Corebridge Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Corebridge Financial Bundle
Corebridge Financial navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry and the looming threat of substitutes. Understanding the power of buyers and the influence of suppliers is crucial for any strategic move within this sector.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Corebridge Financial’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of Corebridge Financial's suppliers is significantly shaped by supplier concentration and the specialized nature of their offerings. When a few vendors dominate the market for critical services, like advanced actuarial modeling software or proprietary data analytics platforms essential for managing a diverse insurance and retirement product portfolio, their leverage increases. This concentration means Corebridge might face limited alternatives, potentially leading to higher costs.
For example, if a specialized data provider offers unique insights crucial for risk assessment and pricing, and only a handful of companies possess this capability, Corebridge's ability to negotiate favorable terms is diminished. In 2023, the global market for insurance technology solutions, which includes actuarial software, was valued at approximately $10.8 billion, with specialized analytics being a key growth driver, indicating the importance of these niche providers.
Furthermore, the degree of specialization plays a vital role. If a supplier provides highly customized solutions that are deeply integrated into Corebridge's existing operational infrastructure, the cost and complexity of switching to an alternative vendor can be substantial. This creates a strong incentive for Corebridge to maintain good relationships with these specialized suppliers, potentially conceding some bargaining power in exchange for stability and continued access to essential, tailored services.
Corebridge Financial depends on reinsurers to manage significant risks from its insurance policies. The availability and cost of this reinsurance can fluctuate, impacting Corebridge's profitability and the types of products it can offer. For instance, in 2023, global reinsurer capital remained robust, but concerns over inflation and climate-related events continued to influence pricing, giving reinsurers leverage.
When reinsurance capacity tightens, perhaps due to increased claims from natural disasters or economic instability, reinsurers gain considerable bargaining power. This can lead to higher premiums for Corebridge, potentially squeezing its underwriting margins and forcing adjustments to its product pricing or availability. The global reinsurance market saw a significant increase in property catastrophe reinsurance rates in early 2024, reflecting these pressures.
Corebridge Financial's reliance on technology and digital platform providers is growing as the industry embraces digitization. These suppliers are crucial for operational efficiency, customer interaction, and data protection.
Providers of specialized AI, cloud services, and robust cybersecurity solutions wield considerable influence, particularly when their offerings are unique or widely adopted industry standards. For instance, the global cybersecurity market was valued at over $214 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, highlighting the essential nature of these services.
Corebridge's strategic imperative to innovate and improve customer experience through digital channels further amplifies the bargaining power of these technology suppliers. Companies that can offer cutting-edge solutions that differentiate Corebridge in the market are in a strong negotiating position.
Investment Management and Advisory Services
The bargaining power of suppliers in Corebridge Financial's investment management and advisory services segment is influenced by the strategic importance of external partners. When Corebridge utilizes specialized external managers, their leverage increases if their investment strategies are unique or consistently outperform benchmarks. For instance, a manager with a proven track record in a niche market can command higher fees or more favorable terms, impacting Corebridge's profitability.
The ability of these external partners to distribute Corebridge's products also plays a significant role. A financial advisor or firm with an extensive and loyal client base can exert considerable influence, especially if Corebridge relies on them for reaching specific customer segments. This reliance can lead to negotiations over commission structures or product placement, directly affecting Corebridge's revenue streams.
Strategic partnerships, such as the one with Blackstone, highlight the potential for suppliers to hold significant bargaining power. These collaborations are often long-term and involve substantial assets under management, giving the partner considerable leverage in shaping the terms of the relationship. The success of such alliances is contingent on mutual benefit, but the supplier's unique capabilities or market position can tilt the scales in their favor during negotiations.
- Unique Investment Strategies: External managers with proprietary strategies or exceptional historical performance can increase their bargaining power.
- Distribution Network Breadth: Partners with wide-reaching client networks are more influential in product distribution.
- Asset Under Management (AUM) Influence: The scale of assets managed by an external partner can amplify their negotiating leverage.
- Strategic Partnership Terms: Long-term agreements with key partners, like Blackstone, often involve terms that reflect the supplier's critical role and capabilities.
