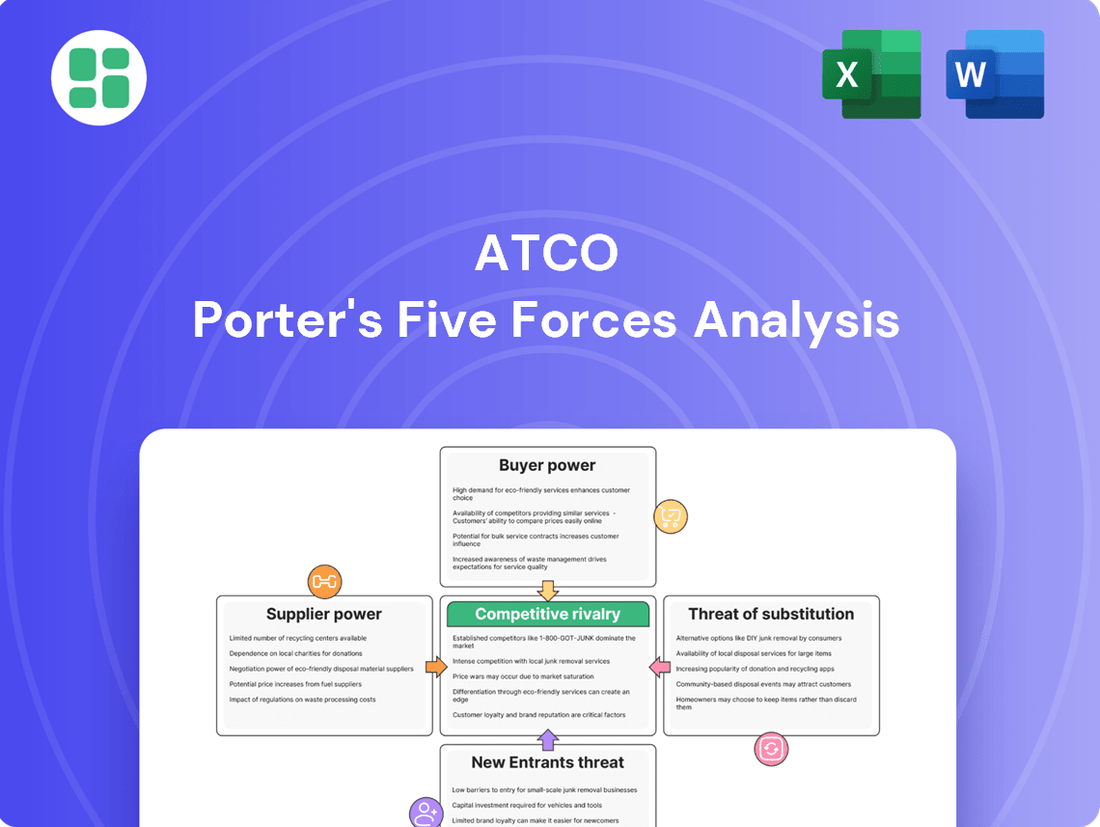
ATCO Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ATCO Bundle
ATCO's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping ATCO’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
ATCO's reliance on specialized equipment like turbines and transformers from a select group of global manufacturers gives these suppliers considerable leverage. For instance, the advanced technology required for modern gas turbines often comes from only a handful of companies, meaning ATCO has fewer alternatives when sourcing these critical components.
The high cost and unique specifications of such assets, potentially running into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars per unit, further amplify supplier bargaining power. This financial commitment makes switching suppliers difficult and costly, solidifying the suppliers' position. In 2023, global capital expenditures in the energy infrastructure sector saw significant increases, reflecting the demand for such specialized, high-value equipment.
To counter this, ATCO often enters into long-term supply agreements and fosters strategic partnerships. These arrangements can secure favorable pricing and ensure a stable supply chain, effectively mitigating the inherent bargaining power of these specialized equipment providers and ensuring operational continuity for ATCO's utility and energy projects.
