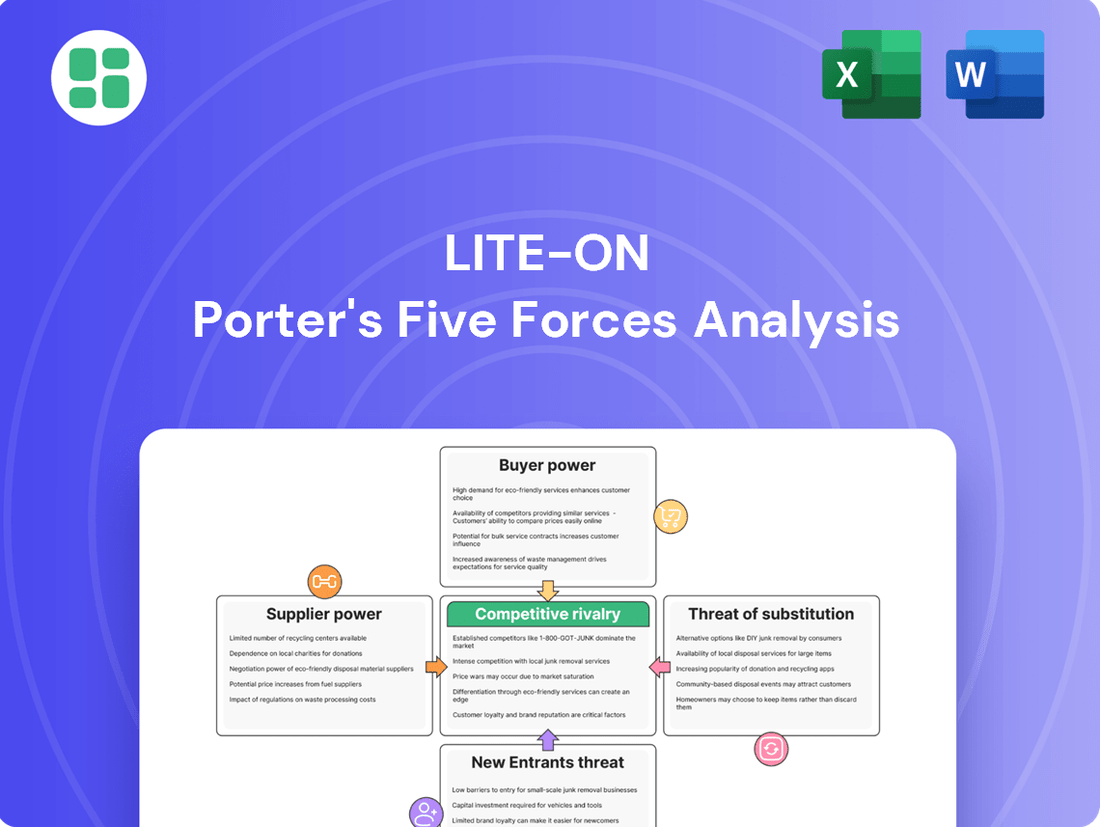
Lite-On Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Lite-On Bundle
Lite-On faces a dynamic competitive landscape, with moderate buyer power and the threat of substitutes influencing its market position. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Lite-On’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Lite-On's reliance on a global supply chain for specific raw materials and highly specialized electronic components places it at the mercy of its suppliers. If these suppliers are few, or if their products are highly differentiated, their ability to dictate terms, including pricing and delivery schedules, grows significantly. This is especially true for proprietary technologies or components with no readily available substitutes.
For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key supplier sector for Lite-On, continued to face supply chain pressures. Lead times for certain advanced chips remained extended, giving manufacturers of these critical components considerable leverage. Companies that control unique manufacturing processes or possess patents for essential components can command premium pricing, directly impacting Lite-On's cost of goods sold.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Lite-On is significantly influenced by switching costs. For Lite-On, the expense and effort involved in moving from one supplier to another can be considerable. This often necessitates redesigning components, re-qualifying new suppliers' products, and potentially re-tooling manufacturing processes.
