Commercial International Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Commercial International Bank Bundle
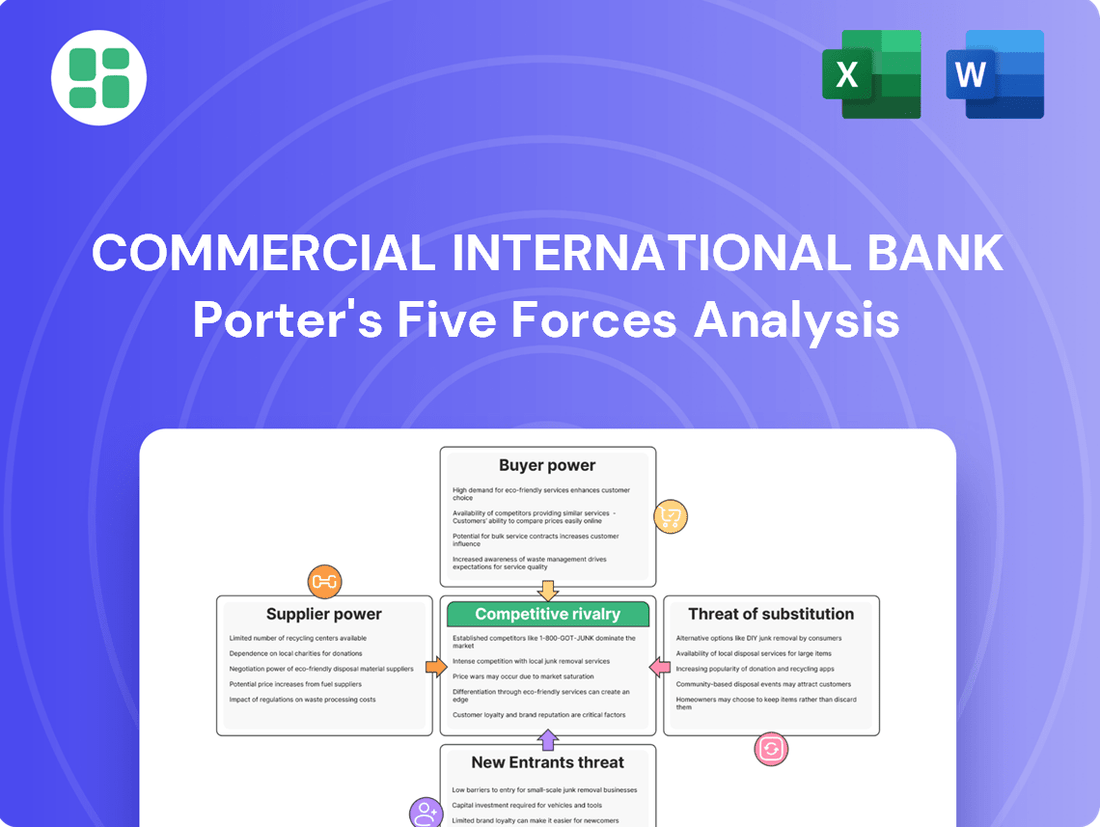
Commercial International Bank navigates a landscape shaped by intense rivalry, the growing power of buyers, and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp CIB's strategic positioning and future outlook.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Commercial International Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
For Commercial International Bank (CIB), the primary suppliers are its depositors and capital market investors. If CIB were to heavily depend on a small number of large depositors or institutional investors, these entities would gain significant bargaining power, potentially influencing interest rates and terms.
CIB, as Egypt's largest private sector bank, benefits from a broad and diversified base of individual and corporate depositors. This wide distribution of funding sources generally mitigates the risk of concentrated supplier power, as no single depositor or small group holds excessive sway over the bank's funding costs.
The cost of funds for Commercial International Bank (CIB) is heavily influenced by the prevailing interest rate environment, largely shaped by the Central Bank of Egypt's (CBE) monetary policies. When the CBE raises interest rates, CIB's cost of acquiring capital, primarily through customer deposits, naturally increases. For instance, if the CBE's policy rate in mid-2025 is trending upwards, depositors will likely seek higher yields, directly impacting CIB’s operational expenses and potentially reducing its net interest margin.
