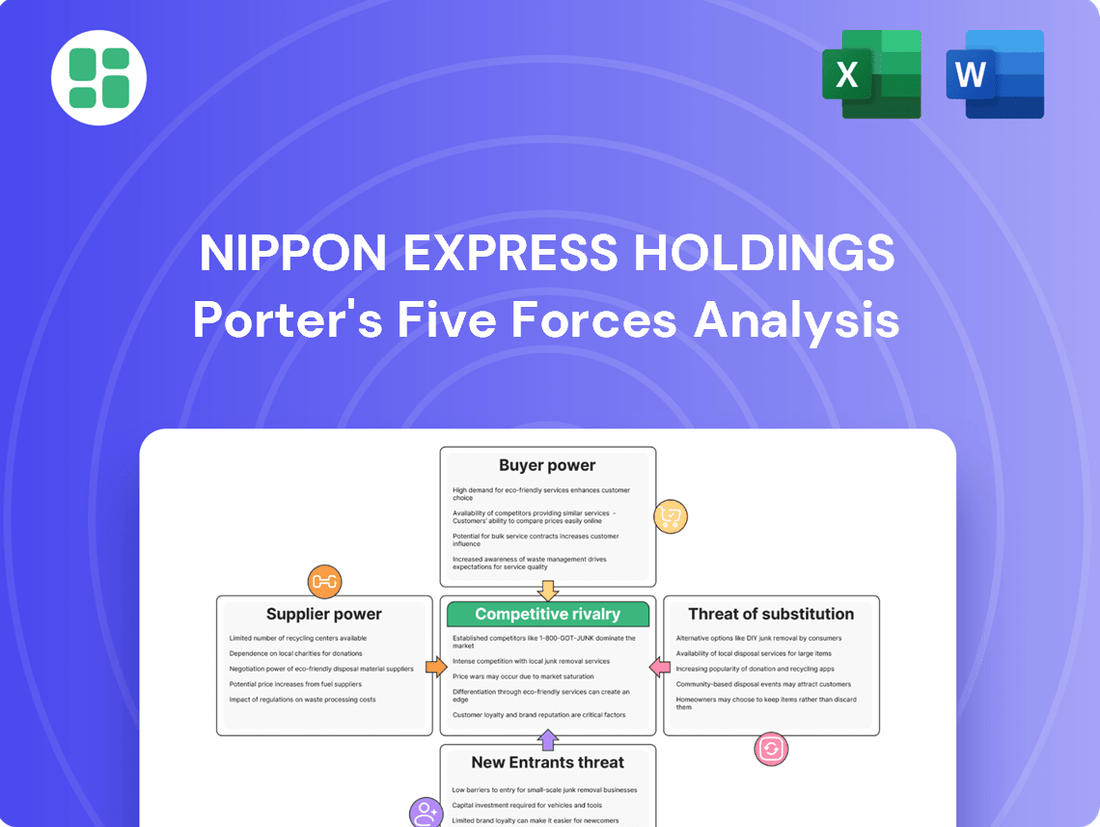
NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS Bundle
NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS operates in a dynamic logistics landscape where intense rivalry and the threat of substitutes significantly shape its market. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate this complex industry.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for critical resources like fuel, specialized transport equipment such as aircraft and vessels, and advanced IT systems significantly influences NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS. A limited number of dominant suppliers for these vital inputs can grant them increased bargaining power, potentially driving up costs or dictating less favorable contract terms for Nippon Express.
The specialization of these inputs further amplifies supplier leverage. For highly specialized components or unique services, the availability of alternative suppliers is often restricted, strengthening the position of existing providers. For example, in 2024, global aviation fuel prices saw considerable volatility, impacting logistics companies like Nippon Express, with a few major oil producers often dictating terms.
The costs Nippon Express Holdings might incur when switching logistics or IT suppliers significantly influence supplier bargaining power. These costs can include the expense of integrating new systems, reconfiguring complex logistics networks, and retraining personnel on unfamiliar platforms, all of which can be substantial.
