BAIC Motor Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
BAIC Motor Bundle
BAIC Motor faces significant competitive pressures from established global automakers and a growing number of domestic rivals, impacting its pricing power and market share. The threat of new entrants is moderate, as capital requirements are high but technological advancements are lowering barriers. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping BAIC Motor’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of BAIC Motor's suppliers is significantly shaped by the concentration of manufacturers for critical components, especially in high-tech areas like electric vehicle (EV) batteries and semiconductors. Suppliers of advanced battery technology, such as CATL, wield substantial influence due to their specialized expertise and dominant market position in the rapidly expanding NEV sector.
Switching costs for BAIC Motor can be substantial, particularly when dealing with suppliers of proprietary technologies or deeply integrated systems. For instance, transitioning to a new supplier for electric vehicle powertrains or advanced intelligent driving systems necessitates extensive re-engineering, rigorous testing, and lengthy qualification procedures, all of which translate to significant time and financial investment.
The availability of substitute inputs is a critical factor influencing supplier power. While some raw materials might have readily available alternatives, the automotive sector, particularly for specialized components, faces significant challenges. For example, the persistent semiconductor shortage throughout 2021 and 2022, which continued to affect production lines into 2023, demonstrated how limited availability of essential inputs grants substantial bargaining power to the few dominant chip suppliers. This situation directly impacts automakers like BAIC Motor, forcing them to accept less favorable terms due to the inability to easily switch suppliers for these vital components.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers can threaten BAIC Motor by integrating forward, essentially becoming competitors. Imagine a major battery supplier for electric vehicles deciding to start building their own cars, or perhaps partnering directly with another automaker. This would significantly shift the power dynamic, as they’d no longer be just a component provider but a direct rival.
This forward integration strategy reduces the supplier's dependence on existing customers like BAIC Motor. By controlling more of the value chain, they gain leverage over pricing and supply conditions, making it harder for automakers to negotiate favorable terms. This is a growing concern across the automotive sector, particularly with the rise of electric vehicles and the specialized components they require.
For instance, in 2024, several advanced materials suppliers for EV batteries have been rumored to explore joint ventures or even direct manufacturing of EV models, aiming to capture a larger share of the burgeoning EV market. This trend highlights the increasing strategic options available to key suppliers, potentially impacting BAIC Motor's cost structure and supply chain stability.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers may develop their own vehicle manufacturing capabilities or forge direct partnerships with other Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs).
- Increased Supplier Influence: This integration reduces supplier reliance on traditional automakers, enhancing their power over pricing and supply terms.
- Automotive Industry Trend: The broader automotive industry is witnessing an uptick in suppliers exploring vertical integration, driven by new technologies and market shifts.
- Impact on BAIC Motor: Such moves can lead to higher component costs and potential supply disruptions for BAIC Motor, necessitating strategic supplier relationship management.
Importance of Supplier's Input to BAIC
The importance of a supplier's input to BAIC Motor is critical, particularly for components that significantly differentiate the final product in terms of performance, safety, or smart features. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, the quality and innovation provided by key suppliers directly impact BAIC's competitiveness and market appeal.
For instance, advanced battery technology suppliers are crucial for BAIC's electric vehicle (EV) strategy. In 2024, the global EV battery market saw continued growth, with companies like CATL and LG Energy Solution leading in innovation. BAIC's reliance on such suppliers for high-density, fast-charging batteries directly influences its EV product line's attractiveness and range capabilities.
- Critical Components: Suppliers of advanced powertrain systems, intelligent driving sensors, and high-performance infotainment units hold significant sway.
- Technological Dependency: BAIC's ability to integrate cutting-edge technology hinges on the innovation and reliability of its component suppliers.
- Market Differentiation: The unique features and quality derived from supplier inputs are key differentiators in the highly competitive automotive market.