This dynamic grants suppliers, in this case, depositors, significant bargaining power. As interest rates climb, depositors can more easily find alternative, higher-yielding avenues for their savings, forcing CIB to offer more competitive rates to retain their business. This heightened leverage for depositors means CIB must carefully manage its deposit pricing strategies to mitigate the impact of rising interest rate cycles on its profitability.
The Central Bank of Egypt's (CBE) regulations on deposit insurance, capital adequacy, and liquidity significantly shape the bargaining power of depositors. These rules, like those mandating specific liquidity coverage ratios, can limit a bank's flexibility in offering highly competitive rates, thereby influencing depositor leverage.
While robust regulations instill confidence, they also add to a bank's operational expenses and constraints. For instance, in 2024, Egyptian banks continued to navigate evolving capital adequacy ratios, impacting their cost of funds and, consequently, their ability to attract deposits solely on price.
The CBE's proactive approach to updating these frameworks directly affects the banking sector's stability and the cost structure for banks. This ongoing regulatory evolution means that banks must balance compliance with competitive deposit strategies, a dynamic that influences supplier (depositor) power.
Availability of Alternative Funding
The availability of alternative funding sources significantly impacts a bank's reliance on core depositors. Banks like Commercial International Bank (CIB) also tap into interbank lending, wholesale funding markets, and capital markets, such as issuing bonds, to manage their liquidity. If these alternative avenues become restricted, costly, or unreliable, the bargaining power of their primary depositors naturally grows.
CIB's financial structure, where customer deposits form a substantial part of its total liabilities, indicates a lower dependence on potentially volatile wholesale funding. This strong deposit base, a key indicator of stability, means CIB is less susceptible to fluctuations in external funding markets. For example, as of the first quarter of 2024, CIB reported total deposits of EGP 785 billion, highlighting the strength of its core funding.
- Reduced Reliance on Wholesale Funding: CIB's substantial customer deposit base provides a stable and cost-effective funding source, lessening its need for more expensive and volatile wholesale market borrowings.
- Impact of Limited Alternatives: Should interbank lending or capital markets become less accessible or more expensive, the bargaining power of CIB's depositors, who represent a core funding pillar, would consequently increase.
- Deposit Stability as a Strength: In 2023, CIB's customer deposit growth reached approximately 17%, demonstrating consistent client confidence and a robust core funding profile that mitigates supplier bargaining power.
Technology and Infrastructure Providers
Technology and infrastructure providers, including those for core banking systems and digital platforms, hold considerable bargaining power in the current financial sector. Commercial International Bank's (CIB) commitment to digital advancement, evidenced by its significant investments in technology, means it relies heavily on these specialized vendors. For instance, in 2023, CIB continued to invest in upgrading its core banking systems and expanding its digital service offerings, underscoring this dependency.
- High Switching Costs: Banks often face substantial costs and operational disruptions when changing core technology providers, which strengthens the suppliers' negotiating position.
- Vendor Concentration: The market for specialized banking technology can be concentrated, with a few dominant players offering critical solutions, further amplifying their power.
- CIB's Digital Strategy: CIB's strategic emphasis on digital transformation and robust cybersecurity measures necessitates reliance on leading-edge technology, potentially increasing its dependence on key suppliers.
For Commercial International Bank (CIB), the bargaining power of suppliers, primarily depositors and technology providers, is a key consideration. While CIB benefits from a broad depositor base, limiting individual leverage, significant reliance on specialized technology vendors can increase their influence due to high switching costs and market concentration.
In 2023, CIB's substantial customer deposit growth of approximately 17% highlights a strong, stable funding base. This robust core funding profile effectively mitigates the bargaining power of individual depositors. However, CIB's ongoing investment in digital transformation, as seen in its 2023 upgrades to core banking systems, means it remains dependent on key technology suppliers.
