Codan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Codan Bundle
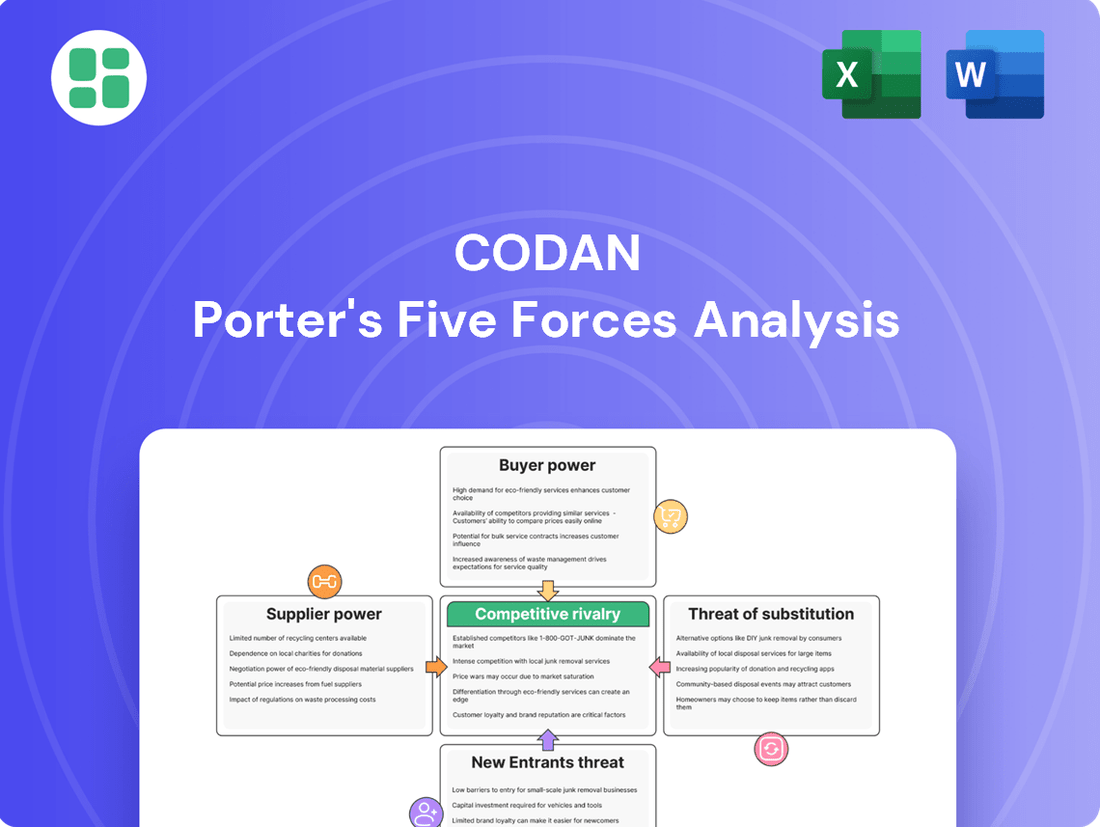
Porter's Five Forces provides a powerful lens to understand Codan's competitive landscape. By examining buyer power, supplier bargaining, threat of new entrants, substitutes, and industry rivalry, we can pinpoint key strategic challenges and opportunities.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Codan’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Codan's dependence on specialized electronic components, crucial for its advanced radio communications and metal detection systems, can significantly amplify supplier bargaining power. The proprietary nature of some of these parts, especially those for defense applications, makes it difficult and costly for Codan to switch suppliers, potentially impacting product performance and delivery schedules.
In specialized sectors like tactical communications, where Codan operates, the pool of suppliers capable of providing niche technologies and components is often quite small. This limited supplier base means fewer alternatives for Codan when sourcing critical inputs, thereby strengthening the bargaining power of these select suppliers.
When only a handful of companies can produce a specific, high-performance component, such as advanced signal processing chips for military radios, those suppliers face less pressure to compete on price or terms. This scarcity directly impacts Codan's ability to negotiate favorable deals, potentially leading to higher acquisition costs for essential parts.
The integration of components into Codan's sophisticated technology solutions is a resource-intensive undertaking. This often necessitates substantial investment in research and development, rigorous testing, and stringent certification procedures. For instance, in the telecommunications sector, a key area for Codan, the qualification of a new component supplier can take 12-18 months and cost hundreds of thousands of dollars in testing and validation.
