Ingles Markets Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ingles Markets Bundle
Ingles Markets operates in a highly competitive grocery sector, facing significant pressure from both powerful buyers and a constant threat of new entrants. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ingles Markets’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The grocery sector, including Ingles Markets, depends on a wide array of suppliers for everything from fresh produce to packaged goods. However, in certain niche or specialized product areas, the number of available suppliers can be quite limited.
For instance, if Ingles Markets seeks unique organic ingredients or specific regional specialty items, they might find only a handful of producers capable of meeting those demands. This scarcity grants those particular suppliers greater bargaining power, allowing them to potentially dictate terms or prices to Ingles Markets.
Ingles Markets encounters moderate switching costs with many of its suppliers for standard grocery items. This is because there are typically other vendors readily available for common products, meaning Ingles isn't heavily reliant on any single supplier for these basic needs. For instance, in 2024, the grocery sector saw continued competition among distributors of fresh produce and packaged goods.
However, the situation changes for more specialized or unique supply arrangements. If Ingles has developed private label products with specific manufacturers or relies on specialized equipment for its operations, such as its milk processing plant, the costs to switch suppliers can become significantly higher. These specialized relationships often involve unique formulations or technical specifications that are not easily replicated by other vendors.
The financial and time investment required to establish new supplier relationships, integrate new products into their inventory, and potentially reconfigure logistics can represent a substantial hurdle. This is a common challenge across the retail industry, where supply chain disruptions or the need to find new partners can lead to increased operational expenses and potential delays in product availability.
Ingles Markets' considerable scale, operating nearly 200 supermarkets across six Southeastern states and generating over $5 billion in annual sales, makes it a significant customer for a wide array of suppliers. This substantial purchasing volume inherently grants Ingles considerable leverage in its negotiations.
The company's large order volumes allow it to command favorable pricing, negotiate advantageous payment terms, and dictate specific delivery schedules with many of its suppliers. This robust purchasing power generally serves to diminish the bargaining power of most suppliers who rely on Ingles as a key sales channel.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers for Ingles Markets is generally low. While some large food brands or agricultural groups might consider direct-to-consumer sales, the immense capital and logistical hurdles of running a supermarket chain make this an unlikely strategy for most of Ingles' suppliers. For instance, establishing a fully operational grocery store requires significant investment in real estate, inventory management, and staffing, which most suppliers are not equipped to handle.
Ingles Markets itself mitigates supplier power through backward integration, notably with its own milk processing plant. This internal capability reduces reliance on external dairy suppliers, giving Ingles more control over costs and supply in that crucial segment. This strategic move directly counters potential price increases or supply disruptions from dairy vendors.
- Low Threat of Supplier Forward Integration: Most food suppliers lack the capital and expertise to operate retail grocery chains, making direct competition unlikely.
- Capital Intensity of Retail: The significant investment required for store operations, supply chain, and marketing deters most suppliers from entering the retail space.
- Ingles' Backward Integration: Ingles' ownership of a milk processing plant reduces its vulnerability to dairy supplier power, ensuring a more stable and cost-effective supply.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly curtails supplier bargaining power for Ingles Markets. For many common grocery items, a wide array of alternative products exists, meaning no single supplier holds substantial leverage. Ingles can readily find comparable goods from various manufacturers or agricultural producers.
This is particularly true for Ingles' private label brands, such as Laura Lynn and Harvest Farms. By developing these in-house brands, Ingles diversifies its sourcing options, lessening its reliance on any particular external vendor. This strategic approach enhances Ingles' ability to negotiate favorable terms and maintain cost control.
- Numerous Substitute Inputs: For standard grocery items, a broad range of alternative products are available, limiting the power of individual suppliers.
- Private Label Diversification: Ingles' private label brands, like Laura Lynn and Harvest Farms, allow for sourcing from multiple manufacturers, reducing dependence on single vendors.
- Enhanced Negotiation Power: The availability of substitutes empowers Ingles to negotiate better pricing and terms with its suppliers.
For many standard grocery items, Ingles Markets faces a low bargaining power from suppliers due to the availability of numerous substitute inputs. This allows Ingles to easily switch between vendors for common products, maintaining cost control. In 2024, the grocery sector continued to see robust competition among distributors for essential goods.
