Central National-Gottesman Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Central National-Gottesman Bundle
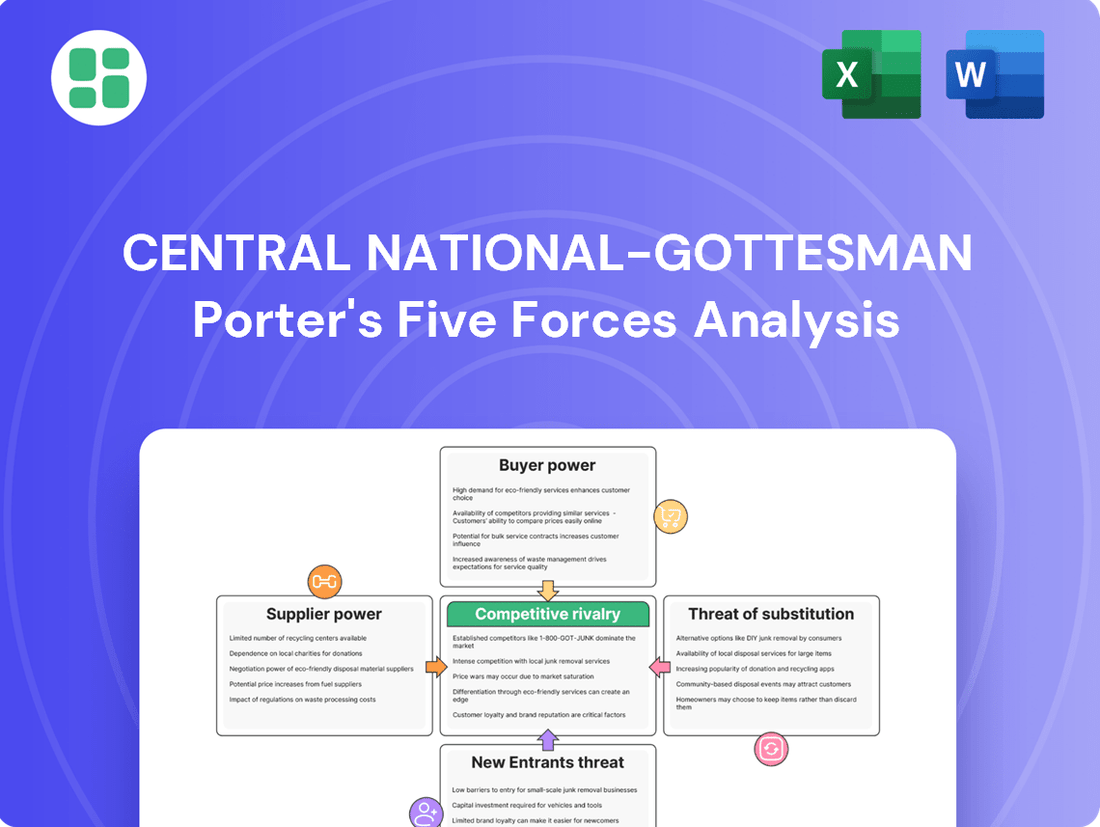
Central National-Gottesman operates in a dynamic market shaped by intense competition and evolving customer demands. Understanding the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of new entrants is crucial for navigating this landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Central National-Gottesman’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration within the pulp, paper, packaging, tissue, and wood products sectors significantly influences Central National-Gottesman's (CNG) bargaining power. If a limited number of large suppliers dominate these markets, they can exert considerable leverage over CNG. This concentration means CNG has fewer viable options for sourcing critical raw materials and finished goods, potentially leading to higher input costs and less favorable contract terms.
For instance, in 2024, the global pulp market saw consolidation, with major players controlling substantial production capacity. A similar trend is observable in specialized packaging materials. This limited supplier base empowers these key entities to dictate pricing and supply volumes, directly impacting CNG's cost of goods sold and its ability to maintain a stable supply chain. The fewer the alternatives, the stronger the supplier’s position.
The uniqueness of inputs significantly shapes supplier bargaining power for Central National-Gottesman (CNG). If suppliers provide highly specialized grades of pulp, paper, or wood that are critical for CNG's customers and lack easy substitutes, their leverage grows. For instance, in 2024, the demand for sustainably sourced and certified wood products continued to rise, making suppliers with such credentials more influential. This differentiation can come in the form of unique certifications, proprietary treatments, or specific quality standards that are difficult for competitors to replicate.
