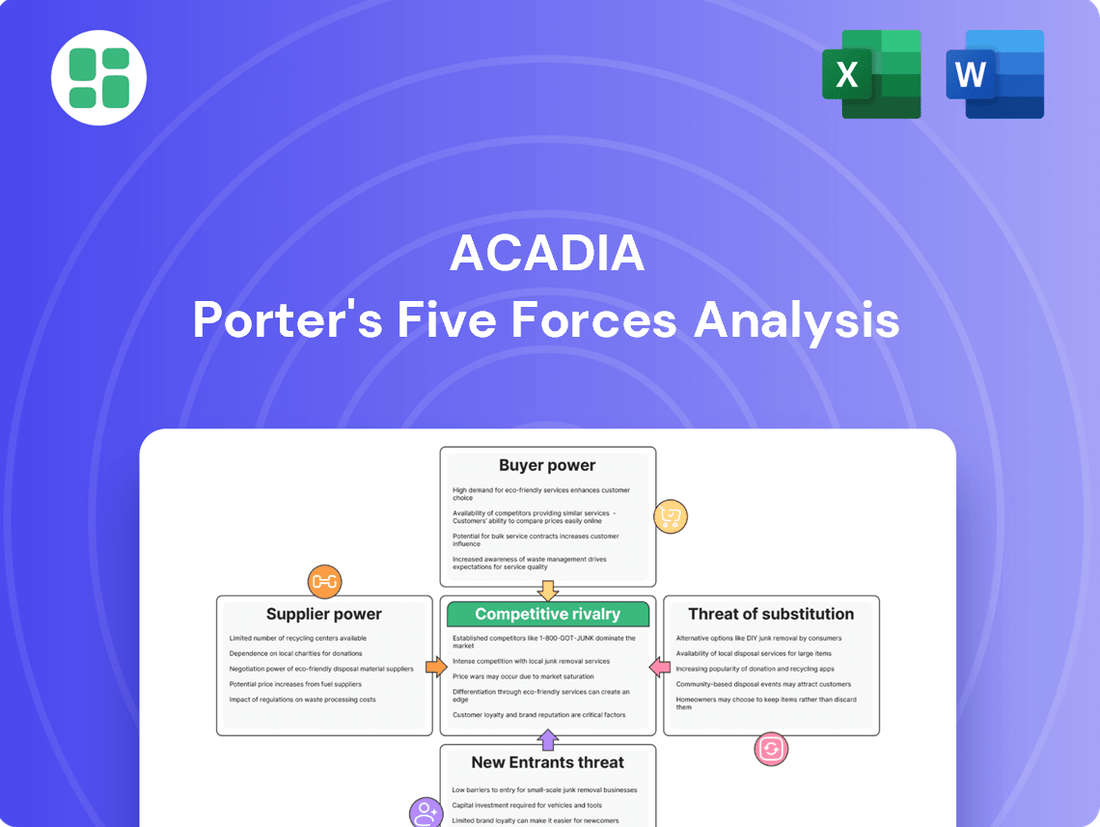
Acadia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Acadia Bundle
Acadia's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals a dynamic competitive landscape, highlighting the intense rivalry among existing players and the significant threat posed by substitute products. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating Acadia's market effectively.
The complete report unlocks a comprehensive strategic breakdown of Acadia’s market position, detailing the power of buyers and suppliers, and the barriers to entry for new competitors. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making and secure Acadia's competitive edge.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The behavioral healthcare sector, including providers like Acadia Healthcare, is grappling with a critical shortage of qualified clinical staff such as nurses, physicians, and mental health counselors. This scarcity directly amplifies the bargaining power of these specialized professionals. Consequently, healthcare organizations face escalating wage demands and rising labor expenses as they compete for limited talent.
By 2025, the deficit in nursing staff is expected to become particularly acute. This ongoing shortage poses a significant threat to operational capacity and can negatively impact the profitability of companies like Acadia Healthcare, as they are forced to offer higher compensation and benefits to attract and retain essential personnel.
