Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical Bundle
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical faces moderate bargaining power from its buyers, as the pharmaceutical industry often sees a degree of price sensitivity. However, the threat of new entrants is also a significant factor to consider, given the industry's capital requirements and regulatory hurdles.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical's bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by supplier concentration. If the market for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and other critical raw materials is dominated by a few key players, these suppliers can exert considerable leverage. This is particularly true for specialized or patented compounds where Hubei Biocause has limited alternatives.
The global API supply landscape is heavily reliant on China, which by 2023, controlled an estimated 80% of the market. This significant concentration means Chinese API suppliers can possess substantial bargaining power, potentially dictating terms and pricing to pharmaceutical manufacturers like Hubei Biocause.
The cost and complexity for Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical to switch suppliers for critical Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and specialized medical device components can be substantial. This often involves extensive regulatory re-approvals, rigorous validation processes, and the potential for significant disruption to ongoing production schedules. For instance, a shift in a key API supplier could necessitate months of testing and documentation to meet stringent pharmaceutical standards, impacting output and potentially delaying product launches.
These high switching costs significantly enhance the bargaining power of Hubei Biocause's established and compliant suppliers. Suppliers who have already navigated the complex approval pathways and demonstrated consistent quality can command better terms, as the financial and operational burden of finding and qualifying an alternative falls heavily on Biocause. This dynamic is particularly pronounced for niche or technologically advanced components where fewer qualified suppliers exist.
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical's reliance on unique or specialized inputs significantly influences supplier bargaining power. If the company sources patented intermediates or advanced manufacturing technologies, suppliers of these critical components gain leverage. This dependency is especially pronounced in sectors like innovative pharmaceuticals and high-value medical devices, where specialized knowledge and proprietary materials are paramount.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers to Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical could threaten its market position by integrating forward. This means they might start producing finished pharmaceutical preparations or even medical devices themselves, effectively becoming direct competitors. Such a move would directly challenge Biocause's existing business model.
However, this threat is often tempered by significant barriers to entry in the pharmaceutical sector. The substantial capital required for setting up manufacturing facilities and navigating stringent regulatory approvals, like those from the China National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), makes forward integration a costly and complex endeavor for many suppliers. For instance, the average capital expenditure for a new pharmaceutical manufacturing plant can easily run into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities demands significant upfront capital, often exceeding the financial capacity of typical raw material suppliers.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and obtaining necessary product registrations are complex and time-consuming, posing a substantial barrier.
- Specialized Expertise: Pharmaceutical production requires specialized knowledge in formulation, quality control, and sterile processing, which suppliers may lack.
Importance of Hubei Biocause to Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers to Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical is significantly influenced by the proportion of their business Hubei Biocause represents. If Hubei Biocause is a major customer, accounting for a substantial percentage of a supplier's revenue, the supplier's leverage is diminished. This reliance makes them more amenable to Hubei Biocause's terms, as losing this business would be detrimental.
Conversely, if Hubei Biocause constitutes only a small fraction of a supplier's overall sales, the supplier gains considerable bargaining power. In such scenarios, suppliers are less dependent on Hubei Biocause and can afford to dictate terms or even withdraw their services if their demands are not met, potentially leading to higher input costs for Hubei Biocause.
For instance, in the pharmaceutical ingredient sector, a supplier of a specialized active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) might hold more power if Hubei Biocause is one of many clients sourcing that particular ingredient. However, if Hubei Biocause is the primary purchaser of a unique raw material, the supplier's power is curtailed.
- Supplier Reliance: Hubei Biocause's importance as a customer directly impacts supplier bargaining power.
- Market Share: Suppliers with a larger customer base for their products generally have less dependency on any single buyer like Hubei Biocause.
- Input Specificity: The uniqueness of the inputs supplied to Hubei Biocause plays a crucial role; specialized inputs reduce supplier power.
- Industry Dynamics: The overall competitive landscape among suppliers of raw materials and intermediates for pharmaceuticals influences their ability to negotiate terms.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical is significantly shaped by the concentration of the API market. With China dominating global API production, holding an estimated 80% share by 2023, Chinese suppliers possess considerable leverage, often dictating terms and pricing due to Hubei Biocause's reliance on these inputs.