Central National-Gottesman (CNG) likely faces moderate switching costs when changing CNG suppliers. These costs can include the time and resources spent on re-negotiating supply agreements, validating the quality and specifications of new CNG sources, and potentially adjusting existing distribution or storage infrastructure to accommodate different suppliers. For instance, a change in supplier might necessitate recertification processes for the CNG itself, which can be time-consuming and add to operational expenses.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into distribution or sales presents a significant challenge for Central National-Gottesman (CNG). If major paper and pulp producers, who are CNG's suppliers, possess the capital and market access to sell directly to end-users, they could effectively bypass CNG's distribution network. This would diminish CNG's role and bargaining power, as suppliers would capture more of the value chain.
This risk is amplified for large, vertically integrated suppliers who already have established customer relationships and logistical capabilities. For instance, a major paper manufacturer with its own sales force and warehousing could decide to directly serve large printing companies or packaging firms, cutting out intermediaries like CNG. Such a move would directly compete with CNG’s core business model.
- Supplier Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers may leverage their production scale and existing customer relationships to sell directly to end-consumers, bypassing distributors like CNG.
- Impact on CNG: This would reduce CNG's revenue streams and market share by eliminating its intermediary role in the supply chain.
- Key Factor: The likelihood increases with suppliers who have strong brand recognition and existing logistical infrastructure.
Importance of CNG to Suppliers
The significance of Central National-Gottesman (CNG) to its suppliers plays a crucial role in determining supplier bargaining power. If CNG constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier is likely to be more accommodating, seeking to maintain the relationship. For instance, if a key packaging material supplier derives 15% of its annual sales from CNG, they may be hesitant to push for significantly higher prices or unfavorable terms.
Conversely, if CNG represents a minor segment of a supplier's customer base, the supplier possesses greater leverage. Suppliers catering to a broad market, where CNG is just one of many clients, can more easily absorb the loss of CNG's business if negotiations turn sour. This is particularly true for commodity suppliers who can readily redirect their products to other buyers, potentially increasing their willingness to demand better terms from CNG.
- Supplier Dependence: If a supplier's business heavily relies on CNG, their bargaining power is diminished.
- Customer Diversification: Suppliers with a diverse customer portfolio are less dependent on any single client like CNG, enhancing their leverage.
- Market Share Impact: The percentage of a supplier's total sales that CNG accounts for directly influences the supplier's negotiating stance.
- Alternative Buyers: The availability of alternative buyers for a supplier's goods or services dictates how much power CNG holds in negotiations.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Central National-Gottesman (CNG) is influenced by the concentration of suppliers in the pulp, paper, and packaging industries. When fewer suppliers control a large share of production, they can command higher prices and dictate terms to CNG, as seen in 2024 with consolidation among major pulp producers. This limited choice reduces CNG's ability to negotiate favorable pricing and secure a stable supply chain.
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Central National-Gottesman, revealing industry attractiveness and strategic positioning within the paper and packaging sector.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual representation of each Porter's Five Forces factor.
Gain immediate clarity on market dynamics, allowing for proactive strategy adjustments to reduce competitive pressure.
Customers Bargaining Power
Central National-Gottesman's (CNG) customer concentration is a key factor in assessing customer bargaining power. A significant portion of CNG's revenue may depend on a limited number of large clients across its diverse product lines and geographical markets. If a few major customers, for instance, represent over 10% of total sales, their ability to negotiate favorable pricing or terms increases substantially, potentially impacting CNG's profitability.
Central National-Gottesman's customers, particularly those in the commodity pulp, paper, packaging, tissue, and wood products sectors, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This sensitivity is amplified because these products often represent a substantial portion of a customer's cost of goods sold, and in many cases, the products are largely undifferentiated.
For instance, in the paper and packaging industry, which saw global market growth projected to reach over $1.2 trillion by 2024, buyers frequently seek the lowest cost options. When customers can easily switch suppliers with little switching cost and when the purchased product is not critical to their own product's differentiation, their bargaining power to demand lower prices naturally increases.
