Amway Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Amway Corporation Bundle
Amway's direct selling model faces unique pressures from intense rivalry among distributors and the constant threat of new, innovative direct selling companies entering the market. Understanding the bargaining power of both its suppliers and its vast network of distributors is crucial for Amway's sustained success.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Amway Corporation’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Amway's reliance on specialized ingredients, particularly for its Nutrilite brand which sources from company-owned organic farms, suggests that some suppliers of unique botanical raw materials may possess moderate bargaining power. For instance, specific rare plant extracts used in premium Nutrilite products could command higher prices if Amway faced limited sourcing options.
However, for more common components like packaging or standard vitamins, supplier power would likely be lower due to a wider availability of alternatives. In 2024, Amway's robust supply chain management, which includes strategic sourcing and long-term supplier relationships, helps to mitigate excessive supplier leverage across its diverse product portfolio.
For Amway, the bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by switching costs. When Amway requires highly specialized ingredients or components, potentially protected by patents, the cost and time involved in finding and qualifying a new supplier can be substantial. This includes research, development, and navigating regulatory hurdles, which can significantly increase switching costs.
Conversely, for more commoditized inputs like standard packaging materials or widely available raw ingredients, Amway faces lower switching costs. This flexibility allows Amway to more readily negotiate pricing or change suppliers if terms become unfavorable, thereby reducing supplier leverage in these instances.
The threat of suppliers moving into Amway's direct selling or manufacturing operations is quite minimal. Most suppliers provide raw materials and don't have the established infrastructure for direct consumer sales or product development that Amway has cultivated over decades.
For instance, Amway's global network of independent business owners, numbering in the millions, represents a significant barrier to entry for any raw material supplier looking to replicate their distribution model. This extensive network is a core competitive advantage that suppliers typically cannot easily replicate.
Furthermore, Amway's strong brand equity and deep understanding of the direct selling business model are not easily acquired by suppliers focused on material production. This disparity in expertise and market presence significantly diminishes the threat of forward integration from these suppliers.
Importance of Amway as a Customer
Amway's position as the world's largest direct-selling company, with reported sales of $7.4 billion in 2024, makes it a highly significant customer for its suppliers.
This substantial purchasing volume grants Amway considerable bargaining power, enabling it to negotiate advantageous terms, pricing, and specialized support from its supply chain partners.
Suppliers are therefore motivated to maintain strong relationships with Amway, as the company represents a significant portion of their revenue.
- Significant Revenue Stream: Amway's $7.4 billion in 2024 sales translates to substantial orders for its suppliers.
- Negotiating Leverage: This scale allows Amway to demand favorable pricing and terms.
- Supplier Dependence: Suppliers may prioritize Amway's needs to secure consistent business.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly mitigates the bargaining power of suppliers for Amway Corporation. For many of its core product lines, such as home care and personal care items, a wide array of alternative raw materials and components exist within the global market. This abundance of choices allows Amway to diversify its supplier base and avoid over-reliance on any single entity.
This broad availability of substitutes directly limits the leverage individual suppliers hold. Amway can readily switch between providers if pricing becomes unfavorable or if supply chain disruptions occur. For instance, in 2024, the global chemical industry continued to see diverse sourcing options for common ingredients used in cleaning and beauty products, meaning no single supplier could unilaterally dictate terms to a large buyer like Amway.
- Diverse Sourcing Options: Amway benefits from a wide selection of raw materials for its extensive product portfolio.
- Reduced Supplier Dependency: The presence of substitutes prevents any single supplier from gaining excessive control over Amway's costs or supply continuity.
- Competitive Pricing: Amway can leverage the availability of alternatives to negotiate more favorable pricing from its suppliers, maintaining cost efficiency.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Access to multiple substitute inputs enhances Amway's ability to manage potential disruptions and ensure consistent product availability for its distributors and customers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Amway is generally moderate, largely due to Amway's significant purchasing volume and the availability of substitute inputs for many of its product lines. While specialized ingredients for brands like Nutrilite might offer some suppliers leverage, common components face less supplier power.
