Burns & McDonnell Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Burns & McDonnell Bundle
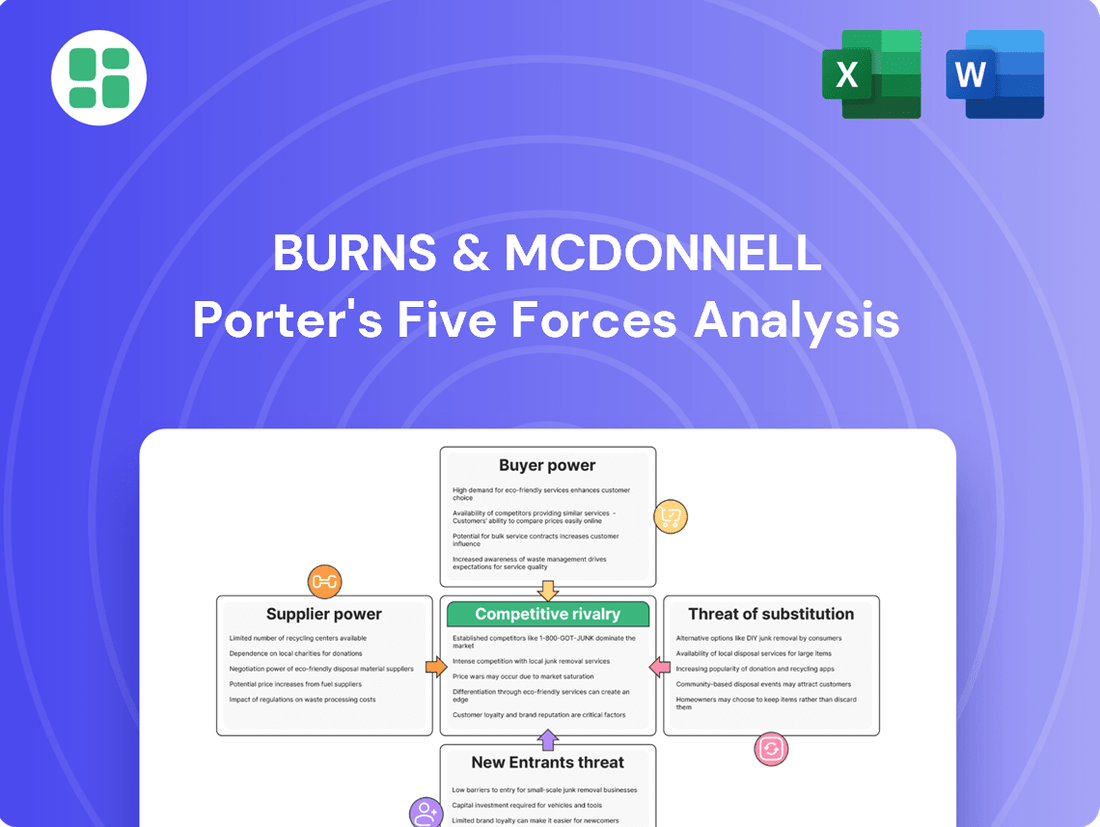
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Burns & McDonnell reveals the intense competitive landscape they navigate, from the bargaining power of their clients to the constant threat of new entrants in the engineering and consulting sector. Understanding these forces is crucial for any business operating in this space.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Burns & McDonnell’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly those providing specialized labor, is a significant factor for firms like Burns & McDonnell. Ongoing talent shortages in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) sector mean that highly skilled engineers, architects, and craftworkers hold considerable leverage. The demand for this expertise, especially for complex projects, outstrips supply, allowing these specialized individuals to command higher wages and better terms.
Providers of advanced technology and software, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Computer-Aided Design (CAD) platforms, wield significant bargaining power. These tools are indispensable for modern engineering and construction projects, offering enhanced efficiency and innovation. For a firm like Burns & McDonnell, which emphasizes an integrated approach, the reliance on these sophisticated digital solutions makes suppliers of AI-driven tools and digital twin technologies particularly influential.
