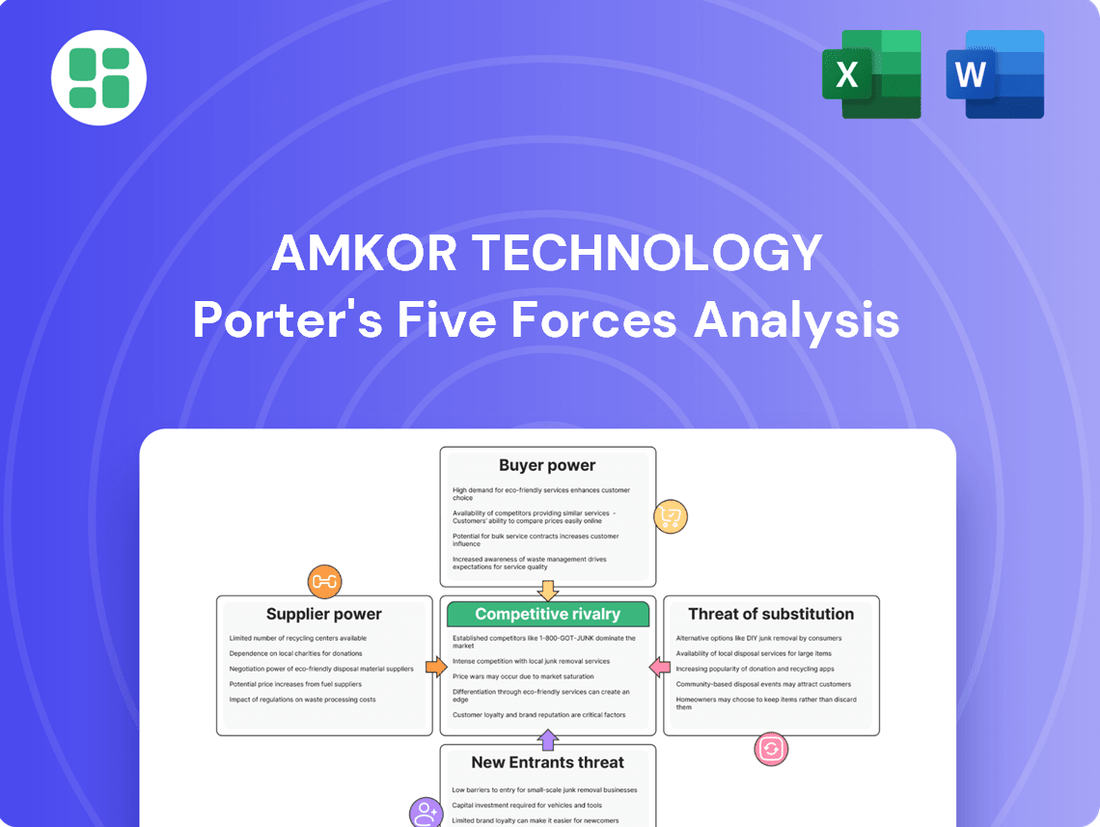
Amkor Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Amkor Technology Bundle
Amkor Technology navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry and the substantial bargaining power of its major customers. Understanding these forces is crucial for any player in the semiconductor packaging industry.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Amkor Technology’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Amkor Technology depends on suppliers for essential components like substrates, bonding wires, and molding compounds, along with specialized semiconductor assembly and testing equipment. When the market for these advanced materials or unique machinery is dominated by a small number of providers, their bargaining power escalates.
This concentration among suppliers limits Amkor's options, thereby strengthening the suppliers' leverage in price negotiations and supply terms. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor materials market saw significant consolidation, with key substrate suppliers reporting strong revenue growth, indicating their increased market influence.
Switching suppliers for the highly specialized materials and equipment Amkor Technology relies on presents significant hurdles. These often involve costly requalification processes, potential product redesigns, and the risk of production line disruptions, all of which can impact Amkor's operational efficiency and output.
