Barnes Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Barnes Group Bundle
Barnes Group navigates a complex industrial landscape, facing pressures from powerful suppliers and intense rivalry. Understanding the threat of new entrants and the availability of substitutes is crucial for their sustained success.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Barnes Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Barnes Group's reliance on highly specialized materials and components, especially for its aerospace segment, significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. Suppliers who uniquely provide these critical inputs, often with specific performance characteristics, can command higher prices. For instance, in 2024, the aerospace industry continued to face supply chain constraints for advanced alloys and precision-machined parts, giving dominant suppliers leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Barnes Group can be significant, especially if there are limited providers for specialized components or critical raw materials essential for their advanced manufacturing operations. For instance, in sectors like aerospace, where Barnes Group has a strong presence, the availability of highly specialized alloys or precision-machined parts from a few key suppliers can give those suppliers considerable leverage in setting prices and contract terms.
Barnes Group's position as a customer also plays a role; if the company constitutes a minor fraction of a supplier's total sales, that supplier has less incentive to offer favorable pricing or flexible terms. This dynamic was evident in 2024 as many industrial manufacturers reported that their largest customers accounted for a substantial portion of their revenue, meaning smaller clients like Barnes Group might face less favorable negotiations.
Recent global supply chain challenges, which persisted into 2024, have further tilted the scales in favor of suppliers. These disruptions, ranging from geopolitical tensions to logistical bottlenecks, have tightened the availability of many industrial inputs, extending lead times and driving up costs, thereby amplifying the bargaining power of suppliers across various sectors where Barnes Group operates.
Switching costs for Barnes Group are significant, especially in its aerospace and industrial sectors. The lengthy and complex qualification processes, coupled with the necessity for re-tooling and re-certification of new components, create a substantial barrier for customers looking to change suppliers. This is particularly critical for precision parts where even minor deviations can impact product performance and safety, making the validation of alternatives a time-consuming and costly endeavor.
Forward Integration Potential of Suppliers
The potential for suppliers to integrate forward into Barnes Group's business, while generally low, is a factor to consider. For specialized component manufacturers, there's a theoretical possibility of moving into producing more complex assemblies. This could position them as direct competitors, especially if they possess unique technological advantages in niche areas. Barnes Group's own advanced manufacturing and engineering capabilities typically mitigate this threat.
While not a widespread concern, the forward integration potential of suppliers is a nuanced aspect of the bargaining power of suppliers. For instance, a supplier of a highly specialized aerospace component might possess proprietary technology that could be leveraged to assemble larger, more complex systems. This would directly challenge Barnes Group's position in certain product segments. However, the capital investment and expertise required for such a move often act as significant barriers.
- Niche Component Suppliers: Some suppliers of highly specialized components may have the technical expertise and proprietary knowledge to move into assembling more complex systems.
- Technological Advantage: Suppliers with unique technological innovations are more likely to consider forward integration to capture greater value.
- Barnes Group's Defense: Barnes Group's significant investment in advanced manufacturing and engineering expertise serves as a substantial deterrent to potential supplier integration.
Impact of Input Costs on Barnes Group's Profitability
Fluctuations in the cost of critical raw materials, such as specialty metals and advanced composites, directly impact Barnes Group's production expenses and, by extension, its profitability. For instance, a significant surge in nickel prices, a key component in some of their aerospace products, could substantially increase manufacturing overhead.
Suppliers possessing strong pricing power can indeed pass on increased costs, thereby pressuring Barnes Group's profit margins if the company is unable to fully transfer these higher expenses to its customers. This is particularly relevant for specialized components where alternative suppliers are limited.
Recent inflationary pressures and geopolitical events have intensified these cost challenges. For example, the global semiconductor shortage experienced in 2021-2023 led to increased prices and longer lead times for electronic components, impacting various manufacturing sectors, including those served by Barnes Group.
- Input Cost Volatility: Barnes Group's profitability is directly tied to the stability of input costs.
