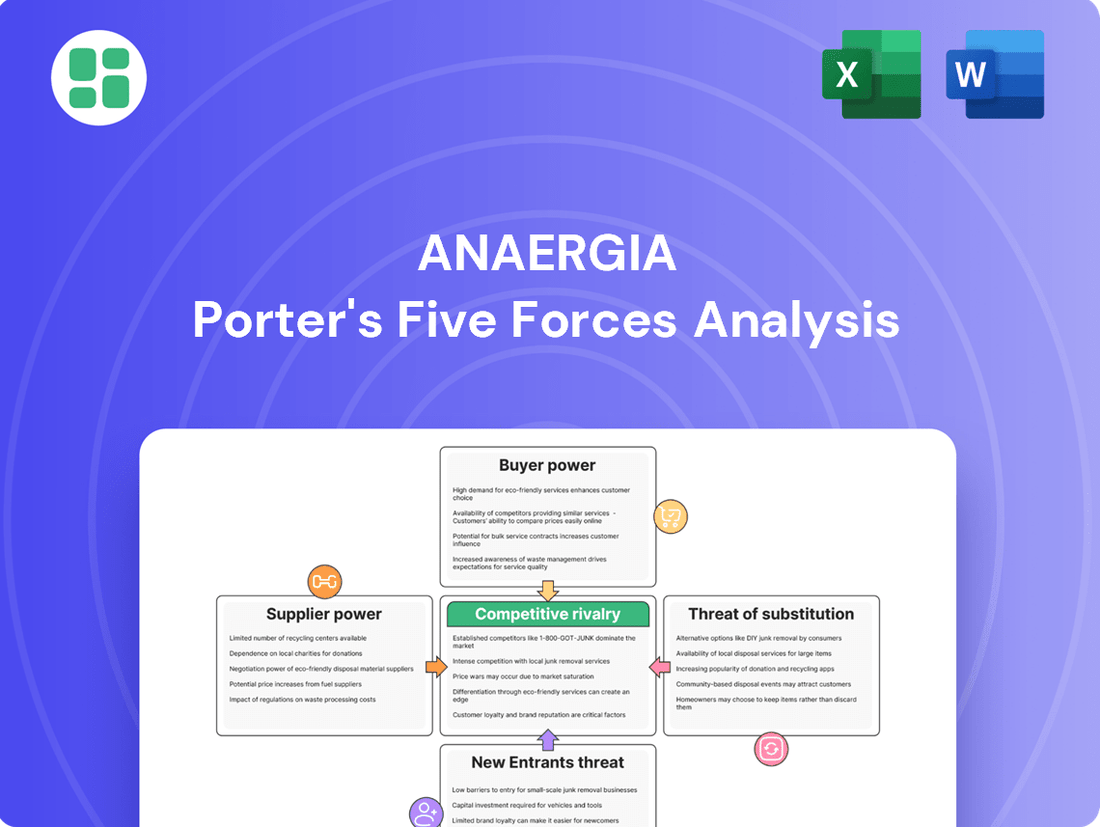
Anaergia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Anaergia Bundle
Anaergia operates in a dynamic market where supplier power can significantly impact project costs, and the threat of new entrants is moderate due to high capital requirements. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Anaergia’s industry—from buyer power to substitute threats. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Anaergia Inc. hinges significantly on how concentrated the market is for specialized technology providers and how unique their products are. Anaergia employs its own set of advanced, end-to-end solutions, but it also depends on external equipment manufacturers. This reliance means that the availability and cost of specific components can directly affect Anaergia's expenses and how quickly it can complete projects.
When there are only a limited number of companies that can supply essential technologies or highly specialized services, those suppliers gain more leverage. For instance, if a particular type of anaerobic digester component is only produced by a few firms, these firms can command higher prices or dictate terms, thereby increasing their bargaining power over Anaergia.
Anaergia faces considerable switching costs when changing suppliers for its core anaerobic digestion technologies and specialized components. These costs aren't just monetary; they encompass the substantial time and effort required for integration, retraining staff, and ensuring seamless compatibility with their established infrastructure. For instance, a shift in a critical sensor supplier could necessitate extensive recalibration and testing, impacting project timelines and operational efficiency.