Amway's position as a major customer, evidenced by its $7.4 billion in sales in 2024, grants it considerable negotiating power. This scale allows Amway to secure favorable terms and pricing, making suppliers keen to maintain a relationship.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Amway's business is minimal, as suppliers typically lack Amway's extensive direct-selling network and brand recognition.
| Factor | Impact on Amway | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Purchasing Volume | Lowers Supplier Power | Amway's $7.4 billion in 2024 sales gives it leverage to negotiate terms. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Lowers Supplier Power | Numerous alternative raw materials exist for many Amway products. |
| Switching Costs (Specialized Inputs) | Increases Supplier Power | High costs to find new suppliers for patented or unique ingredients. |
| Switching Costs (Commoditized Inputs) | Lowers Supplier Power | Easy to switch suppliers for common packaging or ingredients. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Lowers Supplier Power | Suppliers lack Amway's direct-selling infrastructure and brand. |
What is included in the product
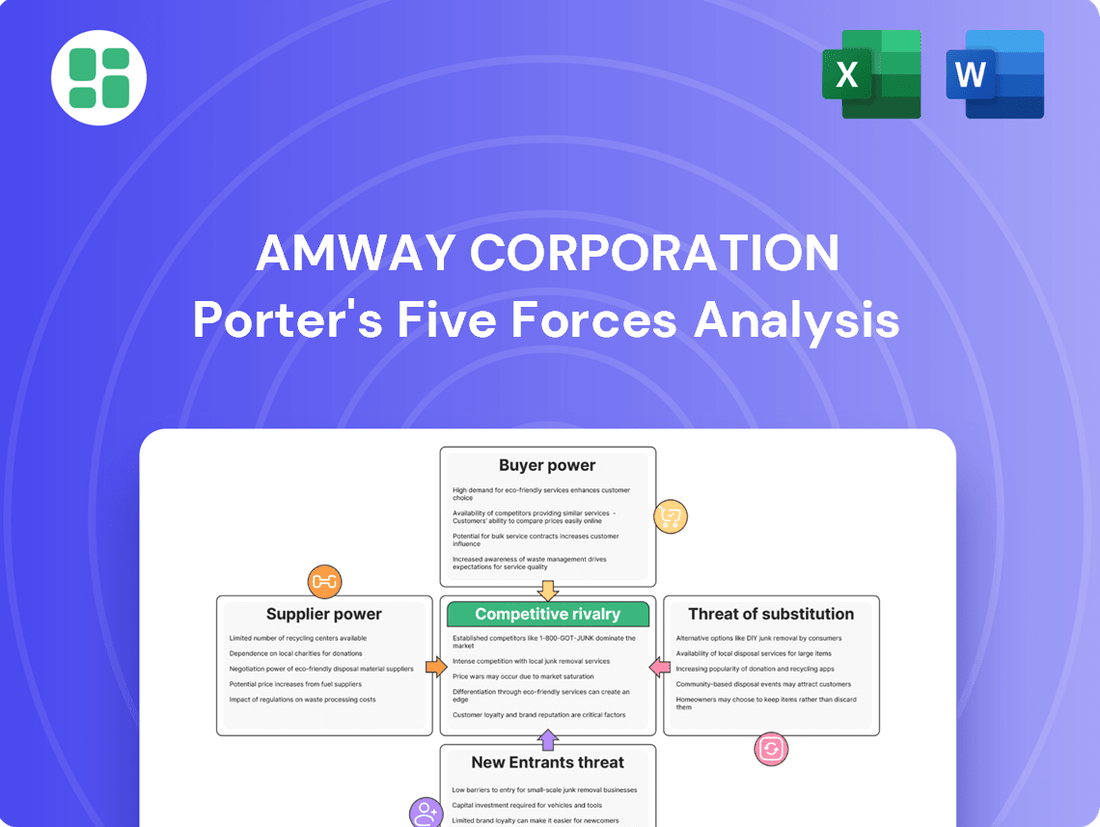
This Porter's Five Forces analysis specifically examines Amway Corporation's competitive environment, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its direct selling business model.