Human Capital and Expert Talent
The financial and insurance sectors, including companies like Corebridge Financial, are deeply dependent on specialized human capital. This includes actuaries who assess risk, investment professionals managing assets, data scientists analyzing market trends, and compliance experts navigating regulations. A significant shortage of these highly skilled individuals can tip the scales, giving them more leverage. This increased bargaining power often translates into higher salary expectations and increased recruitment expenses for Corebridge, making talent acquisition and retention a crucial aspect of managing supplier-side pressures.
The demand for specialized financial talent remains robust. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a 10% growth for financial analysts between 2022 and 2032, faster than the average for all occupations. This continued demand underscores the importance of human capital as a key supplier to Corebridge.
- Actuaries: Essential for risk assessment and pricing, their specialized knowledge is in high demand.
- Investment Professionals: Crucial for managing portfolios and generating returns, expertise in specific markets is highly valued.
- Data Scientists: Increasingly vital for predictive analytics and identifying market opportunities, their skills are a significant asset.
- Compliance Experts: Navigating complex regulatory landscapes requires specialized knowledge, making these professionals indispensable.
Corebridge Financial's suppliers, particularly those providing specialized technology and data analytics, hold significant bargaining power due to the critical nature and limited alternatives for their services. The increasing reliance on advanced actuarial software and proprietary data platforms means Corebridge faces potential cost increases when few vendors dominate these niche markets. For example, the global insurance technology market, including actuarial software, was valued at approximately $10.8 billion in 2023, with specialized analytics being a key growth area.
Reinsurers also exert considerable influence, especially when reinsurance capacity tightens due to events like natural disasters or economic instability. This can lead to higher premiums for Corebridge, impacting its underwriting margins. In early 2024, property catastrophe reinsurance rates saw a notable increase globally, reflecting these pressures.
Furthermore, the scarcity of highly skilled financial professionals, such as actuaries and data scientists, grants them increased bargaining power. This translates to higher compensation demands and recruitment costs for Corebridge, as evidenced by the projected 10% growth for financial analysts in the U.S. from 2022 to 2032.
| Supplier Type | Key Services | Bargaining Power Factors | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology & Data Providers | Actuarial Software, Data Analytics, Cloud Services, Cybersecurity | Supplier Concentration, Specialization, Integration Costs | Global Insurtech Market: ~$10.8 Billion (2023) |
| Reinsurers | Risk Transfer for Insurance Policies | Reinsurance Capacity, Catastrophe Events, Economic Instability | Increased Property Catastrophe Reinsurance Rates (Early 2024) |
| Human Capital (Skilled Professionals) | Actuarial Services, Investment Management, Data Science | Talent Shortage, Demand for Specialized Skills | Financial Analyst Job Growth Projection: 10% (2022-2032) |
What is included in the product
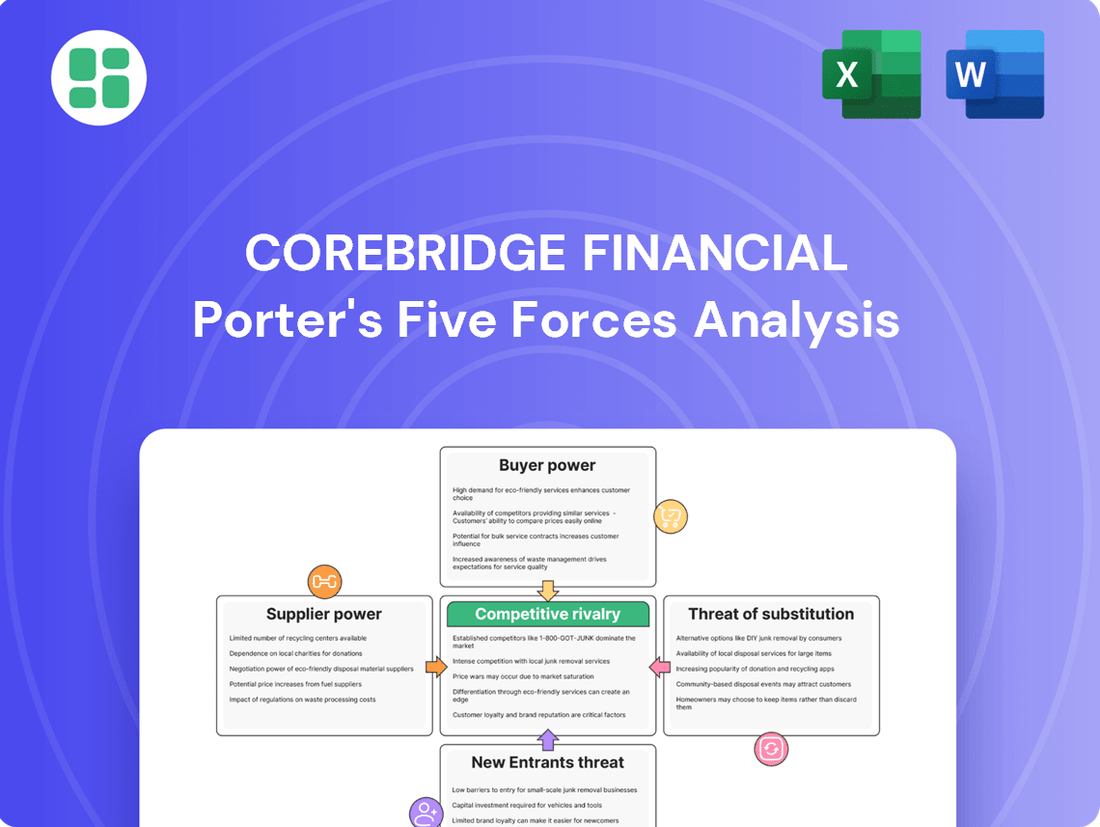
Analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability potential for Corebridge Financial by examining threats from new entrants, buyer and supplier power, and the availability of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Corebridge Financial's Porter's Five Forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers of Corebridge Financial, from individuals to large institutions, are increasingly well-informed. Digital platforms and financial advisors provide easy access to details on various financial products and what competitors offer. This transparency means clients can readily compare features, benefits, and costs for products like annuities and life insurance.
This heightened awareness directly translates into greater bargaining power for customers. They are more likely to shop around and demand the best possible terms, putting pressure on Corebridge Financial to offer competitive pricing and superior value propositions. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer spent over 15 hours researching financial products online before making a decision, highlighting the impact of readily available information.
While Corebridge’s more complex offerings like long-term annuities might involve surrender charges, the ease with which customers can switch between simpler insurance or investment products significantly impacts their bargaining power. This low friction environment means clients can readily move to competitors offering superior rates or service.
For example, in the broader life insurance market, customer retention can be influenced by factors beyond contract terms. A 2024 report indicated that over 60% of consumers consider price as a primary driver when choosing financial products, highlighting Corebridge's need to remain competitive to mitigate this customer leverage.
Corebridge Financial's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by its institutional clients and financial professionals. The company serves large entities for group retirement plans, and its partnerships with independent marketing organizations and broker-dealers are extensive. These substantial relationships grant these customers and intermediaries considerable leverage.
These large-volume clients and key intermediaries can negotiate for more favorable terms, specialized product offerings, or enhanced compensation structures. For instance, a major institutional client could demand lower fees or customized plan features, directly impacting Corebridge's revenue and margins. Similarly, financial professionals, acting as gatekeepers to many individual investors, can influence product selection and pricing through their commission demands.
Availability of Diverse Distribution Channels
Corebridge Financial's diverse distribution channels significantly bolster customer bargaining power. With options like Corebridge Direct and a wide network of financial institution partnerships, customers have numerous avenues to explore and compare offerings. This accessibility means customers are not locked into a single provider, empowering them to seek out the best terms and prices.
The proliferation of these channels, from online platforms to traditional financial advisors, means customers can easily shop around. For instance, Corebridge's expansion into direct-to-consumer sales in 2024, aiming to capture a larger share of the digitally savvy market, directly contributes to this increased customer choice.
- Broad Reach: Corebridge's multi-channel approach ensures widespread product availability.
- Customer Choice: Multiple access points empower customers to compare and select the most favorable options.
- Reduced Switching Costs: The ease of accessing different channels lowers the barrier for customers to move between providers.
Evolving Customer Preferences and Digital Engagement
Customer preferences are shifting significantly, with a growing demand for personalized, digital-first financial solutions. This trend means customers expect intuitive online platforms and tailored advice, making it easier for them to switch to providers offering a superior digital experience.