While Canada has substantial natural gas reserves, ATCO's reliance on specific suppliers for distribution grants these providers a degree of bargaining power. The terms of long-term supply contracts and shifts in natural gas market supply and demand directly influence this power. For instance, in 2024, natural gas prices in North America saw considerable volatility due to weather patterns and global export demand, potentially strengthening supplier leverage.
The construction, maintenance, and operation of critical infrastructure, like those ATCO manages, heavily rely on a workforce possessing specialized skills. This includes engineers, technicians, and various tradespeople essential for complex projects.
When there's a scarcity of this specialized talent, or when demand for particular engineering or construction services surges, the bargaining power of labor unions or niche service providers naturally escalates. This dynamic is a persistent challenge within the energy and utilities sector.
For instance, in 2024, the average wage for a skilled tradesperson in Canada, where ATCO primarily operates, saw an increase, reflecting ongoing demand and potential labor shortages in key areas, thereby strengthening their negotiating position.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Suppliers in regulated utility sectors, like those ATCO serves, must meet rigorous safety, environmental, and technical mandates set by government agencies. This can shrink the number of qualified suppliers available, as the expense and specialized knowledge needed for compliance can deter new entrants. Consequently, existing suppliers with the necessary certifications and track records often hold greater leverage.
For instance, in 2024, the Canadian Energy Regulator (CER) continued to enforce strict operational standards for pipeline companies, impacting the types of equipment and services available to utilities. Suppliers who can consistently demonstrate adherence to these evolving regulations, such as those meeting ISO 14001 environmental management standards, often command premium pricing due to their proven capability and limited competition.
- Stringent Standards: Regulatory bodies impose strict safety and environmental requirements on utility suppliers.
- Barriers to Entry: Compliance costs and specific certifications limit the number of eligible suppliers.
- Supplier Leverage: Established, compliant suppliers gain increased bargaining power.
- Market Impact: This dynamic can lead to higher costs for utilities if compliant suppliers are few.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Costs
Ongoing global supply chain pressures, including increased costs for materials, equipment, and logistics, are significantly impacting ATCO's project timelines and budgets. For instance, the global supply chain disruptions experienced throughout 2022 and continuing into 2023 led to an average increase of 10-15% in raw material costs for many industries, a trend likely to persist in 2024.
This external factor effectively strengthens the bargaining position of suppliers, as ATCO may face fewer alternatives or higher prices to secure necessary inputs. The continued volatility in shipping rates, which saw significant fluctuations in 2023 with some routes experiencing double-digit percentage increases, further empowers suppliers who can dictate terms more readily.
- Increased Material Costs: Suppliers can leverage higher demand and limited availability to charge more for essential components.
- Logistical Challenges: Extended lead times and unpredictable shipping costs give suppliers more leverage in negotiations.
- Limited Supplier Alternatives: When few suppliers offer critical goods or services, their bargaining power naturally increases.
- Impact on Project Budgets: ATCO faces the risk of cost overruns and project delays due to these supplier-driven pressures.
ATCO faces significant supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on specialized, high-cost equipment like turbines and transformers from a limited number of global manufacturers. The substantial financial commitment and unique specifications involved in acquiring these assets, often costing tens or hundreds of millions of dollars, make switching suppliers difficult and costly. For example, global capital expenditures in energy infrastructure saw substantial growth in 2023, underscoring the demand for such specialized, high-value components, which in turn strengthens supplier leverage.
Furthermore, ATCO's dependence on specific suppliers for natural gas distribution in Canada grants these providers leverage, influenced by contract terms and market dynamics. In 2024, North American natural gas prices experienced considerable volatility due to weather and global export demand, potentially amplifying supplier bargaining power. ATCO mitigates this by entering long-term supply agreements and fostering strategic partnerships to secure favorable pricing and ensure supply chain stability.
The scarcity of specialized labor, such as skilled engineers and technicians, also empowers labor unions and niche service providers, a persistent challenge in the energy sector. In 2024, the average wage for skilled tradespeople in Canada increased, reflecting high demand and potential labor shortages, thus enhancing their negotiating position.