The Central Bank of Egypt's monetary policy, including interest rate adjustments, directly impacts CIB's cost of funds. For instance, if policy rates are trending upwards in mid-2025, depositors gain leverage to seek higher yields, increasing CIB's funding costs. This dynamic underscores the indirect influence of regulatory bodies on supplier power.
| Supplier Type | Key Considerations for CIB | Impact on Bargaining Power | Relevant Data/Context (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Depositors | Broad, diversified base vs. interest rate sensitivity | Generally low for individuals; increases with rising rates | 17% deposit growth in 2023; EGP 785 billion in total deposits (Q1 2024) |
| Technology Providers | Reliance on core banking & digital platforms | High due to switching costs and vendor concentration | Continued investment in system upgrades and digital offerings in 2023 |
| Central Bank of Egypt (CBE) | Monetary policy and regulatory frameworks | Indirectly influences depositor bargaining power through interest rates and compliance requirements | Evolving capital adequacy ratios impacting cost of funds in 2024 |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Commercial International Bank (CIB) dissects the competitive forces shaping its market, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Instantly identify and address competitive pressures by visualizing CIB's Porter's Five Forces, allowing for proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Commercial International Bank (CIB) caters to a wide array of customers, from individuals and small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to major corporations. This diversity means customer bargaining power isn't uniform across the board.
Large corporate clients, by virtue of their substantial transaction volumes and the potential for significant business, often wield considerable bargaining power. They can negotiate more favorable terms, interest rates, and fees, and frequently maintain relationships with multiple banking institutions, further strengthening their position.
Individual retail customers, while possessing less individual leverage, can exert influence collectively. Their increasing adoption of digital banking channels and their willingness to switch providers based on competitive offerings and customer experience are key factors that banks like CIB must consider.
For many individual and small business clients of Commercial International Bank (CIB), the effort and expense involved in switching to another financial institution are quite low. This is particularly true in 2024, with the widespread adoption of user-friendly mobile banking apps and streamlined online account opening procedures, making it simpler than ever to move money or services. This ease of transition directly empowers customers, allowing them to easily explore and move to competitors offering more attractive rates or superior service if they are unhappy with CIB's current offerings.
Customers today are incredibly well-informed, thanks to the internet. They can easily find out about different banking products, what services are offered, and compare prices across various institutions. This ease of access to information means they're much better equipped to negotiate favorable terms with banks like Commercial International Bank (CIB).
This increased transparency directly fuels the bargaining power of customers. They can readily see who offers the best deals, pushing banks to compete more aggressively on price and service quality. For instance, in 2023, the number of digitally active customers for Egyptian banks, including CIB, continued to surge, with many transactions happening via mobile apps and online portals, underscoring this shift towards informed digital engagement.
CIB's strategic focus on enhancing its digital channels and mobile banking capabilities is a direct response to these empowered customers. While these investments are crucial for meeting customer expectations and remaining competitive, they simultaneously amplify the customers' ability to compare and demand better value, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Availability of Alternative Financial Service Providers
The bargaining power of customers for Commercial International Bank (CIB) is significantly influenced by the increasing availability of alternative financial service providers. The rise of fintech companies and various online lending platforms offers consumers and businesses a wider array of choices beyond traditional banking institutions.
These alternatives often compete by providing specialized services, more competitive pricing, or expedited transaction processes. This directly enhances customer leverage, allowing them to seek better terms or switch providers more readily if traditional banks like CIB do not meet their expectations. For instance, by mid-2024, Egypt has seen a notable surge in fintech adoption, with reports indicating that digital payment transactions grew by over 40% year-on-year, showcasing the expanding landscape of alternatives.
- Fintech Growth: The proliferation of digital-only banks and payment solutions presents direct competition to established players like CIB.
- Specialized Offerings: Niche providers can cater to specific customer needs more effectively, drawing segments away from universal banks.
- Price Sensitivity: Lower fees and more transparent pricing structures from alternative providers empower customers to negotiate or switch.
