Applied Superconductor Ltd. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Applied Superconductor Ltd. Bundle
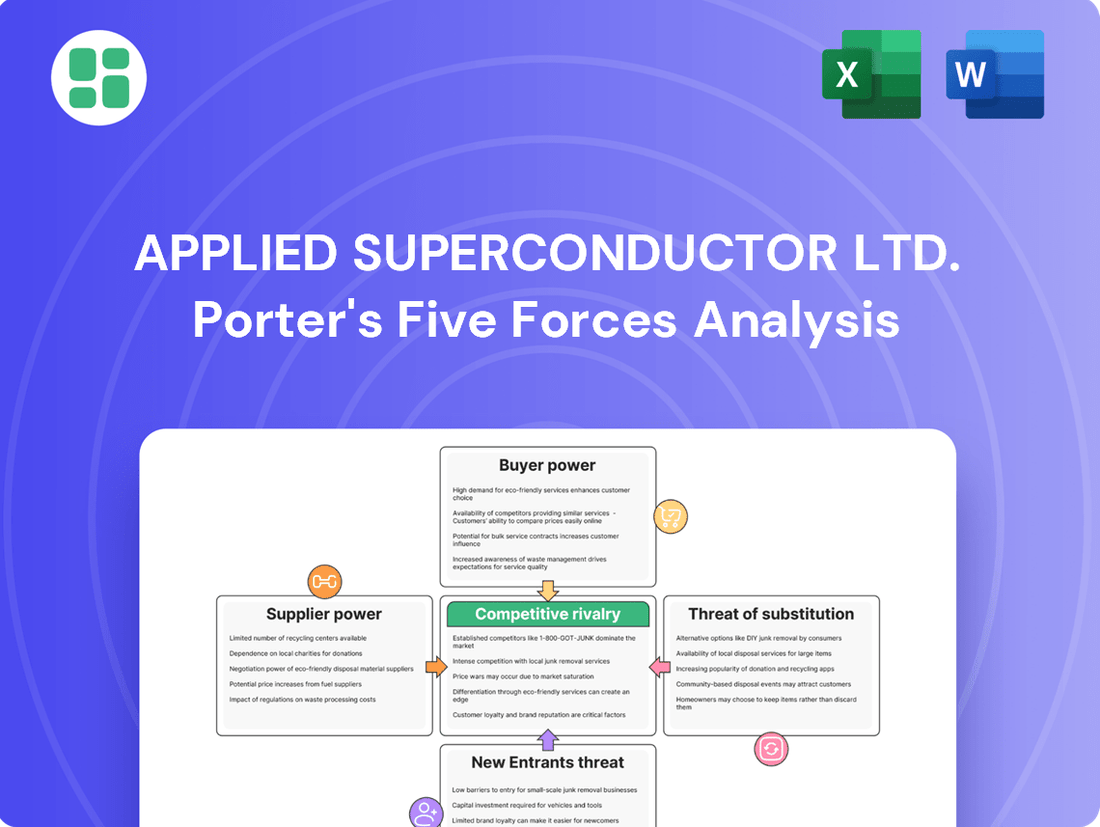
Applied Superconductor Ltd. faces a dynamic competitive landscape, with moderate bargaining power from buyers and suppliers influencing its market position. The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by high capital requirements, but the availability of substitutes presents a significant challenge.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Applied Superconductor Ltd.’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The production of high-temperature superconducting (HTS) wire, a core component for Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC), is heavily dependent on specialized and often rare earth materials. This inherent requirement for unique inputs means the supplier pool is naturally restricted, concentrating significant influence in the hands of a few providers.
For AMSC, this limited supplier base translates directly into increased bargaining power for these specialized raw material providers. In 2024, the global supply chain for critical rare earth elements, essential for HTS wire, remained tight, with geopolitical factors and concentrated mining operations in specific regions influencing availability and pricing.
AMSC's reliance on specific, high-purity inputs for its advanced HTS wires means that any disruption or price escalation from a key supplier could substantially impact its production costs and project timelines. For instance, a 10% increase in the cost of a critical rare earth element could add millions to AMSC's cost of goods sold, affecting its profitability and competitiveness.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC) is significantly influenced by high switching costs for alternative materials. Developing or sourcing new high-temperature superconductor (HTS) materials requires extensive research, rigorous testing, and thorough qualification, making it a costly and time-consuming endeavor for AMSC. For instance, the specialized nature of HTS wire manufacturing means that AMSC is deeply integrated with its current material suppliers, limiting its ability to easily transition to new ones.