Suppliers of specialized medical equipment and pharmaceuticals for inpatient psychiatric and substance use disorder treatments hold moderate bargaining power. Acadia Healthcare's substantial purchasing volume provides some leverage, but the specialized nature of certain medications and diagnostic tools can limit readily available alternatives, enabling suppliers to influence pricing. For instance, a significant portion of psychiatric medications are produced by a limited number of manufacturers, granting them pricing advantages.
The growing integration of digital health tools, telehealth, and AI in behavioral healthcare significantly boosts the bargaining power of technology providers. As Acadia Healthcare adopts these advanced solutions for diagnostics and patient management, its dependence on these specialized vendors increases, allowing them to charge premium prices for their innovations.
Real Estate and Facility Development
Acadia Healthcare's expansion necessitates significant real estate and facility development, making the bargaining power of suppliers in this sector a key consideration. As Acadia grows, its demand for land, construction services, and leased facilities increases, potentially strengthening the hand of developers, builders, and landlords.
The costs involved in acquiring suitable land and constructing specialized healthcare facilities are considerable, particularly in sought-after geographic markets. This can grant suppliers leverage, especially when specialized construction expertise or prime locations are involved.
- Construction Costs: The U.S. construction industry experienced significant cost inflation in 2023 and early 2024, with materials like lumber and steel seeing price fluctuations. For instance, the Producer Price Index for construction materials saw increases throughout 2023.
- Real Estate Market Dynamics: Availability of suitable land and prevailing rental rates in target expansion areas directly influence Acadia's facility development costs and the bargaining power of property owners.
- Specialized Facility Requirements: Healthcare facilities often require specific designs and infrastructure, limiting the pool of qualified developers and potentially increasing supplier leverage for these unique projects.
Accreditation and Regulatory Bodies
Accreditation and regulatory bodies, while not traditional suppliers, wield considerable influence over behavioral healthcare providers. Compliance with mandates from entities like The Joint Commission or the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is non-negotiable. For instance, in 2024, behavioral health providers faced ongoing scrutiny regarding patient safety protocols and data privacy, with potential penalties for non-compliance.
These agencies' evolving standards, such as updated guidelines for the use of psychotropic medications or new reporting requirements for quality metrics, can necessitate significant operational changes and investments. This indirect bargaining power stems from the provider's need to maintain licensure and reimbursement eligibility, making adherence a critical business imperative.
- Mandatory Compliance: Behavioral healthcare providers must adhere to standards set by accreditation and regulatory bodies to operate legally and receive payment.
- Cost of Non-Compliance: Failure to meet regulatory requirements can result in fines, loss of accreditation, and exclusion from payment programs, impacting revenue significantly.
- Influence on Operations: Changes in regulations, such as those impacting staffing ratios or treatment modalities, directly shape how providers deliver services and manage costs.
- 2024 Focus Areas: In 2024, key regulatory concerns included mental health parity enforcement and expanded telehealth regulations, impacting service delivery models and infrastructure investments.
Suppliers in the behavioral healthcare sector, particularly those providing specialized medical equipment and pharmaceuticals, hold moderate bargaining power. While large purchasers like Acadia Healthcare can negotiate favorable terms due to volume, the limited number of manufacturers for certain psychiatric medications and diagnostic tools allows these suppliers to influence pricing and terms. This is exacerbated by the need for specialized, often proprietary, equipment and drugs essential for patient care.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Acadia Healthcare | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturers | Limited alternatives for specialized medications | Potential for higher drug costs, impacting profitability | Concentration in psychiatric drug manufacturing continues, with key drugs often having few generic equivalents. |
| Medical Equipment Providers | Proprietary technology, specialized maintenance needs | Increased capital expenditure and potential reliance on single suppliers for critical equipment. | Demand for advanced diagnostic tools and monitoring systems is rising, with technology providers having significant leverage. |
| Construction & Real Estate | Demand for specialized facilities, prime locations | Higher costs for facility expansion and development. | Construction material costs remained elevated in early 2024, impacting project budgets for facility expansion. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Acadia, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its industry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive, visual breakdown of industry pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Insurance payers, including commercial insurers and government programs like Medicare and Medicaid, wield considerable bargaining power over healthcare providers such as Acadia Healthcare. These entities represent a substantial portion of Acadia's revenue, giving them leverage in negotiating reimbursement rates.
