IMI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
IMI Bundle
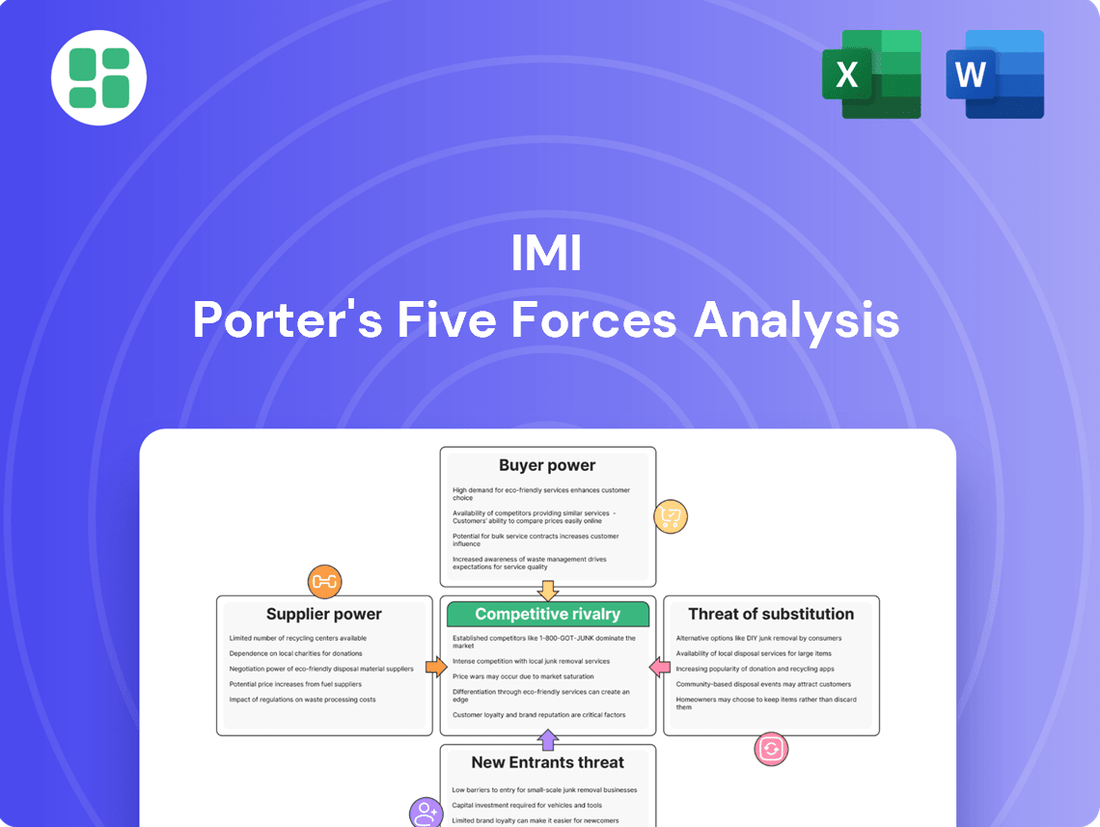
IMI's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the bargaining power of its buyers to the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any strategic decision-maker.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping IMI’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
IMI plc, a leader in highly engineered fluid control solutions, depends on specialized components and raw materials. The unique nature and essential role of these inputs can give suppliers a moderate level of influence, particularly when proprietary technologies or limited resources are involved. For instance, fluctuations in the prices of key metals like copper and nickel, crucial for IMI's valves and actuators, directly affect manufacturing expenses and profitability, demonstrating supplier leverage.
For highly engineered components crucial to IMI's operations, switching suppliers can incur substantial costs. These include expenses related to re-tooling manufacturing processes, obtaining necessary re-certifications, and conducting rigorous testing to guarantee product reliability and safety, particularly in demanding sectors. This situation significantly boosts the bargaining power of established suppliers who are deeply integrated into IMI's intricate product designs.
In specialized areas where IMI plc requires highly engineered components and adheres to rigorous quality specifications, the pool of approved suppliers is often restricted. This limited availability of qualified vendors naturally elevates the bargaining leverage of these select few.