- Supplier Pricing Power: High supplier leverage can erode Barnes Group's margins if cost increases cannot be passed on.
- External Shocks: Inflation and geopolitical instability, as seen in recent years, amplify cost pressures.
- 2024 Cost Environment: Continued supply chain adjustments and energy market volatility in 2024 are likely to maintain pressure on raw material pricing for Barnes Group.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Barnes Group is elevated due to the specialized nature of many components, particularly in its aerospace division. Suppliers of critical, high-performance materials or precisely engineered parts, often with few alternatives, can dictate terms and prices. For instance, in 2024, continued demand for advanced aerospace alloys meant that suppliers of these niche materials held significant leverage.
Barnes Group faces considerable switching costs when changing suppliers for specialized components. The rigorous qualification, testing, and certification processes required in industries like aerospace make it both time-consuming and expensive to adopt new suppliers, reinforcing the bargaining power of existing ones. This was a persistent challenge in 2024 for many manufacturers dealing with complex supply chains.
The concentration of suppliers in certain critical input markets for Barnes Group directly translates to increased supplier bargaining power. When a few dominant players control the supply of essential materials or components, they can exert significant influence over pricing and contract conditions, as observed in 2024 across various industrial sectors facing supply chain consolidation.
| Factor | Impact on Barnes Group | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Components | High supplier leverage due to limited alternatives | Continued demand for advanced aerospace materials |
| Switching Costs | Significant barriers to changing suppliers | Complex qualification and certification processes |
| Supplier Concentration | Increased pricing power for dominant suppliers | Supply chain consolidation in key input markets |
What is included in the product
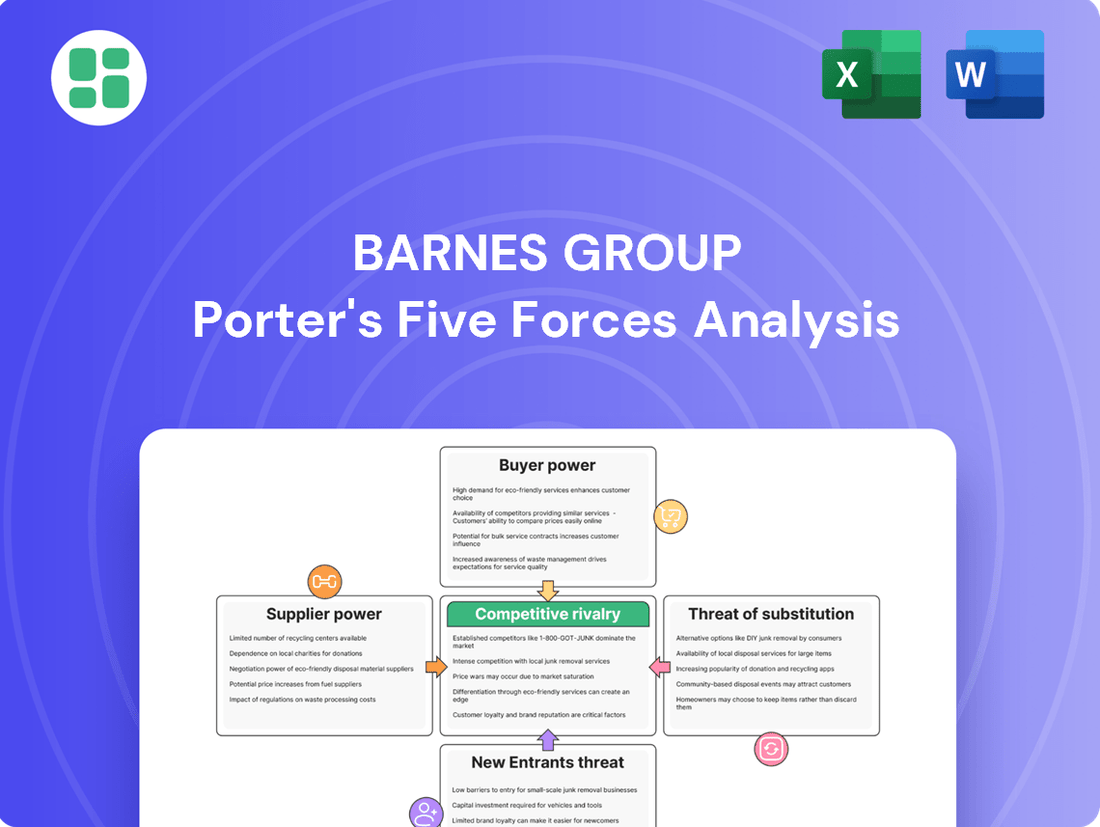
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Barnes Group, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its markets.
