Western Union Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Western Union Bundle
Western Union navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense competition, buyer power, and the ever-present threat of new entrants in the digital payments space. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Western Union’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Western Union's extensive global agent network, numbering over 550,000 locations as of early 2024, represents a crucial supplier of physical access for its customers. This widespread presence is a core asset, but it also creates a dependency. While individual agents may have limited power due to the sheer volume of the network, concentrated activity in high-demand remittance corridors could empower specific agents, giving them more bargaining leverage.
Technology and software providers hold significant sway over Western Union, as their offerings are fundamental to the company's digital platforms, robust cybersecurity, and overall operational smoothness. The leverage these suppliers possess is directly tied to how unique and essential their technologies are; specialized or proprietary solutions can grant them greater bargaining power.
Western Union's considerable investment in information and communication technology (ICT), projected at $109.7 million for 2024, underscores a deep reliance on external software and services. This substantial spending highlights the critical nature of these partnerships and the potential for suppliers to influence terms.
Western Union relies on banking and financial institution partners for critical functions like settlement and regulatory compliance. In 2024, the concentration of banking infrastructure in certain regions, or the dominance of a few major banks, can significantly amplify the bargaining power of these partners. These relationships are foundational for Western Union's ability to facilitate global money transfers and maintain necessary liquidity.
Telecommunications and Digital Infrastructure Providers
Western Union's reliance on telecommunications and digital infrastructure providers is growing significantly as it pushes its digital transformation. This dependence grants these providers a notable degree of bargaining power, as reliable connectivity and robust online platforms are critical for Western Union's mobile app and online money transfer services. For instance, in 2024, the global digital payments market was projected to reach over $1.5 trillion, underscoring the essential nature of the infrastructure supporting these transactions.
The company's strategic investments in areas like artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and blockchain technology further solidify the importance of its digital infrastructure partners. These advanced technologies require stable and high-capacity networks, giving providers of these services leverage in negotiations. The increasing demand for high-speed internet and secure cloud solutions means that companies like Western Union must secure favorable terms with these infrastructure giants.
- Increased Digital Dependence: Western Union's shift to digital channels directly increases its need for telecommunication and internet services.
- Critical Infrastructure: Reliable internet and cloud services are non-negotiable for Western Union's core digital operations.
- Technological Investments: AI, cloud, and blockchain initiatives amplify the need for advanced digital infrastructure, strengthening supplier power.
- Market Growth: The expanding digital payments market, valued in the trillions, highlights the foundational role of infrastructure providers.
Labor and Human Capital
While not traditional suppliers, the availability of skilled labor for technology development, compliance, and customer service is vital for Western Union. A shortage of specialized talent in areas like fintech, cybersecurity, or global compliance could significantly increase the bargaining power of employees in these critical functions.
Western Union's strategic initiatives, such as its Evolve 2025 plan, heavily depend on a skilled workforce to drive its digital transformation forward. This reliance means that the company must effectively manage its human capital to maintain operational efficiency and competitive advantage.
- Talent Demand: The global demand for cybersecurity professionals, for instance, remained high in 2024, with organizations actively seeking to fill these roles.
- Wage Pressures: In 2024, certain tech sectors experienced upward wage pressure due to the scarcity of highly specialized skills, impacting companies like Western Union.
- Digital Transformation Needs: Western Union's commitment to digital innovation necessitates continuous investment in attracting and retaining talent with expertise in areas such as blockchain and AI.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Western Union is moderate, influenced by the diverse nature of its inputs. While individual agents have limited power, technology providers and financial institutions can exert significant influence due to the critical nature of their services and the consolidation within certain markets.
