China International Marine Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
China International Marine Bundle
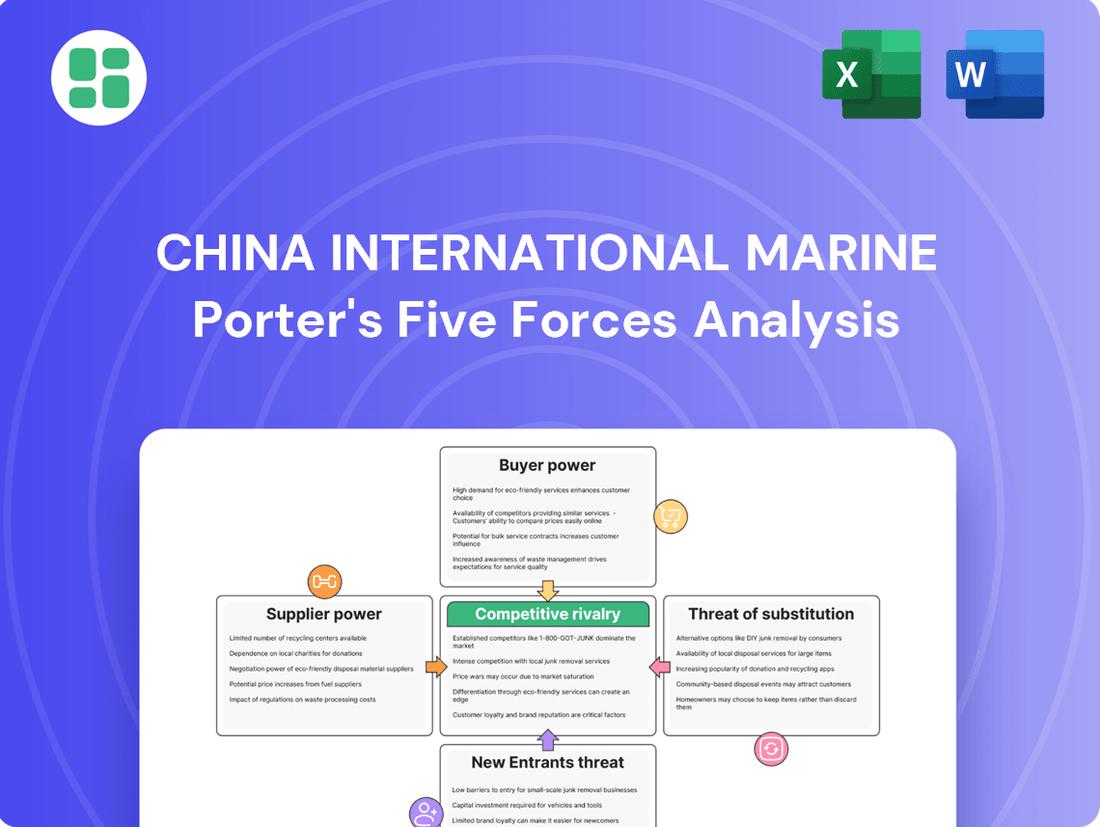
China International Marine operates within a dynamic industry, facing significant pressures from buyers and suppliers, alongside the constant threat of new entrants and substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping China International Marine’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for China International Marine Porter (CIMC) is significantly influenced by the costs and availability of key raw materials. In 2024, global steel prices, a primary input for container and vehicle manufacturing, experienced fluctuations driven by geopolitical events and production levels. For instance, benchmark hot-rolled coil prices in Asia saw considerable volatility throughout the year, impacting CIMC's direct material expenses.
Concentration among suppliers of specialized components, such as advanced electronic systems for intelligent vehicles or high-strength steel alloys, can amplify their bargaining power. If a few dominant suppliers control these critical inputs, they can command higher prices or restrict supply, directly affecting CIMC's production costs and profit margins. The ability of these suppliers to differentiate their offerings further strengthens their position.
CIMC employs various strategies to mitigate supplier power. Long-term procurement contracts help secure stable pricing and supply, providing a degree of insulation from market volatility. Furthermore, CIMC's ongoing exploration of vertical integration, particularly in securing key raw material sources or manufacturing critical components in-house, aims to reduce its reliance on external suppliers and enhance its cost control capabilities.