Ingles' own private label brands, such as Laura Lynn and Harvest Farms, further reduce supplier leverage by diversifying sourcing options. This strategic move enhances Ingles' negotiation power, enabling them to secure favorable pricing and terms by having multiple viable options for similar products.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Ingles Markets is generally moderate, leaning towards low for most products. While specialized items might present a higher threat, Ingles' large scale and backward integration strategies effectively mitigate supplier influence across its operations.
| Factor | Assessment for Ingles Markets | Impact on Bargaining Power |
| Availability of Substitutes | High for most standard goods | Low supplier power |
| Supplier Concentration | Varies by product category | Moderate to low supplier power |
| Switching Costs | Low for standard, high for specialized | Low for most, moderate for specialized |
| Ingles' Scale & Purchasing Power | Significant (nearly 200 stores) | Lowers supplier power |
| Backward Integration (e.g., Milk Processing) | Present | Significantly lowers supplier power in specific segments |
What is included in the product
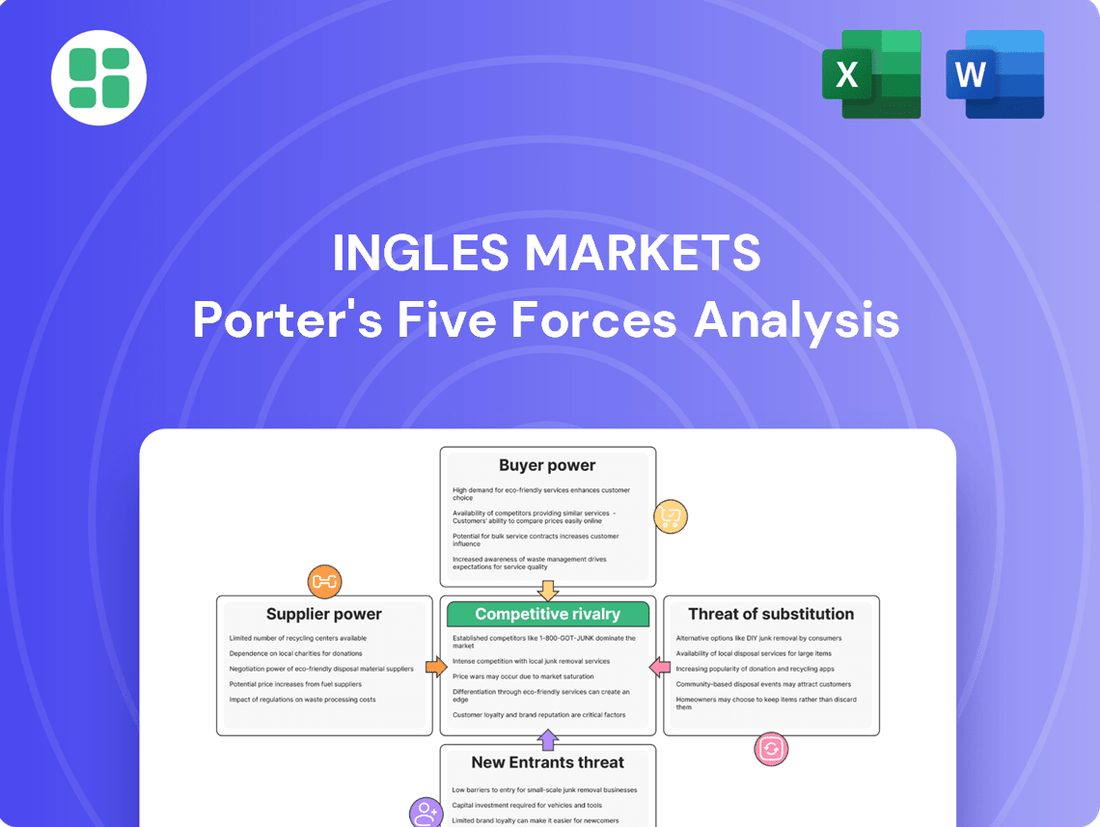
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ingles Markets dissects the competitive intensity within the grocery sector, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the overall rivalry among existing players.