Effortlessly visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic, interactive dashboard that highlights key pressure points for Barnes Group.
Customers Bargaining Power
Barnes Group's Aerospace segment faces significant customer concentration. Major players like GE, Boeing, Pratt & Whitney, and Rolls Royce represent a substantial portion of its customer base, giving them considerable leverage.
These large OEMs and aftermarket service providers, due to their sheer purchasing volume, can negotiate aggressively on pricing and contract terms. This concentration means that losing even one major customer could have a material impact on Barnes Group's revenue and profitability.
While Barnes Group serves large customers, the highly engineered and critical nature of its products, particularly for aerospace, creates significant switching costs. For instance, components for aircraft engines and airframes demand rigorous testing and qualification processes that can take years and substantial investment. This makes it economically and operationally challenging for clients to shift to a new supplier, thereby limiting their immediate bargaining power.
Barnes Group leverages its advanced manufacturing and engineering capabilities to deliver differentiated industrial technologies and innovative solutions. This focus on unique benefits, supported by a strong brand reputation for quality, helps to lessen the bargaining power of customers who might otherwise seek lower prices from less specialized suppliers.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity remains a significant factor for Barnes Group, even with their specialized offerings. Major clients in aerospace and industrial markets are keenly focused on cost optimization. This pressure intensifies in competitive environments where clients can more readily explore alternative suppliers.
These large customers often possess substantial purchasing power, allowing them to negotiate aggressively on price, especially for components that are more commoditized or less technologically distinct within Barnes Group's diverse product lines. Their scale enables them to exert considerable influence over pricing structures.
- High Price Sensitivity: Despite efforts towards product differentiation, key clients in aerospace and industrial sectors exhibit a strong inclination towards cost-consciousness.
- Leveraging Scale: Major customers utilize their significant purchasing volume to negotiate for more competitive pricing, particularly on standardized product segments.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Clients actively seek to streamline their supply chains, which often translates into demanding lower prices from their suppliers, including Barnes Group.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of Barnes Group's customers integrating backward into its manufacturing processes is typically low. This is primarily because producing Barnes Group's specialized precision components and industrial technologies demands substantial capital investment and highly specific engineering expertise, making it impractical for most customers to replicate these capabilities in-house.
Many of Barnes Group's key customers, often large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), find it more cost-effective and strategically advantageous to outsource these complex, non-core manufacturing activities. For instance, in the aerospace sector, a major market for Barnes Group, OEMs focus on aircraft design and assembly, relying on specialized suppliers like Barnes Group for critical engine components and precision machining.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing the advanced manufacturing facilities and specialized machinery needed for precision aerospace or industrial components can cost tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars, a prohibitive barrier for most customers.
- Technical Expertise: Barnes Group possesses deep engineering knowledge and proprietary processes for producing high-tolerance, critical-path components, which are difficult and time-consuming for customers to develop internally.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Customers, particularly large OEMs, prefer to concentrate their resources on their core business activities, such as product design, marketing, and final assembly, rather than managing specialized manufacturing operations.