Consequently, these substantial switching costs empower Amkor's existing suppliers. The financial and operational burdens associated with finding and integrating a new supplier make Amkor less inclined to frequently change its vendor base, thereby strengthening the suppliers' leverage in negotiations.
The increasing demand for advanced packaging technologies, fueled by sectors like AI and high-performance computing, necessitates highly specialized and unique input materials. This trend directly impacts Amkor Technology's supply chain dynamics.
When suppliers possess proprietary technology or exclusive access to these critical materials, their bargaining power escalates. For instance, advancements in substrate materials or specialized molding compounds, often developed through significant R&D, can create dependencies. In 2023, the global advanced packaging market was valued at approximately $45 billion, with growth projected to exceed 8% annually, underscoring the importance of these specialized inputs.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Amkor Technology's outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) services is a potential concern. If a supplier of a crucial material or component, like advanced packaging substrates or specialized testing equipment, were to develop its own OSAT capabilities, it could directly compete with Amkor. This move would allow the supplier to capture a larger portion of the value chain, potentially leading to increased pricing power and reduced negotiation leverage for Amkor.
While not a widespread occurrence, the possibility exists, especially for suppliers of highly specialized or proprietary inputs. For instance, a company that manufactures advanced wafer-level packaging materials might consider offering assembly services if the market opportunity is sufficiently attractive and they possess the necessary technical expertise. Such a scenario could disrupt Amkor's existing supply relationships and introduce a new competitive dynamic.
Consider the semiconductor industry's trend towards greater vertical integration in certain segments. In 2024, the OSAT market is highly competitive, with companies constantly seeking ways to differentiate and capture market share. If a key supplier sees an opportunity to offer a more integrated solution, from material production to final testing, it could certainly pose a threat to established OSAT players like Amkor.
- Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers of critical components (e.g., advanced substrates, testing equipment) could enter the OSAT market.
- Value Chain Capture: Such integration allows suppliers to capture more value, increasing their leverage.
- Competitive Landscape: The OSAT market's competitiveness in 2024 makes such strategic moves more plausible for suppliers.
- Potential Impact: This could lead to pricing pressures and altered supply dynamics for Amkor.
Impact of Geopolitical Factors on Supply Chains
Geopolitical tensions and trade restrictions, such as tariffs on semiconductor manufacturing equipment and materials, can significantly impact Amkor Technology's supply chain. These factors can limit the availability of certain inputs, increase their cost, and force Amkor to adjust its sourcing strategies. For instance, in 2024, ongoing trade disputes between major economies continued to create uncertainty around the global flow of critical components, potentially increasing the bargaining power of suppliers located in more stable or favorable regions.
These disruptions can increase the bargaining power of suppliers who are less affected by geopolitical instability or who possess diversified supply chains. Amkor may find itself more reliant on these suppliers, giving them leverage in price negotiations or terms of service. For example, a supplier with a robust, geographically dispersed manufacturing base might be able to maintain production and delivery schedules when others cannot, thereby commanding better terms.
- Geopolitical tensions can lead to tariffs on essential semiconductor manufacturing equipment and materials, directly impacting Amkor's input costs.
- Trade restrictions can limit the availability of specific components, forcing Amkor to seek alternative suppliers, potentially at higher prices.
- Suppliers in regions less affected by geopolitical instability or with diversified operations may see their bargaining power strengthened.
When suppliers of critical components like advanced substrates or specialized testing equipment possess unique technologies or limited production capacity, their bargaining power significantly increases. This is particularly true in 2024, as the demand for sophisticated semiconductor packaging solutions continues to surge, driven by AI and 5G technologies. For instance, the global advanced packaging market was projected to reach over $50 billion by 2024, highlighting the intense competition for specialized inputs.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Amkor's core business of outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) services also empowers them. If a key material provider were to develop its own OSAT capabilities, it could capture more value and exert greater pricing influence. This is a plausible scenario given the OSAT sector's competitive landscape in 2024, where companies are actively seeking to expand their service offerings.