In 2023, Medicare and Medicaid combined accounted for a significant percentage of U.S. healthcare spending, and their ability to set payment levels directly impacts providers' financial performance. This power is amplified by their capacity to influence patient referrals, further strengthening their position in rate discussions.
The ongoing transition to value-based care models and evolving regulatory landscapes, such as changes in Medicare reimbursement policies for behavioral health services, continue to shape the dynamics of this buyer power, potentially pressuring Acadia's margins.
While individual patients historically had less direct sway, their collective power is growing. Increased awareness of mental health and readily available information allow patients to actively select providers based on quality, specialized services, and ease of access. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of patients consider provider reviews and online accessibility when choosing a mental health professional.
This shift means that dissatisfaction with prior care, such as long waiting lists or perceived poor treatment, can prompt patients to switch facilities. This directly fuels competition among healthcare providers, forcing them to enhance their offerings and patient experience to retain and attract individuals seeking mental health support.
Referral sources like primary care physicians and general hospitals wield considerable indirect bargaining power over Acadia. Their choices directly influence patient volume, as they decide which behavioral healthcare facilities receive referrals. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of patient admissions in the behavioral health sector were driven by physician referrals, highlighting the critical nature of these relationships.
Acadia must cultivate robust relationships with these referral partners. Demonstrating consistent, positive patient outcomes is paramount to securing a steady stream of patient admissions. Facilities that can prove high success rates in patient recovery and satisfaction are more likely to be favored by referring physicians, impacting Acadia's revenue and market position.
Employer-Sponsored Programs
Large employers are increasingly taking a more active role in providing mental health benefits, often negotiating directly with behavioral health providers. This direct engagement empowers them with significant bargaining power. For instance, by 2024, many large corporations were prioritizing integrated behavioral health solutions, seeking to consolidate services and achieve economies of scale. This allows them to demand more competitive pricing and tailored service packages from providers.
This trend is driven by the recognition that employee well-being directly impacts productivity and retention. As employers invest more heavily in these programs, their ability to influence the market grows.
- Increased Demand for Integrated Care: Employers are seeking one-stop solutions for mental health, leading to consolidation among providers.
- Focus on Cost-Effectiveness: A primary driver for employers is securing high-quality mental health services at a manageable cost.
- Direct Negotiation Power: Large employers can leverage their size to negotiate favorable terms, impacting provider pricing and service models.
Advocacy Groups and Community Organizations
Patient advocacy groups and community organizations significantly amplify customer bargaining power. They raise public awareness regarding the quality of healthcare services and champion specific treatments or access improvements. For instance, in 2024, organizations like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) continued to advocate for better mental healthcare access, influencing provider policies and patient expectations.
While these groups don't directly negotiate prices, their collective voice can compel healthcare providers to enhance service quality, increase transparency, and address critical unmet needs. This indirect pressure shapes customer perceptions and choices, ultimately impacting provider competitiveness and operational strategies.
- Influence on Quality: Advocacy groups highlight service quality issues, pushing providers for improvements.
- Service Advocacy: They lobby for specific services, expanding patient options and influencing provider offerings.
- Access Disparities: Community organizations often spotlight access issues, pressuring providers to serve underserved populations.
- Indirect Price Pressure: By improving service perception and demand, they indirectly influence a provider's ability to command premium pricing.
The bargaining power of customers for Acadia Healthcare is multifaceted, stemming from payers, individual patients, referral sources, and large employers. Payers like Medicare and Medicaid hold significant sway due to their substantial share of revenue, enabling them to dictate reimbursement rates, a factor amplified by their influence on patient flow.