Instantly understand strategic pressure with a powerful spider/radar chart, clarifying Ingles Markets' competitive landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Grocery shoppers, especially with ongoing inflation, are very focused on price and actively look for good deals. This means Ingles Markets needs to keep its prices competitive because customers will switch to cheaper brands or shop around to save money.
In 2023, the U.S. inflation rate averaged 4.12%, impacting consumer spending habits and increasing price sensitivity across the grocery sector.
The availability of private label options, such as Ingles' own brands, provides customers with ways to control their spending and manage their grocery budgets more effectively.
The bargaining power of customers for Ingles Markets is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative retailers. In the Southeast, where Ingles operates, consumers have a wealth of grocery shopping choices. This includes major national players like Walmart and Kroger, alongside established regional chains such as Publix.
Furthermore, the presence of discount grocers like Aldi and Lidl, and specialty food stores, intensifies this competition. For instance, in 2024, the grocery market in the Southeast saw continued expansion from these various formats, offering consumers ample opportunities to compare prices and product assortments. This broad selection empowers customers to easily switch providers if they find better value or convenience elsewhere, thereby increasing their bargaining leverage over Ingles Markets.
The bargaining power of customers is a significant factor for grocery retailers like Ingles Markets. For consumers, the costs associated with switching from Ingles to a competitor are remarkably low. This typically boils down to the inconvenience of travel time and the minor effort of learning a new store's layout and product placement. In 2024, the average American household shops at multiple grocery stores per month, indicating a low barrier to switching.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today are more informed than ever, thanks to readily available digital tools and mobile devices. They can easily compare prices across various retailers and access detailed product information, significantly boosting their ability to negotiate or switch to competitors offering better value. This heightened transparency directly translates to increased customer bargaining power.
Ingles Markets faces this reality as consumers actively seek out the best deals. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer spent over $1,000 annually on groceries, making price comparisons a critical factor in their purchasing decisions. Ingles' strategy to counter this involves emphasizing its commitment to quality and local sourcing, aiming to build loyalty that transcends mere price competition.
- Informed Consumers: Digital platforms and mobile apps empower shoppers to compare prices and product details instantly, increasing their leverage.
- Price Sensitivity: With the average grocery spend being substantial, customers are motivated to find the most economical options.
- Ingles' Differentiation: The company aims to mitigate customer bargaining power by highlighting unique selling propositions like superior quality and local product partnerships.
Impact of Online Grocery Shopping
The proliferation of online grocery shopping and delivery services has undeniably amplified customer convenience and broadened their options, moving beyond the confines of traditional physical stores. Ingles Markets does offer online ordering for in-store pickup, but the expanding online landscape presents consumers with an even wider array of choices, thereby bolstering their leverage to insist on greater convenience and more competitive pricing.
This shift means customers can easily compare prices and delivery options across multiple platforms. For instance, in 2024, the online grocery market continued its robust growth trajectory, with various reports indicating double-digit percentage increases in sales year-over-year. This increased accessibility to alternatives directly translates to a stronger bargaining position for consumers who can readily switch to providers offering better value or more convenient service models.
- Increased Consumer Choice: Online platforms provide access to a wider selection of brands and products than typically available in a single physical store.
- Price Transparency: Customers can effortlessly compare prices from different online grocers, forcing retailers to remain competitive.
- Demand for Convenience: The ease of home delivery or scheduled pickup has become a significant factor influencing purchasing decisions.
The bargaining power of Ingles Markets' customers is substantial due to the readily available alternatives and low switching costs. Consumers can easily compare prices and product offerings from numerous competitors, including national chains, regional players, and discount grocers, especially in the Southeast. This heightened price sensitivity, fueled by inflation and informed by digital tools, compels Ingles to maintain competitive pricing and differentiate through quality and local sourcing to retain shopper loyalty.
