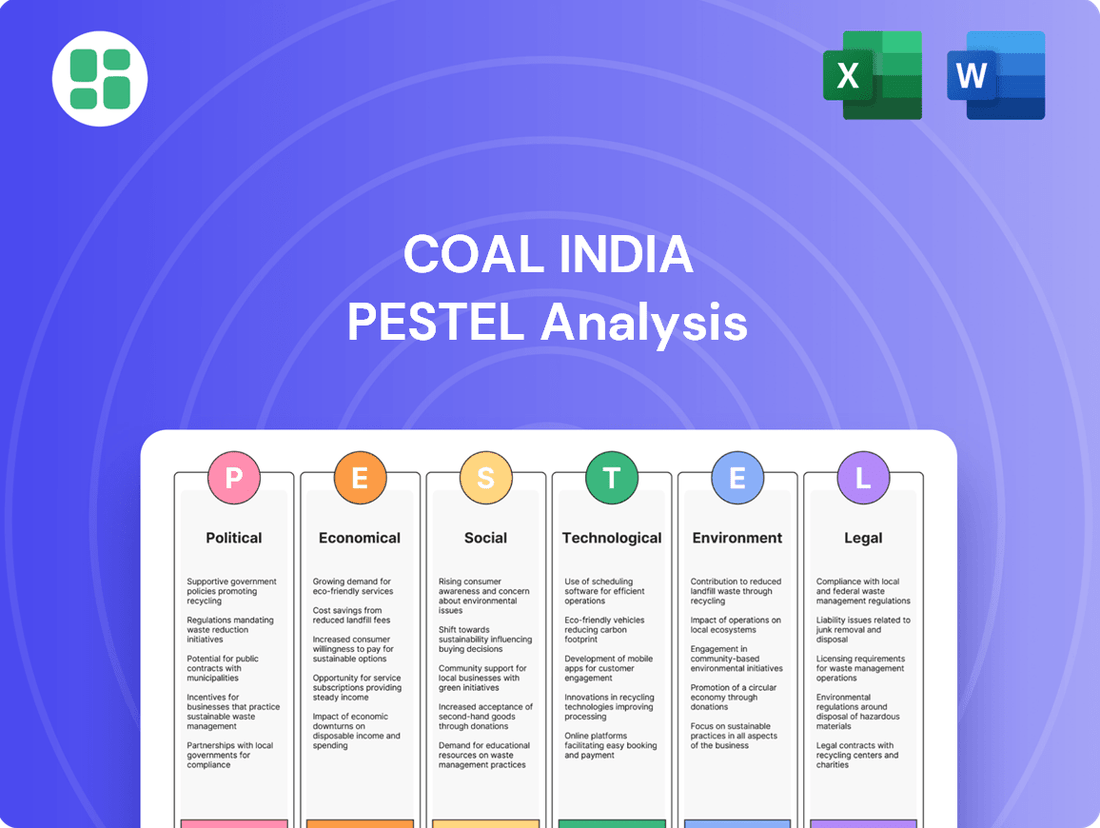
Coal India PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Coal India Bundle
Navigate the complex external forces shaping Coal India's future with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand the political landscape, economic shifts, technological advancements, social trends, environmental regulations, and legal frameworks impacting this vital industry. Gain a strategic advantage by leveraging these critical insights to inform your business decisions and investment strategies. Download the full PESTLE analysis now for actionable intelligence.
Political factors
As a state-owned enterprise, Coal India Limited (CIL) is significantly shaped by government policies and directives, influencing everything from its operational strategies to production targets. This direct government oversight means CIL's path is closely aligned with national energy priorities.
The Indian government's commitment to energy security and reducing import dependence, exemplified by programs like 'Coal Reforms 3.0', directly boosts CIL's role and expansion plans. For instance, in FY24, CIL achieved a record production of 773.6 million tonnes, demonstrating its crucial contribution to meeting domestic demand.
India's commitment to Paris Agreement goals and ambitious renewable energy targets, aiming for 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030, directly influences the policy landscape for Coal India Limited (CIL). This push for green energy necessitates strategic adaptation for CIL, even as coal remains crucial for energy security.