Geopolitical factors and trade restrictions can further amplify supplier leverage. Tariffs or supply chain disruptions in 2024 can limit component availability and increase costs, making Amkor more dependent on suppliers operating in more stable regions, thereby strengthening their negotiating position.
| Factor | Impact on Amkor | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Proprietary Technology/Limited Capacity | Increased reliance on specialized inputs | High |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for new OSAT competitors | Moderate to High |
| Geopolitical Tensions/Trade Restrictions | Supply chain disruptions, cost increases | High |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Amkor Technology's competitive landscape reveals the intense pressure from rivals, the significant bargaining power of its customers, and the barriers to entry in the semiconductor packaging and test industry.
Quickly assess Amkor's competitive landscape and identify key threats with a pre-built, easy-to-understand model of Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Amkor Technology's customer base is global, featuring many of the largest semiconductor firms, foundries, and electronics original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). The significant volume of business from its top ten customers, who contribute a substantial portion of net sales, highlights their considerable influence.
Major semiconductor companies, particularly those in the communications and computing sectors, wield significant bargaining power. This leverage stems directly from the sheer volume of business they entrust to Amkor, allowing them to negotiate favorable terms and pricing.
Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) and some major fabless semiconductor companies are expanding their in-house capabilities for testing and advanced packaging. This trend directly impacts OSAT providers like Amkor Technology.
When customers can perform assembly and testing services themselves, their dependence on external OSATs diminishes. This self-sufficiency significantly boosts their bargaining power, allowing them to negotiate more favorable terms or even bring more business in-house.
The standardization of some outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) services can significantly amplify customer bargaining power. When many OSAT providers offer similar, commoditized solutions, customers can readily switch suppliers. This interchangeability reduces the switching costs for customers, allowing them to demand lower prices and more favorable terms from Amkor Technology.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers in sectors such as consumer electronics often exhibit significant price sensitivity, particularly when inventories are high or market demand is soft. This means they're actively looking for the best deals and are less loyal to a single supplier if a competitor offers a lower price. For companies like Amkor Technology, this translates directly into pressure to keep their own prices competitive.
This price sensitivity can be amplified during economic downturns or when specific product cycles are nearing their end. For instance, during the 2023-2024 period, many electronics manufacturers faced inventory build-ups, leading them to push harder on pricing with their component suppliers. Amkor, as a key player in the OSAT (Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test) market, felt this pressure as its clients sought to reduce overall product costs.
- Price Sensitivity Impact: Customers' focus on cost optimization can drive down OSAT service prices.
- Market Conditions: Periods of inventory correction or slow market recovery intensify customer price demands.
- Competitive Pressure: High customer price sensitivity forces OSAT providers like Amkor to manage costs rigorously.
- 2024 Data Insight: While specific pricing data for Amkor's contracts isn't publicly detailed, the broader semiconductor industry experienced pricing adjustments in 2024 due to fluctuating demand across various end markets.
Customer Access to Multiple OSAT Providers
The outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) market is quite competitive. Major players like ASE Technology Holding and JCET Group operate globally, offering customers a variety of choices. This intense competition means customers can easily switch between providers, giving them significant leverage.
Customers often have access to multiple OSAT providers, enabling them to compare pricing, service quality, and technological capabilities. For instance, in 2023, the global OSAT market was valued at approximately $45 billion, with Amkor Technology holding a notable share but facing strong competition from companies like ASE, which generated over $5.5 billion in revenue that year. This accessibility allows customers to negotiate better terms with Amkor, directly impacting Amkor's bargaining power.
- Competitive Landscape: The OSAT industry features several large, established companies and numerous smaller players, fostering a buyer's market.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers frequently prioritize cost-effectiveness, driving providers to offer competitive pricing to secure business.
- Service Differentiation: While price is key, customers also evaluate specialized services and technological advancements, but the availability of alternatives limits Amkor's pricing power.
- Switching Costs: Although switching OSAT providers can involve some effort in qualifying new suppliers, the potential cost savings often outweigh these hurdles for customers.