These high switching costs effectively increase Lite-On's dependence on its current suppliers. This reliance can empower suppliers, giving them leverage to negotiate more favorable terms or implement price increases, knowing that Lite-On faces substantial hurdles in finding alternatives. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to experience supply chain complexities, making supplier stability a critical factor for manufacturers like Lite-On.
If suppliers possess the capability and motivation to move into manufacturing components or even finished goods that Lite-On produces, their bargaining power significantly increases. This threat can constrain Lite-On's ability to secure favorable terms, as suppliers might choose to bypass Lite-On altogether.
For instance, a key semiconductor supplier to Lite-On could potentially develop their own finished power supply units, directly competing with Lite-On's product lines. In 2024, the global power supply market was valued at approximately $25 billion, with significant growth potential, making forward integration an attractive strategy for some component manufacturers looking to capture more value.
However, the sheer breadth and complexity of Lite-On's product portfolio, which spans from power supplies to optoelectronics and IoT solutions, often makes widespread forward integration by any single supplier across all segments a less probable scenario.
Uniqueness of Supplier Inputs
The uniqueness and criticality of Lite-On's supplier inputs significantly shape supplier bargaining power. Suppliers providing highly specialized components, such as advanced semiconductor chips or proprietary optical lenses, can wield considerable influence. This is often due to limited alternative sources and substantial R&D investment required for these unique inputs. For example, in 2024, the global semiconductor industry continued to face supply chain complexities, with leading-edge foundries commanding premium pricing due to high demand and specialized manufacturing processes.
Lite-On's reliance on specific, technologically advanced components means that suppliers of these critical inputs possess a degree of leverage. If a particular supplier's technology is essential for Lite-On's product differentiation or performance, and few other suppliers can match that capability, their bargaining power increases. This can translate into less favorable pricing or supply terms for Lite-On.
- Criticality of Inputs: Lite-On's dependence on specialized components like advanced optical sensors or high-performance power management ICs increases supplier leverage.
- Technological Expertise: Suppliers with unique, patented technology or significant R&D investment in niche areas often have higher bargaining power.
- Limited Competition: A small number of suppliers capable of producing highly specific or advanced materials and components grants those suppliers more power.
- Industry Trends (2024): The ongoing demand for advanced AI-driven components and specialized materials in consumer electronics and automotive sectors in 2024 has bolstered the bargaining power of key suppliers in these segments.
Supplier's Importance to Lite-On's Business
Suppliers whose components represent a significant portion of Lite-On's total cost or are crucial for the performance and differentiation of its end products wield considerable bargaining power. For example, in 2024, Lite-On's reliance on specialized semiconductor suppliers for its advanced optical drives and power supply units means these providers can influence pricing and availability.
Lite-On’s diverse product portfolio means the impact of supplier power varies across different business segments. While some components are readily available from multiple sources, others, particularly those requiring proprietary technology or facing supply chain constraints, are more critical. This variability necessitates tailored supplier management strategies for each product line.
Managing these key supplier relationships effectively is vital for Lite-On's operational stability and profitability. In 2023, Lite-On reported its cost of goods sold was approximately TWD 147.1 billion, highlighting the substantial financial impact of its supply chain. Ensuring favorable terms and reliable supply from critical vendors is therefore a strategic imperative.
- Component Cost Concentration: Suppliers providing components that constitute a large percentage of Lite-On's production expenses have increased leverage.
- Critical Component Dependence: Lite-On’s reliance on unique or high-performance components from specific suppliers enhances those suppliers' bargaining power.
- Segment-Specific Impacts: The influence of suppliers differs significantly across Lite-On's various product categories, from consumer electronics to industrial solutions.
- Strategic Relationship Management: Proactive management of key supplier partnerships is crucial to mitigate risks and secure competitive advantages in component sourcing.