CIMC's reliance on specialized components, especially for its advanced logistics and energy equipment, can significantly influence supplier bargaining power. If a substantial portion of CIMC's high-tech product lines depends on unique, patented parts from a few key providers, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. For instance, in the energy sector, specialized cryogenic tanks or advanced valve systems might be sourced from a limited number of manufacturers with proprietary technology. This dependency translates directly into higher costs and potential production delays if suppliers dictate terms.
The degree of uniqueness in these components is crucial. Suppliers holding patents or possessing highly specialized manufacturing processes for critical parts used in CIMC's container manufacturing or specialized vehicle production can command premium pricing. In 2024, the global supply chain for advanced materials and components saw price increases, and companies like CIMC, dependent on such specialized inputs, would feel this pressure acutely. The cost of switching these specialized suppliers can be prohibitively high, involving extensive retooling, new quality assurance processes, and potential product redesigns, further strengthening the incumbent supplier's position.
The bargaining power of labor in China's manufacturing sector, particularly for skilled roles in high-end equipment and complex engineering, presents a significant factor for China International Marine Container Group (CIMC). As of early 2024, wage inflation in key industrial hubs continues to exert upward pressure on labor costs. The availability of specialized talent, crucial for CIMC's advanced manufacturing operations, directly influences their ability to negotiate terms with the workforce.
Labor unions, while varying in influence across different regions and sectors within China, can impact wage demands and working conditions. For CIMC, managing these dynamics, alongside strategies for talent retention, is critical in mitigating potential increases in operational expenses stemming from labor. Strong labor relations and effective talent management are therefore key levers for CIMC in managing its supplier power with its own workforce.
Technology and R&D Providers
Technology and R&D providers can exert considerable bargaining power over China International Marine (CIMC) if they possess unique, indispensable intellectual property or advanced manufacturing processes. CIMC’s reliance on specialized software for design and simulation, or on specific components developed through exclusive licenses, can amplify these suppliers' influence. For instance, if a key supplier of advanced marine propulsion software holds a patent that CIMC cannot replicate, their pricing power increases significantly.
However, CIMC's own substantial investments in research and development, which reached approximately RMB 2.5 billion in 2023, aim to mitigate this dependency. By developing proprietary technologies and fostering in-house innovation, CIMC can reduce its reliance on external R&D partners. This strategic focus on internal capabilities strengthens CIMC's position, potentially lowering the bargaining power of technology suppliers who offer less differentiated solutions.
- Supplier Dependence: CIMC's reliance on specialized marine engineering software and advanced component manufacturers influences supplier power.
- R&D Investment: CIMC's 2023 R&D expenditure of approximately RMB 2.5 billion indicates a strategy to reduce external technology dependence.
- Proprietary Technology: CIMC's ability to develop and utilize its own patented technologies directly counters the bargaining power of external R&D providers.
- Innovation Capabilities: Suppliers with exclusive licenses or unique innovation capabilities hold greater leverage over CIMC.
Logistics and Transportation Service Providers
The bargaining power of logistics and transportation service providers for China International Marine Porter (CIMC) is a critical factor. Freight forwarders and shipping lines hold significant sway, especially when global trade volumes surge. For instance, in 2024, the Red Sea crisis and ongoing geopolitical tensions continued to disrupt shipping routes, leading to increased freight rates and longer transit times. This directly impacts CIMC's inbound raw material costs and outbound product delivery schedules, potentially affecting its supply chain efficiency.
CIMC's ability to negotiate favorable terms with these providers is largely influenced by its own scale and global operational footprint. A larger volume of goods handled can provide leverage. However, the industry has seen consolidation among major shipping lines, which can sometimes shift the balance of power. Capacity constraints, such as limited container availability or port congestion, further empower logistics providers during peak demand periods. For example, during the peak shipping season of late 2023 and into 2024, many ports experienced significant delays, with some container spot rates doubling compared to earlier in the year.
- Freight Forwarder Influence: Freight forwarders can exert considerable power due to their role in consolidating shipments and managing complex logistics chains, especially in fragmented markets.