Individual patients are increasingly empowered, with a growing emphasis on quality and accessibility, as evidenced by a 2024 survey showing over 60% of patients consider online reviews when selecting a provider. Referral sources, such as physicians, also exert considerable indirect power by directing patient volumes, making strong relationships crucial for Acadia's admissions.
Large employers are actively negotiating for integrated behavioral health solutions, seeking cost-effectiveness and tailored services, which by 2024, was a growing trend. Patient advocacy groups further amplify customer power by influencing public perception and demanding higher service quality and transparency.
| Customer Segment | Source of Power | Impact on Acadia | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payers (Medicare, Medicaid) | Significant revenue share, rate setting | Pressure on reimbursement rates, margin impact | Medicare and Medicaid represent a large portion of U.S. healthcare spending. |
| Individual Patients | Increased awareness, choice based on quality/access | Need for enhanced patient experience, service quality | >60% of patients consider online reviews in provider selection (2024 survey). |
| Referral Sources (Physicians) | Direct influence on patient volume | Crucial for patient admissions, revenue generation | Physician referrals are a primary driver of admissions in behavioral health. |
| Large Employers | Negotiation for integrated benefits, cost-effectiveness | Demand for competitive pricing, tailored services | Growing trend of corporations prioritizing integrated behavioral health solutions. |
What You See Is What You Get
Acadia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Acadia Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase. The document meticulously details each force, including threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You're looking at the actual document, fully formatted and ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The U.S. behavioral healthcare market is intensely competitive and highly fragmented. Acadia Healthcare navigates this landscape alongside numerous rivals, including large, diversified healthcare systems such as Universal Health Services (UHS), which also operates behavioral health facilities. This means Acadia isn't just competing with other specialized behavioral health providers but also with broader healthcare entities.
Beyond the major players, Acadia faces competition from a multitude of specialized regional operators and smaller, independent clinics. This diversity in competitors, from national giants to local practices, underscores the need for continuous differentiation and strategic positioning to maintain market share and attract patients.
The escalating demand for mental health and substance abuse treatment is a significant catalyst for expansion within the industry. This surge in need compels established providers like Acadia Healthcare to not only increase their existing capacity through bed expansions but also to forge new joint ventures.
These strategic moves by Acadia, aiming to capture a larger share of the growing patient base, directly intensify competitive rivalry. As more providers invest in expanding their services and geographical footprint, the competition for patient volume and market dominance becomes more pronounced across various regions.
Competitors in the behavioral healthcare space actively seek market share by offering highly specialized programs tailored to specific conditions, such as eating disorders or child and adolescent mental health services. They also differentiate through unique care delivery models, like intensive residential treatment or flexible outpatient clinics.
Acadia Healthcare, for instance, emphasizes its commitment to providing consistent, high-quality, and compassionate care across a broad spectrum of settings. This dedication to a comprehensive and empathetic approach serves as a significant point of distinction in a crowded and competitive landscape.
Technological Adoption and Innovation
The healthcare industry is seeing a surge in technological adoption, with telehealth and AI becoming key battlegrounds for providers. For instance, in 2023, the global telehealth market was valued at approximately $105.8 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth. This innovation is not just about offering new services; it's about fundamentally changing how patient care is delivered and accessed.
Providers are actively integrating these digital tools to boost accessibility, improve patient outcomes, and make their operations more efficient. This competitive pressure is forcing rivals to also invest heavily in digital transformation to avoid falling behind.
- Telehealth Growth: The telehealth market is expected to reach over $300 billion by 2027, highlighting its rapid expansion and competitive importance.
- AI in Healthcare: AI is being implemented in areas like diagnostics and drug discovery, with the AI in healthcare market projected to grow significantly, reaching tens of billions in the coming years.
- Provider Investment: Major health systems are allocating substantial capital towards digital health initiatives, often in the billions, to enhance patient engagement and operational efficiency.
- Digital Transformation Mandate: Failure to adopt these technologies risks a loss of market share and a diminished ability to attract and retain patients.
