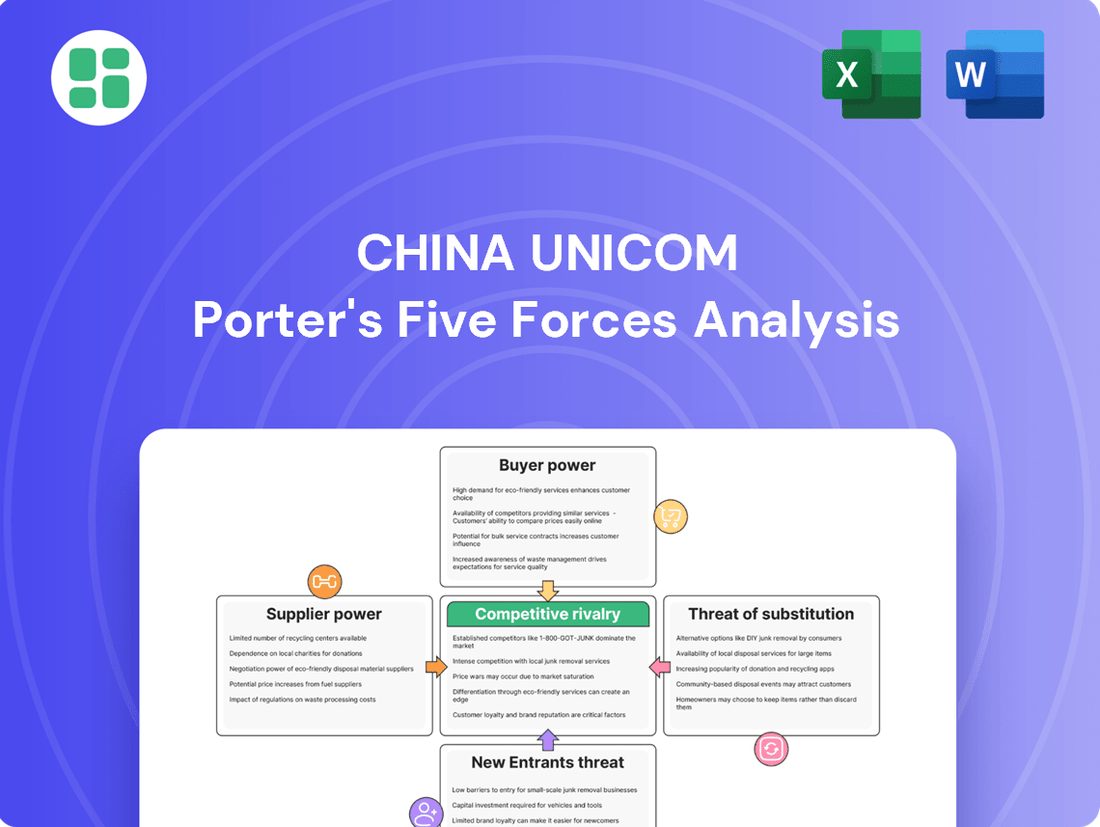
China Unicom Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
China Unicom Bundle
China Unicom navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry and significant buyer power, as customers have numerous choices for telecommunication services. The threat of substitutes is also a considerable factor, with evolving technologies constantly offering new ways to communicate and access information.
The full analysis reveals the strength and intensity of each market force affecting China Unicom, complete with visuals and summaries for fast, clear interpretation.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
China Unicom faces a concentrated network equipment market, relying on a few major global and domestic suppliers for its 5G and core network infrastructure. Key players like Huawei, ZTE, Ericsson, and Nokia hold significant sway due to their specialized, advanced technology and the limited number of viable alternative providers in the market.
This dependency on a small group of vendors for critical components grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power. Their ability to dictate terms is amplified by the specialized nature of the technology required for modern telecommunications networks, making it difficult for China Unicom to switch providers easily.
Suppliers of core technologies, such as advanced chipsets and proprietary software essential for 5G network infrastructure, hold significant bargaining power. China Unicom's reliance on these specialized components, often from a limited number of vendors, means switching suppliers can be costly and disruptive, impacting network performance and deployment timelines. For instance, the global semiconductor shortage experienced in 2021-2022 highlighted the dependency on key chipset manufacturers, with lead times extending significantly and prices increasing, directly affecting infrastructure rollout budgets.
