Takeda Pharmaceutical Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Takeda Pharmaceutical Bundle
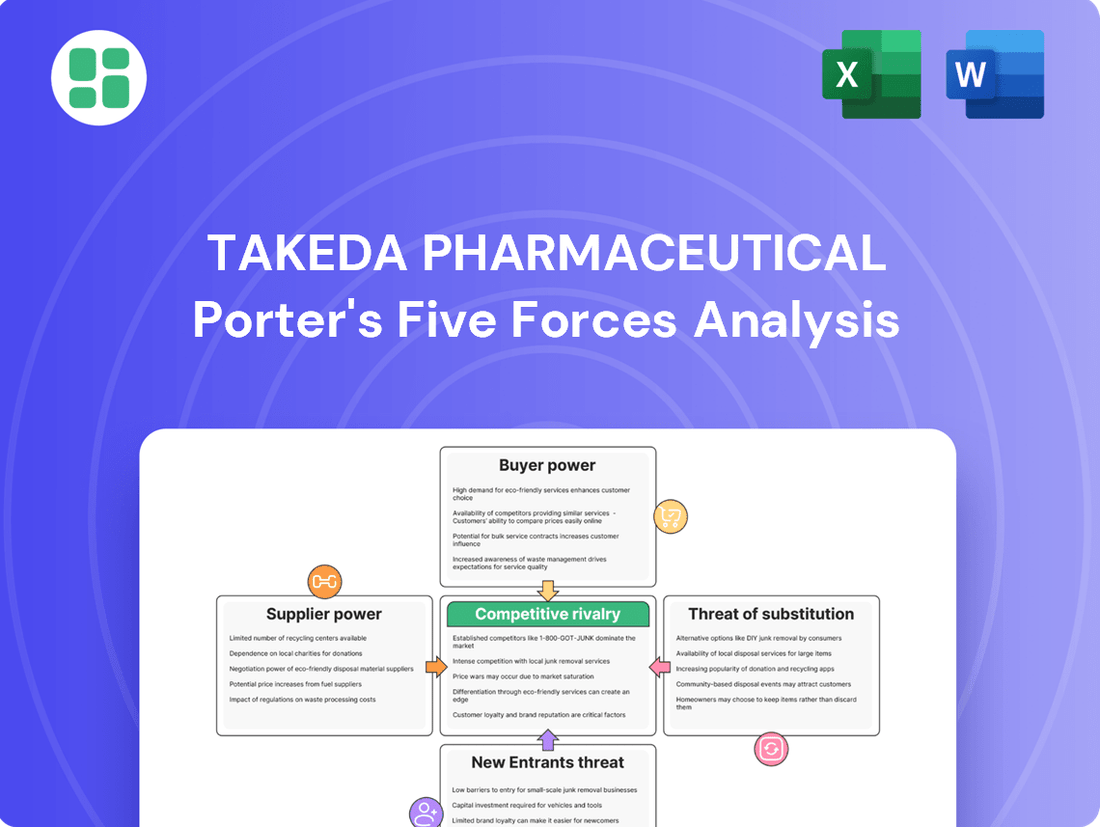
Takeda Pharmaceutical faces intense rivalry, with established players and emerging biotechs vying for market share, while the threat of new entrants is moderated by high R&D costs and regulatory hurdles. Buyer power is significant, driven by healthcare providers and payers demanding value and efficacy. The full analysis reveals the real forces shaping Takeda Pharmaceutical’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Takeda Pharmaceutical, much like its peers in the biopharmaceutical sector, faces a significant challenge due to its reliance on a select group of suppliers for highly specialized raw materials, active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), and critical components for advanced biologics. This limited supplier base, especially for novel treatments, can tip the scales, granting considerable leverage to these suppliers.
The scarcity and often proprietary nature of these essential inputs amplify supplier power. For instance, in the realm of plasma-derived therapies, Takeda's dependence on biological source material, which is inherently complex to source and process, further underscores this dependency and the bargaining power held by its suppliers.
Suppliers in the pharmaceutical sector face rigorous regulatory hurdles, including adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). These stringent requirements significantly limit the number of eligible suppliers, thereby strengthening the position of those already approved.