- Shipping Line Dynamics: Major shipping lines, often operating in alliances, can dictate terms based on capacity and route availability, with global shipping capacity remaining a key concern throughout 2024.
- Impact of Disruptions: Fluctuating freight rates, driven by events like the aforementioned Red Sea disruptions, directly increase CIMC's transportation costs and can erode profit margins.
- CIMC's Negotiating Position: CIMC's substantial global presence and consistent shipping volumes provide a degree of leverage, but this is counterbalanced by the overall tightness in global logistics capacity experienced in 2024.
The bargaining power of suppliers for China International Marine Porter (CIMC) is significantly influenced by the costs and availability of key raw materials, particularly steel. In 2024, global steel prices experienced volatility due to geopolitical factors and production levels, directly impacting CIMC's material expenses. Concentration among suppliers of specialized components, such as advanced electronics or high-strength alloys, further amplifies their leverage, potentially leading to higher prices and restricted supply for CIMC.
CIMC actively manages supplier power through long-term procurement contracts and strategic vertical integration efforts. These strategies aim to secure stable pricing, ensure supply chain reliability, and reduce dependence on external providers for critical inputs. By developing in-house capabilities and exploring direct sourcing, CIMC seeks to enhance its cost control and mitigate the impact of supplier-driven price increases.
| Factor | Impact on CIMC | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Prices | Directly affects manufacturing costs for containers and vehicles. | Volatile due to geopolitical events and production levels. |
| Specialized Component Suppliers | Can command higher prices and restrict supply due to unique offerings. | Concentration in advanced electronics and high-strength alloys increases leverage. |
| Supplier Differentiation | Suppliers with unique or patented technologies have greater power. | Proprietary marine propulsion software and advanced valve systems are examples. |
| Switching Costs | High costs associated with changing specialized suppliers strengthen their position. | Includes retooling, new quality assurance, and potential product redesigns. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting China International Marine, revealing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the prevalence of substitute services within the maritime industry.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats in China's marine logistics sector by visualizing the impact of each Porter's Five Forces factor.
Gain actionable insights into the competitive landscape of China's marine porter industry, allowing for strategic adjustments to mitigate potential risks and capitalize on opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
China International Marine Container (CIMC) deals with a diverse customer base, including major global shipping lines, extensive logistics firms, and large industrial conglomerates. The volume of business these clients represent is substantial, with a few key players often accounting for a significant portion of CIMC's revenue. This concentration can grant these dominant customers considerable leverage in price negotiations and the ability to dictate contract terms.
Switching from China International Marine Porter's (CIMC) products can involve significant costs for customers. These can include expenses related to retooling manufacturing lines, addressing compatibility issues with existing infrastructure, or making adjustments to their supply chain. For instance, a customer heavily invested in CIMC's specialized port machinery might face substantial capital expenditure to integrate equipment from a new supplier.
CIMC's strategy of offering comprehensive solutions, encompassing not only the core products but also robust after-sales service and integrated offerings, effectively elevates these switching costs. Clients who rely on CIMC's bundled services and support find it more complex and potentially disruptive to transition to a competitor that may only offer standalone products.
The degree of product standardization versus customization also plays a role. While standardized products might seem easier to switch from, CIMC's ability to offer tailored solutions can foster deeper customer loyalty. Customers who have co-developed or customized equipment with CIMC are likely to incur higher costs, both financial and operational, if they decide to seek alternatives, as their specific needs are already met by CIMC's offerings.
Customer price sensitivity for China International Marine Container (CIMC) varies. For standard dry containers, which can be seen as a commodity, customers are generally more price-sensitive, especially when there are many alternative suppliers. However, CIMC's strong performance in 2024, marked by record revenues and profits, with a notable surge in dry container sales, indicates a robust demand that may lessen this sensitivity in the short term.
Information Availability and Product Differentiation
Customers' bargaining power is influenced by their access to information and the degree of product differentiation. For China International Marine Porter (CIMC), its emphasis on high-end equipment, specialized solutions, and technological innovation, such as smart containers and clean energy equipment, plays a crucial role. This focus aims to reduce customers' ability to easily compare and substitute offerings, thereby mitigating their bargaining power.