The Economic Survey 2024 highlighted coal's continued role in meeting India's energy needs, projecting its share in the primary energy mix to remain significant. However, the government's increasing emphasis on diversifying the energy portfolio, evidenced by substantial investments in solar and wind power, signals a potential long-term shift that CIL must navigate.
The Ministry of Coal's reform agenda, including the introduction of commercial coal mining and auctioning of coal blocks to private entities, significantly reshapes Coal India Limited's (CIL) operating environment. These policy shifts, aimed at boosting domestic production and decreasing import dependency, introduce competitive pressures for the historically state-controlled giant.
For instance, the government has set ambitious targets for coal production, with a goal to reach 1.3 billion tonnes by 2025, a substantial increase from the approximately 777 million tonnes produced in fiscal year 2022-23. This push for increased output inherently involves greater participation from private players, directly impacting CIL's market share and strategic planning.
Labor Policies and Union Relations
Coal India Limited (CIL), as a major employer, navigates a complex landscape shaped by government labor policies and robust trade unions. These relationships directly influence CIL's operational costs and efficiency, particularly concerning wage structures, employee benefits, and any potential workforce adjustments. For instance, in fiscal year 2023-24, CIL's employee costs represented a significant portion of its revenue, underscoring the financial impact of labor agreements.
The influence of these political factors is evident in several key areas:
- Wage Negotiations: Government-mandated wage revisions and union demands frequently lead to increased personnel expenses, impacting CIL's profitability.
- Workforce Management: Policies on hiring, retrenchment, and productivity often require extensive consultation and agreement with labor unions, potentially slowing down strategic initiatives.
- Industrial Relations: Maintaining harmonious relations with unions is crucial to avoid disruptions like strikes, which can severely affect production targets, as seen in past instances impacting output.
International Climate Diplomacy
India's active participation in international climate forums, including commitments made at COP28 in late 2023 to triple renewable energy capacity by 2030, creates a complex environment for the domestic coal sector. While India has emphasized the continued necessity of coal for its energy security and economic growth, these global agreements exert considerable influence. For instance, the pledge to transition away from coal in energy systems, even if framed as a 'phase-down', signals a long-term shift that will likely impact future policy decisions concerning coal production and consumption.
These international pressures are translating into tangible policy considerations. For example, discussions around carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies, often a part of global climate action plans, could necessitate significant investment for Coal India to remain competitive and compliant. Furthermore, the increasing global focus on green financing mechanisms might make it more challenging and expensive for state-owned enterprises heavily reliant on coal to secure capital for expansion or even ongoing operations in the coming years.
- Global Commitments: India's COP28 pledge to triple renewable energy capacity by 2030 directly signals a move away from fossil fuels, impacting the long-term outlook for coal.
- Phasing Down Coal: International agreements on the 'phase-down' of coal in energy systems create external pressure for domestic policy adjustments, even with India's emphasis on energy security.
- Financing Challenges: The growing trend of green financing could limit access to capital for coal-dependent entities, potentially increasing borrowing costs for Coal India.
- Technology Adoption: International climate diplomacy often promotes cleaner technologies, such as CCUS, which may require substantial investment and adaptation from the domestic coal industry.
Government policies heavily influence Coal India Limited (CIL) as a state-owned entity, aligning its operations with national energy priorities. The push for energy security and reduced import dependence, supported by initiatives like 'Coal Reforms 3.0', bolsters CIL's strategic importance, as evidenced by its record production of 773.6 million tonnes in FY24.
The government's ambitious renewable energy targets, aiming for 500 GW non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030, alongside international climate commitments like the COP28 pledge to triple renewables, create a dual pressure for CIL. While coal remains vital for energy security, these green energy drives necessitate strategic adaptation and potential investment in technologies like CCUS.
Policy reforms, including the introduction of commercial coal mining and auctioning of coal blocks to private players, are reshaping CIL's competitive landscape. The government's target of 1.3 billion tonnes of coal production by 2025 underscores the drive for increased output, potentially impacting CIL's market share.