The substantial investment in time and resources necessary to qualify new suppliers means Takeda, like other pharmaceutical giants, faces high switching costs. This dependency on established, compliant vendors grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power.
Suppliers holding patents on crucial manufacturing processes or unique chemical intermediates can significantly boost their bargaining power with Takeda. These intellectual property rights can essentially grant them a monopoly on essential components, enabling them to dictate pricing and supply terms for Takeda's drug development pipeline. This is a prevalent dynamic in the biopharmaceutical industry, where innovation frequently results in proprietary technologies and materials.
Concentration of Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs)
Takeda Pharmaceutical, like many major drug manufacturers, may engage contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) for specific production needs. The concentration of specialized CMOs in the market can significantly influence Takeda's operational costs and flexibility.
If a limited number of CMOs possess unique capabilities, such as advanced sterile injectable production or complex biologics manufacturing, they can wield considerable bargaining power. This concentration means Takeda might have fewer alternatives, potentially leading to higher pricing or less favorable contract terms.
- Market Concentration: The global pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market, particularly for specialized services, is characterized by a degree of consolidation. For instance, in 2024, the top 10 CMOs are estimated to hold a substantial share of the market, indicating a concentrated supplier landscape for advanced manufacturing needs.
- Specialized Capabilities: CMOs with expertise in high-demand areas like aseptic filling, lyophilization, or the production of highly potent active pharmaceutical ingredients (HPAPIs) often operate with higher utilization rates and can command premium pricing due to their specialized infrastructure and regulatory compliance.
- Capacity Constraints: Periods of high demand for specific drug types or the introduction of novel therapies can strain the capacity of available CMOs, further amplifying their bargaining power as pharmaceutical companies compete for limited production slots.
- Impact on Takeda: For Takeda, reliance on a concentrated pool of CMOs for critical manufacturing steps could translate into increased cost of goods sold and potential delays if supplier capacity is stretched, impacting overall profitability and product launch timelines.
Global Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Global supply chain vulnerabilities, amplified by events like geopolitical tensions and natural disasters, significantly bolster supplier bargaining power. For Takeda Pharmaceutical, operating across a complex international network, these disruptions can create scarcity. In 2024, for instance, continued geopolitical instability in Eastern Europe and extreme weather events in Asia impacted the availability and cost of certain raw materials critical for pharmaceutical production, potentially increasing Takeda's reliance on fewer, more powerful suppliers.
This increased leverage for suppliers means Takeda may face higher input costs or even shortages if alternative sourcing options are limited or require extensive qualification. The ability of suppliers to dictate terms, especially for specialized active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or advanced manufacturing components, becomes more pronounced during periods of widespread disruption. For example, reports from early 2024 indicated that lead times for certain high-purity chemicals essential for novel drug synthesis had lengthened by up to 30% due to these global pressures.
- Increased Input Costs: Suppliers can command higher prices for essential raw materials and components.
- Supply Shortages: Disruptions can lead to scarcity of critical ingredients, impacting production schedules.
- Limited Sourcing Options: Geopolitical and environmental factors can reduce the number of viable alternative suppliers.
- Extended Lead Times: The time taken to procure necessary materials can significantly increase, affecting Takeda's operational efficiency.
Takeda's bargaining power with its suppliers is notably constrained by the specialized nature of pharmaceutical inputs and the stringent regulatory environment. This means suppliers of critical raw materials, APIs, and advanced manufacturing components, particularly those with proprietary technologies or unique capabilities, hold significant leverage. For instance, in 2024, the limited number of qualified suppliers for certain complex biologics components means Takeda faces higher costs and potential capacity constraints, impacting its ability to scale production efficiently.
