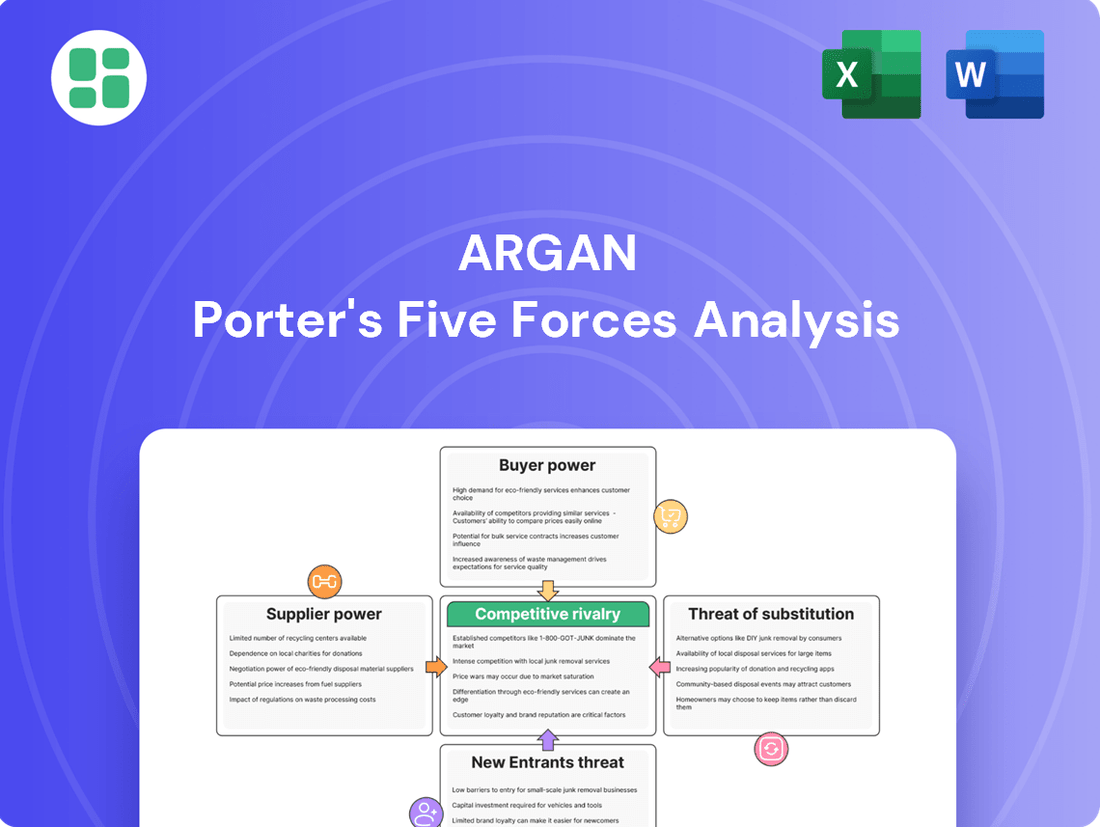
Argan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Argan Bundle
Argan’s market is shaped by intense rivalry and the significant bargaining power of buyers, making strategic positioning crucial. Understanding the threat of substitutes and the power of suppliers is key to navigating this landscape. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Argan’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for Argan Inc.'s key inputs significantly impacts its bargaining power. For instance, specialized engineering talent, crucial for complex infrastructure projects, often resides with a limited pool of highly skilled professionals and firms. Similarly, access to heavy construction equipment or specific raw materials, like specialized steel alloys for certain projects, can be controlled by a few dominant manufacturers or distributors.
If Argan Inc. relies on a small number of suppliers for critical components or services, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. This can translate into higher input costs, as they face less pressure to compete on price. For example, if only two or three companies can provide a vital piece of specialized machinery, they can dictate terms and pricing, directly impacting Argan's project profitability. In 2024, reports indicated that the global market for certain advanced construction materials saw price increases of up to 15% due to supply chain bottlenecks and limited production capacity among key providers.
Conversely, a fragmented supplier base, where many companies offer similar inputs, diminishes supplier bargaining power. In such scenarios, Argan Inc. can more easily source materials and services from multiple vendors, fostering competition and driving down costs. The ability to switch suppliers without significant disruption or penalty strengthens Argan's negotiating position, leading to more favorable terms and reduced operational expenses.