Disruptions in global supply chains, like the ongoing semiconductor shortages that impacted the tech industry throughout 2023 and into 2024, significantly bolster supplier power. These shortages made it more challenging for companies like China Unicom to secure essential network equipment at favorable terms, potentially hindering their expansion plans.
Geopolitical tensions, particularly those affecting technology exports, further exacerbate these vulnerabilities. For instance, restrictions on certain advanced chip technologies can limit the available suppliers and drive up prices, directly impacting China Unicom's procurement costs and operational efficiency in 2024.
High Switching Costs for Infrastructure
The bargaining power of suppliers for China Unicom is significantly influenced by high switching costs related to network infrastructure. Replacing or migrating from deeply integrated vendor technology demands substantial capital expenditure, intricate operational planning, and carries the risk of service interruptions. This situation inherently limits China Unicom's negotiating leverage, as suppliers of critical network components can command more favorable terms.
These high switching costs translate into increased supplier power. For instance, in 2024, the telecommunications infrastructure market continues to be dominated by a few key global players. Companies like Huawei and Ericsson, which provide essential 5G network equipment, benefit from the significant investment required for China Unicom to transition to alternative solutions. This dependence means suppliers can exert considerable influence over pricing and contract terms.
- High Capital Investment: Transitioning network infrastructure, especially for advanced technologies like 5G, can cost billions of dollars.
- Operational Complexity: Integrating new systems and ensuring interoperability with existing networks is a complex and time-consuming process.
- Potential Service Disruptions: Any shift in suppliers carries the inherent risk of impacting service quality and customer experience.
- Vendor Lock-in: Once a supplier's technology is deeply embedded, it becomes economically and technically challenging to switch.
Innovation and R&D Capabilities
Suppliers at the forefront of telecommunications innovation, particularly in areas like 5G-Advanced and AI-driven network management, can command higher prices. China Unicom's need to remain competitive often necessitates adopting these cutting-edge solutions from leading suppliers, further enhancing their bargaining position.
- 5G-Advanced Rollout: As China Unicom continues its 5G network expansion, suppliers of advanced base stations and core network components with superior performance and energy efficiency can leverage their technological edge.
- AI in Network Operations: Companies offering sophisticated AI-powered network management and optimization software, which can reduce operational costs and improve service quality for China Unicom, gain significant leverage.
- R&D Investment: Suppliers with substantial R&D investments in next-generation technologies, such as quantum communication or advanced edge computing, are positioned to negotiate favorable terms as China Unicom seeks to integrate these future capabilities.
The bargaining power of suppliers for China Unicom is substantial due to the concentrated nature of the network equipment market and high switching costs. Key vendors like Huawei and Ericsson provide critical 5G infrastructure, and their advanced technology, coupled with the significant investment and operational complexity involved in switching, limits China Unicom's negotiating leverage.
Supply chain disruptions, such as the ongoing semiconductor shortages impacting 2023 and 2024, further empower these suppliers. Geopolitical factors can also restrict the availability of advanced components, driving up prices and affecting China Unicom's procurement costs and expansion timelines.
Suppliers leading in innovation, particularly in 5G-Advanced and AI-driven network management, can command premium pricing as China Unicom seeks to maintain a competitive edge. This reliance on cutting-edge solutions from a limited pool of providers solidifies supplier influence over terms and pricing.
| Supplier Type | Key Players | Impact on China Unicom (2024) | Supplier Bargaining Power Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Equipment (5G Core) | Huawei, ZTE, Ericsson, Nokia | High dependency for advanced infrastructure; high switching costs | Concentrated market, specialized technology, vendor lock-in |
| Advanced Chipsets | Qualcomm, MediaTek, Intel | Vulnerability to shortages and price increases; critical for performance | Limited alternative providers, high R&D investment |
| Software & AI Solutions | Various specialized vendors | Need for cutting-edge solutions for efficiency and competitiveness | Technological differentiation, integration complexity |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to China Unicom's position in the telecommunications sector.