The high switching costs associated with qualifying new suppliers, coupled with supplier patents on essential manufacturing processes, further solidify their bargaining power. This dependency allows suppliers to dictate terms, especially for novel drug development inputs where alternatives are scarce. For example, lead times for specific high-purity chemicals used in cutting-edge therapies saw increases of up to 30% in early 2024 due to global supply chain pressures, directly impacting Takeda's procurement costs and timelines.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Takeda | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Supplier Specialization & Scarcity | Reliance on few suppliers for unique APIs, biologics components. | High input costs, potential supply disruptions. | Limited qualified suppliers for advanced biologics components. |
| Regulatory Hurdles & Qualification Costs | Stringent GMP requirements limit supplier pool; high switching costs. | Supplier pricing power, dependency on established vendors. | Extensive time and resources needed to approve new suppliers. |
| Intellectual Property (Patents) | Suppliers holding patents on key processes or intermediates. | Suppliers can act as near-monopolies, dictating terms. | Proprietary technologies are common for novel drug synthesis. |
| Contract Manufacturing (CMOs) Concentration | Consolidation in specialized CMO market. | Increased costs, reduced flexibility due to limited alternatives. | Top 10 CMOs hold significant market share in specialized services. |
| Global Supply Chain Vulnerabilities | Geopolitical instability, extreme weather impacting material availability. | Increased costs, extended lead times, fewer sourcing options. | Lead times for critical chemicals increased up to 30% in early 2024. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Takeda Pharmaceutical's unique position in the global pharmaceutical industry.
Instantly understand strategic pressure with a powerful spider/radar chart, visualizing Takeda's competitive landscape to pinpoint key areas for pain point relief.
Customers Bargaining Power
Takeda's main customers are major healthcare systems, hospitals, and government payers, who buy drugs in bulk. These large purchasers have considerable power to negotiate prices, formulary placement, and reimbursement terms, especially in markets with multiple treatment options.
The growing influence of payers, driven by a strong focus on cost containment, directly affects Takeda's ability to set prices. For instance, in 2024, many national health systems continued to implement stricter drug pricing regulations and value-based purchasing agreements, putting pressure on pharmaceutical companies like Takeda to demonstrate clear cost-effectiveness.
Governmental pricing regulations, like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act, are directly curtailing Takeda's pricing flexibility for its innovative drugs. This legislation, enacted in 2022, allows Medicare to negotiate prices for certain high-cost prescription drugs, a move that could significantly impact Takeda's revenue streams for key products.
European legislative revisions also aim to control pharmaceutical expenditures, further amplifying the bargaining power of governments as major purchasers. These policy shifts are a growing concern for pharmaceutical companies like Takeda, as they represent a substantial increase in customer leverage over pricing.
The availability of generics and biosimilars significantly erodes Takeda's bargaining power. When patents expire, as seen with the generic competition for Takeda's ADHD medication VYVANSE®, customers gain access to much cheaper alternatives, directly impacting Takeda's pricing leverage.
This trend forces Takeda to confront price competition, especially for its high-revenue products, diminishing its ability to dictate terms and increasing customer influence over purchasing decisions.
Patient Advocacy and Awareness
While individual patients usually have limited direct sway, organized patient advocacy groups and growing patient knowledge regarding treatment choices and expenses can indirectly impact healthcare providers and insurance companies. This dynamic can create pressure for more cost-effective or accessible therapies, influencing Takeda's strategic market approaches.
For instance, in 2024, patient advocacy organizations continued to play a crucial role in shaping policy discussions around drug pricing and access. Groups like the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) actively engage with pharmaceutical companies and policymakers to advocate for patient needs, potentially influencing market access and reimbursement for Takeda's products, particularly in specialized therapeutic areas.
- Increased Patient Awareness: Patients are increasingly informed about treatment alternatives and associated costs, empowering them to seek more value.
- Advocacy Group Influence: Collective action by patient groups can exert significant pressure on pricing and access policies.
- Impact on Takeda: This can lead to demands for more affordable or accessible treatments, influencing Takeda's market strategies and R&D priorities.
Shift towards Value-Based Healthcare Models
The increasing adoption of value-based healthcare models significantly amplifies the bargaining power of customers in the pharmaceutical industry. Instead of simply paying for the quantity of drugs, payers and providers are now increasingly tying reimbursement to demonstrable patient outcomes and real-world effectiveness. This paradigm shift places greater risk on pharmaceutical companies like Takeda.
This means customers are demanding robust evidence of a drug's value, which strengthens their position in negotiations. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of US healthcare providers are actively participating in value-based care arrangements, directly impacting how they procure pharmaceuticals.
Consequently, Takeda and its peers face heightened pressure to prove their products deliver superior clinical and economic benefits compared to alternatives. This necessitates a focus on real-world data generation and outcome-based contracting, giving customers more leverage to negotiate pricing and access.