High switching costs for critical APIs, involving extensive regulatory re-approvals and validation, empower established suppliers. These costs, potentially running into months of testing and documentation to meet stringent pharmaceutical standards, make it financially and operationally burdensome for Hubei Biocause to change suppliers.
Suppliers' power is also amplified when Hubei Biocause depends on unique or patented intermediates. This dependence is particularly acute in specialized pharmaceutical sectors where proprietary materials and advanced technologies are essential, giving suppliers a stronger negotiating position.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is mitigated by high barriers to entry in pharmaceuticals, including substantial capital investment, estimated in the tens or hundreds of millions of dollars for new plants, and complex regulatory hurdles like GMP compliance.
What is included in the product
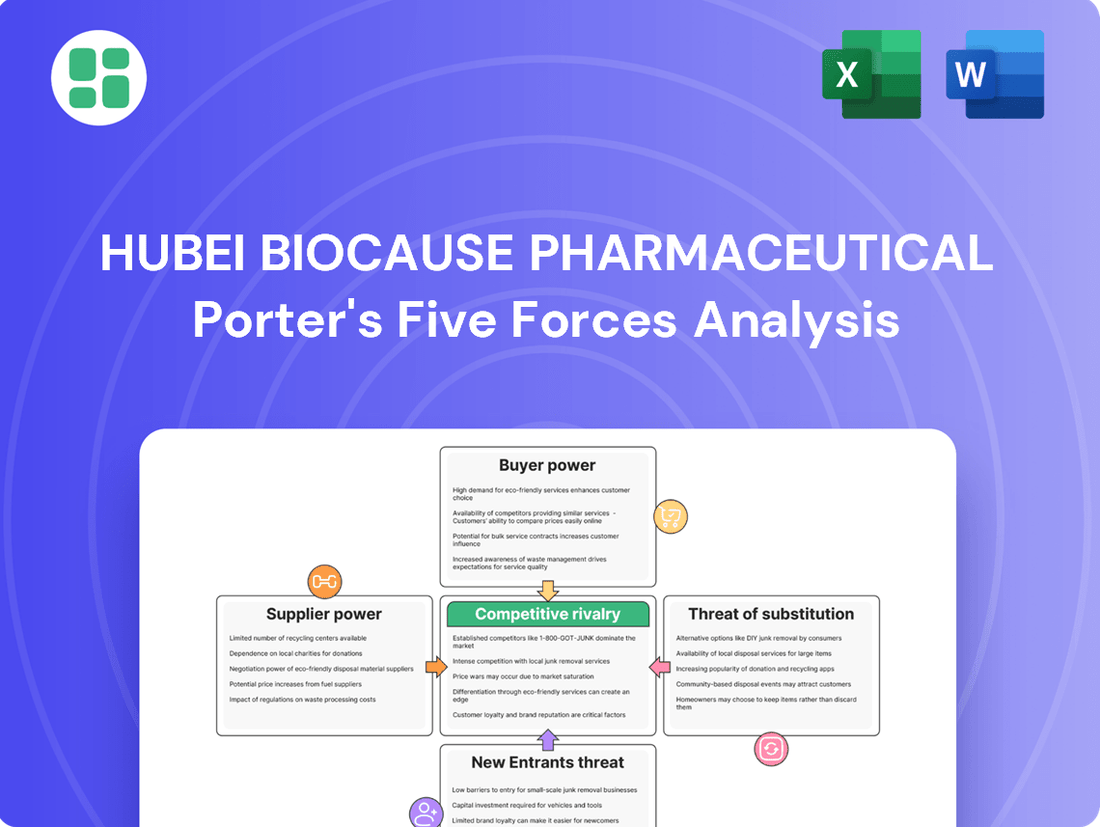
This analysis tailors Porter's Five Forces to Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its market position.
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical's Porter's Five Forces analysis acts as a pain point reliever by providing a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive forces, perfect for quick strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical's customer base, including hospitals, distributors, and government procurement agencies, particularly within China, holds considerable bargaining power. This strength stems from their substantial purchase volumes and the influence of government-driven volume-based procurement (VBP) policies.
These VBP initiatives are designed to reduce drug prices, directly affecting Hubei Biocause's revenue streams and overall profitability. For instance, in 2023, China's VBP tenders continued to exert downward pressure on pharmaceutical pricing, with many drugs seeing price reductions of 30-50% or more, impacting companies like Hubei Biocause that rely on these markets.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical, especially within the generic drug segment. Patients and healthcare providers are increasingly scrutinizing costs due to escalating healthcare expenses and constraints in insurance coverage. This trend is further fueled by government initiatives aimed at improving access to more affordable medications.