Navigate the competitive landscape of China's telecom market with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis for China Unicom, providing instant insights into bargaining power and competitive intensity.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in China benefit from a highly competitive telecommunications landscape, with China Mobile and China Telecom posing significant alternatives to China Unicom. This direct access to multiple major state-owned operators for mobile, broadband, and enterprise services significantly bolsters customer bargaining power, allowing them to push for more favorable pricing and service conditions.
The bargaining power of customers in China Unicom's mobile services is amplified by low switching costs, largely due to mobile number portability (MNP). This feature allows individuals to change providers without losing their existing phone numbers, effectively removing a significant barrier to switching. For instance, in 2023, MNP uptake continued to grow, with millions of subscribers porting their numbers across different operators in China, demonstrating its widespread use and impact.
This ease of migration directly pressures China Unicom. Consumers can readily compare and switch to competitors offering better pricing, superior network coverage, or more attractive service packages. This dynamic forces China Unicom to focus on customer retention through competitive pricing strategies and service improvements to avoid losing subscribers to rivals.
China Unicom faces significant customer bargaining power, especially in its consumer segment where price sensitivity is a major factor. For many individuals, basic mobile and broadband services are seen as commodities, leading them to actively seek out the most affordable options. This dynamic directly impacts Unicom's ability to set premium prices.
The high price sensitivity among China Unicom's consumer base compels the company to continuously offer competitive pricing and promotional deals. For instance, in 2023, the average revenue per user (ARPU) for China's mobile market remained relatively stable, indicating intense competition on price. This pressure can lead to compressed profit margins, limiting Unicom's overall pricing flexibility and impacting its profitability.
Information Access and Service Comparison
Customers of China Unicom, like those of any major telecommunications provider, benefit significantly from readily available information. They can easily compare service offerings, pricing plans, and network coverage across various providers through online platforms, review sites, and social media channels. This ease of access to information empowers them by fostering transparency in the market.
This transparency directly enhances customer bargaining power. Being well-informed allows consumers to quickly identify and switch to more attractive alternatives if they are dissatisfied with China Unicom's current offerings or pricing. For instance, in 2024, the average monthly mobile data cost in China saw continued competition, with consumers actively seeking out the best value.
- Informed Decision Making: Customers can access detailed comparisons of network speeds, data allowances, and customer service ratings, enabling them to make informed choices.
- Price Sensitivity: The ability to easily compare prices makes customers more sensitive to price differences, pressuring providers like China Unicom to remain competitive.
- Switching Behavior: Increased information access facilitates customer switching, as the perceived costs and complexities of changing providers are reduced.
- Demand for Value: Customers are more likely to demand greater value for their money, pushing companies to innovate and improve their service packages.
Demand for Value-Added Services
China Unicom's customers are increasingly seeking more than just basic phone and internet service. The demand for value-added services, such as integrated digital solutions, cloud computing, and smart home technologies, is growing significantly. This shift means customers are more likely to select providers based on the comprehensive nature and quality of these additional offerings, rather than solely on core connectivity pricing.
This growing appetite for bundled digital experiences grants customers greater bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the digital services market in China continued its robust expansion, with telecommunications companies like China Unicom actively investing in and promoting these offerings to differentiate themselves. Customers can leverage this by comparing the integrated service packages offered by various providers, pushing for better value and tailored solutions.
- Growing Demand for Integrated Digital Services: Customers are prioritizing providers that offer a seamless experience across multiple digital platforms and services.
- Cloud Solutions and Smart Home Adoption: The increasing adoption of cloud-based applications and smart home devices means customers expect their telecom provider to support and integrate these technologies.
- Customer Leverage through Service Bundles: The ability to choose providers based on the breadth and quality of value-added services gives customers significant leverage beyond simple connectivity pricing.
- Differentiation in a Commoditized Market: For China Unicom, offering superior value-added services is crucial for attracting and retaining customers in a market where basic connectivity is becoming increasingly commoditized.
China Unicom's customers possess considerable bargaining power due to the intensely competitive telecommunications market, where giants like China Mobile and China Telecom offer comparable services. This competitive pressure, coupled with low switching costs facilitated by mobile number portability, allows consumers to readily demand better pricing and service terms. For example, in 2023, millions of Chinese subscribers utilized MNP, highlighting the ease with which customers can move between providers, forcing Unicom to focus on retention through competitive offers and service enhancements.