Suppliers of critical construction materials like steel and concrete, as well as specialized components for renewable energy projects, hold significant bargaining power. This is particularly true in 2024, with persistent supply chain snags and fluctuating material prices impacting project costs and timelines.
For an Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) firm like Burns & McDonnell, these supplier dynamics directly influence their ability to deliver projects on budget and schedule. For instance, the price of structural steel, a key input for many projects, saw significant volatility in late 2023 and early 2024, with some reports indicating price increases of 10-15% year-over-year for certain grades.
Subcontractors and Specialty Firms
For large, complex projects, Burns & McDonnell relies on a network of subcontractors and specialty firms. The availability and reputation of these partners, especially in niche fields or during periods of high demand, can grant them leverage over project schedules and expenses. For example, in 2024, the engineering and construction sector experienced significant demand for specialized labor, potentially increasing the bargaining power of firms possessing unique skill sets.
- Specialized Expertise: Certain subcontractors possess highly specialized knowledge or certifications crucial for specific project components, making them indispensable.
- Market Conditions: During periods of high construction activity, like that observed in many infrastructure projects throughout 2024, the demand for skilled subcontractors often outstrips supply, enhancing their negotiating position.
- Reputation and Track Record: Firms with a proven history of successful project delivery and reliability can command better terms due to their perceived lower risk.
- Project Complexity: The more intricate and technically demanding a project, the greater the reliance on specialized subcontractors, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Proprietary Technologies or Patented Solutions
Suppliers possessing proprietary technologies or patented solutions, like specialized components for advanced renewable energy systems, can significantly increase their bargaining power. For instance, a unique, highly efficient solar module design or a patented energy storage system creates a situation where Burns & McDonnell, a major player in renewable energy projects, has limited direct substitutes. This exclusivity allows these suppliers to dictate terms and pricing, as their innovations are critical to project success and cannot be easily replicated by competitors.
The impact of these suppliers is evident in the market dynamics. In 2024, the global solar energy market saw continued growth, with innovation in panel efficiency being a key driver. Companies holding patents for next-generation photovoltaic materials or advanced inverter technology were able to secure premium contracts. Burns & McDonnell, engaging in projects that often require cutting-edge performance, must account for the higher costs associated with such exclusive technological offerings.
- Proprietary Technology as a Barrier: Suppliers with unique, patented technologies, such as advanced renewable energy components, can command higher prices due to the absence of direct alternatives.
- Limited Substitutability: The lack of interchangeable options for these specialized components restricts Burns & McDonnell's ability to negotiate lower prices or switch suppliers.
- Impact on Project Costs: This supplier power directly influences the overall cost of renewable energy projects, as critical, exclusive technologies often come at a premium.
- Market Trends: In 2024, the demand for enhanced efficiency in solar modules and energy storage solutions further solidified the bargaining power of suppliers holding key patents in these areas.
Suppliers of specialized labor and critical materials hold significant bargaining power, especially in 2024, due to talent shortages and supply chain disruptions. For firms like Burns & McDonnell, this translates to higher costs for essential inputs and skilled personnel, impacting project profitability and timelines. Proprietary technologies in areas like renewable energy further concentrate power with exclusive suppliers, limiting negotiation flexibility.
| Supplier Type | Key Factor | Impact on Burns & McDonnell | 2024 Market Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Labor (e.g., Engineers) | Talent Shortage | Increased wage demands, potential project delays | High demand for skilled AEC professionals |
| Advanced Technology (e.g., BIM Software) | Indispensability | Higher licensing fees, reliance on vendor updates | Growing adoption of AI and digital twin tech |
| Critical Materials (e.g., Steel) | Supply Chain Volatility | Price fluctuations, increased material costs | Steel prices saw 10-15% YoY increases in early 2024 |
| Proprietary Renewable Energy Components | Patented Technology | Premium pricing for exclusive solutions | Demand for high-efficiency solar components |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Burns & McDonnell's engineering and consulting services.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visually intuitive breakdown of industry dynamics, making strategic planning less daunting.
Customers Bargaining Power
Burns & McDonnell's large-scale project clients, such as major utilities and government agencies, wield considerable bargaining power. These clients often account for substantial project values, allowing them to negotiate favorable terms and secure repeat business, directly impacting the firm's revenue streams.