Amway's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of competitive pressures—perfect for quick strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Amway's customer base can exhibit significant price sensitivity, especially when comparing its products to those found in conventional retail channels. For instance, while Amway emphasizes the quality and unique benefits of its nutritional supplements and personal care items, their price points are often higher than mass-market alternatives. This can be a challenge, particularly for consumers with tighter budgets who may prioritize cost savings.
This sensitivity necessitates strategic pricing by Amway. While the direct selling model is built on highlighting product value and distinct advantages, competitive pricing remains a crucial factor in customer acquisition and retention. In 2024, with inflation impacting household budgets globally, this pressure on pricing is likely to be even more pronounced for Amway and its distributors.
Customers for Amway's health, beauty, and home care products face a vast array of alternatives. These include everything from major retailers like Walmart and Target, to online giants such as Amazon, and even other direct selling companies. This wide availability means consumers can easily find similar products elsewhere.
The sheer volume of substitute options significantly boosts customer bargaining power. For instance, the global beauty and personal care market was valued at over $500 billion in 2023, with numerous brands competing for market share, making it simple for consumers to switch if Amway's pricing or product offerings are not competitive.
The widespread availability of information, amplified by digital platforms and social media, significantly enhances customer bargaining power. Consumers can easily access product reviews, compare prices across competitors, and research the direct selling model itself, increasing their awareness and leverage.
This transparency empowers customers to make more informed choices, potentially leading them to negotiate more effectively with Amway's Independent Business Owners (IBOs) or to explore alternative product options. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of consumers research products online before making a purchase, a trend that directly impacts the bargaining dynamics in direct selling.
Low Switching Costs for Customers
For end consumers, the cost of switching away from Amway products to those offered by competitors is typically minimal. This is largely due to the absence of binding long-term contracts or substantial exit fees that would penalize a customer for changing brands.
This ease of transition directly empowers customers. If they find Amway's product offerings, pricing strategies, or the overall experience with their Independent Business Owners (IBOs) unsatisfactory, they can readily explore and adopt alternative brands. This flexibility inherently amplifies their bargaining power within the market.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers face no significant financial or contractual barriers when choosing to buy from a competitor instead of Amway.
- Increased Customer Leverage: The ability to easily switch brands gives consumers more power to demand better prices, quality, or service from Amway.
- Competitive Landscape Impact: In 2024, the direct selling industry, including companies like Amway, continues to face intense competition, making it easier for consumers to find alternatives.
Bargaining Power of Independent Business Owners (IBOs)
Amway's Independent Business Owners (IBOs) hold a notable degree of bargaining power, primarily because they function as both distributors and customers. They purchase Amway products at wholesale rates, and their purchasing decisions directly impact Amway's sales volume.
IBOs have the autonomy to select which products they order, and this choice can subtly influence Amway's product development and inventory management. Furthermore, the potential for IBOs to shift their efforts to competing multi-level marketing (MLM) or direct selling ventures means Amway must remain competitive with its product quality and compensation structures.
- Product Choice: IBOs can decide which Amway products to stock and promote, impacting demand for specific lines.
- Switching Costs: While building an Amway business requires investment, the ability to join other direct selling companies represents a degree of leverage.
- Compensation Influence: IBOs' collective desire for favorable commission rates and bonuses can pressure Amway to adjust its compensation plans.
The bargaining power of Amway's customers is significant due to low switching costs and the availability of numerous alternatives in the vast global consumer goods market. Consumers can easily compare prices and research products online, with over 70% of consumers conducting online research before purchasing in 2024, which empowers them to seek better value.