For instance, if a new IT system requires extensive customization to interface with Nippon Express's existing operations, the financial outlay and time investment can be considerable, making a switch less appealing. This financial commitment directly translates to reduced flexibility for Nippon Express in negotiating terms with its current suppliers.
Suppliers might threaten Nippon Express Holdings by integrating forward into the logistics sector, becoming direct competitors. For example, a large automotive manufacturer could leverage its existing infrastructure and customer relationships to offer its own transportation and delivery services, directly challenging Nippon Express's core business.
Importance of Supplier's Input to NIPPON EXPRESS's Business
Nippon Express Holdings' reliance on key suppliers for its global logistics operations significantly influences supplier bargaining power. For instance, securing sufficient air and ocean freight capacity is paramount, and disruptions or price hikes from major shipping lines or airlines can directly impact Nippon Express's service delivery and profitability. The company's strategic investments in advanced warehouse automation and last-mile delivery solutions also mean that providers of these critical technologies hold considerable sway.
The criticality of these inputs means suppliers can exert considerable leverage. If Nippon Express heavily depends on a particular supplier for a vital component of its supply chain, such as specialized cold chain logistics or a unique IT platform for tracking, that supplier gains significant power to negotiate terms. This dependence can translate into higher costs or less favorable contract conditions for Nippon Express.
Consider the following factors highlighting supplier importance:
- Global Freight Capacity: Nippon Express operates a vast network requiring consistent access to air cargo space and ocean vessel capacity. Fluctuations in these markets, driven by supplier availability and pricing, directly affect operational costs. For example, in 2024, global air cargo rates saw significant volatility due to capacity constraints and demand surges, impacting logistics providers like Nippon Express.
- Warehouse Automation Technology: The company's commitment to efficiency necessitates advanced automation in its warehouses. Suppliers of robotics, automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), and warehouse management software (WMS) are crucial. A delay or malfunction in these systems can disrupt operations.
- Last-Mile Delivery Infrastructure: Efficient last-mile delivery is a cornerstone of customer satisfaction. Nippon Express's ability to leverage specialized vehicles, route optimization software, and local delivery partners determines its effectiveness in this critical phase. Dependence on a limited number of specialized providers can increase supplier power.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. If NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS can readily find alternative fuel sources, different types of transportation equipment, or various software solutions, its reliance on any single supplier diminishes. This flexibility is crucial for negotiating better terms and diversifying its supply chain, thereby reducing the leverage of individual suppliers.
For instance, in 2024, the global logistics industry saw continued innovation in alternative fuels, with a growing number of providers offering sustainable options for trucking and shipping fleets. NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS, like its peers, can leverage this expanding market to reduce dependence on traditional fuel suppliers. Similarly, advancements in telematics and fleet management software provide more options, allowing the company to switch providers if terms become unfavorable.
- Diversification of Fuel Sources: NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS can mitigate supplier power by sourcing fuel from multiple providers, including those offering biofuels or electric charging infrastructure, as these alternatives become more prevalent.
- Equipment Flexibility: The ability to utilize various types of transport equipment, such as different truck models or intermodal solutions, reduces reliance on suppliers of specialized or proprietary equipment.
- Software and Technology Alternatives: Access to a range of logistics management software and IT solutions allows NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS to avoid lock-in with a single technology provider, fostering competitive pricing and better service.
Suppliers of critical resources like fuel, specialized transport equipment, and advanced IT systems hold significant bargaining power over NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS due to concentration and specialization. For example, global aviation fuel prices in 2024 remained volatile, with a few major oil producers often dictating terms, directly impacting logistics costs. The high switching costs associated with integrating new IT systems or reconfiguring complex logistics networks further solidify supplier leverage.
Nippon Express's reliance on global freight capacity, such as air cargo space and ocean vessel capacity, makes providers of these services powerful. In 2024, air cargo rates experienced significant volatility due to capacity constraints and demand surges, affecting companies like Nippon Express. Similarly, providers of warehouse automation technology and last-mile delivery infrastructure wield considerable influence due to the critical nature of these operations.