Amkor Technology's customers, particularly large semiconductor manufacturers and electronics OEMs, possess substantial bargaining power due to the significant volume of business they represent. This leverage allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, especially when they have the option to bring assembly and testing services in-house or switch to competing OSAT providers. The commoditization of certain OSAT services further amplifies this power, as customers can readily compare and switch suppliers, putting pressure on Amkor to remain competitive on price and service.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Amkor |
|---|---|---|
| Major Semiconductor Firms | High volume, potential for in-house capabilities, price sensitivity | Negotiate lower prices, demand customized solutions |
| Electronics OEMs | Price sensitivity, availability of alternative suppliers, inventory levels | Pressure on margins, need for cost efficiency |
| Foundries | Standardized service needs, focus on cost of goods sold | Competitive pricing essential, differentiation through advanced packaging |
Same Document Delivered
Amkor Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Amkor Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the semiconductor packaging and testing industry. You're looking at the actual document; once purchased, you'll gain instant access to this exact, professionally formatted report, ready for immediate use and strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The OSAT market is quite concentrated, with a few major companies leading the pack. ASE Technology Holding and Amkor Technology are consistently at the forefront, holding substantial market shares. However, it's important to note that Chinese OSAT providers are steadily increasing their presence and competitive edge.
This high concentration means Amkor operates in an environment where competition is fierce. The struggle to maintain and expand its market share against established rivals like ASE, and increasingly, emerging Chinese players, is a constant challenge. For instance, in 2023, the top two OSAT companies, ASE and Amkor, accounted for a significant portion of the global market, underscoring this intense rivalry.
The semiconductor packaging industry is in a constant state of flux due to rapid technological evolution, especially in areas like 2.5D, 3D, fan-out, and System-in-Package (SiP) technologies. This innovation is fueled by the growing demand for advanced computing power in AI, High-Performance Computing (HPC), and the widespread adoption of 5G networks. Amkor Technology, like its peers, faces intense pressure to stay ahead of the curve.
To remain competitive, Amkor must commit significant resources to research and development and capital expenditures. For instance, in 2023, Amkor's R&D spending was approximately $330 million, a testament to the industry's need for continuous innovation. This investment is crucial for developing and offering state-of-the-art packaging solutions that differentiate them from competitors and meet the increasingly sophisticated needs of their clients.
Competitive rivalry is heating up across the globe, especially with Chinese OSAT providers aggressively expanding. These companies benefit from strong government backing and a robust domestic market, allowing them to capture market share. For instance, China's share of the global OSAT market has been steadily growing, putting pressure on established players.
Amkor's advantage lies in its widespread global presence, enabling it to serve diverse markets. However, this also means facing intense competition in various regions, particularly in Asia where pricing pressures are significant. Navigating these varied regional competitive landscapes is crucial for Amkor's continued success.
Industry Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The global Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) industry is experiencing significant consolidation. In 2024, this trend is evident as major OSAT providers forge strategic alliances with semiconductor foundries and Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs). These partnerships are designed to create more efficient and integrated chip supply chains, reflecting a maturing market where scale and collaboration are key differentiators.
This consolidation aims to enhance competitive advantages by:
- Streamlining operations: Partners can optimize production flows and reduce lead times.
- Gaining market share: Larger, consolidated entities can better compete on price and volume.
- Driving innovation: Collaborative development between OSATs and chip designers can accelerate new technology adoption.
- Improving cost efficiencies: Economies of scale achieved through mergers and acquisitions can lead to lower per-unit costs.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity Utilization
The semiconductor assembly and test sector, where Amkor Technology operates, is inherently capital-intensive. This means companies must make substantial investments in advanced machinery and manufacturing facilities. For instance, the capital expenditure for leading players in this industry can run into hundreds of millions of dollars annually.
Because of these high fixed costs, achieving profitability hinges significantly on maintaining high capacity utilization rates. Companies like Amkor must secure a consistent flow of orders to cover their substantial overheads. This necessity often drives intense competition for business, particularly when market demand softens.