| Supplier Type | Key Dependence | Bargaining Power Factor | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agent Network | Physical distribution | Low for individual agents, potentially moderate for concentrated groups | 550,000+ global locations |
| Technology Providers | Software, platforms, cybersecurity | Moderate to High (depending on uniqueness of tech) | $109.7 million ICT investment |
| Banking Partners | Settlement, liquidity, compliance | Moderate to High (depending on market concentration) | Essential for global money transfers |
| Telecom/Digital Infrastructure | Connectivity, online services | Moderate to High (due to digital dependence) | Digital payments market > $1.5 trillion |
| Skilled Labor | Fintech, cybersecurity, compliance expertise | Moderate (due to talent shortages) | High demand for cybersecurity professionals |
What is included in the product
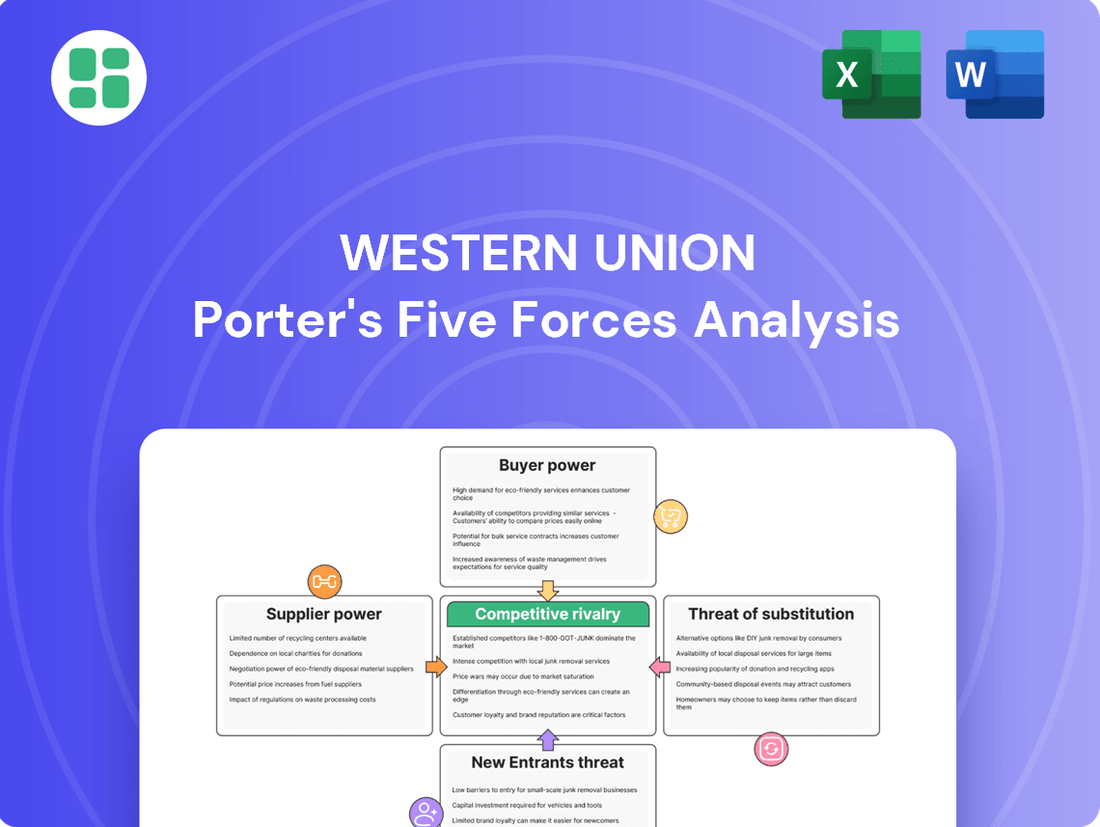
This analysis delves into the five competitive forces impacting Western Union, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes within the global money transfer market.
Instantly identify competitive threats and opportunities by visualizing Western Union's market position across all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers can easily switch between money transfer providers, especially with the rise of digital options. Many fintech firms offer attractive rates and simple platforms, encouraging customers to move if they find better deals or service. This low barrier to switching amplifies customer power.