Lite-On's bargaining power with its suppliers is constrained by the criticality and uniqueness of the components it sources. Suppliers of specialized semiconductors and proprietary optical elements, for example, hold significant leverage due to limited alternatives and high switching costs for Lite-On. In 2024, extended lead times for advanced chips in the semiconductor industry underscored this supplier advantage, impacting Lite-On's cost of goods sold, which was TWD 147.1 billion in 2023.
| Factor | Impact on Lite-On | 2024 Context |
| Criticality of Inputs | High leverage for suppliers of unique components (e.g., advanced optical sensors). | Continued demand for specialized AI components. |
| Switching Costs | Increases dependence on existing suppliers, enabling price negotiation. | Component redesign and requalification are time-consuming. |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Potential for direct competition if suppliers enter Lite-On's markets. | Global power supply market valued at $25 billion in 2024, attractive for integration. |
| Component Cost Concentration | Suppliers of high-percentage cost components have greater influence. | Managing TWD 147.1 billion in COGS requires favorable supplier terms. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping Lite-On's industry, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry. It provides strategic insights into Lite-On's competitive positioning and profitability.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive overview of Lite-On's industry landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Lite-On's customer base includes major global manufacturers in IT, consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial markets. When a few of these large clients represent a substantial percentage of Lite-On's revenue, their collective bargaining power increases significantly. This allows them to negotiate for reduced prices or more advantageous contract conditions, a common dynamic in the business-to-business electronics components sector.
Customers often face moderate to high switching costs when moving from one component supplier to another. This is largely due to the effort involved in redesigning products, the lengthy qualification processes for new parts, and the potential for supply chain disruptions during the transition. For instance, in the electronics sector, integrating new components can require significant engineering resources and re-testing, which can cost thousands of dollars per component change.
However, if Lite-On's components are highly standardized or readily available from multiple sources, the costs for customers to switch are significantly lower. This directly increases their bargaining power. For example, if Lite-On supplies a common type of capacitor, a customer can easily find alternatives, putting pressure on Lite-On's pricing and terms.
Lite-On's strategic emphasis on providing integrated solutions and specialized components can serve as a key differentiator. By offering unique functionalities or bundled services that are difficult for competitors to replicate quickly, Lite-On can effectively raise the switching costs for its customers, thereby mitigating their bargaining power and strengthening its own market position.
Customers in intensely competitive sectors, like consumer electronics, are highly attuned to pricing and will push hard for reduced component expenses. For instance, in 2024, the global consumer electronics market experienced significant price competition, with average selling prices for many devices seeing a slight decline year-over-year due to increased supply and cautious consumer spending.
Lite-On can mitigate this by offering products with unique features, superior quality, or bundled services, thereby lessening customer focus on price alone. However, components that are easily replicated or lack distinct advantages will continue to face considerable price pressures. This is evident as many standard component manufacturers reported thinner profit margins in 2024 as they competed on price alone.
The substantial order volumes placed by major clients often magnify their bargaining power, enabling them to demand more favorable pricing terms. In 2024, large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in the PC and smartphone industries continued to leverage their scale, securing bulk discounts that averaged between 5-10% on key components compared to smaller buyers.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large customers, particularly those with substantial R&D and manufacturing capacity, may explore producing certain components internally. This potential for backward integration directly enhances their bargaining power, pushing Lite-On to provide competitive pricing and superior value-added services to maintain customer loyalty. For instance, in the competitive semiconductor industry, major electronics manufacturers have historically demonstrated a willingness to invest in their own fabrication capabilities when it offers significant cost or strategic advantages.
While the threat of customers integrating backward exists, it is often tempered by the highly specialized nature of many of Lite-On's products and manufacturing processes. Developing the necessary expertise and capital investment for certain advanced components can be a significant barrier for many customers. For example, the intricate processes involved in producing high-performance optical components or advanced power management solutions require specialized knowledge and equipment that are not easily replicated.
- Customer Integration Potential: Large clients with significant R&D and manufacturing scale may consider in-house production of certain components.
- Impact on Lite-On: This threat strengthens customer bargaining power, pressuring Lite-On for competitive pricing and enhanced services.
- Mitigating Factors: The specialized nature of many Lite-On offerings can make backward integration challenging for customers.
Availability of Alternative Suppliers
Lite-On's customers frequently encounter a broad selection of alternative suppliers for electronic components worldwide. This abundance of choices directly enhances their negotiating leverage.