Burns & McDonnell's client base, while diverse, shows a notable concentration in sectors like power, aviation, and water. This means that if these key industries experience a slowdown or if major clients within them gain more purchasing power, it could shift the balance, giving those customers more leverage in negotiations. For instance, in 2023, the energy sector, a significant market for Burns & McDonnell, saw continued investment in renewables, but also faced challenges related to grid modernization and regulatory shifts, potentially impacting client spending patterns.
The engineering, architecture, and construction (EAC) sector in 2024 features a robust landscape with many established, large-scale competitors. This means clients have a wealth of choices when selecting a firm, significantly boosting their leverage in negotiations regarding pricing, project scope, and contract terms.
Clients can readily obtain competitive bids from multiple highly reputable EAC firms. For instance, major projects often see dozens of proposals submitted by industry leaders, allowing clients to compare offerings and secure more favorable deals.
In-house Capabilities
Burns & McDonnell's clients, particularly larger ones, may possess their own internal engineering or project management departments. This capability allows them to handle certain project aspects internally, reducing their dependence on external firms for every service. For instance, a major industrial client might have a dedicated team capable of performing preliminary design reviews or managing specific construction phases, thereby increasing their leverage in negotiations with engineering consultants.
This in-house capacity directly impacts the bargaining power of customers by enabling them to:
- Perform select services internally, diminishing the need for outsourced expertise.
- More effectively vet and negotiate terms with external engineering and consulting firms.
- Reduce overall project costs by leveraging existing internal resources and expertise.
- Increase their control over project scope and execution when engaging with external partners.
Project Complexity and Criticality
For highly complex, mission-critical projects, Burns & McDonnell's specialized expertise significantly diminishes customer bargaining power. Clients undertaking endeavors such as large-scale renewable energy infrastructure or advanced water treatment facilities often find their options limited due to the unique demands and high stakes involved.
The specialized nature of these projects inherently restricts the pool of qualified alternatives, effectively increasing switching costs for the client. This is particularly true when Burns & McDonnell can demonstrate a proven track record of successful delivery in similar high-complexity environments. For instance, in the engineering and construction sector, projects exceeding $100 million often see reduced client leverage when specialized engineering and project management are paramount.
- Reduced Leverage on Mission-Critical Projects: For projects where failure carries severe consequences, clients are less likely to exert significant price pressure.
- High Switching Costs: The investment in learning and integrating a new provider for complex, long-term projects can be substantial, deterring clients from switching.
- Limited Qualified Alternatives: The scarcity of firms with comparable technical capabilities and experience in niche sectors strengthens Burns & McDonnell's position.
- Indispensable Expertise: When Burns & McDonnell offers unique solutions or intellectual property, their bargaining power is amplified.
The bargaining power of customers for Burns & McDonnell is a key factor influencing their market position. When clients have numerous choices, especially for standardized services, their ability to negotiate favorable terms increases significantly. This is evident in 2024, where the competitive landscape of the engineering, architecture, and construction (EAC) sector offers clients a wide array of highly reputable firms, allowing them to solicit and compare multiple bids, thereby driving down prices and influencing project scope.
However, this power diminishes considerably for highly specialized or mission-critical projects. In such cases, the scarcity of firms with the requisite technical expertise and proven track record, like those involved in advanced water treatment or complex renewable energy installations, limits client options. This scarcity, coupled with high switching costs and the critical nature of the projects, strengthens Burns & McDonnell's position, as seen in instances where projects exceed $100 million and demand unparalleled specialized engineering.
| Customer Characteristic | Impact on Bargaining Power | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| High number of alternative suppliers | Increases bargaining power | Client seeking standard civil engineering design services |
| Low switching costs | Increases bargaining power | Client engaging a firm for a single, non-critical project phase |
| Low customer importance (low revenue contribution) | Decreases bargaining power | Small municipal project for a large engineering firm |
| Ability to backward integrate (in-house capabilities) | Increases bargaining power | Large utility client with its own design and project management teams |
| Low product differentiation (standardized services) | Increases bargaining power | Routine environmental impact assessments |
| High customer bargaining power (mission-critical projects) | Decreases bargaining power | Client requiring specialized engineering for a new nuclear power plant component |
Same Document Delivered
Burns & McDonnell Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Burns & McDonnell Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing an in-depth examination of competitive and market forces within their industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and instant access to valuable strategic insights.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) sector is densely populated with numerous large, seasoned companies, both within the United States and globally. These firms directly challenge Burns & McDonnell for significant projects and broader market influence, creating a highly competitive environment.