In 2024, the digital engagement of financial services customers continued to climb. For instance, a significant portion of retail banking transactions in the US occurred through mobile apps, demonstrating this shift. Corebridge Financial must invest in its digital infrastructure and data analytics to deliver the personalized service customers now expect, thereby mitigating the increased bargaining power stemming from readily available digital alternatives.
- Evolving Preferences: Customers increasingly favor personalized, self-service, and digital financial solutions.
- Digital Expectations: Seamless online experiences and tailored advice are becoming standard expectations.
- Increased Bargaining Power: Customers can easily switch to competitors offering better digital tools or personalized services.
- Corebridge's Imperative: Continuous adaptation of offerings and digital capabilities is crucial for customer retention.
Customers of Corebridge Financial possess considerable bargaining power due to the increasing availability of information and the ease with which they can compare financial products. In 2024, the average consumer dedicated over 15 hours to researching financial products online, underscoring the impact of readily accessible data on their decision-making process. This transparency allows clients to readily assess features, benefits, and costs for various offerings, pressuring Corebridge to maintain competitive pricing and deliver superior value.
The company's extensive network of financial professionals and institutional clients further amplifies customer leverage. Large-volume clients and key intermediaries can negotiate for more favorable terms, specialized products, or enhanced compensation structures, directly influencing Corebridge's revenue and margins. For instance, a significant portion of consumers, over 60% in 2024, cited price as a primary factor in their financial product choices, highlighting the need for Corebridge to remain competitive.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Information Accessibility | High | Average consumer research time: 15+ hours |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Over 60% of consumers prioritize price |
| Institutional Client Leverage | High | Negotiation for lower fees/customized plans |
| Financial Professional Influence | High | Commission demands affecting product selection |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Corebridge Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Corebridge Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape, including threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the intensity of rivalry. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the industry's attractiveness and Corebridge's strategic positioning within it. No surprises, no placeholders, just the complete, professionally formatted analysis ready for your use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Corebridge Financial navigates a fiercely competitive U.S. market for retirement solutions and insurance. It contends with major players like Prudential Financial, MetLife, Principal Financial Group, and Lincoln National, all possessing substantial resources and established market presences. This intense rivalry necessitates continuous innovation in product offerings, competitive pricing strategies, and superior customer service to secure and grow market share.
While Corebridge Financial provides a broad range of annuities and life insurance, many of its fundamental offerings can be seen as similar to those of competitors in the insurance sector. This inherent similarity fuels a highly competitive environment.
To stand out, companies like Corebridge are compelled to invest significantly in differentiating their products. This often involves introducing unique features, enhanced guarantees, or advanced digital capabilities. For instance, Corebridge has recently launched its Registered Index Linked Annuity (RILA) and the Power Select AICO Index Annuity, aiming to capture market share through innovation.
The U.S. life insurance and retirement market is quite mature, meaning growth isn't typically explosive but rather linked to things like population changes and the overall economy. This maturity fuels intense competition as companies battle for the same customers, often leading to price wars and higher spending on advertising. For instance, some companies in the sector experienced slight revenue declines in 2023 as they navigated this competitive landscape.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The insurance sector, including companies like Corebridge Financial, operates with substantial fixed costs. These stem from the necessity of robust regulatory compliance, significant investments in technology infrastructure for data management and customer service, and the long-term nature of policy liabilities. For instance, in 2023, the insurance industry globally continued to grapple with the ongoing costs of digital transformation and cybersecurity measures, essential for maintaining customer trust and operational efficiency.
These high fixed costs create considerable exit barriers. Companies are often reluctant to divest or cease operations, even when facing profitability challenges, due to the difficulty in recouping these sunk costs. This situation perpetuates a highly competitive environment where existing players remain invested, intensifying rivalry as they vie for market share. In 2024, this dynamic remains a key feature, as insurers focus on optimizing their existing asset bases rather than exiting the market.
- High Fixed Costs: Regulatory compliance, technology infrastructure, and long-term liabilities are major cost drivers in insurance.
- Exit Barriers: The difficulty in recouping substantial fixed costs discourages companies from leaving the market.
