Alpha Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Alpha Bank Bundle
Alpha Bank faces significant competitive pressures, particularly from the intense rivalry among existing players and the growing threat of new entrants, especially fintech disruptors. Understanding the bargaining power of both customers and suppliers is crucial for navigating this landscape. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Alpha Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Alpha Bank's access to core funding sources, primarily retail and corporate deposits, is a critical element in understanding supplier power. While a stable deposit base is fundamental, recent trends show that persistently low deposit rates in 2023 and early 2024 have nudged some customers toward alternative savings vehicles, suggesting a slight increase in depositor bargaining power as they seek higher yields.
However, Alpha Bank has actively diversified its funding by accessing international capital markets and adhering to stringent regulatory standards. This strategic move broadens its supplier base for capital, mitigating the concentrated power of any single deposit segment and providing greater financial flexibility.
Alpha Bank's increasing reliance on technology and digital solutions providers for its transformation amplifies their bargaining power. As the bank integrates advanced software, hardware, and AI tools, these specialized suppliers become critical. For instance, partnerships with giants like Microsoft and EY Greece for AI integration in 2024 highlight the influence of providers offering cutting-edge capabilities essential for enhancing efficiency and customer experience.
The banking industry, including institutions like Alpha Bank, heavily relies on specialized expertise. Professionals skilled in digital transformation, cybersecurity, and sophisticated financial modeling are in high demand. This scarcity of talent means that employees with these in-demand skills can negotiate for better compensation and benefits, giving them a degree of bargaining power.
Financial Market Infrastructure Providers
Financial market infrastructure providers, including vital services like payment systems, clearing houses, and interbank lending platforms, wield considerable bargaining power. Their critical role in facilitating daily banking operations means institutions like Alpha Bank are deeply reliant on their seamless functioning. For instance, the global payments market was valued at over $2 trillion in 2023, highlighting the sheer scale and importance of these infrastructure providers.
The interconnectedness of these systems further amplifies their influence. A disruption in one area can have cascading effects across the entire financial ecosystem, making banks hesitant to challenge these essential suppliers. In 2024, regulatory scrutiny on financial market infrastructure has intensified, with bodies like the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) emphasizing resilience and efficiency, indirectly reinforcing the power of established providers who meet these stringent standards.
- High Switching Costs: Banks face substantial costs and operational risks when attempting to change their core financial market infrastructure providers.
- Criticality of Services: Payment, clearing, and settlement systems are non-negotiable for daily banking operations, creating a strong dependency.
- Limited Alternatives: For certain specialized infrastructure services, the number of viable alternative providers is often limited.
- Regulatory Influence: While regulators set standards, established infrastructure providers often have the expertise and resources to meet these requirements, giving them an advantage.
Regulatory and Legal Compliance Services
The financial sector's intricate and constantly changing regulatory environment grants significant bargaining power to suppliers of specialized compliance services. These firms, offering expertise in areas such as anti-money laundering (AML) and capital requirements, become indispensable for institutions like Alpha Bank. For example, the European Banking Authority's (EBA) ongoing efforts to refine Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR) III, with finalization expected in 2024, highlights the demand for up-to-date legal and compliance guidance.
Adherence to these demanding regulations directly translates into leverage for these specialized service providers. Their knowledge of evolving legal frameworks, including those related to data privacy (like GDPR updates) and cybersecurity, is critical for operational integrity. In 2024, the focus on digital operational resilience, driven by regulations like DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act), further solidifies the indispensable nature of these expert suppliers.
- Regulatory Complexity: The financial industry faces a dense web of regulations, including Basel III/IV, AML, KYC (Know Your Customer), and data protection laws.
- Specialized Expertise: Suppliers offering deep knowledge in these niche areas, such as legal firms focusing on financial crime or consultancies specializing in regulatory reporting, are in high demand.
- Cost of Non-Compliance: Penalties for regulatory breaches can be substantial, often running into millions of euros, making proactive compliance services a necessity rather than an option. For instance, fines levied by regulators in 2023 for compliance failures across the EU financial sector underscore this risk.
- Supplier Concentration: In certain highly specialized compliance fields, the number of truly expert providers can be limited, increasing their bargaining power.