BAIC Motor faces considerable supplier bargaining power, especially from providers of specialized EV components like batteries and semiconductors. Suppliers of critical, high-tech parts can command higher prices and dictate terms due to limited alternatives and high switching costs for BAIC. This power is amplified when suppliers can integrate forward into vehicle manufacturing, directly competing with their automotive clients.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on BAIC Motor | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (EV Batteries) | High Power | CATL, a dominant player, holds a significant market share, enabling strong pricing leverage. |
| Switching Costs (Proprietary Tech) | High Power | Re-engineering for new intelligent driving systems can cost millions and take years. |
| Availability of Substitutes (Semiconductors) | High Power | Persistent shortages in 2023-2024 forced automakers to accept premium pricing from chip manufacturers. |
| Forward Integration Threat | High Power | Rumors of battery suppliers exploring EV manufacturing ventures in 2024 increase supplier leverage. |
| Importance of Input (Advanced Batteries) | High Power | BAIC's EV strategy relies heavily on suppliers like LG Energy Solution for competitive range and charging speeds. |
What is included in the product
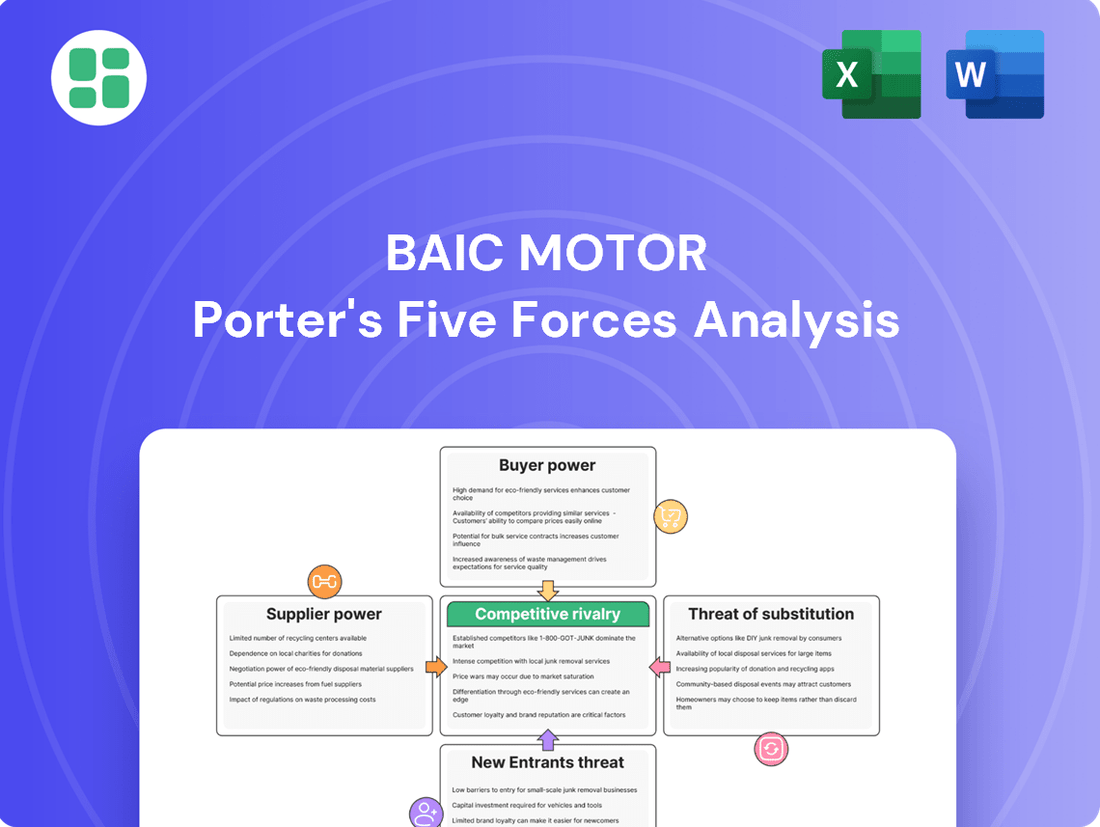
This analysis of BAIC Motor's competitive environment reveals the intensity of rivalry among existing players, the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of BAIC Motor's Porter's Five Forces, making strategic adjustments effortless.
Customers Bargaining Power
Chinese automotive consumers, especially those in the mass market segments where BAIC Motor primarily competes, are notably price-sensitive. This means they are highly responsive to changes in price, often opting for the most affordable option available, which directly impacts BAIC's pricing strategies and profit margins.
The Chinese auto market is characterized by aggressive price wars, particularly in the New Energy Vehicle (NEV) sector. For instance, in early 2024, several major automakers engaged in significant price reductions, with some NEV models seeing discounts of over 20%. This intense competition compels manufacturers like BAIC to offer competitive pricing, substantial discounts, and various incentives, thereby amplifying the bargaining power of their customers.