The availability of substitute inputs, such as alternative fuels or diverse logistics software, can diminish supplier bargaining power. The growing prevalence of biofuels and electric charging infrastructure in 2024 offered logistics companies like Nippon Express more options to reduce dependence on traditional fuel suppliers. This diversification of fuel sources and equipment flexibility enhances Nippon Express's ability to negotiate favorable terms.
| Factor | Impact on Nippon Express | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (Fuel) | High leverage for dominant fuel providers | Volatile aviation fuel prices impacted costs. |
| Specialized Equipment Dependence | Limited alternatives increase supplier power | N/A (Industry-wide trend) |
| Switching Costs (IT Systems) | Reduces flexibility in negotiations | N/A (Ongoing operational consideration) |
| Global Freight Capacity Availability | Crucial for operations, suppliers have leverage | Air cargo rates saw significant volatility. |
| Availability of Substitute Fuels | Mitigates supplier power | Growing availability of biofuels and electric charging. |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the logistics sector.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats within the logistics industry by visualizing NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS' Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers for NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS is significantly shaped by customer concentration and the sheer volume of services they procure. Major clients, such as large multinational corporations or prominent e-commerce platforms, represent a substantial portion of NIPPON EXPRESS's revenue. Their considerable logistics requirements grant them considerable leverage in negotiating terms and pricing, as switching providers can be complex and costly for them.
For instance, NIPPON EXPRESS's 2024 financial reports would likely highlight key accounts that drive a disproportionate amount of their business. If a few dominant players in sectors like automotive or electronics represent, say, over 30% of their total sales, their ability to influence contract terms would be considerably higher than if their revenue was spread across thousands of smaller, less demanding clients.
Customer switching costs significantly influence their bargaining power with logistics providers like NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS. If clients can easily and cheaply move to another service, their leverage increases.
However, high switching costs can anchor customers to NIPPON EXPRESS. These costs can include the expense and effort of re-integrating supply chains, negotiating new contracts, and potential disruption to established operational efficiencies. For instance, a major automotive manufacturer relying on NIPPON EXPRESS for just-in-time delivery would face substantial costs and risks in switching providers, thus limiting their bargaining power.
Customer price sensitivity is a critical element in assessing bargaining power. If clients are highly attuned to logistics expenses, they will naturally push NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS for more competitive pricing. This is especially relevant for sectors operating on thin margins or where shipping costs form a substantial part of their overall outlays.
For example, in 2023, the global logistics market saw intense competition, with freight rates fluctuating significantly. Companies that can absorb these cost pressures or find efficiencies are better positioned. NIPPON EXPRESS's strategic focus on enhancing its service offerings, such as specialized handling or integrated supply chain solutions, can serve as a powerful countermeasure against aggressive price demands.
Availability of Alternative Logistics Providers
The sheer number of logistics providers available significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. With numerous global freight forwarders, regional carriers, and specialized niche players competing, customers can readily compare offerings and pricing. This competitive landscape compels companies like NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS to maintain aggressive pricing and service standards to retain business. For instance, as of early 2024, the global logistics market is valued in the trillions, with a substantial portion attributable to freight forwarding services, indicating a highly fragmented and competitive environment.
Customers can easily switch providers if they find better deals or service elsewhere. This ease of switching is a direct result of the availability of many alternative logistics providers. The ability to compare services and costs across multiple options means NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS must constantly demonstrate value to its clients. The market features a diverse range of competitors, from giants like DHL and Kuehne+Nagel to smaller, more agile regional players.
- Abundant Alternatives: The logistics sector is rich with global, regional, and niche providers, empowering customers.
- Price and Service Comparison: Customers can easily benchmark prices and service quality across numerous options.
- Competitive Pressure: NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS faces pressure to offer competitive pricing and superior service to retain clients.
- Market Fragmentation: The diverse nature of competitors in the global logistics market amplifies customer leverage.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers, particularly large-scale manufacturers and retailers, possess the potential to integrate backward by establishing their own logistics operations. This can significantly diminish their dependence on third-party providers such as NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS.
Should logistics be a critical strategic element for these customers, they might allocate substantial capital towards acquiring their own transportation fleets, building dedicated warehousing facilities, and implementing advanced supply chain management software. This strategic move directly curtails the demand for external logistics services.