Customers are highly price-sensitive, particularly for basic mobile and broadband services, viewing them as commodities. This leads them to actively seek the most economical options, limiting China Unicom's ability to command premium prices. The average revenue per user (ARPU) in China's mobile market remained competitive in 2023, underscoring the pressure on providers to offer attractive pricing, which can compress profit margins for Unicom.
The increasing demand for integrated digital solutions, cloud services, and smart home technologies further empowers customers. They now evaluate providers based on the breadth and quality of these value-added services, not just core connectivity. This trend, evident in China's expanding digital services market in 2024, allows customers to negotiate for better bundled packages and tailored solutions, pushing companies like China Unicom to innovate and differentiate.
| Factor | Impact on China Unicom | Customer Action | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Competition | High pressure on pricing and service offerings | Switch to competitors for better deals | China Mobile, China Telecom as major alternatives |
| Switching Costs | Low due to Mobile Number Portability (MNP) | Easily change providers without losing number | Millions of MNP users in 2023 |
| Price Sensitivity | Limits premium pricing ability, compresses margins | Seek lowest cost basic services | Stable ARPU in 2023 indicating price competition |
| Information Availability | Empowers informed choices and price comparisons | Compare plans, network, and service ratings online | Continued competition on average monthly mobile data costs in 2024 |
| Demand for Value-Added Services | Requires investment in digital solutions and bundles | Choose providers offering integrated digital experiences | Robust expansion of China's digital services market in 2024 |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
China Unicom Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of China Unicom, detailing the competitive landscape, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the telecommunications sector. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You'll gain valuable insights into the strategic positioning and potential challenges faced by China Unicom, enabling informed decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Chinese telecommunications landscape is dominated by three major state-owned players: China Unicom, China Mobile, and China Telecom. This oligopolistic structure fuels intense competition across all service areas, including mobile, fixed broadband, and enterprise solutions. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, China Mobile reported 1.13 billion mobile subscribers, China Telecom had 419 million, and China Unicom served 337 million, highlighting the sheer scale and market share concentration.
The battle for 5G network superiority is fierce, with China Unicom and its competitors pouring resources into infrastructure to offer faster speeds, lower latency, and broader coverage. This intense rivalry means operators are constantly upgrading their networks to stay ahead.
China Unicom, along with rivals like China Mobile and China Telecom, is actively expanding its 5G-Advanced network capabilities. For instance, by the end of 2023, China Unicom had built out over 1.3 million 5G base stations, a significant portion of the nation's total, highlighting the scale of investment and deployment in this competitive landscape.
China Unicom faces intense competition, with operators frequently engaging in aggressive pricing wars and promotional campaigns, especially for mobile and broadband services. This strategy aims to capture market share and customer loyalty in a saturated market. For instance, in 2023, the average revenue per user (ARPU) for China's mobile services saw a slight decline, reflecting the impact of such competitive pricing pressures.
Differentiation Through Value-Added Services
Competitive rivalry in China's telecom sector is intensifying beyond basic mobile and broadband services. Companies like China Unicom are increasingly focusing on value-added services to stand out. This includes offerings in cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics. They are also developing specialized solutions tailored for different industries, aiming to become partners in digital transformation for businesses.
China Unicom's strategy involves leveraging its network infrastructure to provide integrated digital solutions. For instance, in 2023, the company reported significant growth in its cloud services, contributing to its overall revenue diversification. This move allows them to capture a larger share of the enterprise market by offering more than just connectivity, but comprehensive digital transformation support.
- Cloud Computing Growth: China Unicom's cloud business saw substantial expansion in 2023, reflecting a broader industry trend towards cloud adoption.
- IoT Solutions: The company is actively developing and deploying IoT solutions, particularly for smart city and industrial applications.
- Big Data Analytics: China Unicom is investing in big data capabilities to offer insights and services to enterprise clients.
- Industry-Specific Offerings: Development of tailored solutions for sectors like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing is a key differentiator.
Government Influence and Policy Direction
The competitive landscape for China Unicom is significantly shaped by government influence and policy direction. While the market is indeed competitive, government mandates regarding spectrum allocation and strategic development directives play a crucial role in guiding the telecom sector's evolution. This means that competition can often be influenced by national strategic objectives, sometimes superseding pure market-driven forces.