- Egyptian Market Trends: The increasing digital financial services penetration in Egypt underscores the growing bargaining power of informed customers.
Price Sensitivity and Demand for Tailored Solutions
Customers, especially major corporations and affluent individuals, often show significant price sensitivity. They frequently seek customized financial packages, putting pressure on Commercial International Bank (CIB) to offer competitive loan interest rates, reduced service charges, or specialized investment banking support. This ability to negotiate can directly affect CIB's profit margins and overall financial performance.
The bargaining power of customers is a key factor influencing CIB's operations. For instance, in 2024, the average interest rate on corporate loans in Egypt, a primary market for CIB, remained a significant consideration for businesses seeking financing. CIB's strategy to cater to diverse financial requirements across various customer segments is crucial in mitigating this pressure.
- Price Sensitivity: Large corporate clients and high-net-worth individuals often compare rates and terms rigorously.
- Demand for Customization: Tailored financial products and services are frequently requested, increasing operational complexity.
- Negotiating Leverage: Customers can exert pressure for better loan pricing, lower fees, or enhanced investment banking services.
- Impact on Profitability: Customer bargaining power can directly squeeze profit margins on financial products and services offered by CIB.
The bargaining power of customers for Commercial International Bank (CIB) is substantial, driven by increased market transparency and the ease of switching providers. In 2024, the widespread availability of digital banking tools in Egypt has significantly lowered switching costs for both individual and corporate clients. This allows customers to readily compare CIB's offerings against competitors, pushing the bank to maintain competitive pricing and service quality to retain its client base.
| Factor | Impact on CIB | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Ease of Switching | Increases customer leverage | High adoption of user-friendly mobile banking apps |
| Information Availability | Empowers negotiation | Surge in digitally active customers comparing products online |
| Alternative Providers | Diversifies customer options | 40%+ year-on-year growth in digital payment transactions in Egypt |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressures pricing and margins | Key consideration for corporate loan interest rates in Egypt |
Same Document Delivered
Commercial International Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Commercial International Bank, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, offering no surprises or placeholders. It provides an in-depth examination of buyer power, supplier power, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector, specifically for CIB.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Egyptian banking sector is quite crowded, with a mix of major players. You have big state-owned banks like the National Bank of Egypt and Banque Misr, which together control a substantial chunk of the market. Then there are numerous private and foreign commercial banks operating alongside Commercial International Bank (CIB), the largest private sector bank. This diverse group makes for a really competitive environment.
The Egyptian banking sector is indeed seeing healthy growth, with digital initiatives and economic diversification acting as key drivers. However, this expansion doesn't necessarily dilute the competitive landscape. For instance, while the overall market might grow, the battle for market share within high-growth digital segments can be fierce, impacting individual bank profitability.
Banks vie for customers through innovative products, superior service, extensive branch networks, seamless digital platforms, and robust brand reputations. Commercial International Bank (CIB) leverages its strong brand and commitment to digital advancement and customer satisfaction to stand out. For instance, CIB's digital banking initiatives have seen significant adoption, with mobile banking transactions increasing by over 30% in 2023, showcasing their focus on a superior digital experience.
When banking products become indistinguishable, the competition shifts heavily towards pricing, which can unfortunately squeeze profit margins for all players. This commoditization pressure is a constant challenge, as customers may prioritize lower fees or interest rates over unique product features. CIB's strategy to counter this involves not just product development but also enhancing the overall customer journey, aiming to build loyalty beyond mere price sensitivity.
High Exit Barriers
The banking industry, including Commercial International Bank (CIB) in Egypt, faces high exit barriers. These are primarily due to substantial capital investments required for operations, stringent regulatory compliance, and the intricate process of liquidating assets and liabilities. This makes it difficult and costly for banks to leave the market.
These elevated exit barriers mean that even financially strained banks tend to persist, intensifying ongoing competition. This sustained presence can lead to prolonged competitive pressure, especially when the market experiences economic slowdowns. The Egyptian banking sector's resilience is notably bolstered by strong capital adequacy ratios, which contribute to overall market stability.