The availability of alternative vehicles significantly strengthens customer bargaining power in the automotive sector. In China's highly competitive market, consumers have a vast array of choices from numerous domestic and international brands. This abundance of options, especially with the rapid introduction of new energy vehicles (NEVs), empowers customers to easily switch brands if their expectations regarding features or pricing are not met.
The ease with which customers can switch between car brands significantly influences their bargaining power. For BAIC Motor, this means buyers face minimal costs when shifting to a competitor. These costs primarily involve the time and effort spent researching alternative vehicles and completing new purchase paperwork, rather than substantial financial penalties or learning curves associated with complex products.
This low barrier to switching empowers consumers to actively seek out the best deals. They can readily compare pricing, features, and financing options across different manufacturers, including BAIC's direct competitors. In 2024, the automotive market saw intense competition, with many brands offering attractive incentives and discounts to capture market share, further amplifying customer leverage.
Access to Information and Comparison
Digital platforms and automotive media have significantly amplified the bargaining power of customers. Buyers now have unprecedented access to detailed information regarding vehicle specifications, pricing structures, and independent reviews. This transparency allows consumers to meticulously compare offerings from various manufacturers, including BAIC Motor, fostering a more informed and demanding market.
The ease with which consumers can research and compare vehicles empowers them to negotiate more effectively. For instance, a 2024 study by J.D. Power indicated that over 80% of new car buyers utilized online resources to research their purchase. This readily available data allows customers to identify competitive pricing and features, putting pressure on automakers to offer better value and incentives.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers can easily access detailed vehicle specifications, pricing, and expert reviews, leading to more informed purchase decisions.
- Price Transparency: Online platforms and automotive media expose pricing variations across dealerships and brands, enabling customers to seek the best deals.
- Brand Comparison: Buyers can efficiently compare models from different manufacturers side-by-side, increasing competition and customer leverage.
- Negotiation Power: Armed with comprehensive information, customers are better positioned to negotiate prices and demand favorable terms from automakers like BAIC.
Impact of Government Incentives and Policies
Government policies, such as subsidies for New Energy Vehicles (NEVs) and trade-in schemes, significantly influence customer purchasing decisions in the automotive market. For instance, in 2024, China continued to offer substantial NEV purchase tax exemptions, a policy that has been instrumental in driving EV adoption. This has, in turn, made consumers more attuned to price fluctuations and specific vehicle features that align with subsidy eligibility criteria.
This heightened awareness of incentives directly translates into increased bargaining power for customers. They become more discerning, comparing models based on their eligibility for government support and the overall cost savings. This dynamic forces manufacturers like BAIC Motor to be more competitive on price and feature sets that attract these incentives.
- Government subsidies for NEVs directly impact customer price sensitivity.
- Trade-in programs can further empower consumers by reducing the effective purchase price.
- In 2024, the continuation of NEV purchase tax exemptions in key markets like China influenced consumer choices.
- Customers leveraging these incentives gain greater leverage in price negotiations with automakers.
BAIC Motor faces strong customer bargaining power due to price sensitivity and the availability of numerous alternatives in the competitive Chinese auto market. The ease of switching between brands, coupled with readily accessible information online, empowers consumers to negotiate effectively. Government incentives, like NEV tax exemptions, further enhance this leverage, forcing manufacturers to offer more attractive pricing and features.
What You See Is What You Get
BAIC Motor Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete BAIC Motor Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape for the company, including the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate usability for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Chinese automotive market is incredibly crowded, leading to fierce competition for BAIC Motor. In 2023, China's auto sales surpassed 30 million units, a testament to the sheer volume of players vying for market share. This intense rivalry stems from a mix of established state-owned enterprises, dynamic private companies like BYD and Geely which saw significant sales growth in 2023, and numerous international joint ventures all competing for consumer attention and loyalty.
The Chinese auto market, especially the New Energy Vehicle (NEV) sector, is characterized by intense price wars that significantly squeeze profit margins for all players, including BAIC Motor. Automakers consistently employ aggressive discounting and promotional tactics to capture market share, making it a challenging environment for BAIC Motor.