The minimal financial or contractual barriers for customers to switch brands means Amway must consistently offer competitive pricing and high-quality products to retain them. This leverage is amplified by the sheer volume of choices available, as the global beauty and personal care market alone exceeded $500 billion in 2023, presenting a wide array of substitutes.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Amway |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers are often budget-conscious and compare Amway's prices to mass-market alternatives, especially with global inflation in 2024. | Pressures Amway to maintain competitive pricing strategies. |
| Availability of Substitutes | A wide range of competitors exist in retail and online channels, offering similar health, beauty, and home care products. | Increases customer choice and reduces reliance on Amway. |
| Information Accessibility | Digital platforms and social media provide easy access to reviews, price comparisons, and product research. | Empowers customers with knowledge, enhancing their negotiation power. |
| Low Switching Costs | Customers face no significant financial or contractual penalties for switching to competing brands. | Allows customers to easily move away if dissatisfied, increasing their leverage. |
What You See Is What You Get
Amway Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. The comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis of Amway Corporation delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the direct selling industry. Understanding these forces is crucial for assessing Amway's competitive landscape and strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The direct selling and multi-level marketing (MLM) landscape is incredibly crowded, with a vast number of companies vying for market share in overlapping health, beauty, and home care sectors. This fragmentation means Amway constantly encounters rivals offering similar products and business models.
Amway grapples with formidable competition from established direct selling powerhouses such as Herbalife, Natura & Co, and Nu Skin, all of whom have significant global reach and brand recognition. Beyond direct competitors, Amway also contends with the broader consumer goods market, including major fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) companies and the ever-growing influence of online retailers.
The global direct selling industry, which includes multi-level marketing (MLM) companies like Amway, is expected to see continued growth. However, this positive outlook is tempered by Amway's own performance. In 2024, Amway reported a 3% dip in sales, reaching $7.4 billion, a situation partly influenced by a strong US dollar.
This dynamic creates a challenging competitive landscape. While the overall market offers potential, the slight decline in sales for a major player like Amway indicates that companies must fight harder for every customer and distributor. This environment naturally intensifies rivalry as businesses strive to capture and retain market share amidst varying economic conditions and consumer preferences.
Amway differentiates itself through a broad product portfolio, including health supplements under Nutrilite and cosmetics via Artistry. A key strategy involves highlighting science-backed formulations and the use of plant-based ingredients, often sourced from Amway's own agricultural operations.
This commitment to quality and innovation is designed to set Amway apart. However, many competitors in the direct selling and consumer goods space also heavily invest in research and development, creating unique product lines and making it difficult for Amway to maintain a distinct advantage solely on this front.
Brand Identity and Switching Costs
Amway, recognized as the world's leading direct selling company with a significant global footprint, benefits from strong brand recognition. However, in the wider consumer goods market, brand loyalty is often fluid, and switching costs for end-consumers are very low given the vast array of comparable products available.
This dynamic underscores the critical need for Amway to consistently foster community and cultivate loyalty among its Independent Business Owners (IBOs) and end-users alike. For instance, in 2023, Amway reported net sales of $8.4 billion, reflecting its substantial market presence, yet the challenge remains to translate this scale into deeply entrenched customer loyalty against a backdrop of easy product substitution.
- Brand Recognition: Amway is the world's number one direct selling company, boasting significant global brand awareness.
- Low Switching Costs: In the general consumer market, customers face minimal barriers to switching brands due to product availability.
- Loyalty Focus: Amway must continuously invest in building strong relationships and loyalty programs for both its IBOs and end consumers.
- Sales Performance: In 2023, Amway achieved net sales of $8.4 billion, indicating a large customer base but highlighting the ongoing challenge of brand stickiness.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers for a company like Amway are substantial, stemming from its massive investments in production facilities and its extensive global supply chain. For example, Amway operates numerous manufacturing plants worldwide, producing a vast array of products. These fixed assets represent a significant capital commitment, making a complete exit from the market economically unfeasible.
The direct selling industry, while offering relatively low barriers for individual distributors to enter and exit, presents a different scenario for established corporations. Amway's deep investment in research and development for its product portfolio, coupled with the intricate logistics of its worldwide distribution network, creates high exit barriers. This means Amway, and similar large players, are committed to the market, leading to sustained and often intense competition.