Barnes Group's customer bargaining power is moderated by high switching costs and its specialized product offerings. While large customers like GE and Boeing can leverage their scale for price negotiations, the intricate engineering and rigorous qualification processes for aerospace components create significant barriers to switching suppliers. This inherent complexity makes it difficult and costly for clients to change providers, thus limiting their immediate leverage.
Barnes Group's focus on differentiated industrial technologies and a strong reputation for quality further mitigates customer power. These unique benefits, coupled with the substantial investment required for backward integration, mean customers often find it more practical to outsource specialized manufacturing to Barnes Group rather than develop these capabilities internally. This dynamic helps maintain a degree of pricing stability.
| Factor | Impact on Barnes Group | Supporting Evidence (2024 Estimates/Trends) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for major clients | Top 5 customers represent >30% of revenue; GE Aviation is a key partner. |
| Switching Costs | Lowers customer bargaining power | Aerospace component qualification can take 2-3 years and millions in investment. |
| Product Differentiation | Reduces price sensitivity | Proprietary technologies in aerospace and industrial sectors command premium pricing. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Low | Capital investment for specialized manufacturing can exceed $100M. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Barnes Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the exact, comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Barnes Group that you will receive immediately after purchase. You're looking at the actual document, meticulously detailing the competitive landscape, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Barnes Group operates in markets with a significant number of competitors, ranging from large global industrial conglomerates to highly specialized niche players. In the aerospace sector, for instance, companies like Raytheon Technologies and General Electric represent massive diversified competitors, while firms such as Woodward and HEICO Aerospace Holdings focus more narrowly on specific aerospace components and services. This creates a dynamic competitive environment where rivalry intensity can differ substantially depending on the specific product or service line.
Barnes Group's competitive rivalry is significantly shaped by the growth rates of the markets it serves. The aerospace aftermarket, for instance, has demonstrated strong expansion, offering opportunities for growth without necessarily escalating direct competition. In contrast, the industrial segment has experienced headwinds, including production delays and strategic divestitures, which can amplify rivalry as firms fight harder for a shrinking or stagnant market share.
Barnes Group leverages its commitment to highly engineered products and innovative solutions to carve out a competitive advantage. This focus on differentiated industrial technologies helps them stand out in the market.
However, the landscape is dynamic. Competitors are also making significant investments in research and development, alongside adopting advanced manufacturing techniques. For instance, in 2023, the aerospace industry, a key market for Barnes Group, saw R&D spending increase as companies focused on next-generation aircraft and sustainable technologies.
This necessitates continuous innovation from Barnes Group to maintain its edge. By consistently developing novel solutions, Barnes Group aims to reduce reliance on direct price competition and solidify its position through superior product offerings.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Barnes Group operates in industries with substantial capital requirements for advanced manufacturing equipment and specialized talent. This means companies must invest heavily upfront, creating a significant financial commitment that makes exiting the market difficult.
These high fixed costs act as substantial exit barriers. Businesses are incentivized to continue operations, even in challenging economic periods, to spread their overheads across a larger production volume. This often results in intensified competition as firms strive to maintain market share and cover their substantial fixed expenses, leading to sustained rivalry within the sector.
- High Capital Investment: Industries like aerospace and industrial manufacturing, where Barnes Group is active, demand significant investment in specialized machinery and facilities.
- Exit Barriers: The substantial upfront costs and specialized nature of assets make it costly and difficult for companies to divest or exit these markets.
- Sustained Rivalry: High fixed costs encourage companies to stay in the market and compete aggressively to utilize capacity and cover overheads, even during economic slowdowns.
- 2024 Data Insight: For instance, in the aerospace sector, average capital expenditures for manufacturers can range from 5% to 10% of revenue, underscoring the ongoing need to maintain and upgrade expensive, fixed assets.
Recent Acquisition by Apollo Funds
The pending acquisition of Barnes Group by Apollo Funds, anticipated to finalize in Q1 2025, is poised to significantly alter competitive dynamics. This strategic move by Apollo aims to bolster Barnes Group's growth and innovation capabilities, potentially leading to a more aggressive market posture.