For instance, government policies often dictate the pace and direction of 5G deployment, impacting how all players, including China Unicom, invest and compete. In 2024, the Chinese government continued to emphasize the importance of digital infrastructure, pushing for wider 5G coverage and the integration of technologies like AI and IoT into the network. This strategic push can create both opportunities and challenges, as companies must align their strategies with state priorities.
- Government Mandates: China's telecom sector operates under strong government oversight, influencing pricing, network build-out, and technology adoption.
- Spectrum Allocation: The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) controls the allocation of radio spectrum, a critical resource that directly impacts network capacity and service quality for all operators.
- National Strategic Goals: Competition is often framed within broader national goals, such as digital transformation initiatives and the development of a robust digital economy, encouraging cooperation and competition aligned with these aims.
- Policy-Driven Investment: Government support and policy direction can steer investment towards specific areas, such as rural broadband expansion or the development of new telecommunications technologies, influencing competitive dynamics.
The competitive rivalry within China's telecommunications sector is characterized by an oligopolistic structure dominated by three state-owned giants: China Unicom, China Mobile, and China Telecom. This intense competition drives constant innovation and aggressive pricing strategies, particularly in the rapidly evolving 5G and broadband markets.
As of Q1 2024, China Mobile led with 1.13 billion mobile subscribers, followed by China Telecom with 419 million and China Unicom with 337 million, underscoring the concentrated market share. This intense rivalry forces continuous investment in network upgrades, with China Unicom having deployed over 1.3 million 5G base stations by the end of 2023 to maintain its competitive edge.
Beyond core services, competition extends to value-added offerings like cloud computing and IoT, where companies vie to provide integrated digital solutions. For example, China Unicom saw significant growth in its cloud business during 2023, demonstrating a strategic shift to capture a larger enterprise market share through comprehensive digital transformation support.
| Operator | Q1 2024 Mobile Subscribers (Millions) | End 2023 5G Base Stations (Millions) | 2023 Cloud Revenue Growth (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| China Mobile | 1,130 | N/A | N/A |
| China Telecom | 419 | N/A | N/A |
| China Unicom | 337 | 1.3 | Significant |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of Over-The-Top (OTT) communication services presents a significant threat to China Unicom. Applications like WeChat, QQ, and others provide free or very low-cost alternatives for messaging and voice calls, directly competing with traditional SMS and voice revenue. This trend has led to a substantial decline in usage for these legacy services.
By 2024, it's estimated that a vast majority of mobile users in China rely heavily on OTT platforms for their daily communication needs. For instance, WeChat alone boasts over 1.3 billion monthly active users, demonstrating its pervasive reach. This widespread adoption means that a significant portion of communication that would have previously generated revenue for China Unicom is now being handled by these OTT providers, eroding traditional revenue streams.
The widespread availability of free or low-cost public Wi-Fi, particularly in China's bustling urban centers, presents a significant threat of substitution for China Unicom's mobile data services. This accessibility allows consumers to bypass paid mobile data plans for browsing, social media, and even streaming, especially when connected to networks in cafes, malls, and transportation hubs. By mid-2024, China's public Wi-Fi hotspots were estimated to be in the millions, offering a compelling alternative for data-intensive activities.
While satellite internet, particularly from Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellations, is still developing for broad consumer adoption in China, its long-term potential presents a future substitution threat. This emerging technology could offer an alternative to China Unicom's established terrestrial broadband and mobile services, especially in remote or geographically challenging regions where traditional infrastructure is costly to deploy.
Enterprise-Specific Communication Platforms
Businesses are increasingly turning to specialized enterprise communication and collaboration platforms, alongside private networks, for their internal operations. This trend directly impacts China Unicom's traditional enterprise services.
These tailored solutions often provide enhanced security and functionalities that standard offerings may lack, leading businesses to reduce their dependence on general providers like China Unicom.
For instance, the global enterprise collaboration market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly. Companies are investing in platforms like Microsoft Teams, Slack, and Cisco Webex, which offer integrated communication, project management, and file sharing, often with customizable security protocols.