- High Capital Investment: Amway's global manufacturing footprint and R&D spending represent millions in sunk costs.
- Brand Reputation and Network: The established brand name and extensive distributor network are assets difficult to divest.
- Commitment to Market: High exit barriers ensure that major players like Amway are unlikely to leave, intensifying ongoing rivalry.
The competitive rivalry for Amway is intense due to a fragmented market with numerous direct selling companies and broader consumer goods players. Companies like Herbalife and Natura & Co present significant challenges with their global reach. Amway's 2024 sales decline to $7.4 billion, a 3% drop, underscores the pressure to maintain market share in this crowded environment.
Amway's extensive investments in manufacturing and R&D create high exit barriers, meaning major competitors are committed to the market, fueling sustained rivalry. While Amway boasts strong brand recognition as the world's leading direct selling company, low switching costs for consumers in the broader market mean loyalty is hard-won. In 2023, Amway's $8.4 billion in net sales highlights its scale but also the ongoing battle for customer retention.
| Competitor | 2023 Net Sales (Approx.) | Key Market Overlap |
| Herbalife Nutrition | $3.1 billion | Health, Wellness, Weight Management |
| Natura & Co (Avon, The Body Shop) | $3.7 billion (Natura Cosmetics) | Beauty, Personal Care, Home Care |
| Nu Skin Enterprises | $2.1 billion | Personal Care, Nutritional Supplements |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Amway is substantial, primarily stemming from traditional retail and the rapidly expanding e-commerce sector. Consumers have readily available alternatives for health, beauty, and home care products through established brick-and-mortar stores and online marketplaces.
For instance, the global e-commerce market reached an estimated $6.3 trillion in 2023, with significant growth in consumer packaged goods, a key category for Amway. This accessibility and often lower price points from competitors like Amazon or Walmart present a direct challenge to Amway's direct selling approach.
The surge of niche and specialty brands presents a significant threat of substitutes for Amway. These direct-to-consumer (D2C) brands, focusing on organic, natural, or personalized products, directly challenge Amway's traditional product lines. For instance, the global market for organic personal care products alone was valued at over $20 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong consumer preference for these specialized offerings.
These emerging brands often excel at social media and influencer marketing, effectively capturing the attention of specific consumer demographics. This digital-first approach allows them to build strong brand loyalty and appeal to younger consumers who may not be as familiar with or drawn to Amway's established network marketing model. The agility of these smaller brands in responding to evolving consumer trends further intensifies the competitive landscape.
The rise of subscription box services, particularly in beauty and wellness, presents a significant threat of substitutes for Amway. These services, offering curated selections of products delivered regularly, provide a convenient and often discovery-driven alternative to Amway's direct selling model. For example, the subscription box market, valued at approximately $22.7 billion in 2023, is projected to grow steadily, indicating a strong consumer preference for this model.
This growing popularity means consumers may find it easier and more appealing to receive a variety of brands and products through a subscription, potentially diminishing their need or loyalty to Amway's specific offerings. Such services can introduce consumers to new brands and experiences, diverting spending that might otherwise go towards Amway's product lines.
DIY and Homemade Alternatives
For certain home care and personal care items, consumers might turn to do-it-yourself (DIY) or homemade options. This shift is often motivated by a desire for cost savings, a commitment to environmental sustainability, or a preference for natural ingredients. While not a dominant force, this trend contributes to market fragmentation and provides a viable substitute for specific product segments. For example, in 2024, searches for DIY cleaning recipes saw a notable increase, particularly for all-purpose cleaners and laundry detergents, indicating a growing consumer interest in alternatives to commercially produced goods.
These homemade alternatives, while niche, can impact Amway's market share in specific product categories. The appeal of controlling ingredients and potentially reducing costs makes DIY solutions attractive to a segment of the consumer base. This is particularly relevant for products like soaps, lotions, and basic cleaning agents, where the formulation is often straightforward. Data from consumer surveys in late 2024 suggested that approximately 8% of households had experimented with making at least one home or personal care product themselves in the preceding year, primarily driven by ingredient transparency and cost concerns.