Consequently, switching suppliers for these critical components carries significant financial implications for Codan. These costs typically encompass redesigning existing products, retooling manufacturing processes, and undertaking extensive re-qualification of the entire product line. This inherent complexity in integration directly translates into high switching costs, thereby amplifying the bargaining power of suppliers who have already successfully navigated Codan's established production and integration ecosystem.
Impact of Global Supply Chain Disruptions
Global events, including the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and ongoing geopolitical tensions, have significantly disrupted supply chains. This has led to component shortages and extended lead times, a situation that persisted into 2024. For instance, the semiconductor shortage, which began in 2020, continued to impact various industries, with lead times for some components extending well beyond 52 weeks in early 2024.
These disruptions disproportionately affect companies like Codan that rely heavily on global sourcing, particularly for electronic parts. When supply is constrained, suppliers gain considerable leverage, enabling them to dictate terms and increase prices. In 2023, the average price increase for electronic components due to supply chain issues ranged from 5% to 15% for many businesses.
- Component Shortages: Persistent shortages in key electronic components, such as microcontrollers and passive components, continue to plague manufacturers.
- Increased Lead Times: Delivery times for critical parts have remained elevated, with some suppliers quoting lead times of over a year.
- Supplier Pricing Power: Suppliers are leveraging these conditions to implement price hikes, directly impacting the cost of goods sold for companies like Codan.
- Production Stability Risk: Codan must proactively manage these macro-economic factors to mitigate risks to its production schedules and overall operational stability.
Supplier's Forward Integration Potential
If a crucial supplier were to consider forward integration, meaning they start offering products or services that directly compete with Codan, their bargaining power would significantly increase. This potential threat necessitates Codan fostering robust supplier relationships and potentially developing its own internal expertise to mitigate dependency.
Codan's strategic acquisitions, such as the purchase of Kägwerks, can be viewed as a proactive measure to gain greater control over essential technologies, thereby reducing the leverage of suppliers who might otherwise consider forward integration.
- Supplier Forward Integration: The threat of suppliers moving into Codan's market space enhances their leverage.
- Relationship Management: Codan must maintain strong ties with suppliers to counter this risk.
- Internal Capabilities: Investing in in-house expertise can reduce reliance on suppliers with integration potential.
- Acquisition Strategy: Purchases like Kägwerks demonstrate Codan's efforts to secure key technologies and reduce supplier dependence.
Codan's reliance on specialized electronic components, particularly for its advanced communications and detection systems, grants significant leverage to its suppliers. The proprietary nature of some of these parts, especially those for defense applications, makes switching suppliers costly and time-consuming for Codan, impacting performance and delivery.
The limited number of suppliers capable of providing niche technologies in sectors like tactical communications means Codan has fewer alternatives. This scarcity directly impacts Codan's ability to negotiate favorable terms, potentially increasing acquisition costs for essential parts.
The integration of specialized components into Codan's sophisticated technology is complex and resource-intensive, involving substantial R&D, rigorous testing, and certification. For instance, qualifying a new component supplier in the telecommunications sector can take 12-18 months and cost hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Consequently, switching suppliers for these critical components incurs significant financial implications for Codan, including redesign, retooling, and extensive re-qualification. These high switching costs amplify supplier bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Codan | Supplier Leverage | Example Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Component Scarcity | Production delays, increased costs | High | Lead times > 52 weeks for some components in early 2024 |
| Supplier Specialization | Limited alternatives | High | Niche technologies in tactical communications |
| Switching Costs | Financial burden of supplier change | High | $100,000s for component re-qualification |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential competition from suppliers | Moderate to High | Strategic acquisitions by Codan to mitigate this risk |
What is included in the product
Codan's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity and profitability potential within its operating industries, examining threats from new entrants, buyers, suppliers, and substitutes, alongside the rivalry among existing competitors.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Force, enabling targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Codan's diverse customer base, spanning government, defense, humanitarian, commercial, and individual consumers across its communications and metal detection segments, significantly weakens customer bargaining power. For instance, in its communications division, while specific large government contracts are crucial, they are balanced by a multitude of smaller commercial and consumer sales, preventing any single entity from dictating terms. This broad reach means no single customer segment represents an overwhelming portion of revenue, thereby limiting their leverage.