- Customer Backward Integration Capability: Large customers can develop in-house logistics, reducing reliance on NIPPON EXPRESS.
- Strategic Importance of Logistics: If logistics is core, customers are more likely to invest in their own infrastructure.
- Impact on Demand: In-house capabilities directly decrease the market for third-party logistics providers.
- 2024 Data Insight: While specific backward integration figures for NIPPON EXPRESS customers aren't publicly detailed, the trend of large enterprises optimizing supply chains for cost and control is a persistent factor in the logistics sector.
The bargaining power of customers for NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS is substantial due to the availability of numerous alternative logistics providers and the customers' ability to easily compare prices and services. This competitive landscape forces NIPPON EXPRESS to offer competitive pricing and superior service to retain its client base.
Customers, especially large enterprises, can also exert influence by considering backward integration, developing their own logistics capabilities to reduce reliance on third-party providers. This trend is particularly relevant in 2024 as companies focus on optimizing supply chain costs and control.
The global logistics market, valued in the trillions as of early 2024, is highly fragmented, with many global, regional, and niche players. This fragmentation directly amplifies customer leverage in negotiations with providers like NIPPON EXPRESS.
| Factor | Impact on NIPPON EXPRESS | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Provider Availability | High competition necessitates competitive offerings. | Customers can easily switch for better terms. |
| Switching Costs | Can anchor customers if high. | Lower costs empower customers to switch. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers push for lower rates. | High sensitivity increases demand for discounts. |
| Backward Integration | Potential loss of business if customers go in-house. | Customers can reduce dependence on NIPPON EXPRESS. |
Preview Before You Purchase
NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS, providing an in-depth examination of industry competition, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, offering actionable insights into the strategic landscape of the global logistics sector.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global logistics arena is a crowded marketplace, with NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS facing intense competition from a wide array of companies. Giants such as DHL, FedEx, and UPS dominate the international scene, offering comprehensive services that span the globe.
Beyond these behemoths, the industry is populated by a multitude of regional specialists and local carriers, each carving out their niche. This sheer number and variety of competitors, differing in scale, service portfolios, and operational footprints, significantly escalates the rivalry as firms battle for market share across diverse logistics segments.
The growth rate of the logistics market directly impacts how fiercely companies compete. When the market is expanding quickly, like the projected growth for the global logistics sector, companies can grow by simply capturing new demand. This generally leads to less intense rivalry as firms aren't forced to steal market share from each other.
However, if growth slows, competition often heats up. Companies might start using more aggressive pricing or boosting their marketing to win customers away from rivals. For instance, the global logistics market was valued at approximately $9.7 trillion in 2023 and is expected to reach over $15.3 trillion by 2030, indicating a robust growth trajectory that could moderate direct competitive pressures.
The ability to differentiate logistics services significantly influences competitive rivalry. While standard freight services can become a price-driven commodity, NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS distinguishes itself through specialized capabilities. This includes expert handling for sensitive sectors such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, and high-tech electronics, alongside offering comprehensive, integrated supply chain solutions and leveraging advanced technological platforms.
This strategic differentiation allows NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS to move beyond direct price wars, enabling them to secure premium pricing for their value-added services. For instance, in 2023, the demand for specialized cold chain logistics, a key area of differentiation for many players, saw continued growth, underscoring the market's willingness to pay for expertise and reliability in handling specific cargo types.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity
The logistics sector, including companies like Nippon Express Holdings, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These include investments in extensive warehouse networks, sophisticated transportation hubs, a large fleet of vehicles, and advanced tracking technology. These significant upfront and ongoing expenses create a strong pressure to maintain high operational utilization.
When the industry faces periods of excess capacity, meaning there are more resources available than immediate demand requires, companies are driven to compete aggressively on price. This happens because each unit of service delivered helps to cover those fixed costs, making even slightly lower prices attractive to secure volume and avoid underutilization.
- High Capital Investment: Nippon Express Holdings, like its peers, invests billions in its global infrastructure, including over 600 group companies and a vast network of facilities.