Customers wield significant bargaining power when a wide array of substitute products exist for treating conditions like cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and endocrine diseases. This abundance of alternatives directly challenges Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical by offering patients and healthcare providers choices that can be more cost-effective or possess different therapeutic profiles.
The pharmaceutical landscape in China, particularly in 2024, is characterized by a surge in new drug approvals and a growing availability of generic alternatives. This intensified competition further empowers customers, as they can readily switch to comparable treatments if Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical’s pricing or product offerings are perceived as less favorable.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customer information and transparency are increasingly influencing the pharmaceutical market. Digital health platforms and evolving regulatory landscapes are making drug pricing and efficacy data more accessible to consumers. This heightened awareness allows customers to make more informed comparisons between different pharmaceutical products, directly impacting Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical's ability to dictate prices. For instance, in 2024, initiatives aimed at price transparency in healthcare have gained significant traction, providing patients and payers with greater leverage.
This surge in readily available information significantly shifts the bargaining power towards customers. They can now more effectively evaluate value propositions and negotiate for better terms, diminishing Hubei Biocause's pricing flexibility. This trend is expected to continue as technology further democratizes access to critical data.
- Increased Transparency: Digital platforms and regulatory pushes are making drug pricing and efficacy data more accessible.
- Informed Comparisons: Customers can now easily compare Hubei Biocause's products against competitors.
- Reduced Pricing Power: This transparency empowers customers to negotiate better terms, lessening Hubei Biocause's control over pricing.
- 2024 Trends: Regulatory efforts in 2024 focused on enhancing price transparency in the healthcare sector, a key driver of this shift.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, while not a primary concern for Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical, represents a potential challenge. Large hospital groups or major pharmaceutical distributors could, in theory, consider establishing their own manufacturing facilities. This would allow them to produce certain drugs in-house, thereby decreasing their dependence on external suppliers like Hubei Biocause. However, the pharmaceutical industry's significant capital requirements and stringent regulatory hurdles present substantial barriers to entry for such ventures.
For instance, establishing a Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliant facility involves immense investment in specialized equipment, sterile environments, and rigorous quality control systems. The ongoing compliance with evolving pharmaceutical regulations, such as those from the NMPA in China or the FDA in the US, demands continuous investment and expertise. These factors make it economically and operationally challenging for most customer groups to successfully undertake backward integration in the pharmaceutical sector.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing pharmaceutical manufacturing requires hundreds of millions of dollars for facilities and equipment.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating GMP certifications and ongoing compliance is a significant hurdle.
- Specialized Expertise: Pharmaceutical production demands highly skilled personnel in research, development, and manufacturing.
- Limited Scope: Backward integration would likely only be feasible for a narrow range of high-volume, less complex generic drugs.
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical faces significant customer bargaining power, driven by China's volume-based procurement (VBP) policies which aim to lower drug prices. In 2023, VBP tenders often resulted in price reductions of 30-50% or more, directly impacting revenue for suppliers like Hubei Biocause.
Customers are increasingly price-sensitive, especially for generics, due to rising healthcare costs and insurance limitations. The growing availability of alternative treatments for conditions like cardiovascular diseases, amplified by new drug approvals and generics in 2024, further empowers customers to seek more cost-effective options.
Enhanced transparency through digital health platforms allows customers to easily compare drug pricing and efficacy, diminishing Hubei Biocause's pricing flexibility. Regulatory efforts in 2024 specifically targeted increasing price transparency in healthcare, a key factor strengthening customer negotiation power.
While backward integration by large customers is a theoretical concern, the substantial capital investment (often hundreds of millions of dollars) and complex regulatory compliance (e.g., GMP certification) make it a significant barrier for most. This limits the practical ability of customers to produce drugs in-house, thus somewhat mitigating this specific threat for Hubei Biocause.
Preview Before You Purchase
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing a detailed examination of the competitive landscape within the pharmaceutical industry. You're looking at the actual document; once your purchase is complete, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The competitive landscape for Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical is intensely crowded. In the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) sector alone, the company contends with over 1,000 active domestic and international competitors, highlighting a fragmented market. This sheer volume and diversity of players, spanning APIs, finished pharmaceutical preparations, and medical devices, create a challenging environment for market share and profitability.