Codan's offerings, like their vital communication gear and de-mining detectors, are often fundamental to their clients' safety and daily operations. For sectors such as defense and emergency services, the dependable performance of these tools is non-negotiable.
This essential nature means customers are less likely to switch suppliers because the risks and costs of a system failure or interruption are substantial. For instance, a communication breakdown in a disaster zone could have severe consequences, making reliability the primary concern over price alone.
Consequently, the bargaining power of these customers is somewhat diminished, as they prioritize guaranteed performance and support over seeking lower prices from alternative, potentially less reliable, sources. This inherent criticality strengthens Codan's position.
For institutional and commercial clients, especially those deeply integrated with Codan's communication systems like Zetron control rooms or DTC radio solutions, the cost of switching is significant. These expenses encompass retraining staff, adapting current infrastructure, and navigating potential compatibility problems with new technologies.
These substantial switching costs effectively limit customers' freedom to easily transition to rival providers. This inability to switch readily weakens their leverage, thereby reducing their bargaining power against Codan.
Price Sensitivity Varies by Customer Segment
Codan's customer base exhibits varied price sensitivity. For instance, individual consumers and small-scale miners in the metal detection sector are often more attuned to price points. However, major clients, particularly government and defense organizations, tend to place a higher premium on product performance, unwavering reliability, and comprehensive long-term support, often overlooking minor price variations.
This segmentation enables Codan to implement tailored pricing strategies. By understanding these distinct customer needs, the company can effectively manage overall customer bargaining power. For example, in 2024, defense contracts, which represent a significant portion of Codan's revenue, are typically awarded based on stringent technical specifications and proven track records rather than solely on the lowest bid.
- Differentiated Pricing: Codan leverages varying price sensitivities across customer segments to optimize revenue and manage bargaining power.
- Government & Defense Focus: These clients prioritize performance and reliability, reducing their price sensitivity for critical equipment.
- Consumer Segment Sensitivity: Individual and small-scale users in segments like metal detection are generally more price-conscious.
- Strategic Advantage: Understanding these differences allows Codan to reduce the overall bargaining power of its customer base.
Government and Defense Procurement Processes
Government and defense procurement is notoriously intricate, often involving lengthy tender processes and multi-year contracts. This complexity grants these customers substantial leverage during the initial bidding stages. For instance, in 2024, defense procurement budgets globally continued to expand, with NATO members increasing spending, creating a competitive environment for suppliers aiming to secure these large-volume, stable orders.
Once a contract is secured, the power dynamic can shift. While initial negotiations are intense, the long-term nature of these agreements and the specialized requirements often make switching suppliers difficult for the government or defense entity. This entrenchment can limit the customer's ability to extract further concessions post-award.
- Complex Bidding: Government and defense procurement involves detailed tenders, requiring significant supplier resources.
- Negotiation Leverage: The competitive nature of tenders, especially in 2024 with increased defense spending, empowers buyers during contract negotiation.
- Contractual Entrenchment: Post-award, the specialized nature of defense contracts can reduce customer power to demand ongoing concessions.
- Market Dynamics: In 2023, the global defense market was valued at approximately $2.2 trillion, highlighting the scale and importance of these customer relationships.
Codan's broad customer base, encompassing government, defense, humanitarian, and commercial sectors, inherently limits the bargaining power of any single customer. For example, in 2024, while large government contracts are significant, they are balanced by numerous smaller sales, preventing any one entity from dictating terms. This diversification means that even major clients represent a manageable portion of overall revenue, reducing their leverage.
The critical nature of Codan's products, such as vital communication gear and metal detectors, means customers prioritize reliability and performance over price. This is particularly true for defense and emergency services, where failure can have severe consequences. For instance, in 2023, the global defense market was valued at approximately $2.2 trillion, underscoring the high stakes involved in securing reliable equipment.