Alpha Bank's reliance on technology providers for its digital transformation efforts significantly enhances supplier bargaining power. Key partners in areas like AI and cloud computing offer critical, specialized capabilities. For example, in 2024, Alpha Bank's collaboration with Microsoft for AI integration demonstrates the leverage held by providers of essential, cutting-edge technology.
The financial market infrastructure providers, including payment systems and clearing houses, possess substantial bargaining power due to their critical role in daily operations. The global payments market, valued at over $2 trillion in 2023, underscores the importance of these services. Regulatory focus in 2024 on resilience and efficiency, as highlighted by the Bank for International Settlements, further solidifies the position of established infrastructure providers.
Suppliers of specialized compliance services, crucial for navigating complex regulations like AML and capital requirements, also wield significant power. The ongoing refinement of regulations such as CRR III, with expected finalization in 2024, necessitates expert guidance. The high cost of non-compliance, with fines potentially reaching millions of euros, makes these services indispensable.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Power | Impact on Alpha Bank | 2023/2024 Data Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers (AI, Cloud) | Specialized expertise, high switching costs | Increased dependency, potential for higher service costs | Microsoft AI integration partnership (2024) |
| Financial Market Infrastructure | Criticality of services, limited alternatives | Essential for operations, reliance on established players | Global payments market > $2 trillion (2023) |
| Compliance & Legal Services | Regulatory complexity, specialized knowledge | Necessity for operational integrity, risk of high penalties | CRR III finalization expected (2024); AML/KYC regulations |
What is included in the product
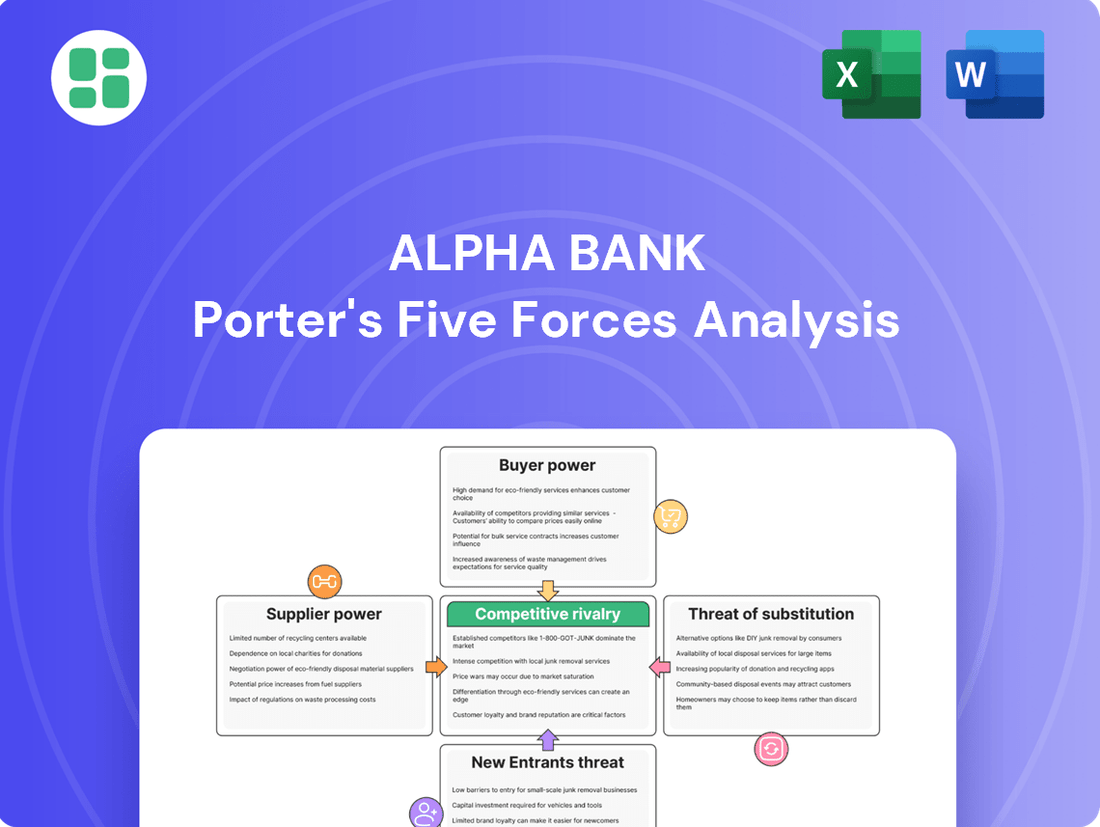
Examines the competitive intensity within the banking sector, assessing the bargaining power of Alpha Bank's customers and suppliers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Instantly visualize Alpha Bank's competitive landscape with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, simplifying complex market pressures for strategic clarity.
