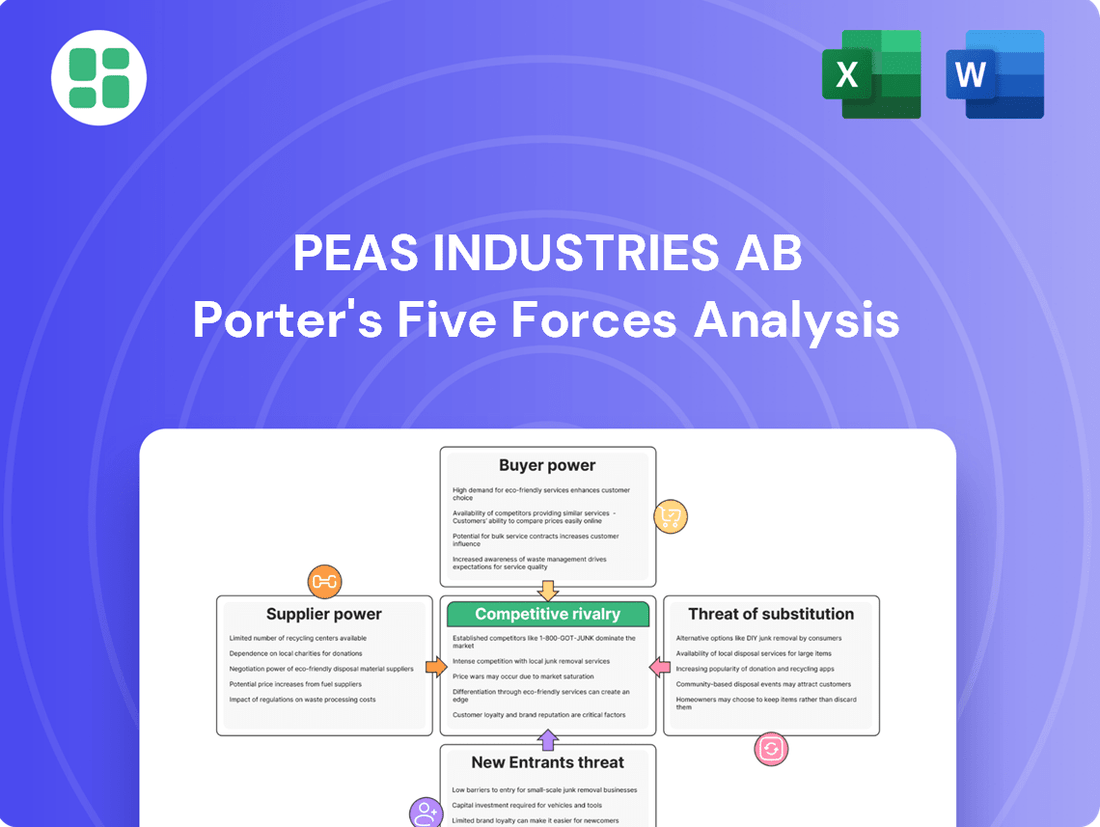
Peas industries AB Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Peas industries AB Bundle
Peas industries AB navigates a landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and the looming threat of substitutes, while supplier power and rivalry intensity present distinct challenges. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Peas industries AB’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The renewable energy sector, especially solar and wind power, depends on a limited number of global suppliers for essential parts like advanced solar panels and big wind turbines. This situation often grants these suppliers considerable leverage, particularly when demand exceeds availability or when few other companies can produce specific technologies.
For PEAS Industries AB, securing these components at favorable prices is directly influenced by this market concentration. For instance, in 2024, the global polysilicon market, a key material for solar panels, saw prices fluctuate significantly due to supply chain constraints, impacting the cost of solar module production for companies like PEAS.
Suppliers in the renewable energy sector, particularly those providing specialized components like high-efficiency solar cells or advanced wind turbine blades, often possess significant bargaining power due to their proprietary technologies and patents. This technological specialization means buyers, such as PEAS Industries AB, face high switching costs or potential performance compromises if they change suppliers. For instance, a patent on a unique solar cell material could lock in buyers who require that specific performance characteristic.
