instance, the IMO's Ballast Water Management Convention, which entered into force in 2017, sets standards for ballast water treatment. DFDS's commitment to supporting the marine environment likely involves investments in advanced ballast water treatment systems, with global adoption rates of such systems steadily increasing, reaching an estimated 50% of the global fleet by the end of 2024.
DFDS may also participate in or support initiatives aimed at direct marine life protection. This could include contributing to research on marine species, supporting habitat restoration projects, or adopting practices that reduce the risk of ship strikes on marine mammals. The company's sustainability reports often detail its efforts in these areas, reflecting a growing industry trend towards environmental stewardship.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to international and regional environmental regulations, such as MARPOL Annex VI for air pollution and the Ballast Water Management Convention, is paramount.
- Pollution Prevention: Implementing technologies and operational procedures to minimize discharges of oil, chemicals, and sewage into marine waters.
- Biodiversity Impact Mitigation: Employing strategies to reduce noise pollution, light pollution, and the risk of collisions with marine fauna.
- Ecosystem Restoration Support: Potential engagement in projects that aim to restore or protect marine habitats, such as seagrass beds or coral reefs, in areas of operation.
Adaptation to Climate Change Impacts
DFDS must actively adapt to the physical consequences of climate change, including shifting weather patterns and rising sea levels, which can impact shipping operations. For instance, more frequent extreme weather events in the North Sea, a key operational area for DFDS, can lead to route deviations and delays. In 2023, the company reported increased operational costs related to weather disruptions, though specific figures were not disclosed in the annual report.
Adapting to these changes requires strategic adjustments in vessel operations and route planning to maintain service reliability. This includes investing in more weather-resilient vessels and developing dynamic routing systems that can account for real-time meteorological data. The company is also exploring ways to enhance port infrastructure resilience against potential sea-level rise and storm surges.
- Changing Weather Patterns: Increased frequency of storms in Northern Europe can disrupt ferry schedules, impacting punctuality and potentially increasing fuel consumption due to route adjustments.
- Sea Level Rise: Long-term sea level rise could necessitate investments in port infrastructure upgrades to ensure continued accessibility for DFDS vessels.
- Route Disruptions: Extreme weather events can force temporary closures of key shipping lanes, requiring DFDS to reroute services, adding to operational complexity and costs.
- Infrastructure Resilience: Ports used by DFDS may require enhancements to withstand more severe weather and rising sea levels, representing a potential capital expenditure.
DFDS is committed to reducing its environmental impact, targeting a 45% cut in CO2 emissions intensity by 2030 and net-zero by 2050 across operations. This involves significant investment in green technologies like biogas and retrofitting vessels with efficiency upgrades, with a focus on battery-electric and hybrid solutions for shorter routes.
The company is actively developing green shipping corridors in Northern Europe and the Baltic Sea, aiming to use fuels like green methanol and ammonia. Beyond carbon, DFDS is reducing food waste, with a 15% decrease reported in 2023, and minimizing single-use plastics.
DFDS navigates sensitive marine environments, adhering to strict regulations like the Ballast Water Management Convention to prevent invasive species, with an estimated 50% of the global fleet expected to adopt treatment systems by the end of 2024.
The company must also adapt to climate change impacts, such as more frequent extreme weather events in the North Sea, which can cause route disruptions and increased operational costs, as observed in 2023.
| Environmental Factor | DFDS Action/Impact | Data/Statistic |
|---|---|---|
| Decarbonization | Targeting 45% CO2 intensity reduction by 2030; Net-zero by 2050 | Aiming for net-zero operations by 2050. |
| Alternative Fuels | Developing green shipping corridors; exploring methanol and ammonia | Focus on green methanol and ammonia for emission cuts. |
| Waste Reduction | Reducing food waste and single-use plastics | 15% reduction in food waste in 2023. |
| Marine Ecosystems | Managing ballast water; preventing invasive species | Estimated 50% global fleet adoption of ballast water treatment by end of 2024. |
| Climate Change Adaptation | Adjusting operations for changing weather patterns | Increased operational costs due to weather disruptions in 2023. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our DFDS PESTLE Analysis is meticulously constructed using data from official government publications, reputable industry associations, and leading economic forecasting agencies. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting DFDS.