The Chinese pharmaceutical market is experiencing significant expansion, with projections indicating it will reach USD 126.58 billion by 2030. This rapid growth, coupled with the medical device market exceeding CNY 1,200 billion in 2024, creates a fertile ground for new entrants.
Such a dynamic and expanding market naturally attracts a greater number of competitors. This influx of new players, all vying for market share in a growing sector, inevitably leads to heightened competitive rivalry within the industry.
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical's ability to stand out through innovation in its active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), preparations, and medical devices is paramount. The market is increasingly favoring high-value, innovative drugs, making R&D a key differentiator. Companies that invest in developing unique products are better positioned to gain a competitive edge.
Exit Barriers
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical faces significant competitive rivalry due to high exit barriers. The pharmaceutical industry, including companies like Hubei Biocause, often requires substantial investment in specialized manufacturing equipment and research facilities. These assets, once acquired, are difficult and costly to repurpose or sell, effectively trapping companies in the market even when profitability declines. This situation can lead to less efficient or less profitable competitors persisting, intensifying price competition and overall rivalry.
The presence of long-term contracts with suppliers and distributors, common in the pharmaceutical sector, also contributes to high exit barriers. Breaking these agreements can incur significant penalties, further discouraging companies from leaving the market. Furthermore, a sense of social responsibility towards employees, particularly in a sector that often employs a large and skilled workforce, can also act as a disincentive to closure, even in challenging economic conditions. For instance, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical market saw continued consolidation, but many smaller players with specialized, illiquid assets remained operational, impacting pricing dynamics.
- Specialized Assets: Pharmaceutical manufacturing plants often contain highly specific machinery for drug production, making them difficult to sell or convert for other uses.
- Long-Term Contracts: Agreements with raw material suppliers, research partners, and distribution networks can create financial penalties for early termination.
- Social Responsibility: Companies may feel obligated to maintain employment for their workforce, even if operations are not highly profitable.
- Industry Dynamics: In 2024, while major pharmaceutical mergers and acquisitions continued, many smaller firms with sunk costs in specialized facilities continued to operate, contributing to a competitive landscape.
Strategic Stakes
The pharmaceutical industry in China, including players like Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical, is a key focus for the government. This strategic importance translates into significant support for domestic innovation and aims to foster market leadership among local companies. For instance, in 2023, China's pharmaceutical market size was estimated to be around $700 billion, with the government actively promoting policies to boost R&D and manufacturing capabilities of domestic firms.
This government backing intensifies the competitive rivalry among Chinese pharmaceutical companies. They are driven to secure market share and achieve technological advancements, leading to sustained investment in research and development. Companies are increasingly competing on the basis of innovation, quality, and cost-effectiveness, creating a dynamic and challenging environment.
The strategic stakes are high, as success in this sector can lead to significant economic benefits and global recognition. This pressure cooker environment fuels a constant drive for improvement and differentiation. For Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical, staying ahead means continuous investment in new drug development and efficient production processes to meet the evolving demands of both domestic and international markets.
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical operates in a highly competitive arena with over 1,000 API competitors globally, creating intense pressure. The expanding Chinese pharmaceutical market, projected to reach $126.58 billion by 2030, attracts numerous new entrants, further intensifying rivalry.
High exit barriers, such as specialized manufacturing assets and long-term contracts, keep even less efficient firms in the market, driving price competition. Government support for domestic innovation in China's pharmaceutical sector, which was around $700 billion in 2023, also fuels aggressive competition among local players focused on R&D and market share.
| Metric | Value | Year | Source |
| Global API Competitors | Over 1,000 | N/A | Industry Reports |
| Chinese Pharma Market Projection | USD 126.58 billion | 2030 | Market Research |
| Chinese Pharma Market Size | Approx. USD 700 billion | 2023 | Government Data |
| Medical Device Market (China) | Exceeding CNY 1,200 billion | 2024 | Industry Analysis |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical's core products, particularly those targeting cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and endocrine conditions, are vulnerable to a range of alternative therapies. These substitutes include lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise, which are increasingly recognized for their efficacy. In 2023, global spending on preventative healthcare and wellness programs saw a significant uptick, indicating growing consumer interest in non-pharmacological approaches.
