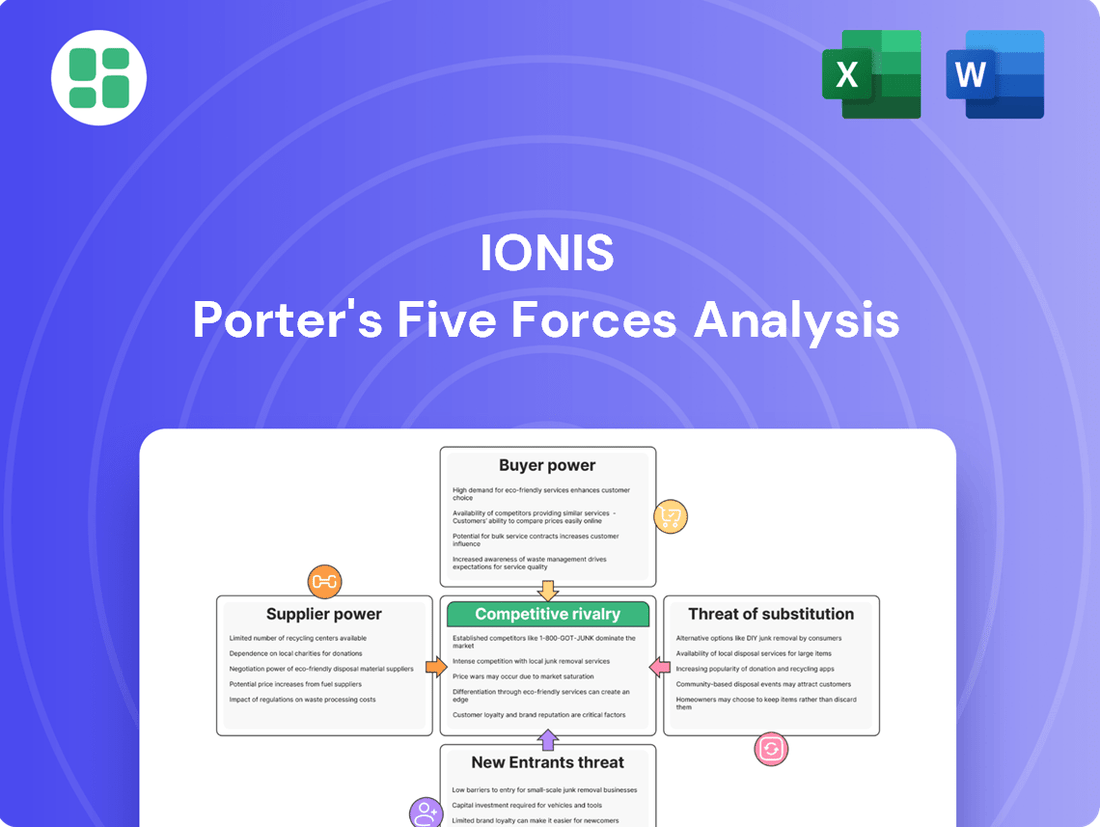
Ionis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ionis Bundle
Ionis Pharmaceuticals navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry, the threat of new entrants, and significant buyer power from payers. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Ionis’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Ionis Pharmaceuticals' reliance on highly specialized raw materials, reagents, and components for its proprietary antisense technology platform significantly influences supplier bargaining power. The very nature of these unique inputs, such as rare oligonucleotides and novel chemical entities, restricts the pool of qualified suppliers.
This limited supplier base grants them greater leverage, as Ionis may have fewer alternatives for critical components. For instance, in 2024, the development of advanced oligonucleotide synthesis often requires custom-manufactured precursors, with only a handful of global chemical manufacturers possessing the necessary expertise and regulatory compliance.
Ionis Pharmaceuticals, operating in the specialized field of RNA-targeted therapeutics, faces a concentrated supplier base for essential components and specialized services. This limited competition among suppliers grants them significant bargaining power, directly influencing Ionis's operational costs and research and development expenditures.