For instance, in the competitive market for power supplies, a critical segment for Lite-On, customers can readily find similar products from numerous global manufacturers. This ease of switching suppliers means Lite-On must consistently offer compelling value propositions.
- Global Component Sourcing: Customers can access a vast network of component manufacturers, reducing reliance on any single supplier.
- Price Sensitivity: The availability of alternatives often leads to increased price sensitivity among buyers.
- Supplier Differentiation: Lite-On needs to differentiate through quality, innovation, and service to mitigate this pressure.
Lite-On's customers, particularly large ones, wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes and the competitive landscape of their respective industries. This power is amplified when Lite-On's products are commoditized or easily substituted, forcing the company to compete on price and terms.
In 2024, the consumer electronics sector, a key market for Lite-On, saw intense price competition, with some component prices experiencing slight year-over-year declines. This environment pressures suppliers like Lite-On to offer more favorable pricing to secure large contracts, with major OEMs in 2024 often securing 5-10% discounts on components due to bulk purchases.
While Lite-On can mitigate this by offering specialized solutions and highlighting switching costs, the threat of customers integrating backward or sourcing from numerous global alternatives remains. The availability of many similar components means Lite-On must continually differentiate itself through quality, innovation, and service to maintain its pricing power.
| Factor | Impact on Lite-On | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Increased power for large clients to negotiate terms. | Diversify customer base, offer value-added services. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate to high, but can be low for standardized parts. | Develop proprietary technology, offer integrated solutions. |
| Price Sensitivity | High in competitive markets like consumer electronics. | Focus on quality, innovation, and cost-efficiency. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Customers can easily source from multiple suppliers. | Strengthen brand loyalty, emphasize unique product features. |
| Backward Integration Potential | Threat of customers producing components in-house. | Maintain technological superiority, offer competitive pricing. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Lite-On Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the entirety of the Lite-On Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a clear and comprehensive view of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing sections. You can be confident that the in-depth analysis of industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes is fully intact and ready for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The electronic components industry, where Lite-On operates, is incredibly fragmented. Think of it as a vast marketplace with countless sellers, from massive global giants to smaller, niche specialists. This means Lite-On isn't just up against a few big names; it's competing with a wide array of companies, each with its own strengths and strategies. For instance, in the power supply segment, you have players like Delta Electronics and TDK, but also many smaller, regional manufacturers focusing on specific product types or customer needs.
This sheer number and diversity of competitors create a challenging environment. Lite-On has to constantly adapt because different rivals will attack the market from various angles. Some might compete on price, others on technological innovation, and still others on specialized customer service. In 2023, the global power supply market alone was valued at over $25 billion, showcasing the scale of this competitive landscape and the numerous entities vying for market share.
The industry growth rate presents a mixed picture, impacting competitive rivalry. While areas like cloud computing solutions are seeing strong expansion, traditional PC components might experience more modest growth. This disparity means that in slower-growing segments, companies like Lite-On face intensified competition as they vie for existing market share. For instance, the global PC market shipments in Q1 2024 were around 57.2 million units, a slight decline year-over-year, highlighting the competitive pressure in this mature segment.
Lite-On actively pursues product differentiation through robust research and development, sophisticated manufacturing processes, and the delivery of integrated solutions, aiming to carve out unique market positions.
Despite these efforts, many of Lite-On's component offerings face rapid commoditization, intensifying competition based on price rather than distinct features.
For instance, in the highly competitive power supply market, where Lite-On is a major player, price wars are common. In 2023, the global power supply market was valued at approximately USD 23.5 billion, with intense competition driving down margins for undifferentiated products.
Consequently, Lite-On's sustained success hinges on its ability to foster continuous innovation, ensuring its products remain ahead of the curve and mitigating the pressure of direct price-based rivalry.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The electronic components manufacturing sector, where Lite-On operates, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These costs stem from significant upfront investments in research and development, advanced machinery, and expansive production facilities. For instance, setting up a state-of-the-art semiconductor fabrication plant can easily run into billions of dollars.
These high capital outlays, coupled with specialized, hard-to-repurpose assets and the complexities of workforce restructuring, erect formidable exit barriers. Companies find it exceptionally difficult and costly to leave the market, even when facing periods of reduced demand or profitability. This predicament compels them to continue operating, often leading to aggressive price competition to maintain market share and cover their fixed obligations.