Furthermore, substantial switching costs for institutional clients, including retraining and infrastructure adaptation, make it difficult for them to move to competitors. This limits their ability to negotiate aggressively, as seen in 2024 defense procurement where, despite competitive bidding, long-term contracts often lead to supplier entrenchment.
| Customer Segment | Price Sensitivity | Bargaining Power Influence | Example (2024) |
| Government & Defense | Low to Moderate | Limited by switching costs and contract entrenchment | Increased defense spending by NATO members |
| Commercial & Enterprise | Moderate | Reduced by system integration and switching costs | Zetron control room integration |
| Individual Consumers & Small Business | High | Potentially higher, but offset by low individual volume | Price-conscious metal detector buyers |
Preview Before You Purchase
Codan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Codan Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis that you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Codan operates in a competitive landscape with both broad-reaching global companies and niche specialists. In its radio communications division, this includes established players offering tactical radios, advanced command center systems, and robust wireless data solutions, all vying for market share. For instance, companies like L3Harris Technologies and Thales Group are significant competitors in the tactical radio space, with substantial government contracts and product portfolios.
The metal detection segment also sees a diverse set of competitors, ranging from manufacturers of consumer-grade detectors to those focused on specialized markets like gold prospecting and humanitarian de-mining. Garrett Metal Detectors and Minelab Electronics are prominent names in the consumer and hobbyist segments. In the more specialized areas, companies like Thetford Metal Detectors contribute to the competitive intensity.
This multi-faceted competition means Codan must continually innovate and differentiate its offerings in each of its core business areas to maintain and grow its market position. The company's performance is therefore directly influenced by the strategic moves and product developments of these varied rivals across its global operations.
Competitive rivalry within Codan's sector is significantly fueled by substantial investments in research and development (R&D). Companies are locked in a continuous race to innovate, aiming to secure and maintain a crucial technological advantage.
Codan's strategic focus on developing next-generation products and solutions underscores this intense R&D battleground. For instance, in the fiscal year 2023, Codan reported a notable increase in R&D expenditure, reflecting its commitment to staying ahead of the curve.
Rival firms are equally aggressive, consistently introducing advanced features, enhancing product performance, and refining the overall user experience to capture market share. This drive for technological superiority means that any company failing to invest heavily in R&D risks falling behind rapidly.
Competitive rivalry in this sector is increasingly driven by acquisition-led market consolidation. Companies are actively pursuing strategic takeovers to broaden their product offerings, extend their geographic reach, and enhance their technological prowess. This M&A activity aims to build scale and create more integrated solutions for customers.
Codan’s strategic acquisitions of businesses like DTC, Zetron, and Kägwerks exemplify this trend. These moves are designed to bolster Codan's standing in the market and sharpen its competitive edge by integrating new technologies and customer bases. For instance, the acquisition of Zetron, a provider of interoperable communication solutions, significantly expanded Codan’s portfolio in the public safety and defense sectors.
This wave of consolidation can, in turn, intensify the rivalry. As larger, more resource-rich entities emerge from these acquisitions, they often possess greater capacity for innovation, marketing, and market penetration, thereby raising the bar for all players in the industry. This dynamic can lead to a more concentrated market structure where fewer, but larger, competitors dominate.
Differentiation Through Ruggedness and Reliability
Codan's competitive edge is sharpened by its focus on rugged and reliable electronics, crucial for demanding sectors like defense and critical infrastructure. This specialization means rivals must also demonstrate exceptional durability and performance to compete effectively. The market values solutions that can withstand extreme conditions, making this a significant battleground for differentiation.
In 2024, the defense electronics market, where Codan is a key player, was projected to reach approximately $120 billion, with a strong emphasis on mission-critical systems requiring extreme resilience. For instance, companies supplying communication equipment for military operations must ensure their products function flawlessly in environments ranging from desert heat to arctic cold, a standard Codan actively meets.
- Ruggedization as a Differentiator: Codan's commitment to creating electronics that endure harsh environmental factors is a primary way it stands out.
- Industry Standards: Competitors in defense and industrial markets face pressure to match Codan's high benchmarks for product longevity and operational integrity.
- Performance in Extremes: The capacity to deliver dependable performance under challenging operational conditions is a core element of rivalry.
- Market Demand: The increasing need for reliable technology in unforgiving environments fuels the importance of this specific competitive factor.
Geographic Market Presence and Distribution Networks
Codan's extensive geographic market presence, reaching over 150 countries, coupled with its robust network of dealers and agents, serves as a significant competitive advantage. This global footprint allows for broader market penetration and customer access.