For instance, the production of complex oligonucleotides, the core of Ionis's drug platform, relies on a handful of highly specialized chemical manufacturers. In 2024, the cost of these raw materials represented a substantial portion of Ionis's cost of goods sold, with price increases from these key suppliers directly impacting profitability.
Switching suppliers in the biotechnology sector, particularly for critical raw materials or specialized manufacturing processes, can be a significant undertaking. For a company like Ionis Pharmaceuticals, this often involves extensive re-validation of materials to ensure they meet stringent quality and purity standards. Furthermore, any change may necessitate new regulatory approvals, adding layers of complexity and time to the process.
These hurdles translate directly into high switching costs. Consider the potential for delays in crucial drug development timelines or disruptions in existing manufacturing schedules if a supplier change is poorly managed. In 2024, the pharmaceutical industry continued to grapple with supply chain resilience, with companies investing heavily in ensuring the stability of their material sourcing, underscoring the importance of these considerations.
Consequently, these high switching costs inherently reduce Ionis's bargaining power. Existing suppliers, aware of the significant effort and investment required for a competitor to step in, are in a stronger position. This dynamic can influence pricing and contract terms, as suppliers leverage the inherent stickiness of their customer relationships within the specialized biotech landscape.
Proprietary Technologies of Suppliers
Suppliers who hold proprietary technologies vital to Ionis Pharmaceuticals' operations wield considerable influence. If Ionis relies on a specific supplier's unique chemical synthesis process or a patented delivery system that cannot be easily replicated or sourced elsewhere, that supplier's bargaining power increases substantially. This dependency can translate into higher input costs or less favorable contract terms for Ionis.
For instance, consider a hypothetical scenario where a key component for Ionis's antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) manufacturing is produced using a patented enzymatic process. If this patent is held by a single supplier, and no viable alternatives exist, Ionis would be compelled to accept that supplier's pricing and supply conditions. This situation is particularly relevant in the biopharmaceutical sector where specialized manufacturing techniques and intellectual property are paramount.
- Supplier Dependency: Ionis may depend on suppliers for specialized reagents or manufacturing equipment incorporating proprietary technology.
- Cost Implications: Exclusive access to these technologies can allow suppliers to command premium pricing for their goods or services.
- Intellectual Property: Patents or trade secrets held by suppliers can create barriers to entry for alternative sourcing, strengthening their negotiating position.
- Operational Risk: A reliance on a single supplier with proprietary technology can also introduce operational risks for Ionis if supply is disrupted.
Quality and Reliability Requirements
Ionis Pharmaceuticals operates in a highly regulated industry where the quality and reliability of raw materials and components are paramount. This means Ionis has limited flexibility in switching suppliers if those suppliers consistently meet stringent pharmaceutical standards. For instance, in 2024, the biopharmaceutical sector continued to see significant investment in quality control and supply chain resilience, underscoring the importance of dependable suppliers.
The critical nature of consistent, high-quality inputs for drug development and manufacturing means Ionis is likely to accept higher prices from suppliers who can demonstrate unwavering adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory mandates. This willingness to pay a premium directly enhances the bargaining power of these specialized suppliers.
- High Regulatory Burden: Pharmaceutical production demands strict adherence to quality and safety regulations, limiting supplier options.
- Critical Input Dependence: Ionis relies on suppliers for specialized materials essential for its drug pipeline.
- Premium for Quality: Suppliers meeting rigorous standards can command higher prices, increasing their leverage.
- Supply Chain Stability: Ensuring a consistent and reliable supply chain is a top priority, making supplier disruption costly.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Ionis Pharmaceuticals is considerable due to the specialized nature of its inputs. Limited qualified suppliers for unique reagents and proprietary technologies mean these entities can command higher prices and dictate terms, impacting Ionis's costs. For example, in 2024, the demand for custom-synthesized oligonucleotide precursors often outstripped supply, giving key manufacturers leverage.