Customers Bargaining Power
Retail customers, though many, do exert some influence, especially regarding the interest rates offered on deposits and the fees charged for banking services. In 2024, with interest rates remaining relatively low for traditional savings accounts, many customers have actively moved their money. For instance, data from the second quarter of 2024 showed a notable increase in retail investment in money market funds and short-term bond ETFs, as individuals sought yields exceeding the typical 0.5% to 1% offered by many banks for standard savings. This demonstrates a clear sensitivity to rate differentials and a willingness to explore other avenues for their capital.
The proliferation of digital banking and mobile applications has further amplified customer bargaining power. These platforms provide customers with unprecedented ease in comparing offers from various financial institutions and accessing information about market rates. In 2024, the average time to open a new bank account online dropped to under five minutes for many neobanks, significantly lowering the friction and cost associated with switching providers. This ease of access and comparison directly translates to reduced switching costs for customers, making them more inclined to move their business if better terms or services are available elsewhere.
Large corporate and institutional clients wield significant bargaining power within the financial sector. Their substantial transaction volumes allow them to negotiate favorable terms, including competitive lending rates and fees for services. For instance, in 2024, major institutional investors often secured preferential pricing on underwriting and advisory services, directly impacting bank profitability.
These sophisticated clients frequently require highly customized financial solutions, ranging from complex derivatives to specialized trade finance. Alpha Bank's strategic emphasis on corporate and investment banking underscores the critical need to cater to these demands effectively. Meeting these specific needs is paramount for retaining and attracting high-value corporate relationships.
The digital revolution has significantly amplified customer bargaining power in the banking sector. With the widespread adoption of digital banking channels and mobile applications, customers now enjoy unprecedented transparency and ease in comparing services and rates. This makes switching providers much simpler, as evidenced by the growing number of customers exploring options beyond traditional banks, including agile neobanks.
In 2024, this trend is particularly pronounced. For instance, data from the European Banking Authority indicated a continued rise in digital-only bank account openings, suggesting customers are actively leveraging digital tools to find better value. This heightened accessibility and the readily available information on fees, interest rates, and product offerings empower customers to demand more, thereby increasing their leverage over financial institutions.
Availability of Alternative Financial Services
The availability of alternative financial services significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Customers now have a wider selection of providers for payments, lending, and investments, moving beyond traditional banking. This trend is particularly evident in Greece, where neobanks and other digital financial players are increasing customer choice.
This expanded competitive arena empowers customers to negotiate for better terms and pricing from established institutions like Alpha Bank. For instance, the growth of digital payment solutions has given consumers alternatives to traditional bank transfers, allowing them to seek lower fees or more convenient options.
- Increased Competition: Fintechs and neobanks offer specialized services, fragmenting the market and giving customers more options.
- Price Sensitivity: The ease of switching to digital alternatives makes customers more sensitive to pricing and fees charged by traditional banks.
- Demand for Innovation: Customers expect seamless digital experiences, pushing incumbent banks to innovate or risk losing market share.
- Access to Information: Online platforms and reviews allow customers to easily compare offerings, further strengthening their negotiating position.
Customer Trust and Brand Loyalty
While digitalization offers more choices, established institutions like Alpha Bank leverage decades of built-up customer trust and brand loyalty, especially within the Greek financial landscape. This deeply ingrained trust acts as a significant deterrent for customers considering a switch, particularly when dealing with intricate financial products or navigating periods of economic instability. For instance, in 2024, Alpha Bank maintained a strong customer base in Greece, reflecting the enduring value of established relationships.
However, this valuable loyalty is not immutable. A decline in service quality or the availability of more competitive products from rivals can gradually erode this trust. For example, a survey in late 2023 indicated that customer satisfaction scores for traditional banking services can be negatively impacted by digital service failures, highlighting the need for continuous improvement.