The sustained presence of numerous players, each burdened by these high fixed costs and exit barriers, naturally intensifies competitive rivalry within the industry. This dynamic can pressure profit margins as companies vie for sales volume to spread their fixed costs over a larger production base. For example, in 2024, the global semiconductor market, a key area for component manufacturers, experienced fluctuating demand, which, for companies with high fixed costs, translated into heightened price pressures in certain segments.
- High R&D and Capital Expenditures: Companies invest heavily in innovation and advanced manufacturing equipment, creating a significant cost base.
- Specialized Assets and Workforce: Production lines and skilled labor are often specific to the industry, making divestment or repurposing challenging.
- Forced Market Presence: High exit barriers compel firms to remain operational, even in unfavorable market conditions, fueling price wars.
- Intensified Rivalry: The need to cover fixed costs drives aggressive competition, impacting profitability for all players.
Strategic Stakes and Global Reach
Lite-On faces intense competition from numerous global players, each vying for significant market share in crucial geographical areas. This global footprint means companies like Lite-On are constantly battling for contracts and aiming for market leadership, understanding that scale is a major advantage.
The strategic importance of market share drives aggressive tactics, with companies frequently prioritizing long-term positioning over immediate profitability. This willingness to sacrifice short-term gains to secure or maintain market dominance escalates the rivalry across various regions and product segments.
- Global Competitors: Lite-On competes with companies like Foxconn, Pegatron, and Wistron, all of which have extensive global manufacturing and sales networks.
- Market Share Focus: In 2024, the demand for consumer electronics and IT components remains high, making market share in regions like North America and Europe particularly valuable for suppliers.
- Aggressive Bidding: Contract wins for major tech brands often involve highly competitive bidding processes where price and volume commitments are key differentiators, impacting profitability.
The competitive rivalry within the electronic components industry is fierce due to a fragmented market with numerous global players, including giants like Foxconn and Pegatron. Lite-On must contend with these entities, all pursuing significant market share and often prioritizing long-term positioning over immediate profits.
This intense competition is further fueled by the industry's high fixed costs and substantial exit barriers. Companies are compelled to remain operational, leading to aggressive pricing strategies to cover their investments in R&D and advanced manufacturing, as seen in the fluctuating demand within the 2024 global semiconductor market.
| Key Competitor | Global Presence | Market Focus |
| Foxconn | Extensive (Asia, Americas, Europe) | Consumer Electronics, IT Components |
| Pegatron | Significant (Asia, Americas) | Consumer Electronics, Computing Devices |
| Wistron | Broad (Asia, Americas) | IT Products, Communication Systems |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Technological advancements, particularly in areas like System-on-Chip (SoC) development, present a significant threat of substitution for Lite-On. These integrated solutions can combine multiple functions previously handled by separate components, potentially bypassing the need for Lite-On's discrete offerings. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to see a strong push towards SoC integration across consumer electronics and automotive sectors, as reported by industry analysts.
The attractiveness of substitutes for Lite-On's products hinges significantly on their price-performance ratio. If alternative technologies or products offer comparable or even better performance at a more competitive price point, customers will naturally be inclined to switch. For instance, in the solid-state drive (SSD) market, where Lite-On is a player, the constant evolution of NAND flash technology and controller chips means that newer, more affordable SSDs with similar or improved speeds can emerge, directly challenging existing offerings.
Lite-On needs to maintain a keen focus on optimizing its internal cost structures and continually enhancing the value proposition of its products. This means not only innovating to improve performance but also finding ways to reduce manufacturing and operational expenses. For example, in 2024, many electronics manufacturers are exploring advanced automation and supply chain efficiencies to combat rising material costs and maintain competitive pricing, a strategy Lite-On would likely need to employ to counter the threat of substitutes.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives hinges on perceived risk, ease of integration, and the value proposition of the substitute. For instance, in the automotive sector, the high cost and rigorous certification requirements for new components, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), significantly dampen the propensity to substitute existing, proven technologies. This cautious approach is also prevalent in medical devices, where patient safety and regulatory hurdles make rapid adoption of alternatives a rarity.