- Increased adoption of specialized platforms: Many enterprises are migrating to dedicated communication suites that offer advanced features beyond basic connectivity.
- Demand for enhanced security: Private networks and secure enterprise platforms are gaining traction as businesses prioritize data protection and regulatory compliance.
- Reduced reliance on traditional telcos: As these internal solutions mature, they can fulfill a larger portion of a company's communication needs, lessening the need for external, general-purpose services.
Advancements in IoT and Non-Traditional Connectivity
The burgeoning Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem presents a growing threat of substitutes for traditional mobile connectivity. As more devices become interconnected, specialized low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs) like LoRaWAN and NB-IoT are emerging as alternatives for specific applications. These networks, while often built upon existing telco infrastructure, can enable certain IoT deployments to bypass standard mobile data plans, opting for more localized or purpose-built connectivity solutions.
This trend is particularly relevant as the global IoT market continues its rapid expansion. For instance, the IoT market was valued at over $1.1 trillion in 2023 and is projected to reach $2.2 trillion by 2028, indicating a significant shift towards diverse connectivity needs. Such specialized networks can offer cost advantages and tailored performance for use cases like smart metering, asset tracking, and environmental monitoring, potentially reducing reliance on China Unicom's core mobile offerings for these segments.
The threat is amplified by the increasing availability and decreasing cost of these alternative connectivity technologies. In 2024, the development and deployment of private IoT networks are accelerating, allowing businesses to manage their own connectivity without relying solely on public mobile networks. This can fragment the market and create opportunities for non-traditional players to offer specialized connectivity services, thereby substituting for China Unicom's broader mobile data services in niche areas.
- IoT Market Growth: Valued at over $1.1 trillion in 2023, with projections to reach $2.2 trillion by 2028, highlighting the increasing demand for connected devices.
- LPWAN Adoption: Technologies like LoRaWAN and NB-IoT offer specialized, low-power connectivity that can serve as alternatives for specific IoT applications.
- Bypassing Traditional Plans: Some IoT applications can utilize these specialized networks, potentially circumventing the need for standard mobile data plans offered by telcos.
- Cost and Performance Advantages: LPWANs can provide cost-effective and tailored connectivity for use cases such as smart metering and asset tracking, posing a direct substitute threat in these segments.
Over-The-Top (OTT) communication services like WeChat and QQ are a major substitute threat, offering free messaging and calls that erode China Unicom's traditional revenue. By 2024, the vast majority of Chinese mobile users rely on these platforms, with WeChat alone exceeding 1.3 billion monthly active users.
The widespread availability of free public Wi-Fi across China presents another significant substitute. Millions of Wi-Fi hotspots in urban areas allow users to bypass paid mobile data for browsing and streaming, directly impacting data service revenue.
Emerging technologies like satellite internet, though still developing for broad consumer use in China, pose a future threat to traditional broadband and mobile services, particularly in remote areas.
Businesses are increasingly adopting specialized enterprise communication platforms and private networks, reducing their reliance on general telco services. The global enterprise collaboration market, valued around $50 billion in 2023, highlights this shift towards tailored, secure solutions.
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a nationwide telecommunications network, especially with the advanced infrastructure needed for 5G, requires massive capital outlays. For instance, China's 5G network build-out alone was projected to cost hundreds of billions of dollars by 2025, with significant portions already invested by major players like China Unicom.
The expenses for securing essential radio spectrum, constructing a vast array of base stations, and deploying extensive fiber optic cabling create an almost insurmountable financial hurdle for most prospective new competitors looking to enter the Chinese market.
The telecommunications industry in China is a heavily regulated space, with state control dictating much of its operation. New entrants face a formidable challenge due to the extensive licensing and approval processes mandated by various government bodies. These stringent regulatory barriers significantly deter potential new competitors from entering the market.
For instance, obtaining the necessary operating licenses in China's telecom sector is a complex and lengthy process, often requiring substantial capital investment and adherence to strict operational standards. In 2023, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) continued to emphasize robust oversight, making it exceptionally difficult for unproven entities to gain a foothold.
China Unicom, alongside its primary competitors China Mobile and China Telecom, benefits from decades of established market presence and deeply ingrained customer loyalty. This creates a significant barrier for any potential new entrants aiming to disrupt the telecommunications landscape.