Switching costs are also a significant factor. Re-validating materials and obtaining new regulatory approvals for any supplier change is time-consuming and expensive, reinforcing the position of existing suppliers. This inherent stickiness in supplier relationships allows them to maintain pricing power, as demonstrated by the industry-wide focus on supply chain resilience in 2024.
Suppliers holding critical intellectual property, such as patented manufacturing processes for antisense oligonucleotides, possess substantial bargaining power. Ionis's reliance on these exclusive technologies limits its alternatives, enabling suppliers to set unfavorable pricing and supply conditions. This dependency is a hallmark of the biopharmaceutical sector, where innovation is often protected by strong patents.
Furthermore, the stringent regulatory environment in pharmaceuticals means Ionis prioritizes suppliers with impeccable quality and GMP compliance. This focus on reliability allows compliant suppliers to charge premiums, as demonstrated by ongoing investments in quality control across the sector in 2024. Disruptions to a reliable supply chain are simply too costly to risk.
| Factor | Impact on Ionis | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High bargaining power for limited suppliers | Few manufacturers for specialized oligonucleotide precursors |
| Switching Costs | Reduces Ionis's leverage; increases supplier power | Time and cost of re-validating materials and seeking regulatory approval |
| Proprietary Technology | Supplier leverage through patents and unique processes | Reliance on patented enzymatic synthesis for ASO production |
| Regulatory Compliance | Premium pricing for GMP-compliant, reliable suppliers | Industry investment in quality control and supply chain stability |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability potential for Ionis by examining supplier power, buyer bargaining, new entrant threats, substitute products, and existing industry rivalry.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces model, streamlining strategic analysis and reducing the pain of complex market assessments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ionis Pharmaceuticals often focuses on rare diseases, meaning there are fewer treatment options available. For instance, their drug WAINUA (eplontersen) targets transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis, a condition with limited approved therapies. This scarcity of alternatives significantly weakens the bargaining power of customers, including patients and healthcare providers, as they have fewer choices for effective treatment.
While individual patients typically have limited sway, powerful entities like major health insurers and government programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid in the US, exert considerable bargaining power over Ionis Pharmaceuticals. These payers negotiate pricing and reimbursement terms, directly impacting the revenue potential for Ionis's therapies, especially those with broader patient populations.
This collective bargaining strength allows payers to push for lower drug prices, a trend that could affect Ionis's profitability, particularly for its commercially successful treatments. For instance, the significant market share of SPINRAZA means that negotiations with large payers are critical for its continued financial success.
Ionis's drugs, like donidalorsen which significantly reduced hereditary angioedema (HAE) attack rates, showcase strong clinical efficacy. This proven benefit enhances the perceived value of its therapies for patients and doctors, which can help mitigate some of the pricing pressure from payers.
Physician Prescribing Habits
Physicians are critical gatekeepers, significantly influencing patient access to Ionis's therapies. Their prescribing habits are directly shaped by their understanding and trust in Ionis's antisense technology and the demonstrated efficacy of its approved drugs. For instance, the strong clinical trial data supporting drugs like Spinraza (nusinersen) for spinal muscular atrophy has fostered physician confidence and adoption, thereby mitigating customer power.
Ionis's ongoing investment in medical education and the dissemination of robust clinical data are paramount. These efforts aim to build physician familiarity and comfort with its novel therapeutic approach. By providing clear evidence of safety and effectiveness, Ionis can cultivate consistent prescribing patterns, effectively reducing the bargaining power of the end-user (patient) by ensuring physician preference for its products.
- Physician as Intermediary: Physicians directly control patient access to Ionis's treatments, acting as a key intermediary between the company and the ultimate consumer.
- Impact of Familiarity and Confidence: A physician's comfort level with Ionis's antisense technology and the proven track record of its approved medications directly influences prescribing behavior, reducing the leverage of patients seeking alternatives.