Anaergia's waste-to-value business model, encompassing design, construction, ownership, and operation of infrastructure, hinges on the consistent quality and availability of inputs from technology suppliers, material providers, and engineering firms. The complexity of projects such as renewable natural gas facilities underscores the critical role these suppliers play, granting significant leverage to those providing essential components or specialized services.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers to Anaergia, particularly those providing key components or technologies for waste-to-value projects, could potentially integrate forward. This means they might develop their own projects or offer complete solutions that directly compete with Anaergia's business model.
While Anaergia typically supplies its advanced systems to project developers, there's a risk that some technology providers might decide to enter the project development and operation arena. This would naturally shrink the market opportunities available for Anaergia.
However, Anaergia's established integrated platform, which encompasses technology, project development, and operations, along with its extensive project development experience, serves as a significant mitigating factor against this threat.
- Potential for Supplier Forward Integration: Suppliers of critical components or technologies for waste-to-value projects may enter project development and operation, directly competing with Anaergia.
- Market Opportunity Reduction: If suppliers become project developers, it could limit the number of clients seeking Anaergia's system supply and project expertise.
- Mitigating Factors: Anaergia's integrated platform and deep project development experience provide a competitive advantage, potentially deterring or lessening the impact of supplier forward integration.
Availability of Alternative Suppliers and Inputs
The bargaining power of suppliers for Anaergia is influenced by the availability of alternative sources for their components and services. A diverse supplier market for non-proprietary equipment and materials generally weakens supplier leverage.
Anaergia actively cultivates strong supplier relationships, focusing on the total cost of ownership. However, the existence of numerous viable suppliers for standard inputs would naturally diminish any single supplier's ability to dictate terms.
- Supplier Concentration: A fragmented supplier base for critical inputs typically reduces supplier power.
- Input Differentiation: If Anaergia can source similar components from multiple vendors, supplier power is lessened.
- Switching Costs: High costs for Anaergia to switch suppliers would increase supplier bargaining power.
- Supplier's Forward Integration: The potential for suppliers to enter Anaergia's business would also increase their power.
Anaergia's reliance on specialized technology providers and critical components means suppliers can wield significant influence. For example, if a key component for their anaerobic digestion systems is only available from a few manufacturers, these suppliers can command higher prices, impacting Anaergia's project costs and timelines. In 2023, Anaergia reported that the cost of goods sold was $260.4 million, a figure directly tied to its supplier relationships and the pricing of essential materials and equipment.
| Factor | Impact on Anaergia | 2023 Data Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration of specialized technology suppliers increases their bargaining power. | Cost of Goods Sold: $260.4 million |
| Switching Costs | High integration and retraining costs for new suppliers limit Anaergia's ability to switch. | Not directly quantifiable in public financial statements, but implied in operational efficiency. |
| Input Differentiation | Availability of multiple suppliers for non-proprietary inputs weakens supplier leverage. | Anaergia's diverse project portfolio suggests varied input sourcing strategies. |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Potential for suppliers to enter project development could reduce Anaergia's market. | Strategic focus on integrated solutions aims to mitigate this risk. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Anaergia's position in the renewable energy and waste-to-value sectors.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive pressures, transforming complex market dynamics into actionable insights for strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
Anaergia's customer base is largely concentrated among municipalities, private entities, and project developers, who typically engage in large-scale, long-term contracts. This concentration means that while Anaergia secures substantial revenue from individual clients, these clients can wield significant bargaining power due to the sheer volume of business they represent. For instance, recent contracts with major players like PepsiCo Colombia and the City of Riverside highlight the importance of these large clients.
The substantial scale of these contracts, often involving significant capital investment and customized solutions, inherently grants these customers leverage. They can negotiate more favorable terms, pricing, and service level agreements, especially when Anaergia's offerings are highly specialized or require extensive upfront investment. This dynamic is a critical factor in Anaergia's operational and financial planning.
For Anaergia's customers, the decision to switch from an existing waste-to-value solution provider is often complicated by significant costs. These can include the substantial capital outlay required for anaerobic digestion facilities, which represent a major investment for any municipality or industrial partner.