During periods of slower economic growth or reduced consumer electronics demand, the pressure intensifies. Companies are compelled to compete more aggressively on price and service to keep their production lines running at optimal levels. This can lead to price wars and thinner profit margins for all participants in the market.
- Capital Intensity: The semiconductor assembly and test industry requires significant upfront investment in specialized equipment and infrastructure.
- Profitability Driver: High fixed costs necessitate high capacity utilization to spread expenses and achieve profitability.
- Competitive Pressure: The need for high utilization fuels aggressive competition for orders, especially during demand downturns.
Competitive rivalry within the OSAT sector is intense, driven by a concentrated market structure and rapid technological advancements. Amkor Technology faces significant competition from established players like ASE Technology Holding and increasingly aggressive Chinese OSAT providers who benefit from government support. This necessitates substantial R&D investment, with Amkor spending around $330 million in 2023, to develop cutting-edge packaging solutions like 2.5D, 3D, and SiP technologies, crucial for AI, HPC, and 5G applications.
| Competitor | Approximate Market Share (2023) | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| ASE Technology Holding | Leading | Broad service portfolio, strong foundry relationships |
| Amkor Technology | Second Largest | Global presence, advanced packaging expertise |
| JCET Group (China) | Growing | Government backing, cost competitiveness |
| SPIL (Taiwan) | Significant | Specialized packaging solutions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
A notable substitute threat emerges from Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) that are increasingly bringing their packaging and testing operations in-house. This trend is particularly pronounced for advanced packaging solutions crucial for high-performance chips, such as those powering AI applications.
While outsourcing to OSATs like Amkor Technology remains attractive for cost efficiencies and specialized skills, the strategic value of controlling advanced packaging is prompting some IDMs to bolster their internal capacities. For instance, Intel has been investing heavily in its own advanced packaging technologies, aiming to capture more value chain control.
The threat of substitutes in semiconductor packaging is amplified by the rapid evolution of alternative technologies. New, disruptive methods could emerge from outside traditional OSAT (Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test) players, potentially bypassing Amkor's current core offerings.
For instance, advancements in materials science or novel manufacturing processes originating from unrelated industries might present a viable substitute solution. This is particularly concerning as the semiconductor industry continues to innovate at a breakneck pace, with global semiconductor sales projected to reach over $600 billion in 2024, highlighting the significant market for packaging solutions.
The increasing trend of System-on-Chip (SoC) integration presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional semiconductor packaging services. As more functionalities are consolidated onto a single chip, the demand for assembling and testing multiple discrete components diminishes, directly impacting companies like Amkor Technology that specialize in these areas. For instance, advancements in mobile processors, which are prime examples of SoCs, have led to fewer separate chips being needed for a smartphone's core functions.
This integration means that the need for packaging individual integrated circuits (ICs) may decline as chip designers embed more capabilities directly into the silicon. However, the threat isn't absolute; SoCs themselves often necessitate sophisticated, advanced packaging solutions to manage thermal performance, signal integrity, and the integration of diverse functionalities. For example, the demand for high-density interconnect (HDI) packaging and 2.5D/3D stacking technologies remains robust, even for SoCs, as these advanced packaging methods are crucial for unlocking the full potential of integrated systems.
Wafer-Level Testing and Burn-in
The threat of substitutes for traditional final test services offered by OSATs like Amkor Technology is evolving with advancements in wafer-level testing and burn-in. If foundries can increasingly perform comprehensive testing at the wafer stage, it could diminish the need for some outsourced final test operations. For instance, the increasing complexity of advanced packaging, which often requires extensive post-assembly testing, currently limits the extent to which wafer-level testing can fully substitute traditional methods.
However, the growing capability of wafer-level testing presents a potential substitute. For example, the market for wafer sort services, a precursor to final test, is projected to grow significantly. Some analysts estimate the wafer sort market could reach over $10 billion globally by 2025, indicating a shift in where testing is performed. This trend could reduce the volume of certain types of testing outsourced to OSATs, particularly for less complex integrated circuits.