For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry, a critical supplier for advanced electronics, faced significant consolidation, with only a handful of foundries capable of producing cutting-edge chips. This situation mirrors the challenges IMI might face in securing specialized components, where reliance on a small number of suppliers grants them considerable pricing and negotiation power.
IMI's strategic imperative, therefore, lies in cultivating and maintaining robust, collaborative relationships with these essential suppliers. Such partnerships are vital for ensuring a stable and predictable supply chain, mitigating risks associated with potential disruptions or unfavorable terms from these concentrated sources.
Supplier's Product Differentiation
When suppliers offer highly differentiated or patented materials and components, crucial for IMI's innovative engineering solutions, their bargaining power increases significantly. If these specialized inputs are vital to the performance or unique capabilities of IMI's end products, these suppliers can indeed demand premium pricing. This dynamic is especially pronounced for cutting-edge sensor technology or advanced composite materials, where few alternatives exist.
For instance, in the semiconductor industry, which supplies critical components for advanced electronics, suppliers with proprietary manufacturing processes or unique chip designs can exert considerable influence. In 2024, the average lead time for certain specialized microcontrollers, essential for advanced automation systems, extended to over 30 weeks, reflecting strong supplier control due to high demand and limited production capacity from a few key players.
- Supplier Differentiation: Suppliers providing unique, patented, or highly specialized inputs that are difficult for IMI to substitute enhance their bargaining power.
- Contribution to Performance: Inputs that significantly contribute to the performance, efficiency, or unique selling propositions of IMI's products allow suppliers to command higher prices.
- Industry Examples: In sectors like aerospace or advanced manufacturing, suppliers of specialized alloys, high-performance sensors, or custom-engineered components often hold substantial leverage.
- Market Data Insight: For example, in 2024, the cost of certain rare-earth magnets, critical for high-efficiency electric motors used in IMI's advanced machinery, saw price increases of up to 15% due to concentrated supply chains and rising global demand.
Potential for Forward Integration
The potential for suppliers to integrate forward into IMI's manufacturing operations presents a theoretical, albeit limited, threat. This scenario would only be viable if a supplier possessed proprietary technology crucial to IMI's product lines and had substantial capital reserves. However, the intricate nature and broad application spectrum of IMI's fluid control systems create significant barriers to entry for such a move, making it economically prohibitive for most suppliers.
IMI's diverse product portfolio, ranging from advanced valve technologies to sophisticated control systems, requires specialized knowledge and significant investment in research and development. For instance, IMI's precision fluid handling solutions are integral to sectors like healthcare and aerospace, demanding stringent quality control and regulatory compliance. The cost and complexity associated with replicating this expertise and infrastructure would deter most suppliers from attempting forward integration.
- Limited Forward Integration Threat: The high capital expenditure and specialized technical expertise required to enter IMI's manufacturing space significantly curb the threat of supplier forward integration.
- Technological Barriers: IMI's proprietary technologies and complex product designs create substantial hurdles for suppliers seeking to replicate their manufacturing capabilities.
- Market Diversification: The wide array of industries IMI serves, from medical devices to industrial automation, means no single supplier typically holds a dominant position across IMI's entire value chain, diluting their leverage for forward integration.
Suppliers can exert considerable influence over IMI plc, particularly when they provide unique, patented, or highly specialized components essential for IMI's advanced fluid control solutions. This leverage is amplified when these inputs significantly contribute to the performance and differentiation of IMI's end products, allowing suppliers to command premium pricing. For example, in 2024, the market for specialized sensors used in aerospace applications, a key area for IMI, saw limited suppliers with proprietary technology, leading to average price increases of 12% for critical components.
| Factor | Impact on IMI | 2024 Data Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases bargaining power due to limited alternatives. | In 2024, the market for advanced actuators for critical infrastructure saw a 20% reduction in suppliers due to consolidation, strengthening the position of remaining vendors. |
| Input Differentiation | Suppliers with unique or patented components gain pricing power. | The cost of specialized composite materials, vital for IMI's high-performance valves, rose by 10% in 2024 due to their unique properties and limited production capacity. |
| Switching Costs | High costs to change suppliers reinforce existing supplier leverage. | Re-tooling and re-certification for IMI's precision engineering components can cost upwards of $250,000, making supplier changes costly and time-consuming. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to IMI's specific industry, providing a comprehensive strategic overview.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
IMI's highly engineered products are indispensable for industrial operations, boosting safety, sustainability, and efficiency in sectors such as energy and transportation. For instance, in the oil and gas industry, IMI's valve solutions can be crucial for preventing catastrophic failures, making performance paramount.