- DIY Trend: Growing consumer interest in homemade cleaning and personal care products, driven by cost and ingredient control.
- Market Impact: Contributes to market fragmentation and offers substitutes for specific product categories.
- Consumer Motivation: Cost savings, environmental concerns, and desire for natural ingredients are key drivers.
- 2024 Data: Searches for DIY cleaning recipes increased, and an estimated 8% of households experimented with DIY products.
Shift in Consumer Preferences towards Accessibility
Modern consumers increasingly prioritize convenience and instant access to products. This shift strongly favors traditional retail and e-commerce platforms, which offer immediate gratification, over direct selling models like Amway's that depend on individual business owner (IBO) interactions. For instance, the global e-commerce market was projected to reach over $6.3 trillion in 2024, highlighting the dominance of easily accessible online channels.
Amway is actively investing in its digital infrastructure and e-commerce capabilities to counter this trend. However, the fundamental change in consumer buying habits, leaning towards readily available and easily purchased goods, continues to present a significant threat from substitutes. This means consumers might opt for a similar product found on Amazon or in a local store rather than waiting for an IBO interaction.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by the growing preference for quick delivery and the ease of comparison shopping online. Consumers can effortlessly compare prices and features across numerous brands and retailers, making the direct selling model's reliance on personal relationships and product demonstrations a less appealing alternative for many.
- Consumer Preference Shift: Modern consumers increasingly value convenience and immediate gratification, favoring retail and online purchasing over direct selling.
- E-commerce Dominance: The global e-commerce market is expected to exceed $6.3 trillion in 2024, underscoring the appeal of accessible purchasing channels.
- Amway's Adaptation: Amway is enhancing its digital and e-commerce presence to align with changing consumer buying habits.
- Substitute Threat: The fundamental shift towards readily available products poses a significant threat as consumers may choose easily accessible alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for Amway is substantial, driven by the widespread availability of comparable products through traditional retail and e-commerce. Consumers can easily access health, beauty, and home care items from numerous online marketplaces and physical stores, often at competitive prices. For example, the global e-commerce market was projected to reach over $6.3 trillion in 2024, indicating the immense reach of these channels.
Niche direct-to-consumer (D2C) brands, focusing on specialized attributes like organic or personalized products, also pose a significant threat. The organic personal care market alone was valued at over $20 billion in 2023, demonstrating a strong consumer demand for alternatives that may bypass Amway's model. These brands often leverage social media effectively, appealing to demographics less familiar with network marketing.
Subscription box services further dilute Amway's market by offering curated product selections with convenience. The subscription box market, valued at approximately $22.7 billion in 2023, highlights a consumer preference for regular, discovery-driven product delivery. This model can divert consumer spending and loyalty away from Amway's direct sales approach.
Even do-it-yourself (DIY) and homemade alternatives for certain home and personal care items present a threat, driven by cost savings and ingredient control. Searches for DIY cleaning recipes saw a notable increase in 2024, with an estimated 8% of households experimenting with DIY products, underscoring a growing consumer interest in alternatives to commercial goods.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Market Size/Growth Indicator | Impact on Amway |
| Traditional Retail & E-commerce | Wide availability, competitive pricing, convenience | Global E-commerce Market > $6.3 Trillion (2024) | Direct competition for consumer spending |
| Niche D2C Brands | Specialized ingredients, targeted marketing, brand loyalty | Organic Personal Care Market > $20 Billion (2023) | Appeals to specific consumer segments |
| Subscription Boxes | Convenience, curated discovery, regular delivery | Subscription Box Market ~$22.7 Billion (2023) | Diverts spending and loyalty |
| DIY/Homemade Products | Cost savings, ingredient control, sustainability | Increased DIY recipe searches (2024), 8% household experimentation | Niche impact on specific product categories |
Entrants Threaten
While a small direct selling operation might not demand much upfront cash, building a global multi-level marketing giant like Amway is a different story. Think about the massive investments needed for product research and development, setting up manufacturing facilities, creating a complex logistics network, and supporting a vast independent business owner (IBO) base. This substantial capital outlay creates a significant hurdle for potential competitors aiming to enter the market at a comparable scale.