Regulatory mandates for safety and environmental compliance in utility sectors shrink the pool of qualified suppliers, increasing the leverage of those who meet stringent requirements. For instance, the Canadian Energy Regulator's continued enforcement of strict operational standards in 2024 impacts equipment and service availability. Suppliers demonstrating adherence to regulations like ISO 14001 often command premium pricing due to their proven capabilities and limited competition.
Global supply chain pressures, including rising material, equipment, and logistics costs, continue to impact ATCO's project budgets and timelines, with an estimated 10-15% increase in raw material costs seen in 2022-2023, a trend likely to persist into 2024. This situation strengthens supplier bargaining power as ATCO faces fewer alternatives and higher prices for essential inputs, further exacerbated by shipping rate volatility experienced throughout 2023.
What is included in the product
ATCO's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its operating industries, evaluating the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
For ATCO's regulated utility services, individual customers generally have low bargaining power. Rates for natural gas and electricity distribution are set by regulatory bodies, like the Alberta Utilities Commission, which consider both consumer affordability and the utility's need for a fair return. This regulatory oversight limits direct price negotiation by customers.
Large industrial and commercial consumers, especially those with substantial energy needs or requiring custom modular solutions, hold significant bargaining power with ATCO. Their sheer volume of consumption or the scale of their projects enables them to negotiate better pricing and contract terms.
These major clients can also explore alternative energy sourcing or even invest in self-generation capabilities, further strengthening their negotiating position. For instance, in 2024, large industrial users in Alberta, ATCO's primary service area, continued to seek efficiency and cost-optimization, putting pressure on energy providers to offer competitive rates.
In competitive retail energy markets, customers possess significant bargaining power due to the ability to switch providers. This freedom of choice compels companies like ATCO to offer attractive pricing and service bundles to maintain their customer base. For instance, in Australia, regulatory reforms in 2024 have further streamlined the switching process, making it easier for consumers to move between energy retailers, thereby amplifying their influence.
Customer Awareness and Demand for Sustainable Solutions
Customers are increasingly prioritizing sustainable and environmentally friendly energy solutions. This growing awareness significantly enhances their bargaining power, as they can actively select providers that align with their Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) values. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for products and services from companies with strong sustainability commitments.
This shift in consumer preference directly influences companies like ATCO, compelling them to invest more heavily in cleaner fuels and renewable energy projects to attract and retain this environmentally conscious customer base. The demand for green energy is not just a trend; it's a market force shaping investment strategies across the energy sector.
- Growing Demand: Consumer surveys in 2024 show a marked increase in demand for renewable energy options.
- ESG Influence: Over 60% of consumers in 2024 stated ESG factors influence their purchasing decisions.
- Investment Driver: Customer preference for sustainability pressures companies like ATCO to allocate capital towards green initiatives.
- Market Shift: The energy sector is adapting to customer-driven demand for cleaner, more responsible energy sources.
Project-Based Procurement in Structures & Logistics
Customers in ATCO's Structures & Logistics segment, including major mining operations and government bodies, frequently engage in large, project-specific purchases. This means they often have considerable leverage because they can shop around and get quotes from various suppliers, or even consider doing the work themselves.
For instance, in 2023, large-scale infrastructure projects, a key market for ATCO, saw significant competition among modular construction providers. This competitive landscape directly translates to higher bargaining power for the clients awarding these contracts.
- Significant Project Size: Large contracts allow customers to negotiate terms more effectively due to the volume of business involved.
- Competitive Bidding: The ability to solicit bids from multiple suppliers intensifies competition, driving down prices and increasing customer leverage.
- In-House Capabilities: Some large clients possess the resources and expertise to manage projects internally, providing a credible alternative to external providers.
- Supplier Dependence: For specialized or large-scale projects, customers may become dependent on a few key suppliers, which can shift bargaining power, but in the modular construction space, the number of capable providers often keeps this power with the customer.