This intense rivalry is evident in the competition for large-scale infrastructure and energy projects. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. construction industry saw a significant number of bids on major public works projects, with established players like Fluor Corporation and Jacobs Engineering Group consistently vying for these contracts alongside Burns & McDonnell.
The sheer volume of capable competitors means that differentiation and strategic positioning are crucial. Firms are constantly innovating and leveraging their expertise to secure lucrative contracts, driving up the stakes for market share and profitability within the industry.
The engineering and construction services market anticipates consistent expansion, especially within infrastructure and clean energy sectors, yet competition for substantial projects remains fierce. In 2024, firms are actively vying for lucrative opportunities, often fueled by significant government funding initiatives, to bolster their future project portfolios.
Burns & McDonnell leverages its integrated engineer-procure-construct (EPC) model and deep specialization in high-growth sectors like renewables and aviation to stand out. This comprehensive approach allows them to manage projects from conception to completion, offering clients a streamlined experience.
Despite this, the competitive landscape is intense, with many rivals also boasting broad service offerings or focused expertise. For instance, in the renewable energy sector, companies like Black & Veatch and AECOM are also significant players, vying for market share. The rivalry often hinges on demonstrable track records, a commitment to innovation, and the strength of established client relationships.
In 2023, the global engineering and construction market was valued at approximately $12.7 trillion, with significant growth anticipated in infrastructure and energy transition projects, areas where firms like Burns & McDonnell are actively competing. This robust market size underscores the high stakes involved in differentiating services and building strong client loyalty.
Cost Structures and Fixed Costs
The engineering and consulting sector, where Burns & McDonnell operates, often demands substantial upfront investments. These include maintaining a highly skilled, large workforce, acquiring and updating advanced technological tools, and building and sustaining extensive operational infrastructure, such as offices and testing facilities.
These high fixed costs create pressure on companies to secure a steady stream of projects. Firms may engage in aggressive bidding to ensure their resources are utilized efficiently, which can intensify price-based competition among rivals. For instance, in 2023, major engineering firms reported significant capital expenditures related to technology upgrades and talent acquisition, underscoring the industry's cost structure.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant investments in talent, technology, and infrastructure are typical.
- Capacity Utilization Drive: Pressure to keep resources busy can lead to aggressive bidding.
- Price Competition: The need for project flow can result in competition based on price.
- Impact on Profitability: High fixed costs can squeeze profit margins if revenue streams are inconsistent.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) continue to be a significant driver of competitive intensity within the engineering and construction sector. In 2023, the global M&A market saw robust activity, with deal volumes in the industrials sector, which includes engineering and construction, remaining strong despite economic headwinds. This ongoing consolidation leads to the emergence of larger, more formidable competitors, often boasting expanded service offerings and a broader geographic footprint.
These larger entities, formed through strategic acquisitions, can leverage economies of scale and greater financial resources to compete more aggressively on price and project scope. For instance, a hypothetical acquisition of a specialized environmental consulting firm by a large infrastructure engineering company could create a more integrated competitor capable of handling complex, multi-faceted projects that smaller firms might not be equipped to pursue. This dynamic necessitates that existing players, including Burns & McDonnell, continuously evaluate their own strategic positioning and consider how M&A or strategic partnerships can bolster their competitive advantages.
- Increased Scale and Scope: M&A activity creates larger players with enhanced capabilities to undertake larger, more complex projects.
- Market Consolidation: Ongoing consolidation reshapes the competitive landscape, potentially reducing the number of independent competitors.
- Enhanced Capabilities: Acquired firms often bring specialized expertise or technologies, broadening the service offerings of the acquiring entity.