Conversely, the consumer electronics landscape, characterized by rapid technological evolution and shorter product lifecycles, exhibits a much higher propensity for substitution. Consumers readily embrace new smartphones, laptops, or wearable devices, often driven by incremental performance gains or novel features. This dynamic was evident in 2024 with the widespread adoption of AI-integrated personal devices, where early adopters quickly replaced older models to access new capabilities.
Alternative Energy and Power Solutions
The threat of substitutes for traditional power supply units is growing, particularly with the rise of alternative energy and more efficient power management integrated circuits (ICs). Lite-On, while a producer of components for these newer technologies, faces a potential substitution risk if their core power supply architectures become less relevant.
For instance, advancements in direct energy harvesting or highly integrated power management solutions could bypass the need for conventional power supplies. The global renewable energy sector experienced significant growth, with solar power capacity alone increasing by approximately 26% in 2023, reaching over 1,400 GW worldwide. This trend highlights a potential shift in energy consumption patterns that could impact demand for traditional power solutions.
- Alternative Energy Integration: As renewable energy sources like solar and wind become more prevalent, the demand for grid-tied inverters and energy storage solutions that manage these sources may reduce reliance on standard AC-DC power supplies.
- Power Management IC Efficiency: Innovations in power management ICs, which can significantly reduce energy waste within electronic devices, might decrease the overall power requirements, indirectly affecting the market for power supply units.
- Lite-On's Component Role: Lite-On's involvement in supplying components for electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy systems, such as power modules and chargers, positions them to adapt but also underscores the evolving nature of the power solutions market. In 2024, the global EV market is projected to exceed 15 million units sold, a substantial increase that necessitates advanced power conversion technologies.
Software-Defined Solutions and Virtualization
The rise of software-defined infrastructure and virtualization presents a significant threat of substitutes for Lite-On's hardware-centric cloud computing solutions. As organizations increasingly embrace virtualized environments, the demand for specialized, dedicated hardware components may diminish. This shift means that the core value proposition could move from the physical hardware itself to the software that manages and optimizes it.
For instance, in 2024, the global server virtualization market was valued at approximately $7.5 billion and is projected to grow substantially. This indicates a clear preference for flexible, software-driven solutions over traditional hardware deployments. Lite-On needs to consider how its hardware integrates with and enhances these software-defined architectures rather than competing solely on the hardware itself.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Storage (SDS): These technologies abstract hardware functions, allowing for greater flexibility and potentially reducing the need for proprietary hardware.
- Cloud-native architectures: Containerization and microservices, enabled by platforms like Kubernetes, abstract underlying infrastructure, making it less critical which specific hardware is used.
- Managed Services Providers (MSPs): MSPs often offer integrated hardware and software solutions, acting as a substitute for companies building their own on-premises infrastructure.
The threat of substitutes for Lite-On's products is multifaceted, driven by technological advancements and evolving market demands. Integrated solutions like System-on-Chips (SoCs) can replace discrete components, while advancements in energy harvesting and power management ICs challenge traditional power supplies. Furthermore, the shift towards software-defined infrastructure diminishes the need for specialized hardware.
For example, the semiconductor industry's continued focus on SoC integration in 2024 across consumer electronics and automotive sectors directly impacts the market for individual components. Similarly, the global renewable energy sector's growth, with solar power capacity increasing by approximately 26% in 2023, highlights a potential shift away from conventional power solutions. The server virtualization market, valued at around $7.5 billion in 2024, also demonstrates a growing preference for software-driven infrastructure over dedicated hardware.
| Technology Area | Substitute Threat | Impact on Lite-On | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semiconductors | System-on-Chips (SoCs) | Reduced demand for discrete components | Strong SoC integration trend in consumer electronics and automotive |
| Power Solutions | Energy Harvesting, Advanced Power Management ICs | Potential decline in traditional power supply market | Significant growth in renewable energy (e.g., ~26% solar capacity increase in 2023) |
| Cloud Computing | Software-Defined Infrastructure, Virtualization | Decreased need for specialized hardware | Server virtualization market ~$7.5 billion in 2024, with substantial projected growth |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the electronic components manufacturing sector, where Lite-On operates, demands significant upfront capital. This includes substantial investments in research and development, advanced manufacturing machinery, and establishing worldwide distribution channels. For instance, setting up a state-of-the-art semiconductor fabrication plant alone can cost billions of dollars.