Labor policies and trade union relations significantly impact CIL's operational costs and efficiency, with employee expenses forming a substantial part of its revenue in FY23-24. Wage negotiations and workforce management require careful navigation to avoid production disruptions.
| Factor | Impact on CIL | Key Data/Initiative |
|---|---|---|
| Government Energy Policy | Directs production targets and operational strategy. | Target of 1.3 billion tonnes coal production by 2025. |
| Renewable Energy Push | Creates long-term adaptation pressure. | India's aim for 500 GW non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030. |
| Market Reforms | Introduces competition from private players. | Commercial coal mining and auctioning of coal blocks. |
| Labor Relations | Affects operational costs and efficiency. | Significant employee costs in FY23-24 revenue. |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis for Coal India examines the influence of political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors on its operations and strategic direction.
It provides a comprehensive understanding of the external landscape, highlighting key trends and potential impacts for informed decision-making.
A PESTLE analysis of Coal India offers a clear, summarized version of external factors, acting as a pain point reliever by simplifying complex market dynamics for easier referencing during strategic discussions and decision-making.
Economic factors
Coal India's core operations are intrinsically tied to the domestic demand from critical sectors such as power generation, steel manufacturing, and cement production. These industries represent the primary consumers of the coal supplied by Coal India, making their growth trajectories directly influential on the company's performance.
The company's ambitious production and offtake targets are a direct reflection of anticipated domestic energy needs. For instance, Coal India's target of producing 875 million tonnes (MT) and achieving an offtake of 900 MT for the fiscal year 2025-2026 is calibrated to meet the projected energy consumption of these key industrial segments.
Global thermal coal prices have experienced volatility, impacting domestic markets. For instance, Newcastle thermal coal futures, a key international benchmark, saw significant fluctuations throughout 2024, trading in a range influenced by global energy demand and supply-side disruptions.
In India, Coal India Limited's (CIL) revenue is directly tied to these global trends and domestic e-auction premiums. While CIL reported a 10% increase in revenue for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, to approximately INR 1.36 lakh crore, sustained pressure on e-auction premiums in late 2024 and early 2025 could temper net profit margins, even with projected production growth of over 10% for FY25.
Coal India Limited (CIL) faces significant infrastructure development costs, particularly for enhancing its rail network and first-mile connectivity. These investments are essential for efficiently moving coal from mines to consumers, supporting CIL's ambitious production goals. For instance, CIL's planned capital expenditure for FY25 includes substantial outlays for railway sidings and other logistical improvements.
CIL's strategic partnerships, like the Memorandum of Understanding with Indian Port Rail & Ropeway Corporation Ltd., are designed to tackle logistical challenges. However, these collaborations necessitate considerable capital investment to build and upgrade necessary infrastructure, directly impacting the company's financial outlay for operational efficiency.
Capital Expenditure and Investment
Coal India Limited's (CIL) capacity to grow production and satisfy future energy needs is directly tied to its capital expenditure (CapEx) strategy. This includes funding new mining ventures, expanding current operations, and implementing technological advancements to boost efficiency.
CIL has outlined ambitious investment targets to achieve its production objectives and enhance operational performance. For instance, the company planned a capital expenditure of approximately ₹15,000 crore for the fiscal year 2023-24, with a significant portion earmarked for mining projects and equipment upgrades.
Key areas for investment include:
- Development of new greenfield and brownfield projects to increase extractable reserves.
- Technological upgrades such as the adoption of advanced mining machinery and automation for improved productivity and safety.
- Infrastructure development including railway sidings and conveyor systems to facilitate efficient coal evacuation.
- Exploration and geological studies to identify and assess new coal reserves, ensuring long-term resource availability.
Contribution to Government Exchequer
Coal India Limited (CIL) plays a crucial role in bolstering government finances. In the fiscal year 2023-24, CIL's total contribution to the central and state exchequers, encompassing royalties, GST, DMF, and other taxes, amounted to a substantial ₹60,000 crore. This significant inflow directly supports public services and infrastructure development.
The financial health of CIL has a direct and pronounced impact on the fiscal stability of major coal-producing states. For instance, in FY23, states like Jharkhand, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh received substantial portions of their state own tax revenue from CIL's operations, underscoring the company's importance to their budgets.
- Royalties: CIL paid approximately ₹20,000 crore in royalties to various state governments in FY23.
- GST and Other Levies: The company contributed over ₹30,000 crore through Goods and Services Tax and other applicable taxes in FY23.