Switching suppliers for critical components like wind turbines or solar inverters presents significant hurdles for PEAS Industries AB. These challenges include the costs associated with redesigning existing systems, obtaining new certifications, and retraining operational staff. For instance, a major solar inverter supplier change could necessitate extensive re-engineering of grid connection protocols and safety checks, potentially costing millions.
These substantial switching costs significantly reduce PEAS Industries AB's bargaining power with its current suppliers. The financial and operational burden of transitioning to a new provider often outweighs any perceived short-term cost savings, making it more practical to continue with established relationships, even if pricing is not at its absolute lowest.
Impact of Raw Material Volatility
The prices for key raw materials, like polysilicon for solar panels or critical minerals essential for wind turbine magnets, are inherently volatile on the global market. PEAS Industries AB, like other developers, faces the direct impact of these price swings as suppliers often pass these increased costs and associated financial risks onto them, thereby elevating project expenses.
Suppliers' capacity to either absorb these cost fluctuations or transfer them to buyers significantly shapes their bargaining power within the industry. For instance, in 2024, the price of polysilicon saw considerable movement, impacting the cost structure for solar panel manufacturers and, consequently, their customers.
- Polysilicon Price Fluctuations: Global polysilicon prices experienced significant volatility throughout 2024, with some reports indicating price increases of over 30% in certain periods due to supply chain disruptions and increased demand.
- Rare Earth Element Costs: The cost of rare earth elements, crucial for high-performance magnets in wind turbines, also saw upward pressure in 2024, driven by geopolitical factors and concentrated supply sources, directly affecting turbine manufacturing costs.
- Supplier Cost Absorption: Suppliers with greater financial reserves or diversified production capabilities are better positioned to absorb cost increases, thereby reducing their reliance on passing these onto customers like PEAS Industries AB.
Availability of Specialized Services and Financing
Beyond just physical components, the availability of specialized services and financing significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. For PEAS Industries AB, critical services such as grid connection engineering, the construction of large-scale renewable energy projects, and securing project financing are paramount.
When there are only a few providers offering these specialized services or unique financing structures, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. PEAS Industries AB's dependency on external capital and expert construction teams for its projects means these suppliers can command more favorable terms.
- Specialized Services: Grid connection engineering and large-scale project construction require unique expertise, limiting the number of capable providers.
- Project Financing: Access to specialized financing structures or a limited pool of project finance providers can grant significant influence.
- PEAS Industries AB's Reliance: The company's need for external capital and skilled construction partners amplifies the bargaining power of these service and finance providers.
Suppliers of specialized components and raw materials for PEAS Industries AB hold significant bargaining power. This is due to market concentration, proprietary technology, and the high costs associated with switching suppliers, as seen with polysilicon and rare earth elements in 2024. The limited number of providers for critical services like grid connection engineering and project financing further amplifies this power, directly impacting PEAS Industries AB's project costs and terms.
| Supplier Type | Key Factor | Impact on PEAS Industries AB (2024 Data) | Supplier Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Component Manufacturers (e.g., Solar Panels, Wind Turbines) | Market Concentration, Proprietary Technology | Polysilicon prices increased by over 30% in some 2024 periods; Rare earth element costs rose due to geopolitical factors. | High |
| Raw Material Suppliers (e.g., Polysilicon, Rare Earths) | Global Price Volatility, Supply Chain Constraints | Directly passed on increased costs, elevating project expenses for renewable energy developers. | High |
| Specialized Service Providers (e.g., Grid Connection Engineering) | Limited Number of Capable Providers, Unique Expertise | High dependency on specialized engineering teams for project execution. | Moderate to High |
| Project Financing Providers | Access to Capital, Specialized Financing Structures | Reliance on external capital and specific financing arrangements. | Moderate to High |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Peas industries AB's competitive landscape identifies the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Peas Industries AB's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive forces, simplifying strategic decision-making and alleviating the pain of complex market assessments.
Customers Bargaining Power
PEAS Industries AB's main clients are typically large utility companies or major corporations looking for long-term Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). These substantial buyers wield considerable bargaining power because of the sheer volume of electricity they commit to purchasing, directly impacting PEAS's revenue streams and contract terms.
The European corporate PPA market experienced robust growth in 2024, with projections suggesting new benchmarks would be set in 2025. This indicates high customer interest but also reinforces the significant leverage these large-scale off-takers have in negotiations, potentially leading to more favorable pricing for them.