Suppliers of highly differentiated or proprietary materials crucial for high-temperature superconductor (HTS) wire performance, like specific rare earth compounds or advanced ceramic precursors, hold considerable bargaining power. The unique properties demanded by high-performance HTS wire make these suppliers difficult to replace, granting them leverage over companies such as AMSC in pricing and contract negotiations.
Potential for forward integration by suppliers
The potential for suppliers to integrate forward into HTS wire manufacturing, while not a widespread current threat for Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC), represents a theoretical source of bargaining power. If key raw material suppliers developed the necessary technical acumen and financial resources, they could directly enter AMSC's market, creating a competitive dynamic. This possibility, however remote, grants them leverage in pricing and contract negotiations.
The significant technical hurdles and capital investment required for High-Temperature Superconductor (HTS) wire production act as a substantial deterrent to suppliers considering forward integration. This complexity inherently limits the practical realization of this threat, thereby moderating the suppliers' bargaining power in this specific regard.
- Supplier Forward Integration Risk: While theoretically possible, suppliers integrating forward into HTS wire manufacturing is currently a low probability due to high technical barriers.
- Leverage from Potential: The mere possibility, however slim, of forward integration grants suppliers some additional negotiating leverage with AMSC.
- Manufacturing Complexity as a Barrier: The intricate nature of HTS wire production is a significant impediment, discouraging suppliers from undertaking such a venture.
Impact of global supply chain dynamics
Global supply chain dynamics, including geopolitical tensions and rising demand for critical minerals, are significantly influencing the bargaining power of suppliers for essential high-temperature superconductor (HTS) components. These trends can empower suppliers, particularly those controlling unique or scarce materials, by giving them more leverage in pricing and availability negotiations with companies like Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC).
Disruptions or restrictions in the global market for these specialized materials can directly translate into price volatility and potential supply shortages. This scenario inevitably increases the bargaining power of suppliers over AMSC, as the company becomes more dependent on securing these vital inputs. For instance, in 2024, the International Energy Agency reported that the demand for critical minerals essential for advanced technologies, including superconductors, saw a substantial increase, putting pressure on existing supply chains.
AMSC's financial reports from 2024 and early 2025 have consistently highlighted the company's efforts to navigate these complex supply chain challenges. This ongoing focus underscores the real-world impact of supplier power on AMSC's operational costs and strategic planning.
- Increased Demand for Critical Minerals: Global demand for minerals like rare earths, crucial for advanced HTS components, has surged, impacting supplier leverage.
- Geopolitical Instability: Trade disputes and regional conflicts can disrupt supply routes and concentrate production, enhancing supplier power.
- Supply Shortages and Price Volatility: Limited production capacity and logistical hurdles in 2024 led to noticeable price fluctuations for key superconductor precursor materials.
- AMSC's Supply Chain Management: The company's financial disclosures reflect a continuous effort to mitigate risks associated with supplier dependency.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC) is substantial due to the specialized nature of high-temperature superconductor (HTS) wire components. A limited pool of providers for rare earth materials and advanced precursors, coupled with high switching costs for AMSC, grants these suppliers significant leverage in pricing and contract terms. Geopolitical factors and increasing global demand for critical minerals in 2024 further amplified this supplier power, leading to price volatility and potential supply chain disruptions for AMSC.
| Factor | Impact on AMSC | 2024/2025 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Supplier Base | Concentrates power with a few providers | Critical rare earth element supply chain remained tight |
| High Switching Costs | Difficult and expensive to change material suppliers | Extensive R&D and qualification needed for new HTS materials |
| Proprietary Materials | Suppliers of unique HTS precursors have leverage | Specific rare earth compounds essential for performance |
| Global Demand for Critical Minerals | Increases supplier leverage and price volatility | IEA reported substantial increase in demand for advanced tech minerals |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Applied Superconductor Ltd. reveals the intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the threat of substitutes, while also highlighting barriers to entry and supplier leverage within the advanced materials market.
Applied Superconductor Ltd.'s Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces, perfect for quick decision-making by alleviating the pain of complex market assessments.