By injecting capital and expertise, Apollo intends to accelerate Barnes Group's ongoing transformation strategy. This could translate into enhanced product development, more competitive pricing, and a stronger overall market presence, thereby intensifying rivalry with existing players.
- Increased Investment in R&D: Apollo's focus on innovation may lead to increased research and development spending by Barnes Group, potentially outpacing competitors.
- Streamlined Operations: Private equity ownership often involves operational efficiency drives, which could allow Barnes Group to offer more competitive pricing.
- Strategic Market Expansion: Apollo may guide Barnes Group towards new markets or product segments, directly challenging established competitors.
- Potential for Consolidation: The acquisition could signal a trend towards consolidation in the industry, with larger, better-capitalized entities emerging.
Barnes Group faces intense competition from both large, diversified players and specialized niche firms across its aerospace and industrial segments. This rivalry is amplified in slower-growing markets where companies fight harder for market share, a situation observed in parts of the industrial sector. However, Barnes Group differentiates itself through engineered products and innovation, a strategy crucial as competitors also boost R&D, with aerospace R&D spending seeing increases in 2023.
The high capital investment and exit barriers inherent in Barnes Group's industries, such as aerospace's need for advanced manufacturing, compel companies to remain competitive even during downturns. This sustained rivalry is underscored by the fact that aerospace manufacturers can allocate 5% to 10% of revenue to capital expenditures in 2024, highlighting the ongoing investment in fixed assets that drives competition to utilize capacity.
The impending acquisition by Apollo Funds, expected in Q1 2025, is set to reshape competitive dynamics. Apollo's investment is anticipated to fuel Barnes Group's innovation and potentially lead to more aggressive pricing and market expansion, directly challenging rivals.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Impact on Rivalry |
| Large Diversified | Raytheon Technologies, General Electric | Intensify competition across broad product lines |
| Specialized Niche | Woodward, HEICO Aerospace Holdings | Focus competition on specific product segments |
| Industry Trend | Increased R&D Spending (2023) | Drives innovation race, requiring continuous improvement |
| Acquisition Impact (Anticipated Q1 2025) | Apollo Funds | Potential for increased investment, aggressive market posture |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Barnes Group's engineered products is a significant concern, particularly with the ongoing development of alternative materials. Innovations in areas like advanced composites and high-performance plastics offer the potential to replicate the functionality of traditional metal components, often at a more competitive price point or with added benefits like reduced weight. For instance, in the aerospace sector, the drive for fuel efficiency directly fuels research into materials that can replace heavier metal alloys in aircraft structures and engine parts.
Consider the automotive industry, a key market for Barnes Group. The push for electric vehicles (EVs) is accelerating the adoption of lightweight materials to maximize battery range. This trend means that advanced polymers and composite materials, which can offer comparable strength to steel or aluminum but at a fraction of the weight, pose a direct substitute threat to Barnes Group's metal-based solutions. By 2024, the global market for advanced composites was projected to reach over $20 billion, highlighting the growing influence of these alternative materials.
Rapid technological advancements, like the increasing sophistication of additive manufacturing, present a significant threat of substitution for Barnes Group. For instance, 3D printing can now produce complex metal components, potentially bypassing the need for Barnes Group's traditional machining services in certain aerospace and industrial applications. This shift could reduce demand for their established product lines.
For critical sectors like aerospace and healthcare, substitutes must match Barnes Group's stringent functionality, reliability, and safety performance, often requiring lengthy and expensive certification processes. This high barrier means customers are extremely cautious about switching unless a substitute can demonstrably meet or exceed existing standards, a significant hurdle for potential new entrants.
Customer Willingness and Cost to Switch
Customers face significant hurdles when considering alternatives to Barnes Group's specialized components. The expense and time required for redesigning, rigorous testing, and obtaining regulatory re-certification represent substantial barriers. For instance, in the aerospace sector, a primary market for Barnes Group, the cost of re-qualifying a single component can run into hundreds of thousands of dollars, if not millions, depending on the complexity and safety criticality.