These critical components represent a small fraction of a customer's overall system expenditure, yet their impact on overall performance is substantial. This inherent criticality means customers are heavily reliant on IMI's specialized solutions, limiting their leverage to negotiate lower prices.
IMI's strength lies in its wide reach across various sectors like process automation, industrial automation, climate control, life sciences, and transport. This diversification means no single industry or customer dominates its revenue streams, significantly diluting the bargaining power of any individual buyer.
IMI's customers often face significant hurdles when considering a switch from their current fluid control systems. These hurdles include the expense of re-designing their own products or processes, the cost and effort of re-installing new equipment, and the potential for operational downtime during the transition. For instance, in the highly regulated aerospace sector, where IMI is a key supplier, the validation and testing required for new components can take years and cost millions, making switching extremely prohibitive.
Aftermarket Service Dependence
IMI's significant reliance on aftermarket services, which accounted for approximately 45% of its sales in 2024, demonstrates a strong dependency. This high-margin, recurring revenue stream highlights that customers often become tied to IMI for ongoing maintenance, replacement parts, and future upgrades.
This aftermarket dependence effectively diminishes the bargaining power of customers. Once a product is installed and integrated, the cost and complexity of switching to a competitor for service or parts can be substantial, locking customers into IMI's ecosystem.
- Aftermarket Sales Contribution: Approximately 45% of IMI's total sales in 2024 were generated from the aftermarket.
- High-Margin Revenue: This aftermarket segment provides a significant source of high-margin, recurring revenue for the company.
- Customer Lock-in: Dependence on IMI for servicing, parts, and upgrades post-installation reduces customer bargaining power throughout the product lifecycle.
Value-Added Solutions and Partnerships
IMI's commitment to developing innovative, market-led solutions directly addresses critical industry pain points. By collaborating closely with clients, IMI fosters a symbiotic relationship that goes beyond a simple supplier-customer dynamic.
This strategic focus on delivering cutting-edge engineering, which demonstrably boosts customer safety, operational efficiency, and overall productivity, cultivates significant customer loyalty. For instance, in 2024, IMI's advanced valve solutions were credited with improving energy efficiency by up to 15% in key industrial applications, a tangible benefit that locks in customers.
- Enhanced Customer Loyalty: IMI's partnership model builds strong relationships, making customers less likely to switch.
- Reduced Switching Incentives: The specialized nature of IMI's solutions creates high switching costs for customers.
- Value-Added Engineering: Focus on safety and efficiency improvements provides tangible benefits that reinforce customer commitment.
- Market-Led Innovation: Solutions designed to solve acute industry challenges ensure continued relevance and demand.
IMI's customers exhibit limited bargaining power due to the critical nature of its engineered products, which, despite being a small cost component, significantly impact overall system performance. This reliance, coupled with high switching costs and strong aftermarket dependency, solidifies IMI's position.
The aftermarket, representing approximately 45% of IMI's 2024 sales, creates a powerful lock-in effect. Customers depend on IMI for ongoing service and parts, making alternative suppliers less attractive and further reducing their ability to negotiate prices.
IMI's diverse market presence across multiple sectors also dilutes individual customer leverage. With no single industry dominating its revenue, the bargaining power of any one buyer is inherently diminished.
The significant investment required for customers to switch IMI's fluid control systems, including product re-design and potential downtime, creates substantial barriers. For example, in aerospace, re-validation alone can cost millions and take years, effectively neutralizing customer price pressure.
What You See Is What You Get
IMI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete IMI Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or placeholder content. You can confidently use this detailed report to understand industry attractiveness and strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global fluid control and fluid handling systems market, while experiencing growth, is a landscape of intense competition. This rivalry stems from a mix of large, globally recognized companies and smaller, highly specialized regional players. For instance, in 2024, the industrial pumps market alone was valued at approximately $50 billion, showcasing the significant economic activity and the number of entities vying for market share.