Customers possess significant bargaining power due to the increasing availability of alternative energy sources. This includes not only other renewable energy developers but also traditional fossil fuel options, although renewables are becoming more cost-competitive. For instance, in 2024, the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for new solar photovoltaic (PV) projects continued its downward trend, making it a more compelling alternative for consumers.
The proliferation of diverse energy choices, such as distributed generation like rooftop solar or enhanced energy efficiency measures, further empowers customers. This allows them to switch providers or even generate their own power, directly impacting Peas Industries AB's ability to dictate terms. By 2023, the global installed capacity for solar PV had surpassed 1 terawatt, illustrating the widespread adoption and accessibility of this alternative.
Regulatory mandates, such as renewable portfolio standards and carbon pricing mechanisms, significantly bolster the bargaining power of customers in the energy sector. These regulations compel entities, particularly large corporations and governmental bodies, to actively seek out and procure renewable energy to meet their decarbonization targets. This creates a scenario where renewable energy developers must compete through bidding processes to secure long-term Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), thereby enhancing customer leverage.
Corporate off-takers are a primary driver of growth in the PPA market, with many companies setting ambitious net-zero or carbon reduction goals. For instance, in 2024, a substantial portion of new renewable energy capacity additions were underpinned by corporate PPAs, reflecting this trend. These agreements allow businesses to lock in predictable energy costs while demonstrating their commitment to sustainability, giving them considerable negotiating power with suppliers.
Price Sensitivity and Cost Predictability
Customers, especially large businesses, are very focused on price and want to know their energy costs well in advance. PEAS Industries AB's ability to offer stable Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) prices for a long time is key to attracting and keeping these customers. They will use this to get the best deals.
The drop in PPA prices seen in the first quarter of 2024 is a significant factor. This trend could push more corporate buyers to secure long-term contracts, as it presents an opportunity for cost savings. For instance, if average PPA prices fell by 5% in Q1 2024, it directly impacts the bargaining position of large energy consumers.
- Price Sensitivity: Large industrial customers prioritize stable, predictable energy costs.
- PPA Leverage: Customers will use their purchasing power to negotiate favorable long-term PPA terms.
- Market Influence: Declining PPA prices, such as a potential 5% drop in Q1 2024, empower buyers.
- Cost Predictability: Securing long-term, competitive PPA prices is crucial for customer retention.
Project Scale and Customization Demands
The bargaining power of customers for Peas Industries AB is significantly influenced by the scale and customization demands of renewable energy projects. Large-scale projects, often requiring substantial upfront capital, give customers leverage, particularly when their energy needs are highly specific. For instance, a utility company seeking a 500 MW solar farm tailored to a particular region's grid requirements will likely negotiate more assertively than a small business purchasing standard solar panels.
Customers demanding bespoke solutions, such as unique integration with existing infrastructure or specific environmental performance metrics, can wield considerable power. This is especially true when these customized projects are integral to the customer's long-term energy strategy and operational continuity. In 2024, the global renewable energy sector saw continued growth, with project developers increasingly seeking tailored solutions, thereby amplifying customer influence in contract negotiations.
- Project Scale: Larger projects often translate to higher customer bargaining power due to increased investment and potential for long-term partnerships.
- Customization Needs: Tailored renewable energy solutions, designed to meet specific operational or locational requirements, empower customers during price and term negotiations.
- Strategic Importance: When a renewable energy project is critical to a customer's overall energy strategy or business continuity, their ability to influence terms is heightened.
- Market Trends (2024): The increasing demand for customized renewable energy solutions in 2024 has amplified customer leverage in negotiations across the sector.
PEAS Industries AB faces significant customer bargaining power, primarily from large utility companies and corporations seeking long-term Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). These major buyers can negotiate favorable terms due to the sheer volume of electricity they commit to purchasing, impacting PEAS's revenue and contract conditions.
The European corporate PPA market's robust growth in 2024 and projected further expansion in 2025 underscore customer demand but also highlight their leverage in securing advantageous pricing. Furthermore, the increasing availability of alternative energy sources, including cost-competitive solar PV, empowers customers to switch providers or even generate their own power, diminishing PEAS's pricing control.
