Daicel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Daicel Bundle
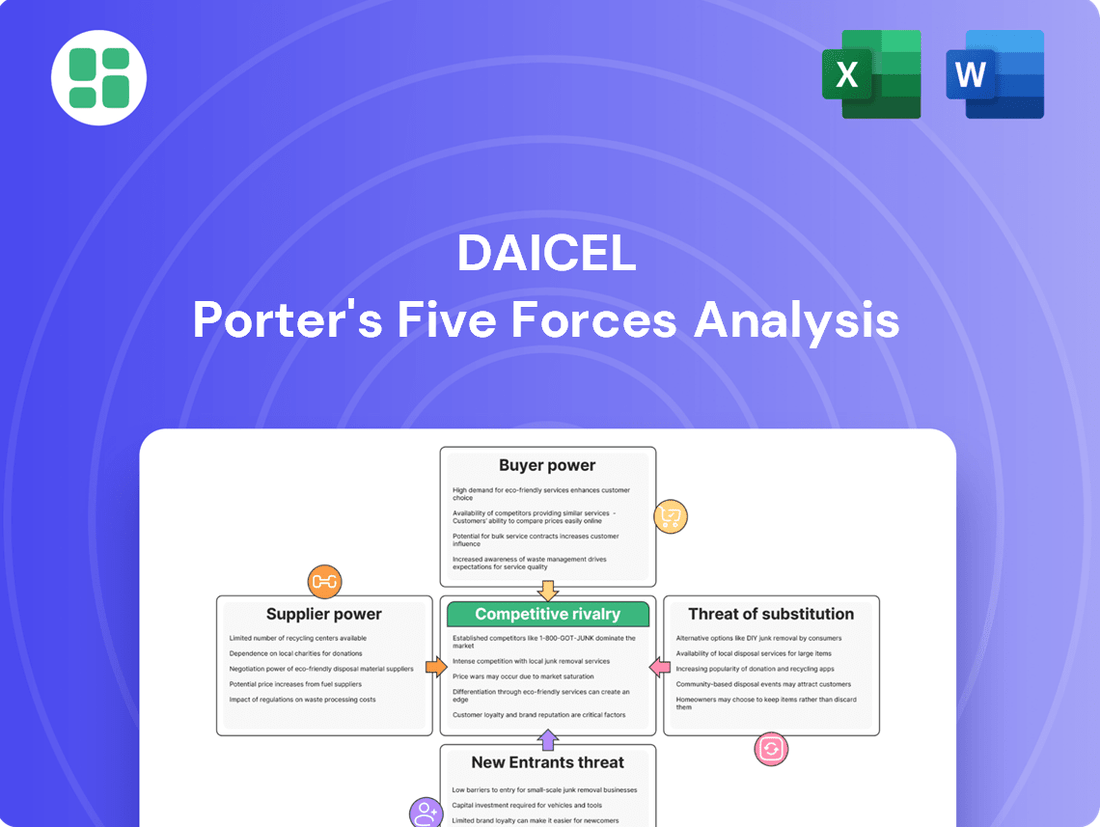
Daicel's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces, revealing the underlying pressures and opportunities within its industry. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any strategic decision-making.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Daicel’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Daicel's broad product range, encompassing cellulose derivatives, plastics, and organic chemicals, necessitates a wide array of raw materials. The concentration of suppliers for key inputs, such as specialized cellulose pulp or particular organic compounds, directly influences their leverage.
A situation where a limited number of major suppliers control essential raw materials grants them significant bargaining power. This could translate into increased raw material costs for Daicel, thereby affecting its operational expenditures and overall profitability. For instance, in 2023, the global market for specialty cellulose pulp saw price increases driven by supply chain disruptions, impacting companies reliant on this material.
Daicel's commitment to advanced materials and innovation means they likely rely on suppliers providing highly specialized or proprietary inputs. When these suppliers offer unique, high-quality, or patented components that are hard to find elsewhere, their bargaining power significantly increases. This can compel Daicel to nurture these supplier relationships and potentially accept higher costs for these critical differentiated materials, impacting Daicel's cost structure.
