Compagnie Industriali Riunite Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Compagnie Industriali Riunite Bundle
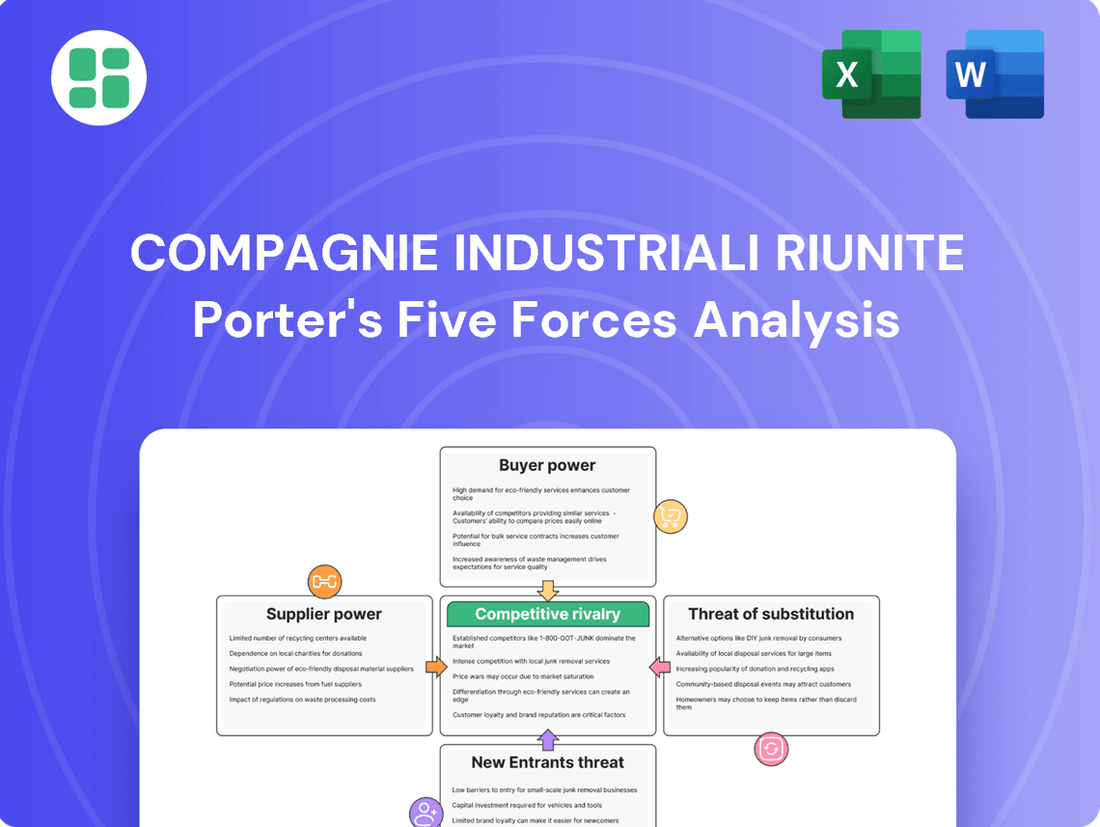
Understanding the competitive landscape for Compagnie Industriali Riunite through Porter's Five Forces reveals the intricate interplay of industry forces. This analysis highlights the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats posed by new entrants and substitutes. These factors collectively shape the profitability and strategic direction of the company.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Compagnie Industriali Riunite’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) varies significantly across its diverse sectors. In the automotive segment, while there are numerous component manufacturers globally, the supply of highly specialized or patented parts, such as advanced engine control units or unique composite materials, might be concentrated among a few key players. This can give these suppliers considerable leverage, especially if CIR relies heavily on their specific innovations.
Similarly, in the healthcare sector, the procurement of advanced medical devices, critical pharmaceuticals, or specialized diagnostic equipment often involves a limited number of highly regulated and technologically advanced manufacturers. For instance, a specific type of surgical robot or a novel drug formulation might only be available from one or two global leaders. This concentration directly translates to increased bargaining power for these suppliers, potentially impacting CIR's procurement costs and supply chain stability.