Furthermore, long-term operations and maintenance (O&M) contracts, commonly ranging from 5 to 10 years, lock customers into a relationship. These agreements are designed to ensure consistent performance and reliability, but they also create a barrier to easily changing providers.
The presence of these high switching costs effectively diminishes the bargaining power of customers once a project is operational or an O&M agreement is in force. This creates a more stable revenue stream for Anaergia, as customers are less likely to seek alternative solutions due to the financial and operational hurdles involved.
Anaergia's waste-to-value solutions are crucial for customers aiming to comply with stringent environmental mandates and reduce their carbon footprint. For instance, in 2024, numerous municipalities and industrial clients are under increasing pressure to divert organic waste from landfills, a challenge Anaergia directly addresses.
The company's proprietary technologies, enabling the conversion of waste into valuable commodities like renewable natural gas and fertilizer, create a strong dependency for customers. This reliance on Anaergia's specialized expertise and patented processes limits the customers' ability to easily switch to alternative providers, thereby reducing their bargaining power.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Anaergia, especially when dealing with municipalities and large corporations. These entities often operate under strict budget limitations, making cost-effectiveness a primary driver in their decision-making for waste management and energy solutions. For instance, in 2024, many municipal budgets faced increased pressure due to rising inflation and infrastructure demands, intensifying the focus on upfront costs and operational expenses for new projects.
While Anaergia’s advanced technologies offer substantial long-term advantages, such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions and valuable resource recovery, the initial capital outlay and ongoing operational costs remain critical negotiation points. Customers are carefully weighing these expenditures against the projected financial and environmental benefits. This sensitivity means that pricing strategies and the clear articulation of return on investment are paramount in securing contracts.
- Municipal Budgets: Many local governments in 2024 were allocated specific, often fixed, budgets for waste management and energy infrastructure, leading to a strong emphasis on price.
- Corporate Sustainability Goals: While corporations are increasingly focused on ESG metrics, the economic viability of solutions remains a key hurdle, with many seeking cost-neutral or cost-saving approaches.
- Financing Models: The availability and terms of financing for Anaergia's projects can directly impact customer price sensitivity, as attractive financing can offset higher initial costs.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of alternative waste-to-energy or waste management solutions in the market can also heighten customer price sensitivity, as they can compare Anaergia's offerings against competitors.
Availability of Alternative Solutions for Customers
Customers have a range of waste management and energy generation options, from traditional landfilling and incineration to other renewable sources like solar and wind power. This variety of alternatives directly impacts Anaergia's position. For instance, in 2024, the global waste-to-energy market saw continued growth, with various technologies competing for market share, potentially offering customers more leverage.
The expanding competitive landscape within the waste-to-value sector means customers are increasingly presented with more choices. If Anaergia's integrated platform doesn't offer a sufficiently unique or compelling value proposition compared to these alternatives, customers' bargaining power can grow significantly. This is particularly relevant as investments in diverse renewable energy infrastructure continue to rise, with projections showing substantial growth in the sector through 2030.
- Increased Choice: Customers can opt for landfilling, incineration, or various renewable energy solutions.
- Competitive Market: The waste-to-value industry is becoming more crowded, offering customers more options.
- Differentiation is Key: Anaergia's bargaining power hinges on how unique its integrated platform is compared to alternatives.
- Market Trends: Global investments in renewable energy infrastructure are increasing, providing customers with more viable substitutes.
Anaergia's large-scale clients, including municipalities and major corporations, possess significant bargaining power due to the substantial volume of their contracts. These clients can negotiate more favorable terms, particularly when Anaergia's specialized solutions involve considerable upfront investment or long-term operational commitments, as seen in recent large contracts.
While high switching costs associated with capital investment and long-term O&M agreements reduce customer leverage once a project is underway, initial price sensitivity remains a key factor. Many municipal budgets in 2024 faced pressure, intensifying the focus on cost-effectiveness and return on investment for waste management solutions.