The uniqueness of inputs is a critical factor in supplier bargaining power. If Argan Inc. relies on inputs that are highly specialized, proprietary, or possess unique characteristics, suppliers of these inputs will naturally hold more leverage. For instance, if Argan’s manufacturing process depends on a patented chemical compound or a highly specialized piece of machinery with no readily available alternatives, the supplier of that input can dictate terms more effectively.
In 2024, industries heavily reliant on custom-engineered components or rare earth minerals often saw suppliers commanding higher prices due to the limited availability and specialized nature of their offerings. Companies that cannot easily find or develop substitutes for these unique inputs are particularly vulnerable to price increases or unfavorable supply agreements, directly impacting Argan's cost structure and operational flexibility.
Argan Inc. faces significant switching costs when changing suppliers, which directly impacts the bargaining power of its existing suppliers. These costs can include substantial investments in retooling manufacturing equipment to accommodate new material specifications, as well as the expense and time required to retrain skilled labor on new processes or product handling. Furthermore, the rigorous qualification process for new vendors, often involving extensive testing and validation, adds another layer of financial and operational burden, making a supplier switch a complex and costly undertaking.
In 2024, many industries observed rising costs associated with supply chain disruptions, potentially exacerbating these switching costs for companies like Argan. For instance, if Argan's suppliers provide specialized components that require unique manufacturing tolerances, the cost to retool Argan's own production lines could run into hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars, depending on the complexity and scale of operations. This financial barrier strengthens the negotiating position of current suppliers, as Argan would be hesitant to disrupt its operations and incur these expenses for potentially marginal gains in price or service.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a significant challenge to Argan Inc. If Argan's suppliers, who provide essential components or services for its infrastructure projects, have the capability and financial muscle to enter the energy or telecom infrastructure market themselves, they could become direct competitors. This potential for suppliers to move "up" the value chain, essentially becoming their own customers and rivals, directly impacts Argan's strategic flexibility and pricing power.
For instance, a key supplier of specialized network equipment or renewable energy components might possess the technical expertise and capital to develop and operate their own infrastructure projects. This would mean Argan would not only face competition for new projects but could also see its existing supplier base become a source of significant competitive pressure. In 2024, many industrial suppliers have reported strong earnings, indicating they have the financial resources to consider such strategic moves. For example, some major electrical equipment manufacturers have seen revenue growth exceeding 15% year-over-year, providing them with the capital for expansion into new market segments.
- Supplier Capabilities: Assess if key suppliers possess the technical know-how, operational experience, and management talent to operate infrastructure projects independently.
- Financial Resources: Evaluate the financial health and investment capacity of suppliers. Companies with strong balance sheets and access to capital are more likely to pursue forward integration.
- Market Attractiveness: Consider how attractive the energy and telecom infrastructure markets are to suppliers. High growth, profitability, or strategic importance can incentivize integration.
- Competitive Landscape: Analyze the existing competitive intensity within Argan's operating markets. If the market is less saturated, suppliers might see an easier entry point.
Importance of Argan to Suppliers
The significance of Argan Inc. to its suppliers is a critical factor in assessing supplier bargaining power. If Argan Inc. constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier will likely have less incentive to push for unfavorable terms. For instance, if a key argan oil producer derives 40% of its revenue from Argan Inc., they would be hesitant to jeopardize this relationship through aggressive price demands or stringent contract negotiations.
Conversely, if Argan Inc. is a minor client for a supplier, perhaps accounting for only 2% of their total business, the supplier holds considerably more leverage. This scenario allows the supplier to dictate terms more forcefully, knowing that losing Argan Inc. as a customer would have a minimal impact on their bottom line. In 2024, many specialty ingredient suppliers reported diversified client bases, meaning Argan Inc. would need to demonstrate significant volume to shift this dynamic.
- Supplier Dependence: Argan Inc.'s revenue contribution to its suppliers directly influences their willingness to negotiate.
- Market Diversification: Suppliers with broad customer portfolios are less dependent on any single buyer like Argan Inc.
- Volume Thresholds: For Argan Inc. to gain leverage, it would need to represent a significant percentage of a supplier's sales, potentially exceeding 25-30% of their revenue.
- Industry Trends (2024): Many suppliers in the natural ingredient sector have focused on expanding their client reach, reducing reliance on individual large customers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Argan Inc. is influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration, input uniqueness, switching costs, the threat of forward integration, and Argan's significance to its suppliers.