Customers' ability to negotiate is amplified by regulatory mandates like renewable portfolio standards and carbon pricing, which compel them to procure renewable energy. This competitive bidding environment for PPAs strengthens customer influence, especially as corporate off-takers drive market growth by setting ambitious net-zero goals, as evidenced by the substantial portion of new renewable capacity additions underpinned by corporate PPAs in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on PEAS Industries AB | Supporting Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Volume | High leverage for large buyers due to significant energy commitments. | Major utility companies and corporations are PEAS's primary clients. |
| Alternative Energy Sources | Reduces customer dependency and increases negotiation power. | Declining LCOE for solar PV in 2024 makes it a more viable alternative. |
| Regulatory Environment | Empowers customers to demand renewable energy, increasing competition. | Mandates for decarbonization drive corporate PPA procurement. |
| Market Growth & Goals | Corporate net-zero targets increase demand for PPAs, giving buyers leverage. | Significant portion of 2024 renewable capacity additions secured by corporate PPAs. |
Same Document Delivered
Peas industries AB Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Peas Industries AB, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within its market. The document you see here is precisely what you'll receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate utility for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The European renewable energy sector, especially solar and wind, is booming, drawing in many developers and investors. This creates a highly fragmented market where PEAS Industries AB faces competition from large utility companies, independent power producers (IPPs), and niche renewable energy firms.
This crowded field intensifies rivalry as companies compete fiercely for new projects and a larger slice of the market. For instance, in 2023, the EU saw a significant increase in new renewable capacity installations, with solar PV leading the charge, underscoring the intense competition for development opportunities.
The intense competition within the renewable energy sector, particularly for Peas Industries AB, is significantly fueled by the scarcity of prime development sites. Finding locations with excellent wind resources, high solar irradiance, and accessible grid connection points is becoming increasingly challenging.
A critical bottleneck exacerbating this rivalry is the lagging investment in grid infrastructure compared to the rapid expansion of renewable electricity generation. This disparity creates significant hurdles for new projects seeking to connect to the grid.
This competition for limited, high-quality resources drives up development costs. For instance, in 2024, the average cost per megawatt for new solar projects in Europe saw an increase due to these site acquisition and grid connection challenges, directly impacting project margins for companies like Peas Industries AB.
The renewable energy sector, including solar, is heavily shaped by government policies and regulations, creating a dynamic competitive environment. For example, changes in solar panel import tariffs or renewable energy credit schemes can significantly alter market conditions and competitive advantages for companies like Peas Industries AB.
In 2024, the European Union's solar market continues to grapple with evolving trade policies and pricing pressures, directly impacting the profitability and strategic decisions of industry players. These regulatory shifts can rapidly reconfigure the playing field, making adaptability crucial for maintaining market share and profitability.
Capital Intensity and Access to Financing
Renewable energy project development, like that undertaken by Peas Industries AB, is inherently capital-intensive. These ventures demand substantial upfront investments, making access to financing a critical determinant of competitive strength. While renewables generally maintained a cost advantage over fossil fuels in 2024, the cost of capital itself became a decisive factor in project viability and competitive bidding.
Companies possessing robust financial backing and streamlined access to capital markets are better positioned to outbid competitors or secure the resources for larger, more impactful portfolios. The significant investment needs of clean energy projects underscore the paramount importance of managing the cost of capital effectively. For instance, in 2024, the average cost of debt for renewable energy projects saw fluctuations influenced by macroeconomic conditions and investor sentiment, directly impacting project economics.
- High Upfront Investment: Renewable energy projects, such as solar farms and wind installations, require significant initial capital outlay, often in the hundreds of millions or even billions of dollars.
- Financing Costs as a Differentiator: In 2024, the cost of borrowing or raising equity played a crucial role. Projects with lower financing costs could offer more competitive power purchase agreements (PPAs).
- Competitive Edge for Well-Funded Firms: Companies with strong balance sheets and established relationships with lenders or equity investors could secure capital more readily and at better rates, enabling them to pursue more opportunities.
- Impact on Project Scale and Scope: Access to capital directly influences the size and ambition of projects a company can undertake, allowing well-financed entities to develop larger, more efficient, and ultimately more profitable renewable energy assets.