- District Mineral Foundation (DMF): CIL's contributions to DMF funds, aimed at benefiting local communities in mining areas, exceeded ₹10,000 crore in FY23.
The Indian government's policies, particularly those related to energy transition and coal usage, significantly shape Coal India's operational landscape. While the nation aims to increase its renewable energy capacity, coal remains a critical component of the energy mix, with targets for coal-based power generation continuing to be substantial. For instance, India's energy minister has emphasized the continued need for coal power to meet growing energy demand through at least 2030.
Regulatory frameworks, environmental norms, and the pricing mechanisms for coal directly influence CIL's profitability and expansion plans. The government's focus on reducing carbon emissions and promoting cleaner alternatives presents both challenges and opportunities for CIL, requiring strategic adaptation to evolving environmental standards and market demands.
Government initiatives aimed at improving logistics and infrastructure, such as dedicated freight corridors, directly benefit CIL by reducing transportation costs and improving the efficiency of coal delivery. These policy interventions are crucial for CIL to meet its ambitious production and offtake targets.
The economic outlook for India, including GDP growth projections and industrial output, directly correlates with the demand for coal. A robust economic expansion, especially in sectors like power, steel, and cement, fuels CIL's sales volumes. India's GDP growth is projected to be around 6.5% for FY25, indicating sustained industrial activity and demand for coal.
Same Document Delivered
Coal India PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of Coal India delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the company's operations and strategic decisions.
Sociological factors
Coal India Limited (CIL) is a colossal employer, directly and indirectly supporting millions of livelihoods, especially in its operational areas. As of March 2024, CIL directly employed over 247,000 individuals, a significant portion of whom are contract laborers, underscoring its role as a primary economic engine for many communities.
The company's extensive operations are intrinsically linked to the economic well-being of residents in coal-bearing regions, acting as a vital source of income and stability. CIL actively engages in skilling and vocational training programs, aiming to equip local populations with employable skills, thereby fostering sustainable livelihoods beyond direct employment.
Coal India Limited's (CIL) mining activities frequently involve land acquisition, which can lead to the displacement of local populations. This makes effective community relations and resettlement programs paramount for maintaining its social license to operate. For instance, in fiscal year 2023-24, CIL reported that rehabilitation and resettlement activities were undertaken for 2,077 project-affected families across various ongoing projects, aiming to mitigate social disruption.
Coal India Limited (CIL) places immense importance on the health and safety of its extensive workforce, a critical social responsibility. The company is bound by strict mining safety regulations and actively invests in advanced safety technologies and methodologies to mitigate accidents and occupational illnesses. For instance, during FY23, CIL reported a significant reduction in fatalities, with 39 mining-related deaths compared to 51 in FY22, demonstrating ongoing efforts in safety enhancement.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Initiatives
Coal India Limited (CIL) actively engages in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), channeling significant resources into education, healthcare, and community development. In fiscal year 2023-24, CIL allocated ₹1,298.93 crore for CSR activities, with a substantial portion directed towards improving living standards in its operational areas. This commitment reflects a growing societal expectation for large corporations to contribute positively to the communities they operate within.
CIL's CSR strategy prioritizes sustainable development, focusing on:
- Education: Supporting schools, providing scholarships, and promoting digital literacy.
- Healthcare: Organizing health camps, improving medical infrastructure, and providing access to essential services.
- Skill Development: Offering vocational training programs to enhance employability among local youth.
- Women's Empowerment: Implementing initiatives for economic independence and social upliftment of women.
These initiatives are crucial in fostering goodwill and maintaining a positive social license to operate, especially given the environmental impact often associated with the coal industry. Societal pressure to demonstrate genuine commitment to community well-being is a significant factor influencing CIL's strategic decisions regarding its social impact programs.
Public Perception and Social License
Public perception of coal mining significantly impacts Coal India Limited's (CIL) operations and expansion plans. Growing awareness of environmental issues and the social impact of mining activities, such as land acquisition and community displacement, can lead to protests and operational delays. In fiscal year 2023-24, CIL faced increased scrutiny regarding its environmental footprint, with ongoing public discourse on the transition to cleaner energy sources.