However, competitors with a strong foothold in specific regions or highly developed distribution channels can exert considerable pressure. This is particularly true in emerging markets where localized expertise and established networks are crucial for success. For instance, in 2024, a competitor with a dominant presence in Southeast Asia might leverage its local distribution agreements to offer more competitive pricing or faster delivery times, directly challenging Codan's market share in that area.
- Global Reach: Codan's sales in over 150 countries.
- Distribution Strength: Network of dealers and agents worldwide.
- Competitive Threat: Rivals with strong local presence or extensive distribution.
- Market Impact: Particularly in emerging or highly localized markets.
Competitive rivalry within Codan's operating segments is intense, driven by both established global players and specialized niche companies. In radio communications, rivals like L3Harris Technologies and Thales Group compete aggressively on advanced tactical radios and command systems. The metal detection market sees competition from Garrett Metal Detectors and Minelab Electronics, alongside specialized providers.
This rivalry necessitates continuous innovation, with companies like Codan investing heavily in R&D to maintain a technological edge. For example, Codan's fiscal year 2023 saw increased R&D spending, mirroring a broader industry trend where firms like those in the defense electronics sector, projected to reach $120 billion in 2024, prioritize mission-critical system resilience.
Market consolidation through acquisitions, such as Codan's integration of DTC and Zetron, further intensifies competition by creating larger, more capable entities. Codan's focus on ruggedized electronics, a key differentiator in demanding sectors, forces competitors to match high standards for durability and performance in extreme conditions.
Codan's global reach, serving over 150 countries through its dealer network, is countered by competitors with strong regional distribution. For instance, in 2024, a competitor with a dominant Southeast Asian presence could leverage local networks for competitive pricing, directly impacting Codan's market share.
| Competitor Type | Key Segments | Notable Competitors | Competitive Factor | 2024 Market Context |
| Global Players | Radio Communications, Defense Electronics | L3Harris Technologies, Thales Group | Technological Advancement, Government Contracts | Defense electronics market projected at $120 billion |
| Niche Specialists | Metal Detection (Consumer & Specialized) | Garrett Metal Detectors, Minelab Electronics | Product Specialization, Price Point | High demand for specialized gold prospecting equipment |
| Acquired Entities | Public Safety Communications, Interoperable Solutions | Zetron (part of Codan), DTC (part of Codan) | Integrated Solutions, Expanded Portfolios | Acquisitions aim to bolster market standing and technological prowess |
| Regional Leaders | Various, depending on geography | (Varies by region) | Local Distribution Networks, Market Penetration | Emerging markets favor localized expertise and established networks |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Codan's specialized communication solutions is significant, primarily stemming from readily available alternative technologies. These include satellite phones, which offer global coverage, and widespread commercial cellular networks, providing cost-effective voice and data services. For instance, the global cellular IoT connections reached over 2.4 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of this alternative infrastructure.
Furthermore, the increasing sophistication and accessibility of internet-based communication platforms like VoIP services and messaging apps present a viable substitute for many communication needs. While these may lack the ruggedness and specific mission-critical features of Codan's offerings, they can effectively replace them for less demanding applications, potentially eroding market share in certain segments.
For non-specialized communication needs, customers may turn to generic or multi-purpose electronics. These devices, often consumer-grade, can offer basic functionalities at a lower price point. For instance, the global consumer electronics market was valued at approximately $1.1 trillion in 2023, indicating a substantial availability of such alternatives.
While these substitutes are cheaper, they typically lack the specialized performance, ruggedness, and advanced security features inherent in Codan's purpose-built equipment. This means that for critical applications requiring high reliability and specific capabilities, these generic options are often not viable substitutes.
Software-based solutions can emerge as significant substitutes for hardware-centric detection and tracking systems. For example, advancements in AI-powered image analysis of satellite data, which saw significant investment and development throughout 2023 and into 2024, offer a less hardware-intensive approach to monitoring large areas. Companies are increasingly leveraging cloud-based platforms for data processing, potentially reducing the need for specialized on-site equipment.
Evolution of Sensor Technology
The rapid evolution of sensor technology poses a significant threat of substitution for Codan. As new detection and communication methods emerge, they could render existing product lines obsolete. For instance, advancements in drone-mounted sensors for aerial mapping or surveillance might offer more efficient alternatives to traditional ground-based metal detection or communication systems, potentially impacting Codan's market share in those segments.