Switching costs for customers in the paper and packaging distribution industry, like those served by Central National-Gottesman (CNG), are generally considered moderate. If a customer decided to switch from CNG, they would likely need to re-establish relationships with new suppliers, potentially renegotiate terms, and ensure continuity in their supply chain. For instance, a business relying on specific paper grades or packaging solutions might face minor delays or the need to qualify new products from an alternative distributor.
The ease with which customers can find alternative distributors significantly impacts their bargaining power. In 2024, the global paper and packaging market, valued at approximately $1.1 trillion, offers numerous players, making it relatively straightforward for many customers to source similar products from competitors. This accessibility means that if CNG's pricing or service levels were perceived as unfavorable, customers could more readily explore options from other distributors without facing substantial operational disruption.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Central National-Gottesman's customers, particularly large industrial consumers of paper and packaging, possess the potential to integrate backward. This means they could bypass distributors like CNG and source directly from paper mills or even invest in their own distribution networks. In 2024, the trend towards vertical integration across many industries, driven by a desire for cost control and supply chain resilience, makes this a tangible threat.
If significant customers, such as major packaging manufacturers or large printing companies, were to pursue backward integration, their bargaining power over CNG would substantially increase. This would allow them to negotiate lower prices or demand more favorable terms, directly impacting CNG's margins and market position.
- Potential for direct sourcing by large industrial consumers.
- Increased negotiation leverage for customers if they integrate backward.
- Risk of disintermediation for CNG from major clients.
- Industry-wide trend towards vertical integration in 2024.
Information Availability to Customers
Customers today have unprecedented access to information about product prices, quality, and competing suppliers. This transparency, amplified by the digital age, significantly enhances their ability to negotiate favorable terms. For instance, online price comparison tools and customer review platforms, which saw a significant surge in usage in 2024, empower buyers to make well-informed decisions, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
The ease with which consumers can research and compare offerings directly impacts their leverage. In 2024, e-commerce platforms and review sites continued to be primary sources of information, with over 80% of consumers consulting online reviews before making a purchase decision for significant items. This readily available data allows customers to identify the best value and put pressure on sellers to offer competitive pricing and superior quality.
- Information Access: Customers can easily compare prices and product specifications across multiple vendors.
- Digital Empowerment: Online platforms and reviews provide detailed insights into product quality and supplier reliability.
- Negotiating Leverage: Increased information allows customers to demand better terms and pricing.
- Market Transparency: Greater availability of data fosters a more competitive and customer-centric market environment.
Central National-Gottesman's (CNG) customers, especially those in commodity markets like paper and packaging, wield considerable bargaining power due to price sensitivity and the availability of alternatives. In 2024, the global paper and packaging market, valued at approximately $1.1 trillion, offered numerous suppliers, making it easier for buyers to switch if CNG's pricing or service faltered. This ease of switching, coupled with low switching costs for many customers, allows them to demand more favorable terms.
The potential for backward integration by large industrial consumers also significantly boosts customer bargaining power. If major clients, such as large packaging manufacturers, were to source directly from mills or develop their own distribution, their leverage over CNG would increase, potentially impacting margins. Furthermore, enhanced information access in 2024, through online comparison tools and reviews, empowers customers to negotiate better pricing and terms, fostering a more competitive market.
| Factor | Impact on CNG's Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Context/Data |
| Customer Concentration | High concentration of revenue from a few large clients increases their leverage. | If a few clients represent over 10% of sales, their negotiation power is substantial. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers in commodity sectors are highly sensitive to price. | Paper and packaging products often represent a significant cost for buyers, driving price focus. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Numerous suppliers in the market allow customers to easily switch. | Global paper and packaging market valued at ~$1.1 trillion in 2024, offering many distribution options. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs empower customers to seek better deals elsewhere. | Minimal disruption for customers switching paper grades or packaging solutions. |
| Potential for Backward Integration | Customers can bypass distributors by sourcing directly or building internal capabilities. | Vertical integration trend in 2024 makes this a tangible threat for cost control and resilience. |
| Information Transparency | Easy access to pricing and supplier information enhances negotiation leverage. | Over 80% of consumers consult online reviews before significant purchases in 2024. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Central National-Gottesman Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Central National-Gottesman Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate usability.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Central National-Gottesman operates in a global market for pulp, paper, packaging, tissue, and wood products that features a substantial number of competitors. While specific market share data for all players is fragmented, the industry is characterized by both large, established multinational corporations and numerous smaller, regional distributors, creating a diverse competitive landscape.