While the media sector might appear more fragmented, the supply of critical digital infrastructure, specialized content creation software, or exclusive distribution rights can also be concentrated. For example, if CIR’s media operations depend on a unique streaming technology or a particular content licensing agreement controlled by a few entities, those suppliers would possess significant bargaining power.
Switching suppliers for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) involves significant costs across its diverse business segments, directly impacting the bargaining power of its current suppliers. For instance, in the automotive components sector, CIR might face substantial expenses related to retooling production lines if it were to change suppliers for specialized materials or machinery. This investment in new equipment and recalibration of existing processes can easily run into millions of euros, making a swift switch economically prohibitive.
The healthcare IT segment presents another area where switching costs are considerable. Implementing new IT systems often requires extensive staff retraining, data migration, and integration with existing hospital infrastructure. For example, a change in a core electronic health record system supplier could necessitate months of training for hundreds of medical professionals and IT staff, alongside complex data conversion processes that carry the risk of information loss or corruption. These operational disruptions and training expenses empower existing IT solution providers.
Conversely, in segments where CIR sources more commoditized raw materials, switching costs might be relatively lower. However, even here, establishing new relationships, ensuring consistent quality, and potentially renegotiating bulk purchase agreements can incur time and administrative burdens. CIR's 2024 financial reports indicate a strategic focus on supply chain optimization, suggesting an awareness of these costs and an effort to mitigate them through long-term supplier partnerships where feasible.
The uniqueness of inputs significantly influences supplier bargaining power for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR). If CIR relies on suppliers providing highly specialized or proprietary components, such as advanced composite materials for its automotive sector or unique chemical formulations for its industrial applications, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. For instance, a supplier of a critical, patent-protected automotive sensor that enhances vehicle safety and performance would command higher prices and more favorable terms.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Compagnie Industriali Riunite's (CIR) core businesses, such as healthcare services, automotive components, or media, could significantly alter the competitive landscape. If suppliers possess the financial muscle and strategic foresight, they might decide to bypass CIR and directly serve the end customers. This would transform them from mere suppliers into direct competitors, intensifying rivalry and potentially eroding CIR's market share.
This forward integration risk is particularly pronounced if a supplier's current offerings represent a substantial component of CIR's value chain. For instance, a key supplier of specialized medical equipment to CIR's healthcare division might consider launching its own service provision arm. In 2024, the healthcare services sector saw significant investment, with global healthcare spending reaching an estimated $10 trillion, indicating a lucrative market for potential entrants.
- Supplier Capability: Assess if key suppliers have the financial resources and operational expertise to enter CIR's markets.
- Market Attractiveness: Evaluate the profitability and growth potential of CIR's sectors, which could incentivize supplier integration.
- Value Chain Dependence: Determine how critical a supplier's product is to CIR's overall product or service offering.
- Competitive Intensity: Consider how many other players exist in CIR's markets, which could either deter or attract new entrants.
Importance of CIR to Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by their reliance on Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) as a customer. If CIR constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's total sales, that supplier's ability to dictate terms or raise prices is diminished. This is because the supplier would be more dependent on maintaining the relationship with CIR for its own financial stability.
Conversely, if CIR represents only a minor segment of a supplier's customer base, the supplier holds more leverage. In such scenarios, the supplier is less vulnerable to losing business if negotiations falter and can more readily exert pressure on CIR regarding pricing, quality, or delivery schedules. This dynamic is a key consideration in assessing the overall bargaining power within the supply chain.
- Supplier Dependence: If CIR accounts for a large percentage of a supplier's revenue, the supplier's bargaining power decreases.
- CIR's Market Share: A supplier serving many customers, with CIR being a small one, gains stronger bargaining power.
- Impact on Terms: Higher supplier dependence on CIR can lead to more favorable terms for CIR, reducing supplier influence.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) is a critical factor, influenced by supplier concentration and the uniqueness of their offerings. When few suppliers dominate the market for essential components, or when those components are highly specialized and patented, their leverage increases significantly.