Consider the growing capabilities of integrated sensor networks. These systems can collect and transmit data in ways that might bypass the need for specialized, standalone devices. This trend is particularly relevant as the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, embedding sensing capabilities into a wider array of everyday objects and infrastructure.
- Technological Obsolescence: New sensor designs could offer superior performance or lower costs, directly competing with Codan's offerings.
- Emergence of Integrated Solutions: Combined sensor and communication platforms might replace the need for separate Codan products.
- Drone and AI Advancements: Autonomous systems utilizing advanced sensors could perform tasks currently requiring Codan's equipment, such as search and rescue or infrastructure monitoring.
DIY or Low-Cost Hobbyist Alternatives
In the recreational metal detection market, the threat of substitutes is particularly notable from DIY or low-cost hobbyist alternatives. These less sophisticated devices can attract individuals new to the hobby or those with very limited budgets. For instance, the global market for hobbyist electronics, which includes components for DIY metal detectors, saw significant growth in 2024, driven by accessible online tutorials and affordable parts. While these substitutes don't match the precision or depth capabilities of brands like Codan, they can satisfy a basic curiosity for treasure hunting, potentially diverting a portion of the casual user segment.
These lower-cost options can act as entry-level devices, potentially delaying or deterring some consumers from investing in Codan's premium offerings. The affordability of components for building a basic detector, coupled with the rise of maker culture, means that individuals can assemble functional, albeit basic, metal detectors for under $100. This contrasts sharply with the price point of advanced consumer models, creating a price-sensitive segment that might opt for these simpler solutions. This segment might be less concerned with advanced discrimination features or target identification, prioritizing the experience of detection itself.
The appeal of DIY and low-cost hobbyist alternatives lies in their accessibility and the satisfaction derived from building something oneself. This can be a significant draw for a certain demographic, particularly younger hobbyists or those on a tight budget. While Codan focuses on high-performance technology and robust build quality, these substitutes offer a different value proposition. For example, the market for entry-level metal detectors, often priced between $50 and $150, represents a substantial segment that might be less inclined to upgrade to higher-end models if their initial experience is positive with a simpler device.
- DIY detectors can be built for under $100, significantly undercutting premium models.
- The maker culture and accessible online resources facilitate the creation of these alternatives.
- Entry-level metal detectors, priced between $50-$150, cater to a budget-conscious segment.
- Casual users may find satisfaction in basic detection without needing advanced features.
The threat of substitutes for Codan's specialized communication and detection equipment is substantial. Alternatives range from widely available commercial technologies like satellite phones and cellular networks to increasingly sophisticated software-based solutions and even DIY hardware. For instance, global cellular IoT connections exceeded 2.4 billion in 2023, illustrating the vast alternative infrastructure available.
These substitutes, while often less rugged or feature-rich than Codan's offerings, can fulfill less critical communication and detection needs at a lower cost. The global consumer electronics market, valued at around $1.1 trillion in 2023, signifies the broad availability of generic alternatives. For recreational metal detection, DIY options built for under $100 pose a significant threat to premium models, catering to a segment prioritizing basic functionality and affordability.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on Codan | Example Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial Communication | Global coverage (satellite), cost-effective data/voice (cellular) | Erodes market share in non-mission-critical segments | Cellular IoT connections > 2.4 billion (2023) |
| Internet-based Platforms | VoIP, messaging apps | Offers basic communication at low cost, potentially replacing less demanding applications | N/A (software-based) |
| Generic Electronics | Lower price point, basic functionalities | Appeals to budget-conscious users for non-specialized needs | Global consumer electronics market ~$1.1 trillion (2023) |
| DIY/Low-Cost Hobbyist | Affordable, accessible components, basic performance | Captures entry-level and budget-conscious segments in recreational markets | DIY detectors < $100; entry-level models $50-$150 |
| Software/AI Solutions | Cloud-based processing, AI image analysis | Can replace hardware-centric detection/tracking needs | Significant investment in AI satellite data analysis (2023-2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The specialized nature of Codan's products, particularly in communications and defense, necessitates substantial upfront capital investment. This includes building advanced manufacturing facilities and acquiring sophisticated testing equipment, creating a significant barrier for potential new entrants.