Customers Bargaining Power
AMSC's diverse customer base, spanning critical sectors like grid infrastructure, industrial, and defense, significantly dilutes customer bargaining power. Key clients include major utilities and the U.S. Navy, ensuring no single entity dominates AMSC's revenue stream. This broad market reach means that the loss of one customer, or even a segment, would not disproportionately impact the company's financial stability.
The bargaining power of customers for AMSC's High-Temperature Superconducting (HTS) wire solutions is significantly influenced by high switching costs. Once a utility or defense contractor integrates these advanced systems, the expense and intricacy of transitioning to another provider or technology become substantial.
This lock-in effect stems from the custom engineering, installation, and long-term operational integration inherent in HTS applications. For instance, a major grid modernization project utilizing AMSC's HTS cables would involve extensive site-specific modifications, demanding a complete overhaul if a different supplier were chosen. This deep integration minimizes customer willingness to switch, thereby reducing their bargaining power.
Applied Superconductor Ltd.'s (AMSC) high-temperature superconductor (HTS) solutions are absolutely vital for the smooth operation, enhanced performance, and overall resilience of power grids and specialized industrial and defense applications. These are not just components; they are mission-critical elements that directly impact a customer's core business functions.
Because AMSC's products are so integral to their customers' operations, particularly in areas like grid stability and national defense, customers find it difficult to push for significant price reductions. The high value and essential nature of these HTS systems mean that reliability and performance take precedence over seeking minor cost savings.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for grid modernization and increased energy efficiency has highlighted the importance of AMSC's technology. Customers in these sectors understand that the cost of failure or underperformance in power transmission far outweighs any potential savings from negotiating lower prices on AMSC's advanced superconductor materials.
Customer price sensitivity varies by application
Customer price sensitivity for American Superconductor (AMSC) products isn't uniform; it shifts based on the intended use. For critical infrastructure like defense systems or grid upgrades, where failure is not an option, customers prioritize reliability and performance, making them less inclined to focus solely on price.
In contrast, for more standard industrial uses or in markets where cost is a primary driver, customers might be more sensitive to price. However, even in these scenarios, AMSC's High-Temperature Superconductor (HTS) technology offers distinct advantages that can justify a higher cost.
- Defense and Grid Modernization: High demand for mission-critical applications where reliability outweighs cost.
- Industrial Applications: Price sensitivity is higher, but HTS benefits still provide a competitive edge.
- Market Differentiation: AMSC's technology offers unique selling points that can mitigate direct price comparisons.
Government and defense contracts influence
A significant portion of AMSC's business, especially following the acquisition of NWL, Inc., is tied to U.S. government and defense contracts. These long-term engagements, with their specific requirements, tend to lessen the direct bargaining power of customers on individual project terms. For instance, AMSC's involvement in U.S. Navy shipbuilding programs provides a stable, albeit contractually defined, revenue stream.
However, the influence of these government contracts on AMSC is multifaceted. While specific project terms might be less negotiable, government budget cycles and evolving procurement policies can significantly impact overall demand and pricing structures for AMSC's superconductor technologies. The company's backlog, a key indicator of future revenue, is heavily influenced by these government funding decisions.
- Government Contracts as a Stabilizer: AMSC's substantial work with the U.S. Navy, particularly in supplying high-temperature superconductor (HTS) wire for ship systems, creates a degree of customer stickiness. This reduces the ability of any single naval program to exert downward price pressure on existing contracts.
- Procurement Policy Influence: Changes in defense spending priorities or procurement regulations can indirectly affect AMSC's bargaining position. For example, a shift towards more competitive bidding processes for new programs could introduce greater price sensitivity.
- Long-Term Relationship Dynamics: The nature of defense contracting often fosters long-term relationships, where reliability and performance are as critical as price. This can mitigate the typical customer bargaining power seen in more commoditized markets.
- Budgetary Constraints: While contracts are in place, the ultimate funding for these projects comes from government appropriations. Delays or reductions in these budgets can indirectly influence the overall leverage customers have by impacting the pace and scale of AMSC's work.