Amway benefits from a deeply entrenched global brand and an extensive network of over 1 million independent business owners (IBOs) built over many years. This strong brand loyalty and established distribution infrastructure present a significant barrier to new entrants.
New competitors would find it incredibly difficult and costly to replicate Amway's brand recognition and the trust it has fostered with its distributor base. Building a comparable network and achieving similar market penetration would demand substantial time and capital investment, making the threat of new entrants relatively low in this regard.
The multi-level marketing (MLM) sector, including companies like Amway, faces intensifying regulatory oversight and legal challenges worldwide. Concerns frequently arise regarding pyramid scheme accusations and the truthfulness of income representations made to distributors. For instance, in 2024, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) issued updated guidance that clarified expectations for MLMs, emphasizing the need for legitimate retail sales to end consumers, not just recruitment. This evolving regulatory environment acts as a substantial deterrent and risk for potential new entrants who must navigate these complex and often changing legal frameworks.
Access to Distribution Channels
Amway's direct selling model is built upon a vast, established network of independent business owners (IBOs). This proprietary distribution system is incredibly difficult and time-consuming for potential new entrants to replicate. Building and motivating a comparable sales force capable of reaching consumers directly presents a significant barrier.
The sheer scale and loyalty of Amway's IBO network provide a substantial competitive advantage. This entrenched distribution capability makes it challenging for newcomers to gain market access and effectively compete. For instance, as of 2024, Amway reported millions of active IBOs globally, a testament to the strength and reach of its distribution.
- Proprietary Distribution: Amway's direct selling network of IBOs is a key barrier to entry.
- Sales Force Mobilization: Replicating Amway's motivated and expansive sales force is a major hurdle for competitors.
- Market Access: The established IBO network provides Amway with direct and widespread access to consumers.
- Competitive Advantage: This unique distribution model creates a significant and difficult-to-overcome advantage for Amway.
Product and R&D Expertise
Amway's substantial investment in product and R&D expertise, particularly evident in its nutrition and beauty lines, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. The company holds a considerable portfolio of patents, underscoring its commitment to innovation and proprietary formulations. For instance, Nutrilite, Amway's flagship nutrition brand, has a long history of scientific research and development, contributing to its strong market position.
New companies aiming to enter Amway's markets would need to replicate this level of product innovation and scientific validation. This necessitates substantial, long-term financial commitments and the cultivation of specialized expertise in areas like biochemistry, pharmacology, and product development. Without comparable capabilities, new entrants would struggle to offer products that can effectively challenge Amway's established reputation for quality and efficacy.
- Significant R&D Investment: Amway consistently allocates substantial resources to research and development, a critical factor for innovation in its core sectors.
- Patent Portfolio: The company's numerous patents, especially in nutrition and beauty, create intellectual property barriers that new entrants must overcome.
- Scientific Backing: Establishing credibility requires new entrants to invest in rigorous scientific research and clinical trials, mirroring Amway's approach with brands like Nutrilite.
- Time and Resource Intensive: Developing comparable product innovation and scientific expertise is a time-consuming and capital-intensive process, deterring many potential new competitors.
The threat of new entrants for Amway is generally considered low due to several significant barriers. These include the immense capital required for global operations, the established brand loyalty and extensive distributor network, and the complex regulatory landscape. For instance, Amway's global reach and millions of active independent business owners (IBOs) as of 2024 represent a formidable challenge for any newcomer seeking to establish a similar presence.
New entrants would face substantial hurdles in replicating Amway's proprietary distribution system and mobilizing a comparable sales force. The time and financial investment needed to build such a network, coupled with the need for robust product innovation and scientific validation, act as powerful deterrents.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Amway Corporation is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, investor relations reports, and comprehensive industry research from reputable market analysis firms. We also incorporate data from regulatory filings and trade publications to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.