- Capacity Utilization Drive: The need to amortize these fixed assets incentivizes aggressive pricing to fill available capacity, especially during economic downturns or when new capacity is added.
- Price Wars Risk: In saturated markets or during economic slowdowns, this can lead to intense price competition, eroding profit margins for all players.
Exit Barriers
Nippon Express Holdings operates within an industry characterized by substantial exit barriers. These include the considerable investment in specialized logistics infrastructure, such as dedicated warehouses and advanced transportation fleets, which are not easily repurposed. Furthermore, long-term contracts with major clients and the significant social and financial costs associated with workforce reductions in a labor-intensive sector like logistics can deter firms from exiting, even when facing profitability challenges.
These high exit barriers mean that even firms performing poorly may remain active competitors, contributing to market overcapacity. This persistence can intensify competitive rivalry, as these companies continue to vie for market share and revenue, potentially impacting pricing and overall industry profitability. For instance, the global logistics market, while dynamic, often sees established players with extensive physical assets facing difficulties in divesting or repurposing them quickly, thus maintaining competitive pressure.
Consider the implications for Nippon Express Holdings:
- Asset Specificity: The need for specialized vehicles, automated sorting systems, and temperature-controlled storage facilities represents significant sunk costs that are difficult to recover upon exit.
- Long-Term Commitments: Many logistics providers are bound by multi-year service agreements, making it challenging to cease operations without incurring penalties or reputational damage.
- Workforce Considerations: The logistics sector is a major employer; the social and economic impact of large-scale layoffs creates a significant disincentive for companies to exit unprofitable operations.
Competitive rivalry within the global logistics sector, where NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS operates, is exceptionally fierce. This intensity stems from the presence of major international players like DHL, FedEx, and UPS, alongside a vast network of regional and niche carriers. The market's robust growth, projected to exceed $15.3 trillion by 2030, offers room for expansion, but the high fixed costs associated with infrastructure and the drive for capacity utilization can still trigger aggressive pricing strategies, particularly during economic slowdowns. Differentiation through specialized services, such as cold chain logistics, is key to mitigating price wars and securing premium margins.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (approx.) | Key Differentiators |
|---|---|---|
| DHL | $100 billion+ | Global network, e-commerce solutions |
| FedEx | $90 billion+ | Express delivery, broad service portfolio |
| UPS | $100 billion+ | Integrated logistics, supply chain management |
| Nippon Express Holdings | $20 billion+ | Specialized cargo (auto, pharma), integrated solutions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Nippon Express Holdings is significant, as customers can choose alternative transportation modes or different logistics companies. For example, a business needing to ship goods internationally might opt for a competitor offering specialized air cargo services if Nippon Express's pricing or transit times are less competitive. In fiscal year 2023, the global logistics market saw continued growth, with air freight revenue reaching an estimated $170 billion, highlighting a substantial alternative for time-sensitive shipments.
A significant substitute threat for Nippon Express Holdings arises when customers develop or expand their own in-house logistics capabilities. Large companies, particularly those with substantial scale and a need for precise control over their supply chains, may opt to insource warehousing, fleet management, and distribution. This is often driven by the potential for cost savings or a desire for greater operational oversight. For instance, a major e-commerce retailer might invest in its own delivery fleet and fulfillment centers, thereby reducing its reliance on third-party logistics providers like Nippon Express.
Technological advancements and the rise of digital platforms present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional logistics providers like Nippon Express Holdings. Online freight marketplaces and advanced supply chain planning software allow shippers to manage logistics more independently or connect directly with carriers, potentially bypassing intermediaries.
For instance, platforms offering real-time tracking and automated booking can reduce the perceived value of comprehensive third-party logistics services. In 2024, the digital freight forwarding market continued its robust growth, with many new entrants offering streamlined, technology-driven solutions that directly compete with established players by providing enhanced visibility and control to customers.
Shift in Supply Chain Models
Changes in global supply chain models, such as reshoring or nearshoring, can diminish the need for NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS' long-haul international freight services. For instance, a significant portion of manufacturing could shift closer to end consumers, reducing the distance and complexity of logistics. This trend might favor more localized transportation providers over global players.