Anaergia's proprietary technologies create customer dependency, limiting their ability to switch providers easily. However, the growing number of alternative waste management and renewable energy options, including a competitive waste-to-value market, can increase customer bargaining power if Anaergia's differentiation is not sufficiently strong.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Contract Size | High (Larger contracts = more leverage) | Major contracts with entities like PepsiCo Colombia highlight this. |
| Switching Costs | Low (High capital/O&M costs reduce power) | Long-term O&M contracts (5-10 years) lock in customers. |
| Price Sensitivity | High (Budget constraints drive negotiation) | Municipal budgets in 2024 faced inflationary pressures. |
| Alternative Solutions | Moderate to High (More options = more leverage) | Growth in waste-to-energy market offers customers choices. |
| Technology Dependence | Low (Proprietary tech reduces customer power) | Anaergia's patented processes create reliance. |
Same Document Delivered
Anaergia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Anaergia, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the biogas and waste-to-energy sector. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This analysis provides a robust framework for understanding Anaergia's market dynamics and identifying potential strategic advantages.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Anaergia operates in waste-to-value and renewable energy sectors, facing a broad and diverse competitive landscape. This includes specialized equipment manufacturers, dedicated project developers, and large-scale environmental services firms, all vying for market dominance.
Key players such as Viridor, Severn Trent, Summerleaze, Greyter, Cambi, EnviTec Biogas AG, Hitachi Zosen Corporation, Suez Group, Ameresco, and Montauk Renewables demonstrate the wide array of companies competing for Anaergia's business. This extensive competition can significantly increase the intensity of rivalry.
For instance, in 2024, the global biogas market was valued at approximately $33.5 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth. This expanding market attracts numerous entrants and existing players, intensifying the competitive pressure on companies like Anaergia.
The renewable natural gas (RNG) sector is experiencing robust growth, with forecasts suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 12% through 2030. This expansion is fueled by supportive regulations and corporate commitments to reduce carbon emissions.
While this expanding market offers ample room for various participants, it doesn't eliminate competitive pressures. Companies are actively pursuing aggressive expansion strategies into lucrative regions such as Japan, Latin America, and Europe, intensifying rivalry as they vie for market share in these high-growth areas.
Anaergia distinguishes itself through its comprehensive, proprietary suite of integrated solutions. This end-to-end approach, encompassing solid waste processing, wastewater treatment, organics recovery, and advanced anaerobic digestion for renewable natural gas (RNG) production, offers a distinct advantage over rivals offering only standalone technologies.
This integrated model allows Anaergia to capture more value across the entire waste-to-energy lifecycle, potentially leading to greater efficiency and cost savings for clients. For instance, the company's ability to process diverse waste streams and convert them into valuable RNG positions it favorably in a market increasingly focused on circular economy principles and sustainable energy.
Switching Costs for Customers Among Competitors
While Anaergia's customers experience significant switching costs once a project is operational, the initial selection phase for new infrastructure projects is highly competitive. During this evaluation period, potential clients weigh proposals from multiple providers, making the early stages crucial for securing business.
Competitors actively work to reduce the perceived barriers to switching for prospective clients. This often involves offering attractive incentives or aggressive pricing strategies, particularly during the bidding and negotiation stages of new project acquisition, thereby heightening the intensity of rivalry.
- High initial investment locks in customers post-implementation.
- Competitors use pricing and incentives to attract new clients.
- Rivalry intensifies during the project bidding and negotiation phases.
Exit Barriers from the Industry
Anaergia, like many in the waste-to-value industry, faces substantial exit barriers. The significant capital required for specialized infrastructure, such as anaerobic digestion facilities and advanced processing equipment, makes it difficult for companies to divest or cease operations without substantial losses. For instance, the construction of a new anaerobic digestion plant can easily run into tens of millions of dollars, a sunk cost that is hard to recoup.
These high upfront investments, coupled with long-term contracts for waste processing and energy offtake, create a sticky situation. Companies are often locked into these commitments for years, meaning that even if market conditions deteriorate or profitability shrinks, exiting the industry isn't a simple or financially viable option. This can lead to a scenario where underperforming firms continue to operate, adding to the overall competitive intensity.
- High Capital Investments: Building waste-to-value facilities requires substantial capital, often in the tens or hundreds of millions of dollars, making it difficult to recover costs upon exit.