- Shift in Reimbursement: From fee-for-service to outcomes-based payments.
- Increased Customer Leverage: Payers and providers demand proof of value.
- Risk Transfer: Pharmaceutical companies bear more risk for product efficacy.
- Negotiation Power: Customers can negotiate based on demonstrated real-world benefits.
Takeda's customers, primarily large healthcare systems and government payers, wield significant bargaining power due to their bulk purchasing and focus on cost containment. In 2024, stricter pricing regulations and value-based purchasing agreements, like those under the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act, directly limited Takeda's pricing flexibility. The increasing availability of generics and biosimilars further erodes Takeda's leverage, forcing price competition and diminishing its ability to dictate terms.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Takeda (2024 Focus) |
| Major Healthcare Systems/Hospitals | Bulk purchasing, formulary control, demand for evidence-based value | Negotiate lower prices, influence product placement, require outcome data |
| Government Payers (e.g., Medicare, National Health Systems) | Price negotiation mandates (e.g., IRA), strict reimbursement policies, cost containment focus | Directly reduces pricing flexibility, limits revenue for key products, increases focus on cost-effectiveness |
| Generics/Biosimilar Manufacturers (indirect customer influence) | Patent expiry, lower production costs, market entry | Erodes pricing power, forces price competition, reduces market share for branded products |
| Patient Advocacy Groups | Influence on policy, public awareness, advocacy for access and affordability | Indirectly pressures providers and payers, potentially influencing market access and reimbursement strategies |
Full Version Awaits
Takeda Pharmaceutical Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Takeda Pharmaceutical, detailing the competitive landscape through bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and industry rivalry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, offering an in-depth strategic overview of Takeda's market position. You're looking at the actual document, ready for download and use the moment you buy, providing actionable insights for your business strategy.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The biopharmaceutical sector thrives on innovation, compelling companies like Takeda to pour substantial resources into research and development. In 2023, Takeda reported R&D expenses of approximately ¥517.9 billion (around $3.5 billion USD at the time), highlighting the significant financial commitment required to stay competitive.
Takeda actively competes in key therapeutic areas such as Oncology, Rare Diseases, Neuroscience, and Gastroenterology. In these fields, multiple companies are vying to develop breakthrough treatments, intensifying the rivalry for market share and scientific leadership. For instance, in the oncology space, numerous companies are developing CAR-T therapies and targeted small molecules, directly challenging Takeda's existing and pipeline products.
The success of a robust late-stage pipeline, a hallmark of companies like Takeda, is vital for future growth. However, this segment is inherently risky, with high attrition rates meaning many promising drug candidates fail during clinical trials. This dynamic adds another layer of competitive pressure, as companies must continuously replenish their pipelines to offset potential failures and maintain a strong market position.
Takeda faces intense competition from other global pharmaceutical heavyweights like AbbVie, Merck (MSD), Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), and Pfizer. These companies possess broad product offerings and substantial market presence, directly challenging Takeda across numerous therapeutic categories.
The rivalry is amplified by these competitors' extensive research and development pipelines and their established global distribution networks. For instance, in 2024, major pharmaceutical companies continued to invest heavily in R&D, with companies like Pfizer reporting billions in R&D expenditure, aiming to bring innovative treatments to market and capture significant market share, directly impacting Takeda's competitive landscape.
The pharmaceutical sector, including Takeda, is navigating a substantial patent cliff. This means many blockbuster drugs are losing their patent protection, opening the door for generic and biosimilar alternatives. For instance, several major drugs that previously generated billions in revenue are now facing or have recently faced generic competition, directly impacting market share and pricing power.
This loss of exclusivity significantly intensifies rivalry. Companies like Takeda must contend with lower-priced generics, which can rapidly erode sales of previously protected medications. In 2024, the impact of these patent expirations continues to be a major factor, forcing aggressive strategies to mitigate revenue declines and maintain market presence against a growing number of competitors.
Product Differentiation and Innovation Race
Competitive rivalry in the pharmaceutical sector, particularly for Takeda, is intensely fueled by the relentless pursuit of innovation and product differentiation. This is especially true in areas like orphan drugs and treatments for conditions with significant unmet medical needs. Companies are constantly striving to develop therapies that offer a clear advantage in terms of effectiveness, safety profiles, or ease of use. Successfully bringing such breakthrough treatments to market allows firms to capture substantial market share and command premium pricing before the advent of generic competition.