The automotive market, particularly for New Energy Vehicles (NEVs) and advanced smart features, is characterized by an insatiable demand for continuous innovation. This fuels incredibly rapid product cycles and extensive diversification efforts across the industry. Companies like BAIC Motor are compelled to make substantial, ongoing investments in research and development to stay abreast of rapidly evolving consumer tastes and cutting-edge technological advancements. This dynamic environment intensifies competitive pressure significantly.
High Stakes and Market Growth
The automotive landscape in China, the world's largest car market, is characterized by fierce rivalry. Despite this intensity, the market's substantial growth potential, especially in the New Energy Vehicle (NEV) segment, fuels aggressive competition. This dynamic environment compels established players to continually invest and vie for dominance.
The sheer size and growth trajectory of the Chinese automotive market, projected to reach 30 million units in 2024, create a high-stakes environment. This growth, particularly the rapid expansion of NEVs, which accounted for over 30% of new car sales in early 2024, incentivizes significant capital expenditure and aggressive market share acquisition strategies among all participants.
- Market Size: China's automotive market is the largest globally, with sales expected to exceed 30 million units in 2024.
- NEV Growth: The NEV sector is a key driver of competition, with its market share surpassing 30% of new vehicle sales in early 2024.
- Investment Focus: High growth potential encourages substantial investment from existing manufacturers to capture market share.
- Competitive Intensity: The dynamic nature of the market leads to aggressive strategies and a fight for dominance among automakers.
Brand Loyalty and Differentiation Challenges
While BAIC Motor benefits from some existing brand loyalty, particularly in its home market, maintaining strong differentiation is a significant hurdle. The automotive sector is flooded with choices, and competitors are relentlessly employing aggressive marketing tactics. This environment makes it tough for BAIC to carve out a distinct and lasting identity in the minds of consumers.
The modern car buyer's priorities have shifted. Technology, seamless connectivity, and overall cost-effectiveness are now paramount. These evolving consumer demands mean that simply relying on traditional brand appeal isn't enough. BAIC, like its rivals, must continuously innovate and offer compelling value propositions that go beyond just the badge on the car.
- Brand Loyalty: BAIC's brand loyalty is moderate, facing pressure from a highly competitive market.
- Differentiation: Competitors' aggressive marketing and focus on tech/cost-effectiveness challenge BAIC's differentiation efforts.
- Consumer Priorities: Technology, connectivity, and value for money are key purchasing drivers for today's consumers.
- Innovation Imperative: BAIC must innovate to meet evolving consumer expectations and stand out from the crowd.
Competitive rivalry is a major force for BAIC Motor, driven by China's vast and rapidly growing auto market. With over 30 million units sold in 2023 and an expected continued expansion in 2024, the sheer volume of manufacturers, including domestic giants like BYD and international joint ventures, creates an intensely crowded space. This rivalry is further amplified by aggressive price wars, particularly in the burgeoning New Energy Vehicle (NEV) segment, which is projected to capture over 30% of new car sales in 2024. Such conditions necessitate continuous innovation and significant investment from BAIC to maintain its market position.
| Competitor | 2023 Sales (Units - Approx.) | NEV Share (Approx.) | Key Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| BYD | 3,000,000+ | 90%+ | Dominant NEV player, vertical integration |
| Geely | 1,600,000+ | 20%+ | Brand diversification, technology focus |
| SAIC Motor | 4,000,000+ | 15%+ | Joint ventures, broad product portfolio |
| BAIC Motor | 1,000,000+ (Group) | 25%+ (BAIC BluePark) | Focus on NEVs, strategic partnerships |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The expansion of public transportation in China presents a substantial threat of substitution for BAIC Motor. By 2024, major Chinese cities boast extensive metro systems, bus networks, and high-speed rail, offering convenient and cost-effective alternatives to private car ownership for urban dwellers.
This robust public transit infrastructure directly impacts car demand, especially for daily commutes. For instance, Shanghai's metro system alone carried over 3.6 billion passengers in 2023, highlighting its capacity to serve a significant portion of the urban population's transportation needs.
The rapid expansion of ride-sharing services in China presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional car ownership, directly impacting BAIC Motor. Platforms like Didi Chuxing have become incredibly popular, offering a readily available and often cheaper alternative to personal vehicle use, particularly in urban areas. In 2023, Didi reported over 10 million average daily completed orders, highlighting the immense scale of this substitute.