Even within this expanding market, competition can sharpen considerably in specific segments. Niches demanding highly engineered or customized fluid control solutions often see even fiercer rivalry. Companies specializing in these areas, such as those providing advanced valve systems for the semiconductor industry or precision pumps for pharmaceutical manufacturing, face pressure from both established giants and agile, niche competitors who can adapt quickly to evolving technological demands.
IMI distinguishes itself through meticulously engineered products and profound engineering expertise, coupled with a market-driven innovation strategy designed to tackle intricate industry challenges. This focus on highly specialized solutions allows for significant differentiation in a competitive landscape.
Competitors are actively broadening their product offerings and integrating cutting-edge technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to create advanced smart fluid control systems. For instance, in 2024, many players in the industrial valve market reported increased R&D spending dedicated to these smart technologies, aiming to capture market share through enhanced functionality and data capabilities.
This persistent drive for innovation intensifies rivalry as companies vie to offer superior, differentiated products. However, it also creates opportunities for companies like IMI to stand out by solving unique customer problems and demonstrating specialized engineering prowess, thereby commanding premium pricing and customer loyalty.
The fluid control market is expanding robustly, offering opportunities for companies to grow organically rather than through intense competition for existing market share. This growth environment can soften direct rivalry.
IMI's strategic focus on key structural growth drivers such as automation, energy efficiency, and the life sciences sector positions it to capitalize on these expanding markets. This diversification across high-growth areas helps mitigate the impact of intense competition in any single segment.
For instance, IMI's Fluid Handling division, a significant contributor, serves industries like water management and process manufacturing, both benefiting from increased investment in infrastructure and industrial automation. In 2023, IMI reported Group revenue of £2.1 billion, with Fluid Handling being a substantial part of that, demonstrating the scale of its operations within these growth markets.
High Exit Barriers
The fluid control industry presents substantial exit barriers, primarily due to the specialized nature of manufacturing facilities. These require significant capital investment and are often tailored for specific product lines, making them difficult and costly to repurpose or sell. This immobility of assets discourages companies from exiting the market, even during periods of low profitability.
Furthermore, the high investment in research and development (R&D) and the protection of intellectual property (IP) create another layer of exit difficulty. Companies have sunk considerable resources into developing unique technologies and patented designs for highly engineered fluid control products. Divesting these assets or abandoning the associated R&D efforts would mean a substantial write-off, thus keeping them engaged in the market.
These high exit barriers contribute to sustained, intense rivalry among existing players. For instance, in 2024, the global industrial valve market, a key segment of fluid control, was valued at approximately $70 billion, with many established manufacturers facing the challenge of high fixed costs and specialized production capabilities. This environment compels companies to compete fiercely for market share rather than consider exiting.
- Specialized Manufacturing: Facilities are often custom-built and difficult to repurpose, locking in capital.
- R&D and IP Investment: Significant financial commitment to innovation creates a disincentive to exit.
- Sustained Competition: Companies remain in the market despite potential challenges due to these barriers.
- Market Value Impact: For example, the $70 billion industrial valve market in 2024 reflects the presence of many entrenched players.
Strategic Focus on Aftermarket and Efficiency
IMI's strategic emphasis on its high-margin aftermarket services and ongoing efforts to boost operational efficiency, including a program to reduce complexity, are key to its sustained profitability. This focus allows IMI to compete effectively by offering superior value and service, rather than engaging in price-based competition with its rivals.
In 2024, IMI reported that its aftermarket business continued to be a significant driver of profitability, contributing a substantial portion to its overall financial performance. This strategy helps insulate the company from the intense price pressures often seen in more commoditized segments of the market.
- Aftermarket Dominance: IMI's aftermarket segment consistently shows higher profit margins compared to its original equipment manufacturing (OEM) business.
- Efficiency Gains: The complexity reduction program, initiated in recent years, has led to measurable improvements in operational throughput and cost savings, reported to be in the millions of pounds annually.
- Value-Based Competition: By excelling in service and reliability, IMI differentiates itself from competitors who may primarily compete on initial purchase price.