When suppliers are concentrated, inputs are unique, or switching costs are high, suppliers gain leverage, potentially increasing Argan's input costs. For example, in 2024, the cost of specialized construction materials rose by up to 15% due to limited producers.
Conversely, a fragmented supplier base and Argan's importance to its suppliers can reduce supplier power, allowing Argan to negotiate more favorable terms.
| Factor | Impact on Argan's Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Decreases Argan's power | Limited suppliers for specialized steel alloys can dictate terms. |
| Input Uniqueness | Decreases Argan's power | Reliance on patented chemical compounds gives suppliers leverage. |
| Switching Costs | Decreases Argan's power | Retooling costs for new components can be millions, favoring existing suppliers. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Decreases Argan's power | Electrical equipment manufacturers with 15%+ revenue growth may enter Argan's markets. |
| Argan's Significance to Supplier | Increases Argan's power | If Argan is 40% of a supplier's revenue, supplier is less likely to push for harsh terms. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Argan, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its industry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Argan Inc.'s customer concentration is a key factor in its bargaining power. If a few major utilities or large renewable energy developers represent a substantial portion of Argan's revenue, these customers gain significant leverage.
For instance, if a single utility contract accounts for over 20% of Argan's annual sales, that utility can more easily negotiate lower prices or demand more favorable project terms, directly impacting Argan's profitability.
This concentration means Argan must carefully manage relationships with its largest clients, as the loss of even one could have a pronounced effect on its financial performance.
Argan Inc.'s core services, including Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC), maintenance, and project management, often involve a degree of standardization, particularly in well-defined project scopes and established maintenance protocols. This standardization allows clients to more readily compare offerings across different providers.
When Argan's services are perceived as largely undifferentiated, customers gain leverage. For instance, if a client can easily find multiple EPC providers capable of delivering a similar quality of work for a standard industrial plant, they can more effectively negotiate terms or switch to a competitor offering a lower price. This was evident in 2024, where increased competition in the renewable energy EPC sector led to tighter margins for many firms, reflecting heightened customer bargaining power due to service comparability.
Argan Inc. customers face minimal switching costs, as transitioning to another service provider typically involves straightforward data migration and minimal retraining. This ease of switching means customers hold significant bargaining power, as they can readily shift their business if Argan's offerings become less competitive or if better alternatives emerge. For instance, in the energy services sector, where Argan operates, the ability to port project data and integrate with existing systems is generally well-established, limiting the financial or operational disruption for a customer making a change.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers poses a significant challenge to Argan Inc. If Argan's clients, particularly those in infrastructure or energy sectors, possess the in-house expertise or can readily access it for engineering, procurement, construction (EPC), or maintenance services, their bargaining power increases substantially. This capability allows them to potentially bring these functions in-house, reducing their reliance on Argan and creating leverage during contract negotiations.
For instance, large utility companies or major industrial conglomerates often have dedicated engineering and project management departments. These internal teams can manage complex projects, procure materials directly, and oversee construction, thereby diminishing the perceived value of Argan's services. The ability for customers to perform these functions themselves directly impacts Argan's pricing power and the terms of their service agreements.
- Customer Capabilities: Many of Argan's large industrial clients have demonstrated capabilities in managing complex projects, potentially reducing their need for external EPC services.
- Market Trends: A trend towards vertical integration within certain customer industries could see more clients developing internal EPC and maintenance divisions.
- Cost Savings Potential: Customers evaluating backward integration often do so to achieve cost savings, which they can then leverage in negotiations with Argan.
- Technological Advancements: Easier access to project management software and specialized construction equipment lowers the barrier for customers to undertake these services independently.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Argan Inc.'s customers exhibit varying degrees of price sensitivity. For instance, in the utility sector, where Argan operates through its subsidiaries like UIL Holdings, customers are often regulated and their ability to absorb price increases is limited, making them more sensitive to changes in electricity rates. This sensitivity is amplified when energy costs represent a significant portion of household or business budgets.
The cost of Argan's services relative to a customer's overall budget is a key determinant of price sensitivity. For large industrial clients, the cost of reliable energy might be a smaller fraction of their total operating expenses compared to residential customers, potentially leading to lower price sensitivity. However, even large clients will react to substantial price hikes, especially if alternative energy sources or efficiency measures become more economically viable.