CIMC's strategy to differentiate its products through advanced technology and specialized solutions directly impacts customer bargaining power. For instance, their development in smart container technology, which offers enhanced tracking and monitoring capabilities, creates a unique value proposition. This makes it harder for customers to find direct, easily comparable alternatives, thus strengthening CIMC's position.
- Information Availability: Customers have increasing access to information on pricing and product specifications across the global market.
- Product Differentiation: CIMC differentiates through high-end, specialized equipment and technological innovation, such as smart containers and clean energy solutions.
- Reduced Substitutability: This differentiation makes it more difficult for customers to find easily substitutable products, thereby limiting their bargaining power.
- Market Position: CIMC's focus on innovation and specialized segments allows it to command premium pricing and maintain stronger customer relationships, reducing price sensitivity.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, particularly large shipping lines, poses a potential challenge to China International Marine Container (Group) Ltd. (CIMC). If major clients were to invest in their own container manufacturing facilities, it could diminish their need for CIMC's products. However, the substantial capital outlay and specialized technical know-how required for container production make this a significant hurdle for most customers.
CIMC's established global dominance in container manufacturing, evidenced by its consistent market share, acts as a powerful deterrent against such a move. For instance, in 2023, CIMC maintained its position as the world's largest container manufacturer, producing millions of TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units). This scale and expertise create a high barrier to entry for any customer considering backward integration.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing a container manufacturing plant requires hundreds of millions of dollars in machinery, infrastructure, and skilled labor.
- Specialized Expertise: Container production involves complex welding, painting, and quality control processes that CIMC has honed over decades.
- Economies of Scale: CIMC's massive production volumes allow it to achieve cost efficiencies that would be difficult for individual customers to replicate.
- Market Leadership: CIMC's commanding market share and long-standing relationships with clients make it a difficult competitor to displace.
Customers' bargaining power over China International Marine Container (CIMC) is moderate, influenced by product differentiation and switching costs. While CIMC's focus on specialized equipment and smart technology reduces substitutability, the availability of standardized container options means price sensitivity can still be a factor for some segments. However, CIMC's strong market position and the complexity of integrating new suppliers generally limit the extent to which customers can exert significant downward pressure on prices.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
China International Marine Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete China International Marine Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you are viewing is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing sections. You can confidently expect this professionally formatted analysis to be ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
China International Marine Containers (CIMC) operates in highly competitive sectors. In container manufacturing, key rivals include Maersk Container Industry and CIMC's own subsidiaries, alongside numerous smaller Asian manufacturers. The road transportation vehicle segment sees competition from global players like Daimler Truck and Volvo, as well as domestic Chinese brands.
The energy equipment market is characterized by a mix of large international firms such as Siemens Energy and GE, and specialized Chinese manufacturers. Offshore engineering faces competition from established global players like Keppel Offshore & Marine and Sembcorp Marine, alongside emerging Chinese shipbuilders. CIMC holds a dominant global market share in container manufacturing, often exceeding 40% in certain years, solidifying its leadership.
The global logistics and energy equipment industries are experiencing varied growth trajectories. While the energy equipment sector might see slower expansion due to shifts in energy sources, the logistics industry, particularly container trade, is projected for continued growth. For instance, the global container trade volume was estimated to be around 170 million TEUs in 2024, with expectations of further increases leading up to 2025.
A slower overall industry growth rate can significantly heighten competitive rivalry. When the pie isn't expanding quickly, companies are more inclined to aggressively pursue market share from competitors. This can lead to price wars, increased marketing spend, and a greater focus on differentiation to capture existing demand.
Conversely, rapid industry growth typically offers ample opportunities for all participants, potentially softening rivalry. During periods of robust expansion, companies can grow their revenues by simply meeting the increasing market demand without necessarily needing to steal customers from rivals. This environment often allows for more collaborative strategies or at least a less cutthroat competitive landscape.
China International Marine's (CIMC) competitive rivalry is influenced by product differentiation and customer switching costs. CIMC strives to differentiate through technological innovation in areas like smart container technology and specialized equipment, aiming to reduce direct comparability with rivals. For instance, CIMC's investment in R&D for reefer containers with advanced temperature control aims to capture a premium market segment.