Customers, especially those sending remittances, are very aware of prices. They are often sending money that is crucial for their families' needs, making cost a significant factor in their choices. This inherent price sensitivity means they actively look for the most affordable ways to transfer funds.
The cost of sending money can really add up. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, the average fee for sending $200 via traditional cash-to-cash methods was 6.6%. This figure highlights why customers are drawn to cheaper options, such as digital remittance services that often offer lower transaction costs.
This strong customer focus on price puts direct pressure on companies like Western Union. To remain competitive, they must consistently offer attractive fees and favorable exchange rates. Failing to do so risks losing customers to providers who can meet their demand for lower-cost remittance services.
The availability of alternatives significantly amplifies customer bargaining power in the money transfer market. Western Union faces intense competition from a broad spectrum of providers, including established players like MoneyGram, digital disruptors such as Wise (formerly TransferWise) and Remitly, and even traditional banks offering international wire services. This saturation means customers can easily switch providers if they find better rates, faster transfer times, or more convenient options.
In 2023, the global remittance market was valued at an estimated $831 billion, with a significant portion of that volume handled by digital channels. This growth in digital alternatives, often with lower overheads, allows new entrants to offer competitive pricing, directly challenging Western Union’s market share and giving customers more leverage to negotiate better terms or simply choose a cheaper alternative.
Increasing Digital Adoption
The increasing adoption of digital channels by customers significantly bolsters their bargaining power within the money transfer industry. This trend is driven by the inherent convenience and often more competitive pricing offered through online platforms. Western Union itself reported a 13% increase in digital transactions during the first quarter of 2024, underscoring this customer preference.
As more consumers become comfortable and adept at using digital tools, they gain greater ease in comparing services and prices across various providers. This enhanced digital savviness directly translates into stronger leverage for customers seeking the best value.
- Growing preference for digital money transfers
- Convenience and cost savings drive digital channel adoption
- Western Union's digital transactions increased by 13% in Q1 2024
- Increased digital savviness empowers customers to compare and negotiate
Demand for Financial Inclusion and Accessibility
The demand for financial inclusion significantly empowers Western Union's customers, particularly migrant workers and aspiring populations. These individuals often operate in regions with limited traditional banking infrastructure, making accessible and reliable remittance services crucial. Their need for convenient and cost-effective money transfers grants them considerable bargaining power, compelling providers like Western Union to offer competitive pricing and widespread accessibility. Western Union's Evolve 2025 strategy directly addresses this by aiming to deliver high-value, accessible financial services to these underserved segments.
Western Union reported that in 2023, approximately 70% of its digital transactions were initiated by customers in emerging markets, highlighting the critical role of accessibility for its user base. This demographic, often comprising migrant laborers, relies heavily on services that are both affordable and readily available, especially in areas where traditional financial institutions are scarce. Their ability to switch between providers based on fees, exchange rates, and network reach directly influences Western Union’s service offerings and pricing strategies.
- Demand for Accessibility: Migrant workers and aspiring populations require financial services in underserved regions where traditional banking is limited.
- Bargaining Power: The need for reliable and convenient services gives these customers the power to choose providers that best meet their unique financial needs.
- Evolve 2025 Strategy: Western Union's strategic focus is on delivering high-value, accessible financial services to these specific customer segments.
- Market Reliance: In 2023, a significant portion of Western Union's digital transactions originated from emerging markets, underscoring the importance of accessible services for this demographic.
Customers possess significant bargaining power due to the ease of switching between money transfer providers, especially with the proliferation of digital options. This price sensitivity means customers actively seek the most affordable solutions, putting pressure on companies like Western Union to offer competitive fees and exchange rates.
