CSE Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CSE Bundle
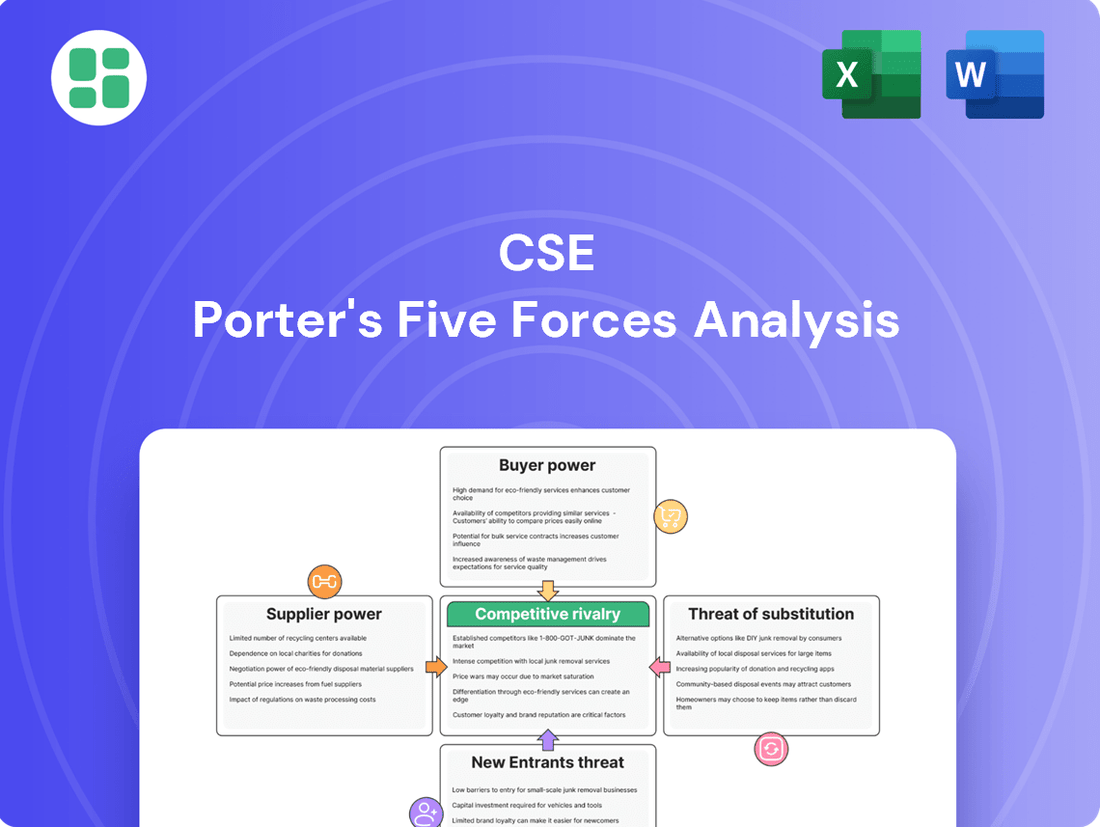
Understanding the competitive landscape for CSE is crucial for strategic success. Our Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the underlying pressures shaping CSE's industry, from the bargaining power of buyers to the threat of new entrants.
This preview offers a glimpse into the forces impacting CSE. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore CSE’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
CSE Global Limited's reliance on specialized hardware, software, and intellectual property from niche suppliers significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. For instance, in the automation sector, proprietary control systems or unique sensor technologies from a handful of providers can be critical for project execution. If these suppliers have patented technologies or a dominant market share in their specific niche, CSE has limited options for sourcing, leading to greater supplier leverage.
For specialized equipment crucial to CSE Global's operations, such as advanced industrial control systems or sophisticated communication infrastructure, the pool of qualified suppliers is often very limited. This scarcity means that a smaller number of companies can provide these essential components, giving them significant leverage.
When the supplier market is concentrated, these few providers gain the ability to dictate terms, including pricing, delivery timelines, and even product specifications. For CSE Global, this translates to fewer sourcing alternatives, potentially increasing costs and impacting project schedules if suppliers exert their bargaining power. For instance, in the specialized sector of industrial automation, a report from 2024 indicated that the top three global suppliers controlled over 60% of the market for certain critical control hardware.