The bargaining power of AMSC's customers is generally low due to high switching costs and the mission-critical nature of their high-temperature superconductor (HTS) solutions. For instance, the integration of AMSC's HTS wire into U.S. Navy vessels or critical grid infrastructure involves significant engineering and customization, making it prohibitively expensive and complex to switch to an alternative supplier. This technological lock-in significantly limits customers' ability to negotiate price reductions, as reliability and performance are paramount. In 2024, the ongoing demand for grid modernization and enhanced defense capabilities further solidifies this position, with customers prioritizing the proven performance of AMSC's technology over minor cost savings.
| Customer Segment | Price Sensitivity | Bargaining Power Factor |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. Navy/Defense | Low | Mission-critical, high switching costs, long-term contracts |
| Grid Infrastructure (Utilities) | Moderate to Low | High switching costs, critical infrastructure needs, reliability focus |
| Industrial Applications | Moderate | Price can be a factor, but HTS benefits offer differentiation |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Applied Superconductor Ltd. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis for Applied Superconductor Ltd., offering a detailed examination of competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for immediate use without any surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The high-temperature superconductor (HTS) market is a highly specialized arena, meaning competition for Applied Superconductor Ltd. primarily comes from other firms focused on HTS wire development and established utility solution providers. This niche focus creates a concentrated competitive landscape.
Key players vying for market share include Superconductor Technologies, Superpower (a Furukawa subsidiary), Fujikura, Sumitomo, SuNAM, BASF Corporation, Innova, and SuperOx. These companies possess significant technical expertise and are actively engaged in advancing HTS technology.
Despite the growing demand for HTS solutions, the specialized nature of the market results in intense rivalry among a relatively small group of highly capable competitors. This dynamic underscores the importance of Applied Superconductor Ltd.'s technological innovation and market positioning.
Competitive rivalry in the high-temperature superconductor (HTS) sector, including companies like Applied Superconductor Ltd., is intense due to the substantial investments in research and development. This focus on innovation is crucial for protecting intellectual property, as advancements in HTS technology are the primary differentiator.
Companies are locked in a battle for market share by competing on key performance indicators such as critical current density, operational stability, and the overall cost-effectiveness of their HTS wires. For instance, in 2024, the global superconductor market was valued at approximately USD 1.8 billion, with HTS technologies representing a significant and growing segment, underscoring the importance of continuous R&D to maintain a competitive edge and broaden product portfolios.
The high-temperature superconductor (HTS) wire market is poised for substantial expansion, with projections indicating a strong compound annual growth rate from 2024 through 2030. This upward trend is fueled by increasing demand across critical sectors like power and energy, medical applications, and scientific research.
This expanding market landscape offers considerable growth avenues for all participants. The rising demand could potentially temper intense price wars, shifting the competitive focus towards capturing market share and innovating for broader adoption.
Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC) demonstrated this market vitality in its financial performance. For fiscal year 2024 and the first quarter of fiscal year 2025, the company reported significant year-over-year revenue increases, underscoring the tangible growth occurring within the HTS wire industry.
Product differentiation and technological advantage
Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC) distinguishes itself by offering integrated solutions focused on power resiliency and grid infrastructure, such as its Gridtec™ and Marinetec™ offerings. This means competition extends beyond just the high-temperature superconductor (HTS) wire itself to encompass the entire system and the crucial engineering services provided.
AMSC's competitive edge is further sharpened by its commitment to technological advancements that boost both efficiency and performance in its superconducting systems. For instance, in 2023, the company reported progress on its Distributed FACTS (D-FACTS) devices, which are designed to enhance grid stability and capacity, showcasing a tangible area of technological differentiation.
- Integrated Solutions: AMSC competes on its complete system offerings, not just HTS wire.
- Technological Edge: Advancements in efficiency and performance are key differentiators.
- Engineering Services: The value of engineering expertise and system integration is a significant competitive factor.
Global and regional competitive landscape
The competitive rivalry for high-temperature superconductor (HTS) wire is intensely global, with significant manufacturing and innovation hubs located across the United States, Japan, South Korea, Europe, and China. This broad geographical distribution means Applied Superconductor Ltd. faces competition from established players and emerging companies alike in each of these key regions.
Regional market dynamics play a crucial role in shaping competitive intensity. Government support for HTS technology, through subsidies, research grants, and policy initiatives, can significantly bolster domestic players and influence the global competitive balance. For example, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to experience the fastest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for superconductors from 2024 to 2030, indicating a dynamic and potentially intensifying competitive environment in that area.
- Global HTS Wire Market: Key players are spread across the US, Japan, South Korea, Europe, and China.
- Regional Influence: Government support and local market conditions significantly impact competition.
- Asia-Pacific Growth: Expected to show the fastest CAGR for superconductors between 2024 and 2030.