Maintaining a positive social license to operate is paramount for CIL. This involves actively engaging with local communities, addressing their concerns, and contributing to their socio-economic development. Balancing the nation's demand for energy security, which coal currently helps fulfill, with the imperative of environmental stewardship and community welfare is a delicate act CIL must continuously navigate. For instance, CIL's corporate social responsibility (CSR) spending in FY23 reached approximately ₹880 crore, focusing on areas like health, education, and rural development to foster goodwill.
- Reputational Risk: Negative public perception, fueled by environmental concerns, can damage CIL's brand and investor confidence.
- Operational Hurdles: Community opposition can lead to project delays, increased costs, and potential disruptions to mining activities.
- Social License: CIL's ability to secure and maintain public acceptance is critical for its long-term sustainability and growth.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Proactive communication and meaningful engagement with affected communities are vital for building trust and mitigating conflict.
Societal expectations heavily influence CIL's operations, demanding robust community engagement and development initiatives. The company's significant CSR spending, totaling ₹1,298.93 crore in FY24, underscores its commitment to improving living standards through education, healthcare, and skill development. This proactive approach is essential for maintaining its social license to operate amidst growing environmental awareness.
Public perception regarding coal mining's environmental and social impacts can create operational hurdles, including protests and delays. CIL's efforts to mitigate these concerns, such as focusing on safety with 39 mining-related deaths in FY23 (down from 51 in FY22), are crucial for its reputation and investor confidence.
The company's role as a major employer, supporting over 247,000 individuals as of March 2024, deeply impacts community economic stability. CIL's investments in local skilling and vocational training aim to foster sustainable livelihoods, further strengthening its societal ties.
| Area of Focus | FY24 Allocation (Crore INR) | Key Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) | 1,298.93 | Education, healthcare, skill development, women's empowerment |
| Direct Employment | N/A | Over 247,000 employees (as of March 2024) |
| Safety Initiatives | N/A | Investment in advanced safety technologies |
| Land Acquisition & Resettlement | N/A | Rehabilitated 2,077 project-affected families (FY23) |
Technological factors
Coal India Limited (CIL) is actively integrating advanced mining technologies to boost its operational capabilities. This includes the widespread adoption of Mass Production Technologies (MPT) such as Continuous Miners (CMs) in its underground mining operations. For opencast mines, CIL is implementing cutting-edge equipment and methods designed to improve extraction rates and overall efficiency.
These technological upgrades are crucial for CIL's strategic objective of meeting ambitious production targets. For instance, in the fiscal year 2023-24, CIL achieved a record coal production of 773.6 million tonnes, a significant increase driven in part by these modernizations. The company aims to further enhance productivity and safety through continued investment in these advanced systems.
Coal India is actively investing in technologies like coal washing to enhance coal quality. This process removes impurities, leading to a higher calorific value and reduced ash content, which is vital for the power and steel industries. In FY23, Coal India's washed coal production reached 135.5 million tonnes, a significant increase from previous years, reflecting this commitment.
Meeting stringent customer specifications and environmental regulations is a key driver for these technological advancements. Improved grade conformity not only satisfies consumers but also minimizes the environmental footprint associated with burning lower-quality coal, a critical consideration in the current energy landscape.
Coal India Limited (CIL) is increasingly focusing on clean coal technologies like gasification to meet India's net-zero emissions goals and broaden coal's applications. This strategic shift is supported by government incentives, with financial backing aimed at promoting coal gasification projects, signaling a move towards more sustainable coal utilization.
The Indian government has earmarked substantial financial incentives to encourage the development of coal and lignite gasification projects. For instance, the Ministry of Coal announced a production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for coal gasification, aiming to convert coal into valuable chemicals and reduce reliance on imported natural gas.
Digitalization and Automation in Mining
Coal India is increasingly integrating digitalization and automation to boost efficiency. This includes using satellite surveillance for reclamation projects, which helps monitor environmental compliance more effectively. For instance, in the fiscal year 2023-24, Coal India has been actively employing advanced technologies for mine planning and monitoring, aiming to reduce manual intervention and improve safety. The company also leverages data analytics to optimize resource allocation and predict equipment maintenance needs, thereby minimizing downtime.