- Specialized Technology: The industry relies on proprietary and specialized technologies, which have limited resale value outside of the waste-to-value sector.
- Long-Term Commitments: Companies typically enter into long-term contracts for waste supply and energy sales, creating operational and financial obligations that hinder a swift exit.
- Continued Operation at Lower Profitability: The inability to exit easily can force companies to continue operating even at reduced profit margins, thereby maintaining competitive pressure.
Competitive rivalry in Anaergia's sector is intense due to a wide array of players, from specialized manufacturers to large environmental services firms. The growing global biogas market, valued at approximately $33.5 billion in 2024, attracts numerous competitors, increasing pressure. The renewable natural gas (RNG) sector's projected 12% CAGR through 2030 further fuels this competition as companies aggressively expand into lucrative regions.
Anaergia's integrated solutions offer a competitive edge, but the initial project selection is highly contested. Competitors often use aggressive pricing and incentives to win new clients, intensifying rivalry during bidding phases. High switching costs for customers post-implementation are offset by these efforts to attract new business.
Exit barriers are substantial due to high capital investments, specialized technology, and long-term contracts. This inability to easily exit can lead to continued operation by less profitable firms, maintaining overall competitive intensity in the market.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional waste disposal methods, such as landfilling and incineration, continue to be significant substitutes for Anaergia's advanced waste-to-value technologies. These older methods are often favored in areas with less strict environmental oversight or where their immediate costs are perceived as lower. For instance, in 2024, landfilling still accounted for a substantial portion of municipal solid waste disposal globally, despite its environmental drawbacks.
Anaergia's renewable natural gas (RNG) faces competition from other renewable energy sources, notably solar and wind power. These alternatives have seen significant cost reductions, with solar photovoltaic (PV) module prices falling by over 80% in the last decade, making them increasingly attractive for grid-scale applications. For instance, the global average unsubsidized levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for utility-scale solar PV was around $38 per megawatt-hour (MWh) in 2024, while onshore wind was approximately $33 per MWh. While RNG provides the dual benefit of waste management and energy production, customers prioritizing solely renewable energy generation, particularly for large-scale power needs, may find solar and wind more economical choices.
New innovations in composting technology, like fully automated organic waste converters and smart composting machines with IoT integration, are appearing as alternatives to anaerobic digestion for some uses. For instance, the global composting market was valued at approximately $4.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, showcasing a significant alternative pathway for organic waste management.
Furthermore, advancements in AI and machine learning for waste segregation are streamlining other waste treatment processes, indirectly challenging integrated solutions. These technologies can improve the efficiency of pre-treatment for various waste streams, potentially making them more competitive against purely anaerobic digestion approaches.
Shifting Regulatory and Policy Landscapes
Changes in environmental regulations can significantly impact the attractiveness of Anaergia's core business. For instance, evolving mandates for landfill diversion or emissions standards directly influence the demand for anaerobic digestion and related technologies. A shift in government incentives, such as changes to renewable energy credits or carbon pricing mechanisms, can either bolster or diminish the competitive advantage of Anaergia's solutions compared to alternatives.
The threat of substitutes is heightened by policy shifts that favor competing waste management or energy production methods. For example, if governments increase subsidies for waste-to-energy incineration or electric vehicle infrastructure, these could draw investment and market share away from renewable natural gas (RNG) projects, a key area for Anaergia. Conversely, policies promoting RNG, like those seen in the US with the Inflation Reduction Act, create a more favorable environment.
Consider these points regarding regulatory shifts:
- Policy Impact on RNG: In 2024, the US EPA's Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program continues to be a significant driver for RNG, with RIN generation providing a crucial economic incentive. However, any future adjustments to RFS volumes or eligibility criteria could alter the competitive landscape for RNG producers.
- Global Regulatory Trends: European Union directives, such as those promoting circular economy principles and setting targets for renewable energy integration, generally support Anaergia's model. Nevertheless, specific national implementations can vary, creating regional differences in the threat of substitutes.
- Incentive Structures: The availability and structure of tax credits or grants for biogas upgrading and injection into natural gas grids are critical. A reduction in these incentives, or the introduction of more attractive incentives for alternative green energy sources, would increase substitution threats.