- Strategic Adaptation: Firms must adapt their strategies to compete with these more diversified and resource-rich competitors.
The competitive rivalry within the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) sector is exceptionally high, with Burns & McDonnell facing numerous well-established domestic and international firms. This intense competition is particularly noticeable in securing large-scale infrastructure and energy projects, where established players consistently bid for contracts. For example, in 2023, the U.S. construction industry witnessed robust bidding activity on major public works, with companies like Fluor and Jacobs Engineering being key rivals.
The market for engineering and construction services is projected for steady growth, especially in infrastructure and clean energy. However, competition for significant projects remains fierce, with firms actively pursuing opportunities in 2024, often driven by government funding. This necessitates continuous innovation and strategic positioning for companies like Burns & McDonnell to differentiate themselves and secure market share.
The sector is characterized by high fixed costs, including substantial investments in talent, advanced technology, and extensive operational infrastructure. This cost structure pressures firms to maintain high capacity utilization, potentially leading to aggressive bidding and price-based competition. In 2023, major engineering firms reported significant capital expenditures, highlighting the industry's cost dynamics.
Mergers and acquisitions further intensify this rivalry, creating larger, more capable competitors with expanded service offerings and broader geographic reach. For instance, ongoing consolidation in 2023 saw strong M&A activity in the industrials sector, reshaping the competitive landscape and requiring firms to adapt their strategies to compete with these consolidated entities.
| Key Competitors in AEC Sector | Key Sectors of Competition | Competitive Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Fluor Corporation | Infrastructure, Energy, Government Projects | Scale, Global Reach, Project Management Expertise |
| Jacobs Engineering Group | Infrastructure, Aerospace, Technology, Energy | Technical Expertise, Innovation, Diverse Service Offerings |
| Black & Veatch | Energy, Water, Infrastructure, Telecommunications | Specialized Expertise in Utilities, Sustainable Solutions |
| AECOM | Infrastructure, Environment, Buildings, Transportation | Broad Service Portfolio, Global Presence, Design & Consulting Strength |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large organizations increasingly build out their internal engineering, procurement, and construction management (EPCM) capabilities. This trend directly substitutes the need for external consulting and EPCM services, especially for routine maintenance and smaller projects. For instance, in 2024, many utility companies and large industrial conglomerates are investing heavily in upskilling their internal teams to handle a greater portion of their project lifecycle.
The rise of standardized and modular construction methods presents a significant threat to traditional engineering and construction firms. These approaches, often incorporating Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DfMA) principles, allow for faster project completion and reduced on-site labor requirements. For instance, the global modular construction market was valued at approximately $109.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear shift in industry practices.
The increasing sophistication of AI and advanced software presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional engineering services. Generative design tools and AI-powered automation can now perform tasks previously requiring extensive human input, potentially reducing the need for certain specialized roles.
By 2024, investments in AI and automation within the engineering sector are projected to reach billions, with companies like Autodesk reporting substantial growth in their AI-driven design platforms. This technological evolution could lead to a scenario where software solutions directly substitute for a portion of the human-led design and analysis processes, impacting demand for specific engineering skill sets.
Alternative Project Delivery Models
Clients increasingly explore alternative project delivery models that can bypass the need for integrated Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) services. For instance, a growing trend in 2024 sees owners opting for pure Construction Management (CM) or even self-performing aspects of development, effectively reducing the demand for a single, comprehensive service provider.
These alternative approaches, such as CM at Risk or Design-Build-Operate, allow clients to retain more control and potentially distribute risk differently. This can lead to a fragmentation of the project lifecycle, where specialized firms handle specific phases, thereby diminishing the comprehensive scope typically offered by integrated EPC firms like Burns & McDonnell.
- Shift in client preference: Growing interest in Construction Management (CM) and owner-led development models.
- Risk and responsibility redistribution: Alternative models often shift project risks away from a single integrated provider.
- Reduced scope for EPC firms: Fragmentation of services can limit opportunities for full-service engineering and construction companies.
- Market adaptation: Firms may need to adapt their offerings to compete with more flexible, specialized delivery methods in 2024 and beyond.