Switching costs also play a crucial role; high expenses associated with changing suppliers, such as retooling or extensive retraining, empower existing providers. For example, in 2024, the automotive sector saw continued investment in advanced manufacturing, highlighting the potential for high switching costs when integrating new specialized parts.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into CIR's business operations, particularly in lucrative sectors like healthcare services where global spending neared $10 trillion in 2024, presents another avenue for increased supplier power. Conversely, if CIR represents a large portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier's bargaining power is reduced.
| Factor | Impact on CIR's Bargaining Power | Example Scenario |
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases supplier power. | A single supplier for a patented automotive sensor. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs empower suppliers. | Retooling production lines for new automotive components. |
| Input Uniqueness | Unique inputs grant suppliers leverage. | Proprietary chemical formulations for industrial applications. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Increases supplier power. | Medical equipment supplier entering healthcare services. |
| Supplier Dependence on CIR | Low dependence increases supplier power. | CIR is a small client for a large component manufacturer. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Compagnie Industriali Riunite, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products on its profitability.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats by visualizing Compagnie Industriali Riunite Porter's Five Forces with a dynamic, interactive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer concentration within Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) significantly impacts its bargaining power. In its automotive components division, a few major global car manufacturers often represent a substantial portion of sales. For instance, in 2024, it's estimated that the top three automotive clients could account for over 40% of that segment's revenue, giving them considerable leverage in price negotiations.
Similarly, in the healthcare services sector, large hospital networks or government health bodies act as key customers. If CIR's medical device or service contracts are heavily weighted towards a handful of these entities, their ability to demand better terms or switch suppliers increases. This concentration is a critical factor in assessing customer bargaining power across CIR's diverse operations.
The price sensitivity of customers for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) varies significantly across its diverse business segments. In healthcare, where public funding and insurance play a major role, price sensitivity can be moderated as third parties often bear a substantial portion of the cost. However, for direct-to-consumer offerings or specific medical devices, price remains a key consideration.
Within the automotive sector, CIR's position as a supplier means its customers, primarily large manufacturers, are highly attuned to pricing. These manufacturers face intense market competition and often pass cost pressures down their supply chains. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry continued to grapple with rising material costs, forcing component suppliers like CIR to offer competitive pricing to maintain order volumes.
For CIR's media operations, the widespread availability of free or low-cost digital content directly impacts consumer price sensitivity. This makes advertising revenue, often a primary income stream, vulnerable to shifts in audience engagement driven by price perceptions of premium content or services. The digital advertising market in 2024 saw continued pressure on CPMs (cost per mille), reflecting this underlying price sensitivity.
The availability of substitutes significantly impacts Compagnie Industriali Riunite's (CIR) customer bargaining power. If CIR's diverse customer base, spanning healthcare, automotive, and media sectors, can easily find comparable products or services elsewhere, their ability to negotiate better terms or switch providers intensifies. For instance, in the automotive components sector, if suppliers offer similar quality parts at lower prices, CIR faces pressure to match those offerings.
This heightened bargaining power necessitates that CIR consistently focuses on competitive pricing and superior quality across its various business segments. In 2023, the global automotive components market was valued at approximately $1.5 trillion, with numerous players offering a wide array of parts, underscoring the competitive landscape CIR operates within. Similarly, in healthcare services, the proliferation of private clinics and specialized medical centers provides patients with more choices, thereby strengthening their negotiating position.
Customer Switching Costs
Customer switching costs for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) are a critical factor influencing their bargaining power. If customers can easily move to a competitor with minimal effort or expense, their ability to demand lower prices or better terms increases significantly.
Conversely, when switching involves substantial costs, such as retraining personnel, integrating new systems, or losing accumulated benefits, customer power is diminished. For CIR, understanding these costs is key to managing customer relationships and pricing strategies.
For example, if CIR operates in sectors where its products are deeply integrated into a customer's production process, like specialized industrial components, the cost to switch suppliers would likely be high. This could involve retooling, extensive testing, and potential disruption to operations. In such scenarios, CIR would have greater leverage.