Furthermore, surgical interventions and advancements in medical technology offer alternatives to drug-based treatments for many conditions. For instance, minimally invasive procedures are becoming more common for cardiovascular issues. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) also presents a significant substitute, especially within China, where it holds a strong cultural and market presence. In 2024, the TCM market in China was projected to reach over $150 billion, demonstrating its substantial competitive force.
The constant evolution of medical science means new non-pharmacological therapies are regularly emerging, posing an ongoing threat. Innovations in areas like gene therapy or advanced medical devices can rapidly create viable substitutes, potentially eroding market share for traditional pharmaceutical preparations. This dynamic landscape necessitates continuous research and development from Hubei Biocause to stay competitive.
Technological advancements in adjacent sectors pose a significant threat of substitution for Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical. For instance, breakthroughs in gene therapy and cell therapy are rapidly evolving, offering potentially more targeted and curative treatments that could bypass the need for traditional small-molecule drugs. As of late 2024, the global gene therapy market is projected to reach over $15 billion, indicating substantial investment and rapid innovation in this area, directly impacting the demand for existing pharmaceutical products.
The threat of substitutes for Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical is significantly influenced by the price-performance trade-off. If alternative treatments emerge that offer comparable or even better therapeutic results at a lower price point, Hubei Biocause's market position could be weakened.
Government initiatives, such as the inclusion of more affordable generics or biosimilars on China's National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL), can further amplify this threat. For instance, if NRDL updates in 2024 or 2025 prioritize cost-effective substitutes for Hubei Biocause's key products, it could directly impact sales volumes and pricing power.
Switching Costs for Patients/Healthcare Providers
The ease with which patients and healthcare providers can switch to alternative treatments significantly influences the threat of substitutes for Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical. Low switching costs, where minimal changes to treatment protocols or the ready availability of comparable drugs exist, amplify this threat.
For instance, if a patient can easily transition from one antibiotic to another with similar efficacy and minimal out-of-pocket expense, the bargaining power of Hubei Biocause diminishes. In 2024, the global pharmaceutical market saw a continued rise in generic drug penetration, with generics accounting for approximately 90% of prescriptions dispensed in many developed markets, highlighting the inherent pressure from substitutes.
- Low Switching Costs: Patients often face minimal hurdles when switching between similar medications, especially if insurance coverage is comparable.
- Availability of Alternatives: The presence of numerous generic and biosimilar options for many drug classes directly increases the threat of substitution.
- Provider Inertia: While some providers may have established relationships, the increasing emphasis on cost-effectiveness and evidence-based medicine can encourage shifts to demonstrably superior or more affordable alternatives.
Public Awareness and Acceptance of Substitutes
Public awareness is increasingly shifting towards holistic health management, including preventative care and non-pharmacological interventions. This trend directly impacts the demand for traditional pharmaceutical products offered by companies like Hubei Biocause.
The growing acceptance of personalized medicine and digital health solutions presents a significant substitute threat. For instance, by 2024, global spending on digital health was projected to reach over $600 billion, indicating a substantial market shift away from solely drug-based treatments.
- Growing acceptance of preventative healthcare strategies.
- Increased demand for personalized medicine approaches.
- Rise of digital health solutions and wearable technology.
- Consumer preference for natural and alternative therapies.
The threat of substitutes for Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical is amplified by the increasing consumer interest in non-pharmacological health solutions. Lifestyle changes, such as improved diet and exercise, are gaining traction, with global spending on preventative healthcare rising significantly in 2023. This shift indicates a growing preference for wellness programs over traditional drug therapies.
Furthermore, advancements in medical technology, including minimally invasive procedures and innovative devices, offer viable alternatives to pharmaceutical treatments for various conditions. The market for Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in China, projected to exceed $150 billion in 2024, also represents a substantial substitute. Emerging fields like gene and cell therapy are also rapidly developing, with the global gene therapy market expected to surpass $15 billion by late 2024, posing a direct challenge to existing drug markets.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Impact on Hubei Biocause | Market Trend/Data Point (2023-2024) |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Diet, Exercise, Wellness Programs | Reduces demand for drugs treating lifestyle-related diseases. | Global preventative healthcare spending increased significantly in 2023. |
| Medical Technology | Minimally Invasive Surgery, Medical Devices | Offers alternatives to drug treatments for certain conditions. | Increasing adoption of advanced medical procedures. |
| Alternative Medicine | Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) | Strong market presence, particularly in China. | China's TCM market projected over $150 billion in 2024. |
| Advanced Therapies | Gene Therapy, Cell Therapy | Potentially curative treatments bypassing traditional drugs. | Global gene therapy market projected over $15 billion by late 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
The pharmaceutical industry, particularly in the realm of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and intricate formulations, presents a formidable barrier to entry due to exceptionally high capital requirements. New companies must typically invest billions in research and development, state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities adhering to stringent Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and robust quality assurance and control systems. For instance, establishing a new, compliant API manufacturing plant can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a sum that deters many potential competitors.