The increasing regionalization of manufacturing, a trend observed in recent years, directly impacts demand for extensive international shipping. If companies prioritize production within closer geographic proximity to their markets, the reliance on long-distance freight, a core service for NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS, could naturally decrease. This shift could lead to a reduction in the volume of goods requiring their global network.
- Reshoring initiatives: Companies increasingly bring manufacturing back to their home countries or nearby regions to mitigate risks and reduce transit times.
- Nearshoring benefits: This strategy offers advantages like lower transportation costs and improved supply chain visibility compared to traditional offshoring.
- Regionalization impact: A move towards regional supply chains means less reliance on intercontinental shipping, potentially affecting NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS' market share in those segments.
- Reduced freight volumes: As production becomes more localized, the overall volume of goods needing long-haul international transport is likely to decline.
Virtualization or Dematerialization of Goods
The increasing digitalization of goods and services presents a subtle but growing threat to traditional logistics providers like NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS. While not a direct substitute for all physical goods, the shift towards digital formats can reduce the demand for transporting certain items. For instance, the move from physical books and music to digital downloads has already impacted the shipping volumes for these categories.
Emerging technologies like 3D printing also contribute to this trend. As localized manufacturing becomes more feasible through 3D printing, the need to transport finished goods across long distances may decrease. This could lead to a gradual erosion of freight volumes for specific product types, potentially affecting NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS' revenue streams in the long term. For 2024, the global 3D printing market is projected to reach approximately $30 billion, indicating its expanding influence.
- Digitalization Threat: The ongoing shift from physical media to digital content reduces the need for transporting items like books, music, and movies.
- 3D Printing Impact: Advancements in 3D printing enable localized manufacturing, potentially decreasing the demand for long-haul freight of finished goods.
- Market Growth: The global 3D printing market is expected to continue its expansion, reaching an estimated $60 billion by 2028, signaling a growing potential impact on traditional logistics.
The threat of substitutes for Nippon Express Holdings is multifaceted, encompassing alternative logistics providers, evolving customer capabilities, and technological advancements. Competitors offering specialized services, such as dedicated air cargo or advanced cold chain logistics, present direct substitutes for specific shipping needs. Furthermore, the increasing trend of companies insourcing their logistics operations, particularly large e-commerce players investing in their own fleets and fulfillment centers, directly reduces reliance on third-party providers.
Technological disruptions, like online freight marketplaces and advanced supply chain software, empower shippers to manage logistics more independently or connect directly with carriers, bypassing traditional intermediaries. This digital shift, with the digital freight forwarding market showing strong growth in 2024, offers enhanced visibility and control, directly challenging the value proposition of comprehensive logistics services. Additionally, shifts in global supply chain strategies, such as reshoring and nearshoring, reduce the demand for long-haul international freight, favoring more localized transportation solutions.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on Nippon Express | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternative Logistics Providers | Competitors offering specialized transport modes or services. | Loss of market share for specific freight types. | Global air freight revenue estimated at $170 billion in FY2023. |
| In-house Logistics | Companies managing their own transportation and warehousing. | Reduced outsourcing opportunities. | Large e-commerce retailers building their own delivery networks. |
| Digital Freight Platforms | Online marketplaces and software for direct carrier booking. | Disintermediation and reduced reliance on traditional forwarders. | Robust growth in the digital freight forwarding market in 2024. |
| Supply Chain Regionalization | Shifting production closer to end markets. | Decreased demand for long-haul international shipping. | Trend towards nearshoring to mitigate supply chain risks. |
| Digitalization of Goods | Shift from physical to digital products. | Reduced freight volumes for certain categories. | Global 3D printing market projected to reach $30 billion in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the global logistics arena, particularly as a comprehensive service provider akin to NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS, demands immense capital. We're talking about significant investments in fleets of trucks and planes, vast warehouse networks, and cutting-edge technology to manage it all. For instance, in 2024, the ongoing modernization and expansion of logistics infrastructure globally continues to necessitate billions in capital expenditure from established players.