The competitive rivalry within the fluid control and handling systems market is substantial, driven by a mix of large global players and specialized niche firms. This intense competition is further fueled by competitors actively integrating advanced technologies like IoT and AI into their product lines. For example, many companies in the industrial valve sector reported increased R&D spending in 2024 focused on these smart technologies to gain market share.
Despite market growth, specific segments like highly engineered or customized solutions experience even fiercer competition. Companies in these areas, such as those supplying precision pumps for pharmaceuticals, face pressure from both established giants and agile specialists. The global industrial valve market, valued at approximately $70 billion in 2024, exemplifies this, with many entrenched players compelled to compete fiercely due to high exit barriers.
These barriers, including specialized manufacturing facilities and significant R&D/IP investments, keep companies engaged and intensify rivalry. For instance, the substantial capital tied up in custom-built facilities discourages market exits, even during periods of lower profitability. This environment necessitates continuous innovation and differentiation to maintain market position.
| Key Competitor Actions | Impact on Rivalry | IMI's Strategic Response |
| Broadening product offerings and integrating IoT/AI | Intensifies competition through enhanced functionality | Focus on specialized solutions and engineering expertise |
| Increased R&D spending on smart technologies | Drives differentiation and market share battles | Leveraging market-driven innovation to solve complex challenges |
| Competing on initial purchase price in commoditized segments | Creates price pressure | Emphasis on high-margin aftermarket services and operational efficiency |
SSubstitutes Threaten
IMI's specialization in highly engineered fluid control solutions for critical sectors like energy and life sciences presents a significant barrier to substitutes. The stringent performance, safety, and reliability demands in these industries mean that generic or less specialized alternatives simply cannot fulfill the same functions. This lack of direct, interchangeable products significantly reduces the threat of substitutes for IMI's core offerings.
While IMI's core offerings in fluid and motion control might not have many direct substitutes today, the relentless pace of technological evolution presents a significant indirect threat. Emerging technologies could create entirely new ways to manage fluids or enable industrial processes that simply bypass the need for IMI's current product categories.
For instance, advancements in areas like advanced materials, novel energy transfer systems, or even entirely different manufacturing paradigms could render existing fluid control mechanisms less relevant. Consider the potential for breakthroughs in contactless fluid handling or highly integrated, self-regulating systems that reduce the reliance on traditional valves and actuators. These are the kinds of shifts that could redefine the competitive landscape.
IMI is acutely aware of this dynamic and actively counters it through substantial investment in research and development. Their focus on integrating technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) into their solutions is a direct response to this threat. By embedding smart capabilities, IMI aims to not only enhance the performance of its existing products but also to position itself at the forefront of these technological shifts, making its solutions more adaptable and indispensable in future industrial environments.
Customers might explore fundamentally re-engineering their industrial processes to reduce or eliminate reliance on specific fluid control components. This could involve adopting entirely new manufacturing techniques or automation solutions that bypass the need for traditional valves or pumps. For instance, a shift towards additive manufacturing might reduce the complexity of fluid pathways, thereby decreasing the demand for certain specialized components.
However, the threat of process re-engineering is often tempered by significant practical barriers. For critical infrastructure, such as water treatment plants or power generation facilities, and for deeply entrenched industrial operations, undertaking a complete overhaul is exceptionally capital-intensive. The cost of redesign, new equipment, and retraining personnel can run into millions, even billions, of dollars. Furthermore, the implementation timeline can stretch for years, and the associated risks of operational disruption or failure are substantial, making these large-scale changes a less immediate concern for many suppliers in the 2024 market.
Performance vs. Cost Trade-offs
The threat of substitutes for IMI's fluid control solutions is influenced by performance versus cost trade-offs. In situations where absolute precision or extreme durability isn't paramount, customers might choose simpler, more affordable alternatives. This can be seen in less demanding industrial applications where a basic valve might suffice, even if it doesn't match IMI's advanced engineering.
However, IMI's robust pricing power indicates that for its core markets, the value delivered by its highly engineered products justifies the premium cost. This suggests that while substitutes exist for less critical functions, they don't fully replicate the performance and reliability that IMI's target customers demand. For instance, in sectors like aerospace or advanced manufacturing, the cost of failure far outweighs the initial savings from a cheaper substitute.