The competitive rivalry in the high-temperature superconductor (HTS) market is characterized by a concentrated group of technically advanced firms, including Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC). Competition centers on critical performance metrics like current density and stability, alongside the overall cost-effectiveness of HTS wires. The global superconductor market, valued around USD 1.8 billion in 2024, sees HTS technologies as a key growth driver, intensifying the need for continuous R&D to maintain market position.
AMSC differentiates itself by offering integrated solutions for grid infrastructure and power resiliency, moving beyond just HTS wire sales to include crucial engineering services. This broader approach means competition encompasses not only HTS wire suppliers but also providers of complete system solutions. The company’s focus on technological advancements, such as its D-FACTS devices, further sharpens its competitive edge by improving system efficiency and performance.
The HTS wire market is experiencing global competition with major players in the US, Japan, South Korea, Europe, and China. Government support, including research grants and subsidies, significantly influences regional competitive dynamics. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, is projected to have the fastest CAGR for superconductors from 2024 to 2030, suggesting a rapidly evolving and potentially more competitive landscape there.
| Key Competitor | Primary Focus | 2024 Market Insight |
| Superconductor Technologies | HTS Wire Development | Active R&D in HTS technology |
| Fujikura | Integrated Superconducting Solutions | Global presence in advanced materials |
| Sumitomo Electric Industries | Superconducting Magnets & Cables | Significant investment in power infrastructure |
| SuNAM | High-Performance HTS Wires | Focus on critical current density improvements |
| BASF Corporation | Advanced Materials & Chemicals | Leveraging material science for superconductor applications |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitutes for Applied Superconductor Ltd.'s high-temperature superconductor (HTS) wire in power transmission and distribution are conventional copper and aluminum conductors. These traditional materials are considerably cheaper, with copper prices fluctuating around $9,000-$10,000 per metric ton in early 2024, and aluminum around $2,200-$2,500 per metric ton. While HTS wire boasts superior efficiency and power density, its higher cost, often many times that of copper or aluminum per unit length, presents a substantial barrier to widespread adoption.
Advanced conventional transmission technologies pose a significant threat. Solutions like high-temperature, low-sag conductors and grid-enhancing technologies such as Dynamic Line Ratings (DLR) and Advanced Power Flow Control offer ways to boost grid capacity without relying on High-Temperature Superconductors (HTS). These alternatives focus on optimizing existing infrastructure, which could lead utilities to delay or reduce their investment in HTS.
The increasing adoption of distributed energy resources (DERs) and microgrids poses a significant threat of substitution for Applied Superconductor Ltd.'s high-temperature superconductor (HTS) cable technology. These decentralized energy systems, which generate and consume power locally, diminish the need for extensive, centralized power transmission networks that HTS cables are designed to serve. For instance, by 2024, the global microgrid market was projected to reach tens of billions of dollars, with significant growth driven by renewable energy integration, directly impacting the demand for traditional grid infrastructure.
Alternative energy storage solutions
While high-temperature superconductors (HTS) offer unique advantages for energy storage, they face significant competition from established and emerging alternative solutions. Advanced batteries, particularly lithium-ion, have seen substantial cost reductions and performance improvements, making them a viable substitute for many grid-scale storage needs. For instance, the global average cost of lithium-ion battery packs for electric vehicles fell by 89% between 2010 and 2023, according to BloombergNEF. This makes them increasingly competitive against HTS in terms of upfront investment.
Pumped-hydro storage also remains a formidable substitute, especially for very large-scale, long-duration energy storage. Despite requiring specific geographical conditions, pumped-hydro accounts for the vast majority of global installed energy storage capacity. In 2023, pumped-hydro storage represented over 90% of the world's installed storage capacity, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). The choice between HTS and these substitutes hinges on critical factors like the required scale of storage, the desired discharge duration, overall cost-effectiveness, and the specific technical requirements for grid integration.
The competitive landscape directly impacts the demand for HTS in energy storage applications. Applied Superconductor Ltd. must consider these alternatives when strategizing market entry and pricing for its HTS-based storage systems. The ongoing advancements and cost declines in battery technology and the continued reliance on pumped-hydro for bulk storage present a continuous threat that could limit the market penetration of HTS solutions.
- Lithium-ion batteries: Significant cost reductions and performance gains make them a strong competitor for grid-scale storage.