- Educational Initiatives: Ionis's commitment to educating healthcare professionals on the benefits and application of its therapies is vital for solidifying physician preference.
- Clinical Data as a Driver: Strong, positive clinical trial results, such as those for Spinraza, are instrumental in building physician trust and encouraging consistent prescription of Ionis's products.
Availability of Alternative Treatments
The availability of alternative treatments significantly influences the bargaining power of customers in the pharmaceutical sector, particularly for companies like Ionis Pharmaceuticals that focus on RNA-targeted therapies. Even when a company offers a novel RNA-based approach, the existence of other therapeutic options, whether they are small molecules, biologics, or even different RNA modalities, can empower patients and healthcare providers. This is because these alternatives provide choices, potentially limiting the pricing power of any single therapy. For instance, in 2024, the market saw continued advancements in gene therapy and CRISPR-based treatments, which, while distinct, could be perceived as alternatives for certain genetic disorders where Ionis might also have a presence.
The presence of these alternatives, even if they are not as effective or convenient as an RNA-targeted therapy, creates a competitive landscape. This competition naturally drives down prices as companies vie for market share. Customers, armed with these options, can negotiate more effectively, demanding better pricing or more favorable terms. For example, if a new small molecule drug emerges that offers comparable efficacy for a specific rare disease, it directly challenges the pricing flexibility of an Ionis therapy for that same condition.
- Alternative Treatment Landscape: The emergence of diverse therapeutic modalities, including small molecules, biologics, and other RNA-based approaches, provides customers with choices.
- Price Competition: The existence of viable alternatives intensifies price competition, forcing companies to justify their pricing based on efficacy, safety, and convenience.
- Customer Empowerment: Patients and healthcare systems can leverage the availability of alternatives to negotiate better terms and pricing for RNA-targeted therapies.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the pharmaceutical market continued to see innovation across various therapeutic classes, directly impacting the bargaining power of customers for specialized treatments.
The bargaining power of customers for Ionis Pharmaceuticals is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative treatments. Even for rare diseases, the emergence of new therapeutic modalities like gene therapy or CRISPR in 2024 can introduce competitive pressures. For example, while Ionis targets specific genetic mechanisms, advancements in other fields offer patients and payers more options, potentially limiting pricing flexibility for Ionis's therapies.
This competitive landscape, fueled by innovation across different treatment classes, empowers customers. They can leverage the presence of alternatives to negotiate more favorable pricing and terms, as seen in the broader pharmaceutical market. For instance, if a new small molecule drug demonstrates comparable efficacy for a rare condition, it directly challenges the pricing power of an Ionis RNA-targeted therapy for that same indication.
| Factor | Impact on Ionis | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Alternative Treatments | Weakens pricing power | Advancements in gene therapy and CRISPR |
| Customer Negotiation | Increased leverage | General trend of payer scrutiny on drug costs |
| Therapeutic Innovation | Drives competition | Emergence of new modalities for rare diseases |
What You See Is What You Get
Ionis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Ionis Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the biotechnology industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or missing sections.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The biotechnology sector, particularly in RNA therapeutics, thrives on relentless research and development. Ionis Pharmaceuticals, a leader in this space, invests heavily in innovation to create novel RNA-targeted medicines, fueling a fast-paced and competitive landscape where scientific advancements can rapidly redefine market standing.
This intense R&D focus means companies are continually pushing the boundaries of what's possible, leading to a dynamic environment. For instance, the global biotechnology market was valued at approximately $1.37 trillion in 2023 and is projected to reach $2.77 trillion by 2030, highlighting the significant investment and competition in discovering new therapies.
Ionis Pharmaceuticals faces intense competition within the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors. The landscape is populated by a vast number of companies, from giants like AstraZeneca and Biogen, who are also Ionis' partners, to nimble, emerging biotechs focused on novel therapies.