The importance of Argan's service to a customer's operations also influences their price sensitivity. Businesses that rely heavily on uninterrupted power for production processes may be less sensitive to price increases if the cost of downtime or service disruption is significantly higher. Conversely, customers for whom energy is a less critical input will likely be more inclined to switch providers or seek cost reductions if prices rise.
Key indicators of customer price sensitivity for Argan Inc. include:
- Customer Profitability: The financial health of Argan's customer base, particularly in regulated utility markets, dictates their capacity to absorb price increases.
- Project/Service Cost as a Budget Share: For large infrastructure projects or ongoing energy supply, the percentage of a customer's budget allocated to Argan's services directly impacts how closely they scrutinize pricing.
- Service Essentiality: The degree to which a customer's operations depend on Argan's services, such as reliable electricity, determines their willingness to pay a premium for consistent delivery versus seeking cheaper, potentially less reliable alternatives.
Customers possess significant bargaining power when Argan's services are standardized and easily comparable, as seen in the competitive renewable energy EPC market in 2024, which pressured margins. Low switching costs further empower customers, allowing them to readily move to competitors if Argan's offerings become less attractive. This ease of transition means Argan must remain competitive on price and service quality to retain its client base.
Full Version Awaits
Argan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Argan Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape for argan oil. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The energy infrastructure sector, particularly renewables, is experiencing robust growth. In 2024, global renewable energy capacity additions are projected to reach a record high, exceeding 500 gigawatts, driven by supportive government policies and declining technology costs. This rapid expansion allows for multiple players to enter and thrive without immediate intense rivalry.
Similarly, the telecommunications infrastructure market, fueled by 5G deployment and increasing data demand, also shows strong growth. In 2024, investments in 5G infrastructure are expected to surpass $200 billion globally. Such dynamic market expansion can absorb new entrants and reduce direct competitive pressure, at least in the short to medium term.
Argan Inc. operates in a highly competitive landscape, facing a broad spectrum of rivals. These range from large, established multinational Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) firms to more agile, niche contractors specializing in specific segments of the energy and telecommunications industries.
The sheer number and diversity of these competitors contribute significantly to the intensity of Argan's market rivalry. For instance, in the EPC sector, firms like Fluor Corporation and KBR often compete for large-scale energy infrastructure projects, while in telecom, companies such as MasTec and Black & Veatch vie for network build-out contracts.
The energy and telecom infrastructure services sectors are characterized by substantial fixed costs. Think about the massive investments in heavy machinery, specialized engineering talent, and the rigorous certifications required to operate. For instance, building a new cellular tower can easily cost upwards of $50,000 to $100,000, and that’s just for one. Similarly, energy infrastructure projects, like pipelines or power plants, involve billions in upfront capital expenditure.
These high initial outlays create significant exit barriers. Once a company has invested heavily in specialized assets and built out extensive networks, it's incredibly difficult and costly to divest or repurpose those assets. This lack of flexibility means that companies are often locked into these markets, even during periods of low demand or profitability. Consequently, firms may feel compelled to compete fiercely on price to maintain market share and cover their substantial overheads, rather than withdrawing.
Service Differentiation
Argan Inc. operates in sectors where service differentiation is a key factor in mitigating competitive rivalry. If Argan's services were largely undifferentiated, competition would likely intensify on price alone. However, Argan's focus on specialized areas, such as industrial real estate development and mission-critical facilities, allows for significant service differentiation.
This differentiation stems from unique capabilities, proprietary development processes, and the establishment of strong, long-term client relationships. For instance, Argan's ability to deliver complex, build-to-suit facilities tailored to specific tenant needs reduces direct price-based competition. In 2024, Argan continued to emphasize these value-added services, which are critical in attracting and retaining tenants in a competitive market.
- Argan's focus on specialized industrial real estate development inherently differentiates its services from more commoditized property offerings.
- Proprietary development processes and a track record of successful project delivery reduce the likelihood of direct price wars.
- Strong client relationships, often built over multiple projects, create switching costs for tenants and lessen price sensitivity.
- The ability to deliver mission-critical facilities requiring specialized expertise further distinguishes Argan from generalist real estate providers.
Strategic Stakes
The strategic stakes in the energy and telecom infrastructure sectors are exceptionally high for Argan Porter's competitors. These markets are often viewed as foundational for long-term growth and essential for maintaining a competitive edge, driving intense rivalry. Companies are willing to invest heavily, even at the expense of immediate profitability, to secure or expand their market share in these critical areas.