The cost and complexity Daicel faces when changing suppliers are key factors in how much power suppliers hold. If Daicel needs to invest heavily in new equipment or extensive testing to adopt a different supplier's materials, its existing suppliers gain leverage. This can make it difficult for Daicel to seek out more favorable terms, even if other options become available.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If Daicel's raw material suppliers possess the capability or motivation to move into producing intermediate or finished chemical products that Daicel currently makes, this presents a substantial threat. Such a development would transform suppliers into direct rivals, potentially destabilizing Daicel's supply chain and its standing in the market.
This threat is particularly relevant as suppliers could leverage their existing knowledge of raw material properties and production inputs to compete. For instance, if a key supplier to Daicel in the specialty chemicals sector, such as one providing high-purity solvents, were to backward integrate into Daicel's product lines, it could significantly alter the competitive landscape.
- Supplier Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers entering Daicel's product markets directly challenges its competitive position.
- Market Disruption Potential: Suppliers becoming competitors can disrupt established supply chains and pricing structures.
- Mitigating Factors: The highly specialized nature of Daicel's chemical synthesis and purification processes may act as a barrier to entry for many suppliers, limiting this threat.
- Industry Example: In 2024, the specialty chemicals industry saw some raw material providers exploring downstream integration, though significant capital investment and technical expertise remain hurdles for widespread adoption against established players like Daicel.
Importance of Daicel to Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers in Daicel's industry is influenced by how crucial Daicel is as a customer. If Daicel accounts for a substantial percentage of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier is more likely to offer competitive pricing and prioritize Daicel's needs. This is particularly true for specialized chemical inputs where supplier options might be limited.
Conversely, if Daicel represents a minor portion of a supplier's business, the supplier has less motivation to offer concessions. For instance, if a supplier's primary clients are much larger entities, Daicel's purchasing volume might not be enough to sway their negotiation stance significantly. This dynamic shifts the leverage towards the supplier.
- Daicel's dependence on key suppliers for specialized chemicals can increase supplier bargaining power.
- If Daicel constitutes a small fraction of a supplier's revenue, suppliers have less incentive to offer favorable terms.
- Conversely, if Daicel is a major customer, it can negotiate better pricing and service.
Daicel's reliance on a concentrated supplier base for critical inputs, such as specialty cellulose pulp, grants these suppliers significant leverage. This concentration was evident in 2023 with price hikes in specialty cellulose pulp due to supply chain issues, directly impacting raw material costs for companies like Daicel. The bargaining power of these suppliers is further amplified when Daicel faces high switching costs, requiring substantial investment in new equipment or testing to change suppliers, thus limiting Daicel's ability to negotiate favorable terms.
| Factor | Impact on Daicel | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier leverage | Price increases in specialty cellulose pulp in 2023 due to supply chain disruptions. |
| Switching Costs | Limits Daicel's negotiation power | High capital investment and testing required for new material adoption. |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Potential competitive threat | Specialty chemical suppliers exploring downstream integration in 2024, though hurdles remain. |
| Customer Importance | Influences negotiation leverage | Daicel's significance as a customer can lead to better pricing and service. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Daicel, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its industry.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of supplier power, buyer bargaining, and new entrant risks.
Customers Bargaining Power
Daicel's diverse customer base spans automotive, electronics, healthcare, and packaging industries, indicating a fragmented market. This broad reach generally dilutes the bargaining power of individual customers or specific industry segments. For instance, in 2023, Daicel's automotive sector sales represented a significant portion of its revenue, but no single automotive manufacturer accounted for more than 10% of total sales, limiting their leverage.
Daicel's customer price sensitivity is directly tied to how crucial its products are for their operations and the ease with which they can find substitutes. For instance, in sectors relying on Daicel's high-performance polymers for critical applications like automotive safety components, where unique properties are paramount, customers tend to exhibit lower price sensitivity. This is because the value derived from enhanced performance or safety outweighs minor price fluctuations.
However, when Daicel offers more standard chemical products that are easily replaceable by competitors, price becomes a much more significant factor in purchasing decisions. In 2024, the global chemical market saw increased price competition in certain segments, making it vital for Daicel to differentiate its offerings through innovation and value-added services rather than solely competing on price for commoditized goods.
The availability of substitute products significantly influences customer bargaining power. If customers can easily find alternative solutions that perform a similar function to Daicel's products, they are more likely to demand lower prices or switch suppliers. This is a key consideration for Daicel as it navigates competitive markets.