| Factor | Impact on Ingles Markets | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Alternatives | High customer bargaining power due to numerous competitors | Continued expansion of discount and specialty grocers in the Southeast |
| Switching Costs | Very low for customers, facilitating easy movement between retailers | Average American household shops at multiple grocery stores monthly |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers actively seek deals, especially with inflation | U.S. inflation averaged 4.12% in 2023, increasing price focus |
| Information Availability | Digital tools empower price and product comparisons | Increased use of mobile apps for grocery shopping and price checks |
What You See Is What You Get
Ingles Markets Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Ingles Markets Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive understanding of the industry's forces. You're looking at the final version; what you're previewing is precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying, ready for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Ingles Markets operates within the highly competitive Southeast U.S. grocery retail sector, facing a diverse array of competitors. Major national players like Walmart and Kroger, along with strong regional grocers such as Publix, exert significant pressure on market share and customer loyalty.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by the presence of discount grocers like Aldi and Lidl, as well as the growing influence of dollar stores that increasingly offer grocery items. This crowded environment necessitates continuous innovation and strategic pricing for Ingles to maintain its position.
The U.S. grocery market's projected slow growth, estimated between 0.5% and 4% annually for 2024 and 2025, directly fuels competitive rivalry. This limited expansion means companies like Ingles Markets must vie more intensely for market share rather than benefiting from a rapidly growing overall market. Expect this environment to drive aggressive pricing strategies and heightened promotional activities as players fight for every customer.
While groceries are often seen as commodities, Ingles Markets strives to stand out by focusing on fresh food, its own brand of products, and excellent customer service. They also offer unique shopping experiences. For example, Ingles highlights quality perishables, organic selections, and partnerships with local suppliers. Adding pharmacies and fuel centers further enhances their appeal.
These efforts aim to build customer loyalty and differentiate Ingles from rivals. However, it's important to note that customers can easily switch between grocery stores, meaning keeping them loyal through differentiation remains a continuous challenge. In 2024, the grocery industry continued to see intense competition, with companies like Kroger and Walmart also investing heavily in private label brands and loyalty programs.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The supermarket sector, including players like Ingles Markets, is burdened by significant fixed costs. These involve substantial outlays for prime real estate, sophisticated store infrastructure, extensive inventory, and complex supply chain networks. For instance, the average cost to build a new supermarket can range from $5 million to $15 million, depending on size and location, a figure that Ingles Markets would also consider in its capital planning.
These high initial investments create formidable exit barriers. Companies find it exceedingly difficult and costly to divest assets or leave the market, even when facing profitability challenges. This sticky situation means that even underperforming firms tend to stay put, intensifying competition as they fight to maintain their market share and recoup their investments, a dynamic Ingles Markets navigates regularly.
- High Fixed Costs: Supermarkets require significant capital for real estate, store build-out, and inventory.
- Exit Barriers: The sunk costs in physical assets make exiting the industry challenging and expensive.
- Intensified Rivalry: Companies remain in the market despite lower returns, leading to sustained competitive pressure.
Strategic Investments and Innovation
Competitors in the grocery sector are heavily investing in modernizing stores, adopting advanced technologies like AI and automation, building robust omnichannel capabilities, and enhancing loyalty programs. These strategic moves aim to elevate the customer experience and boost operational efficiency.
Ingles Markets is actively participating in this investment race, allocating significant capital towards new store development, store renovations, and technological enhancements. For example, Ingles reported capital expenditures of $214.3 million in fiscal year 2023, a substantial increase from $166.5 million in fiscal year 2022, demonstrating their commitment to staying competitive and adapting to changing consumer demands.
- Store Modernization: Competitors are updating store layouts and aesthetics to attract more shoppers.
- Technology Adoption: Investments in AI for inventory management and automation for checkout processes are common.
- Omnichannel Presence: Expanding online ordering, delivery, and curbside pickup options is crucial.
- Loyalty Programs: Personalized discounts and rewards are being used to retain customers.
The competitive rivalry for Ingles Markets is fierce due to a crowded grocery landscape in the Southeast U.S., featuring national giants, strong regional players, and discount chains. This intense competition is amplified by slow market growth, forcing companies to fight harder for market share, often through aggressive pricing and promotions.
Ingles differentiates itself through fresh offerings, private labels, and enhanced services like pharmacies and fuel centers, but customer switching remains easy. The industry's high fixed costs and exit barriers mean even struggling competitors remain, sustaining pressure on Ingles.