This rivalry is particularly pronounced in the burgeoning field of RNA-based therapeutics. Multiple entities are actively developing treatments utilizing technologies such as small interfering RNA (siRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), and antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), directly competing with Ionis' core expertise.
Ionis Pharmaceuticals leverages its proprietary antisense technology as a key differentiator, offering a unique approach to drug development. However, the pharmaceutical landscape is highly competitive, with rivals also boasting distinct platforms and robust intellectual property portfolios. For instance, companies like Alnylam Pharmaceuticals are prominent in RNA interference (RNAi) therapies, representing a significant competitive force.
The capacity to stand out through enhanced efficacy, improved safety, or innovative mechanisms of action, all safeguarded by strong patent protection, is paramount for Ionis to maintain its competitive edge. In 2023, Ionis reported approximately $725 million in revenue, underscoring its market presence, while the broader rare disease drug market, where many of its products compete, is projected to grow significantly, highlighting the intense rivalry for market share.
High Stakes and Market Growth
The RNA therapeutics market is poised for significant expansion, with projected Compound Annual Growth Rates (CAGRs) ranging from 9.55% to over 35% by 2035. This robust growth attracts substantial investment, fueling intense competition among companies eager to capture market share in this dynamic sector.
This rapid market expansion means more players are entering, and existing ones are investing heavily in research and development. Companies are racing to develop innovative RNA-based treatments for a wide range of diseases, from rare genetic disorders to common infections.
- Projected Market Growth: RNA therapeutics market expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.55% to over 35% by 2035.
- Increased Investment: High growth potential attracts significant capital, intensifying competition.
- Competitive Landscape: Companies are vying for market share through innovation and strategic partnerships.
- Therapeutic Areas: Focus on diverse applications, including rare diseases and infectious diseases.
Strategic Collaborations and Partnerships
Ionis Pharmaceuticals actively pursues strategic collaborations, a key factor influencing competitive rivalry. For instance, its partnership with AstraZeneca for WAINUA and with Biogen for SPINRAZA are significant. These alliances not only bolster Ionis's market reach but also introduce competitive dynamics through co-commercialization, potentially strengthening rivals' existing portfolios or creating new competitive fronts.
These collaborations can intensify rivalry by bringing established players with extensive commercial infrastructure into direct competition with Ionis's products, even if they are developed jointly. For example, if a partner company has a strong presence in a therapeutic area where Ionis is also active, the co-commercialization agreement can lead to a more aggressive competitive landscape. By 2024, the pharmaceutical industry continues to see an increasing number of such strategic alliances, highlighting their importance in navigating market complexities and competitive pressures.
The nature of these partnerships means that Ionis must constantly assess the competitive positioning of its collaborators and their broader portfolios. A successful partnership can inadvertently empower a competitor if the partner company leverages the jointly developed product to gain market share in a segment where it already holds a strong position. This dynamic underscores the intricate balance Ionis must maintain between leveraging external expertise and managing the inherent competitive risks associated with such strategic alliances.
The competitive rivalry for Ionis Pharmaceuticals is fierce, driven by the rapid innovation in RNA therapeutics. Companies like Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, with its RNAi platform, represent significant competition, pushing for advancements in efficacy and safety. This intense R&D environment means that market positions can shift quickly based on scientific breakthroughs and patent protection.
The expanding RNA therapeutics market, projected to grow substantially, attracts numerous players, intensifying the race for market share. Ionis's strategic collaborations, such as those with AstraZeneca and Biogen, while beneficial, also introduce competitive dynamics as partners leverage these alliances. The industry saw significant R&D spending in 2024, with major pharmaceutical companies allocating billions to discover and develop new treatments, directly impacting the competitive landscape.