- High switching costs like those in complex B2B supply chains reduce customer bargaining power.
- Low switching costs, common in consumer goods, empower customers to demand better terms.
- CIR's specific industry segments will dictate the magnitude of these costs.
- In 2024, many industrial sectors reported increased efforts to lock in suppliers due to supply chain volatility, potentially raising switching costs for customers.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) hinges on the capacity of its clients to produce its offerings internally. This is especially pertinent for large, well-resourced customers in sectors like healthcare or automotive who could potentially develop their own healthcare services, automotive components, or even media content, thereby diminishing their need for CIR's specialized services.
For instance, a major healthcare provider might consider developing in-house capabilities for certain diagnostic or therapeutic services that CIR currently supplies. Similarly, a large automotive manufacturer could explore producing specialized components internally if the cost-benefit analysis favors self-sufficiency over relying on external suppliers like CIR. This strategic move by customers directly impacts CIR's revenue streams and market position.
- Customer Size and Resources: CIR's customers, particularly large corporations, possess the financial clout and technical expertise to invest in backward integration.
- Industry Dynamics: In industries where proprietary technology or specialized manufacturing processes are involved, customers may see a strategic advantage in internalizing these functions.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Customers will weigh the costs of internal production against the current costs of sourcing from CIR, considering factors like economies of scale and quality control.
- Market Concentration: If CIR serves a limited number of large clients, the potential for any single client to integrate backward poses a more significant threat.
The bargaining power of customers for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) is a crucial element in understanding its competitive landscape. When customers are concentrated, highly price-sensitive, have many substitutes available, face low switching costs, or can integrate backward, their ability to negotiate favorable terms with CIR increases substantially.
For CIR, managing these customer dynamics is key. For example, in 2024, the automotive sector continued to see intense price pressure, with major manufacturers leveraging their scale to negotiate component prices. This directly impacts CIR's profitability in that segment.
Conversely, in healthcare, while price sensitivity exists, factors like regulatory compliance and specialized technology can sometimes limit customer power, especially if switching costs are high due to integration with existing medical systems.
CIR's strategy must therefore balance offering competitive pricing and quality with building customer loyalty through differentiated offerings and managing switching costs effectively across its diverse portfolio.
| Factor | Impact on CIR | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High concentration = High bargaining power | Top 3 automotive clients potentially >40% of segment revenue. |
| Price Sensitivity | High sensitivity = High bargaining power | Automotive sector faces cost pressures; digital media CPMs under pressure. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Many substitutes = High bargaining power | Automotive components market highly competitive; numerous digital content options. |
| Switching Costs | Low costs = High bargaining power | High for integrated industrial components, low for consumer-facing media. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | High threat = High bargaining power | Large clients in healthcare/automotive may explore internal production. |
What You See Is What You Get
Compagnie Industriali Riunite Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Compagnie Industriali Riunite provides an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape, including threats of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You'll gain actionable insights into the strategic positioning and future outlook of the company.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) operates in diverse sectors, each with a unique competitive landscape. The Italian healthcare market, for instance, is characterized by a mix of public and private entities, with growth driven by an aging population and increased health awareness. This sector sees competition from both large, established private hospital groups and smaller, specialized clinics.
In the European automotive components market, CIR faces intense rivalry from global manufacturers and a growing number of regional players. This segment is grappling with technological shifts, such as the move towards electric vehicles, which introduces new competitors and necessitates significant investment in research and development. Profitability pressures are a constant concern due to fluctuating raw material costs and intense price competition.
The media industry, where CIR has interests, is highly fragmented. It includes traditional broadcasters and publishers competing with a vast array of digital-native companies and streaming services. This dynamic environment demands continuous adaptation to evolving consumer preferences and advertising models, with companies like Vivendi and Sky remaining significant players in the broader European media space.
Industry growth rate significantly influences competitive rivalry. For instance, the Italian healthcare sector is expected to see robust expansion, creating opportunities for all players and potentially dampening intense competition.