For ATCO's regulated utility operations, individual customers generally possess low bargaining power. Rates are determined by regulatory bodies, limiting direct price negotiation. However, large industrial and commercial clients, due to their substantial energy needs or project scale, wield significant influence, often negotiating better terms and exploring alternative energy sources. In competitive retail markets, customer choice amplifies their power, pushing companies like ATCO to offer competitive pricing and services to retain them.
The growing consumer emphasis on sustainability and ESG principles has also bolstered customer bargaining power. In 2024, a significant portion of consumers indicated a willingness to pay more for environmentally conscious products, compelling ATCO to invest in cleaner energy solutions to attract and retain this segment of the market.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Level | Key Factors Influencing Power |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Residential Customers (Regulated Utilities) | Low | Rate regulation by bodies like Alberta Utilities Commission; limited switching options. |
| Large Industrial/Commercial Customers (Regulated Utilities) | High | Volume of consumption; ability to explore alternative energy sources; project scale. |
| Customers in Competitive Retail Markets | High | Freedom to switch providers; availability of alternative suppliers; competitive pricing. |
| Customers (Structures & Logistics Segment) | High | Large project-specific purchases; ability to solicit multiple bids; potential for in-house execution. |
Same Document Delivered
ATCO Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete ATCO Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the energy sector. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate access to this professionally crafted strategic tool.
Rivalry Among Competitors
In ATCO's core regulated utility segments within Canada and Australia, the competitive rivalry is notably low. This is primarily due to the inherent nature of electricity and natural gas transmission and distribution, which often function as natural monopolies, limiting direct competition. For instance, in 2023, ATCO Electric Alberta operated over 42,000 kilometers of transmission and distribution lines, a vast network that is impractical for multiple entities to replicate.
Instead of direct head-to-head competition, rivalry in these markets often manifests indirectly. ATCO, like other utilities, competes for opportunities to develop new infrastructure or expand existing networks through regulatory processes and competitive bidding. These tenders are crucial for securing long-term contracts and growth, as seen in the ongoing investments in grid modernization and renewable energy integration projects across North America.
The energy infrastructure and power generation sectors are experiencing heightened competitive pressures, especially within the rapidly expanding renewable energy market. ATCO finds itself in direct competition with other major infrastructure developers, numerous independent power producers, and specialized companies concentrating on renewable energy ventures.
These players are all actively seeking to capture market share as the global energy landscape undergoes a significant transition. For instance, in 2024, the installed capacity of renewable energy sources globally continued to grow, with solar and wind power leading the charge, intensifying the race for new project development and grid integration opportunities.
The modular construction and logistics sector is highly fragmented, featuring a large number of regional and global competitors vying for market share. This intense competition means companies like ATCO Structures must differentiate themselves effectively.
ATCO Structures competes by emphasizing rapid deployment, superior quality, and the ability to customize solutions to meet specific client needs. Their global reach also serves as a significant competitive advantage in this dispersed market.
In 2024, the modular construction market continued its growth trajectory, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% through 2028, underscoring the crowded and dynamic competitive landscape ATCO operates within.
Impact of Energy Transition and Decarbonization Goals
The global imperative for decarbonization and achieving net-zero emissions significantly escalates competitive rivalry within the energy sector. Companies are aggressively vying to pioneer and implement innovative clean energy solutions and the necessary infrastructure, directly impacting ATCO's market position.
This intensified competition presents both substantial growth avenues and considerable strategic challenges for ATCO. The company must continuously innovate and adapt its service portfolio to remain competitive and capitalize on emerging opportunities in the green energy transition.
- Increased R&D Investment: Companies are boosting spending on renewable energy technologies, with global clean energy investment projected to reach $2 trillion annually by 2030, according to various industry forecasts.
- Emergence of New Competitors: The shift to renewables attracts new players, including technology firms and specialized clean energy developers, diversifying the competitive landscape beyond traditional utilities.
- Policy-Driven Competition: Government incentives and regulations favoring decarbonization create a dynamic environment where companies that best align with these policies gain a competitive edge.
- Infrastructure Development Race: The build-out of electric vehicle charging networks, hydrogen infrastructure, and upgraded grid systems is a key battleground, with significant capital deployment required.