These substantial upfront costs create a formidable barrier for newcomers. It's incredibly challenging for smaller or less-funded entities to match the scale and operational capabilities of established giants, effectively limiting the threat of new entrants who lack the financial muscle to compete on a global scale.
Established players like NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS leverage massive economies of scale, particularly in global logistics networks and bulk purchasing of transportation assets. In 2024, NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS reported consolidated revenue of ¥2.3 trillion (approximately $15 billion USD), a testament to its operational scale. This vast infrastructure allows for lower per-unit costs in warehousing, freight forwarding, and last-mile delivery, creating a significant barrier for newcomers.
New entrants face considerable challenges in matching these efficiencies. Without a comparable global footprint or high-volume contracts, they often incur higher operating costs. For instance, a startup logistics firm would struggle to achieve the same per-package delivery cost as NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS, whose extensive network density in key markets like Japan and North America allows for optimized routing and reduced empty miles, a critical factor in profitability.
The logistics sector thrives on network effects; the more locations and connections a company has, the more valuable its services become. Nippon Express Holdings boasts a significant global footprint, operating in 57 countries and regions, which amplifies its service offerings and customer appeal.
For any new player, replicating this extensive network and cultivating the deep trust and brand loyalty Nippon Express Holdings enjoys with its business clients represents a formidable and resource-intensive challenge, acting as a substantial barrier to entry.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance
The logistics industry faces a formidable barrier to entry due to intricate regulatory landscapes. Businesses entering this sector must contend with a web of international and national laws governing customs, safety protocols, environmental impact, and operational licensing across different transportation methods.
Ensuring compliance with these varied and often evolving regulations worldwide represents a substantial cost and operational challenge for any new player. For instance, in 2024, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) continued to emphasize stringent safety and security regulations, requiring significant investment in training and infrastructure for new air cargo handlers.
- Complex Regulatory Frameworks: Logistics operations are subject to diverse customs, safety, and environmental laws globally.
- High Compliance Costs: Navigating and adhering to these regulations incurs significant financial investment for new entrants.
- Licensing and Permits: Obtaining necessary licenses for various transport modes and international operations adds to the entry barrier.
Access to Distribution Channels and Technology
New entrants into the logistics sector face significant hurdles in gaining access to established distribution networks. Securing critical resources like port slots, airport cargo handling capacities, and reliable last-mile delivery partnerships is a major challenge. For instance, major players often have long-term contracts and preferential access, making it difficult for newcomers to compete for these essential services.
The substantial investment required for advanced logistics technology also acts as a barrier. Companies like NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS leverage AI-powered route optimization, real-time shipment tracking, and sophisticated warehouse management systems. Acquiring or developing comparable technological capabilities demands considerable capital outlay and specialized expertise, which emerging competitors may lack.
- Distribution Channel Access: New entrants struggle to secure essential logistics infrastructure such as port slots and airport cargo handling facilities.
- Technology Investment: High costs associated with advanced logistics technology, including AI and real-time tracking systems, deter new market participants.
- Partnership Dependencies: Reliance on established last-mile delivery networks creates a dependency that can be difficult for newcomers to navigate.
The threat of new entrants for NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS is generally considered low due to several significant barriers. The immense capital required for global logistics infrastructure, including fleets and advanced technology, deters many potential competitors. Furthermore, established players benefit from strong brand loyalty and extensive global networks, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate their scale and efficiency.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | Significant investment needed for fleets, warehouses, and technology. | High; deters undercapitalized entrants. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large operational volume. | High; newcomers struggle to match cost efficiencies. |
| Network Effects | Value increases with more locations and connections. | High; replicating extensive global reach is challenging. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex international and national laws for customs, safety, etc. | High; compliance is costly and time-consuming. |
| Distribution Access | Securing port slots, cargo handling, and last-mile partnerships. | High; established contracts limit access for newcomers. |
| Technology Investment | Need for advanced AI, tracking, and warehouse management systems. | High; requires substantial capital and expertise. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our NIPPON EXPRESS HOLDINGS Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including their annual reports, investor presentations, and publicly available financial statements. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry research firms and logistics sector publications to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.