For instance, in the realm of specialty chemicals and advanced materials, the emergence of new, potentially more cost-effective substitute materials can directly empower customers. Daicel's focus on innovation is crucial, but the market for biodegradable plastics, a sector Daicel is involved in, exemplifies how alternative technologies can shift the balance of power. In 2024, the global biodegradable plastics market was valued at approximately $5.5 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth, suggesting increasing customer options and thus, enhanced bargaining power.
Customer's Threat of Backward Integration
The threat of backward integration by Daicel's customers can significantly amplify their bargaining power. If key clients possess the financial and technical wherewithal to manufacture Daicel's chemical components in-house, they gain leverage, potentially diminishing demand for Daicel's offerings, particularly for standardized, high-volume chemicals.
However, this threat is often mitigated by the substantial capital investment and intricate technical expertise required for chemical production. For instance, establishing a new chemical plant can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a barrier that many potential integrators find prohibitive. Daicel's focus on specialized, high-performance chemicals further complicates direct backward integration for many of its diverse customer base.
- Customer Capability: Daicel's customers range from automotive manufacturers to electronics firms, many of whom operate in capital-intensive industries themselves, possessing some degree of manufacturing expertise.
- Incentive to Integrate: For customers with very large order volumes of specific, less differentiated chemicals, the incentive to control supply and potentially reduce costs through backward integration can be considerable.
- Barriers to Integration: The chemical industry's need for specialized equipment, stringent safety protocols, and proprietary process knowledge creates significant hurdles for customers looking to self-manufacture.
- Daicel's Specialization: Daicel's strategic focus on advanced materials and high-value-added chemicals, rather than basic commodity chemicals, inherently limits the ease with which most customers can replicate their production processes.
Information Asymmetry and Product Differentiation
When Daicel's products are highly differentiated, patented, or require specialized technical support, customers face information asymmetry and fewer viable alternatives. This significantly reduces their bargaining power, as switching to a competitor becomes more complex and costly. For instance, Daicel's focus on advanced materials in sectors like automotive safety, where precise specifications are critical, limits customer options.
Daicel's strategic emphasis on developing proprietary technologies and advanced materials directly enhances its ability to differentiate its offerings. This makes it substantially harder for customers to conduct direct comparisons or find readily available substitutes, thereby diminishing their leverage. In 2024, Daicel continued to invest heavily in R&D for high-performance polymers and chiral separation technologies, areas where its intellectual property provides a strong competitive moat.
- Information Asymmetry: Daicel's proprietary technologies create knowledge gaps, making it difficult for customers to fully assess comparable offerings.
- Product Differentiation: Advanced materials and specialized applications reduce substitutability, limiting customer choices.
- Switching Costs: The technical expertise and integration required for Daicel's products increase the cost and complexity for customers to change suppliers.
- Reduced Bargaining Power: These factors collectively empower Daicel to command better terms and pricing from its customer base.
Daicel's diverse customer base, spread across various industries, generally limits the bargaining power of individual customers due to market fragmentation. For example, in 2023, while the automotive sector was a significant revenue driver, no single automotive client accounted for over 10% of Daicel's total sales, reducing their individual leverage.
Customer price sensitivity is lower when Daicel's products are critical for performance and difficult to substitute, such as high-performance polymers in automotive safety components. Conversely, for more commoditized chemicals, price becomes a key factor, especially with increased competition in the global chemical market in 2024.
The availability of substitutes, like those in the growing biodegradable plastics market (valued at $5.5 billion in 2024), can empower customers by offering alternatives. However, Daicel's focus on specialized, advanced materials and proprietary technologies, supported by significant R&D investment in 2024, creates information asymmetry and switching costs that diminish customer bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Daicel's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Low (fragmented base) | Daicel's broad customer reach dilutes individual power. |
| Price Sensitivity | Varies (low for critical, high for commoditized) | Differentiated products reduce sensitivity; competition in commoditized areas increases it. |
| Substitute Availability | High for commoditized, low for specialized | Innovation in advanced materials limits substitutes, but growing markets like biodegradable plastics offer alternatives. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Low (high capital/technical barriers) | Specialized production and high investment costs deter most customers. |
Full Version Awaits
Daicel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Daicel Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of industry competition and profitability. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises. You'll gain immediate access to this valuable strategic tool, ready for your business planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global chemical manufacturing industry is intensely competitive, with a wide array of companies, from massive multinational giants to focused niche players, all vying for dominance. Daicel, a significant player, faces this broad competitive spectrum, particularly in its core areas of cellulose derivatives and specialty chemicals, where it contends with other major global chemical manufacturers.