| Competitor | Key Technology | Therapeutic Focus | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alnylam Pharmaceuticals | RNA interference (RNAi) | Rare genetic diseases, hepatic infectious diseases | $1.1 billion |
| Moderna | Messenger RNA (mRNA) | Vaccines, therapeutics for various diseases | $7.5 billion |
| BioNTech | Messenger RNA (mRNA) | Vaccines, cancer immunotherapies | $2.1 billion |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Despite the advancements in RNA-targeted therapies, traditional small molecule drugs and biologics continue to represent a significant threat of substitutes, particularly for widespread conditions. These established treatment modalities often boast extensive clinical histories, demonstrating well-understood safety and efficacy profiles, which can be a strong deterrent for adoption of newer technologies. For instance, in 2024, the global small molecule drug market was valued at over $1.3 trillion, showcasing its entrenched position and broad market penetration.
Physician familiarity and established reimbursement pathways further bolster the competitive advantage of traditional therapies. Many healthcare providers are deeply accustomed to prescribing and managing these treatments, and insurance providers have well-defined protocols for coverage. This inertia can create a barrier for RNA-based therapies, even when demonstrating superior clinical outcomes, as they navigate a landscape where existing solutions are readily available and often perceived as less risky or complex.
Emerging gene therapy and gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, pose a significant threat of substitution to RNA-targeted medicines. These advanced biotechnologies aim to address diseases at their genetic root, offering potentially curative solutions by directly correcting or replacing faulty genes. This could reduce the long-term demand for therapies that manage disease by modulating gene expression.
While still in development and facing regulatory hurdles, the potential for one-time, curative treatments from gene therapies is compelling. For instance, by mid-2024, the FDA had approved over a dozen gene therapies, with many more in late-stage clinical trials for conditions ranging from rare genetic disorders to certain cancers. The increasing investment in this sector, with billions poured into research and development annually, underscores its disruptive potential.
The threat of substitutes for Ionis Pharmaceuticals' products hinges on the comparative efficacy, safety, and convenience of alternative treatments. If new therapies emerge that deliver similar or better clinical results with fewer side effects or simpler administration, they could significantly impact Ionis's market share.
For instance, in the rare disease space where Ionis often operates, a breakthrough in gene therapy or a novel small molecule drug offering a one-time cure or significantly reduced treatment burden would pose a substantial threat to Ionis's antisense oligonucleotide therapies, which typically require ongoing administration.
By late 2024, the landscape of genetic medicine is rapidly evolving. Companies are investing billions in R&D for various modalities, including CRISPR-based gene editing and RNA interference (RNAi) therapies, which could offer alternative mechanisms of action and potentially improved patient profiles compared to current antisense approaches.
Cost-Effectiveness and Reimbursement Landscape
The high development and manufacturing costs associated with advanced therapies, such as Ionis' RNA-targeted drugs, often translate into premium pricing. This can create significant pushback from payers, especially when considering the overall healthcare budget. For instance, the cost of gene therapies, which share some similarities in complexity, has frequently been a point of contention, with list prices often exceeding hundreds of thousands of dollars per treatment.
The availability of more cost-effective alternatives or shifts in reimbursement policies that favor established, less expensive treatments can significantly amplify the threat of substitution. If payers perceive similar efficacy at a lower price point from other therapeutic modalities, or if reimbursement frameworks are slow to adapt to novel drug pricing, patients and providers may opt for these substitutes, directly impacting Ionis' market share.
Consider these factors impacting the threat of substitutes:
- High Development Costs: Ionis' investment in research and development for novel RNA-targeting platforms can be substantial, contributing to higher initial drug prices.
- Payer Resistance: Reimbursement challenges are common for high-cost innovative therapies, as evidenced by ongoing negotiations for many advanced treatments in the market.
- Availability of Alternatives: The emergence of more affordable treatments for the same or similar conditions, whether traditional drugs or other novel modalities, directly increases substitution risk.
- Reimbursement Policy Shifts: Changes in healthcare policy or payer strategies that prioritize cost-effectiveness over therapeutic innovation could favor substitutes.