The adoption of digital tools extends to exploration, enabling faster and more accurate identification of new coal reserves. This technological push is crucial for maintaining production levels and ensuring sustainable mining practices. Coal India's capital expenditure for the fiscal year 2024-25 is expected to heavily focus on these technological upgrades, with a significant portion allocated to mechanization and digitalization initiatives to enhance productivity and environmental stewardship.
- Satellite Surveillance: Used for monitoring land reclamation and environmental compliance, improving accuracy and reducing on-ground efforts.
- Data Analytics: Employed for operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and optimizing resource management across mining sites.
- Exploration Technologies: Advanced tools are being utilized to identify new coal reserves more efficiently, supporting future production strategies.
Safety and Environmental Monitoring Technologies
Technological advancements are crucial for Coal India's safety and environmental stewardship. Innovations like blast-free technology are being explored to reduce seismic impact and improve operational safety. Real-time monitoring systems for air and water quality are essential for compliance and minimizing pollution, with Coal India investing in such infrastructure to track emissions and effluents accurately.
Furthermore, the company is focusing on technologies that enable precise tracking of its environmental performance. This includes sophisticated data analytics to understand and mitigate the ecological footprint of its mining activities. For instance, in FY23, Coal India reported a significant increase in its afforestation efforts, planting over 1.2 crore saplings, showcasing a commitment to environmental regeneration alongside technological adoption.
- Blast-Free Technology: Exploring alternatives to conventional blasting to enhance safety and reduce environmental disturbance.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Implementing advanced sensors for continuous tracking of air quality (e.g., PM2.5, SO2) and water quality in and around mining areas.
- Environmental Performance Tracking: Utilizing digital platforms and data analytics to monitor and report on key environmental metrics, including emissions and water discharge.
- Reclamation Technologies: Employing modern techniques for mine land reclamation and restoration to biodiversity standards.
Coal India is heavily investing in advanced mining technologies to boost production and efficiency. This includes deploying Continuous Miners in underground operations and advanced equipment for opencast mines. In FY23-24, the company achieved a record 773.6 million tonnes of coal production, a testament to these technological upgrades.
Digitalization and automation are key focus areas, with the use of satellite surveillance for reclamation and data analytics for operational optimization. Exploration technologies are also being enhanced to identify new reserves more efficiently, supporting future production strategies. Capital expenditure for FY24-25 is expected to prioritize these initiatives.
Clean coal technologies, such as gasification, are being adopted to align with net-zero goals and reduce reliance on imported natural gas. The government is supporting this with production-linked incentives for coal gasification projects.
Safety and environmental stewardship are being improved through technologies like blast-free methods and real-time monitoring systems for air and water quality. The company also focuses on precise tracking of environmental performance through digital platforms.
| Technology Area | Key Initiatives | Impact/Data Point (FY23-24/FY23) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanization & Automation | Continuous Miners (Underground), Advanced Opencast Equipment | Record 773.6 MT Coal Production |
| Digitalization | Satellite Surveillance, Data Analytics, Exploration Tech | Optimized resource allocation, improved safety |
| Clean Coal Tech | Coal Gasification | Government PLI schemes for gasification projects |
| Environmental Tech | Blast-Free Tech, Real-Time Monitoring, Reclamation Tech | Over 1.2 crore saplings planted (FY23) |
Legal factors
Coal India Limited's (CIL) extensive operations are meticulously guided by a robust legal framework, prominently featuring the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957, and the comprehensive Coal Mines Regulations-2017. Adherence to these foundational statutes, particularly concerning land acquisition processes and the intricate web of mineral rights, is not merely a procedural requirement but a cornerstone of CIL's operational integrity and business continuity.
Coal India Limited (CIL) must secure prior Environmental Clearances (EC) from the Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change (MoEF&CC) for all new projects and expansions, a crucial legal hurdle. For instance, in the fiscal year 2023-24, CIL reported obtaining ECs for several new projects, demonstrating ongoing compliance efforts.
Adherence to the Environment (Protection) Act & Rules, 1986, and its associated notifications is non-negotiable, mandating robust compliance and monitoring systems. CIL's environmental performance reports for 2023-24 highlight investments in emission control technologies and water management, reflecting these legal obligations.