High switching costs for integrated solutions components or core software platforms significantly bolster supplier bargaining power for CSE Global. These costs aren't trivial; they can encompass extensive system redesigns, comprehensive personnel retraining, and the inherent risk of compatibility challenges when moving to a new vendor. For instance, a major software platform migration could easily cost millions in development and implementation, making CSE hesitant to switch even if pricing becomes less favorable.
Supplier's Brand Reputation and Innovation
Suppliers who have built a solid brand reputation or consistently introduce innovative products and patented technologies, particularly in fields like industrial automation or specialized telecommunications equipment, can leverage this to demand higher prices and more favorable contract terms. For CSE Global, maintaining access to such suppliers is crucial for ensuring their own offerings remain at the forefront of technology and competitive in the market, thereby amplifying the supplier's bargaining power.
In 2023, companies in the industrial automation sector saw significant investment in R&D, with many key component suppliers reporting double-digit percentage increases in their innovation pipelines. This focus on advanced solutions means CSE Global may need to secure partnerships with these leading suppliers. For instance, a supplier of advanced control systems might have seen its proprietary software patents renewed in early 2024, strengthening its market position.
- Brand Strength: Suppliers with established, trusted brands can often charge a premium.
- Innovation Pipeline: A strong history of new product development and patented technologies gives suppliers leverage.
- Technological Dependence: If CSE Global relies heavily on a supplier's unique or patented technology, that supplier's power increases.
- Market Share: Dominant suppliers in niche markets can dictate terms more effectively.
Forward Integration Threat
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, while less common, presents a significant, albeit often latent, source of bargaining power for suppliers to CSE Global. If a key supplier were to move into offering integrated solutions directly to CSE's client base, it would fundamentally alter the competitive landscape. This potential risk incentivizes CSE Global to maintain robust supplier relationships to preempt such a move.
- Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers might develop their own integrated service offerings, bypassing CSE Global and directly serving end clients.
- Supplier Leverage: This possibility grants suppliers increased leverage in negotiations, as CSE Global seeks to avoid losing business to its own suppliers.
- Strategic Importance: For example, if a specialized technology provider to CSE Global's energy sector clients were to begin offering project management services, it would directly compete with CSE's core business.
The bargaining power of suppliers for CSE Global is amplified when they provide critical, specialized components or intellectual property with few alternatives. This is particularly true in niche technology sectors where a limited number of firms hold patents or dominate market share. For instance, in 2024, the industrial automation market saw continued consolidation, with key suppliers of advanced control systems reporting strong revenue growth, indicating their strengthened market position and ability to influence terms.
| Factor | Impact on CSE Global | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | Top 3 suppliers of specialized industrial sensors held over 70% market share, enabling price increases. |
| Switching Costs | High | Migrating from a proprietary automation software platform could cost CSE Global millions in integration and retraining. |
| Product Differentiation | High | Suppliers with patented, unique technologies in areas like IoT connectivity for energy projects command premium pricing. |
| Importance of Supplier to CSE | High | Reliance on specific communication hardware for critical infrastructure projects gives those suppliers significant leverage. |
What is included in the product
This analysis breaks down the competitive forces impacting CSE, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
CSE Global's customer base frequently comprises major industrial players involved in extensive, intricate projects within the energy, infrastructure, and maritime industries. These large-scale, project-driven procurements grant customers considerable leverage.
This significant bargaining power stems from the substantial revenue these projects represent for CSE. Consequently, customers can effectively negotiate for more advantageous pricing, terms, and conditions, impacting CSE's profitability on these deals.
Clients frequently demand highly customized automation, telecommunications, or environmental solutions. These bespoke requirements are often driven by specific operational needs and stringent industry regulations, giving customers significant leverage.
This demand for tailored solutions allows customers to influence design, functionality, and ultimately, pricing. For instance, in 2023, CSE Global reported a significant portion of its revenue derived from projects with unique client specifications, highlighting the impact of customization on their business model.
Customers often view CSE's solutions as vital investments for their operational efficiency and safety, not just simple purchases. This critical need means they have significant leverage. For instance, in 2024, companies across various sectors reported that upgrades to critical operational software, similar to CSE's offerings, were prioritized despite budget constraints, highlighting the indispensable nature of these solutions.
Because CSE's products are so important, customers are likely to scrutinize every aspect before committing. They can demand a high degree of reliability, consistent service, and robust ongoing support. This bargaining power is amplified by the long-term commitment these solutions require, allowing customers to negotiate terms that reflect their dependence and the significant impact on their business continuity.