The rise of micromobility solutions like electric scooters, e-bikes, and shared bicycle programs presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional car ownership, particularly for short urban journeys. For instance, in 2024, cities globally saw continued growth in shared micromobility usage, with some reporting millions of rides annually, offering a cost-effective and often faster alternative to driving in congested areas.
Shifting Consumer Lifestyles and Urbanization
Evolving urban lifestyles and increasing population density in Chinese cities are influencing transportation choices, potentially reducing reliance on private cars. This shift is particularly noticeable among younger generations who may favor accessible, diverse transport options over outright vehicle ownership.
Factors driving this trend include growing environmental awareness, financial prudence, and the sheer convenience offered by integrated mobility solutions. For instance, by 2024, China's urban population reached over 66% of its total, highlighting the concentration of potential users for alternative transport.
- Urbanization Impact: Over 66% of China's population resided in urban areas by 2024, increasing the feasibility of shared and public transportation.
- Younger Generation Preferences: Studies in 2024 indicated a growing preference among urban youth for mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) platforms over traditional car ownership due to cost and convenience.
- Environmental Concerns: A significant portion of Chinese consumers, especially in major cities, expressed willingness to adopt greener transportation alternatives in 2024 surveys.
Technological Advancements in Alternative Transport
Future advancements in alternative transport technologies, such as more efficient and widespread hydrogen fuel cell vehicles or advanced autonomous public transport systems, could pose a long-term threat to traditional automakers like BAIC Motor.
While still in nascent stages, these innovations, including the projected growth in the global hydrogen fuel cell vehicle market which was valued at approximately USD 2.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach over USD 13 billion by 2030, could eventually offer superior or more convenient mobility solutions.
This potential shift could impact traditional car sales, especially if these alternatives become more cost-effective and accessible to a broader consumer base.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Growth: Expected to surge from USD 2.5 billion in 2023 to over USD 13 billion by 2030.
- Autonomous Public Transport: Advancements could offer compelling alternatives to private vehicle ownership.
- Consumer Convenience: Future transport solutions might prioritize ease of use and integration, potentially drawing customers away from traditional car models.
The increasing availability and appeal of public transportation, ride-sharing, and micromobility solutions in China directly challenge BAIC Motor's market. By 2024, extensive urban transit networks and popular ride-hailing platforms offer convenient and often more economical alternatives to private car ownership, especially for daily commutes.
| Substitute Type | 2023/2024 Data Point | Impact on BAIC Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Shanghai Metro: 3.6 billion+ passengers (2023) | Reduces demand for personal vehicles in urban areas. |
| Ride-Sharing | Didi Chuxing: 10 million+ average daily completed orders (2023) | Offers a direct, often cheaper, alternative to car ownership. |
| Micromobility | Millions of rides annually in major cities (2024) | Appeals to short-distance urban travel, bypassing car use. |
Entrants Threaten
The automotive sector, particularly for new energy vehicles (NEVs), presents a formidable barrier to entry due to its exceptionally high capital requirements. Companies venturing into this space need substantial funds for research and development, establishing advanced manufacturing facilities, and building robust supply chains. For instance, setting up a modern EV production line can easily cost billions of dollars, a figure that naturally dissuades many aspiring competitors.
Stringent regulatory and policy hurdles significantly deter new entrants in the Chinese automotive market. For instance, the nation's New Energy Vehicle (NEV) credit system, implemented to boost electric vehicle production, requires manufacturers to meet specific quotas or purchase credits, a complex financial and operational challenge for newcomers.
Navigating the intricate web of vehicle safety standards, emissions regulations, and licensing procedures demands substantial investment and established connections within the Chinese government. Companies lacking this experience and infrastructure find it exceptionally difficult to gain a foothold, effectively shielding established players like BAIC Motor.
Established brand recognition and loyalty are significant barriers for new entrants in the automotive industry. Incumbent players like BAIC Motor have cultivated trust and preference over many years, supported by extensive dealership networks and robust marketing efforts. For instance, BAIC Motor's brand awareness in China, a key market, allows them to leverage existing customer relationships, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market share without substantial investment in building similar credibility and reach.