Patient and Physician Acceptance
Patient and physician acceptance of novel RNA-targeted therapies, like those developed by Ionis, is a significant factor when considering substitute treatments. If patients and doctors perceive established treatments or even other new therapies as safer, easier to administer, or backed by more robust long-term data, Ionis could face challenges. For instance, a therapy requiring frequent injections might be less appealing than an oral medication, even if the RNA therapy offers superior efficacy in the long run.
The perceived risk associated with new modalities plays a crucial role. While Ionis's platform is innovative, potential side effects or uncertainties about long-term outcomes compared to more familiar treatments could deter adoption. A strong existing preference for a particular class of drugs or a readily available, well-understood alternative can create a substantial barrier to market penetration for Ionis's RNA-targeted therapies.
- Patient Preference: Ease of administration and perceived safety are key drivers for patient adoption.
- Physician Trust: Long-term clinical data and established treatment protocols influence physician prescribing habits.
- Market Penetration: A strong preference for existing or alternative therapies can limit the market share for novel RNA-targeted treatments.
- Competitive Landscape: The availability and acceptance of substitute treatments directly impact Ionis's ability to gain traction.
The threat of substitutes for Ionis's RNA-targeted therapies is significant, stemming from both established small molecule drugs and emerging gene therapies. Traditional treatments, with over $1.3 trillion in market value in 2024, benefit from physician familiarity and robust reimbursement pathways, presenting a substantial hurdle for newer modalities.
Advanced gene therapies, like CRISPR, offer potentially curative genetic interventions, directly challenging RNA-based approaches that modulate gene expression. By mid-2024, the FDA had approved over a dozen gene therapies, with billions invested annually in this rapidly advancing field, highlighting its disruptive potential.
The comparative efficacy, safety, and convenience of alternatives, especially in rare diseases, will shape Ionis's market share. For example, a one-time gene therapy cure could significantly reduce demand for Ionis's ongoing antisense treatments, particularly if development costs lead to premium pricing, as seen with gene therapies often exceeding hundreds of thousands of dollars per treatment.
| Therapy Type | Market Value (Approx. 2024) | Key Substitute Advantage | Potential Impact on Ionis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Molecule Drugs | >$1.3 Trillion | Established history, physician familiarity, reimbursement | Continued preference for known treatments |
| Gene Therapies | Growing rapidly (Billions in R&D) | Potential for one-time cure, genetic root cause correction | Reduced long-term need for RNA-targeting |
| RNA Interference (RNAi) | Emerging | Alternative RNA modulation mechanism | Competition within RNA-based therapies |
Entrants Threaten
The biotechnology sector, especially for innovative drug discovery and development, demands substantial financial commitments. Companies must allocate significant capital towards rigorous research, extensive preclinical testing, and multi-phase clinical trials, often spanning years and requiring hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, bringing a new drug to market can cost upwards of $2.6 billion, according to some industry estimates. This formidable financial hurdle significantly discourages new players from entering the market, thereby reducing the threat of new entrants.
Stringent regulatory hurdles significantly deter new entrants in the pharmaceutical sector. Companies like Ionis must navigate complex and lengthy approval processes overseen by bodies such as the FDA and EMA. These processes demand rigorous clinical trials, proof of safety and efficacy, and adherence to strict manufacturing standards, all of which represent substantial time and financial commitments, effectively acting as high barriers to entry.
The development of RNA-targeted therapeutics, such as antisense drugs, demands a deep well of specialized scientific knowledge. This includes expertise in molecular biology, genomics, and the intricate chemistry of oligonucleotides. Companies entering this field must possess or acquire these sophisticated capabilities.
Furthermore, proprietary technology platforms are crucial for success in this area. Ionis Pharmaceuticals, a leader in the field, has invested heavily in its antisense technology platform, which underpins its drug discovery and development processes. This technological moat, combined with scientific acumen, presents a significant hurdle for potential new entrants.