This sheer number and variety of competitors mean that market share is constantly under pressure. For instance, in the cellulose acetate market, a key segment for Daicel, companies like Eastman Chemical and Celanese are significant global competitors, each with substantial production capacities and established market presence. This diversity fuels intense rivalry as businesses compete on price, innovation, and product quality to capture customer demand.
The chemical industry's growth rate is a mixed bag, with overall moderate expansion but significant variation across its many segments. This unevenness directly impacts competitive rivalry. For instance, while the global chemical market was projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4.5% in 2024, certain mature segments might be experiencing much slower growth, perhaps in the low single digits.
When some chemical markets mature and their growth slows, companies often find themselves fighting harder for the same slice of the pie. This intensified competition can manifest as price wars or increased spending on sales and marketing. For example, if a particular commodity chemical market sees demand flatten, established players might engage in aggressive pricing strategies to maintain their market share, putting pressure on profitability.
Conversely, high-growth areas within the chemical sector, such as advanced materials, sustainable chemicals, or those catering to burgeoning industries like electric vehicles, present different competitive dynamics. Companies in these segments are more focused on innovation and capturing new market opportunities rather than simply defending existing positions, though competition can still be fierce among innovators.
Daicel strives to stand out through innovation, but the chemical industry often sees products become commodities, intensifying price wars. For instance, in 2024, the global specialty chemicals market, while growing, still faces pressure from established players and emerging low-cost producers, impacting pricing strategies.
High customer switching costs, like the rigorous testing and regulatory hurdles required for new material adoption in sectors such as automotive or electronics, can significantly reduce competitive rivalry. These barriers protect Daicel's market share by making it costly for customers to switch to alternatives, even if slightly cheaper.
However, if competitors successfully introduce materials with comparable quality and performance at a lower price point, the competitive pressure on Daicel intensifies. This scenario forces a greater focus on cost management and value proposition to retain customers.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity Utilization
The chemical sector, including companies like Daicel, faces intense competitive rivalry driven by substantial fixed costs. These costs stem from building and maintaining manufacturing facilities, investing in research and development, and adhering to stringent environmental and safety regulations. For instance, establishing a new chemical plant can easily cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars.
To offset these significant investments, chemical manufacturers are strongly motivated to run their plants at high capacity utilization rates. This strategy helps spread the fixed costs over a larger output, improving profitability. However, when demand falters, this pursuit of utilization can lead to oversupply in the market, forcing companies to engage in aggressive price competition to move inventory.
The issue of overcapacity is further exacerbated by global production trends. For example, significant capacity expansions in regions like China have introduced substantial volumes of chemicals into the global market. This influx, particularly during periods of economic slowdown, intensifies price pressures and makes it more challenging for established players like Daicel to maintain margins.
- High Fixed Costs: Chemical manufacturing requires massive upfront investment in plants, R&D, and compliance, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars per facility.
- Capacity Utilization Imperative: Companies like Daicel must operate at high capacity to spread these fixed costs, impacting their cost per unit.
- Oversupply Risk: High utilization, coupled with fluctuating demand, frequently results in market oversupply, leading to price wars.
- Global Capacity Impact: Overcapacity, especially from major production hubs like China, significantly intensifies global competitive rivalry and pricing pressures.
Strategic Objectives and Aggressiveness of Competitors
Daicel's competitors are driven by varied strategic objectives, with some prioritizing market share expansion, others focusing on robust profitability, and a select few aiming for technological leadership in niche segments. This diversity in goals directly fuels the intensity of competitive rivalry.
For instance, in the advanced materials sector, key players might be aggressively pursuing market share through price competition, while in specialty chemicals, the focus could be on differentiating through R&D and innovation to capture higher margins. Understanding these underlying objectives helps anticipate competitor actions and reactions.
The market landscape is further shaped by aggressive expansion strategies, including mergers and acquisitions. For example, in 2024, several significant consolidation activities were observed in the chemical industry, with companies like [Competitor A] acquiring [Competitor B] to broaden their product portfolios and geographical reach. Such moves can significantly alter market dynamics, forcing companies like Daicel to re-evaluate their competitive positioning and potentially engage in similar strategic maneuvers to maintain or enhance their market standing.