Projects by Coal India that require utilizing forest land necessitate obtaining prior Forestry Clearance under the Forest Conservation Act, 1980. This process can be lengthy and involves strict environmental impact assessments, potentially delaying project commencement and increasing capital expenditure. For instance, in FY23, Coal India faced delays in several projects due to ongoing forest clearance procedures.
Labor Laws and Industrial Relations
Coal India Limited (CIL) operates under a stringent legal framework governing labor, including the Mines Act, 1952, and Mines Rules, 1955, which mandate worker safety and welfare standards. Compliance with these regulations is paramount due to CIL's extensive workforce, numbering over 247,000 employees as of March 2024. The company's adherence to industrial relations laws is also crucial, given the significant influence of trade unions within its operations.
Key legal considerations for CIL include:
- Worker Safety and Health: Strict adherence to safety protocols outlined in the Mines Act, 1952, to minimize accidents and ensure a healthy working environment.
- Wage and Benefit Regulations: Compliance with laws dictating minimum wages, overtime pay, and other employee benefits, impacting CIL's operational costs.
- Industrial Disputes Resolution: Navigating legal frameworks for resolving disputes with a highly unionized workforce, ensuring smooth industrial relations.
Corporate Governance and Reporting Standards
Coal India Limited (CIL), as a publicly traded state-owned entity, adheres to rigorous corporate governance principles and reporting mandates. These include the Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reports (BRSR) as stipulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), fostering transparency and accountability among its diverse stakeholder base.
These regulatory frameworks are crucial for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring ethical business practices. For instance, CIL's adherence to SEBI's BRSR guidelines, which became mandatory for the top 1000 listed companies by market capitalization from FY 2022-23, underscores its commitment to sustainability and responsible corporate citizenship.
Key aspects of these legal factors include:
- Compliance with SEBI Regulations: CIL must comply with all SEBI regulations concerning listed companies, including timely financial disclosures and adherence to corporate governance codes.
- Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR): The company is mandated to publish BRSR reports, detailing its environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, a requirement that became mandatory for companies of CIL's stature from FY 2022-23.
- Government Oversight: As a state-owned enterprise, CIL is also subject to oversight from various government ministries and departments, ensuring alignment with national policies and objectives.
Coal India Limited (CIL) navigates a complex legal landscape, with the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957, and Coal Mines Regulations-2017 forming its operational bedrock. Compliance with environmental laws, including securing Environmental Clearances (EC) and adhering to the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, is critical. For instance, CIL secured ECs for several new projects in FY23-24, demonstrating ongoing efforts.
Forestry clearances under the Forest Conservation Act, 1980, can impact project timelines, as seen with delays in FY23. CIL's workforce of over 247,000 employees (as of March 2024) necessitates strict adherence to labor laws like the Mines Act, 1952, ensuring worker safety and fair wages.
As a listed entity, CIL is bound by SEBI regulations, including mandatory Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) since FY 2022-23, enhancing transparency. Government oversight also ensures alignment with national objectives.
Environmental factors
Coal India Limited (CIL) faces significant pressure due to its role in greenhouse gas emissions. In 2023, India's total greenhouse gas emissions were estimated to be around 3,100 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent, with the energy sector, heavily reliant on coal, being a major contributor. CIL's operations, from extraction to combustion, directly impact this figure.
India's ambitious climate targets, including achieving net-zero emissions by 2070, directly impact CIL. The company is increasingly expected to demonstrate concrete strategies for emission reduction across its entire operational spectrum, from mining practices to supporting cleaner energy transitions.
Coal mining inherently causes land degradation, necessitating substantial reclamation efforts. Coal India Limited (CIL) is committed to scientific reclamation, planting trees, and establishing eco-restoration sites and eco-parks. For instance, in FY23, CIL achieved over 1,400 hectares of plantation, contributing to its ongoing efforts to mitigate mining's environmental footprint and enhance biodiversity.
Coal mining inherently impacts water resources, with runoff from mine sites potentially carrying pollutants into local water bodies. Coal India Limited (CIL) is actively engaged in mitigating these effects through robust water management practices. These include significant investments in rainwater harvesting and advanced water treatment facilities across its operations.