The diversity among these competitors is significant. Some focus on specific product niches like fine papers or specialty packaging, while others offer a broad portfolio. Geographic reach also varies widely, from companies with a truly global footprint to those concentrating on particular continents or even single countries, influencing the intensity and nature of rivalry in different markets.
The global pulp, paper, packaging, tissue, and wood products distribution industry experienced a moderate growth rate in recent years. For instance, the global packaging market was valued at approximately $1.1 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4.5% through 2030. This indicates a generally expanding market, which can temper the intensity of competitive rivalry as companies can pursue growth through market expansion rather than solely through aggressive market share capture.
Central National-Gottesman operates in markets where product differentiation can vary significantly. In some segments, like standard paper grades, offerings are largely undifferentiated, intensifying competition on price. For instance, the global paper and pulp market, valued at approximately $340 billion in 2023, often sees price as a primary competitive lever.
However, the company also engages in areas where differentiation is more pronounced. By offering specialized paper products, tailored logistics, and value-added services, Central National-Gottesman can reduce direct price-based competition. This is crucial as the demand for sustainable and specialty papers continues to grow, allowing for premium pricing and stronger customer loyalty.
Exit Barriers
Central National-Gottesman, like many in the paper and packaging distribution sector, faces significant exit barriers. These barriers can trap companies in an industry even when profitability wanes, leading to intensified competition. For instance, the need for specialized warehousing and logistics infrastructure, including temperature-controlled storage and efficient transportation networks, represents a substantial sunk cost. Once these assets are in place, divesting them without significant loss is challenging.
The industry also often involves long-term supply agreements and customer contracts. Breaking these commitments can result in penalties or reputational damage, making a clean exit difficult. In 2024, the paper and packaging industry continued to grapple with fluctuating demand and raw material costs, exacerbating the impact of these exit barriers. Companies may find themselves compelled to continue operations, even at reduced margins, to avoid the substantial costs associated with ceasing operations, such as severance packages, lease terminations, and asset write-downs.
The implications of high exit barriers for Central National-Gottesman include the potential for persistent overcapacity. When firms cannot easily leave the market, they may continue to supply products even if demand is low, leading to price wars. This dynamic can suppress overall industry profitability.
- High Capital Investment: Specialized machinery for handling and processing various paper grades and packaging materials requires significant upfront investment, making it difficult to recoup costs upon exit.
- Long-Term Contracts: Existing agreements with suppliers and major clients often lock distributors into operations for extended periods, penalizing early termination.
- Brand Reputation and Relationships: The established trust and relationships built over years with both suppliers and customers are assets that are hard to transfer or sell, discouraging a complete withdrawal.
- Inventory Management: Holding diverse and often bulky inventory of paper and packaging products necessitates substantial warehousing and logistics, which can be costly to liquidate or repurpose.
Strategic Stakes
Central National-Gottesman operates in the paper and packaging industry, a sector where strategic stakes are quite high for many participants. Companies view their presence here not just as a standalone business, but as a crucial component of their broader material supply chains or a gateway to diverse end markets. This perception fuels a drive for market share, even if it means accepting lower margins in the short term.
The intensity of competition is directly linked to how vital this industry is perceived by major players. For instance, if a large conglomerate sees paper and packaging as essential for its diversified portfolio, it's likely to invest heavily and compete fiercely. This strategic importance can lead to sustained, aggressive rivalry, impacting pricing and innovation across the board.
- Strategic Importance Drives Aggression: Companies prioritizing paper and packaging for portfolio strength or future expansion will compete more intensely, potentially sacrificing immediate profits for long-term market positioning.
- Impact on Profitability: This strategic imperative can result in sustained, heightened rivalry, influencing pricing strategies and the overall profitability of the sector.
- Market Share Focus: A key driver of this intense competition is the desire to capture and maintain significant market share, seen as vital for overall business health.
Competitive rivalry within the paper and packaging distribution sector is significant, driven by a large number of players ranging from global corporations to smaller regional firms. This diverse competitive landscape means that while some competitors focus on niche products, others offer a broad range, and their geographic reach also varies greatly, influencing the intensity of competition in different markets.