- High Capital Investments: Banks require significant capital for infrastructure, technology, and regulatory reserves, making divestment a complex financial undertaking.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Winding down a bank involves extensive approvals and oversight from financial authorities, adding layers of complexity and time.
- Sustained Competition: The difficulty in exiting the market encourages existing players to remain, potentially leading to a more crowded and competitive landscape.
Impact of Digitalization and Fintech
The digital revolution and the burgeoning fintech sector are fundamentally altering how banks compete. Commercial International Bank (CIB) faces intensified rivalry as customers increasingly favor digital banking solutions and innovative fintech offerings. This necessitates substantial and ongoing investment in technology and digital platforms to maintain relevance and customer engagement.
CIB's strategic focus on enhancing its digital capabilities, including its mobile banking app and online services, is a critical response to this trend. For instance, in 2023, CIB reported a significant increase in digital transactions, underscoring the growing customer reliance on these channels. This continuous development, while crucial for competitiveness, also contributes to increased operational expenses and a perpetual need for innovation to stay ahead of agile fintech disruptors.
- Digital Transformation Investment: Banks like CIB are channeling significant capital into upgrading IT infrastructure and developing new digital products.
- Fintech Competition: Specialized fintech firms often offer niche, user-friendly digital services that challenge traditional banking models.
- Customer Expectations: The demand for seamless, instant digital banking experiences is a primary driver of competitive pressure.
- Operational Agility: CIB's ability to adapt quickly to technological advancements and evolving customer preferences is paramount.
Competitive rivalry within the Egyptian banking sector is intense, with Commercial International Bank (CIB) operating in a crowded market alongside large state-owned banks and numerous private and foreign institutions. This dynamic environment is fueled by healthy market growth, driven by digital initiatives and economic diversification, which, while expanding the pie, also intensifies the battle for market share, particularly in lucrative digital segments. Banks actively compete by offering innovative products, superior customer service, extensive branch networks, and seamless digital platforms, with CIB notably leveraging its strong brand and digital advancements. For example, CIB saw over a 30% increase in mobile banking transactions in 2023, highlighting its focus on digital customer experience amidst this fierce competition.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most substantial threat of substitution for Commercial International Bank (CIB) stems from financial technology (fintech) firms providing digital payment solutions, mobile wallets, and instant payment networks. These innovative services often circumvent traditional banking infrastructure for everyday transactions, diminishing the necessity for conventional bank accounts and credit cards.
In Egypt, the adoption of mobile banking and digital payment methods has experienced a notable acceleration. For instance, by the end of 2023, the number of active mobile banking users in Egypt reached approximately 50 million, demonstrating a significant shift towards digital alternatives for financial services.
Alternative lending platforms, such as peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and digital microfinance, offer financing that bypasses traditional banks like Commercial International Bank (CIB). These platforms often present a compelling alternative by providing more adaptable terms and quicker access to capital, directly challenging bank loan portfolios, especially for those segments that are less served by conventional financial institutions.
The growth of these alternative channels is particularly notable in emerging markets. For instance, the digital lending sector in Egypt has seen significant expansion. While specific 2024 figures for CIB's direct exposure to this threat are not publicly detailed, the overall market trend indicates a growing competitive landscape. The Egyptian FinTech scene, which includes many of these alternative lenders, attracted over $200 million in investment in 2023, signaling robust investor confidence and further development in this area.
Informal financial channels, such as savings groups and peer-to-peer lending, can act as substitutes for formal banking services, particularly in regions with lower financial inclusion. In 2023, an estimated 1.4 billion adults globally remained unbanked, highlighting the persistent demand for alternative financial solutions. While these informal networks offer accessibility, they often lack the regulatory oversight and security of traditional banks.