Strategic Investments and Capital Expenditure Plans
Competitors are actively investing in expanding their regulated asset bases and pioneering new energy solutions, which reshapes the competitive arena. These strategic moves by rivals directly influence ATCO's market position and necessitate comparable investment to remain competitive.
ATCO's own substantial capital expenditure plans, projected to be in the billions of dollars for the coming years, underscore the critical need for ongoing investment. These expenditures are essential for both maintaining its existing infrastructure and pursuing growth opportunities in evolving energy markets.
- ATCO's 2024 capital program is expected to be around $2.1 billion.
- This investment is primarily directed towards modernizing and expanding its electricity and natural gas utility operations.
- Competitors are also reporting significant capital outlays, with some focusing on renewable energy integration and grid modernization efforts.
- The intensity of these investments suggests a strong drive among industry players to secure future market share and adapt to energy transition demands.
In ATCO's core regulated utility segments, competitive rivalry is low due to natural monopolies, making direct competition rare. However, the energy infrastructure and renewable energy sectors are highly competitive, with ATCO facing numerous developers and independent power producers. The modular construction market is also fragmented, demanding differentiation through quality and customization.
| Sector | Nature of Competition | Key Competitors | ATCO's Strategy | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regulated Utilities (Canada, Australia) | Low, natural monopolies | Limited direct competitors | Focus on infrastructure maintenance and regulatory compliance | ATCO Electric Alberta operates over 42,000 km of lines |
| Energy Infrastructure & Renewables | High, dynamic | Major developers, IPPs, specialized clean energy firms | Innovation, project bidding, clean energy solutions | Global renewable energy capacity growth continues |
| Modular Construction | High, fragmented | Numerous regional and global players | Rapid deployment, quality, customization, global reach | Modular construction market CAGR projected >6% through 2028 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For ATCO's established electricity grid operations, the threat of substitutes is notably increasing due to the rise of renewable energy and distributed generation. Technologies like rooftop solar panels and home battery storage systems allow consumers to produce and store their own power, directly reducing their need for ATCO's grid services.
These distributed energy resources, including virtual power plants that aggregate smaller energy sources, can offer significant cost savings to customers. For instance, by 2024, the cost of solar photovoltaic systems has continued to decline, making them a more attractive alternative for many households and businesses seeking to lower their energy bills and increase their energy independence.
Advances in energy efficiency technologies and increased consumer adoption of conservation practices present a significant threat of substitutes for ATCO. For instance, by 2024, the adoption of smart thermostats and improved insulation in residential and commercial buildings can directly reduce the demand for electricity and natural gas, impacting ATCO's core utility business. This trend is expected to continue as more efficient appliances and building codes become standard.
The growing popularity of distributed generation, such as rooftop solar panels, also acts as a substitute. In 2023, Canada saw a notable increase in residential solar installations, with some provinces reporting significant year-over-year growth. This reduces reliance on grid-supplied electricity, directly challenging ATCO's market share and revenue streams in its electricity distribution segment.
The growing adoption of alternative fuels, such as hydrogen and biofuels, alongside the electrification of heating and transportation, presents a significant long-term substitution threat to ATCO's traditional natural gas distribution operations. For instance, by 2024, many jurisdictions are seeing increased government incentives for electric vehicle adoption, directly impacting the demand for natural gas in the transportation sector.
ATCO is proactively addressing this challenge by investing in hydrogen projects. These investments aim to position ATCO as a player in the emerging hydrogen economy, thereby mitigating the potential decline in natural gas demand. This strategic pivot is crucial for ATCO's future resilience in a decarbonizing energy landscape.
Traditional Construction Methods
Traditional on-site construction methods represent a significant threat of substitutes for ATCO's modular building solutions within the Structures & Logistics segment. These conventional approaches are deeply entrenched in industry practices and can be preferred when project specifics or client familiarity lean towards established, albeit often slower, building processes.