- Customer Trust: Decades of operation build significant trust, especially in Greece.
- Brand Loyalty: Established brands like Alpha Bank benefit from ingrained customer loyalty.
- Switching Barrier: Trust discourages customers from switching, particularly for complex needs.
- Erosion Risk: Poor service or uncompetitive offerings can undermine loyalty.
The bargaining power of customers for Alpha Bank is a significant factor, amplified by digital advancements and increased competition. Customers, both retail and corporate, can easily compare offerings and switch providers, especially with the rise of neobanks and fintech solutions. This forces banks like Alpha Bank to remain competitive on pricing and service quality.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Driver | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Customers | Ease of switching, digital comparison tools | Shift to higher-yield alternatives from typical 0.5%-1% savings rates |
| Corporate Clients | Large transaction volumes, demand for customized solutions | Negotiation of preferential pricing on underwriting and advisory services |
| Digital-Savvy Customers | Low switching costs, readily available information | Increased demand for competitive fees and seamless digital experiences |
Preview Before You Purchase
Alpha Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Alpha Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the banking sector. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. Gain immediate access to this comprehensive strategic tool to understand Alpha Bank's competitive landscape and inform your decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Greek banking sector's intense rivalry is largely due to the dominance of four systemic banks, including Alpha Bank. This concentration means that any strategic move by one of these major institutions, such as a new lending product or a pricing adjustment, directly and significantly impacts the competitive landscape for the others.
These leading banks are actively engaged in efforts to bolster their asset quality, enhance profitability, and grow their market share. For instance, by mid-2024, Alpha Bank reported a significant reduction in its non-performing exposures (NPEs) ratio, a key indicator of asset quality, as part of its ongoing strategic initiatives to strengthen its financial position and compete more effectively.
Competitive rivalry in the banking sector is intensifying, largely fueled by a digital transformation and innovation race. Banks are pouring significant resources into technology and artificial intelligence (AI) to differentiate themselves by improving customer experiences and streamlining operations. This dynamic environment compels institutions like Alpha Bank to prioritize technological advancements to stay competitive.
Alpha Bank's commitment to an AI-first strategy underscores the critical role of technological leadership in today's banking landscape. This strategic focus aims to create superior digital services that attract and retain customers, setting a benchmark for the industry. The ongoing pursuit of innovation ensures that banks are constantly evolving to meet changing customer expectations and market demands.
Greek banks, including Alpha Bank, have made substantial strides in asset quality, significantly reducing non-performing exposures (NPEs). For instance, Alpha Bank's NPE ratio stood at 3.6% by the end of 2023, a notable improvement from previous years, reflecting a healthier loan portfolio.
This cleanup of balance sheets fuels intensified competition as banks actively pursue new lending opportunities and aim for higher profitability. Alpha Bank reported a net profit of €713 million for 2023, demonstrating its enhanced earning power.
The emphasis on robust earnings and strong capital generation has become a critical differentiator. Banks that can consistently deliver strong financial performance are better positioned to attract customers and gain market share, making profitability a key battleground.
Strategic Mergers and Acquisitions
Strategic mergers and acquisitions are significantly reshaping the Greek banking sector, directly impacting competitive rivalry. For instance, in 2023, Eurobank's acquisition of Hellenic Bank in Cyprus, a move valued at approximately €200 million, aimed to bolster its market presence. Similarly, Alpha Bank's own acquisition of Astrobank in Cyprus, completed in early 2024, further illustrates this trend. These consolidations are driven by a desire to increase market share, realize cost synergies, and fortify competitive standing against both domestic and international players.
These strategic maneuvers have a direct ripple effect on the competitive intensity within the market. As larger entities absorb smaller ones or merge to create stronger entities, the remaining independent banks face increased pressure to innovate and improve efficiency. This consolidation can lead to a more concentrated market, where fewer, larger banks dominate, potentially altering pricing strategies and service offerings. The pursuit of scale and efficiency through M&A is a key factor in the ongoing competitive dynamics.