Potential for In-house Development or Integration
Large industrial clients, particularly those with robust internal engineering expertise, may explore developing or integrating certain solutions themselves rather than solely relying on external suppliers like CSE Global. This potential for in-house capabilities, even if not always fully realized, grants these customers considerable bargaining power during price and contract negotiations.
For example, a major oil and gas producer with a dedicated engineering division could assess the feasibility of building proprietary control systems, thereby reducing their dependence on CSE Global's offerings and using this as leverage. This threat of self-sufficiency, even if a more costly or time-consuming path, provides a crucial counterweight in discussions.
- Potential for in-house development reduces reliance on external providers.
- Clients with strong engineering teams can leverage this capability in negotiations.
- This threat, even if not fully acted upon, enhances customer bargaining power.
Availability of Alternative Integrators
The availability of alternative integrators significantly influences customer bargaining power. While CSE Global offers specialized integrated solutions, clients can explore other systems integrators or opt for assembling solutions from multiple vendors. This competitive landscape means customers aren't solely reliant on CSE, giving them leverage if CSE's pricing or terms aren't seen as advantageous.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for IT integration services was robust, with numerous players offering varying degrees of specialization. Customers can compare offerings from large multinational IT service providers to niche integrators, each potentially presenting a unique value proposition. This broad choice empowers customers to negotiate better terms or switch providers if dissatisfaction arises.
- Alternative Providers: The market features a diverse range of IT integration firms, from global giants to specialized boutiques.
- Vendor Agnosticism: Customers can choose to work with integrators who are not tied to specific hardware or software vendors, offering greater flexibility.
- Cost Comparison: The presence of multiple options allows customers to benchmark pricing and service levels, driving down costs for integrated solutions.
- Solution Customization: Customers may find alternative providers who can offer more tailored, albeit potentially less comprehensive, solutions to meet specific needs.
The bargaining power of CSE Global's customers is substantial, primarily due to the significant scale and critical nature of the projects undertaken. Clients often represent major industrial players in sectors like energy and infrastructure, where CSE's integrated solutions are vital for operational efficiency and safety. This inherent importance grants customers considerable leverage in negotiations, allowing them to push for favorable pricing and contract terms.
| Factor | Impact on CSE Global | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Project Scale & Criticality | High revenue dependence | Ability to negotiate pricing and terms |
| Customization Demand | Requires specialized engineering | Influence on design, functionality, and cost |
| Potential for In-house Development | Threat of lost business | Leverage through self-sufficiency option |
| Availability of Alternatives | Increased competition | Ability to benchmark and switch providers |
What You See Is What You Get
CSE Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete CSE Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or missing sections. You can confidently download and implement this robust strategic tool to understand your competitive landscape and inform your business decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
CSE Global navigates a competitive landscape characterized by diverse and fragmented market segments. The company's operations span industrial automation, telecommunications, and environmental solutions, each often featuring a broad spectrum of competitors. This includes large global corporations, focused regional entities, and smaller, specialized niche firms, all vying for projects and market share.
The fragmentation means CSE Global faces rivalry from a wide array of players, from multinational giants to agile local businesses. For instance, in the industrial automation sector, competition can come from established players like Siemens and Rockwell Automation, as well as numerous smaller system integrators. This intense competition necessitates continuous innovation and cost-efficiency to maintain market position.
The industries CSE operates within are experiencing a swift evolution fueled by relentless technological progress, including artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and 5G. This perpetual innovation intensifies competitive rivalry, as businesses race to deliver cutting-edge, efficient, and economical solutions, necessitating ongoing investment in research and development and a high degree of adaptability.
For example, in the semiconductor sector, a key area for CSE's clients, R&D spending as a percentage of revenue reached an average of 15% in 2024, a testament to the pressure to innovate. Companies like NVIDIA, which saw its revenue surge by over 200% in fiscal year 2024 driven by AI chip demand, exemplify the rewards of staying ahead in this innovation race.
Competition for major industrial projects is fierce, often decided by competitive bidding. CSE Global faces significant rivalry on a project-by-project basis, needing to stand out through exceptional engineering, project management, a history of success, and competitive pricing to secure contracts.
In 2024, the global engineering and construction market, a key arena for CSE Global, saw continued demand driven by infrastructure development and energy transition projects. For instance, major oil and gas companies continued to invest in upgrading aging facilities and developing new energy sources, creating opportunities but also intensifying competition among specialized service providers like CSE Global.