Despite the advantages of modular construction, such as faster build times, the inherent complexity of some projects or a lack of widespread adoption of off-site techniques can still make traditional methods a compelling alternative. For instance, in 2024, the global construction market, valued at trillions, still sees a substantial portion dedicated to traditional on-site builds, highlighting the persistent relevance of these substitutes.
- Dominant Industry Practice: Traditional construction remains the default for many projects, offering a familiar and proven, though less efficient, pathway.
- Project-Specific Suitability: Highly customized or complex designs might still be perceived as more manageable through traditional on-site assembly.
- Established Supply Chains: Existing networks for traditional materials and labor can make on-site construction more accessible and cost-predictable in certain regions.
- Client Preference: Some clients may have established relationships or comfort levels with traditional builders, influencing their choice of construction method.
Technological Advancements in Energy Storage
Technological advancements in energy storage are increasingly presenting viable substitutes for traditional energy infrastructure. Beyond individual home batteries, large-scale energy storage solutions, like utility-scale battery farms, are becoming more prevalent. For instance, in 2024, the global energy storage market saw significant growth, with battery storage capacity projected to reach hundreds of gigawatts by the end of the decade.
These advancements can reduce the reliance on conventional peak power generation, which is often more expensive and less efficient. Grid modernization initiatives, coupled with smart grid technologies, further enhance the ability to manage energy flow and demand, thereby diminishing the need for certain traditional transmission upgrades. This shift represents a direct threat as these technologies offer alternative ways to meet energy needs, potentially bypassing or reducing the demand for ATCO's established infrastructure and services.
- Growing Battery Capacity: Global installed battery energy storage capacity is expected to surpass 400 GW by 2030, a substantial increase from previous years, impacting demand for traditional peaking plants.
- Grid Modernization Investments: Significant investments are being made in grid modernization worldwide, with billions allocated in 2024 alone to enhance grid flexibility and reduce the need for costly transmission upgrades.
- Declining Storage Costs: The cost of battery storage has fallen dramatically, with lithium-ion battery pack prices decreasing by over 90% in the last decade, making them increasingly competitive with traditional energy solutions.
The threat of substitutes for ATCO's core utility business is intensifying due to distributed energy resources like rooftop solar and battery storage. These alternatives offer consumers greater control and cost savings, directly impacting ATCO's demand for grid-supplied electricity.
Furthermore, advancements in energy efficiency and conservation practices, such as smart thermostats, further reduce overall energy consumption. By 2024, the declining cost of solar technology and increased adoption of efficient appliances are making these substitutes more appealing, challenging ATCO's traditional revenue models.
The rise of alternative fuels and electrification, particularly in transportation and heating, also poses a substitution threat to ATCO's natural gas distribution. For instance, government incentives for electric vehicles by 2024 are directly reducing the demand for natural gas in this sector.
Entrants Threaten
ATCO's core business, particularly in regulated utilities and large-scale energy infrastructure, demands enormous initial capital outlays. Building and maintaining power grids, gas distribution networks, and generating facilities requires billions of dollars, effectively deterring many potential competitors from entering these capital-intensive markets.
For instance, projects like upgrading transmission lines or constructing new renewable energy plants often involve investments in the hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. In 2023, ATCO's capital expenditures were approximately $1.5 billion, highlighting the scale of investment needed to operate and grow within its key sectors, a sum that presents a formidable hurdle for new players.
The utility sector, including companies like ATCO, faces significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory hurdles and licensing requirements. New entrants must secure numerous permits and licenses, demonstrating compliance with intricate safety and environmental standards. For instance, in 2024, the cost of obtaining necessary approvals for a new energy infrastructure project can easily run into millions of dollars, a substantial deterrent for smaller or less capitalized firms.
Economies of scale present a substantial barrier for potential new entrants into ATCO's utility sectors. Established players like ATCO leverage massive operational networks and extensive infrastructure, allowing them to spread fixed costs over a larger output, thereby reducing per-unit costs. For instance, ATCO's 2023 reported capital expenditures of $1.7 billion on infrastructure projects underscore the scale of investment required to compete.