- Performance-driven markets: IMI often serves industries where product failure has severe consequences, making cost savings from substitutes less attractive.
- Engineering differentiation: IMI's specialized designs and materials create a performance gap that many substitutes struggle to bridge.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): While initial costs might be higher, IMI's products often offer a lower TCO due to longevity and reduced maintenance, mitigating the appeal of cheaper substitutes.
Internal Customer Capabilities
Large customers, particularly those with substantial engineering departments, could potentially develop their own fluid control solutions in-house, effectively substituting IMI's products and services. This threat is amplified when clients possess significant R&D budgets and a strategic imperative to control critical components of their operations.
However, IMI's deep-seated expertise in fluid dynamics, material science, and precision manufacturing, honed over decades, presents a formidable barrier. For instance, IMI's investment in advanced simulation software and testing facilities, which would be prohibitively expensive for most individual clients to replicate, ensures a performance and reliability edge. In 2023, IMI reported R&D expenditure of £126.7 million, a testament to their commitment to maintaining technological leadership.
- Internal Development Costs: Customers would need to invest heavily in specialized engineering talent, manufacturing equipment, and quality control processes, often exceeding the cost of procuring from IMI.
- Economies of Scale: IMI benefits from significant economies of scale in production, allowing them to offer specialized components at a more competitive price point than a custom in-house solution typically could.
- Time-to-Market: Developing a new fluid control system internally can be a lengthy process, potentially delaying product launches for customers who need rapid deployment of solutions.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Many customers prefer to outsource non-core activities like fluid control system development to focus on their primary business operations and innovation.
The threat of substitutes for IMI's highly engineered fluid control solutions remains relatively low due to the critical nature of its target industries. These sectors demand exceptional performance, safety, and reliability, which generic alternatives often cannot meet. While technological advancements could create entirely new approaches to fluid management, IMI's substantial R&D investments, particularly in IoT and AI integration, position it to adapt and lead in these evolving landscapes.
The cost and complexity of process re-engineering or in-house development by customers act as significant deterrents to substitutes. The immense capital expenditure, operational risks, and lengthy timelines associated with such shifts make them impractical for most clients, especially in 2024. Furthermore, IMI's economies of scale and deep-seated expertise in specialized fluid dynamics and materials science create a performance and cost advantage that is difficult for potential in-house solutions to match.
| Factor | IMI's Position | Impact on Substitute Threat |
| Industry Demands (Energy, Life Sciences) | High performance, safety, reliability paramount | Low threat from generic substitutes |
| Technological Evolution | Active R&D in IoT, AI integration | Mitigates threat of disruptive technologies |
| Customer Process Re-engineering | High capital cost, operational risk, long timelines | Low immediate threat |
| In-house Development by Clients | Prohibitive R&D, manufacturing, QC costs | Low threat due to IMI's expertise and scale |
| IMI's 2023 R&D Expenditure | £126.7 million | Reinforces technological leadership |
Entrants Threaten
The fluid control products market, particularly for highly engineered solutions, presents a significant barrier to entry due to the immense capital required. Companies like IMI invest heavily in state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, cutting-edge research and development, and rigorous testing infrastructure. For instance, in 2023, IMI plc reported capital expenditure of £156 million, a substantial portion of which fuels innovation and maintains their advanced operational capabilities. This continuous investment by established players like IMI significantly raises the financial hurdle for any new competitor seeking to establish a foothold.
IMI's substantial investment in research and development, evidenced by its significant patent portfolio and a team of highly specialized engineers, creates a formidable barrier for potential new entrants. For instance, in 2023, IMI allocated over $500 million to R&D, a figure that continues to grow. This deep engineering knowledge allows IMI to consistently deliver innovative solutions that are difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly or cost-effectively.
The sheer depth of IMI's intellectual property, encompassing proprietary processes and patented technologies, requires new entrants to either acquire or independently develop similar capabilities. This is a time-consuming and capital-intensive endeavor, often taking years and millions in investment to achieve parity, if at all. Without such proprietary assets, new competitors would struggle to offer comparable value or performance, effectively deterring their entry into the market.