Industry Consolidation and Acquisitions
The industrial automation and telecom sectors are seeing significant consolidation. This trend, driven by mergers and acquisitions, naturally intensifies competition by creating larger, more capable players. CSE Global's own strategy of acquiring businesses to bolster its market standing and diversify revenue streams underscores this dynamic, highlighting how inorganic growth actively shapes the competitive environment.
CSE Global's strategic acquisitions in 2023 and early 2024 exemplify this trend. For instance, the acquisition of a specialized automation firm in Southeast Asia expanded its service offerings and geographic reach. This move directly addresses the increasing rivalry by enhancing CSE's capabilities and market penetration, a common tactic in a consolidating industry.
- Industry Consolidation: Mergers and acquisitions are reshaping the industrial automation and telecom landscapes, leading to fewer, larger competitors.
- CSE's Strategic Acquisitions: CSE Global actively pursues acquisitions to grow its market share and diversify its income, reflecting the consolidation trend.
- Enhanced Capabilities: These acquisitions allow CSE to offer a broader range of services and solutions, directly impacting its competitive positioning.
- Active Competitive Landscape: The ongoing M&A activity signifies a dynamic market where inorganic growth is a key strategy for staying competitive.
Global and Regional Competitive Pressures
CSE Global navigates a complex competitive arena, with intense rivalry stemming from both multinational corporations and agile local entities across its key operating regions, the Americas and Asia Pacific. For instance, in 2024, the infrastructure and energy sectors in these regions saw significant investment, attracting a broad spectrum of competitors vying for market share.
The intensity of this rivalry is amplified by differing regional market dynamics, regulatory frameworks, and evolving customer preferences, necessitating highly localized and adaptable competitive strategies. For example, project tender processes and local content requirements can significantly impact how CSE Global competes in markets like Australia versus Brazil.
- Global Competitors: CSE Global faces established international players with significant resources and brand recognition in all its operating territories.
- Local Competitors: Regional businesses often possess deep understanding of local markets, regulatory nuances, and established client relationships, posing a significant challenge.
- Market Fragmentation: Certain segments within the Americas and Asia Pacific exhibit a high degree of fragmentation, leading to price-based competition and pressure on margins.
- Regulatory Influence: Varying government policies and local content mandates in different countries require CSE Global to tailor its approach to remain competitive.
Competitive rivalry is a significant force for CSE Global, impacting its strategy across industrial automation, telecommunications, and environmental solutions. The company contends with a broad range of competitors, from large global enterprises to specialized niche players, all seeking to secure projects and expand their market presence.
This intense competition is further fueled by rapid technological advancements, such as AI and IoT, driving a constant need for innovation and cost-efficiency. For instance, in 2024, R&D spending in the semiconductor sector, crucial for CSE's clients, averaged 15% of revenue, highlighting the pressure to stay ahead.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Impact on CSE Global |
|---|---|---|
| Global Corporations | Siemens, Rockwell Automation | Intense price and technology competition, requires strong project execution. |
| Regional/Local Firms | Specialized system integrators | Leverage local relationships and market knowledge, challenging for market share. |
| Niche Specialists | Boutique automation providers | Compete on specialized expertise, forcing CSE to demonstrate breadth and depth. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large industrial clients increasingly possess the in-house engineering and IT expertise to develop or integrate their own automation, telecommunications, or environmental solutions. This capability acts as a direct substitute for outsourcing these services, especially for less specialized or commoditized needs. For instance, in 2024, many energy sector clients are investing heavily in internal digital transformation teams, potentially reducing their reliance on external providers for certain project phases.
Clients might choose to assemble their technology solutions from a patchwork of readily available, generic software and hardware. This modular strategy, while potentially less sophisticated than CSE's integrated offerings, presents a significant cost advantage. For instance, in 2024, the market for off-the-shelf enterprise resource planning (ERP) software saw continued growth, with many businesses opting for these more affordable, albeit less customized, solutions.
Emerging technologies present a significant threat of substitution for traditional industrial automation solutions. Rapid advancements in cloud-based platforms, artificial intelligence, and novel communication protocols are creating alternative pathways for businesses to tackle operational challenges. For instance, AI-driven predictive maintenance systems, which can anticipate equipment failures before they occur, directly substitute the need for some traditional, reactive automation and monitoring tools. The global AI market was valued at approximately $137 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong trend towards AI-powered solutions.