- Sustained Rivalry: This environment fosters intense competition among established players, impacting Corebridge Financial's competitive landscape.
Impact of Technological Advancements and Innovation
The insurance industry's competitive rivalry is intensifying due to rapid technological advancements. Insurers like Corebridge are increasingly using artificial intelligence and advanced analytics to improve efficiency and customer service. For instance, in 2024, many leading insurers reported significant investments in AI-driven claims processing, aiming to reduce settlement times by up to 30%.
This digital transformation allows companies to offer more personalized products and experiences, directly impacting customer loyalty and market share. Those who fail to keep pace risk falling behind competitors who are effectively leveraging these innovations. The ongoing digital race means that continuous investment in new technologies is not just an advantage, but a necessity for survival and growth.
- AI in Claims: In 2024, insurers saw an average reduction of 25% in claims processing time through AI implementation.
- Digital Customer Experience: Companies with advanced digital platforms reported a 15% higher customer retention rate.
- Personalized Products: The adoption of data analytics enabled a 20% increase in the uptake of tailored insurance solutions.
- Investment in Innovation: The global insurtech market saw investments exceeding $10 billion in 2024, highlighting the competitive pressure to innovate.
Corebridge Financial faces intense competition from established players like Prudential and MetLife, driving a need for constant product innovation and competitive pricing. The U.S. retirement and insurance market is mature, leading to battles for market share and increased advertising spend, with some companies seeing slight revenue dips in 2023. High fixed costs associated with regulatory compliance and technology create significant exit barriers, ensuring sustained rivalry among existing firms throughout 2024.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Product Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Prudential Financial | 50.9 | Retirement, Life Insurance |
| MetLife | 59.4 | Group Benefits, Retirement, Life Insurance |
| Principal Financial Group | 15.1 | Retirement, Investment Services |
| Lincoln National | 17.2 | Retirement, Life Insurance |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Corebridge Financial's offerings is substantial, primarily stemming from direct investment in financial markets. Individuals and institutions have readily available alternatives like investing directly in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), bypassing the need for annuities or managed retirement plans. This direct approach is increasingly accessible and appealing, particularly for those who are comfortable managing their own investments or prioritize greater liquidity.
The rise of low-cost brokerage platforms and robo-advisors has significantly lowered the barrier to entry for direct market participation. For instance, by the end of 2023, the average expense ratio for actively managed equity mutual funds was 0.74%, while index funds and ETFs often had expense ratios below 0.10%, presenting a clear cost advantage for direct investors. This cost efficiency, combined with user-friendly technology, makes direct investing a compelling substitute for Corebridge's managed solutions, especially for younger investors or those with smaller initial capital.
Beyond traditional stocks and bonds, alternative savings and investment vehicles pose a significant threat. Real estate, commodities, and even high-yield savings accounts or Certificates of Deposit (CDs) can siphon capital that might otherwise go into Corebridge's wealth accumulation products. For instance, as of early 2024, the average interest rate on a 1-year CD hovered around 4.5%, making them an attractive, low-risk alternative for some savers.
The attractiveness of these substitutes is dynamic, heavily influenced by prevailing economic conditions and interest rate environments. When interest rates rise, as they have in recent years, lower-risk options like CDs become more competitive against the longer-term, potentially higher-return, but also higher-risk, insurance and annuity products. This shift can divert funds, impacting the demand for Corebridge's offerings.
Government Social Security and employer-sponsored pensions represent a significant threat of substitutes for Corebridge Financial. Social Security, for instance, is a guaranteed income stream for many retirees, directly addressing a portion of retirement income needs. In 2024, the maximum Social Security retirement benefit is projected to be $4,873 per month, providing a substantial baseline income that can reduce reliance on private retirement products.
While defined-benefit pensions are less common than in the past, they still exist for some workers, offering a predictable income stream in retirement. These plans, even if not fully covering all retirement expenses, can substitute for the income-replacement aspect of Corebridge's offerings. This directly impacts the demand for comprehensive private retirement solutions as individuals may feel less pressure to fully fund their retirement through private channels.