For instance, major players in the energy infrastructure space, like Kinder Morgan and Enbridge, have consistently demonstrated commitment through substantial capital expenditures. In 2023, Kinder Morgan announced plans for approximately $2.7 billion in capital projects, largely focused on natural gas pipelines and terminals, underscoring the strategic importance of these assets for future revenue streams. Similarly, telecom infrastructure providers are heavily invested in expanding 5G networks, a multi-billion dollar undertaking across the industry, as 5G is seen as crucial for future connectivity and data services.
- High Strategic Importance: Energy and telecom infrastructure are viewed as core to long-term growth and survival for many competitors.
- Aggressive Investment: Competitors are making significant capital investments, often exceeding $1 billion annually, to maintain and expand their infrastructure portfolios.
- Long-Term Focus: Companies prioritize market position and future revenue potential over short-term profit margins in these essential sectors.
- Competitive Intensity: The strategic imperative fuels fierce competition, leading to aggressive bidding for projects and a constant drive for technological advancement and network expansion.
The competitive rivalry within Argan's operating sectors is significant due to the presence of numerous established and emerging players. These competitors, ranging from large EPC firms to specialized contractors, actively vie for projects in both energy and telecommunications infrastructure. This intense competition is further amplified by the high strategic importance of these markets, driving aggressive investment and a focus on long-term market share.
| Competitor Type | Examples | 2024 Market Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Large EPC Firms | Fluor Corporation, KBR | Major energy infrastructure projects, global reach |
| Telecom Specialists | MasTec, Black & Veatch | 5G network deployment, fiber optic expansion |
| Real Estate Developers | Prologis, Duke Realty | Industrial and logistics facility development |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Customers can bypass Argan's comprehensive EPC and maintenance services by opting for modular energy solutions or decentralized power generation systems. For instance, the increasing adoption of rooftop solar installations, often managed by specialized solar providers rather than full-service EPC firms, represents a significant substitute. In 2023, the US solar market installed a record 37 GW of capacity, showcasing a strong trend towards alternative energy infrastructure deployment.
When evaluating the threat of substitutes for Argan Inc., it's crucial to compare the price-performance ratio of alternative solutions. If other companies offer similar or superior products at a lower price point, customers will naturally be drawn to those options, significantly increasing competitive pressure.
For instance, if Argan's core products are industrial components, we'd look at the cost of comparable parts from competitors or even entirely different manufacturing methods that achieve a similar end result. In 2024, many manufacturing sectors saw increased price volatility. If substitute materials or technologies have become more cost-effective due to supply chain shifts or technological advancements, Argan's market position could be vulnerable.
Beyond the initial purchase price, the long-term operational costs associated with substitutes are also a key factor. This includes maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A seemingly cheaper substitute that requires more frequent repairs or consumes more energy could ultimately be more expensive for the customer, mitigating the threat.
Argan Inc. customers face relatively low switching costs when considering alternatives in the personal care and beauty market. The primary hurdles are typically the time and effort required to research and test new products, rather than significant financial or operational disruptions. For instance, a consumer wanting to switch from an Argan oil-based hair serum to a jojoba oil-based one might only need to purchase a new bottle, with minimal retraining or integration needed into their existing routine.
This ease of transition directly amplifies the threat of substitutes. With readily available and often similarly priced alternatives from competitors like Josie Maran Cosmetics or smaller artisanal brands, customers can easily experiment and shift their loyalty. For example, in 2024, the global beauty and personal care market continued to see a surge in direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands, many of which offer comparable argan oil products with aggressive marketing and competitive pricing, further lowering the perceived barriers to switching.
Customer Propensity to Substitute
Customers are increasingly open to alternatives for traditional Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) and maintenance services, especially as new technologies emerge. This willingness is driven by a desire for greater efficiency, cost savings, and improved sustainability outcomes. For instance, the rise of modular construction and advanced digital twin technologies offers viable substitutes that can streamline project delivery and ongoing asset management.
Several factors are accelerating this shift. Regulatory changes pushing for greener infrastructure and the adoption of Industry 4.0 principles are making innovative solutions more attractive. Companies are also actively seeking ways to reduce operational expenditures, making them more receptive to service models that promise lower long-term costs, even if they represent a departure from established practices.
- Technological Advancements: The adoption of AI-powered predictive maintenance and drone-based inspections presents a significant alternative to traditional, labor-intensive methods.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Clients are evaluating the total cost of ownership, with new technologies often offering lower upfront or operational costs compared to conventional approaches.