- Market Share Focus: Competitors like [Competitor C] have publicly stated their aim to increase their global market share in cellulose derivatives by 5% annually, often through aggressive pricing strategies.
- Profitability Drive: Companies such as [Competitor D] are emphasizing high-margin specialty products, aiming for a 15% operating profit margin in their performance chemicals division, influencing their investment in R&D over volume growth.
- Technological Leadership: In the chiral separation technology space, [Competitor E] has consistently led with a significant portion of its revenue reinvested into research and development, aiming to maintain a technological edge.
- Aggressive M&A Activity: The chemical sector saw approximately $50 billion in M&A deals in the first half of 2024, signaling a trend of consolidation that intensifies rivalry by creating larger, more formidable competitors.
Competitive rivalry within the chemical industry, impacting Daicel, is fierce due to numerous global players, including giants like Eastman Chemical and Celanese in cellulose acetate. This intense competition drives companies to vie for market share through price, innovation, and quality. For instance, while the overall chemical market grew moderately around 4.5% in 2024, mature segments faced slower growth, intensifying the fight for existing demand.
The industry's high fixed costs, often in the hundreds of millions for new plants, necessitate high capacity utilization. This pursuit of efficiency, coupled with global overcapacity, particularly from regions like China, frequently leads to oversupply and price wars, pressuring margins for companies like Daicel.
Competitors' varied strategic goals—market share, profitability, or technological leadership—further fuel rivalry. Aggressive mergers and acquisitions, with around $50 billion in chemical sector deals in the first half of 2024, also consolidate power, creating larger rivals and forcing strategic re-evaluation.
| Key Competitor Strategic Focus | Example Action/Goal | Impact on Rivalry |
| Market Share Expansion | [Competitor C] aiming for 5% annual growth in cellulose derivatives via pricing | Increased price pressure, reduced margins for others |
| Profitability Drive | [Competitor D] targeting 15% operating margin in performance chemicals | Focus on high-margin products, potentially less aggressive on volume |
| Technological Leadership | [Competitor E] reinvesting heavily in chiral separation R&D | Drives innovation race, creates differentiation opportunities |
| Consolidation | $50B in M&A deals (H1 2024) | Creates larger, stronger competitors, alters market landscape |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Daicel hinges on whether alternatives present a better performance-price balance. For example, in the plastics sector, the emergence of affordable, high-performing biodegradable options could challenge Daicel's traditional plastic products.
Customers are likely to shift to substitutes if they deliver equivalent or superior functionality at a reduced cost. In 2024, the global bioplastics market was valued at approximately $58.4 billion, and it is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong trend towards these alternatives.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives is shaped by growing environmental awareness and regulatory shifts. For instance, the automotive sector's push for sustainability in 2024 is driving significant adoption of bio-based and recycled materials over traditional chemicals, directly affecting demand for Daicel's less eco-friendly offerings.
Innovation in alternative materials poses a significant threat to Daicel. Rapid advancements in material science and biotechnology are consistently introducing new substitutes. For instance, ongoing research into nanocellulose-based composites and advanced bio-polymers presents high-performance, sustainable alternatives that could directly compete with Daicel's current product offerings.
Daicel must therefore prioritize continuous innovation to maintain its competitive edge. The company's ability to develop and adapt its product portfolio in response to these emerging material technologies will be crucial for its long-term success. Failure to do so could lead to market share erosion as customers opt for newer, potentially more cost-effective or environmentally friendly options.
Regulatory and Environmental Drivers for Substitution
Growing global regulations and heightened environmental consciousness are compelling industries to actively seek out more sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives to existing products. This increasing regulatory push can significantly accelerate the adoption of substitutes, even if these alternatives currently come with a higher price tag or a slightly different performance profile. For instance, by 2024, the European Union's ambitious Green Deal aims to significantly reduce plastic waste, potentially driving demand for biodegradable materials.
Daicel's strategic investments in areas like biodegradable plastics and other sustainable solutions are crucial for directly addressing and mitigating this escalating threat of substitution. These forward-thinking initiatives position the company to capitalize on the shift towards greener alternatives, thereby reducing its vulnerability to market changes driven by environmental concerns. Daicel's commitment to sustainability is not just a response; it's a proactive strategy to remain competitive.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by the increasing availability and improving performance of eco-friendly materials. Consider these points:
- Regulatory Push: Governments worldwide are implementing stricter environmental laws, such as bans on single-use plastics and mandates for recycled content, directly encouraging the use of substitutes.