Commercial International Bank (CIB) is actively working to broaden financial inclusion, especially within the retail and SME sectors. This strategy directly addresses the threat posed by informal channels by offering more accessible and regulated financial products. For instance, CIB's digital banking initiatives in 2024 aim to onboard a significant portion of previously unbanked customers, thereby formalizing financial activities and reducing reliance on informal lending.
Direct Corporate Financing
Large corporations increasingly bypass traditional bank loans by tapping directly into capital markets, issuing bonds or commercial papers. This trend is particularly pronounced for substantial funding needs, such as infrastructure projects. For instance, in 2024, global corporate bond issuance reached record highs, indicating a significant shift away from bank-centric financing.
The growing involvement of international financial institutions in local loan markets also presents a competitive alternative. These institutions can offer tailored financing solutions, often at competitive rates, further diminishing the exclusive reliance on domestic commercial banks for large-scale corporate funding.
- Capital Market Dominance: Corporations are leveraging bond markets for significant capital needs, reducing dependency on bank lending.
- Infrastructure Funding: Large projects increasingly seek direct funding from capital markets rather than traditional bank loans.
- International Competition: Global financial institutions are expanding their presence in local lending, offering viable alternatives to commercial banks.
- Reduced Bank Reliance: The availability of direct financing and international funding options lessens the bargaining power of commercial banks.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain-based Finance
While still in early stages and subject to evolving regulations in Egypt, cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology present a potential long-term threat of substitution for traditional banking services. These decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions could offer alternative avenues for transactions and investments, potentially bypassing intermediaries like Commercial International Bank (CIB).
Despite the nascent nature of these technologies in the Egyptian market, their global growth signifies a shift in financial paradigms. For instance, the total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies, while volatile, reached trillions of dollars in recent years, indicating significant investor interest and the potential for widespread adoption if regulatory frameworks mature and technological stability is achieved.
- Disruptive Potential: DeFi platforms offer peer-to-peer lending, borrowing, and asset management, potentially reducing reliance on traditional banks for these services.
- Regulatory Landscape: In Egypt, as of mid-2024, the regulatory stance on cryptocurrencies is still being defined, creating uncertainty but also an opportunity for innovation within a controlled environment.
- Challenges: High volatility, security concerns, and the need for significant technological infrastructure remain substantial barriers to widespread adoption as a direct substitute for established banking.
Fintech innovations, particularly digital payment solutions and mobile wallets, present a significant threat by offering convenient alternatives to traditional banking for everyday transactions. The increasing adoption of these digital services, with approximately 50 million active mobile banking users in Egypt by the end of 2023, underscores this shift. Furthermore, alternative lending platforms and informal financial channels cater to segments underserved by conventional banks, reducing reliance on institutions like CIB.
| Threat Type | Description | Impact on CIB | Mitigation Strategy | 2023/2024 Data Point |
| Fintech Payment Solutions | Digital wallets, instant payment networks | Reduced transaction volumes, potential loss of customer base for basic services | Enhance CIB's own digital offerings, partnerships with fintechs | 50 million active mobile banking users in Egypt (end of 2023) |
| Alternative Lending | P2P lending, digital microfinance | Competition for loan portfolios, especially in SME and retail segments | Develop competitive digital lending products, streamline loan application processes | Egyptian FinTech sector attracted over $200 million in investment (2023) |
| Informal Finance | Savings groups, informal lending networks | Undermines formal financial inclusion efforts, loss of potential customers | Expand financial literacy programs, offer accessible micro-savings and micro-loan products | 1.4 billion adults globally remained unbanked (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector in Egypt presents a formidable barrier to entry due to high capital requirements. Potential new players must possess significant financial resources to even consider establishing a presence.
The Central Bank of Egypt mandates substantial minimum capital thresholds for all commercial banks, and even digital banks face these stringent demands. For instance, aspiring digital banks in Egypt are required to meet a capital requirement of EGP 4 billion, effectively limiting the field to well-funded institutions.