Mergers, Acquisitions, and Partnerships
The industry is seeing a consistent trend of consolidation. Companies are actively pursuing strategic mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships as a primary way to gain a competitive edge. This M&A activity is not just about getting bigger; it's about becoming more capable.
Through these deals, companies are broadening their service portfolios and extending their geographical presence. This creates more comprehensive and integrated platforms. Such larger entities often wield more significant influence over the market due to their expanded scale and capabilities.
- Consolidation Trend: The sector is experiencing steady consolidation, with M&A and partnerships being key competitive strategies.
- Service Expansion: Companies are acquiring or partnering to expand their service offerings, aiming for more integrated platforms.
- Market Reach: Acquisitions are a primary method for companies to increase their market reach and influence.
- 2024 Data: In 2024, the global M&A market saw a notable increase in tech-related deals, with over $1 trillion in announced transactions, many focused on integrating AI capabilities and expanding service ecosystems.
The competitive rivalry in the U.S. behavioral healthcare market is fierce, characterized by a fragmented landscape with numerous players ranging from large diversified systems like Universal Health Services to smaller, specialized clinics. This intense competition is further fueled by escalating demand for mental health and substance abuse services, prompting providers like Acadia Healthcare to expand capacity and services, thereby intensifying the struggle for market share.
Providers differentiate themselves through specialized programs and innovative care delivery models, while also investing heavily in digital transformation, including telehealth and AI, to enhance accessibility and efficiency. The market is also witnessing significant consolidation through mergers and acquisitions, as companies seek to broaden service portfolios and increase market reach, with over $1 trillion in global M&A deals announced in 2024, many focused on integrating AI capabilities.
| Competitor Type | Differentiation Strategy | Key Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Large Diversified Systems (e.g., UHS) | Broad service offerings, integrated care | Technological adoption, digital health investment |
| Specialized Regional Operators | Niche programs (e.g., eating disorders), unique care models | Consolidation, M&A activity |
| Independent Clinics | Personalized patient care, local focus | Telehealth expansion, AI integration |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing availability and acceptance of outpatient and community-based mental health services present a significant threat of substitution for traditional inpatient care. These alternatives, often more affordable and flexible, cater to individuals with less severe conditions, potentially drawing patients away from Acadia's facilities.
For instance, the U.S. saw a substantial increase in telehealth mental health services, with utilization rates remaining significantly higher than pre-pandemic levels even into 2024. This trend indicates a growing preference for accessible, remote care options that can substitute for in-person, facility-based treatment.
Telehealth and digital mental health platforms present a significant threat of substitutes for Acadia. These services offer convenient and accessible alternatives to traditional in-person care, particularly for therapy and counseling. For instance, the digital mental health market was projected to reach over $30 billion globally by 2027, indicating substantial growth and patient adoption of these virtual options.
The increasing integration of behavioral health services directly into primary care settings presents a significant threat of substitutes for specialized behavioral healthcare providers. Patients can now receive initial mental health support, including assessments and basic management, from their trusted family physicians.
This shift can divert patients away from traditional psychiatric or counseling practices for less severe conditions. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of primary care physicians reported increased collaboration with mental health professionals, suggesting a growing capacity to handle a broader range of behavioral health needs within their own practices.
Alternative Therapies and Self-Help Resources
Patients increasingly explore alternative therapies and self-help resources, posing a significant threat of substitution for traditional behavioral healthcare providers like Acadia. These options, ranging from wellness retreats to uncertified online coaching, offer perceived lower costs and less formality, directly diverting potential clients. For instance, the global wellness market, which encompasses many of these substitutes, was valued at over $4.5 trillion in 2023 and is projected to continue its growth trajectory through 2025.
These substitutes can impact demand for structured treatment programs by offering accessible, albeit not always clinically validated, solutions. Individuals seeking immediate or more affordable coping mechanisms might bypass professional services. The rise of digital self-help platforms, many offering subscription models, further democratizes access to mental wellness tools, potentially fragmenting the market for established behavioral health services.