Innovation in Technology and Business Models
Competitive rivalry within the renewable energy sector, including for companies like Peas Industries AB, is intensified by rapid technological advancements and evolving business strategies. The constant push for more efficient solar panels, larger wind turbines, and sophisticated energy storage solutions means companies must continually invest in research and development to stay ahead. For instance, by mid-2024, solar panel efficiency in commercial applications frequently exceeded 22%, a significant leap from earlier iterations.
Innovative business models are also a key battleground. Concepts like hybrid power purchase agreements (PPAs) and energy-as-a-service are gaining traction, allowing companies to offer more flexible and customer-centric solutions. Those that can successfully integrate these new models, such as co-locating battery energy storage systems (BESS) with renewable generation projects, can secure a distinct competitive edge and attract a larger market share.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous improvements in solar panel efficiency and wind turbine capacity drive competition.
- Business Model Innovation: Hybrid PPAs and energy-as-a-service models are reshaping market dynamics.
- Integration of Storage: Companies combining renewables with battery energy storage systems (BESS) are gaining an advantage.
- Market Share Impact: Successful innovation directly translates to enhanced competitive positioning and market share gains.
The competitive rivalry for Peas Industries AB is intense, driven by a crowded European renewable energy market. Many developers vie for limited prime sites and grid connection access, pushing up development costs. For example, in 2024, the average cost per megawatt for new solar projects in Europe saw an increase due to these challenges.
Government policies and technological advancements further shape this rivalry. Companies must constantly innovate and adapt to changing regulations, such as evolving solar panel import tariffs, to maintain their market position.
Access to capital is a critical differentiator, with well-funded firms better positioned to secure projects and offer competitive pricing. In 2024, the cost of capital significantly influenced project viability, with average debt costs for renewables fluctuating based on market conditions.
Innovative business models, like hybrid PPAs and integrated battery storage, are also key battlegrounds, allowing agile companies to gain market share.
| Metric | 2023 Data | 2024 Outlook | Impact on Rivalry |
| New Renewable Capacity (GW) | EU: ~50 GW (estimated) | EU: ~55 GW (projected) | Increased competition for projects |
| Solar Panel Efficiency (%) | Commercial: ~22% | Commercial: ~23-24% | Drives innovation and R&D investment |
| Cost of Capital (Debt) | Varied by region and project | Slight increase due to inflation | Favors companies with strong financing |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional fossil fuel power plants, particularly natural gas, still pose a threat of substitution for renewable energy sources like solar and wind, especially in scenarios demanding high grid stability and dispatchability. While renewables have become significantly more cost-competitive, with new solar and wind projects often being the cheapest for new generation capacity, policy changes or geopolitical instability could create temporary advantages for fossil fuels.
For instance, in 2024, natural gas prices experienced volatility due to global supply concerns, which could, in specific regional markets, make existing fossil fuel plants a more attractive, albeit temporary, option compared to the upfront capital investment for new renewable projects. However, the overarching global trend strongly favors decarbonization, making the long-term viability of fossil fuel generation as a substitute increasingly challenged.
Advanced nuclear and large-scale hydropower represent significant substitutes for solar and wind energy, especially in providing consistent baseload power. While solar and wind deployment is rapid, these alternatives often require longer development cycles, yet substantial investment in them could shift demand and policy focus away from intermittent renewables.
For instance, as of early 2024, global investment in new nuclear capacity is seeing renewed interest, with projects like the Hinkley Point C in the UK progressing, aiming for significant carbon-free electricity generation. Similarly, major hydropower initiatives, such as those in China and Africa, continue to expand, offering a reliable, albeit geographically constrained, low-carbon energy source.
Improvements in energy efficiency and advanced demand-side management programs are increasingly reducing the need for new grid-scale power generation. This trend directly impacts companies like PEAS Industries AB, as customers can effectively substitute new supply with optimized energy consumption, thereby limiting growth opportunities for renewable energy developers.
Emerging Energy Storage Technologies
Advancements in energy storage, such as long-duration batteries and hydrogen systems, present a potential threat by enabling more efficient utilization of existing renewable energy sources, thereby reducing the need for new generation capacity. The energy storage market is experiencing significant growth, with projections indicating continued cost reductions and technological breakthroughs by 2025.
- Potential Substitution: Efficient energy storage can shift renewable output, acting as a substitute for new generation capacity.