The switching costs for customers in the marine equipment sector can be substantial, particularly for large fleet operators. These costs include the expense of retooling, training, and potential disruptions to operations when changing suppliers. CIMC's focus on offering integrated solutions, such as complete logistics equipment packages and after-sales support, further increases these switching costs, binding customers more closely to their ecosystem.
Exit Barriers
Companies operating in the marine equipment and logistics sectors, like those within China International Marine Porter's (CIMC) scope, often face substantial exit barriers. These include highly specialized and expensive assets, such as large manufacturing facilities and unique vessels, which have limited alternative uses. For instance, a significant portion of CIMC's capital expenditure is tied to shipbuilding and container manufacturing, assets with low resale value outside their intended industries.
These high exit barriers can unfortunately contribute to persistent overcapacity and intensified price competition, particularly when market demand softens. Companies, hesitant to abandon their substantial investments, may continue to operate at reduced profitability rather than cease operations. This dynamic was evident in the container manufacturing sector in late 2023 and early 2024, where oversupply led to sharp price declines for new containers.
CIMC's strategic advantage lies in its diversified business portfolio, spanning offshore engineering, energy and chemical equipment, and logistics services. This broad operational base helps to cushion the impact of downturns in any single sector, as profits from more resilient segments can offset losses elsewhere. For example, while the shipping market experienced volatility in 2023, CIMC's energy equipment division saw robust demand, contributing to overall stability.
- High Asset Specificity: CIMC's investments in specialized shipbuilding yards and container manufacturing plants represent assets with very limited alternative uses, making them difficult to divest.
- Significant Capital Investments: The sheer scale of investment required for facilities and equipment in these capital-intensive industries creates a strong disincentive to exit.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term supply agreements and customer contracts can further lock companies into specific markets, increasing the difficulty of an orderly exit.
- Market Dynamics: The presence of high exit barriers can lead to prolonged periods of overcapacity and aggressive pricing, as seen in the container market during recent downturns.
Competitive Strategies and Innovation
Competitive rivalry within the marine equipment sector is intense, with key players frequently employing aggressive pricing strategies and investing heavily in product innovation to capture market share. Companies are also pursuing geographic expansion and forming strategic alliances to bolster their competitive positions. For instance, in 2024, the global container handling equipment market saw significant activity with major manufacturers announcing new product lines focused on efficiency and automation.
China International Marine Porter (CIMC) actively counters this by implementing its own strategic initiatives. Its 'Star-chained Plan' for semi-trailers, for example, aims to enhance product offerings and streamline supply chains. CIMC's focus on clean energy solutions and digitalization further differentiates it, aligning with industry trends and customer demands for more sustainable and technologically advanced equipment.
- Pricing Wars: Competitors often engage in price competition, particularly in high-volume segments like standard container chassis.
- Innovation Focus: Key rivals are investing in smart technologies, autonomous systems, and alternative fuel powertrains for their equipment.
- Geographic Reach: Companies are expanding their manufacturing and service footprints globally to better serve diverse markets.
- CIMC's Differentiation: CIMC's 'Star-chained Plan,' clean energy initiatives, and digitalization efforts are designed to create a competitive edge through product and operational advancements.
Competitive rivalry within China International Marine's (CIMC) operating sectors is robust, driven by a mix of global giants and specialized domestic players. The container manufacturing segment, for example, sees intense competition where CIMC, despite its market leadership often exceeding 40% share, faces pressure from rivals and numerous smaller Asian manufacturers. This rivalry is further fueled by efforts to differentiate through technological advancements and integrated solutions, aiming to reduce direct price comparisons and increase customer switching costs.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for China International Marine Porter (CIMC) largely stems from alternative logistics solutions and energy storage technologies. In the container shipping sector, while sea freight remains dominant for bulk international trade, disruptions or increased costs could push some businesses towards air cargo for time-sensitive goods or intermodal rail solutions for specific land-based legs of a journey. For instance, the cost of air freight can be significantly higher, often several times that of sea freight, making it a less viable substitute for most non-perishable, bulk cargo. However, in 2024, global supply chain volatility continued to make air cargo a necessary, albeit expensive, alternative for certain industries.