The global remittance market, valued at approximately $831 billion in 2023, saw a substantial shift towards digital channels. This growth, coupled with Western Union's own digital transaction increase of 13% in Q1 2024, highlights customer preference for convenience and cost savings, further empowering them to compare and negotiate for better terms.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Western Union |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Switching | Customers can readily move to competitors offering better rates or service. | Requires Western Union to maintain competitive pricing and service levels. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers, especially in emerging markets, prioritize cost-effectiveness. | Drives demand for lower-fee digital remittance services. |
| Digital Channel Adoption | Growing comfort with online platforms facilitates comparison shopping. | Increases competitive pressure from fintech disruptors. |
Full Version Awaits
Western Union Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Western Union delves into the competitive landscape, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the money transfer industry. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic decision-making in this dynamic market.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The money transfer and cross-border payments arena is incredibly fragmented. Western Union faces competition not only from traditional banks but also from specialized players like MoneyGram and Ria. Furthermore, the rise of fintech startups, offering innovative digital solutions, adds another layer of intense rivalry as all these entities battle for customer transactions.
Fintech disruptors such as Wise and Remitly are shaking up the industry with their lean operating models, enabling them to offer significantly lower fees and faster digital transactions. This competitive pressure compels traditional companies like Western Union to re-evaluate their pricing structures and expedite their digital capabilities to stay relevant.
The cost advantage of digital remittances is substantial. In the first quarter of 2024, digital remittance costs averaged 4.96%, a stark contrast to the 6.94% charged for non-digital transfers, highlighting the growing consumer preference for cost-effective digital solutions.
Western Union's competitive rivalry is intensified by its ongoing digital transformation. The Evolve 2025 strategy aims to pivot the company from its traditional retail focus to a digitally-led financial services model. This strategic shift is crucial as digital-first competitors continue to gain traction.
Despite the progress, the competitive landscape remains challenging. Branded digital transactions demonstrated robust growth, reaching 13% in Q1 2024 and accelerating to 15% in Q3 2024. However, this digital momentum is somewhat offset by pressures in the legacy retail segment, contributing to an overall revenue decline. This dynamic highlights the intense pressure from agile, digitally-native rivals who often operate with lower overheads and can innovate more rapidly.
Global Reach vs. Digital Agility
Western Union's expansive physical network, a historical strength, now presents a challenge as it competes with digitally native fintechs. While Western Union had over 550,000 agent locations across more than 200 countries and territories as of late 2023, this physical infrastructure requires ongoing investment and maintenance.
In contrast, newer players like Wise (formerly TransferWise) and Remitly leverage digital-first strategies. These companies can rapidly deploy new features and reach customers globally without the overhead of a vast physical presence. For instance, Wise reported over 16 million customers globally as of March 2024, demonstrating the scalability of its digital model.
- Global Network vs. Digital Speed: Western Union's extensive physical agent network is a significant asset, but it also entails substantial operational costs and slower adaptation compared to digital-only competitors.
- Fintech Agility: Younger fintech companies, unburdened by legacy physical infrastructure, can innovate and scale digital payment solutions more rapidly, offering competitive advantages in speed and cost.
- Customer Acquisition: Digital agility allows fintechs to attract younger, tech-savvy demographics more effectively, potentially impacting Western Union's market share in key growth segments.
Regulatory and Compliance Landscape
The cross-border payments sector is heavily regulated, creating a complex competitive arena. Western Union, like its peers, faces substantial compliance costs and ongoing investment in robust frameworks to navigate these rules and maintain customer trust. For instance, in 2023, financial institutions globally spent an estimated $12.7 billion on anti-money laundering (AML) compliance alone, a figure expected to rise.
These regulatory demands act as a significant barrier to entry for smaller, less-resourced competitors. However, established players like Western Union must remain vigilant. The introduction of new regulations, such as potential frameworks for digital currencies, can quickly alter the competitive dynamics, requiring continuous adaptation and investment in compliance technology.
- Significant Compliance Burden: The cost of adhering to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations is substantial, impacting operational expenses.
- Barrier to Entry: High regulatory hurdles deter new, smaller companies from entering the market, thus benefiting established players with existing compliance infrastructure.
- Impact of Regulatory Changes: Evolving regulations, such as those concerning digital assets or data privacy, necessitate continuous investment and strategic adjustments to remain competitive and compliant.