For instance, the high cost and time associated with building these specialized R&D capabilities, coupled with the need for advanced manufacturing processes for oligonucleotide-based drugs, act as substantial barriers. The regulatory pathway for novel RNA-based therapies also adds complexity, requiring extensive clinical trial data and scientific validation.
Intellectual Property Landscape and Patent Protection
The intellectual property landscape presents a significant barrier to new entrants in the antisense technology space. Established players like Ionis Pharmaceuticals have built substantial patent portfolios that safeguard their core technologies and specific therapeutic candidates. For instance, Ionis holds hundreds of patents globally covering its proprietary oligo design, chemistry, and delivery methods, which are crucial for the efficacy and safety of its drugs.
New companies entering this field must navigate this complex web of existing patents. Developing novel therapies that avoid infringement is a considerable hurdle, often requiring extensive R&D to create truly distinct approaches. Alternatively, securing licensing agreements for key patented technologies can be prohibitively expensive, adding substantial upfront costs and ongoing royalty payments that can stifle a new entrant's competitiveness. This intellectual property moat significantly raises the cost and risk for potential competitors.
- Ionis Pharmaceuticals holds a vast portfolio of patents covering its antisense technology and drug candidates.
- New entrants must develop non-infringing technologies or face costly licensing fees.
- The complexity and expense of navigating patent law deter many potential competitors.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing players like Ionis Pharmaceuticals benefit significantly from established economies of scale in their advanced manufacturing processes and extensive R&D capabilities. This allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger output, leading to lower per-unit production expenses. For instance, Ionis's mRNA manufacturing infrastructure, developed over years of operation, provides a cost advantage that new entrants would find challenging to replicate quickly.
Furthermore, Ionis possesses a deep experience curve, having navigated the complex drug development and regulatory approval processes for numerous therapies. This accumulated knowledge translates into greater efficiency, reduced trial-and-error, and a higher probability of successful market entry. A new entrant would face substantial hurdles in matching this operational expertise and understanding of the biopharmaceutical landscape, impacting their ability to compete on cost or speed to market.
- Economies of Scale: Ionis leverages its large-scale manufacturing and R&D investments to achieve cost efficiencies not easily matched by newcomers.
- Experience Curve: Years of successful drug development and regulatory navigation provide Ionis with a significant knowledge and efficiency advantage.
- Barriers to Entry: The substantial capital required to build comparable manufacturing facilities and gain regulatory expertise creates a high barrier for potential new competitors.
- Competitive Disadvantage for Entrants: New companies would struggle to compete on price or operational efficiency against an established player like Ionis with these advantages.
The threat of new entrants into the RNA-targeted therapeutics market, particularly for companies like Ionis, is significantly mitigated by several high barriers. These include the immense capital required for research and development, the complex regulatory landscape, and the need for specialized scientific expertise.
The financial investment needed to bring a novel drug to market, often exceeding $2.6 billion, alongside the intricate patent portfolios held by established players like Ionis, creates a formidable deterrent. Furthermore, the deep scientific knowledge and proprietary technology platforms developed over years of operation provide a substantial competitive advantage, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate the necessary capabilities and achieve cost-efficiency.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for R&D, clinical trials, and manufacturing (>$2.6 billion per drug). | Discourages entry due to financial risk and scale. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and lengthy approval processes (FDA, EMA). | Demands significant time, resources, and expertise to navigate. |
| Specialized Knowledge | Expertise in molecular biology, genomics, and oligonucleotide chemistry. | Requires significant investment in talent acquisition and training. |
| Proprietary Technology | Advanced platforms like Ionis's antisense technology. | Difficult to replicate, creating a technological moat. |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patent portfolios protecting core technologies. | Requires non-infringing development or costly licensing. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost efficiencies from large-scale manufacturing and R&D. | New entrants struggle to match cost competitiveness. |
| Experience Curve | Accumulated knowledge in drug development and regulatory affairs. | Provides efficiency and reduces trial-and-error for incumbents. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and expert analyst forecasts to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.