The stringent regulatory framework and licensing requirements imposed by the Central Bank of Egypt (CBE) present a significant barrier to new entrants in the Egyptian banking sector. Navigating these complex compliance procedures, securing necessary approvals, and adhering to strict prudential norms are both time-consuming and capital-intensive endeavors. For instance, the CBE's recent regulations concerning digital banks and payment service providers underscore the rigorous hurdles any new player must overcome to establish operations.
Commercial International Bank (CIB) enjoys a significant advantage due to its deeply ingrained brand loyalty and the trust it has cultivated over many years. This is a major barrier for any new bank trying to enter the Egyptian market.
As the strongest brand in Egypt, CIB's established reputation and extensive network of branches make it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. Building equivalent levels of customer confidence and loyalty is a formidable and costly undertaking in an industry where reliability is key.
Economies of Scale and Distribution Networks
Existing large banks, such as Commercial International Bank (CIB), leverage significant economies of scale. This scale allows them to spread costs across a vast customer base for operations, technology investments, and marketing efforts, leading to more competitive pricing and a broader service portfolio than new entrants can easily match. CIB's robust infrastructure, including 201 branches and 13 units as of recent data, represents a substantial barrier.
New players entering the banking sector face the immense challenge of replicating CIB's established distribution networks, which encompass physical branches, ATMs, and sophisticated digital platforms. Building such an extensive reach requires considerable capital outlay and time, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively on accessibility and convenience.
- Economies of Scale: CIB benefits from cost advantages in operations, technology, and marketing due to its size.
- Distribution Network: CIB operates 201 branches and 13 units, creating a significant physical presence.
- Digital Channels: CIB's extensive digital banking services further solidify its reach.
- Investment Barrier: New entrants need substantial investment to replicate CIB's network and scale.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
The banking industry, including Commercial International Bank (CIB), faces a significant threat from new entrants concerning talent acquisition and retention. The sector demands highly specialized financial expertise, robust IT capabilities, and seasoned management teams. New players entering the market must therefore invest heavily in attracting and retaining these skilled professionals, often necessitating competitive salary packages and comprehensive benefits, which directly inflates their initial operating expenses and ongoing cost structure.
CIB, in particular, recognizes the critical importance of its human capital and makes substantial investments in employee development. These investments include extensive education and training programs designed not only to enhance the skills of their existing workforce but also to foster loyalty and reduce attrition. For instance, in 2023, CIB reported that its total employee development expenses amounted to EGP 250 million, underscoring its commitment to nurturing talent and maintaining a competitive edge.
- Specialized Skill Requirements: Banking demands financial analysts, risk managers, compliance officers, and cybersecurity experts, all of whom are in high demand.
- IT and Digital Expertise: With the increasing digitization of financial services, new entrants need to secure talent proficient in AI, blockchain, and data analytics.
- Competitive Compensation: To attract top talent, new banks must offer salaries and benefits that can rival established institutions like CIB, increasing their initial cost burden.
- CIB's Talent Strategy: CIB's focus on continuous learning and career progression is a key strategy to retain its skilled workforce, posing a challenge for new entrants aiming to poach talent.
The threat of new entrants for Commercial International Bank (CIB) is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements, stringent regulatory hurdles, and the high cost of establishing a competitive presence. For example, aspiring digital banks in Egypt must meet a EGP 4 billion capital requirement, a figure that immediately filters out less capitalized entities.
CIB's established brand loyalty, extensive branch network of 201 branches and 13 units, and significant economies of scale present formidable barriers. Replicating CIB's infrastructure and customer trust demands immense investment, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on accessibility or cost-effectiveness.
Furthermore, the need to attract and retain highly specialized talent, with CIB investing EGP 250 million in employee development in 2023, adds another layer of complexity and expense for potential new entrants. This focus on human capital ensures CIB maintains a skilled workforce, a key differentiator.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for commercial international banks is built upon a foundation of diverse data sources, including financial statements, annual reports, and regulatory filings from leading global institutions. We also leverage industry-specific market research reports, economic indicators from organizations like the IMF and World Bank, and proprietary databases that track banking sector performance and trends.