Lite-On leverages its established economies of scale in both production and purchasing. This allows the company to achieve lower per-unit costs, presenting a formidable challenge for any new entrant aiming to compete on price from the outset. Newcomers must overcome this considerable financial barrier to achieve cost competitiveness.
Lite-On's deep well of proprietary technology and patents, especially in areas like optoelectronics and power management, creates a substantial hurdle for newcomers. Developing comparable innovations or securing licenses requires significant upfront investment in research and development, making it difficult for new players to compete effectively. This accumulated expertise is not easily replicated.
Lite-On's established global distribution network and deep-rooted customer relationships present a significant hurdle for new entrants. Building a comparable network and earning the trust of major manufacturers, Lite-On's core clientele, is a time-consuming and capital-intensive endeavor. For instance, in 2024, securing shelf space or integration with leading electronics brands often requires extensive vetting and proven track records, which new companies lack.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and regulations significantly impact the threat of new entrants in the electronic components sector. For instance, stringent environmental standards, such as those mandated by the European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive, require substantial investment in compliance and can deter smaller, less capitalized newcomers. Lite-On, as an established player, has already integrated these requirements into its operations, creating an incumbent advantage.
The need for various certifications, like those related to product safety and electromagnetic compatibility, also acts as a barrier. Obtaining these can be time-consuming and costly, with many certifications requiring extensive testing and documentation. In 2024, the global electronics market saw continued emphasis on compliance with evolving standards, making the initial investment for new entrants even more substantial.
- Compliance Costs: New entrants face significant upfront costs for meeting diverse regulatory requirements, including environmental, safety, and trade compliance.
- Certification Hurdles: Obtaining necessary product certifications can be a lengthy and expensive process, favoring established firms with existing compliance infrastructure.
- Trade Barriers: Evolving trade policies and tariffs, particularly in key manufacturing regions, can increase the cost of entry and operational complexity for new players.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Robust intellectual property laws and enforcement mechanisms can pose challenges for new entrants needing to navigate existing patents and designs.
Brand Loyalty and Reputation
Brand loyalty and reputation, while perhaps less obvious than in consumer electronics, play a significant role in the B2B electronic components sector. Lite-On's established name, built on years of delivering quality, reliability, and robust technical support, acts as a substantial barrier to entry. For instance, major automotive manufacturers often prioritize suppliers with a proven history of consistency, making it challenging for newcomers to displace incumbents.
New companies entering the market would need considerable time and financial resources to cultivate a similar level of trust and recognition. Overcoming the inertia of existing customer relationships, where manufacturers are hesitant to switch suppliers for critical components due to potential disruptions, requires a compelling value proposition. Lite-On's long-standing partnerships with global leaders in various industries underscore the difficulty new entrants face in replicating this established goodwill.
- Reputation for Quality: Lite-On's consistent product performance is a key differentiator.
- Reliability in B2B: In industrial applications, component failure can lead to significant downtime and costs, favoring established, reliable suppliers.
- Customer Inertia: Manufacturers are often reluctant to change suppliers for critical components without a strong incentive.
- Investment in Trust: Building a comparable reputation to Lite-On requires substantial time and investment in demonstrating consistent quality and support.
The threat of new entrants for Lite-On is moderate, primarily due to the substantial capital required for R&D, advanced manufacturing, and global distribution networks. Lite-On's established economies of scale and proprietary technology further erect significant barriers, making it challenging for newcomers to compete on price or innovation. In 2024, the electronics sector continued to see high investment needs, with semiconductor fabrication plants alone costing billions, reinforcing these entry barriers.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Lite-On Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Lite-On's official investor relations disclosures, annual reports, and financial statements. We supplement this with insights from reputable industry research firms and market intelligence platforms to capture the broader competitive landscape.