Continuous research and development (R&D) is crucial in these sectors, demanding ongoing financial commitment. For instance, companies in the defense communications sector often spend millions on R&D to stay ahead of technological advancements, a hurdle new players must overcome.
New entrants face considerable financial obstacles to establish the necessary infrastructure and develop competitive technologies. The high cost of entry, coupled with the need for specialized expertise, effectively limits the number of new companies that can realistically challenge established players like Codan.
Codan's substantial intellectual property and proprietary technologies, particularly in metal detection through Minelab and communications via DTC and Zetron, present a formidable barrier to new entrants. This deep well of innovation requires significant upfront investment in research and development for any competitor aiming to create comparable, non-infringing products. For instance, Minelab's patented technologies in multi-frequency detection have consistently set industry standards, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate their performance without substantial R&D expenditure or costly acquisitions.
Operating in sectors like defense, public safety, and humanitarian aid means new companies must navigate a maze of strict regulations and certifications. For instance, obtaining necessary government approvals and adhering to international standards, such as those for defense equipment or emergency communication systems, can take years and significant investment. In 2024, the defense industry alone saw billions spent globally on research, development, and compliance, underscoring the substantial hurdles any newcomer must overcome before even bringing a product to market.
Established Brand Reputation and Customer Relationships
Codan’s decades-long cultivation of a robust brand reputation, particularly for reliability and performance in demanding sectors like military, government, and humanitarian aid, presents a significant barrier to new entrants.
Building comparable trust and deep customer relationships, especially in markets where product failure carries severe consequences, would be a substantial undertaking for any new competitor seeking to enter Codan's operational spheres.
For instance, in the defense communications sector, where Codan is a key player, contract awards often hinge on proven track records and established supplier relationships, making it difficult for newcomers to gain initial traction. In 2023, the global defense market was valued at approximately $2.2 trillion, with a significant portion allocated to advanced communication systems where reliability is paramount.
- Established Brand Reputation: Codan's long history fosters trust.
- Critical Customer Base: Military and government sectors demand proven reliability.
- Relationship Barriers: New entrants face challenges in replicating existing trust.
- High Stakes Markets: Product failure in defense can have severe operational impacts.
Complex Global Distribution and Service Networks
Codan's intricate global distribution and service networks present a formidable barrier to new entrants. The company operates through an expansive web of dealers, distributors, and service centers, reaching over 150 countries. Building a comparable infrastructure, capable of effectively reaching and supporting customers worldwide, requires substantial capital investment and years of operational experience.
The sheer scale of Codan's established network, developed over decades, creates a significant competitive moat. For any newcomer, replicating this reach and reliability is a monumental challenge. In 2024, the cost of establishing a comparable global logistics and support system would likely run into hundreds of millions of dollars, if not billions, making market entry prohibitively expensive.
- Extensive Global Reach: Codan's presence in over 150 countries signifies a deeply entrenched distribution system.
- High Capital Investment: New entrants face massive upfront costs to build a similar network.
- Operational Complexity: Managing diverse international regulations, logistics, and service standards is a significant hurdle.
- Established Relationships: Codan's long-standing relationships with distributors and service providers offer preferential terms and market access.
The threat of new entrants for Codan is relatively low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for specialized manufacturing and R&D, coupled with stringent regulatory hurdles in sectors like defense, deter new players. Furthermore, Codan's established brand reputation and extensive global distribution networks require substantial time and investment to replicate, creating a strong competitive moat.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Impact on New Entrants | Relevant Codan Business Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for advanced manufacturing and R&D facilities. | Significant barrier; millions to billions required. | Communications, Defense |
| Intellectual Property | Proprietary technologies and patents in detection and communication. | High barrier; requires substantial R&D or licensing. | Metal Detection (Minelab), Communications (DTC, Zetron) |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating strict certifications and government approvals. | High barrier; time-consuming and costly. | Defense, Public Safety |
| Brand Reputation & Relationships | Decades of trust and established customer ties. | High barrier; difficult to build comparable credibility. | Military, Government, Humanitarian Aid |
| Distribution & Service Networks | Extensive global reach across 150+ countries. | Very high barrier; requires massive investment and time. | All business segments |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Codan leverages data from their official investor relations website, annual reports, and industry-specific market research reports to understand competitive dynamics.