This innovation race is evident in the significant R&D investments made by major pharmaceutical players. For instance, Takeda’s commitment to research and development is substantial, with their R&D expenditure often representing a significant portion of their revenue. In fiscal year 2023, Takeda reported R&D expenses of approximately ¥500 billion (around $3.5 billion USD at current exchange rates), underscoring the high stakes involved in developing novel therapeutics.
- Orphan Drug Dominance: Companies vie for leadership in rare disease markets, where initial market exclusivity can be highly lucrative.
- Biologics and Advanced Therapies: The development of complex biologics, gene therapies, and cell therapies represents a key battleground for differentiation.
- Clinical Trial Success Rates: Pharmaceutical companies face intense rivalry in securing positive clinical trial outcomes, which are critical for regulatory approval and market adoption.
- Patent Cliffs and Pipeline Strength: The looming expiration of patents on blockbuster drugs forces companies to continuously replenish their pipelines with innovative new products to maintain revenue streams.
Strategic Alliances and M&A Activity
Takeda actively participates in strategic alliances and M&A to enhance its competitive standing. These moves are crucial for pipeline expansion, technology acquisition, and market penetration in the dynamic pharmaceutical sector.
In 2024, Takeda continued its strategy of targeted collaborations and acquisitions. For instance, the company has focused on bolstering its oncology and rare disease portfolios through licensing agreements and smaller strategic tuck-in acquisitions.
- Takeda's 2024 focus on strategic alliances aims to strengthen its pipeline in key therapeutic areas.
- The company engages in licensing deals to access novel drug candidates and technologies.
- M&A activity is strategically employed to gain market access and consolidate competitive positions.
Competitive rivalry for Takeda is fierce, driven by numerous global pharmaceutical giants like AbbVie, Merck, BMS, and Pfizer. These companies compete across Takeda's key therapeutic areas, including Oncology, Rare Diseases, Neuroscience, and Gastroenterology.
The intensity of this rivalry is amplified by substantial R&D investments, with major players like Pfizer continuing to invest billions in 2024 to develop innovative treatments. Furthermore, the ongoing patent cliff exposes many drugs to generic competition, intensifying the battle for market share and revenue preservation.
Takeda's strategy involves strategic alliances and acquisitions to bolster its pipeline, as seen in its 2024 focus on collaborations for oncology and rare disease portfolios, aiming to maintain a competitive edge in a highly dynamic market.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most substantial threat of substitutes for Takeda Pharmaceutical stems from generic and biosimilar drugs. These are essentially cheaper versions of Takeda's branded medications that have had their patent protection expire. For instance, the market for ADHD medication VYVANSE® saw a significant impact from generic entrants shortly after patent expiry, demonstrating how quickly market share and revenue can be affected.
For certain medical conditions, non-pharmaceutical interventions like dietary adjustments, increased physical activity, surgical procedures, or physical therapy can function as viable substitutes for Takeda's pharmaceutical products. While Takeda concentrates on developing advanced medicines for challenging diseases, the availability of these alternative approaches, even if they are less effective for severe conditions, can indeed constrain the potential market size for specific drug classes.
In certain markets, particularly in regions with strong cultural traditions or for less severe ailments, patients might view traditional or herbal remedies as viable alternatives to Takeda's pharmaceutical products. While these often lack the clinical trial data characteristic of Western medicine, their accessibility and lower price points can make them a compelling substitute for a segment of the population.
For instance, the global market for traditional and complementary medicine is substantial, with projections indicating continued growth. Reports from 2024 suggest this sector is valued in the hundreds of billions of dollars worldwide, demonstrating a significant existing patient base that may not automatically turn to conventional pharmaceuticals.
Preventative Measures and Vaccines
The increasing emphasis on preventative healthcare and the development of robust vaccines present a significant threat of substitutes for Takeda Pharmaceutical. For instance, Takeda's own QDENGA®, a dengue vaccine, highlights this trend. Successful widespread vaccination campaigns can directly reduce the incidence of diseases, thereby lowering the demand for therapeutic treatments that Takeda might offer for those same conditions.