Competitors are heavily investing in store modernization, technology, omnichannel capabilities, and loyalty programs to enhance customer experience and efficiency. Ingles Markets is matching these investments, as evidenced by its substantial capital expenditures, to remain competitive.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Impact on Ingles |
|---|---|---|
| National Chains | Walmart, Kroger | Significant market share pressure, price competition |
| Regional Chains | Publix | Strong regional loyalty, localized competition |
| Discount Grocers | Aldi, Lidl | Price sensitivity, focus on value |
| Dollar Stores | Various | Increasing competition on essential grocery items |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Consumers have a wide array of options beyond traditional supermarkets like Ingles Markets for their food needs. These include convenience stores, bustling farmers' markets, niche specialty food shops, and even direct-to-consumer meal kit services that deliver pre-portioned ingredients. For example, the meal kit industry saw significant growth, with companies like HelloFresh and Blue Apron serving millions of households, directly competing for consumer food spending.
The growing foodservice industry, including restaurants and prepared meal services, presents a substantial threat of substitution for grocery retailers like Ingles Markets. Consumers increasingly opt for the convenience and experience of dining out or ordering takeout, which directly competes with the need to purchase groceries for home preparation.
In 2024, the U.S. restaurant industry is projected to reach $1.1 trillion in sales, highlighting the significant consumer shift towards off-premise dining and prepared foods. This trend means fewer meals are being prepared at home, potentially reducing Ingles Markets' customer base for traditional grocery items.
Ingles Markets actively addresses this threat by expanding its in-store prepared foods and meal solutions sections. These offerings aim to capture some of that consumer spending on convenience, positioning Ingles as a destination for both raw ingredients and ready-to-eat meals, thereby mitigating the impact of external foodservice substitutes.
The rise of online-only grocery platforms and third-party delivery services poses a significant threat of substitution for Ingles Markets. These services, such as Instacart, offer consumers the ultimate convenience of having groceries delivered directly to their homes, bypassing the need for traditional in-store shopping. This convenience directly competes with Ingles' brick-and-mortar model, even with their own online pickup options.
Changing Consumer Lifestyles and Preferences
Shifting consumer preferences present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional supermarkets like Ingles. As demand grows for sustainability, health-focused options, and locally sourced goods, consumers may increasingly turn to specialized retailers or direct-to-consumer models that cater specifically to these evolving tastes. For instance, the burgeoning market for plant-based foods, valued at over $7 billion in the US in 2023, shows how dedicated vegan or organic grocers can attract customers seeking specific product assortments.
Ingles is making efforts to adapt by expanding its organic and local product offerings, aiming to capture some of this market shift. However, for consumers prioritizing hyper-niche products or unique shopping experiences, smaller, specialized stores or even farmers' markets can act as effective substitutes. These alternatives often provide a more curated selection and a direct connection to producers, which can be highly appealing.
The rise of meal kit delivery services, which saw substantial growth during and after the pandemic, also represents a potent substitute. These services offer convenience and pre-portioned ingredients, directly addressing busy lifestyles and a desire for curated culinary experiences. While Ingles offers prepared foods, the complete convenience and recipe guidance of a meal kit service can be a compelling alternative for some shoppers.
- Evolving Consumer Lifestyles: Consumers are increasingly prioritizing health, sustainability, and convenience, driving demand for specialized food options.
- Rise of Niche Retailers: Dedicated organic, vegan, or local food stores cater to specific consumer segments, offering a direct substitute for traditional supermarkets.
- Meal Kit Services: The convenience and curated experience of meal kit delivery services provide a significant alternative for grocery shopping.
- Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Models: Farmers and specialized producers are increasingly selling directly to consumers, bypassing traditional retail channels.
Impact of Private Label and Value Chains
The increasing prevalence of private label brands across the retail landscape, including discount stores, presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional supermarkets like Ingles Markets. Consumers increasingly choose these lower-priced store brands, which directly compete with national brands typically stocked by full-service grocers. This shift means shoppers can fulfill a larger portion of their needs with these value-oriented alternatives.
The growth of limited-assortment retailers further amplifies this substitution threat. These stores offer a curated selection of essential goods at competitive prices, providing a viable alternative for consumers seeking to manage their grocery spending. This trend impacts the entire shopping basket, not just individual items.