- Advancements in wafer-level testing and burn-in processes: These technologies allow for more thorough testing of semiconductor wafers before they are cut into individual chips.
- Foundry capabilities: If foundries enhance their wafer-level testing capabilities, they might absorb more of the testing process, reducing the scope for OSATs.
- Impact on OSAT services: This could potentially substitute some of the traditional final test services that OSATs have historically provided.
- Continued need for final testing: Despite wafer-level advancements, complex and advanced packaging technologies still necessitate extensive final testing after assembly, mitigating the full substitution effect.
Software-Defined Hardware and Virtualization
The rise of software-defined hardware and increased virtualization presents a subtle, long-term threat to Amkor Technology. While not a direct physical substitute for semiconductor packaging, these trends could indirectly impact demand. Optimization at the software level might reduce the need for the incremental hardware performance gains that advanced packaging often enables.
For instance, in 2024, the continued push for cloud computing and edge AI relies heavily on sophisticated software algorithms to manage and optimize processing power. This could mean that instead of requiring more powerful, and thus more complexly packaged, chips for certain tasks, the same or better results are achieved through smarter software. This shift could dampen the demand for specialized, high-performance packaging solutions if software innovation can sufficiently bridge performance gaps.
- Software-Defined Hardware: Enables greater flexibility and resource allocation without necessarily requiring new physical hardware.
- Virtualization Trends: Allows for the consolidation of workloads and improved utilization of existing computing resources.
- Indirect Impact: Reduced reliance on raw hardware performance improvements could lessen the demand for cutting-edge, high-margin packaging technologies.
The threat of substitutes for Amkor Technology's services is multifaceted. Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) increasingly bringing advanced packaging in-house, like Intel's investments, directly reduce the need for outsourced solutions. Furthermore, advancements in wafer-level testing, with the market projected to exceed $10 billion by 2025, could substitute some final testing operations, though complex packaging still requires post-assembly checks.
The growing trend of System-on-Chip (SoC) integration, where more functions are consolidated onto a single chip, diminishes the demand for assembling discrete components. However, these SoCs themselves often require sophisticated, advanced packaging, thus creating a complex dynamic. Additionally, software-defined hardware and virtualization offer an indirect threat by potentially reducing reliance on raw hardware performance gains that advanced packaging typically provides.
| Substitute Threat | Description | Impact on Amkor | Supporting Data/Example |
| In-house IDM Packaging | IDMs performing their own advanced packaging. | Reduced outsourcing demand. | Intel's investment in advanced packaging technologies. |
| Wafer-Level Testing | Increased testing at the wafer stage. | Potential substitution of final test services. | Wafer sort market projected to exceed $10 billion by 2025. |
| System-on-Chip (SoC) Integration | Consolidating multiple functions onto a single chip. | Decreased demand for assembling discrete components. | Advancements in mobile processors reducing discrete chip needs. |
| Software-Defined Hardware/Virtualization | Software optimization reducing hardware needs. | Indirectly dampens demand for high-performance packaging. | Cloud computing and edge AI relying on software algorithms for performance. |
Entrants Threaten
The semiconductor assembly and test sector demands immense capital, with new entrants needing billions for advanced equipment, cleanrooms, and R&D. For instance, establishing a state-of-the-art facility capable of competing with established players like Amkor Technology would likely require investments exceeding $1 billion. This high upfront cost, coupled with the need to achieve significant economies of scale to drive down per-unit costs, presents a formidable barrier to entry for potential new competitors.
The semiconductor packaging industry, particularly for advanced solutions like 2.5D, 3D, and fan-out packaging essential for AI and high-performance computing, demands substantial and continuous investment in research and development. Amkor Technology, for instance, consistently allocates significant resources to innovation, underscoring the high barrier to entry for newcomers. In 2023, Amkor reported R&D expenses of $310.8 million, highlighting the financial commitment required to remain competitive in this technologically intensive sector.
Amkor Technology, a leader in outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT), benefits from deeply entrenched customer relationships. These partnerships, forged over years of consistent performance and collaborative innovation with major semiconductor firms, represent a formidable barrier to new entrants. Building comparable trust and reliability with these demanding clients is a substantial hurdle for any newcomer seeking to disrupt the market.
Intellectual Property and Patents
The OSAT (Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test) industry, where Amkor Technology operates, is heavily protected by intellectual property and patents. This creates a significant barrier for potential new entrants. Developing and securing patents for advanced packaging designs, intricate manufacturing processes, and sophisticated testing methodologies requires substantial investment and time.
New players entering this market would face the considerable challenge of navigating this existing IP landscape. This could involve substantial licensing fees to utilize patented technologies or the immense cost and effort of developing entirely novel, non-infringing solutions. For instance, Amkor Technology itself holds a robust portfolio of patents that safeguard its innovative approaches to semiconductor packaging. In 2023, the semiconductor industry saw significant R&D spending, with major players investing billions, underscoring the importance of IP in maintaining competitive advantage.
- High R&D Investment: Significant capital is required to develop and patent new packaging technologies.
- Patent Landscape Navigation: New entrants must overcome existing patents, potentially through costly licensing.
- Proprietary Technology Development: Creating unique, non-infringing technologies is a lengthy and expensive process.
- Competitive Advantage: Amkor's patent portfolio provides a strong defense against new competition.
Regulatory and Geopolitical Landscape
The semiconductor industry is increasingly shaped by government policies, subsidies, and trade regulations, especially concerning domestic manufacturing and supply chain resilience. For instance, the US CHIPS and Science Act, enacted in 2022, allocated over $52 billion to boost domestic semiconductor production and research, creating a complex subsidy landscape that new entrants must navigate.
New players may encounter significant hurdles in understanding and complying with the diverse and often evolving regulatory environments across different countries. Geopolitical considerations, such as export controls and national security reviews, can disproportionately favor established companies with existing relationships and a proven track record in sensitive markets.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating differing national standards and compliance requirements for semiconductor manufacturing and intellectual property protection.
- Geopolitical Influence: Managing risks associated with trade disputes, sanctions, and national security concerns that can impact market access and supply chains.
- Subsidies and Incentives: Competing with established firms that benefit from government support aimed at bolstering domestic semiconductor industries, such as those seen in the US and EU.
The threat of new entrants in the semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) sector, where Amkor Technology operates, is significantly mitigated by several factors. The immense capital required for advanced manufacturing facilities and cutting-edge research presents a substantial financial barrier. For example, establishing a competitive OSAT facility in 2024 would likely necessitate investments well over $1 billion, covering specialized equipment and cleanroom infrastructure.
Amkor Technology's robust patent portfolio and deep-seated customer relationships further solidify its market position, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. The industry's reliance on proprietary technology and the need to build trust with major semiconductor clients over years of consistent performance create high switching costs for customers, effectively locking in existing players.
Navigating the complex global regulatory landscape and securing necessary government approvals and subsidies, such as those provided by the US CHIPS Act, also poses a significant challenge for potential new entrants. These regulatory and geopolitical complexities favor established companies with proven track records and existing compliance frameworks.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Amkor Technology's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Extremely High (>$1 billion for a new advanced facility) | Established infrastructure and economies of scale |
| R&D Investment | Substantial and continuous ($310.8 million in 2023 for Amkor) | Leading innovation in advanced packaging |
| Customer Relationships | Difficult to establish trust and reliability | Long-standing partnerships with major semiconductor firms |
| Intellectual Property | Requires costly licensing or extensive development | Strong patent portfolio protecting proprietary technologies |
| Regulatory Environment | Complex navigation of global policies and subsidies | Established compliance and experience with government programs |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Amkor Technology is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Amkor's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We also incorporate insights from leading industry research firms and market intelligence platforms to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.