- Consumer Demand: A growing segment of consumers actively prefers products with a lower environmental impact, creating market pull for alternative materials.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in material science are continuously yielding new, high-performing substitutes that can rival or even surpass traditional materials in certain applications.
- Cost Competitiveness: While initially more expensive, the long-term cost-benefit analysis of sustainable substitutes, including reduced waste disposal fees and potential tax incentives, is becoming increasingly favorable.
Switching Costs for Customers to Adopt Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Daicel is significantly influenced by the switching costs customers face when moving to alternative materials. If adopting a substitute requires substantial investment in redesign, re-certification processes, or new capital equipment, customers are less likely to switch, thereby reducing the threat. For instance, in industries with stringent regulatory approvals, like automotive or aerospace, the cost and time associated with validating a new material can be a major deterrent.
Conversely, if new substitutes emerge that are easy to integrate, offering comparable or superior performance at a lower cost, the threat of substitution intensifies. In 2024, advancements in material science are continuously yielding 'drop-in' replacements that minimize the need for extensive re-engineering. For example, the development of bio-based polymers that directly replace petrochemical plastics without significant process changes presents a growing challenge.
- High Switching Costs: Industries requiring extensive re-tooling or regulatory re-approval, such as pharmaceuticals or specialized electronics, present high switching costs, thus mitigating the threat of substitutes for Daicel's products.
- Low Switching Costs: In contrast, commodity markets or sectors with flexible manufacturing processes, where new materials can be integrated with minimal disruption, face a higher threat from substitutes.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in material science, leading to 'plug-and-play' alternatives, can rapidly decrease switching costs and escalate the threat of substitution for established products.
- Customer Benefits vs. Costs: The perceived benefits of a substitute, such as cost savings, improved performance, or enhanced sustainability, must outweigh the total switching costs for a customer to make the change.
The threat of substitutes for Daicel is significant, driven by increasing customer demand for sustainable and cost-effective alternatives. For instance, the global bioplastics market, valued at approximately $58.4 billion in 2024, is experiencing robust growth, directly impacting traditional plastic markets.
Industries with stringent regulatory requirements, such as automotive, face high switching costs, which can deter the adoption of substitutes. However, ongoing innovations in material science are creating 'drop-in' replacements that minimize these barriers. For example, bio-based polymers that can directly substitute petrochemical plastics without major process changes are becoming more prevalent.
Daicel's strategic investments in sustainable solutions are vital to counter this threat. The company's ability to innovate and adapt its product portfolio to incorporate these emerging, often more environmentally friendly, alternatives will be key to maintaining market share and competitiveness in the evolving landscape.
| Factor | Impact on Daicel | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Bioplastics Market Growth | Increased competition for Daicel's plastic products | Valued at $58.4 billion, projected significant growth |
| Switching Costs (High) | Mitigates threat in regulated industries (e.g., pharma) | Extensive re-tooling and re-certification are deterrents |
| Switching Costs (Low) | Escalates threat in flexible manufacturing sectors | 'Plug-and-play' alternatives reduce integration barriers |
| Environmental Regulations | Drives demand for eco-friendly substitutes | EU Green Deal aims to reduce plastic waste |
Entrants Threaten
The chemical manufacturing sector, particularly for specialty chemicals and advanced materials, demands significant capital. Newcomers face substantial upfront costs for research and development, state-of-the-art production facilities, and robust distribution channels. For instance, building a new, compliant chemical plant can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, a figure that naturally discourages many potential entrants.
Daicel's existing, extensive infrastructure and well-established global supply chain and distribution networks represent a formidable barrier. Acquiring similar capabilities would require immense investment, making it exceedingly difficult for new players to compete effectively on scale and reach. This established operational footprint is a critical deterrent.
Established players like Daicel leverage significant economies of scale in production, procurement, and research and development. This allows them to achieve lower unit costs, making it difficult for new entrants to match their pricing without massive initial investment and production volume.
The chemical synthesis industry also benefits from an experience curve. Companies with years of operational history, like Daicel, have refined their processes, leading to greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This accumulated knowledge represents a substantial barrier for newcomers attempting to enter the market.