- Landfill Regulations: Stricter regulations on landfill methane emissions, while generally beneficial for anaerobic digestion, can also spur investment in other methane capture technologies or waste reduction strategies that bypass the need for biological treatment.
Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes
The cost-effectiveness of substitute solutions is a major concern for Anaergia. If alternative waste processing or energy generation methods become significantly cheaper or simpler to adopt, they could erode Anaergia's market share. This includes both the initial capital investment and ongoing operational expenses.
For instance, the rising cost of natural gas in 2024 could make traditional energy sources less competitive compared to anaerobic digestion, but advancements in solar or wind power efficiency could offer cheaper alternatives for energy generation, impacting Anaergia's biogas-to-energy offerings.
- Capital Expenditure: The upfront cost of building anaerobic digestion facilities versus the cost of installing solar farms or other renewable energy infrastructure.
- Operational Costs: Ongoing expenses such as maintenance, labor, and feedstock acquisition for Anaergia's plants compared to the operating costs of competing energy solutions.
- Energy Output Efficiency: The amount of usable energy produced per unit of input for anaerobic digestion versus other renewable energy technologies.
- Market Price of Energy: Fluctuations in electricity and natural gas prices directly influence the attractiveness of energy produced from anaerobic digestion.
Traditional waste disposal methods like landfilling and incineration remain significant substitutes for Anaergia's advanced technologies, especially where environmental regulations are less stringent or immediate costs are lower. For example, landfilling still accounted for a substantial portion of global municipal solid waste disposal in 2024. Anaergia's renewable natural gas (RNG) also faces competition from increasingly cost-effective solar and wind power, with global average unsubsidized LCOE for utility-scale solar PV around $38/MWh in 2024.
Innovations in composting and AI-driven waste segregation present alternative pathways for organic waste management and treatment, indirectly challenging Anaergia's integrated solutions. The global composting market was valued at approximately $4.5 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of these alternatives.
Shifting environmental regulations and government incentives can significantly alter the competitive landscape. For instance, while the US EPA's Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program in 2024 provides crucial economic incentives for RNG, any future adjustments could impact its competitiveness. Conversely, stricter landfill methane emission regulations can spur investment in alternative methane capture technologies.
| Substitute Technology | Key Characteristic | 2024 Market/Cost Data Point | Impact on Anaergia |
| Landfilling | Traditional, lower perceived immediate cost | Substantial portion of global MSW disposal | Direct competition for waste streams |
| Solar PV | Renewable energy generation | LCOE ~$38/MWh (unsubsidized) | Competition for energy markets |
| Wind Power | Renewable energy generation | LCOE ~$33/MWh (unsubsidized) | Competition for energy markets |
| Composting | Organic waste management | Global market ~$4.5 billion (2023) | Alternative for organic waste streams |
Entrants Threaten
The waste-to-value and renewable energy sectors, especially for large-scale anaerobic digestion facilities, necessitate considerable capital for technology, infrastructure, and project financing. Anaergia's Build, Own, and Operate (BOO) model, for instance, requires significant upfront investment, creating a substantial barrier to entry.
Anaergia's formidable intellectual property portfolio, boasting over 250 patents for its waste-to-energy technologies, presents a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. This robust patent protection, covering processes for converting organic waste into renewable natural gas, fertilizer, and water, effectively shields its integrated, end-to-end solutions from direct replication.
The sheer breadth of Anaergia's patents means that new companies would need to undertake substantial research and development or secure costly licensing agreements to compete, thereby raising the barrier to entry considerably.
The waste-to-value and renewable energy sectors face substantial barriers to entry due to intricate environmental regulations and protracted permitting procedures. For instance, obtaining necessary permits for a new anaerobic digestion facility can take anywhere from 18 to 36 months, often involving multiple federal, state, and local agencies. This complexity demands specialized legal and technical knowledge, alongside significant upfront investment in compliance, making it difficult for less capitalized or inexperienced companies to enter the market.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
Securing consistent access to waste feedstocks and establishing off-take agreements for renewable natural gas, fertilizer, and water are critical for new entrants. This necessitates building robust relationships and intricate supply chains, a significant hurdle for newcomers.