FinTech and Non-Traditional Financial Services
The burgeoning FinTech sector presents a significant threat of substitutes for Corebridge Financial. Companies offering specialized digital solutions, from peer-to-peer lending to sophisticated budgeting apps, can fulfill specific financial needs previously met by traditional insurers and annuity providers. For instance, the global FinTech market was valued at over $2.4 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong consumer shift towards these alternative services.
These innovations can chip away at Corebridge's market share by offering more agile and often lower-cost alternatives for certain customer segments. Consider the rise of robo-advisors, which provide automated investment management, directly competing with traditional wealth management services that might be bundled with insurance products. By 2024, the assets under management for robo-advisors are expected to reach hundreds of billions globally, demonstrating their increasing relevance.
- FinTech's Market Penetration: The global FinTech market's valuation exceeding $2.4 trillion in 2023 highlights the significant scale of these substitute offerings.
- Specialized Service Competition: Platforms offering peer-to-peer lending and advanced payment systems directly challenge traditional financial intermediation.
- Robo-Advisor Growth: The projected growth in robo-advisor assets under management by 2024 underscores the increasing adoption of automated financial management solutions.
- Customer Need Fragmentation: FinTech innovations cater to specific customer needs, potentially fragmenting the market and reducing reliance on comprehensive traditional financial products.
Self-Directed Retirement Accounts and Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
The threat of substitutes for Corebridge Financial's offerings is significant, particularly from self-directed retirement accounts and Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). Individuals can bypass traditional managed plans by choosing self-directed options like IRAs or 401(k)s, where they personally select their investments, gaining greater control.
Furthermore, HSAs present a compelling alternative. These accounts offer tax advantages for healthcare expenses but also function effectively as long-term savings vehicles, directly competing with Corebridge's retirement products. The flexibility and direct control offered by these substitutes can be highly attractive to customers who prefer managing their own financial futures.
- Self-Directed Accounts: IRAs and 401(k)s allow individuals to choose their own investments, bypassing managed plans.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): Offer tax-advantaged savings for healthcare, also serving as a long-term investment tool.
- Customer Preference: Many customers prioritize control and flexibility in managing their retirement and savings.
- Market Trend: In 2024, the trend towards greater individual control over investments continues to grow, impacting demand for managed services.
The threat of substitutes for Corebridge Financial is considerable, driven by direct investment options and alternative savings vehicles. Individuals can bypass traditional insurance and annuity products by investing directly in stocks, bonds, ETFs, or mutual funds, especially with the advent of low-cost platforms. For instance, by late 2023, the average expense ratio for actively managed equity mutual funds was 0.74%, significantly higher than the sub-0.10% often seen in index funds and ETFs, presenting a clear cost advantage for direct investors.
Furthermore, government programs like Social Security and employer pensions act as substitutes by providing a baseline retirement income, reducing the need for extensive private retirement planning. In 2024, the maximum Social Security benefit is projected at $4,873 per month, offering a substantial income floor. Additionally, the growing FinTech sector, with its specialized digital solutions and robo-advisors, offers agile and often cheaper alternatives, with global robo-advisor assets under management expected to reach hundreds of billions by 2024.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Competitive Advantage | Example Data Point (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Market Investment | Stocks, Bonds, ETFs, Mutual Funds | Lower Costs, Greater Liquidity, Control | Average actively managed equity fund expense ratio: 0.74% (vs. <0.10% for index funds/ETFs) |
| Government Programs | Social Security, Employer Pensions | Guaranteed Income, Reduced Reliance on Private Products | Max Social Security benefit projected at $4,873/month (2024) |
| FinTech Solutions | Robo-advisors, P2P Lending, Budgeting Apps | Agility, Lower Costs, Specialized Services | Global robo-advisor AUM projected to reach hundreds of billions (2024) |
| Alternative Savings | CDs, Real Estate, Commodities | Lower Risk (CDs), Tangible Assets | Average 1-year CD rate around 4.5% (early 2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The insurance and retirement solutions sector demands significant upfront investment, particularly in maintaining robust financial reserves to meet future policyholder obligations. For instance, in 2023, the life insurance industry alone held over $3.7 trillion in reserves, a figure that underscores the immense capital barrier for newcomers. This substantial financial commitment makes it exceedingly challenging for new players to enter the market and compete with established entities like Corebridge Financial, which possess considerable financial strength and liquidity.