- Eurobank's acquisition of Hellenic Bank in Cyprus (2023)
- Alpha Bank's acquisition of Astrobank in Cyprus (early 2024)
- M&A activities aim to enhance market share and achieve synergies
- Consolidation reshapes the competitive landscape, pressuring rivals
Economic Outlook and Lending Opportunities
The Greek economy's improving trajectory, marked by a projected GDP growth of 2.9% in 2024 according to the Bank of Greece, directly fuels competitive rivalry among banks. This economic uptick, coupled with increased investment, creates a fertile ground for lending opportunities, intensifying the battle for new clients and business.
Banks are actively vying to finance domestic businesses and infrastructure projects, especially those benefiting from the substantial European recovery funds. This pursuit of market share in a growing economy naturally escalates competition for loan origination and client acquisition.
- GDP Growth: Greece's GDP is anticipated to grow by 2.9% in 2024.
- Investment Increase: Higher investment levels signal greater demand for bank financing.
- EU Funds: Significant European recovery funds are being channeled into Greek projects, creating a competitive lending environment.
- Loan Growth Drive: The push for increased loan portfolios intensifies rivalry among financial institutions.
Competitive rivalry within the Greek banking sector, exemplified by Alpha Bank, is fierce, driven by the dominance of four major systemic banks. These institutions are actively pursuing growth and profitability, with Alpha Bank notably reducing its non-performing exposures ratio to 3.6% by the end of 2023, enhancing its competitive standing.
The race for digital innovation and superior customer experience is a key battleground, compelling banks like Alpha Bank to invest heavily in AI and technology. This focus on technological leadership is crucial for differentiation and customer retention in an increasingly competitive market.
Strategic consolidations, such as Alpha Bank's acquisition of Astrobank in Cyprus in early 2024, are reshaping the landscape. These mergers aim to increase market share and achieve synergies, intensifying pressure on remaining independent players to enhance efficiency and innovate.
The improving Greek economy, with a projected GDP growth of 2.9% for 2024, further fuels rivalry as banks compete for lending opportunities, particularly those funded by European recovery initiatives.
| Bank | NPE Ratio (End 2023) | Net Profit (2023) | Key Strategic Move |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha Bank | 3.6% | €713 million | Acquisition of Astrobank (early 2024) |
| Eurobank | N/A | N/A | Acquisition of Hellenic Bank (2023) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitution for traditional banks like Alpha Bank stems from the rise of neobanks and digital-only financial service providers. These fintech innovators offer a completely branchless banking experience, directly challenging the established physical infrastructure of incumbent institutions. For instance, Snappi, Greece's first homegrown neobank, is slated for launch, promising tailored digital solutions.
These agile, often lower-cost players are particularly adept at attracting tech-savvy customers and individuals who prioritize simplified, efficient, and inexpensive banking services. Their digital-first approach allows them to bypass the overhead associated with maintaining physical branches, translating into competitive pricing and user-friendly interfaces that resonate with a growing segment of the market.
Customers now have a growing array of options beyond traditional banks, including alternative lending platforms and non-bank financial institutions. For instance, the rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) lending allows individuals and businesses to secure funding directly from other individuals or groups, bypassing conventional banking channels entirely. This trend is further amplified by government initiatives, such as the Greek government's exploration of allowing non-financial institutions to offer loans, aiming to inject more competition into the market.
Customers seeking to grow their savings and investments increasingly bypass traditional bank deposit accounts. They can directly invest in stocks, bonds, and mutual funds via numerous investment firms, offering potentially higher returns. This trend is amplified by persistently low deposit rates offered by banks, pushing individuals and businesses to explore capital markets for better yields, thereby diverting funds away from bank balance sheets.
Digital Payment Solutions and E-wallets
The rise of digital payment solutions and e-wallets presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banking services. As more consumers adopt platforms like Revolut, Apple Pay, and Google Pay for everyday transactions, the reliance on physical bank branches and even traditional online banking portals diminishes. This trend, accelerated by the convenience and often lower fees associated with these digital alternatives, directly challenges banks' core transactional business.
By mid-2024, global mobile payment transaction value was projected to exceed $15 trillion, demonstrating the scale of this shift. These services effectively disintermediate banks by providing a seamless payment and money transfer experience, often with integrated foreign exchange capabilities, bypassing traditional banking infrastructure for many everyday financial needs.
- Convenience and Accessibility: Digital wallets and payment apps offer user-friendly interfaces and 24/7 access, appealing to a broad consumer base.