Western Union faces intense competition from a diverse range of players, including traditional banks, specialized money transfer services like MoneyGram, and increasingly, agile fintech companies. These digital-first disruptors, such as Wise and Remitly, leverage lower operating costs and faster digital transactions to attract customers, forcing Western Union to adapt its pricing and accelerate its digital transformation strategy, Evolve 2025.
The cost advantage of digital remittances is a key battleground, with digital transfers averaging 4.96% in Q1 2024 compared to 6.94% for non-digital methods. Western Union's branded digital transactions grew to 15% by Q3 2024, but this growth is challenged by ongoing pressures in its legacy retail segment, highlighting the impact of competitors unburdened by extensive physical networks.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Western Union |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Banks | Established customer base, broad financial services | Offer alternative remittance channels, often with higher fees |
| Specialized Money Transfer (e.g., MoneyGram, Ria) | Similar physical networks, direct competitors | Direct competition for market share in core services |
| Fintechs (e.g., Wise, Remitly) | Digital-first, lower fees, faster transactions, agile innovation | Disrupting market with cost and speed advantages, driving digital adoption |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The proliferation of digital wallets and mobile payment apps like PayPal, Venmo, and Zelle poses a substantial threat of substitution for Western Union, especially for smaller, everyday transactions. These digital alternatives provide speed, ease of use, and often reduced fees for peer-to-peer and domestic transfers, directly competing with Western Union's core services. In 2024, the global digital payment market is projected to reach over $10 trillion, with mobile payments accounting for a significant and growing portion, underscoring the increasing consumer preference for these convenient substitutes.
Direct bank transfers and online banking services present a significant threat of substitution for Western Union. Customers can increasingly leverage these channels for cross-border payments, often finding them more cost-effective, especially for larger transactions. This growing convenience, despite potential speed differences, makes them a compelling alternative for many consumers and businesses.
In 2024, bank transfers captured a substantial 45.32% of the global cross-border payments market, highlighting their strong competitive position against traditional remittance services like Western Union.
Cryptocurrencies and stablecoins present a significant threat by offering alternative, potentially faster, and more cost-effective cross-border payment solutions. These digital assets can bypass traditional financial intermediaries, directly impacting Western Union's core business model.
In Q1 2024, the average cost of sending $200 via traditional remittance networks stood at 6.6%, a stark contrast to the sub-1% fees often achievable with on-chain cryptocurrency transactions. This cost differential is a powerful incentive for consumers seeking cheaper alternatives.
Western Union is not ignoring this shift, actively piloting stablecoin remittance settlements and exploring consumer-facing crypto wallets. This strategic engagement indicates an acknowledgment of the competitive pressure and a proactive approach to adapting to evolving payment landscapes.
Informal Remittance Channels
Informal remittance channels, such as carrying cash or utilizing hawala systems, remain a significant threat, particularly in areas with underdeveloped formal financial infrastructure or low trust in traditional institutions. These methods can offer faster transactions or lower costs in certain corridors, presenting a less transparent but viable alternative for some users.
For instance, in 2023, remittances to low and middle-income countries reached an estimated $839 billion, a substantial portion of which may have utilized informal channels due to convenience or cost savings in specific contexts. The persistence of these channels highlights a gap in the market that formal providers like Western Union must address.
- Informal channels bypass regulatory oversight, potentially offering faster, cheaper transfers in specific, often underserved, corridors.
- The continued prevalence of informal remittances indicates unmet needs in speed, cost, or accessibility within the formal financial system.
- Estimates suggest that informal remittances can account for a notable percentage of total cross-border money flows, particularly in regions with limited formal banking access.
Integrated Financial Super-Apps
The rise of integrated financial "super-apps" presents a significant long-term threat to traditional remittance services like Western Union. These platforms, often backed by major tech companies, consolidate a wide array of financial functionalities, including payments, savings, and even lending, into a single, user-friendly interface. Their goal is to become the primary financial hub for consumers, offering convenience and potentially better rates by bundling services.