Regarding CIMC's energy storage business, substitutes include various battery chemistries beyond those primarily utilized, as well as non-battery energy storage methods. For example, pumped hydro storage and compressed air energy storage (CAES) are established alternatives for grid-scale storage, though they require specific geographical conditions. The cost-effectiveness and efficiency of these substitutes are highly dependent on the scale of the project and location. In 2024, the rapid advancement and cost reduction in lithium-ion battery technology, CIMC's core area, continued to make it a more competitive substitute against some of these other grid-scale solutions.
The price and performance of substitute products for China International Marine Container (CIMC)'s core offerings, such as traditional steel shipping containers, are continually evolving. While steel containers remain dominant, advancements in materials science are introducing alternatives like composite or aluminum containers that offer lighter weight and potentially improved durability, though often at a higher initial cost. For example, by 2024, the global market for advanced composite materials in transportation, which includes potential container applications, was projected to reach tens of billions of dollars, indicating growing interest and investment in these alternatives.
Customers' willingness to switch from traditional shipping and logistics solutions to alternatives is influenced by several factors. Convenience and cost remain paramount, but a growing awareness of environmental impact is also driving change. For instance, the push for reduced emissions in global shipping, a key market for China International Marine Container (CIMC), means that solutions offering lower carbon footprints are becoming more attractive. Regulatory changes mandating cleaner fuels or operational efficiencies can further accelerate this shift.
CIMC is actively addressing this by investing in clean energy equipment, such as LNG-fueled container ships and cryogenic tanks, which directly counters the appeal of less environmentally friendly options. Their focus on smart logistics, utilizing digital technologies for greater efficiency and transparency, also makes their offerings more convenient and appealing compared to less integrated or outdated systems. By aligning their product development with these evolving customer demands and regulatory trends, CIMC aims to solidify its market position and reduce the threat posed by substitute solutions.
Innovation in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Broader innovations in logistics and supply chain management pose a threat to CIMC by potentially reducing the need for its traditional equipment. Advancements like sophisticated cargo optimization software and widespread adoption of just-in-time inventory systems can streamline operations, lessening the reliance on extensive container shipping and the equipment that supports it. Furthermore, the rise of localized production models, driven by factors like reshoring initiatives and advanced manufacturing technologies, could diminish the demand for the long-haul transportation that CIMC's products facilitate.
CIMC is actively engaging with these trends through its own smart logistics solutions. For instance, the company's investments in digital platforms and data analytics aim to enhance efficiency within its operations and for its customers. This proactive approach seeks to mitigate the threat of substitution by adapting to evolving industry needs and offering integrated solutions that leverage technological advancements rather than being replaced by them.
- Reduced Demand: Innovations like optimized cargo loading can decrease the number of containers needed per shipment, impacting CIMC's core product sales.
- Shift in Services: A move towards localized manufacturing reduces the necessity for long-distance container transport, a key market for CIMC.
- CIMC's Response: CIMC's development of smart logistics solutions, such as digital tracking and integrated supply chain management tools, aims to counter this threat by offering value-added services.
- Market Adaptation: The company's strategic focus on intelligent manufacturing and digital transformation reflects an effort to stay relevant amidst evolving logistics paradigms.
Regulatory and Environmental Shifts
The increasing global emphasis on environmental protection and sustainability presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional marine equipment. Stricter regulations regarding emissions and waste disposal are pushing the industry towards greener alternatives. For instance, the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) 2020 sulfur cap and ongoing discussions around decarbonization are driving demand for cleaner fuels and propulsion systems.
China International Marine Porter (CIMC) is actively addressing these shifts by investing in and developing clean energy solutions. Their focus on Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) and hydrogen-powered equipment directly counters the threat posed by environmentally friendlier technologies. CIMC's reported revenue from its clean energy segment, for example, has shown a steady upward trend, indicating market receptiveness to these alternatives.
- Evolving Environmental Regulations: Growing pressure for reduced emissions and sustainable practices in maritime operations.
- Rise of Greener Technologies: Increased adoption of alternative fuels (LNG, hydrogen) and electric propulsion systems.
- CIMC's Strategic Response: Expansion of its clean energy equipment portfolio, including LNG and hydrogen solutions, to meet market demand.
- Market Impact: Potential for substitutes to erode demand for traditional, less environmentally compliant marine equipment.