Conversely, the European automotive components industry is experiencing stagnation, which often fuels more aggressive competition as companies fight for a shrinking or slow-growing market.
The Italian media market presents a mixed picture; while digital segments are growing, traditional print media is declining, leading to varied competitive pressures across sub-sectors.
Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) operates in sectors where differentiation is a significant factor. In healthcare, specialized medical services and cutting-edge technology, as seen in its Mediobanca stake which has exposure to healthcare investments, can create strong customer loyalty and pricing power.
In the automotive components sector, where CIR has historical interests, technological innovation and superior quality are paramount for distinguishing products from competitors. This focus on advanced features and reliability is crucial for maintaining market share and commanding premium pricing.
The media industry, a segment where CIR has had significant involvement, relies heavily on unique content creation and personalized user experiences to stand out in a crowded digital environment. Differentiated offerings are key to capturing and retaining audience attention, driving revenue growth.
Exit Barriers
Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) operates in sectors where exit barriers can significantly influence competitive intensity. High exit barriers mean that companies find it difficult and costly to leave the market, even when facing poor financial performance. This can trap resources and perpetuate overcapacity, leading to sustained pressure on pricing and profitability for all players, including CIR.
Factors contributing to high exit barriers for CIR might include:
- Specialized Assets: The presence of highly specific machinery or production facilities that have limited alternative uses can make it prohibitively expensive to divest or repurpose them. For instance, if CIR has invested heavily in unique paper-making machinery, selling it off without a substantial loss would be challenging.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant ongoing fixed costs, such as long-term leases, contractual obligations, or substantial decommissioning expenses for industrial sites, can make exiting the market financially punitive. These costs must be absorbed or paid out, even if operations cease.
- Emotional and Strategic Commitments: Sometimes, companies or their management have deep-seated emotional or strategic ties to a particular business line or market, making it difficult to let go even when it's no longer strategically sound. This loyalty can prolong the presence of underperforming competitors.
Strategic Stakes
The strategic importance of industries for participants significantly fuels competitive rivalry. If companies like Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) view their involvement in sectors such as healthcare, automotive, or media as fundamental to their long-term vision and brand image, they are likely to engage in more intense competition. This can manifest as a willingness to accept lower short-term profits to maintain market share or achieve strategic objectives.
For instance, in 2024, the automotive sector saw significant investment and aggressive competition driven by the transition to electric vehicles. Major players, including those with diversified interests like CIR might have, committed billions to R&D and new manufacturing capabilities. This strategic imperative to lead in electrification means companies are less likely to back down from competitive pressures, even if it impacts immediate financial returns.
- Strategic Imperative: Companies may prioritize market position and technological leadership in key sectors over immediate profitability.
- Reputational Stakes: Presence in high-profile industries like automotive or media can be crucial for a company's overall reputation and brand perception.
- Sustained Aggression: This strategic importance often leads to sustained high levels of rivalry, with companies willing to invest heavily to defend or expand their presence.
The intensity of competitive rivalry for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) is shaped by industry growth rates and differentiation opportunities. In 2024, the automotive components sector, facing slower growth, intensified competition as firms fought for market share, particularly with the ongoing EV transition. Conversely, the expanding Italian healthcare market offered more room for growth, potentially moderating direct rivalry, though specialization remains key to competitive advantage.
High exit barriers, such as specialized assets and significant fixed costs, can trap companies in CIR's operating sectors, perpetuating rivalry even in less profitable periods. For example, the substantial capital investment required for advanced manufacturing in automotive components can make exiting difficult. This strategic importance, as seen in the automotive sector's 2024 push for EV leadership, encourages sustained aggressive competition, with companies prioritizing market position over immediate profits.
| Sector | 2024 Growth Expectation | Differentiation Factor | Rivalry Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Italian Healthcare | Robust Expansion | Specialized Services, Technology | Moderate to High |
| European Automotive Components | Stagnant to Slow Growth | Technological Innovation, Quality | High |
| European Media | Mixed (Digital Growth, Print Decline) | Unique Content, User Experience | High to Very High |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) hinges on the price-performance trade-off. For instance, in sectors where CIR operates, like industrial components, emerging material technologies or advanced manufacturing processes might offer similar functionalities at a lower cost or with improved efficiency. For example, advancements in additive manufacturing could provide alternatives to traditional machined parts, impacting demand for CIR's established product lines if the cost savings are significant and performance is comparable.