This shift towards prevention can shrink the addressable market for certain Takeda products. While Takeda benefits from its vaccine portfolio, the overall reduction in disease prevalence due to effective preventative measures means fewer patients will require treatment for those specific illnesses. This dynamic directly impacts the revenue potential for their therapeutic drug lines.
- Preventative Healthcare Growth: The global preventative healthcare market is projected to reach USD 75.3 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2022, indicating a strong trend away from solely reactive treatments.
- Vaccine Market Expansion: The worldwide vaccine market size was valued at USD 60.4 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 5.9% from 2024 to 2030, demonstrating significant investment and uptake.
- Impact on Therapeutic Demand: For diseases where effective vaccines are widely adopted, the demand for corresponding treatments can decline by as much as 70-80% in well-vaccinated populations.
Off-label Use of Existing Drugs
The off-label use of existing drugs poses a significant threat of substitution for Takeda Pharmaceutical. Physicians may prescribe established medications for unapproved conditions, particularly if they are more affordable or readily available. This practice can divert patients from newer, more specialized therapies that Takeda might be developing. For instance, in 2024, the market for repurposed drugs continued to expand, with a notable increase in clinical trials exploring existing compounds for novel indications. This trend directly impacts the potential market share for Takeda's innovative treatments.
This substitution threat is amplified when older, less expensive drugs demonstrate efficacy in treating conditions for which Takeda has new, patented medications. Such scenarios can delay or diminish the adoption of Takeda's therapies, impacting revenue projections. By 2024, several studies highlighted instances where off-label prescribing of older antivirals or anti-inflammatories successfully managed conditions that were later targeted by new drug development. This creates a competitive pressure that Takeda must actively monitor and strategize against.
- Off-label prescribing can cannibalize sales of new Takeda drugs.
- Repurposed drugs offer a cost-effective alternative, pressuring Takeda’s pricing.
- Regulatory bodies’ stance on off-label use influences this substitution threat.
- The growing market for drug repurposing in 2024 underscores this competitive dynamic.
The threat of substitutes for Takeda Pharmaceutical is multifaceted, primarily driven by generic and biosimilar drugs that emerge post-patent expiry, significantly impacting revenue streams. Furthermore, non-pharmaceutical interventions and traditional remedies, though often less potent, offer accessible alternatives for certain patient segments. The growing emphasis on preventative healthcare, including vaccines, directly reduces the incidence of diseases, thereby diminishing the need for Takeda's therapeutic treatments.
| Threat Category | Description | 2024 Data/Projections |
| Generic/Biosimilar Drugs | Cheaper versions of branded drugs after patent expiry. | Market impact observed post-patent expiry for key drugs. |
| Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions | Lifestyle changes, surgery, physical therapy. | Constrains market size for specific drug classes. |
| Traditional/Herbal Remedies | Accessible and lower-priced alternatives. | Global market in hundreds of billions of dollars, showing existing patient base. |
| Preventative Healthcare & Vaccines | Reduces disease incidence, lowering demand for treatments. | Vaccine market valued at USD 60.4 billion in 2023, growing at 5.9% CAGR (2024-2030). |
| Off-label Drug Use | Existing drugs prescribed for unapproved conditions. | Repurposed drug market expanding in 2024, impacting new therapy adoption. |
Entrants Threaten
The biopharmaceutical sector presents a formidable barrier to entry due to exceptionally high research and development (R&D) costs. Bringing a new drug from discovery to market typically demands billions of dollars, with estimates often exceeding $2 billion, and this process can easily span more than a decade. These immense financial requirements act as a significant deterrent for any new company looking to compete with established players like Takeda Pharmaceutical.
Stringent regulatory approval processes represent a formidable barrier to entry in the pharmaceutical sector, significantly impacting Takeda Pharmaceutical. Companies seeking to introduce new drugs must navigate complex and lengthy clinical trials, often spanning years and costing hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) demand extensive data on safety and efficacy, making the path to market a substantial hurdle.
Takeda Pharmaceutical benefits significantly from strong intellectual property protection, particularly its extensive patent portfolios for innovative drugs. These patents grant Takeda market exclusivity for extended periods, creating a substantial barrier for potential new entrants seeking to offer similar treatments. For instance, in 2024, the pharmaceutical industry continued to see blockbuster drugs protected by patents, allowing companies like Takeda to recoup significant R&D investments and maintain pricing power.