- Market Evolution: The energy storage sector is rapidly evolving with expected cost declines and innovations through 2025.
- Impact on PEAS: This could reduce demand for PEAS's generation services if storage solutions become more cost-effective than new power plants.
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
The growing availability of distributed energy resources (DERs) presents a significant threat of substitutes for PEAS Industries AB. Rooftop solar installations, for instance, allow both residential and commercial customers to generate their own electricity, decreasing their dependence on traditional, large-scale energy providers. This trend could directly impact PEAS Industries AB's business model, which often centers on large, centralized energy projects.
While PEAS Industries AB's core business involves substantial energy assets, the increasing adoption of DERs signals a potential shift in energy consumption patterns. This decentralization of power generation means that a larger portion of energy demand might be met locally, thereby reducing the overall demand within the wholesale energy market. Consequently, the need for some of PEAS Industries AB's larger infrastructure projects could diminish.
Consider the global growth in solar power: by the end of 2023, cumulative global solar PV capacity reached over 1,300 GW. This expansion, largely driven by distributed generation, illustrates the tangible impact of substitutes. As more consumers and businesses invest in their own energy solutions, the market share available for utility-scale projects, like those PEAS Industries AB undertakes, could contract.
- Distributed Energy Resources (DERs): Rooftop solar, battery storage, and microgrids are increasingly viable alternatives to traditional grid power.
- Reduced Reliance on Centralized Projects: Consumers generating their own power lessen demand from utility-scale power plants.
- Market Shift: Widespread DER adoption can divert energy demand from wholesale markets, impacting the need for large infrastructure investments.
- Growth in Solar PV: Global solar PV capacity surpassed 1,300 GW by the end of 2023, highlighting the scale of the substitute threat.
While renewable energy sources are growing, traditional fossil fuels, particularly natural gas, remain a substitute, especially for grid stability. In 2024, fluctuating gas prices in some regions made existing fossil fuel plants temporarily more appealing than new renewable investments. However, the long-term global push for decarbonization continues to challenge fossil fuels' role.
Advanced nuclear and large-scale hydropower also act as substitutes, offering consistent baseload power. Despite rapid solar and wind growth, these alternatives often have longer development times, but significant investment could shift focus from intermittent renewables.
Improvements in energy efficiency and demand management reduce the need for new power generation, directly impacting companies like PEAS Industries AB. Customers can substitute new supply with smarter energy use, limiting growth for renewable developers.
| Substitute Technology | Key Characteristic | 2024/2025 Relevance |
| Natural Gas Power Plants | Dispatchability, Grid Stability | Temporary regional price advantages due to supply volatility |
| Advanced Nuclear Power | Baseload Power, Carbon-Free | Renewed global investment interest, e.g., Hinkley Point C progress |
| Large-Scale Hydropower | Baseload Power, Low-Carbon | Continued expansion in regions like China and Africa |
| Energy Efficiency & Demand Management | Reduced Energy Consumption | Directly lowers demand for new generation capacity |
| Energy Storage (Long-Duration Batteries, Hydrogen) | Enhanced Renewable Utilization | Expected cost reductions and technological breakthroughs by 2025 |
| Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) | Customer Self-Generation | Global solar PV capacity exceeded 1,300 GW by end of 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the utility-scale renewable energy sector, like that of Peas Industries AB, demands significant upfront capital. Developing and constructing large-scale solar farms or wind parks can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a substantial barrier for new companies looking to enter the market.
For instance, a typical 100 MW solar project in 2024 could require an investment exceeding $100 million, encompassing land acquisition, equipment purchase, construction, and grid connection. This immense financial commitment, coupled with the long-term nature of these assets, makes access to affordable capital a critical determinant of success and a major deterrent for potential new entrants.
New entrants into the pea industry face substantial barriers due to intricate and time-consuming regulatory and permitting procedures. These hurdles demand specialized knowledge and can lead to multi-year delays, escalating costs and risks for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, permitting delays were reported to have impacted project completion timelines by roughly 15% across various European agricultural sectors, a trend likely to affect pea cultivation and processing as well.
Securing access to existing grid infrastructure and obtaining timely interconnection agreements presents a significant hurdle for new entrants in the energy sector. The grid modernization necessary to accommodate renewable energy sources, which are increasingly prevalent, still has substantial investment deficits and a shortage of resources. This makes it challenging for new companies to connect their projects efficiently.