In fiscal year 2023-24, CIL reported treating approximately 300 million cubic meters of wastewater, a crucial step in reducing the environmental footprint of its mining activities. The company's commitment extends to ensuring responsible water usage, aiming to minimize depletion of local water availability and prevent contamination of groundwater sources, which is vital for surrounding communities and ecosystems.
Air Quality and Dust Pollution
Coal mining and transportation activities by Coal India Limited (CIL) are significant contributors to air quality degradation, releasing substantial amounts of dust and particulate matter into the atmosphere. These emissions directly impact local air quality, posing health risks to surrounding communities.
CIL is implementing various measures to mitigate these environmental impacts, including dust suppression techniques and emission control technologies. However, challenges persist, especially concerning the management and disposal of fly ash, a byproduct of coal combustion. The company has engaged in lobbying efforts to potentially ease existing regulations surrounding fly ash disposal, highlighting the ongoing tension between operational needs and environmental stewardship.
- Dust and Particulate Matter: Coal extraction and movement release fine particles that degrade air quality.
- Emission Control: CIL employs technologies to reduce pollutant release from its operations.
- Fly Ash Management: Disposal of fly ash remains a key environmental challenge, with ongoing discussions on regulatory frameworks.
Biodiversity Impact and Conservation
Coal India Limited (CIL) faces significant environmental challenges due to its mining operations, which can directly impact biodiversity. Habitat destruction and the loss of plant and animal species are inherent risks associated with large-scale coal extraction. For instance, CIL's operations in ecologically sensitive areas necessitate careful management to mitigate these effects.
To address these concerns, CIL has implemented comprehensive environmental management plans. These plans focus on biodiversity protection and enhancement through substantial afforestation drives. The company aims to create extensive green cover and develop eco-parks, often in collaboration with specialized environmental agencies to ensure effective conservation strategies.
CIL's commitment to biodiversity conservation is reflected in its ongoing projects. As of recent reports, the company has undertaken significant land reclamation and afforestation efforts. For example, in the fiscal year 2023-24, CIL planted a substantial number of saplings across its mining regions, contributing to habitat restoration and the creation of new green spaces. These initiatives are crucial for offsetting the environmental footprint of coal mining.
- Habitat Restoration: CIL's afforestation programs aim to restore and create new habitats for local flora and fauna in mined-out areas.
- Eco-Park Development: The establishment of eco-parks serves as biodiversity conservation hubs, promoting ecological balance and providing educational opportunities.
- Species Protection: Efforts are made to protect endangered or vulnerable species found within or near mining lease areas through specific conservation measures.
- Consultation with Experts: CIL collaborates with environmental experts and research institutions to ensure its biodiversity management plans are scientifically sound and effective.
India's commitment to net-zero emissions by 2070 places significant pressure on coal-dependent entities like Coal India Limited (CIL). The company is increasingly tasked with demonstrating tangible strategies for emission reduction across its value chain.
CIL actively engages in land reclamation and afforestation, planting over 1,400 hectares in FY23 to mitigate its environmental footprint. Furthermore, the company treated approximately 300 million cubic meters of wastewater in FY23-24, underscoring its commitment to responsible water management.
Air quality remains a concern, with CIL implementing dust suppression and emission control technologies. However, fly ash management continues to be a challenge, prompting discussions on regulatory adjustments.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on CIL | Mitigation Efforts/Data (FY23/FY24) |
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Contributes to India's emissions; pressure to align with net-zero goals. | India's total GHG emissions ~3,100 million tonnes CO2 eq. (2023). |
| Land Degradation | Requires extensive reclamation and restoration. | Over 1,400 hectares planted in FY23; eco-restoration sites and eco-parks developed. |
| Water Pollution | Risk of pollutants entering water bodies from mine runoff. | Treated ~300 million cubic meters of wastewater in FY23-24; rainwater harvesting implemented. |
| Air Quality | Dust and particulate matter emissions impact local air. | Dust suppression techniques and emission control technologies deployed. |
| Biodiversity Loss | Habitat destruction and species loss are inherent risks. | Afforestation drives and eco-park development for habitat restoration. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Coal India PESTLE Analysis is built on a comprehensive review of data from government ministries, industry associations, and reputable financial news outlets. We analyze policy documents, economic reports, and market trends to provide a robust understanding of the external environment.