The pharmaceutical sector faces significant barriers to entry due to rigorous regulatory oversight. Companies must navigate complex processes for drug approval, adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and maintain strict quality control. For instance, in 2024, the average time for a new drug to receive approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) remained substantial, often spanning several years and requiring extensive clinical trial data.
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical benefits from its existing portfolio of patents on active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and drug formulations. These intellectual property rights act as a significant barrier, making it challenging for new companies to enter the market without developing their own proprietary technologies or waiting for existing patents to expire, which can take years.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing players in the pharmaceutical sector, like Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical, often leverage significant economies of scale. This means they can produce drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in larger volumes, driving down per-unit costs for manufacturing, research and development, and distribution networks. For instance, in 2024, major pharmaceutical companies reported substantial cost savings through optimized supply chains and bulk purchasing of raw materials, which new entrants would find challenging to replicate immediately.
The experience curve also plays a crucial role. Over time, companies gain efficiency and knowledge in production processes, leading to further cost reductions and quality improvements. Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical, having operated for years, has likely refined its manufacturing techniques, potentially reducing waste and increasing output speed. A new entrant would face a steep learning curve, initially incurring higher operational costs and possibly lower yields compared to established firms.
- Economies of Scale: Large-scale production by incumbents leads to lower per-unit costs in manufacturing and R&D.
- Experience Curve: Established firms benefit from accumulated knowledge, improving efficiency and reducing costs over time.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants face difficulty matching the cost structures and operational efficiencies of established players.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Start-ups would struggle to achieve comparable pricing and profitability without significant upfront investment.
Brand Loyalty and Distribution Channels
Building strong brand loyalty and securing effective distribution channels in the pharmaceutical industry presents a significant hurdle for new entrants. This is particularly true in markets where established players have cultivated trust and patient relationships over time.
Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical benefits from its existing brand recognition, a testament to years of operation and product development. This established reputation acts as a formidable barrier, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction and market share.
Furthermore, the company's extensive distribution network, which facilitates exports to over 85 countries, provides a crucial competitive advantage. New entrants would face substantial investment and time requirements to replicate such a global reach.
- Brand Recognition: Hubei Biocause has a long-standing reputation in the pharmaceutical sector.
- Distribution Network: The company exports to more than 85 countries, creating a significant barrier for new entrants.
- Market Access: Established relationships with healthcare providers and pharmacies are difficult for new companies to establish quickly.
The threat of new entrants for Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical is generally low due to substantial barriers. High capital investment for R&D and manufacturing, coupled with stringent regulatory approvals that can take years, deters many potential competitors. For instance, in 2024, the pharmaceutical industry continued to see lengthy drug approval processes, requiring extensive clinical trials.
Existing patents held by Hubei Biocause on APIs and formulations create significant intellectual property barriers. Furthermore, established players benefit from economies of scale, achieving lower per-unit costs through large-volume production and optimized supply chains, a feat difficult for newcomers to match quickly.
Brand loyalty and established distribution networks, with Hubei Biocause exporting to over 85 countries, present further challenges. Replicating this global reach and the trust built with healthcare providers requires considerable time and investment, making market entry arduous for new pharmaceutical companies.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Billions needed for R&D, GMP facilities, and quality control. | High deterrent due to substantial upfront costs. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex drug approval processes and strict quality standards. | Significant time and resource commitment required. |
| Intellectual Property | Existing patents on APIs and formulations. | Limits ability to produce key ingredients without licensing or innovation. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for established, high-volume producers. | New entrants face higher initial production costs. |
| Brand & Distribution | Established brand recognition and extensive global networks. | Difficult to gain market access and customer trust. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Hubei Biocause Pharmaceutical Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.