- Private Label Growth: In 2023, private label sales in the U.S. grocery market reached approximately $199 billion, accounting for 20.7% of total sales, up from 19.7% in 2022, according to NielsenIQ data. This demonstrates a clear consumer preference for store brands.
- Discounters' Impact: Discount grocers, which heavily feature private label options, saw their market share grow by 1.5% in 2023, reaching 25.5% of the total grocery market, according to IRI.
- Value Proposition: The average price difference between national brands and private label equivalents can range from 15% to 30%, making them an attractive substitute for budget-conscious shoppers.
The threat of substitutes for Ingles Markets is significant, driven by a diverse range of alternatives that cater to evolving consumer needs and preferences. From convenience stores and farmers' markets to specialty shops and direct-to-consumer meal kits, consumers have numerous options beyond traditional supermarkets.
The foodservice industry, including restaurants and prepared meal services, also presents a strong substitute. In 2024, the U.S. restaurant industry is projected to reach $1.1 trillion in sales, indicating a substantial consumer shift towards off-premise dining and prepared foods, which directly competes with home grocery shopping.
Online grocery platforms and third-party delivery services offer unparalleled convenience, allowing consumers to bypass physical stores entirely. Furthermore, the growing demand for organic, vegan, and locally sourced products has fueled the rise of niche retailers and direct-to-consumer models, capturing specific market segments.
The increasing prevalence of private label brands, especially within discount grocery stores, offers a compelling lower-cost alternative. In 2023, private label sales in the U.S. grocery market accounted for approximately 20.7% of total sales, demonstrating a clear consumer preference for value-oriented options.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Key Driver | 2024 Impact Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convenience & Specialty Retail | Convenience stores, farmers' markets, specialty food shops | Convenience, unique product offerings | Growth in niche food sector sales |
| Foodservice Industry | Restaurants, takeout, prepared meal services | Convenience, dining experience | Projected $1.1 trillion U.S. restaurant sales in 2024 |
| Online & Delivery Services | Online grocers, third-party delivery platforms (e.g., Instacart) | Ultimate convenience, home delivery | Increased online grocery penetration rates |
| Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) & Niche Models | Meal kit services, organic grocers, local producers | Health, sustainability, specific dietary needs, curated experience | Growth in plant-based food market (over $7 billion in 2023) |
| Private Label & Discount Retail | Store brands, limited-assortment discounters | Price sensitivity, value for money | Private label market share at 20.7% in 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
The supermarket industry demands immense capital. Building a new store, stocking shelves, and establishing a robust supply chain can easily run into millions of dollars. For instance, a new large-format supermarket could cost upwards of $10 million to $20 million to construct and equip, not including land acquisition. This significant financial hurdle deters many smaller players from even attempting to enter the market.
Ingles Markets' existing infrastructure, including its nearly 200 stores and a dedicated milk processing plant, represents a massive sunk cost. This established operational scale and the capital already invested create a substantial barrier. A new entrant would need to match or surpass this level of investment to compete effectively, making the threat of new entrants relatively low.
Established players like Ingles Markets benefit from significant economies of scale in purchasing, distribution, and marketing, allowing them to negotiate better prices with suppliers and achieve lower operating costs. For instance, in 2023, Ingles Markets reported over $5.5 billion in net sales, a testament to their purchasing power.
New entrants would struggle to match these cost efficiencies immediately, putting them at a competitive disadvantage. The company's long-standing operational experience, cultivated over decades, also provides a valuable intangible asset that is difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly.
Ingles Markets benefits from established brand loyalty, a key barrier for new entrants. Many consumers stick with familiar supermarkets due to consistent service and community ties, making it difficult for newcomers to attract customers. For instance, Ingles' long-standing presence and community involvement foster a sense of trust that new competitors must work hard to replicate.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
Developing an efficient and reliable supply chain, particularly for fresh groceries, is a significant hurdle for new entrants. Ingles Markets benefits from its established distribution network, which includes its own milk processing facility, a considerable asset that new competitors would struggle to replicate. This infrastructure allows Ingles to manage costs and ensure product freshness more effectively than a newcomer without similar capabilities.