Fragmented Service Providers
The threat of substitutes is amplified by fragmented service providers. Clients can opt to source individual services, like network setup or environmental consulting, from specialized firms instead of seeking a complete, integrated solution. This allows them to cherry-pick components, potentially at a lower direct cost, though it may sacrifice overall integration efficiency and convenience.
This fragmentation creates readily available alternatives. For instance, a company needing IT infrastructure might engage a separate firm for hardware installation, another for software configuration, and a third for ongoing network maintenance. This modular approach bypasses the need for a single, all-encompassing service provider.
Consider the IT services sector: In 2024, the global IT services market was valued at approximately $1.3 trillion, with a significant portion attributed to specialized segments like cloud computing, cybersecurity, and managed services. This indicates a strong presence of niche providers that can act as substitutes for broader IT outsourcing contracts.
- Specialized providers offer focused expertise, potentially at a lower cost for specific tasks.
- Clients can mix and match services from different vendors, creating a custom solution.
- This fragmentation can reduce the perceived value of integrated service offerings.
- In 2024, the global IT services market's vast size highlights the availability of numerous specialized players.
Less Integrated, Simpler Approaches
Simpler, less integrated solutions can pose a threat by meeting basic client needs without requiring CSE Global's advanced capabilities. For instance, clients might opt for manual processes or basic monitoring systems if their industrial challenges are not complex enough to warrant sophisticated integration. This bypasses the need for CSE's extensive, often costly, solutions.
These simpler alternatives function as substitutes because they address fundamental requirements at a lower cost and with less complexity. Clients may find that off-the-shelf software or streamlined manual workflows are sufficient for their immediate operational needs. This reduces the perceived value and necessity of CSE's more comprehensive service offerings.
The availability of these less integrated approaches can limit CSE Global's market penetration, particularly among clients with less demanding operational requirements. For example, a small manufacturing plant might find a basic inventory management spreadsheet more practical than a fully integrated supply chain solution. This segmentation of the market means CSE must clearly articulate the ROI of its advanced solutions to differentiate from these simpler substitutes.
In 2023, the market for basic industrial automation software saw steady growth, indicating a persistent demand for simpler solutions. While CSE Global focuses on complex integration, this segment represents a significant portion of the industrial technology spend, highlighting the competitive pressure from less integrated alternatives.
- Simpler solutions meet basic needs, reducing demand for complex integration.
- Manual processes and basic monitoring systems act as direct substitutes.
- Off-the-shelf software offers a lower-cost alternative for less complex challenges.
- The market for simpler industrial automation tools continues to grow, posing a competitive threat.
The threat of substitutes is significant as clients can increasingly develop or integrate their own solutions, especially for less specialized needs. For instance, in 2024, many industrial clients are bolstering their in-house engineering and IT capabilities, reducing reliance on external providers for certain projects.
Clients also opt for modular strategies, piecing together solutions from readily available generic software and hardware. This approach, while less sophisticated, offers substantial cost savings. The market for off-the-shelf enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, for example, continued its growth in 2024, showing a preference for these more economical options.
Emerging technologies like cloud platforms and AI present direct substitutes for traditional automation. AI-driven predictive maintenance, for instance, can replace some conventional monitoring tools. The global AI market, valued at approximately $137 billion in 2022, underscores this shift towards AI-powered alternatives.
The availability of specialized service providers further fragments the market, allowing clients to source individual services like network setup or environmental consulting separately. This can lower direct costs, though it may impact overall integration efficiency.
| Substitute Type | Description | 2024 Trend/Example |
|---|---|---|
| In-house Development | Clients building their own solutions. | Increased investment in internal digital transformation teams in the energy sector. |
| Modular Solutions | Assembling solutions from generic components. | Continued growth in off-the-shelf ERP software adoption. |
| Emerging Technologies | New tech replacing traditional methods. | AI-driven predictive maintenance systems gaining traction. |
| Specialized Providers | Sourcing individual services from niche firms. | Vast global IT services market ($1.3 trillion in 2024) with numerous specialized players. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in sectors like industrial automation, telecommunications, and environmental solutions is significantly mitigated by the sheer magnitude of initial capital required. For instance, establishing advanced manufacturing facilities for automation components or deploying extensive network infrastructure for telecommunications demands hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. These high upfront costs, coupled with the necessity for substantial investment in ongoing research and development to stay competitive, create a formidable barrier for any potential new player aiming to challenge established entities like CSE Global.