- Reduced Transaction Costs: Many fintech payment providers offer lower fees for transfers and currency exchange compared to traditional banks.
- Disintermediation of Core Services: These substitutes directly compete with banks' fundamental roles in facilitating payments and managing funds.
- Growing Market Share: The increasing adoption rates highlight a tangible shift in consumer behavior away from traditional banking for transactional purposes.
Insurance Products for Savings and Financial Planning
The threat of substitutes for Alpha Bank's savings and financial planning services is significant, primarily stemming from the insurance sector. Insurance companies offer a diverse array of products that directly compete with traditional bank offerings for wealth accumulation and long-term financial security. These include unit-linked insurance policies, which combine insurance coverage with investment components, and annuities, providing guaranteed income streams. In 2023, the global life insurance market alone was valued at over $3.5 trillion, demonstrating the substantial financial resources and customer base available to these providers.
Alpha Bank's own involvement in the insurance market, through its subsidiaries or partnerships, highlights the perceived overlap. However, the broader insurance landscape presents a compelling alternative for consumers looking to manage their finances and plan for the future. For instance, the popularity of investment-linked insurance products, which saw significant growth in many European markets during 2023, indicates a consumer preference for bundled solutions that offer both protection and potential returns, often with tax advantages not always available through standard bank accounts.
- Unit-linked policies offer investment growth potential alongside life cover, attracting clients seeking dual benefits.
- Annuities provide predictable income streams, appealing to individuals planning for retirement and seeking financial stability.
- The global life insurance market's substantial size, exceeding $3.5 trillion in 2023, underscores the competitive pressure from this sector.
- Investment-linked insurance products gained traction in 2023, indicating a growing consumer interest in alternatives to traditional bank savings.
The threat of substitutes for Alpha Bank is multifaceted, encompassing digital payment solutions, alternative lending platforms, and insurance products. Digital wallets and payment apps are rapidly gaining traction, offering convenience and lower transaction costs, with global mobile payment transaction value projected to exceed $15 trillion by mid-2024. This directly challenges banks' core transactional business and disintermediates their role in facilitating payments.
Alternative lending platforms and non-bank financial institutions also present a significant substitute, particularly for loan origination. Peer-to-peer lending bypasses traditional banking channels, and initiatives like the Greek government exploring non-financial institutions offering loans further intensify this competition. This trend is amplified by customers seeking higher returns through capital markets rather than traditional bank deposits, which offer persistently low rates.
Furthermore, the insurance sector offers compelling substitutes for savings and financial planning. Unit-linked policies and annuities provide investment growth potential and guaranteed income streams, respectively, attracting customers seeking dual benefits and financial stability. The substantial global life insurance market, valued at over $3.5 trillion in 2023, highlights the significant competitive pressure from these providers.
| Substitute Category | Key Offerings | Impact on Alpha Bank | Supporting Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Payments & E-wallets | Seamless transactions, lower fees, currency exchange | Disintermediation of payment services, reduced reliance on branches | Global mobile payment value > $15 trillion (mid-2024 projection); Platforms like Revolut, Apple Pay, Google Pay |
| Alternative Lending Platforms | Peer-to-peer loans, direct funding | Competition for loan origination, bypass traditional banking | Greek government exploring non-financial institutions for loans |
| Insurance Sector | Unit-linked policies, annuities | Competition for savings and investment, wealth accumulation | Global life insurance market > $3.5 trillion (2023); Growth in investment-linked insurance |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the Greek banking sector presents formidable hurdles, primarily due to the stringent regulatory framework established by the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Bank of Greece. These authorities mandate substantial capital adequacy ratios, requiring new players to demonstrate robust financial health from the outset. For instance, as of early 2024, the ECB's capital requirements, including Pillar 1, Pillar 2, and capital conservation buffers, can push the total required Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio significantly higher than the minimum regulatory floor.
Securing the necessary operating licenses is another complex and time-consuming process, often involving extensive due diligence and proving the viability of the business model. This bureaucratic labyrinth, coupled with the substantial upfront capital needed to establish a credible presence and compete with established institutions, effectively deters potential new entrants. These high barriers to entry act as a protective shield for incumbent banks, including Alpha Bank, by limiting the influx of new competition.