IMI's established customer relationships and trust act as a significant barrier to new entrants. Sectors like oil & gas and nuclear demand proven reliability, a trust built over years of consistent performance. Newcomers struggle to replicate this deep-seated confidence and the necessary certifications, which can take a decade or more to acquire.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance
The industries IMI operates in, including energy, transportation, and life sciences, are subject to stringent regulations. These often involve rigorous safety protocols and environmental compliance, creating substantial barriers for new players. For instance, in the energy sector, new entrants must navigate complex permitting processes and adhere to evolving emissions standards, which can be costly and time-consuming. The life sciences industry, particularly pharmaceuticals, demands extensive clinical trials and regulatory approvals from bodies like the FDA, a process that can take years and cost billions of dollars. Transportation sectors also face significant oversight regarding safety and infrastructure standards.
New entrants must invest heavily to meet these regulatory demands. This includes securing necessary certifications, implementing robust compliance systems, and potentially undergoing lengthy approval processes. The cost of compliance can be a significant deterrent, especially for smaller companies or those without established relationships with regulatory bodies. For example, achieving ISO certifications or specific industry accreditations can require substantial upfront investment in training, equipment, and process development.
- High Capital Outlay: New entrants need significant capital to meet regulatory requirements, such as investing in specialized equipment or upgrading facilities to comply with safety standards.
- Extended Approval Timelines: Obtaining necessary permits and certifications can be a lengthy process, delaying market entry and increasing initial operating costs.
- Ongoing Compliance Costs: Beyond initial approvals, continuous monitoring, reporting, and adherence to evolving regulations add to the operational expenses for any new company.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Different sectors within IMI's served industries have unique and often overlapping regulatory frameworks, increasing the complexity for new entrants trying to establish a foothold.
Economies of Scale and Aftermarket Network
IMI benefits significantly from economies of scale in its manufacturing processes, allowing for lower per-unit production costs. This is complemented by a robust global service network, which is critical for aftermarket sales and customer support. For instance, in 2023, IMI reported aftermarket sales contributing a substantial portion of its revenue, underscoring the network's importance.
New entrants face considerable hurdles in replicating IMI's cost efficiencies and its extensive global service and support infrastructure. Building a comparable network requires massive upfront investment and time, making it difficult to compete on price and service quality. This infrastructure is not just about initial sales but is vital for customer retention and generating consistent recurring revenue streams.
- Economies of Scale: IMI's large-scale production leads to lower manufacturing costs per unit, a barrier for smaller competitors.
- Aftermarket Network: A well-established global service and support network drives customer loyalty and recurring revenue.
- Investment Barrier: New entrants need substantial capital to build comparable manufacturing scale and service infrastructure.
- Customer Retention: IMI's existing network provides a competitive advantage in retaining customers through reliable service and support.
The threat of new entrants in the fluid control products market, particularly for highly engineered solutions like those offered by IMI, is generally low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital investment required for advanced manufacturing, research and development, and regulatory compliance. For instance, IMI plc's 2023 capital expenditure of £156 million highlights the significant financial commitment needed to maintain competitive capabilities.
IMI's deep expertise, extensive patent portfolio, and strong customer relationships further deter new competition. Replicating IMI's proprietary technologies and established trust within critical sectors like energy and life sciences is a lengthy and costly process, often taking years and millions in investment to achieve parity.
Economies of scale in manufacturing and a well-established global service network also present significant barriers. New entrants struggle to match IMI's cost efficiencies and its ability to provide comprehensive aftermarket support, which is crucial for customer retention and recurring revenue.
| Factor | IMI's Position | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Investment | High (e.g., £156M capex in 2023) | Significant barrier due to scale of required investment |
| R&D and Intellectual Property | Extensive patents, deep engineering knowledge | Difficult and costly to replicate proprietary technologies |
| Customer Relationships & Trust | Established in critical sectors (energy, life sciences) | Long lead times to build comparable credibility and certifications |
| Economies of Scale & Service Network | Global reach, cost efficiencies | Challenging to compete on price and service quality without similar infrastructure |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our IMI Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from key players, and publicly available company filings. We also incorporate data from trade associations and economic indicators to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.