These super-apps can erode Western Union's customer base by providing a more comprehensive and seamless experience. For instance, by mid-2024, many neobanks and fintech platforms have reported substantial user growth, with some super-apps boasting tens of millions of active users globally. This broad adoption means a larger pool of customers can access remittance services as part of a broader financial ecosystem, making it less necessary to use specialized providers.
- Consolidation of Services: Super-apps combine payments, savings, and lending, offering a one-stop financial solution.
- Customer Acquisition: These platforms attract users with convenience and potentially lower costs for bundled financial products.
- Erosion of Niche Markets: By integrating remittances, super-apps can draw customers away from single-service providers.
- Competitive Landscape: The growth of these comprehensive financial tools intensifies competition for global money transfer services.
The threat of substitutes for Western Union is multifaceted, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. Digital wallets, direct bank transfers, and cryptocurrencies offer faster, cheaper, and more convenient alternatives for cross-border payments.
These substitutes are increasingly capturing market share, particularly for everyday transactions and remittances to developing countries. For example, in 2024, the global digital payment market is expected to exceed $10 trillion, with mobile payments playing a dominant role.
Furthermore, informal remittance channels, though less transparent, continue to pose a threat due to their potential for speed and lower costs in specific corridors, especially where formal financial infrastructure is less developed.
| Substitute Type | Key Advantages | Market Penetration (Illustrative 2024 Data) | Impact on Western Union |
| Digital Wallets/Apps | Speed, low fees, ease of use | Global digital payment market > $10 trillion | Direct competition for P2P and smaller transfers |
| Direct Bank Transfers | Cost-effectiveness (especially for large sums) | 45.32% of global cross-border payments | Alternative for value-conscious customers |
| Cryptocurrencies/Stablecoins | Speed, potentially lower transaction costs | Sub-1% fees vs. 6.6% for traditional methods (avg. $200 transfer) | Disruptive potential, bypassing intermediaries |
| Informal Channels | Speed, cost savings in specific contexts | Significant portion of $839 billion remittances to LMICs (2023) | Underserved market needs, regulatory challenges |
Entrants Threaten
The money transfer sector faces substantial regulatory challenges, including stringent anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) mandates that vary significantly by country. These complex compliance requirements, along with the associated operational costs, act as a significant deterrent for potential new entrants seeking to establish a foothold in the market.
Western Union's formidable global agent network, built over decades, acts as a significant barrier for newcomers. This extensive physical footprint, coupled with deeply ingrained brand trust, especially among migrant communities, is not easily replicated. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, Western Union reported operating in approximately 200 countries and territories, a reach that is incredibly challenging and costly for new entrants to match.
New players entering the money transfer market face substantial hurdles related to capital and technology. Establishing competitive digital platforms, integrating advanced technologies like AI and blockchain, and securing the required regulatory licenses demand significant upfront investment.
While venture capital flows into fintech, building a global money transfer operation necessitates ongoing capital for technology upgrades and infrastructure expansion. For instance, Western Union's investment in information and communication technology (ICT) was projected to be around $109.7 million in 2024, highlighting the scale of required expenditure.
Customer Acquisition Costs
Customer acquisition costs represent a significant barrier for new entrants in the money transfer market, particularly for established players like Western Union. Competing for customers in a saturated environment demands substantial investment in marketing and promotions. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to acquire a new customer in the digital financial services sector has seen an upward trend, with some estimates placing it in the hundreds of dollars, especially for services requiring significant trust and habit formation.
Newcomers must often resort to aggressive pricing strategies or compelling unique selling propositions to lure customers away from trusted brands. This can severely impact initial profitability, as the cost of attracting and retaining these customers may outweigh the revenue generated. Western Union, with its extensive global network and brand recognition, benefits from lower relative customer acquisition costs due to its existing customer base and established marketing channels.