These incumbents possess vast, pre-existing customer bases and a strong brand recognition built over many years, making it incredibly challenging for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, as of the end of 2023, China Mobile, China Unicom, and China Telecom collectively served over 1.7 billion mobile subscribers in China, highlighting the sheer scale of their operations and customer reach.
New entrants would face an uphill battle in replicating the economies of scale and the trust that these established players command. The cost of building a comparable network infrastructure and acquiring a significant customer base from scratch is exceptionally high, further deterring potential competition.
Control over Essential Infrastructure and Spectrum
China Unicom, like other established players, benefits from significant control over its existing network infrastructure. This includes a vast and intricate web of cell towers, fiber optic cables, and data centers, representing a massive capital investment. For instance, in 2023, China Unicom reported capital expenditures of approximately RMB 70.7 billion (around $9.8 billion USD), primarily focused on network upgrades and expansion.
Furthermore, access to crucial spectrum licenses is a formidable barrier. These licenses, allocated by regulatory bodies, are essential for providing wireless telecommunications services. Acquiring comparable spectrum holdings would involve substantial financial outlay and regulatory hurdles, making it exceedingly difficult for new entrants to establish a competitive presence in the market.
The threat of new entrants is therefore significantly mitigated by these entrenched advantages:
- Proprietary Infrastructure: China Unicom's extensive and complex network infrastructure is a costly and time-consuming asset for any new competitor to replicate.
- Spectrum Access: Control over valuable spectrum licenses, essential for wireless services, presents a significant barrier to entry due to acquisition costs and regulatory complexities.
- Capital Intensity: The telecommunications industry is highly capital-intensive, requiring massive upfront investments in infrastructure and technology, which deters potential new players.
Government's Strategic Control of the Sector
The Chinese government's strategic control over the telecommunications sector significantly deters new entrants. Given the industry's critical role in national security and economic growth, Beijing maintains a firm grip, effectively barring independent companies from entering the market. This state-controlled environment means new players face immense regulatory hurdles and a lack of access to essential infrastructure, making it nearly impossible to compete with established state-owned enterprises like China Unicom.
This tight government control is a powerful barrier. For instance, in 2024, state-owned enterprises continued to dominate the landscape, with China Unicom, China Mobile, and China Telecom holding virtually all market share. The capital requirements for building out a telecommunications network are astronomical, and without government approval and licensing, which are exceptionally difficult to obtain for private entities, any new entrant would be severely disadvantaged.
- Strategic Sector Control: The Chinese government designates telecommunications as a strategic industry, ensuring state dominance.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining licenses and approvals for new telecommunications operators is extremely challenging for non-state entities.
- Infrastructure Access: New entrants are unlikely to gain access to essential network infrastructure controlled by state-owned incumbents.
- Dominant State-Owned Players: China Unicom, China Mobile, and China Telecom, all state-controlled, held nearly 100% of the market share in 2024, demonstrating the lack of independent competition.
The threat of new entrants in China's telecommunications market, where China Unicom operates, is exceptionally low. This is primarily due to the immense capital required to establish a competitive network, with 5G infrastructure alone demanding hundreds of billions of dollars in investment. Coupled with stringent government regulations and licensing processes, these factors create substantial barriers for any potential newcomers seeking to enter this heavily controlled sector.
The established market presence and customer loyalty of incumbents like China Unicom, China Mobile, and China Telecom, who collectively served over 1.7 billion mobile subscribers by the end of 2023, further solidify their dominant positions. New entrants would struggle to match the economies of scale and brand trust these companies have cultivated over decades, making market penetration exceedingly difficult.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Data (2023/2024) |
| Capital Intensity | Massive upfront investment in infrastructure and technology. | China Unicom's 2023 CapEx: ~RMB 70.7 billion (~$9.8 billion USD) |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing and approval processes for new operators. | State-owned enterprises held nearly 100% market share in 2024. |
| Economies of Scale | Established player advantage due to vast customer base and network reach. | China's top 3 carriers served over 1.7 billion mobile subscribers in 2023. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for China Unicom leverages data from official company filings, including annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like Statista and Analysys International.