The financial services sector, particularly banking, hinges on deep-seated trust and robust brand recognition. For Alpha Bank, its established reputation, cultivated over decades, serves as a significant barrier to entry for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, customer retention rates for established banks like Alpha Bank often exceeded 90%, a stark contrast to the challenges new digital-only banks faced in acquiring and retaining a comparable customer base, frequently struggling to surpass 70% in their initial years.
Established financial institutions, such as Alpha Bank, possess substantial economies of scale that create a significant barrier to entry. Their ability to spread vast fixed costs across a large customer base, encompassing everything from technology infrastructure to extensive branch networks, allows them to operate at a lower per-unit cost compared to potential newcomers. For instance, in 2023, major European banks reported operating expenses that were a fraction of their total assets, a testament to their scale advantages.
Technological Investment and Digital Infrastructure
The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by the significant capital required for technological investment and digital infrastructure. While new players can adopt cutting-edge technology, establishing a secure, scalable, and compliant digital banking platform demands substantial upfront investment. For instance, the global spending on digital transformation in banking was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars annually by 2024, a figure that continues to climb.
Incumbent banks like Alpha Bank are not standing still; they are actively investing in digital transformation and artificial intelligence. This ongoing investment in areas like AI-driven customer service, enhanced cybersecurity, and cloud computing is continuously raising the technological bar. For example, many major banks have allocated billions of dollars to AI initiatives and digital modernization projects in recent years, aiming to improve efficiency and customer experience.
- High Capital Outlay: Building a robust and secure digital banking infrastructure requires significant financial resources, acting as a barrier to entry.
- Incumbent Digital Investment: Established banks are heavily investing in digital transformation and AI, narrowing the technological advantage of potential new entrants.
- Increasingly Sophisticated Technology: The continuous advancement and integration of technologies like AI and blockchain necessitate ongoing, substantial investment for any new player to remain competitive.
Niche Market Entry by Digital Neobanks
The threat of new entrants, particularly from nimble digital neobanks, poses a significant challenge to established players like Alpha Bank. These digital-first entities often bypass the substantial overheads associated with traditional branch networks, enabling them to operate with leaner cost structures. This allows them to target specific, often underserved, customer segments or offer highly specialized financial services with competitive pricing.
A prime example of this trend is Snappi, a Greek neobank that has successfully carved out a niche by focusing on a completely branchless, digital-native customer experience. While not aiming to replicate Alpha Bank's full suite of services, such neobanks can effectively erode market share in profitable areas like payments, remittances, or specific lending categories. For instance, in 2024, neobanks globally continued to see substantial user growth, with some reporting over 10 million customers, indicating their growing influence.
- Digital Neobanks Target Niche Segments: Neobanks like Snappi focus on specific customer groups, such as young adults or small businesses, offering tailored digital solutions.
- Lower Overhead Structures: By operating without physical branches, neobanks significantly reduce operational costs, allowing for more competitive pricing.
- Erosion of Market Share: Despite not offering a full range of services, neobanks can capture market share in profitable areas like digital payments and specialized lending.
- Growing User Adoption: Global neobank user numbers continued to climb in 2024, demonstrating increasing consumer preference for digital-first banking experiences.
The threat of new entrants into the Greek banking sector is considerably low due to substantial barriers. Stringent capital requirements, complex licensing procedures, and the need for significant upfront investment in technology and infrastructure deter many potential competitors. For instance, as of early 2024, European Central Bank capital requirements necessitate robust financial health, pushing CET1 ratios higher than minimums.
Established trust and brand loyalty are significant advantages for incumbents like Alpha Bank, making it difficult for new players to gain customer traction. In 2024, customer retention rates for established banks often surpassed 90%, while new digital banks struggled to achieve comparable figures.
Economies of scale enjoyed by existing banks, including Alpha Bank, mean lower operating costs per unit due to spreading fixed expenses across a large customer base. This cost advantage is difficult for new entrants to match.
While digital neobanks offer a challenge by operating with lower overheads and targeting niche markets, their overall impact on established players like Alpha Bank remains limited by the high regulatory and capital hurdles present in the broader banking landscape.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Alpha Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including the bank's annual reports, financial statements, and investor relations disclosures. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific publications, market research reports, and macroeconomic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.