Consulting from Technology Vendors or Material Suppliers
The threat of substitutes for consulting services from technology vendors or material suppliers is growing. Companies like Autodesk, a major player in BIM software, are increasingly offering integrated design and engineering consultation services. This can present a compelling alternative for clients seeking end-to-end solutions, potentially bypassing traditional independent consulting firms. For instance, in 2024, the AEC (Architecture, Engineering, and Construction) software market was valued at approximately $15 billion, with significant growth driven by integrated platform offerings.
These vendors can leverage their deep product knowledge to provide specialized advice, often bundled with their software or material packages. This integration can lead to cost efficiencies and streamlined project execution for clients. Consider the case of large construction material suppliers who might offer design assistance for projects utilizing their specific products, effectively substituting for a portion of a traditional engineering firm's scope. The global construction materials market size was estimated to be over $1.1 trillion in 2023, indicating the substantial reach of these suppliers.
- Vendor Integration: Technology vendors are expanding services beyond software to include design and engineering consultation.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Bundled services from vendors can offer a more economical alternative to independent consultants.
- Market Impact: The significant size of markets like AEC software and construction materials highlights the potential for vendor substitution.
The threat of substitutes is significant as clients increasingly opt for internal EPCM capabilities or alternative project delivery models. This trend is driven by a desire for greater control and potential cost savings, directly impacting the demand for traditional, integrated service providers.
Modular construction and advanced AI-driven design tools also represent powerful substitutes, offering faster project timelines and reduced labor needs. The growing adoption of these technologies, exemplified by the substantial investments in AI within the engineering sector in 2024, reshapes project execution and the required skill sets.
Furthermore, technology vendors and material suppliers are expanding their service offerings to include design and engineering consultation, providing bundled, cost-effective alternatives. The vast size of markets like AEC software and construction materials underscores the potential for these integrated solutions to substitute for independent consulting services.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Traditional EPCM | 2024 Market Insight |
| Internal EPCM Capabilities | Increased client self-sufficiency, focus on routine tasks | Reduced demand for external EPCM, especially for smaller projects | Utility and industrial firms investing in internal team upskilling |
| Modular Construction | Faster completion, reduced on-site labor, DfMA principles | Challenges traditional construction methods, impacts labor needs | Global modular construction market valued ~ $109.8 billion in 2023 |
| AI & Advanced Software | Generative design, automation, potential role substitution | Reduces need for certain specialized human roles in design/analysis | Billions invested in AI/automation in engineering; Autodesk growth |
| Alternative Project Delivery | CM at Risk, Design-Build-Operate, owner-led development | Fragments project lifecycle, diminishes scope for integrated EPC | Growing client preference for flexible, specialized delivery |
| Vendor Integrated Services | Bundled software/materials with consultation | Offers cost-efficient, end-to-end solutions, bypassing consultants | AEC software market ~ $15 billion in 2024; large construction material suppliers |
Entrants Threaten
The engineering, architecture, and construction sector, particularly for the large-scale, complex projects characteristic of Burns & McDonnell's operations, demands significant upfront capital. Newcomers must invest heavily in specialized equipment, advanced technology, and a skilled workforce, creating a formidable barrier to entry.
For instance, major infrastructure projects often necessitate multi-million dollar investments in heavy machinery, sophisticated design software, and extensive project management systems before any revenue is generated. This high capital threshold naturally deters many potential competitors from entering the market.
Burns & McDonnell, boasting over 125 years of history, has cultivated an exceptionally strong brand reputation and deep-seated client relationships. This extensive legacy means new entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating the trust and credibility that Burns & McDonnell has earned. Securing major projects often hinges on this established rapport and a proven history of successful delivery, which newcomers will find difficult to immediately match.
The Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) sector faces substantial regulatory complexities. New entrants must contend with a labyrinth of permits, zoning laws, environmental impact assessments, and safety standards that differ significantly across jurisdictions and project scales. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain major construction permits in the US remained a considerable challenge, often extending for months, a significant barrier for agile new firms.