The industry's moderate growth, with the global packaging market valued at approximately $1.1 trillion in 2023 and projected to grow at a CAGR of around 4.5% through 2030, can temper aggressive competition as companies can expand into new markets. However, in segments like standard paper grades, competition often centers on price, as seen in the global paper and pulp market, valued at about $340 billion in 2023.
High exit barriers, including substantial investments in specialized logistics and long-term contracts, can trap companies in the market, leading to persistent overcapacity and price wars. For example, the need for specialized warehousing and efficient transportation networks represents significant sunk costs. In 2024, fluctuating demand and raw material costs further complicated exits, forcing companies to continue operations even at lower margins to avoid substantial closure costs.
The strategic importance of the paper and packaging sector for many companies fuels aggressive competition, with a strong focus on market share. This can lead to sustained rivalry and impact overall industry profitability, as businesses may prioritize long-term market positioning over immediate gains.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for pulp, paper, packaging, tissue, and wood products is significant, especially with the rise of digital alternatives. For instance, digital communication and cloud storage directly compete with paper for information dissemination and record-keeping, potentially reducing demand for printing and writing paper. In 2024, the global digital transformation continues to accelerate, impacting traditional paper consumption across various sectors.
Beyond digital, alternative materials pose a threat in the packaging sector. Plastics, advanced composites, and emerging bioplastics offer comparable or even superior performance in certain applications, such as durability and moisture resistance, directly challenging paper-based packaging solutions. The market for sustainable packaging materials, including bioplastics, is projected to see robust growth in the coming years, further intensifying this substitute threat.
Central National-Gottesman (CNG) faces a threat from substitutes that offer a compelling price-performance ratio. For instance, advancements in lightweight packaging materials can reduce shipping costs and environmental impact compared to traditional paper-based solutions, directly impacting CNG's core paper and packaging segments.
The rise of digital solutions, such as electronic invoicing and cloud-based document management, presents another significant substitute threat. These digital alternatives can offer greater efficiency, lower administrative overhead, and enhanced data accessibility than paper-based processes, potentially eroding demand for traditional paper products.
In 2024, the global market for sustainable packaging solutions, a key substitute area, was projected to reach over $350 billion, indicating strong customer preference for environmentally friendly alternatives. This trend highlights the need for CNG to innovate and adapt its product portfolio to remain competitive against these evolving substitutes.
Central National-Gottesman faces a moderate threat from substitutes. Customers are increasingly aware of alternative packaging materials like plastics and reusable containers, driven by environmental concerns and a desire for cost-effectiveness. For instance, the global flexible packaging market, a key substitute, was valued at approximately $270 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow steadily, indicating a significant alternative for many end-users.
Technological Advancements Enabling Substitution
Technological advancements are a significant driver of the threat of substitutes for Central National-Gottesman's core products. Innovations in areas like advanced materials and digital printing can lead to entirely new ways of delivering information and packaging goods, bypassing traditional paper and pulp needs.
For instance, the ongoing development in biodegradable plastics and plant-based packaging materials presents a direct substitute for paper-based packaging solutions. Furthermore, the increasing digitization of content, from e-books to digital advertising, reduces the demand for printed paper products. In 2024, the global digital advertising market was projected to reach over $600 billion, illustrating the ongoing shift away from print media.
Consider these key areas where technological substitution poses a threat:
- Digitalization of Content: Continued growth in e-readers, online publications, and digital communication platforms directly displaces demand for printing and writing paper.
- Advanced Packaging Materials: Innovations in bioplastics, compostable films, and reusable packaging solutions offer alternatives to paper and cardboard in the packaging sector.
- 3D Printing Technologies: Advancements in 3D printing could reduce the need for certain manufactured wood components or printed materials in specific industries.
- Sustainable Material Alternatives: Research into novel materials derived from agricultural waste or algae could create viable substitutes for wood pulp in various applications.
Impact of Substitution on Industry Demand
The threat of substitutes for the products distributed by Central National-Gottesman (CNG) can significantly impact overall industry demand. If readily available and cost-effective alternatives emerge, customers may switch away from traditional paper and packaging products. This shift can lead to a direct reduction in the volume of goods CNG distributes, pressuring its revenue streams and profitability.