The threat of substitutes for CIMC's container business includes alternative transport modes like air and rail freight, which can be faster but are often more expensive. For its energy storage division, substitutes range from different battery chemistries to non-battery solutions like pumped hydro and compressed air storage, with their viability depending on scale and location.
In 2024, while lithium-ion batteries, a core area for CIMC, saw continued cost reductions, making them more competitive, the overall volatility in global supply chains kept air freight a necessary, albeit costly, alternative for time-sensitive goods. Advancements in composite and aluminum containers also presented a growing, though currently more expensive, substitute for traditional steel containers.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | 2024 Market Trend/Data Point | Impact on CIMC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Freight | Faster, higher cost | Used for time-sensitive goods amid supply chain volatility | Potential reduction in demand for containers on specific routes |
| Rail Freight | Land-based, efficient for certain routes | Integrated into intermodal solutions | Can substitute for parts of the container shipping journey |
| Pumped Hydro/CAES | Grid-scale energy storage, location-dependent | Established alternatives for large-scale needs | Competition for CIMC's energy storage solutions |
| Composite/Aluminum Containers | Lighter, potentially more durable, higher initial cost | Growing interest and investment in advanced materials | Threat to traditional steel container market share |
Entrants Threaten
Entering industries where China International Marine Container (Group) Ltd. (CIMC) operates, such as manufacturing large-scale equipment like containers, road transport vehicles, and offshore platforms, demands substantial capital investment. These high capital barriers effectively deter many potential new entrants from even attempting to compete.
For instance, establishing a modern container manufacturing facility can easily require hundreds of millions of dollars in upfront costs for specialized machinery, factory construction, and initial raw material procurement. Similarly, developing the capabilities to produce complex offshore platforms involves billions of dollars in investment for advanced engineering, specialized shipbuilding yards, and heavy-lift equipment.
CIMC's existing vast manufacturing infrastructure, spread across numerous global locations, represents significant sunk costs that are incredibly difficult for newcomers to replicate. This established global presence and extensive production capacity create a formidable barrier to entry, making it challenging for new players to achieve economies of scale and compete on cost.
Established players in China's marine industry, such as CIMC, benefit significantly from economies of scale. Their high production volumes allow them to spread fixed costs over more units, leading to lower per-unit costs. For instance, CIMC's extensive manufacturing capacity and established supply chains mean they can procure raw materials at more favorable rates than a new entrant could hope to achieve.
The experience curve further solidifies this advantage. Over years of operation, CIMC has refined its design, manufacturing processes, and logistics, resulting in greater efficiency and reduced waste. This accumulated knowledge translates into cost savings and improved quality that newcomers would find challenging to replicate quickly.
CIMC's dominant market share, estimated to be a substantial portion of the global container manufacturing market, acts as a powerful barrier. This leading position allows them to negotiate better terms with suppliers and customers, further entrenching their cost efficiencies and making it difficult for new companies to compete on price or scale.
New entrants into China International Marine Container (CIMC)'s market would face considerable hurdles in securing access to established distribution channels. CIMC's extensive global sales network and sophisticated logistics infrastructure, built over years of operation, are not easily replicated by newcomers.
Gaining entry into CIMC's vast customer base and leveraging its existing supply chain efficiencies presents a significant barrier. For instance, CIMC's 2023 annual report highlighted its robust global presence, serving clients across over 100 countries, a testament to its deeply entrenched distribution capabilities.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
CIMC's significant investment in research and development, evidenced by its substantial R&D expenditure, creates a formidable barrier for new entrants. In 2023, CIMC's R&D spending reached RMB 3.9 billion, a 15% increase from the previous year, focusing on areas like smart manufacturing and new energy technologies. This commitment fosters proprietary technology and advanced product lines, making replication by newcomers both costly and time-consuming.
The company holds a robust portfolio of patents, particularly in container manufacturing and specialized equipment. As of late 2024, CIMC secured over 500 new patents, many related to energy-efficient designs and automated production processes. These intellectual property rights protect its market position and deter potential competitors who would need to navigate complex licensing or develop entirely novel, potentially less efficient, technologies.
- Proprietary Technology: CIMC's advanced manufacturing techniques and specialized know-how in areas like cryogenic tanks and offshore engineering equipment are difficult for new players to acquire quickly.