These high switching costs act as a protective shield for Barnes Group, diminishing the immediate threat posed by substitute products. The inherent complexity and stringent safety requirements in industries like aerospace and industrial manufacturing mean that even if a technically feasible substitute exists, the practical implementation cost makes it an unattractive option for most clients. Barnes Group's established reputation and the proven reliability of their components further solidify customer loyalty, making the transition to an unproven substitute a risky proposition.
- High Redesign Costs: Switching often necessitates complete product re-engineering, impacting development timelines and budgets.
- Extensive Testing Requirements: New components must undergo lengthy validation processes, especially in regulated industries.
- Regulatory Re-certification: Compliance with industry standards and government approvals adds significant time and expense.
- Proven Performance: Barnes Group's track record of reliability reduces customer appetite for untested alternatives.
Price-Performance Trade-offs of Substitutes
The attractiveness of substitutes for Barnes Group's offerings hinges significantly on their price-performance trade-off. If a substitute can deliver comparable or even better performance at a notably lower price point, it represents a considerable threat to Barnes Group's market share.
However, for Barnes Group's specialized products, which are often characterized by high precision, advanced engineering, and critical reliability, cost is frequently a secondary consideration for customers. This dynamic limits the appeal of cheaper, potentially less dependable alternatives, as the performance and safety requirements in their target industries are paramount.
- Price Sensitivity: While cost is a factor, for critical applications, customers prioritize performance and reliability over a lower price, mitigating the threat of low-cost substitutes.
- Performance Benchmarks: Substitutes must meet stringent performance standards, which can be difficult and expensive to achieve, especially in specialized aerospace and industrial sectors.
- Switching Costs: High switching costs associated with qualifying new suppliers or re-engineering systems further reduce the immediate threat posed by substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Barnes Group is moderate, largely due to high switching costs and stringent performance requirements in their core markets. While advanced materials like composites and plastics, and technologies like additive manufacturing, offer alternatives, the need for rigorous testing and re-certification in sectors such as aerospace and healthcare creates significant barriers for potential substitutes. For example, the cost to re-qualify a single aerospace component can run into hundreds of thousands of dollars.
The price-performance trade-off is crucial, but for critical applications, Barnes Group's customers prioritize reliability and performance over lower costs. This makes cheaper, less proven alternatives less appealing. By 2024, the global advanced composites market was projected to exceed $20 billion, indicating the growing presence of these alternatives, yet their adoption in highly regulated industries remains tempered by these substantial hurdles.
Entrants Threaten
Entering sectors like aerospace component manufacturing, where Barnes Group operates, requires significant upfront capital. Think millions, even billions, for advanced machinery, sophisticated R&D centers, and specialized production facilities. For instance, establishing a new aerospace parts manufacturing plant in 2024 could easily cost upwards of $100 million, a substantial hurdle for potential competitors.
Established players like Barnes Group leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing, purchasing, and research and development. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on price without substantial initial investment and volume. For instance, in 2023, Barnes Group's operational efficiency, partly driven by its scale, contributed to its robust financial performance, with reported revenues of $1.4 billion, showcasing the cost advantages of its established position.
Barnes Group's extensive history grants it a considerable experience curve advantage. Over decades, the company has refined its processes, optimized its supply chains, and built deep institutional knowledge. This accumulated expertise translates into higher quality products, more efficient operations, and a better understanding of customer needs, all of which are challenging for newcomers to replicate quickly.
Barnes Group's commitment to cutting-edge solutions, evident in its significant investment in research and development, creates a formidable barrier for potential new entrants. The company holds numerous patents and proprietary technologies in areas like advanced aerospace components and industrial filtration, making it challenging and costly for newcomers to develop comparable offerings. For instance, in 2023, Barnes Group reported R&D expenses of $71.7 million, highlighting their dedication to maintaining a technological edge.