- Pumped-hydro storage: Dominates current installed capacity due to its suitability for large-scale, long-duration energy storage.
- Cost-effectiveness: A key differentiator where HTS must compete on total lifecycle cost against established alternatives.
- Grid integration requirements: The specific technical needs of the grid can favor one storage technology over another, influencing HTS market adoption.
Emerging non-superconducting advanced materials
The threat of substitutes for Applied Superconductor Ltd.'s high-temperature superconductors (HTS) is growing as materials science advances. Ongoing research is exploring alternative advanced materials that could offer comparable or superior performance without the need for cryogenic cooling, a significant operational factor for HTS.
While HTS technology operates at higher temperatures than traditional superconductors, its cooling requirements remain a consideration for widespread adoption. Any significant breakthroughs in alternative materials that reduce or eliminate these cooling needs could present a substantial long-term substitute threat.
For instance, advancements in areas like advanced ceramics or novel metallic alloys could potentially offer solutions for applications currently envisioned for HTS, such as high-efficiency power transmission or advanced magnetic levitation systems.
- Materials Science Research: Continuous R&D in non-superconducting materials aims to match or exceed HTS performance metrics.
- Cooling Requirements: HTS still necessitates cryogenic cooling, creating an opportunity for substitute materials that do not.
- Potential Substitutes: Breakthroughs in advanced ceramics and metallic alloys could offer viable alternatives for various applications.
- Long-Term Threat: Successful development of cost-effective, high-performance substitutes could significantly impact HTS market penetration.
The threat of substitutes for Applied Superconductor Ltd.'s high-temperature superconductor (HTS) wire is multifaceted, primarily stemming from advancements in conventional conductors and alternative grid technologies. While HTS offers unparalleled efficiency, its high cost, with prices significantly exceeding those of copper (around $9,000-$10,000 per metric ton in early 2024) and aluminum ($2,200-$2,500 per metric ton), remains a major hurdle.
Furthermore, grid-enhancing technologies like Dynamic Line Ratings (DLR) and advanced power flow control allow for increased capacity using existing infrastructure, presenting a compelling alternative to HTS adoption. The growing adoption of distributed energy resources and microgrids also reduces the reliance on large-scale transmission networks, thereby diminishing the market for HTS cables.
In energy storage, HTS faces stiff competition from increasingly cost-effective lithium-ion batteries, whose prices have seen dramatic reductions, and from established pumped-hydro storage, which dominates global installed capacity. These alternatives offer viable solutions for many applications, forcing HTS to compete on total lifecycle cost and specific grid integration requirements.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantage | Cost Benchmark (Early 2024) | Market Share/Capacity (2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper Conductors | Lower Cost | $9,000-$10,000 / metric ton | Dominant in existing grid |
| Aluminum Conductors | Lower Cost | $2,200-$2,500 / metric ton | Significant share in existing grid |
| Grid-Enhancing Technologies (DLR, etc.) | Optimizes existing infrastructure | Varies by technology | Growing adoption |
| Lithium-ion Batteries | Cost reduction, performance gains | Significant price drops (e.g., EV packs down 89% from 2010-2023) | Rapidly increasing in grid storage |
| Pumped-Hydro Storage | Large-scale, long-duration storage | N/A (infrastructure cost) | >90% of global installed storage capacity |
Entrants Threaten
The high-temperature superconductor (HTS) market demands significant upfront capital for specialized manufacturing plants and ongoing, intensive research and development. For instance, developing advanced HTS wire technologies, like those AMSC produces, involves substantial investment in materials science and engineering, often running into tens of millions of dollars annually.
The sheer cost of HTS materials themselves, coupled with the intricate and precise fabrication processes required, presents a formidable financial hurdle. This inherently limits the number of new companies that possess the financial muscle to challenge established firms like Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC).
The development and production of high-temperature superconducting (HTS) wire and complex integrated systems present a significant hurdle for potential new competitors due to the demanding learning curve and the necessity for highly specialized knowledge. This intricate requirement spans material science, cryogenic engineering, and the integration of power systems, creating a substantial barrier to entry.
New companies would face the considerable challenge of acquiring or cultivating exceptionally rare scientific and engineering talent to even begin competing. For instance, a significant portion of the HTS industry relies on PhD-level researchers with expertise in condensed matter physics and advanced manufacturing techniques, a talent pool that is inherently limited.
Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC) benefits from a robust intellectual property portfolio, including numerous patents covering high-temperature superconductor (HTS) wire composition, advanced manufacturing techniques, and diverse system applications. These patents act as significant deterrents to potential new entrants, effectively creating legal hurdles for those seeking to replicate AMSC's technological advancements.
The sheer volume and complexity of AMSC's patent landscape necessitate considerable investment in legal expertise and research and development for any aspiring competitor. Navigating this intricate web of intellectual property requires substantial financial and technical resources, further elevating the barriers to entry in the HTS wire market.
Established customer relationships and regulatory hurdles
The markets Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC) serves, like grid infrastructure and defense, are characterized by very long sales cycles and demanding qualification procedures. Established customer relationships are a significant barrier, as utilities and government bodies are typically risk-averse and slow to adopt new suppliers.
Newcomers would struggle immensely to build the necessary trust and win contracts with these entrenched entities. Furthermore, navigating the complex web of regulatory compliance and obtaining crucial certifications presents substantial obstacles for any potential entrant aiming to compete in these sectors.
- Long Sales Cycles: AMSC's target markets often involve multi-year engagements, requiring significant upfront investment and patience from suppliers.
- Rigorous Qualification: Potential suppliers must undergo extensive testing and vetting processes, often lasting years, before being considered for projects.
- Entrenched Relationships: Utilities and defense agencies have long-standing partnerships with existing suppliers, making it difficult for new entrants to break in.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with industry-specific regulations and obtaining necessary certifications are critical and time-consuming for new market participants.
Economies of scale and cost competitiveness
Existing high-temperature superconductor (HTS) manufacturers leverage significant economies of scale, enabling them to achieve cost competitiveness through optimized production processes. For instance, companies with established, high-volume production lines can spread fixed costs over a larger output, leading to lower per-unit manufacturing expenses.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in matching this cost efficiency. Building production capacity to a scale that rivals established players requires considerable upfront investment, making it challenging to compete on price from the outset. This initial lack of scale can deter potential new entrants who foresee difficulty in achieving profitability against incumbents.
- Economies of Scale: Established HTS manufacturers benefit from lower per-unit costs due to higher production volumes, a key barrier for new entrants.
- Cost Competitiveness: Incumbents can offer more attractive pricing, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market share without significant initial investment.
- Production Scale Challenge: While manufacturing technologies are advancing, achieving the necessary production scale remains a significant obstacle for new companies entering the HTS market.
The threat of new entrants in the high-temperature superconductor (HTS) market, where Applied Superconductor Ltd. (AMSC) operates, is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements for specialized manufacturing and R&D. For example, establishing a state-of-the-art HTS wire production facility can easily cost upwards of $50 million to $100 million, a prohibitive sum for most aspiring companies.
Furthermore, the intricate nature of HTS materials and fabrication processes, coupled with a steep learning curve in areas like materials science and cryogenic engineering, creates a substantial barrier. This complexity demands highly specialized expertise, often requiring teams of PhD-level scientists and engineers, a talent pool that is both scarce and expensive to acquire.
AMSC's extensive patent portfolio, covering unique wire compositions and manufacturing techniques, acts as a formidable legal deterrent, necessitating significant investment in intellectual property navigation for any newcomer. The long sales cycles and rigorous qualification processes in AMSC's key markets, such as grid infrastructure and defense, further solidify the position of established players by requiring years to build trust and secure contracts.
New entrants also face the challenge of matching the economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents, which drive down per-unit production costs. Without comparable production volumes, new companies struggle to compete on price, making it difficult to gain traction in a market where cost-effectiveness is crucial for widespread adoption.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Specialized HTS manufacturing and R&D facilities | $50M - $100M+ for a new facility |
| Technical Expertise | Materials science, cryogenic engineering, advanced manufacturing | Requires teams of PhD-level specialists |
| Intellectual Property | AMSC's patent portfolio | Significant legal and R&D investment to navigate |
| Market Access | Long sales cycles and rigorous qualification in grid/defense | Years to build trust and secure initial contracts |
| Economies of Scale | Cost competitiveness through high-volume production | Challenging for new entrants to match incumbent pricing |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Applied Superconductor Ltd. is built upon a foundation of publicly available company filings, including annual reports and investor presentations. We also incorporate industry-specific market research reports and news articles from reputable trade publications to capture current competitive dynamics.