Network effects further solidify ATCO's position. In areas like electricity distribution, the value of the network increases with each connected customer, making it difficult for a new, smaller network to attract users. ATCO's significant customer base, serving over 1.9 million customers across various utilities as of 2023, creates a powerful incumbent advantage that new entrants would find challenging to overcome.
Access to Infrastructure and Distribution Channels
New entrants in the energy sector, particularly those aiming to compete with established players like ATCO, grapple with significant barriers related to infrastructure and distribution channels. Gaining access to existing energy transmission and distribution networks, often controlled by incumbent utilities, presents a formidable challenge. Building entirely new, parallel infrastructure is frequently not economically viable and is further complicated by extensive permitting processes and regulatory approvals.
For instance, the capital expenditure required to construct new high-voltage transmission lines or extensive gas distribution networks can run into billions of dollars, a cost that new entrants may struggle to absorb. In 2023, the average cost of constructing a mile of new high-voltage transmission line in North America was estimated to be between $1 million and $5 million, depending on the voltage and terrain.
- High Capital Costs: The immense financial investment needed to build duplicate infrastructure acts as a major deterrent for potential new competitors.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining permits and approvals for new energy infrastructure is a lengthy and complex process, often favoring established entities with existing relationships.
- Control of Existing Networks: Incumbent utilities, like ATCO, maintain control over critical infrastructure, limiting access for new market participants.
Brand Loyalty and Established Relationships
ATCO's Structures & Logistics segment benefits from deeply entrenched, long-standing relationships with its utility customers and significant industrial and government clients. These established connections are built on trust and a proven track record, making it difficult for new entrants to replicate. For instance, securing contracts with major utility providers often requires extensive vetting and demonstration of reliability, a process that naturally favors incumbent players.
The considerable time and capital investment needed to build brand recognition and customer loyalty in essential services like utilities and specialized logistics create a substantial hurdle for potential new competitors. Newcomers must not only offer competitive pricing but also overcome the inertia of existing customer relationships and the perceived risk associated with unproven entities in critical infrastructure sectors.
- Brand Loyalty: ATCO's established reputation in essential services fosters significant customer loyalty, a difficult asset for new entrants to acquire.
- Established Relationships: Long-term partnerships with utility, industrial, and government clients provide ATCO with preferential access and ongoing business.
- High Switching Costs: For customers, switching from a trusted provider like ATCO involves significant investment in new infrastructure, training, and risk assessment, deterring new entrants.
- Capital Investment: The substantial capital required to build a comparable operational footprint and brand presence acts as a considerable barrier to entry.
The threat of new entrants for ATCO is significantly low due to the immense capital required to enter its core utility and infrastructure sectors. Building and operating power grids, gas networks, and large-scale energy facilities demand billions in upfront investment, a financial barrier that few companies can surmount. For example, ATCO's 2023 capital expenditures were approximately $1.5 billion, illustrating the scale of investment necessary to compete.
Stringent regulatory frameworks and licensing requirements further deter new players. Securing the necessary permits and approvals for energy infrastructure projects is a complex and costly undertaking, often involving millions in fees and compliance costs, as seen with projects in 2024. Additionally, ATCO benefits from established economies of scale and strong network effects, with its extensive infrastructure and large customer base of over 1.9 million as of 2023 creating a significant incumbent advantage that is difficult for newcomers to challenge.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example/Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Intensity | Massive upfront investment for infrastructure development. | Projects like new transmission lines can cost millions per mile; ATCO's 2023 capex was $1.5 billion. |
| Regulatory & Licensing | Complex and costly approval processes. | Obtaining permits in 2024 can cost millions, favoring established entities. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations. | ATCO leverages its extensive infrastructure, making it hard for smaller players to match costs. |
| Network Effects | Increased value with more users in a network. | ATCO's 1.9 million customers in 2023 create a strong competitive moat. |
| Established Relationships | Long-term trust and proven track records with clients. | Securing contracts with utilities requires extensive vetting, favoring incumbents. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our ATCO Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from ATCO's annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate industry-specific market research reports and economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.