The challenge for new entrants is amplified by the need to build trust and overcome the inertia of existing customer relationships. This often translates into higher spending on advertising, referral programs, and introductory offers. By 2024, digital-first remittance services are investing heavily in online advertising and partnerships to gain market share, further driving up acquisition costs across the industry.
- High Marketing Spend: New entrants often face substantial marketing expenses to build brand awareness and attract customers in a crowded market.
- Price Competition: To gain traction, new companies may need to offer lower fees or better exchange rates, impacting their profit margins.
- Trust and Loyalty: Overcoming customer loyalty to established providers like Western Union requires significant effort and investment in building trust.
- Digital Acquisition Costs: The increasing reliance on digital channels means that customer acquisition costs in the fintech space can be considerable, with average costs for acquiring a new user in financial services often ranging from $50 to $200 or more in 2024.
Fintech Innovation Lowering Barriers
Fintech innovation is significantly reducing traditional entry barriers for new players in the financial services sector. Technologies like cloud computing, open banking APIs, and blockchain allow startups to bypass the need for extensive physical branch networks and legacy systems. This digital-first approach enables agile, low-cost operations and faster market entry for digitally native competitors.
For instance, the rise of digital payment platforms and remittance services, often built on cloud infrastructure and leveraging APIs for seamless integration, demonstrates this trend. These platforms can offer competitive pricing and user experiences, directly challenging established players like Western Union. By 2024, the global fintech market was valued at over $1.1 trillion, with a substantial portion driven by innovations that lower operational overhead for new entrants.
- Fintech advancements: Cloud computing, open banking APIs, and blockchain technology are key enablers.
- Reduced infrastructure costs: New entrants can offer digital-only solutions without costly physical presence.
- Agile market entry: Digitally native companies can achieve faster market penetration.
- Market impact: The global fintech market's growth highlights the success of these lower-barrier models.
Despite significant barriers like regulatory compliance and established networks, the threat of new entrants in the money transfer sector remains a persistent concern. Fintech innovations are lowering operational costs and enabling agile market entry for digital-first competitors. For example, the global fintech market's substantial growth underscores the success of these new models.
New entrants can leverage advanced technologies to bypass traditional infrastructure requirements, offering competitive pricing and user experiences. This digital-first approach allows for faster market penetration, directly challenging established players. By 2024, the increasing accessibility of cloud computing and APIs facilitates these lower-cost operations.
The capital required for new ventures is also being addressed by venture capital, though scaling remains a challenge. While Western Union invested heavily in ICT, estimated around $109.7 million in 2024, new digital players can achieve significant reach with more focused, albeit still substantial, technology investments.
Customer acquisition costs are a key battleground, with digital acquisition costs in financial services often ranging from $50 to $200 or more in 2024. New entrants must overcome customer inertia and build trust, often through aggressive marketing and pricing strategies, impacting initial profitability.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
| Regulatory Compliance | Stringent AML/KYC mandates vary by country. | High operational costs and complexity deter entry. | N/A (Country-specific) |
| Agent Network & Brand Trust | Decades of building global physical presence and customer loyalty. | Difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate Western Union's reach. | Western Union operates in ~200 countries. |
| Capital & Technology Investment | Need for advanced digital platforms, AI, blockchain, and licenses. | Requires significant upfront and ongoing capital expenditure. | Western Union ICT investment projected ~$109.7 million. |
| Customer Acquisition Costs | High marketing/promotional spend to attract customers from established players. | Impacts initial profitability; digital acquisition can cost $50-$200+. | Digital financial services customer acquisition costs trending upward. |
| Fintech Innovation | Cloud, APIs, blockchain enable digital-first, low-cost operations. | Reduces traditional barriers, allowing agile market entry. | Global fintech market valued over $1.1 trillion. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Western Union leverages data from their annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings to understand their financial health and strategic positioning. We also incorporate industry reports from financial analysis firms and market research providers to gauge competitive intensity and market trends.