Licensing and professional certifications are also critical entry barriers. Engineers and architects must meet stringent educational, experience, and examination requirements, often needing multiple state-specific licenses. In 2024, the number of newly licensed professional engineers continued to grow, but the rigorous, multi-year process ensures a controlled supply of qualified professionals, making it difficult for new, uncredentialed firms to compete effectively.
Access to Skilled Talent and Specialized Workforce
The scarcity of skilled talent, particularly engineers, project managers, and craftworkers, presents a significant barrier for new companies entering the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) sector. This shortage makes it challenging for newcomers to assemble a capable workforce swiftly.
Established players like Burns & McDonnell benefit from robust talent acquisition strategies and employee ownership structures, which foster loyalty and reduce turnover. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a need for over 300,000 additional construction workers annually through 2030 to meet demand.
- Persistent Shortage: The AEC industry faces an ongoing deficit of qualified professionals, impacting new entrants' ability to scale.
- Talent Pipelines: Established firms leverage existing relationships and recruitment channels to secure talent more readily.
- Retention Advantage: Employee-ownership models, like that of Burns & McDonnell, enhance retention, a critical factor in a competitive labor market.
- 2024 Labor Data: The U.S. construction sector reported a job opening rate of 5.3% in early 2024, highlighting the intense competition for workers.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Established players in the engineering and construction sector, like Burns & McDonnell, leverage significant economies of scale. This means they can spread their fixed costs over a larger volume of work, leading to lower per-unit costs in areas like procurement, technology adoption, and administrative overhead. For instance, a large firm securing a major infrastructure project might negotiate bulk discounts on materials or specialized equipment, a benefit unavailable to a smaller, new entrant.
The experience curve also plays a crucial role. Companies that have executed numerous complex projects build institutional knowledge and refine their processes over time. This accumulated expertise translates into greater efficiency, fewer errors, and better risk management. A new entrant, lacking this deep well of experience, will likely face higher initial costs and longer timelines as they learn and adapt, making it challenging to match the cost-competitiveness of incumbents on large-scale endeavors.
Consider the competitive landscape in 2024. Major engineering firms often boast decades of project execution, refining their project management software and supply chain logistics. This allows them to bid more aggressively on projects, knowing their operational efficiencies provide a buffer. New entrants, conversely, must invest heavily in building these capabilities from scratch, often facing a steep uphill battle to achieve similar cost structures and project delivery speeds.
- Economies of Scale: Large firms benefit from lower per-unit costs due to high-volume operations, impacting procurement and overhead.
- Experience Curve: Accumulated expertise leads to improved efficiency, reduced errors, and better risk management for established companies.
- Cost Competitiveness: New entrants struggle to match the cost advantages of incumbents due to a lack of scale and experience.
- Barriers to Entry: These factors create a significant hurdle for new companies seeking to enter and compete effectively in the market.
The threat of new entrants in the engineering, architecture, and construction sector for large-scale projects is considerably low. High capital requirements for equipment and technology, coupled with stringent licensing and regulatory hurdles, create substantial barriers. Established firms also benefit from strong brand loyalty, deep client relationships, and economies of scale, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on cost and project execution.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants (2024 Data/Trends) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Significant investment needed for specialized machinery, software, and infrastructure. | Projects often require multi-million dollar upfront capital; average construction permit times in the US remained a challenge in 2024. |
| Brand Reputation & Client Relationships | Established trust and a proven track record are critical for securing large projects. | New entrants struggle to replicate the credibility of firms with decades of successful project delivery. |
| Regulatory & Licensing | Navigating permits, zoning, environmental assessments, and professional certifications. | Rigorous, multi-year processes for professional licensing; a controlled supply of qualified professionals in 2024. |
| Skilled Labor Shortage | Difficulty in assembling a qualified workforce, especially engineers and project managers. | U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a need for over 300,000 additional construction workers annually through 2030; job opening rate was 5.3% in early 2024. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience Curve | Lower per-unit costs and improved efficiency from high-volume operations and accumulated knowledge. | New entrants face higher initial costs and longer timelines to match incumbent efficiencies and cost-competitiveness. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive suite of data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and proprietary company intelligence.