- Growing Wellness Market: The global wellness market's significant valuation highlights the substantial financial resources consumers allocate to alternative health solutions.
- Accessibility of Digital Tools: Online self-help platforms and apps provide readily available, often low-cost, alternatives to professional therapy.
- Perceived Lower Cost: Many substitutes are positioned as more budget-friendly than traditional, insurance-dependent behavioral healthcare.
- Consumer Preference for Informality: A segment of the population may prefer less structured, non-clinical approaches to managing mental well-being.
Pharmacological Management by Non-Psychiatrists
The availability of pharmacological management by non-psychiatrists presents a significant threat of substitutes for specialized psychiatric services. Primary care physicians and other medical specialists can prescribe medications for common mental health conditions, potentially diverting patients who might otherwise seek psychiatric consultation. This trend is amplified by the increasing integration of mental health services within primary care settings.
In 2024, approximately 55% of individuals with depression or anxiety disorders in the US received initial treatment from their primary care physician. This highlights the substantial reach of non-psychiatric prescribers. While these prescribers may not offer the full spectrum of care, their ability to manage medication can indeed reduce the demand for specialized psychiatric appointments, particularly for less complex cases.
The economic implications are also noteworthy. Patients often find primary care more accessible and less costly than seeing a psychiatrist. For instance, the average co-pay for a primary care visit in 2024 was around $30, compared to over $100 for a specialist psychiatric visit. This cost differential makes non-psychiatric management a compelling substitute for many.
- Primary Care Prescribing Power: A significant portion of mental health medication is managed by non-psychiatrists.
- Accessibility & Cost Savings: Primary care offers a more convenient and affordable entry point for treatment.
- Reduced Demand for Specialists: Medication management by GPs can lessen the need for psychiatric consultations.
- Growing Trend: The integration of mental health into primary care is expanding this substitute's reach.
The rise of digital mental health platforms and telehealth services presents a significant threat of substitution for Acadia's traditional inpatient and outpatient care models. These virtual alternatives offer convenience, accessibility, and often lower costs, appealing to a growing segment of the population seeking mental health support. For example, the global digital health market was valued at approximately $200 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow substantially, indicating a strong consumer shift towards these digital solutions.
Furthermore, the increasing integration of behavioral health services into primary care settings acts as another substitute. Patients can now receive initial assessments and management for less severe mental health conditions from their primary care physicians, diverting potential clients from specialized facilities. In 2024, over 60% of primary care physicians reported increased collaboration with mental health professionals, underscoring this trend.
Alternative therapies and self-help resources, including wellness retreats and online coaching, also pose a threat. The global wellness market, valued at over $4.5 trillion in 2023, demonstrates a significant consumer willingness to invest in non-traditional approaches to well-being, further fragmenting the market for established behavioral health providers.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Acadia | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Health/Telehealth | Convenience, accessibility, lower cost | Patient diversion for less severe conditions | Digital health market ~$200B (2023); high telehealth utilization post-pandemic |
| Primary Care Integration | Accessibility, trusted provider, initial management | Reduced demand for specialized services for common issues | >60% of PCPs collaborating with mental health pros (2024) |
| Alternative Therapies/Self-Help | Perceived lower cost, informality, broad wellness focus | Market fragmentation, diversion of potential clients | Global wellness market >$4.5T (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing and operating inpatient psychiatric facilities and residential treatment centers demands significant capital. Think about the costs for real estate acquisition, building construction, specialized medical equipment, and the necessary infrastructure to support patient care. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to build a new hospital wing can easily run into tens of millions of dollars, with specialized units like psychiatric wards potentially incurring even higher expenses due to unique design and safety requirements.
The behavioral healthcare sector is a minefield of regulations. Newcomers face a daunting array of federal and state licensing, accreditation, and compliance hurdles. For instance, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) mandates specific conditions for participation for providers, impacting everything from patient rights to staffing ratios. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, making entry extremely challenging.