Customer propensity to substitute is a key factor in understanding competitive pressures. In the healthcare sector, for instance, while an aging population and the rise of chronic diseases continue to drive demand for established medical services, there's a noticeable uptick in digital health adoption. This digital shift presents a potential substitute for traditional in-person consultations and treatments, with telehealth services seeing significant growth. For example, in 2024, the global telehealth market was projected to reach over $200 billion, indicating a strong customer willingness to explore alternative delivery methods for care.
Similarly, the media industry exemplifies a high propensity for substitution. Consumers are rapidly migrating from traditional print publications and linear television to on-demand streaming services and digital news sources. This trend is dramatically reshaping the media landscape. By the end of 2023, global spending on subscription video-on-demand services alone surpassed $100 billion, demonstrating a clear customer preference for more flexible and personalized content consumption, thereby substituting older media formats.
The media and publishing industry faces a substantial threat from digital alternatives. Streaming services like Netflix and Disney+, alongside platforms for user-generated content such as YouTube and TikTok, offer compelling substitutes for traditional print newspapers, magazines, and broadcast television. These digital options often provide content at a lower price point, or even for free, and boast greater convenience and personalization, drawing audiences away from legacy media. In 2024, digital advertising spending is projected to reach over $600 billion globally, a clear indicator of where consumer attention and advertiser budgets are shifting.
Technological Advancements Enabling Substitutes
Technological advancements are a significant driver in creating more effective or cost-efficient substitutes for existing products and services. For instance, the rapid development of artificial intelligence in healthcare diagnostics offers a prime example. AI algorithms can analyze medical images with remarkable speed and accuracy, potentially reducing the reliance on certain traditional diagnostic methods or even specialized personnel.
The integration of AI within the Italian healthcare sector is already demonstrating this trend. By enhancing diagnostic capabilities, AI is paving the way for new care models that could substitute or augment established approaches. This evolution means that companies must continually assess how emerging technologies can disrupt their markets by offering compelling alternatives to their current offerings.
Consider the following impacts:
- AI in diagnostics: Studies indicate AI can achieve diagnostic accuracy comparable to or exceeding human experts in specific areas, potentially lowering costs and increasing accessibility. For example, AI models for detecting diabetic retinopathy have shown high performance metrics.
- New materials: Advances in material science, such as lightweight composites in automotive manufacturing, offer substitutes for traditional steel, improving fuel efficiency and performance. The automotive industry in Europe, for instance, is increasingly adopting these materials.
- Digitalization of services: The widespread adoption of digital platforms allows for remote service delivery, substituting in-person interactions in sectors like finance and education. In Italy, the push for digital transformation in public services aims to achieve greater efficiency and reach.
- Biotechnology: Innovations in biotechnology can lead to substitutes for traditional pharmaceuticals or agricultural products, offering more targeted treatments or sustainable farming solutions.
Regulatory or Policy Changes Favoring Substitutes
Government policies can significantly shift the competitive landscape by making substitutes more attractive. For example, in 2024, continued emphasis on renewable energy sources through tax credits and subsidies in many developed nations directly bolsters the viability of solar and wind power as substitutes for traditional fossil fuels in electricity generation.
Stricter environmental regulations, such as those targeting carbon emissions, can also elevate the threat of substitutes. Companies heavily reliant on carbon-intensive processes or products may find their markets shrinking as greener alternatives become more cost-effective and compliant with new mandates. This was evident in 2024 with ongoing discussions and implementations of carbon pricing mechanisms in various regions.
Consider the automotive sector: policies promoting electric vehicle (EV) adoption, including purchase incentives and charging infrastructure investments, directly challenge the market for internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. By 2024, many governments had set ambitious targets for EV sales, thereby increasing the attractiveness and availability of EVs as substitutes.