The stringent regulatory environment acts as a significant barrier to entry for new companies looking to compete with established players like Corebridge Financial. Navigating the complex web of state and federal regulations, including licensing requirements and capital adequacy standards such as Risk-Based Capital (RBC) ratios, demands substantial investment in legal and compliance expertise.
For instance, in 2024, the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) continued to emphasize robust solvency monitoring, with RBC ratios serving as a critical benchmark. This rigorous oversight, coupled with the ongoing evolution of consumer protection laws and data privacy regulations, makes the cost and time commitment for new entrants exceptionally high, thereby limiting their ability to challenge incumbent firms.
In the financial services sector, especially for products like life insurance and retirement solutions, building customer trust is a major hurdle for newcomers. Corebridge Financial, having operated for many years, already possesses a strong reputation and established customer loyalty, making it harder for new players to gain traction.
Challenges in Establishing Extensive Distribution Networks
New players face significant hurdles in replicating Corebridge Financial's established distribution network. Corebridge boasts a comprehensive platform, reaching customers through independent marketing organizations, financial advisors, banks, and broker-dealers.
Establishing comparable reach demands substantial capital, time, and the cultivation of deep industry relationships, acting as a considerable deterrent for potential entrants aiming for broad market penetration.
- Extensive Network: Corebridge utilizes a multi-channel approach including independent marketing organizations, financial advisors, banks, and broker-dealers.
- High Barrier to Entry: Building a similar distribution infrastructure requires significant investment in time, capital, and relationship management.
- Customer Acquisition Cost: New entrants would likely face much higher initial customer acquisition costs compared to established players.
- Market Access: Gaining access to a diverse customer base through these channels is a complex and resource-intensive undertaking for newcomers.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve Advantages
Established companies like Corebridge Financial enjoy significant advantages due to economies of scale and the experience curve. For instance, in 2024, large insurers often process millions of claims annually, leading to highly optimized and cost-effective operations. This vast scale allows them to spread fixed costs, such as technology investments and regulatory compliance, over a larger volume of business, resulting in lower per-unit expenses.
New entrants, in contrast, would struggle to match this operational efficiency from the outset. They would face higher initial costs for building infrastructure, developing sophisticated underwriting models, and establishing robust distribution networks. For example, a new life insurance provider might need to invest hundreds of millions to build the necessary IT systems and actuarial expertise to compete with incumbents who have refined these processes over decades.
- Economies of Scale: Corebridge leverages its size for lower per-unit costs in underwriting, claims, and investment management, a benefit new entrants lack.
- Experience Curve: Decades of operational refinement allow Corebridge to process transactions more efficiently and at a lower cost than a newcomer.
- Pricing Disadvantage: New entrants would likely face higher operating costs, making it difficult to offer competitive pricing against established players.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Significant capital is required for new entrants to build the technological and human capital necessary to match the scale and efficiency of incumbents.
The threat of new entrants for Corebridge Financial is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements, stringent regulatory hurdles, and the immense challenge of building customer trust and brand recognition. Established players benefit from significant economies of scale and refined operational efficiencies, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price or service from the outset.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for financial reserves and regulatory compliance. | Significant financial barrier, limiting the number of potential entrants. | Life insurance industry reserves exceeded $3.7 trillion in 2023. |
| Regulatory Environment | Complex licensing, capital adequacy (RBC ratios), and consumer protection laws. | Demands substantial legal, compliance, and time investment. | NAIC emphasized robust solvency monitoring with RBC ratios in 2024. |
| Brand & Trust | Established reputation and customer loyalty are hard to replicate. | New entrants struggle to gain market share without proven credibility. | Incumbents leverage decades of customer relationships. |
| Distribution Networks | Building extensive multi-channel access (advisors, banks) is costly and time-consuming. | Requires significant capital and relationship management to match incumbents. | Corebridge utilizes independent marketing organizations, financial advisors, banks, and broker-dealers. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high volume processing and optimized operations. | New entrants face higher initial operating costs, impacting pricing competitiveness. | Large insurers process millions of claims annually, driving efficiency in 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Corebridge Financial is built upon a robust foundation of data, including their SEC filings, investor presentations, and annual reports. We supplement this with industry-specific research from leading financial data providers and market intelligence firms.