The difficulty in securing prime supplier relationships and comparable logistics networks presents a substantial barrier. For instance, in 2024, the grocery industry continued to see consolidation among key suppliers, making it harder for smaller or new players to gain favorable terms. Ingles' long-standing relationships and integrated operations, like their milk plant which processes millions of gallons annually, give them a distinct advantage in procurement and delivery efficiency, directly impacting their ability to offer competitive pricing and product availability.
- High Capital Investment: Building a comparable distribution network requires substantial upfront capital, a significant deterrent for new entrants.
- Supplier Exclusivity: Established players like Ingles often have exclusive or preferential agreements with key suppliers, limiting access for newcomers.
- Logistical Expertise: Managing a complex, temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods demands specialized knowledge and infrastructure that is difficult and costly to develop.
- Economies of Scale: Ingles' existing volume allows for greater efficiency and lower per-unit costs in logistics and procurement, a scale that new entrants cannot immediately match.
Regulatory Hurdles and Local Approvals
The grocery sector faces significant regulatory obstacles that can deter new competitors. These include stringent food safety standards, complex zoning requirements for new locations, and evolving labor laws, all of which demand substantial investment and expertise to comply with. For instance, in 2024, the FDA continued to emphasize enhanced traceability requirements for food products, adding another layer of operational complexity for any new entrant.
Securing the necessary permits and local approvals for new store sites presents another formidable barrier. This process can be lengthy and unpredictable, often involving multiple governmental agencies and community consultations. Ingles Markets, like other established players, has navigated these hurdles for decades, building institutional knowledge that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly. The sheer time and resource commitment required for approvals can effectively limit the number of viable new entrants.
- Food Safety Regulations: Compliance with standards like HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) requires significant upfront investment and ongoing monitoring.
- Zoning and Land Use: Obtaining permits for retail locations can be a lengthy process, often requiring environmental impact studies and community feedback.
- Labor Laws: Adherence to minimum wage, benefits, and working condition regulations adds to operational costs for new businesses.
- Permitting Delays: In many regions, the average time to secure all necessary permits for a new retail establishment can extend over 12-18 months, according to industry reports from late 2023 and early 2024.
The threat of new entrants for Ingles Markets is generally low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for store construction, distribution networks, and inventory, often exceeding $10 million for a large-format store, deter many potential competitors. Ingles' existing infrastructure, including nearly 200 stores and a milk processing plant, represents significant sunk costs and operational scale that new entrants would struggle to match, making it difficult to compete on cost and efficiency.
Established brand loyalty and the difficulty in replicating Ingles' logistical expertise and supplier relationships also limit new entrants. For instance, in 2024, supplier consolidation made securing favorable terms harder for newcomers. Ingles' long-standing relationships and integrated operations, like their milk plant processing millions of gallons annually, provide distinct advantages in procurement and delivery, impacting their ability to offer competitive pricing and product availability.
Regulatory hurdles, including food safety standards, zoning, and labor laws, add further complexity and cost for new businesses. Securing permits alone can take 12-18 months, as noted in industry reports from late 2023 and early 2024, requiring significant investment and institutional knowledge that Ingles has cultivated over decades.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data/Fact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Cost of building stores, distribution, and inventory | High deterrent | New large-format store: $10M - $20M+ (2024 estimates) |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high volume | Competitive disadvantage for newcomers | Ingles' 2023 Net Sales: $5.5B+ |
| Brand Loyalty | Customer preference for established brands | Requires significant marketing effort to overcome | Long-standing community ties and consistent service |
| Logistical Infrastructure | Efficient supply chain, including specialized facilities | Difficult and costly to replicate | Ingles' milk processing plant |
| Supplier Relationships | Preferential terms and access to key suppliers | Limited access for new players | 2024 industry trend: supplier consolidation |
| Regulatory Compliance | Food safety, zoning, labor laws | Adds significant cost and time | Permit acquisition: 12-18 months (late 2023/early 2024 reports) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ingles Markets leverages data from their annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific reports from IBISWorld and market share data from Nielsen. This blend of public company disclosures and third-party market intelligence provides a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.