Complex Supply Chain and Distribution Networks
The automotive industry's intricate supply chain and extensive distribution networks present a significant barrier to new entrants. Establishing relationships with component suppliers and building a reliable logistics system requires substantial investment and time. For instance, in 2024, the average lead time for critical automotive components can range from several weeks to months, highlighting the complexity of managing these relationships.
New players face immense difficulty in matching the scale and efficiency that incumbents have cultivated over years, impacting their ability to offer competitive pricing and ensure consistent product availability. This is particularly challenging when considering the need for a nationwide after-sales service infrastructure, which is vital for customer loyalty and brand reputation.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Automotive manufacturing relies on a global network of specialized suppliers for everything from microchips to advanced battery systems.
- Distribution Network Costs: Building a dealership and service center footprint across a large market, as seen with established brands in 2024, can cost billions of dollars.
- Economies of Scale: Incumbents benefit from bulk purchasing power and optimized logistics, making it hard for newcomers to compete on cost per unit.
- After-Sales Service: A comprehensive and responsive service network is crucial for customer retention, a significant hurdle for new entrants to replicate quickly.
Technological Expertise and R&D Costs
The automotive industry's rapid technological evolution, especially in areas like electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving, presents a significant hurdle for newcomers. Companies like BAIC Motor must continually invest heavily in research and development to stay competitive. For instance, global automotive R&D spending reached an estimated $200 billion in 2023, a figure expected to climb as companies push boundaries in battery technology and AI integration.
New entrants face the daunting task of acquiring or developing advanced technological capabilities. This often translates to substantial upfront costs for skilled personnel, specialized equipment, and patent licensing. Consider that developing a new EV platform can cost billions of dollars, a price point that deters many potential players.
The sheer expense and risk associated with mastering these cutting-edge technologies act as a formidable barrier. Without established R&D infrastructure and a proven track record, new companies struggle to match the innovation pace of incumbents. This financial and technical expertise gap is a critical factor limiting the threat of new entrants in the current automotive landscape.
- High R&D Investment: Global automotive R&D spending neared $200 billion in 2023, highlighting the significant capital required for technological advancement.
- Electrification and Autonomy Costs: Developing new EV platforms can easily cost billions, creating a substantial financial barrier for new market participants.
- Talent Acquisition: Securing specialized engineering talent in areas like AI and battery technology is both costly and competitive, further increasing entry barriers.
- Intellectual Property: Acquiring or developing necessary patents for advanced automotive technologies represents another significant financial and strategic challenge for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for BAIC Motor is considerably low due to immense capital requirements, stringent regulations, and established brand loyalty. Building a competitive automotive operation, especially in the NEV sector, demands billions for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution, a hurdle few newcomers can clear. Furthermore, navigating China's complex NEV credit system and safety standards requires deep industry knowledge and significant investment, effectively protecting incumbents.
The established brand equity and extensive dealer networks of companies like BAIC Motor create a formidable barrier. New entrants struggle to replicate the trust and widespread accessibility that incumbents have built over years, requiring massive marketing and infrastructure investment to even begin competing. This makes it exceptionally difficult for new players to gain traction and market share in the current automotive landscape.
The automotive industry's rapid technological advancements, particularly in electrification and autonomous driving, further elevate entry barriers. New companies must commit substantial resources to R&D and talent acquisition to keep pace, a challenge compounded by the need to secure intellectual property. For instance, global automotive R&D spending was projected to exceed $200 billion in 2023, underscoring the financial commitment needed to remain relevant.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023-2024) |
| Capital Requirements | Setting up EV production lines and R&D facilities demands billions. | Deters most potential competitors. | EV platform development costs can exceed $1 billion. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Navigating NEV credits, safety, and licensing. | Requires extensive expertise and connections. | China's NEV credit system adds financial and operational complexity. |
| Brand Loyalty & Networks | Established trust, dealerships, and after-sales service. | Makes customer acquisition difficult and costly. | Building a nationwide dealership network can cost billions. |
| Technological Advancement | High R&D spending on EVs, AI, and autonomy. | Requires continuous, massive investment to compete. | Global automotive R&D spending neared $200 billion in 2023. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for BAIC Motor is built upon a foundation of publicly available data, including BAIC Motor's annual reports and financial statements, as well as industry-specific market research reports and automotive sector news.