- Regulatory Favoritism: Policies like subsidies for renewable energy or EV tax credits make substitutes more competitive.
- Emissions Standards: Stricter environmental rules can penalize traditional products, pushing consumers towards cleaner substitutes.
- Infrastructure Investment: Government backing for substitute-related infrastructure, like EV charging networks, enhances their adoption.
- Market Transformation: These policy shifts can accelerate the transition away from incumbent products, increasing the threat of substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) is amplified by evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements, particularly in sectors like media and healthcare. Digital platforms and AI-driven solutions are increasingly offering cost-effective and convenient alternatives to traditional offerings, forcing companies to adapt. For instance, the global telehealth market was projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024, highlighting a significant shift in healthcare consumption patterns.
In the media industry, the migration to streaming services and digital news sources is pronounced, with global spending on subscription video-on-demand services surpassing $100 billion by the end of 2023. This trend underscores the growing customer willingness to embrace personalized and on-demand content, directly impacting traditional media formats. Digital advertising spending, projected to reach over $600 billion globally in 2024, further illustrates this shift in consumer attention and advertiser investment.
Technological innovation, especially in areas like AI in diagnostics and new materials in manufacturing, presents powerful substitutes. AI models are demonstrating diagnostic accuracy comparable to human experts, potentially reducing reliance on traditional methods. Similarly, advancements in lightweight composites are reshaping the automotive sector, with European manufacturers increasingly adopting these materials as alternatives to steel.
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the substitute landscape. Subsidies for renewable energy and incentives for electric vehicles (EVs) in 2024, for example, directly enhance the competitiveness of these alternatives to fossil fuels and internal combustion engine vehicles. Stricter environmental regulations also push consumers and industries towards greener substitutes, accelerating market transformations.
| Industry Sector | Key Substitute | Impact on Traditional Offerings | Relevant 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Media & Publishing | Streaming Services, Digital News Platforms | Reduced demand for print and broadcast media | Digital ad spending projected > $600B globally |
| Healthcare | Telehealth, AI Diagnostics | Shift from in-person consultations, potential for AI accuracy | Telehealth market projected > $200B globally |
| Automotive | Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Challenge to Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) vehicles | Ambitious government EV sales targets |
| Manufacturing | Advanced Materials (e.g., composites) | Potential replacement for traditional materials (e.g., steel) | Increased adoption in European automotive industry |
Entrants Threaten
The capital required to enter Compagnie Industriali Riunite's (CIR) diverse sectors presents a significant barrier. Establishing healthcare services, particularly building and equipping state-of-the-art medical facilities, demands immense financial investment. Similarly, the automotive component manufacturing industry necessitates substantial upfront capital for machinery, research and development, and production lines. For instance, setting up a new automotive parts plant can easily cost tens of millions of euros.
The complexity and stringency of regulations and licensing requirements present a significant barrier to entry. For instance, the automotive components sector demands adherence to rigorous safety and quality standards, such as ISO/TS 16949, which can be costly and time-consuming for new players to achieve.
Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) and its subsidiaries likely benefit significantly from economies of scale and accumulated experience, particularly in sectors like automotive components. Established players in this industry leverage optimized production processes and bulk purchasing power, making it challenging for newcomers to match their cost efficiencies. For instance, in 2024, the automotive supplier market continued to be dominated by large, integrated players who benefit from long-term contracts and advanced manufacturing techniques, creating a high barrier to entry for smaller, less experienced firms.
Brand Loyalty and Differentiation
Brand loyalty and product differentiation significantly impact the threat of new entrants for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR). In sectors like healthcare services, cultivating a trusted brand and reputation for quality requires substantial, long-term investment, creating a formidable barrier for newcomers aiming to quickly capture market share. Similarly, in automotive components, a proven track record of reliability and performance is crucial, making it difficult for new players to displace established suppliers with strong customer relationships.