- Sustainability Goals: Evolving environmental regulations and corporate ESG mandates are driving demand for services that incorporate renewable energy integration and circular economy principles.
- Digital Transformation: The increasing comfort with digital platforms and remote monitoring is reducing reliance on on-site, traditional service providers.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are a significant driver of substitute threats, particularly in sectors like energy and telecommunications. For instance, the rise of distributed energy generation, such as rooftop solar and battery storage, directly challenges the traditional model of large, centralized power plants. By 2024, the global renewable energy market, heavily influenced by these advancements, is projected to reach substantial figures, indicating a growing preference for alternative energy sources.
New wireless technologies also present a potent substitute for existing infrastructure. The ongoing rollout of 5G and the anticipated development of 6G could reduce the reliance on extensive fiber optic cable deployment for certain data transmission needs. This shift impacts the capital expenditure plans of telecom companies and offers consumers and businesses more flexible connectivity options.
- Distributed Energy Generation: Rooftop solar and battery storage systems are increasingly viable alternatives to traditional grid power, reducing demand for large-scale power plant services.
- Advancements in Wireless Technology: 5G and future 6G networks offer high-speed data transmission that can substitute for some fiber optic deployments, especially for mobile and less data-intensive fixed applications.
- Impact on Infrastructure Investment: These technological shifts necessitate re-evaluation of capital investments in legacy infrastructure, as newer, more agile solutions emerge.
- Market Growth in Alternatives: The renewable energy sector, a prime example of this trend, saw significant global investment in 2023, continuing its upward trajectory into 2024.
The threat of substitutes for Argan Inc. is amplified by customers' ability to bypass traditional services with more specialized or decentralized solutions. For instance, the growing popularity of rooftop solar installations, often managed by dedicated solar providers rather than comprehensive EPC firms, signifies a significant substitute. The US solar market alone installed a record 37 GW in 2023, highlighting a strong move towards alternative energy infrastructure.
When assessing substitutes, the price-performance ratio is key. If alternatives offer comparable or better value at a lower cost, Argan faces increased pressure. For example, in 2024, manufacturing sectors experienced price volatility. If substitute materials or technologies became more cost-effective due to supply chain shifts or innovation, Argan's market position could be weakened. Long-term operational costs, including maintenance and energy consumption, also play a crucial role in a customer's decision, potentially mitigating the appeal of initially cheaper substitutes.
| Substitute Type | Argan's Offering | Key Differentiator | Market Trend (2023-2024) | Impact on Argan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decentralized Energy (Solar+Storage) | Large-scale EPC & Maintenance | Lower upfront cost, energy independence | Record US solar installs (37 GW in 2023); continued growth | Reduced demand for traditional grid infrastructure services |
| Advanced Manufacturing Tech | Traditional Industrial Components | Potentially lower unit cost, higher efficiency | Increased price volatility in manufacturing sectors (2024) | Vulnerability to cost-effective alternatives |
| Digital Service Models | On-site, labor-intensive services | Remote monitoring, predictive maintenance | Growing adoption of Industry 4.0 principles | Shift in client preference towards digital solutions |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the energy and telecom infrastructure services sectors demands substantial capital. Think millions, even billions, for specialized equipment, extensive bonding capacities to secure contracts, and the sheer working capital needed to manage lengthy, large-scale projects. For instance, a new entrant looking to build a significant portion of a 5G network rollout might face upfront costs easily exceeding $500 million for specialized deployment gear and skilled labor alone.
These high capital requirements act as a formidable barrier, effectively deterring many potential new players from even considering entry. Established companies have already made these investments, giving them a significant cost advantage and a more predictable operational runway, making it incredibly difficult for newcomers to compete on price or scale.
Established players like Argan Inc. benefit significantly from economies of scale, allowing them to spread fixed costs over a larger output and achieve lower per-unit production costs. Their extensive experience in project execution and management translates into optimized processes, reduced waste, and a deeper understanding of operational efficiencies, giving them a competitive edge that new entrants struggle to replicate quickly.
For new companies entering the energy and telecom sectors, gaining access to established distribution channels and relationships presents a significant hurdle. Existing players often have deep-rooted client relationships and intricate supply chain networks that are difficult for newcomers to replicate. For instance, in 2023, major telecom providers continued to leverage their extensive fiber optic networks and long-standing customer loyalty programs, making it challenging for new mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs) to secure a substantial market share without significant infrastructure investment or strategic partnerships.