For instance, the increasing adoption of digital communication and document management systems directly substitutes for paper products in many office environments. In 2024, global spending on digital transformation initiatives continued to rise, with a significant portion allocated to cloud-based solutions and software that reduce reliance on physical documents. Similarly, advancements in reusable packaging materials and e-commerce fulfillment methods offer alternatives to traditional cardboard and plastic packaging, impacting CNG's core business.
CNG must actively monitor trends in end-user industries to anticipate and respond to these substitution threats. This involves understanding how customer needs are evolving and identifying emerging technologies or materials that could displace the products they currently supply. For example, the push for sustainability and reduced environmental impact is driving innovation in biodegradable and compostable packaging, which could eventually substitute for conventional options.
- Digitalization Impact: Continued growth in digital alternatives for paper-based communication and record-keeping directly erodes demand for traditional paper products.
- Packaging Innovation: The rise of reusable, biodegradable, and alternative packaging materials poses a significant threat to conventional paper and board packaging distribution.
- End-User Industry Shifts: Changes in consumer behavior and business practices, such as increased e-commerce and a focus on sustainability, drive demand for substitute products.
- Adaptation Necessity: CNG's long-term viability depends on its ability to adapt its product portfolio and distribution strategies to address the evolving threat of substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Central National-Gottesman's products is considerable, driven by both digital advancements and material innovations. For instance, the global market for sustainable packaging, a direct substitute for paper-based solutions, was projected to exceed $350 billion in 2024, underscoring a significant shift in consumer and industry preferences. Digital communication platforms continue to reduce the need for printing and writing paper, with global spending on digital transformation initiatives rising in 2024, further impacting traditional paper demand.
| Substitute Category | Key Examples | 2024 Market Insight | Impact on CNG |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digitalization | E-books, cloud storage, digital advertising | Global digital advertising market projected over $600 billion | Reduced demand for printing and writing paper |
| Alternative Packaging | Bioplastics, reusable containers, advanced composites | Global flexible packaging market valued around $270 billion in 2023 | Competition for paper and board packaging |
| Material Science | Biodegradable films, agricultural waste-based materials | Growth in sustainable packaging solutions | Potential displacement of wood pulp in certain applications |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the global distribution of pulp, paper, packaging, tissue, and wood products demands substantial capital. Significant investments are needed for inventory, extensive warehousing facilities, and robust logistics infrastructure. For instance, major players like International Paper, a significant competitor in these sectors, reported capital expenditures of $1.7 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of investment required to maintain and expand operations.
The need for substantial working capital to manage fluctuating inventory levels and extended payment terms further acts as a barrier. Central National-Gottesman's global presence implies that any new entrant would need to match this scale, necessitating even higher upfront capital outlays to compete effectively in international markets.
Central National-Gottesman (CNG) leverages significant economies of scale in its purchasing power for paper and packaging products. This allows them to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers, a crucial advantage that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly. For instance, in 2024, major paper and packaging manufacturers reported substantial cost savings through bulk procurement, often exceeding 10% compared to smaller volume buyers.
The logistical efficiencies gained through CNG's established global network also present a formidable barrier. Managing complex international shipping routes and warehousing effectively requires substantial investment and expertise. New competitors would face considerable upfront costs to build a comparable distribution infrastructure, impacting their ability to compete on price from the outset.
Achieving the same level of global reach and operational scale as CNG would necessitate massive capital investment and a lengthy period of market penetration. This makes it exceptionally difficult for new entrants to achieve cost parity, as they would lack the established relationships and optimized supply chains that provide CNG with a competitive edge in pricing and service delivery.
Newcomers often struggle to gain access to established distribution channels, a critical hurdle for Central National-Gottesman (CNG). CNG's extensive global network, built over decades, provides a significant advantage. For instance, in 2024, the paper and packaging industry saw continued consolidation, making it even harder for smaller, new entities to secure shelf space or reliable logistics.
Securing strong supplier relationships is another formidable barrier. CNG benefits from long-standing partnerships with key pulp and paper producers, ensuring consistent supply and favorable terms. Replicating these deep, trust-based relationships, which often involve volume commitments and shared R&D, is a time-consuming and capital-intensive endeavor for any potential entrant.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and regulations significantly shape the threat of new entrants in the pulp and paper distribution sector. For instance, in 2024, the European Union's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) could impose additional costs on imported pulp and paper products, potentially deterring new foreign entrants who may not have established efficient carbon management systems. Similarly, stringent environmental regulations regarding waste disposal and emissions, such as those enforced by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), require substantial upfront investment in compliance technology, creating a barrier for smaller, less capitalized new players.