Daicel's significant investment in research and development, evidenced by its R&D expenditure of ¥27.8 billion in fiscal year 2024, underpins its proprietary product technology and patents. These intellectual property assets are a formidable barrier to new entrants, as they protect Daicel's unique chemical formulations and advanced material manufacturing processes. Without access to similar patented technologies, potential competitors face substantial hurdles in replicating Daicel's specialized product offerings, thereby limiting the threat of new entrants.
Access to Distribution Channels
New entrants face significant hurdles in securing access to established distribution channels for chemical products, particularly on a global scale. This is a complex and time-consuming endeavor, requiring substantial investment and relationship-building efforts.
Daicel, for instance, has cultivated strong relationships across diverse industries such as automotive, electronics, and healthcare. These established supply chains are not easily replicated, presenting a formidable barrier for newcomers aiming to penetrate these markets.
- Distribution Network Costs: Building a global chemical distribution network can cost millions, with logistics and warehousing being major components. For example, establishing a presence in key Asian markets alone could require upwards of $50 million in infrastructure and partnerships.
- Customer Relationships: Daicel's long-standing partnerships with major automotive manufacturers, for example, mean that new entrants must offer significantly superior products or pricing to even be considered, a difficult proposition in a competitive market.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the complex and varied regulatory landscapes for chemical distribution in different countries adds another layer of difficulty and expense for potential new entrants.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations significantly impact the threat of new entrants in the chemical industry. Stringent environmental, health, and safety standards, such as those mandated by the EPA and OSHA, necessitate substantial upfront investment in compliance technologies and processes. For instance, in 2024, companies operating in the specialty chemicals sector often face compliance costs that can represent 5-10% of their annual operating expenses, making it a formidable barrier for newcomers.
These regulatory hurdles increase the capital required to establish operations and the complexity of obtaining necessary permits, thereby deterring potential new competitors. Daicel's extensive experience and established infrastructure in navigating these complex regulatory landscapes, including adherence to REACH regulations in Europe and TSCA in the United States, provide a distinct competitive advantage. This deep understanding and proven track record reduce the perceived risk and operational challenges for Daicel compared to a new entrant.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants must invest heavily in meeting environmental and safety standards, which can be a significant deterrent.
- Permitting Complexity: Obtaining the necessary permits for chemical production is often a lengthy and intricate process, adding to the barrier.
- Daicel's Experience Advantage: Daicel's long-standing familiarity with global chemical regulations, including evolving standards in 2024, mitigates these challenges for the company.
- Market Access Barriers: Certain government policies may also include trade restrictions or local content requirements that favor established players.
The threat of new entrants for Daicel is significantly low due to substantial capital requirements, established infrastructure, and strong brand loyalty. High upfront costs for R&D and production facilities, estimated in the hundreds of millions of dollars for compliant chemical plants, act as a major deterrent. Daicel's existing global supply chain and distribution networks, which would cost immense investment to replicate, further solidify this barrier.
Economies of scale and experience curve benefits enjoyed by Daicel, coupled with its significant R&D investment of ¥27.8 billion in fiscal year 2024, create a competitive advantage through proprietary technology and patents. These factors make it exceptionally challenging for newcomers to match Daicel's cost-effectiveness and product offerings.
Regulatory hurdles and the complexity of navigating diverse global compliance standards, which can represent 5-10% of annual operating expenses for specialty chemical firms in 2024, also deter new entrants. Daicel's established expertise in managing these regulations, including REACH and TSCA, provides a distinct advantage.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Daicel's Advantage |
| Capital Requirements | High costs for R&D, production facilities, and distribution networks. | Significant deterrent; new plants can cost hundreds of millions. | Established infrastructure reduces per-unit costs. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower unit costs due to large-scale production and procurement. | New entrants struggle to match pricing without massive initial investment. | Efficient production processes and bulk purchasing power. |
| Proprietary Technology & Patents | Exclusive rights to chemical formulations and manufacturing processes. | Newcomers cannot easily replicate specialized product offerings. | ¥27.8 billion R&D spend in FY2024 fuels innovation and IP. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex environmental, health, and safety standards. | Adds substantial upfront costs and operational complexity. | Deep experience with global regulations (REACH, TSCA). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and regulatory filings. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough understanding of competitive dynamics.