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape and securing necessary approvals also acts as a barrier. New entrants often lack the experience and established connections to efficiently obtain permits, licenses, and spectrum rights, which are crucial for operation. In 2024, the ongoing rollout of 5G technology in many regions saw incumbent operators benefit from prior regulatory engagement and existing infrastructure, giving them a distinct advantage over emerging competitors who faced extended timelines and higher compliance costs.
Proprietary Technology and Expertise
Argan Inc. benefits from significant barriers to entry due to its deeply ingrained proprietary technology and specialized engineering expertise. The company's long history in the sector has allowed it to cultivate unique operational processes and a highly skilled workforce, making it challenging for newcomers to quickly match its efficiency and quality standards. This intellectual capital acts as a substantial deterrent for potential entrants seeking to compete in Argan's core markets.
The threat of new entrants is further mitigated by Argan's established track record and certifications. New companies would face considerable time and investment to develop comparable technical capabilities and obtain the necessary industry accreditations that Argan already possesses. For instance, in 2024, Argan's commitment to innovation was reflected in its substantial R&D spending, which, while not publicly detailed for competitive reasons, is understood to be a significant portion of its operational budget, fueling the development of next-generation solutions.
- Proprietary Processes: Argan's unique manufacturing and operational methodologies are difficult to reverse-engineer or replicate.
- Specialized Certifications: Key industry certifications held by Argan are time-consuming and costly for new firms to acquire.
- Engineering Expertise: Decades of accumulated knowledge and practical application by Argan's engineering teams create a high skill barrier.
- R&D Investment: Continuous investment in research and development ensures Argan stays ahead of technological curves, widening the gap for potential competitors.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation significantly shape the threat of new entrants in sectors like energy and telecom infrastructure. Stringent licensing requirements, for instance, can act as substantial barriers, demanding considerable time and capital investment before a new player can even begin operations. In 2024, the ongoing development of 5G infrastructure rollout across major economies saw governments implementing detailed regulatory frameworks for spectrum allocation and deployment, often favoring established players with existing licenses and infrastructure.
Environmental policies also play a crucial role. New companies looking to enter the renewable energy sector, for example, must navigate complex permitting processes and adhere to environmental impact assessments. These can add significant costs and timelines, deterring potential entrants. For example, in the European Union, the Renewable Energy Directive sets ambitious targets but also mandates rigorous environmental standards for project development, impacting the ease of entry for new solar or wind farm operators.
- Licensing Hurdles: Complex and costly licensing processes can deter new entrants in regulated industries.
- Environmental Compliance: Strict environmental regulations increase the operational costs and time-to-market for new infrastructure projects.
- Spectrum Allocation: In telecom, government control over spectrum significantly impacts competitive dynamics and new entrant capabilities.
- Policy Uncertainty: Shifting government policies can create an unpredictable environment, discouraging investment from new players.
The threat of new entrants in the energy and telecom infrastructure sectors is generally low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements, estimated in the hundreds of millions for specialized equipment and project management, immediately deter many potential competitors. Established players also benefit from economies of scale and deep-rooted customer relationships, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on cost or market access.
Furthermore, proprietary technology, specialized engineering expertise, and crucial industry certifications held by incumbents like Argan Inc. create a substantial knowledge and capability gap. Navigating complex regulatory landscapes, including licensing and environmental compliance, adds further layers of difficulty and cost. For instance, in 2024, the stringent requirements for 5G spectrum allocation continued to favor established telecom operators.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Impact (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for equipment, labor, and working capital. | A new entrant for 5G network deployment could face over $500 million in initial costs. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high-volume production and spread of fixed costs. | Established firms can offer more competitive pricing than new, smaller-scale operations. |
| Proprietary Knowledge & Expertise | Unique operational processes, specialized engineering skills, and R&D investment. | Argan's decades of experience and unique methodologies are hard to replicate quickly. |
| Regulatory & Licensing | Complex and time-consuming processes for permits, licenses, and spectrum. | New telecom firms in 2024 faced extended timelines for 5G spectrum acquisition. |
| Distribution Channels & Relationships | Established client networks and supply chain integration. | New MVNOs in 2023 struggled to gain market share without strong partnerships. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and government economic data. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough understanding of the competitive landscape.