- Patent Portfolio: A substantial and growing number of patents, especially in innovative and sustainable product designs, serve as a significant hurdle for market entry.
- R&D Investment: Continuous and increasing investment in R&D ensures CIMC stays ahead in technological advancements, widening the gap with potential new entrants.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and regulations significantly shape the threat of new entrants in China's marine porter industry. For instance, stringent environmental standards, such as those aimed at reducing emissions from vessels and port operations, can increase the capital expenditure required for new companies to comply, thereby acting as a barrier. In 2024, China continued to emphasize green development, with policies encouraging the adoption of cleaner fuels and more efficient port technologies.
Trade regulations and local content requirements also play a crucial role. For international firms looking to enter, navigating China's complex customs procedures, import duties, and rules mandating the use of domestically produced components or services can be challenging. These measures can elevate operational costs and slow down market entry, making it less attractive for new, unestablished players.
Furthermore, specific certifications and licensing requirements for operating in sensitive marine areas or handling particular types of cargo can deter new entrants. The need to obtain approvals from multiple government bodies, each with its own set of criteria, adds layers of complexity and time to the entry process. For example, offshore engineering projects often require extensive permits and adherence to national safety standards, which can be a substantial hurdle for smaller or less experienced companies.
- Stricter environmental regulations in 2024 increased compliance costs for new port operators.
- Trade policies and local content mandates in China can raise entry barriers for foreign firms.
- Complex certification processes for specialized marine services deter less experienced new entrants.
- Government support for domestic technology adoption can favor established local players over newcomers.
The threat of new entrants into China International Marine Container (CIMC)'s markets remains relatively low due to several significant barriers. Substantial capital requirements for manufacturing facilities, coupled with CIMC's established economies of scale and experience curve advantages, make it difficult for newcomers to compete on cost and efficiency. Furthermore, CIMC's strong brand reputation, extensive global distribution networks, and significant investments in proprietary technology and patents create formidable hurdles for potential competitors seeking to enter the market.
The company's market dominance, built on years of operational expertise and strategic investments, further solidifies its position. For example, CIMC's 2023 financial statements revealed a robust market share in key segments, allowing for favorable negotiations with suppliers and customers alike. This entrenched market position, combined with the high cost of replicating CIMC's established infrastructure and supply chain efficiencies, significantly deters new players from entering the industry.
Additionally, government policies in China, including stringent environmental regulations and trade policies, can act as barriers. Navigating complex certification processes and meeting local content requirements, as emphasized by China's green development initiatives in 2024, adds to the cost and complexity for new entrants. These factors collectively contribute to a low threat of new entrants for CIMC.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | CIMC's Advantage | Example Data (2023/2024) |
| Capital Requirements | High cost of setting up manufacturing facilities and acquiring specialized equipment. | Significant financial barrier, requiring substantial upfront investment. | Established infrastructure and access to financing. | Container plant setup: $100M+; Offshore platform development: $1B+. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience Curve | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes and accumulated operational knowledge. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies and process optimization. | Vast production capacity and refined manufacturing processes. | CIMC's 2023 R&D spending: RMB 3.9 billion (15% increase). |
| Distribution Channels & Customer Base | Established global sales networks and strong customer relationships. | Difficult for new players to gain market access and build a loyal customer base. | Extensive global presence serving over 100 countries. | CIMC's 2023 report highlighted robust global sales network. |
| Proprietary Technology & Patents | Advanced manufacturing techniques and a portfolio of protected intellectual property. | New entrants face challenges in technological replication and potential infringement issues. | Significant investment in R&D and a growing patent portfolio. | Over 500 new patents secured by CIMC in late 2024. |
| Government Policies & Regulations | Environmental standards, trade regulations, and certification requirements. | Increased compliance costs, operational complexities, and potential delays in market entry. | Established relationships with regulatory bodies and expertise in compliance. | China's 2024 focus on green development; strict environmental standards. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our China International Marine Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including official government statistics from China's Ministry of Transport, reports from leading maritime industry associations, and financial disclosures from major shipping companies. We also incorporate insights from reputable market research firms specializing in global logistics and trade to ensure a comprehensive view.