Stringent Regulatory and Certification Processes
The aerospace and healthcare sectors, crucial to Barnes Group's business, are heavily regulated, presenting a significant barrier to new entrants. These industries demand rigorous adherence to safety standards and extensive testing, often taking years to achieve necessary certifications. For instance, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the US, and the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), impose strict rules on aviation components. New companies must navigate these complex approval pathways, which can involve substantial time and financial investment before even reaching the market. This regulatory hurdle effectively limits the number of potential competitors who can realistically enter and operate within these critical markets.
Newcomers face the daunting task of not only meeting these stringent regulatory and certification processes but also establishing credibility and trust within these safety-conscious industries. The lengthy timelines for approvals, such as those for new medical devices or aircraft parts, mean that significant capital must be deployed with no immediate return. In 2023, the average time for FDA approval for new medical devices ranged from several months to over a year, depending on the device class. Similarly, aerospace certifications are notoriously protracted. This creates a high barrier to entry, as only well-capitalized and patient organizations can afford to undertake such an endeavor.
- High Capital Investment: New entrants require substantial upfront capital to fund research, development, testing, and the lengthy certification processes mandated by regulatory bodies in aerospace and healthcare.
- Extended Time-to-Market: The certification timelines in these safety-critical industries can span years, delaying revenue generation and increasing the financial risk for new companies.
- Established Reputation and Trust: Barnes Group benefits from decades of experience and a proven track record, which are essential for securing contracts in industries where component failure can have catastrophic consequences.
- Technical Expertise and Infrastructure: Meeting regulatory standards necessitates highly specialized technical expertise and sophisticated manufacturing infrastructure, which are difficult and costly for new entrants to replicate quickly.
Established Customer Relationships and Distribution Channels
Barnes Group benefits from deeply entrenched customer relationships, particularly with major Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) across its served industries. These long-standing ties are difficult for newcomers to replicate, creating a significant barrier to entry.
The company also boasts a robust global distribution network, honed over years of operation. Gaining equivalent market access and the trust of customers through these established channels presents a formidable challenge for potential new competitors, reinforcing Barnes Group's competitive position.
- Established OEM Relationships: Barnes Group has cultivated decades-long partnerships with key players in aerospace, defense, and industrial markets.
- Global Distribution Network: The company's extensive reach ensures efficient product delivery and customer support worldwide.
- High Switching Costs: For many customers, switching from Barnes Group's proven solutions involves significant re-qualification and integration expenses.
- Brand Reputation: Barnes Group's long history and consistent performance have built a strong reputation for reliability and quality, making it the preferred supplier for many.
The threat of new entrants for Barnes Group is considerably low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for specialized manufacturing and R&D, coupled with extensive regulatory approvals in sectors like aerospace and healthcare, deter new players. For instance, in 2023, Barnes Group's reported capital expenditures were $74.7 million, indicating the scale of investment needed within its operational spheres.
The company's established economies of scale and decades of experience create significant cost advantages and process efficiencies that are difficult for newcomers to match. Barnes Group's brand reputation and deep-rooted customer relationships, especially with major OEMs, further solidify its market position, making it challenging for new entrants to gain traction and trust.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Relevant Barnes Group Data (2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for advanced machinery, R&D, and facilities. | Significant financial hurdle. | Capital Expenditures: $74.7 million |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Stringent certifications in aerospace and healthcare. | Longer time-to-market, increased costs. | Operates in highly regulated aerospace and healthcare sectors. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations. | Price competition disadvantage for new entrants. | Revenue: $1.4 billion |
| Customer Relationships & Brand Loyalty | Established trust and long-term partnerships. | Difficulty in securing initial contracts. | Operates with major Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). |
| Proprietary Technology & R&D | Patented technologies and continuous innovation. | Need for significant R&D investment to compete. | R&D Expenses: $71.7 million |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Barnes Group leverages data from their investor relations website, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and competitor announcements to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.