Trade agreements and tariffs also play a crucial role. In 2024, ongoing trade tensions and the potential for new tariffs on paper products between major economic blocs can increase the cost of doing business for new entrants, especially those relying on international sourcing or export markets. Licensing requirements, while sometimes straightforward, can also add complexity and cost. For example, obtaining necessary permits for warehousing and transportation in different jurisdictions can be a time-consuming and expensive process, effectively limiting the speed and ease with which new competitors can enter the market.
- Tariffs and Trade Barriers: In 2024, the imposition of tariffs on specific paper grades by countries like India could increase import costs, making it harder for new foreign distributors to compete with domestic suppliers.
- Environmental Compliance Costs: Meeting evolving environmental standards, such as those related to sustainable forestry certifications and chemical usage, requires significant investment in operational changes and audits, which can be a substantial hurdle for new entrants.
- Licensing and Permitting: Obtaining necessary distribution licenses and transportation permits across various regions in 2024 can involve lengthy approval processes and fees, adding to the initial capital expenditure for new market participants.
- Subsidies and Incentives: Government incentives for domestic production or specific types of paper products can distort the market, making it more challenging for new entrants that do not qualify for these benefits.
Brand Loyalty and Differentiation
Central National-Gottesman (CNG) and other established distributors benefit from significant brand loyalty, built over years of reliable service and specialized product offerings. This makes it challenging for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, in the paper and packaging distribution sector, customer retention rates can be exceptionally high, often exceeding 90% for key accounts that value consistent quality and delivery performance.
The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by the high switching costs associated with changing distributors. Customers often have established relationships, integrated supply chains, and specific product specifications tied to their current suppliers. In 2024, reports indicated that for many industrial supply chains, the cost of re-qualifying a new supplier could range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the complexity of the products and processes involved.
- High Customer Retention: Established distributors like CNG often boast customer retention rates that are a significant barrier to entry, reflecting deep-seated trust and satisfaction.
- Switching Costs: The financial and operational implications of switching distributors are substantial, deterring potential customers from engaging with new market participants.
- Reputation and Trust: Building a reputation for reliability and quality in the distribution sector is a long-term endeavor, giving incumbents a distinct advantage over nascent competitors.
The threat of new entrants into the pulp, paper, and packaging distribution sector is considerably low due to immense capital requirements for inventory, warehousing, and logistics. For example, major industry players reported substantial capital expenditures in 2023, underscoring the scale of investment needed to compete. Furthermore, established players like Central National-Gottesman (CNG) benefit from strong economies of scale in purchasing and established global distribution networks, making it difficult for newcomers to achieve cost parity or match logistical efficiencies.
The industry also presents significant barriers related to securing established distribution channels and building strong supplier relationships, which are crucial for consistent supply and favorable terms. In 2024, market consolidation has further tightened access to these channels. Additionally, government regulations, including environmental compliance and trade policies, add complexity and cost, requiring substantial upfront investment that deters smaller, less capitalized entrants.
Customer loyalty and high switching costs further solidify the position of incumbents. In 2024, customer retention rates for key accounts in paper and packaging distribution often exceed 90%, as businesses value consistent quality and delivery. The financial and operational implications of re-qualifying a new supplier can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, creating a substantial deterrent for potential customers considering new distributors.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for inventory, warehousing, and logistics. | Major players' capital expenditures exceeded $1.7 billion in 2023. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower costs through bulk purchasing and optimized supply chains. | Bulk procurement savings often exceed 10% compared to smaller buyers in 2024. |
| Distribution Channels | Access to established networks is difficult for new entrants. | Industry consolidation in 2024 made securing shelf space harder. |
| Supplier Relationships | Long-term partnerships ensure supply and favorable terms. | Replicating deep, trust-based relationships is time-consuming and capital-intensive. |
| Customer Loyalty/Switching Costs | High retention rates and significant costs to change suppliers. | Customer retention rates often exceed 90% for key accounts; switching costs can reach hundreds of thousands of dollars. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Central National-Gottesman Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and trade publications to capture the nuances of competitive dynamics.