Anaergia's advantage lies in its extensive history and pre-existing partnerships with municipalities and industrial clients. These established connections create a formidable barrier to entry, as new companies would find it challenging to replicate such a network swiftly.
- Established Relationships: Anaergia has cultivated long-standing ties with over 100 municipalities and numerous industrial partners, ensuring a steady supply of feedstock.
- Off-take Agreements: The company has secured firm off-take agreements for its products, providing revenue certainty that new entrants would need time to establish.
- Supply Chain Control: Anaergia's integrated approach to managing its supply chain, from feedstock sourcing to product distribution, offers operational efficiencies that are difficult for new players to match.
Experience and Track Record
Anaergia's extensive history, dating back to its founding in 2007, and its proven track record in developing and operating anaerobic digestion facilities provide a substantial barrier to new entrants. The company has successfully deployed numerous projects globally, demonstrating its capability in navigating complex regulatory environments and securing financing for large-scale ventures.
Newcomers often struggle to replicate this depth of experience, which is crucial for gaining the trust of off-takers and securing long-term contracts for renewable natural gas (RNG). For instance, Anaergia's ability to leverage existing infrastructure and its established supply chain networks significantly reduces the upfront investment and operational risks that new companies would face.
The specialized nature of the RNG industry, requiring expertise in feedstock sourcing, biological processes, and gas upgrading, means that new entrants typically lack the essential operational know-how. This experience gap hinders their ability to compete effectively for major projects and build the necessary customer confidence. Anaergia's portfolio, which includes projects like the Rialto Bioenergy Facility in California, a significant RNG producer, exemplifies the scale and complexity that new players find challenging to match.
- Established Track Record: Anaergia's operational history since 2007 provides a significant competitive advantage.
- Project Development Expertise: Proven ability to secure and execute complex, large-scale RNG projects globally.
- Infrastructure and Supply Chain Leverage: Existing networks and infrastructure reduce entry barriers for Anaergia but not for new entrants.
- Industry-Specific Know-How: Deep understanding of feedstock, biological processes, and gas upgrading is difficult for new companies to acquire quickly.
The threat of new entrants in Anaergia's waste-to-value and renewable energy sector is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements. Developing large-scale anaerobic digestion facilities demands millions in investment for technology, infrastructure, and project financing, a hurdle that deters many potential competitors. Anaergia's Build, Own, and Operate model, for instance, highlights the extensive upfront capital needed, acting as a strong deterrent.
Anaergia's extensive patent portfolio, encompassing over 250 patents for its waste-to-energy technologies, creates a formidable barrier. These patents protect its proprietary processes for converting organic waste into renewable natural gas and other valuable byproducts, making direct replication by new companies extremely difficult and costly. Acquiring licenses or developing similar technology requires significant R&D investment.
Navigating the complex web of environmental regulations and lengthy permitting processes poses another significant entry barrier. Obtaining approvals for anaerobic digestion facilities can take 18 to 36 months, involving multiple government agencies and requiring specialized expertise. This regulatory complexity, coupled with the need for compliance, discourages less experienced or capitalized entrants.
Securing consistent feedstock supply and establishing reliable off-take agreements for its products are critical for new entrants. Anaergia's established relationships with over 100 municipalities and industrial clients, along with its firm off-take contracts, provide revenue certainty that newcomers struggle to match. This deep integration into the supply chain and customer base is a key competitive advantage.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Anaergia's Advantage |
| Capital Requirements | High investment for technology and infrastructure | Deters less capitalized firms | BOO model requires significant upfront capital |
| Intellectual Property | Over 250 patents for waste-to-energy tech | Requires costly R&D or licensing | Protects proprietary processes from replication |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Lengthy permitting (18-36 months) and compliance | Demands specialized knowledge and time | Proven ability to navigate complex regulations |
| Feedstock & Off-take Access | Securing waste supply and product sales | Challenging without established networks | Strong relationships with 100+ municipalities and industrial clients |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Anaergia Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Anaergia's annual reports, investor presentations, and public filings. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports and data from reputable financial databases to provide a thorough understanding of the competitive landscape.