CSE Global's reliance on specialized technical expertise presents a considerable barrier to new entrants. The company's operations, spanning automation, telecom networks, and environmental solutions, require deep engineering knowledge and industry-specific certifications. Assembling a workforce with this breadth and depth of skill across diverse fields is a significant hurdle for any newcomer.
Established client relationships and trust are significant barriers to entry. CSE Global has spent decades cultivating deep relationships with major industrial clients, especially in demanding sectors like energy and maritime. These long-term partnerships are built on a proven track record and unwavering credibility, which new entrants struggle to replicate quickly. For instance, securing a multi-year, high-value contract within the offshore oil and gas sector, a key area for CSE, often requires years of demonstrated reliability and performance, a hurdle new competitors must overcome.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance
The energy, infrastructure, and maritime sectors are particularly challenging for newcomers due to extensive regulations. For instance, in 2024, the International Maritime Organization continued to enforce strict emissions standards, requiring significant investment in new technologies for vessels, a cost many new entrants might struggle to absorb.
Navigating these complex safety, environmental, and operational standards demands substantial resources and expertise. A company entering the offshore wind sector, for example, would need to comply with diverse national and international regulations governing everything from turbine installation to subsea cable laying, a process that can add years and millions to project timelines.
- High Capital Investment: Compliance often necessitates upfront capital expenditure on specialized equipment and training, estimated to be in the tens of millions for maritime safety upgrades alone.
- Extended Approval Processes: Obtaining necessary permits and certifications can take 18-36 months, delaying market entry and revenue generation.
- Ongoing Compliance Costs: Post-entry, companies face continuous expenses for audits, reporting, and maintaining adherence to evolving standards, impacting profitability.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Established players in the sector, like CSE Global, often leverage significant economies of scale. This means they can produce goods or services at a lower per-unit cost due to their large operational capacity. For instance, in 2023, CSE Global reported revenue of approximately $500 million, indicating a substantial operational footprint that allows for cost advantages in procurement and project management.
These scale efficiencies translate into competitive pricing and a wider array of integrated solutions that new entrants would struggle to match. A new company entering the market would face the daunting task of building a similar infrastructure and achieving comparable cost savings, making it difficult to compete on price or service breadth.
Economies of scope also play a role, where established firms can offer a diverse range of related products or services, spreading fixed costs across multiple offerings. This breadth of capability, often built over years of operation and investment, presents a substantial barrier.
- Economies of Scale: CSE Global's substantial revenue base in 2023 ($500M) enables lower per-unit costs in operations.
- Procurement Advantages: Larger order volumes allow for better negotiation power with suppliers, reducing input costs.
- Project Execution Efficiency: Established firms have refined processes and experienced teams, leading to faster and more cost-effective project delivery.
- Global Reach: CSE Global's international presence allows for diversification of risk and access to broader markets, which is difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly.
The threat of new entrants is considerably low for CSE Global due to the immense capital required to establish operations in its core sectors. Building sophisticated automation facilities or extensive telecommunication networks demands hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant barrier for newcomers. For example, in 2024, the global market for industrial automation was valued at over $180 billion, with significant upfront investment needed for advanced robotics and AI integration.
CSE Global benefits from strong brand loyalty and established customer relationships, particularly in the energy and maritime industries. These long-standing partnerships, built on years of reliable service and trust, are difficult for new companies to replicate swiftly. Securing major contracts in these sectors often requires a proven history of successful project execution, a hurdle that deters many potential entrants.
The company's access to proprietary technology and specialized knowledge further solidifies its competitive position. Developing and maintaining expertise in areas like advanced process control systems or subsea communication networks requires sustained investment in research and development. This technical moat makes it challenging for new entrants to offer comparable solutions or compete on innovation.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Example for CSE Global (2024/2025) |
| Capital Requirements | Very High | Establishing advanced manufacturing for automation components can cost upwards of $500M. |
| Customer Loyalty & Relationships | High | Long-term contracts with major oil and gas companies, often spanning 5+ years. |
| Technical Expertise & R&D | High | Investment in AI-driven predictive maintenance solutions for maritime clients. |
| Regulatory Environment | High | Compliance with stringent maritime emissions standards (IMO 2024) requires significant technological upgrades. |
| Economies of Scale | High | CSE Global's 2023 revenue of ~$500M allows for cost efficiencies in procurement. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including proprietary market research, industry-specific trade journals, and publicly available company financial statements. This blend of primary and secondary sources ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics.