AMG Critical Materials Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
AMG Critical Materials Bundle
AMG Critical Materials operates in a dynamic landscape shaped by intense competition, significant supplier power, and the ever-present threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate this complex market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping AMG Critical Materials’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The sourcing of critical materials for AMG Critical Materials, such as lithium, vanadium, tantalum, niobium, and silicon, is often concentrated geographically and controlled by a small number of mining firms. This limited supply base grants suppliers significant leverage, potentially forcing AMG to accept higher prices for essential inputs due to a lack of viable alternatives.
For example, Brazil's near-monopoly on niobium supply, coupled with Africa's substantial contribution to tantalum production, highlights this supplier concentration. Furthermore, China's dominant position in rare earth elements and graphite refining underscores the potential for suppliers in these key areas to dictate terms, impacting AMG's cost structure and operational flexibility.
AMG Critical Materials operates in a sector where the uniqueness and scarcity of its core products significantly influence supplier power. The company's focus on highly engineered specialty metals like vanadium, lithium, and tantalum means these materials possess properties that are not easily substituted. For instance, tantalum's exceptional dielectric properties make it indispensable in high-performance capacitors, a demand that remains robust.
This inherent difficulty in replication, coupled with the often geographically concentrated sources of these critical minerals, grants suppliers considerable leverage. When substitutes are either nonexistent or require substantial research and development investment, along with considerable switching costs for AMG, suppliers can command higher prices or more favorable terms.
High switching costs significantly bolster the bargaining power of AMG's suppliers. For instance, the specialized nature of critical materials often necessitates rigorous re-qualification of new suppliers, a process that can take months and incur substantial engineering and testing expenses. These costs, coupled with the logistical challenges of integrating new supply chains across AMG's diverse global footprint, create a strong incentive to maintain existing relationships, thereby empowering suppliers in price and term negotiations.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers of critical materials for AMG could indeed move into processing or even manufacturing of specialty metal products, effectively becoming direct rivals. This forward integration is a significant concern, particularly as the demand for these materials grows.
While highly specialized processes might deter some suppliers, a shift towards commoditization in raw material markets or a supplier's ambition to capture greater value could accelerate this trend. For instance, a major lithium producer might consider developing its own battery-grade lithium chemicals, directly competing with companies like AMG that refine and process these materials.
The global push for supply chain resilience and the strategic importance of domestic processing, especially in sectors like electric vehicles and renewable energy, could further incentivize suppliers to integrate forward. This is evident in government initiatives aimed at onshoring critical mineral processing, potentially creating new competitive pressures for companies like AMG. In 2024, several countries announced substantial investments in domestic battery material processing facilities, signaling a growing appetite for vertical integration within the supply chain.
- Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers of critical materials may vertically integrate into downstream processing or manufacturing of specialty metal products, directly challenging AMG's market position.
- Market Dynamics: The threat intensifies if raw material markets become commoditized or if suppliers aim to capture higher margins by moving up the value chain.
- Geopolitical Influence: Increased emphasis on supply chain security and domestic processing, a trend amplified in 2024, could encourage suppliers to pursue forward integration strategies.
Market Dynamics and Price Volatility of Raw Materials
The bargaining power of suppliers for AMG Critical Materials is significantly influenced by the market dynamics and price volatility of essential raw materials. Fluctuations in supply and demand, coupled with geopolitical events and investment shifts, can create substantial price swings. For instance, lithium saw a notable oversupply and subsequent price drop in early 2025, even with robust long-term demand projections. Conversely, vanadium is anticipated to face a supply shortage in 2025.
This inherent volatility directly affects AMG's operational costs and overall profitability. When supply is constrained or prices are on an upward trend, suppliers gain considerable leverage. This can translate into higher input costs for AMG, potentially squeezing profit margins if these increases cannot be passed on to customers.
- Lithium Price Volatility: Oversupply led to price declines in early 2025, impacting producers and consumers.
- Vanadium Supply Deficit: Projected shortfall in 2025 strengthens supplier negotiating positions.
- Geopolitical Impact: Global events can disrupt supply chains, leading to price spikes and increased supplier power.
- Investment Trends: Shifts in investment towards or away from specific critical materials influence their availability and pricing.
Suppliers of critical materials wield significant power due to geographic concentration and limited producers, forcing AMG to accept higher prices. Brazil's niobium dominance and Africa's tantalum contribution exemplify this, as does China's grip on rare earths and graphite. The specialized nature of these materials, like tantalum's unique dielectric properties, makes substitution difficult, further empowering suppliers.
High switching costs, including extensive re-qualification and logistical integration, lock AMG into existing supplier relationships. This significantly strengthens suppliers' leverage in price and term negotiations, making it costly and time-consuming for AMG to find and onboard alternative sources. For instance, integrating a new tantalum supplier could involve months of engineering and testing.
The risk of suppliers moving into downstream processing or manufacturing of specialty metal products presents a direct competitive threat. This forward integration is driven by ambitions to capture greater value, especially as demand for these materials escalates. Government initiatives in 2024 promoting domestic processing, particularly for battery materials, are accelerating this trend.
Market volatility, such as the lithium oversupply and price drop in early 2025 and the projected vanadium shortage for 2025, directly impacts AMG's costs and supplier leverage. Geopolitical events and investment shifts further exacerbate these price swings, granting suppliers increased power during periods of constrained supply or rising prices.
| Critical Material | Key Supplier Concentration | 2025 Price Trend (Projected/Observed) | Supplier Bargaining Power Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Niobium | Brazil (near-monopoly) | Stable/Slight Increase | High (Geographic Concentration) |
| Tantalum | Africa (substantial contribution) | Stable | Moderate to High (Geographic Concentration, Specialization) |
| Rare Earth Elements | China (dominant) | Volatile | Very High (Geographic Concentration, Processing Dominance) |
| Graphite | China (dominant refining) | Volatile | Very High (Geographic Concentration, Processing Dominance) |
| Lithium | Global (various major producers) | Oversupply, Price Decline (Early 2025) | Moderate (Market Oversupply, but Long-term Demand) |
| Vanadium | Global (few major producers) | Projected Shortage (2025) | High (Anticipated Supply Deficit) |
What is included in the product
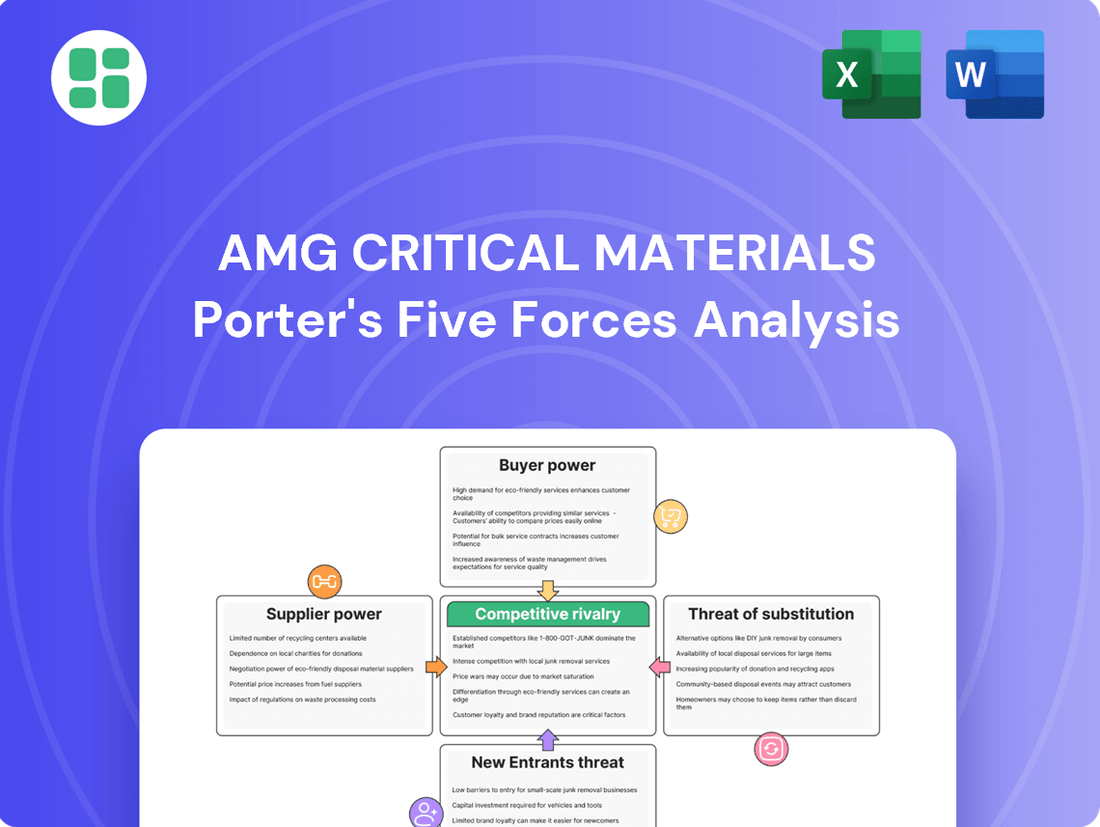
This analysis meticulously examines the competitive forces impacting AMG Critical Materials, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the prevalence of substitutes.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats in the critical materials market with a comprehensive, actionable Porter's Five Forces analysis.
Customers Bargaining Power
AMG Critical Materials' bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the concentration of key customer industries it serves. The company's focus on specialized sectors like infrastructure, energy storage, and aerospace means that a few major players can hold substantial sway. For instance, if a handful of large automotive manufacturers, a primary market for energy storage materials, represent a significant chunk of AMG's revenue, these clients can leverage their purchasing volume to negotiate more favorable pricing and terms. This dynamic is amplified by the fact that these industries often require highly engineered products with very specific performance requirements.
AMG's highly engineered products are integral to demanding sectors like aerospace and sustainable technologies, meaning customers face substantial hurdles if they switch suppliers. These specialty metals are embedded in complex systems, making a change in provider a costly and time-consuming endeavor involving extensive re-design and rigorous qualification.
AMG's strategic positioning as a global leader in critical materials for the energy transition, with a focus on CO2 emission reduction, creates a compelling value proposition. This differentiation is key to mitigating customer bargaining power.
The unique performance characteristics of AMG's products, such as those incorporated into LIVA batteries or advanced CO2 capture systems, make direct substitution by customers difficult. For instance, the specialized nature of materials for high-performance batteries means customers are reliant on AMG's specific formulations and quality, thereby reducing their leverage.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for AMG Critical Materials. While their products are essential for industries like energy storage and automotive, particularly for electric vehicles, these sectors are acutely aware of total system costs. This means raw material prices, including those for lithium, directly impact customer demand and their willingness to absorb higher prices, potentially squeezing AMG's profit margins.
For example, the sharp decline in lithium prices observed in early 2025 directly illustrated this sensitivity. When the cost of a key input like lithium falls, customers naturally expect to see those savings reflected in the final product price. This creates downward pressure on AMG’s pricing power, even for critical materials.
- High Price Sensitivity in Key Sectors: Industries such as electric vehicle manufacturing and energy storage are highly focused on the overall cost of their end products, making them sensitive to the price of critical raw materials supplied by AMG.
- Impact of Lithium Price Fluctuations: The market experienced significant volatility in lithium prices during early 2025, demonstrating how these swings can directly influence customer purchasing decisions and their tolerance for premium pricing.
- Margin Pressure: When raw material costs decrease, customers often demand lower prices for AMG's products, which can lead to reduced profit margins for the company.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers might explore backward integration, essentially producing specialty metals or refining critical materials themselves. This is particularly relevant for high-volume sectors like electric vehicle battery manufacturing, where securing supply is paramount.
However, the significant capital investment, specialized technical knowledge, and stringent regulatory requirements associated with producing highly engineered specialty metals, such as those offered by AMG, present substantial barriers. For instance, establishing a state-of-the-art refining facility for critical materials can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars, making it an unfeasible option for most customers.
- High Capital Outlay: Building new production facilities for specialty metals requires immense upfront investment, often exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Technical Expertise Gap: The complex metallurgical processes and quality control needed for AMG's products demand specialized engineering and operational skills that are not readily available.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Environmental permits and compliance with safety standards for metal production are rigorous and time-consuming to obtain.
- Economies of Scale: Established players like AMG benefit from economies of scale that are difficult for new entrants, including potential customers, to match.
AMG Critical Materials faces significant customer bargaining power, particularly from large players in sectors like electric vehicles and energy storage. These customers are highly sensitive to price, as demonstrated by the early 2025 lithium price drop, which pressured AMG’s margins. While customers could consider backward integration, the immense capital, technical expertise, and regulatory hurdles for producing specialty metals like AMG's create substantial barriers, limiting their ability to exert leverage.
| Factor | Impact on AMG | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High dependence on a few large buyers in key industries. | Significant, as large buyers can command better terms. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers closely monitor raw material costs, impacting demand. | High, especially in price-competitive sectors like EVs. |
| Switching Costs | High due to specialized product integration and qualification. | Low for customers, as changing suppliers is difficult and costly. |
| Backward Integration Potential | Customers may consider in-house production for supply security. | Moderate, but limited by high barriers to entry. |
Same Document Delivered
AMG Critical Materials Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete AMG Critical Materials Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing a thorough examination of industry competitiveness. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, offering actionable insights without any placeholders or surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The critical materials market, particularly for those enabling the energy transition, is booming. Projections show the global critical minerals market reaching hundreds of billions of dollars by 2032, indicating substantial growth potential.
This rapid expansion often tempers direct competition, as firms prioritize securing new supply and meeting burgeoning demand. However, this dynamic isn't uniform; for instance, the lithium market faced oversupply issues in 2025, intensifying price competition among producers.
The specialty metals and critical materials landscape is populated by a wide array of companies, ranging from global giants like BHP and Rio Tinto with their extensive mining operations to niche specialists such as AMG. This diversity means competition isn't just about price but also about technological innovation and supply chain reliability across segments like vanadium, lithium, and tantalum.
In 2024, the critical minerals sector saw continued robust demand, driven by the energy transition and technological advancements. For instance, the global lithium market alone was projected to reach over $30 billion, highlighting the significant revenue potential that attracts both large diversified miners and specialized producers, thereby intensifying rivalry for these valuable resources.
AMG's strategy of focusing on highly engineered specialty metals and mineral products, particularly those critical for the energy transition and CO2 reduction, inherently lowers direct rivalry. For instance, their expertise in vanadium recycling and advanced metallurgy creates a niche, differentiating them from producers of more commoditized raw materials. This specialization means fewer companies are competing directly on the same highly specific product offerings.
While AMG's specialization reduces competition in certain segments, the market for materials like silicon metal, where AMG also operates, is more competitive. In 2023, the global silicon metal market was valued at approximately USD 7.1 billion, with several key players vying for market share. This indicates that even within AMG's broader portfolio, the intensity of rivalry can vary significantly depending on the specific product category.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity Utilization
The production of critical materials, including specialty metals, demands substantial upfront investment in mining, processing, and refining infrastructure. AMG, for instance, has made significant capital commitments to expand its lithium and vanadium operations, underscoring the high fixed costs inherent in this sector.
These substantial fixed costs create pressure for companies to maintain high capacity utilization. When demand softens, there's a strong incentive to lower prices to keep production lines running and cover overheads, which naturally escalates competitive rivalry among players in the market.
- High Capital Expenditure: AMG's investments in lithium and vanadium expansion projects highlight the significant capital outlays required for critical materials production.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: Substantial fixed costs compel companies to operate at high capacity, leading to aggressive pricing strategies during demand downturns.
- Intensified Rivalry: The drive for capacity utilization can result in price wars, intensifying competition among critical materials producers.
Exit Barriers and Industry Consolidation
High capital investments and the need for specialized, often proprietary, assets create substantial exit barriers in the critical materials industry. This can trap less profitable companies in the market, potentially exacerbating oversupply and intensifying competitive rivalry among existing players.
While strategic investments and partnerships do occur, the critical materials sector has not experienced the widespread consolidation seen in some other industries. This lack of significant consolidation means the number of major players remains relatively high, contributing to ongoing competitive pressures.
- High Capital Intensity: Building and maintaining facilities for critical materials often requires billions of dollars in upfront investment, making it difficult for companies to divest or shut down operations easily.
- Specialized Assets: Many assets are highly specific to particular critical materials or processes, limiting their resale value or alternative use, thereby increasing exit costs.
- Limited Consolidation: As of early 2024, the market has seen fewer large-scale mergers and acquisitions that would meaningfully reduce the competitive landscape compared to more mature sectors.
Competitive rivalry in critical materials is influenced by specialization, with companies like AMG focusing on niche, high-value products such as vanadium and lithium compounds, which can temper direct competition. However, in more commoditized segments like silicon metal, where AMG also operates, rivalry is more pronounced, as evidenced by the approximately USD 7.1 billion global silicon metal market in 2023 and the presence of numerous competitors.
High capital expenditures for mining and processing create pressure for high capacity utilization, leading to intensified price competition, especially during demand slowdowns. For example, the lithium market experienced oversupply and price competition in 2025. The lack of significant consolidation in the sector also means a higher number of players, contributing to ongoing competitive pressures.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for AMG Critical Materials is a significant consideration, particularly as alternative materials or different chemistries gain traction in key markets. For instance, in the rapidly evolving energy storage sector, while AMG is heavily invested in lithium and vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs), the emergence of sodium-ion batteries or other novel battery chemistries could present viable alternatives to lithium-ion technology. This diversification of battery chemistries, driven by factors like cost reduction and material availability, poses a direct substitute threat to AMG's core lithium products.
The threat of substitutes for AMG's critical materials hinges on their capacity to rival or surpass current performance benchmarks while simultaneously offering a more attractive price point. For instance, while AMG's specialty metals are vital for advanced battery technologies, research into novel composite materials or alternative chemical formulations could present viable alternatives that reduce reliance on current supply chains, potentially impacting AMG's market share.
Even when alternative materials are available, the financial and operational hurdles for AMG's customers to transition can be substantial. These costs often involve significant investments in new machinery, redesigning existing products, and rigorous validation processes. For instance, in the highly regulated aerospace sector, the certification alone for a new material can take years and cost millions, effectively locking in current material choices.
Technological Advancements in Substitution
Rapid technological advancements are a significant threat, especially in sectors like battery technology. For instance, the ongoing race to improve energy density and reduce charging times in electric vehicles means that new battery chemistries or architectures could emerge, potentially diminishing the demand for current materials used in these applications. This constant evolution in material science means that a breakthrough could render existing solutions less competitive.
The continuous innovation in material science is a key driver of this threat. Companies are investing heavily in research and development to discover and implement novel materials. For example, the pursuit of lighter and stronger alloys for aerospace and automotive industries could lead to substitutes that offer comparable or superior performance at a lower cost or with better environmental profiles, directly impacting AMG's market position.
- Battery Technology Evolution: Innovations in solid-state batteries or alternative chemistries like sodium-ion could reduce reliance on current lithium-based materials.
- Lightweight Material Development: Advances in composites, advanced ceramics, or even bio-based materials may offer alternatives to AMG's specialty alloys in various applications.
- Material Performance Breakthroughs: New material discoveries could offer enhanced conductivity, thermal resistance, or durability, creating viable substitutes.
- Cost-Competitiveness: Emerging materials, especially if driven by scalability and lower input costs, can quickly become attractive alternatives.
Regulatory and Environmental Drivers for Substitution
The threat of substitutes for critical materials is amplified by evolving regulatory and environmental pressures. As governments and international bodies implement stricter environmental standards, companies are increasingly seeking materials with lower carbon footprints or those sourced ethically. For instance, by 2024, the European Union's Critical Raw Materials Act aims to diversify supply chains and promote the use of recycled materials, potentially pushing demand towards substitutes if primary sources remain problematic.
Concerns regarding the supply chain stability and ethical sourcing of certain critical materials, such as cobalt or rare earth elements, directly encourage the exploration and adoption of alternatives. If these issues persist or worsen, customers may be compelled to switch to substitute materials, even if they initially involve higher costs or slightly compromised performance. This trend is already visible in the automotive sector, where efforts to reduce reliance on ethically challenging materials are driving innovation in battery chemistries.
- Regulatory Push: EU's Critical Raw Materials Act (2024) aims to boost recycling and diversification, incentivizing substitutes.
- Environmental Footprint: Growing demand for materials with lower carbon emissions and sustainable sourcing.
- Ethical Sourcing Concerns: Issues with cobalt and rare earth element supply chains are prompting a search for alternatives.
- Performance Trade-offs: Customers may accept slightly inferior performance from substitutes if supply or ethical issues with primary materials are significant.
The threat of substitutes for AMG Critical Materials is influenced by technological advancements and cost-competitiveness. For example, the development of sodium-ion batteries, which use more abundant and cheaper materials, presents a direct substitute threat to lithium-ion batteries, a key market for AMG's lithium products. Similarly, advancements in composite materials or alternative alloys could displace specialty metals in aerospace and automotive applications if they offer comparable performance at a lower price point.
Customer inertia and switching costs also play a role in mitigating the threat of substitutes. Significant investments in new equipment, product redesign, and regulatory approvals can deter customers from adopting alternative materials, even if they appear more attractive on paper. For instance, the aerospace industry's stringent certification processes can create long lead times and high costs for material changes, effectively locking in existing suppliers.
The push for sustainability and ethical sourcing further fuels the search for substitutes. Concerns over the environmental impact and supply chain stability of certain critical materials, like cobalt, are driving innovation in alternative chemistries and material sourcing. The European Union's Critical Raw Materials Act, enacted in 2024, aims to promote recycling and supply chain diversification, potentially increasing the adoption of substitute materials.
| Substitute Material/Technology | Target Market | Potential Impact on AMG | Key Drivers | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium-ion batteries | Energy Storage (EVs, grid storage) | Reduced demand for lithium | Lower cost, material abundance | Emerging battery manufacturers developing sodium-ion solutions |
| Advanced composites | Aerospace, Automotive | Reduced demand for specialty alloys | Lightweighting, performance improvements | Development of carbon fiber reinforced polymers |
| Recycled materials | Electronics, Automotive | Reduced demand for primary critical materials | Sustainability, circular economy initiatives | Increased use of recycled aluminum and copper |
| Alternative battery chemistries (e.g., solid-state) | Energy Storage (EVs) | Potential disruption to current battery material demand | Improved safety, energy density | Ongoing R&D by major automotive and battery companies |
Entrants Threaten
The specialty metals and critical materials sector demands enormous upfront capital. Newcomers must finance extensive exploration, develop sophisticated mining operations, construct processing plants, and establish advanced manufacturing capabilities. This high capital intensity inherently limits the number of potential new entrants.
AMG Critical Materials' own strategic investments underscore this reality. For instance, their significant capital expenditure on lithium and vanadium expansion projects in 2024, totaling hundreds of millions of dollars, demonstrates the substantial financial commitment required to compete. These large-scale investments create a formidable barrier, deterring smaller or less capitalized firms from entering the market.
Developing and producing highly engineered specialty metals and mineral products, like those AMG Critical Materials offers, demands substantial investment in research and development. This R&D focus, coupled with the need for specialized technical expertise and protected intellectual property, creates a formidable barrier for potential newcomers. For instance, the specialty metals sector often sees R&D spending as a significant percentage of revenue, with some companies dedicating over 5% of their sales to innovation and product development, a level that requires deep pockets and advanced metallurgical understanding to match.
Established players like AMG Critical Materials benefit from deeply entrenched global supply chains for crucial raw materials, a significant barrier for newcomers. These existing networks are difficult and costly to replicate, especially when sourcing specialized or geographically concentrated inputs.
Furthermore, AMG's long-standing relationships with customers in high-stakes sectors such as aerospace and advanced energy storage represent another formidable hurdle. Gaining the trust and qualifying for the stringent specifications demanded by these industries requires years of proven performance and reliability, which new entrants lack.
Regulatory Hurdles and Environmental Compliance
The critical materials sector faces substantial regulatory hurdles, especially concerning environmental compliance and permitting. For instance, the European Union's Critical Raw Materials Act, proposed in 2023 and aiming for adoption in 2024, sets ambitious targets for domestic extraction and processing, but also imposes strict environmental and social governance (ESG) requirements. These regulations can significantly increase the upfront investment and operational costs for new players, acting as a considerable barrier to entry.
Navigating these complex requirements, which include obtaining numerous permits for extraction, processing, and waste management, can be a lengthy and costly process. For example, establishing a new mine can take an average of 10-15 years to permit and develop. This extended timeline and the associated expenses deter many potential entrants, particularly those without substantial capital or established expertise in regulatory affairs.
- Stringent Environmental Regulations: Compliance with evolving environmental standards, such as those related to water usage, emissions, and land reclamation, demands significant investment in technology and processes.
- Complex Permitting Processes: Obtaining necessary permits for exploration, extraction, and processing can be time-consuming, often taking over a decade, and requires extensive documentation and stakeholder engagement.
- High Compliance Costs: The ongoing costs associated with maintaining environmental compliance, including monitoring, reporting, and implementing best practices, add to the operational burden for new entrants.
- Quality and Safety Standards: Meeting rigorous quality and safety standards, particularly for materials used in advanced technologies or sensitive applications, necessitates specialized equipment and quality control systems, further increasing entry barriers.
Economies of Scale and Cost Advantages
The threat of new entrants into the critical materials sector, particularly for companies like AMG, is significantly mitigated by substantial economies of scale and inherent cost advantages. Established players have honed their operational efficiencies through years of experience and substantial investment, leading to lower per-unit production costs.
Newcomers would struggle to match these cost efficiencies. For instance, in 2024, the global lithium market saw significant price volatility, but large-scale producers could absorb these fluctuations more readily than smaller, nascent operations. AMG's global footprint allows for bulk purchasing of raw materials and optimized logistics, creating a cost barrier that is difficult for new entrants to overcome. The capital required to build comparable production facilities and establish robust supply chains is immense, acting as a powerful deterrent.
- Economies of Scale: AMG leverages its global production capacity, which in 2023 exceeded 100,000 metric tons for certain materials, to drive down per-unit costs.
- Procurement Advantages: Bulk purchasing of key inputs like lithium hydroxide and rare earth elements in 2024 allowed AMG to secure more favorable pricing compared to smaller potential competitors.
- Distribution Network: AMG's established logistics and distribution channels across multiple continents reduce shipping costs and improve delivery times, a significant hurdle for new market entrants.
- Capital Intensity: The high upfront investment for specialized processing equipment and facilities, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars, deters new companies from entering the market.
The threat of new entrants in the critical materials sector is considerably low due to extreme capital intensity, requiring hundreds of millions in investment for exploration, processing, and advanced manufacturing. AMG Critical Materials' own 2024 capital expenditures on lithium and vanadium expansion, exceeding hundreds of millions, exemplify this barrier. Furthermore, significant R&D investment, often over 5% of revenue, and the need for specialized expertise create a high entry cost that deters many potential competitors.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Data/Impact |
| Capital Intensity | High upfront investment for mining, processing, and manufacturing. | AMG's 2024 lithium/vanadium expansion cost hundreds of millions. |
| R&D and Expertise | Need for specialized technical knowledge and innovation investment. | Sector R&D spending often exceeds 5% of revenue. |
| Supply Chain Entrenchment | Established global networks for raw material sourcing. | Difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate existing networks. |
| Customer Relationships | Long-standing trust and qualification in high-stakes industries. | Years of proven performance required for aerospace and energy sectors. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex environmental compliance and permitting processes. | New mine development can take 10-15 years to permit. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale production and procurement. | AMG's 2023 production capacity exceeded 100,000 metric tons for certain materials. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our AMG Critical Materials Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of verified data, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Wood Mackenzie, and relevant government publications detailing resource availability and policy. We also incorporate insights from financial databases and trade journals to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.