Need for Established Distribution Channels and Market Access
New entrants into the pharmaceutical industry, particularly those aiming to compete with established players like Takeda, face significant hurdles in securing effective distribution channels and achieving broad market access. Building a robust network that reliably reaches hospitals, pharmacies, and diverse healthcare providers worldwide requires substantial investment and time. This is a critical barrier, as without this infrastructure, even innovative treatments struggle to reach patients.
Takeda, for instance, has cultivated decades-long relationships with key stakeholders across the global healthcare ecosystem. This established presence and deep market penetration are not easily replicated by newcomers. Their existing distribution agreements and proven track record provide a competitive advantage that new entrants must overcome, often through strategic partnerships or substantial upfront investment in logistics and sales infrastructure.
- Distribution Network Investment: Establishing a global pharmaceutical distribution network can cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars, encompassing warehousing, cold chain logistics, and regulatory compliance in multiple countries.
- Market Access Challenges: Gaining formulary acceptance and reimbursement from payers and healthcare systems is a lengthy and complex process, often requiring extensive clinical data and negotiation.
- Takeda's Global Reach: As of fiscal year 2023, Takeda reported operations in approximately 80 countries and regions, demonstrating the scale of its established market access.
- Barriers to Entry: The sheer capital required and the time needed to build comparable distribution and market access capabilities present a formidable threat to new entrants.
Brand Loyalty and Reputational Capital
In therapeutic areas where Takeda has established a strong presence, brand loyalty among physicians and patients acts as a significant barrier for new entrants. The trust built over years of delivering effective treatments and maintaining a robust reputation makes it challenging for new companies to gain traction and capture substantial market share.
For instance, Takeda's long-standing commitment to oncology, a core area for the company, has fostered deep relationships with key opinion leaders and patient advocacy groups. This established trust, coupled with proven product efficacy, means new entrants face an uphill battle in displacing Takeda's established market position. In 2024, Takeda continued to invest heavily in its established oncology portfolio, reinforcing its brand strength.
- Physician Loyalty: Doctors often prescribe treatments they trust and have had success with, making it difficult for new, unproven therapies to gain acceptance.
- Patient Trust: Patients who have benefited from Takeda's medications are less likely to switch to alternatives unless there's a compelling clinical or economic reason.
- Reputational Capital: Takeda's history of innovation and patient care contributes to a strong brand image that new competitors must work hard to replicate.
The threat of new entrants for Takeda Pharmaceutical is generally low due to substantial barriers. High R&D costs, often exceeding $2 billion per drug, and lengthy development timelines create significant financial hurdles. Regulatory approval processes are rigorous, requiring years of clinical trials and extensive data submission, further deterring newcomers.
Intellectual property protection, primarily through patents, grants Takeda market exclusivity, preventing direct competition for a considerable period. For example, in 2024, many established drugs remained under patent protection, securing market share. Building robust global distribution networks and gaining market access, which Takeda has cultivated over decades with operations in approximately 80 countries by fiscal year 2023, also presents immense challenges for new companies.
Physician and patient loyalty, particularly in Takeda's core therapeutic areas like oncology, is another key barrier. Established trust and a proven track record of efficacy make it difficult for new entrants to displace Takeda's strong market position. Takeda's continued investment in its established portfolios in 2024 further solidifies this advantage.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Takeda's Advantage |
| R&D Costs | Exceeding $2 billion per drug, taking over a decade. | Prohibitive capital requirement. | Established R&D infrastructure and funding. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex, lengthy clinical trials and data submission. | Significant time and cost to market. | Expertise in navigating global regulatory bodies. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents granting market exclusivity. | Prevents direct competition for patented drugs. | Extensive patent portfolio. |
| Distribution & Market Access | Building global networks and securing payer acceptance. | Requires massive investment and time. | Global presence in ~80 countries (FY2023), established relationships. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Trust built with physicians and patients. | Difficult to gain traction against established brands. | Strong reputation in key therapeutic areas like oncology. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Takeda Pharmaceutical is built upon a foundation of robust data, including Takeda's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like IQVIA and GlobalData. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and regulatory databases to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.