Need for Specialized Expertise and Track Record
The renewable energy sector, particularly for companies like PEAS Industries AB, requires a deep well of specialized knowledge and a history of successful project execution. This includes expertise in areas like project development, securing complex financing, efficient construction, and ongoing operational management. New companies entering this space often find it challenging to assemble the necessary talent pool and cultivate relationships with crucial financing institutions, which are vital for securing the substantial capital required for large-scale renewable energy ventures.
A proven track record is not just a nice-to-have; it's a fundamental requirement for attracting investment and winning competitive bids. Established companies, such as PEAS Industries AB, leverage their years of experience and established reputation to gain a significant advantage. This credibility is essential for navigating regulatory hurdles, securing permits, and building trust with stakeholders, including local communities and government bodies. For instance, in 2024, the global renewable energy investment reached record highs, underscoring the demand but also the competitive landscape where experience is a key differentiator.
- Specialized Expertise: Renewable energy projects demand technical proficiency in engineering, environmental science, and project management.
- Financing Acumen: Accessing capital for multi-million dollar projects requires strong relationships with banks, investment funds, and other financial partners.
- Operational Excellence: Proven ability to operate and maintain renewable energy assets efficiently is critical for long-term profitability and reliability.
- Track Record: A history of successfully delivering projects on time and within budget builds confidence and attracts further investment.
Established Relationships with Off-takers and Supply Chains
Established players like PEAS Industries AB benefit from deeply entrenched relationships with energy off-takers, such as utility companies and large corporations securing Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). These existing ties create significant barriers for new entrants seeking to establish similar off-take agreements.
Furthermore, PEAS Industries AB has cultivated robust supply chains for essential components. New companies entering the market would face the daunting task of replicating these established networks and securing reliable access to materials, often needing to outbid or outmaneuver existing players for limited resources.
The challenge is amplified by market dynamics. For instance, in early 2025, a noticeable decline in corporate PPA volumes in certain regions made securing these crucial agreements even more competitive, presenting a substantial hurdle for any new market participant.
- Established Off-taker Relationships: PEAS Industries AB has long-standing contracts with major energy consumers, making it difficult for new entrants to secure similar deals.
- Supply Chain Advantages: Existing players have secured reliable and cost-effective supply chains for critical materials, a significant advantage over newcomers.
- PPA Market Competition: Declining corporate PPA volumes in early 2025 intensified competition for these vital agreements, disadvantaging new entrants.
The threat of new entrants into the utility-scale renewable energy sector, where Peas Industries AB operates, is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements. Developing a single large-scale solar or wind project can easily cost upwards of $100 million in 2024, a sum that presents a formidable barrier for aspiring companies. This high initial investment, coupled with the long payback periods characteristic of such infrastructure, demands substantial financial backing and a robust credit history, which new players typically lack.
Furthermore, navigating the complex web of regulatory approvals and permitting processes is a time-consuming and knowledge-intensive endeavor. Delays in these areas can extend project timelines by months or even years, increasing costs and risks. For instance, in 2024, agricultural sector permitting issues in Europe were reported to cause an average of 15% in project completion delays, a challenge that would equally impact new entrants in the pea cultivation and processing space.
Established companies like Peas Industries AB also possess a critical advantage through their deeply entrenched relationships with energy off-takers and their well-developed supply chains. Securing Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) with utilities and large corporations is a vital step, and existing players have a significant head start. In early 2025, a contraction in corporate PPA volumes in some markets further intensified competition for these crucial contracts, making it even harder for new entrants to establish a foothold.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024/2025 Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront costs for project development and construction. | A single 100 MW solar project could exceed $100 million in 2024. |
| Regulatory & Permitting | Complex and time-consuming approval processes. | Average 15% project completion delays reported in European agriculture in 2024 due to permitting. |
| Off-taker Relationships & Supply Chains | Difficulty in securing PPAs and establishing reliable supply networks. | Intensified PPA competition in early 2025 due to declining volumes. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Peas Industries AB is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and publicly available financial statements. We also leverage industry-specific market research reports, trade publications, and data from reputable financial information providers to gain a thorough understanding of the competitive landscape.