The media sector presents a different challenge, where established brands often contend with agile, digital-native entities that can rapidly build audiences and offer specialized content. For CIR, this means that while brand loyalty is a defense, continuous innovation and adaptation are necessary to counter the threat posed by more nimble competitors. In 2023, for instance, the global media market saw continued growth in digital advertising, highlighting the shift in consumer preferences and the need for traditional players to adapt their strategies.
- Brand Loyalty in Healthcare: Building trust in healthcare services is paramount; a strong reputation for patient care and outcomes can deter new entrants.
- Product Differentiation in Automotive: CIR's automotive component divisions likely rely on technological innovation and quality certifications to maintain customer loyalty.
- Digital Disruption in Media: The media landscape is vulnerable to new entrants leveraging digital platforms, challenging established brand recognition and reach.
- Investment in Brand Building: Significant capital expenditure is often required to establish and maintain a strong brand presence, acting as a deterrent to potential competitors.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
The automotive sector, for instance, presents significant hurdles for newcomers due to its intricate and established supply chains. New entrants often struggle to secure reliable access to essential components, a challenge amplified by ongoing shortages. In 2024, the persistent scarcity of semiconductors and other critical parts continued to impact production volumes for many manufacturers, making it difficult for unproven entities to establish consistent output and market presence.
Similarly, in the healthcare industry, gaining access to effective distribution channels for services or products is a substantial barrier. New providers may find it difficult to establish partnerships with insurers, hospitals, or pharmacies, which are often locked into long-term relationships with existing, established players. This can limit a new entrant's ability to reach patients and generate revenue.
The difficulty in securing these vital linkages means that even with innovative products or services, new companies can be severely hampered in their ability to compete effectively. For example, a new electric vehicle startup might have a superior battery technology, but if it cannot secure contracts with established Tier 1 suppliers for crucial components like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) or specialized chassis parts, its production capacity will be severely limited.
Key challenges for new entrants in accessing distribution and supply chains include:
- Established supplier relationships: Existing players often have long-standing contracts and preferential treatment from key suppliers.
- High capital investment: Building or acquiring the necessary infrastructure for distribution or securing a place in a complex supply chain requires significant upfront capital.
- Regulatory hurdles: Certain industries have stringent regulations that can make it difficult for new entrants to navigate supply chain requirements.
- Brand loyalty and trust: Distributors and end-customers may be hesitant to switch from trusted, established suppliers to unproven newcomers.
The threat of new entrants for Compagnie Industriali Riunite (CIR) is generally moderate, primarily due to substantial capital requirements and regulatory complexities across its diverse business segments. In 2024, the automotive sector continued to demand significant investment in advanced manufacturing and R&D, with new entrants facing challenges in matching the economies of scale enjoyed by established players like CIR’s subsidiaries. Similarly, the healthcare sector necessitates considerable upfront capital for state-of-the-art facilities and adherence to strict quality standards, such as those for medical device manufacturing.
Brand loyalty and established distribution networks further solidify CIR's position, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, securing long-term contracts with major automotive manufacturers or establishing trusted partnerships within the healthcare ecosystem requires time and a proven track record. The media sector, while more susceptible to digital disruption, still sees established brands benefiting from loyal audiences, though agile digital-native companies can emerge rapidly.
| Barrier Type | Impact on New Entrants | CIR's Advantage | Example Sector | 2024 Relevance |
| Capital Requirements | High | Economies of Scale, Established Infrastructure | Automotive Components, Healthcare Facilities | Continued high investment in EV technology and medical equipment |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Moderate to High | Expertise in Compliance, Established Licenses | Automotive Safety Standards, Healthcare Licensing | Ongoing updates to emissions and safety regulations |
| Brand Loyalty | Moderate | Reputation, Customer Relationships | Healthcare Services, Automotive Components | Emphasis on patient outcomes and supplier reliability |
| Supply Chain Access | High | Existing Supplier Relationships, Negotiating Power | Automotive Manufacturing | Persistent component shortages impacting new entrants |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Compagnie Industriali Riunite is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, annual reports, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms. We also incorporate data from regulatory filings and economic indicators to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.