These intricate rules, including evolving patient safety standards and complex reimbursement frameworks, create a significant barrier. For example, in 2024, many states are implementing stricter telehealth regulations following the pandemic, requiring new licenses or certifications for out-of-state providers. This adds another layer of complexity for any potential new entrant looking to establish a foothold.
Acadia's need for a highly specialized workforce, encompassing psychiatrists, psychologists, nurses, and therapists, presents a significant barrier for new entrants. Widespread staffing shortages in the mental healthcare sector, a persistent issue throughout 2024, make attracting and retaining qualified personnel exceptionally difficult.
New companies entering the behavioral health market would face immense challenges in building a competent team from the ground up. This hurdle directly benefits established providers like Acadia, who have already cultivated experienced teams and robust recruitment pipelines, thereby solidifying their competitive edge.
Payer Relationships and Network Contracts
The threat of new entrants in behavioral healthcare is significantly mitigated by the intricate web of payer relationships and network contracts. Establishing robust connections with major insurance companies and government healthcare programs is paramount for any provider's financial sustainability. Newcomers face a steep uphill battle in replicating the extensive and deeply entrenched payer networks that established players like Acadia Healthcare have cultivated over years.
These established relationships translate into preferred provider status, better reimbursement rates, and guaranteed patient volume. For instance, in 2024, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) continued to refine reimbursement policies, making it even more critical for providers to be in-network. Acadia's ability to secure contracts with a broad spectrum of payers, including Medicare, Medicaid, and numerous commercial insurers, provides a substantial barrier to entry.
- Payer Network Access: New entrants struggle to gain access to the same payer networks as established providers, limiting their patient base and revenue potential.
- Contractual Hurdles: The time and resources required to negotiate and secure favorable contracts with numerous insurance payers are substantial deterrents.
- Reimbursement Rates: Established providers often benefit from higher reimbursement rates due to their long-standing relationships and demonstrated quality of care, creating a cost disadvantage for new entrants.
- Government Program Participation: Navigating the complexities of securing and maintaining contracts with government programs like Medicare and Medicaid is a significant challenge for new organizations.
Reputation and Brand Building
Building a trusted reputation and brand in healthcare, particularly for sensitive behavioral health services, demands significant time and consistent, high-quality care delivery. Newcomers must overcome the hurdle of earning patient and referral source trust when competing with established providers like Acadia Healthcare, which boasts proven track records.
For instance, in 2024, the healthcare sector continued to see a strong emphasis on patient satisfaction scores, with many providers striving for above 85% in key metrics. This highlights the difficulty for new entrants to quickly establish the credibility that established players, like Acadia, have cultivated over years of operation.
- Brand Loyalty: Established brands benefit from existing patient loyalty, making it harder for new entrants to capture market share.
- Trust Factor: In behavioral health, trust is paramount; new entrants need substantial evidence of efficacy and patient safety to gain this.
- Referral Networks: Existing providers have built robust referral networks with physicians and other healthcare entities, a significant barrier for new players.
- Reputational Capital: Acadia Healthcare, for example, has invested heavily in its reputation, which translates to a competitive advantage in attracting both patients and talented staff.
The threat of new entrants for Acadia Healthcare is considerably low due to the immense capital required to establish and operate behavioral health facilities. High startup costs for real estate, construction, and specialized equipment, often running into millions in 2024, act as a significant deterrent.
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape, including federal and state licensing and accreditation, presents another substantial barrier. For example, compliance with Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) conditions for participation, which are continually updated, demands significant expertise and resources.
The need for highly specialized staff, coupled with ongoing shortages in mental healthcare professionals throughout 2024, makes building a competent team extremely challenging for newcomers. This difficulty in recruitment and retention favors established providers with existing talent pools.
Securing robust payer networks and favorable reimbursement contracts is a critical hurdle, as new entrants struggle to match the established relationships of providers like Acadia with insurers and government programs. For instance, in 2024, maintaining in-network status with CMS remained vital for patient volume and revenue.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Acadia Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements of key players, and public company filings. We also incorporate insights from trade associations and economic databases to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.