Hyakugo Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hyakugo Bank Bundle
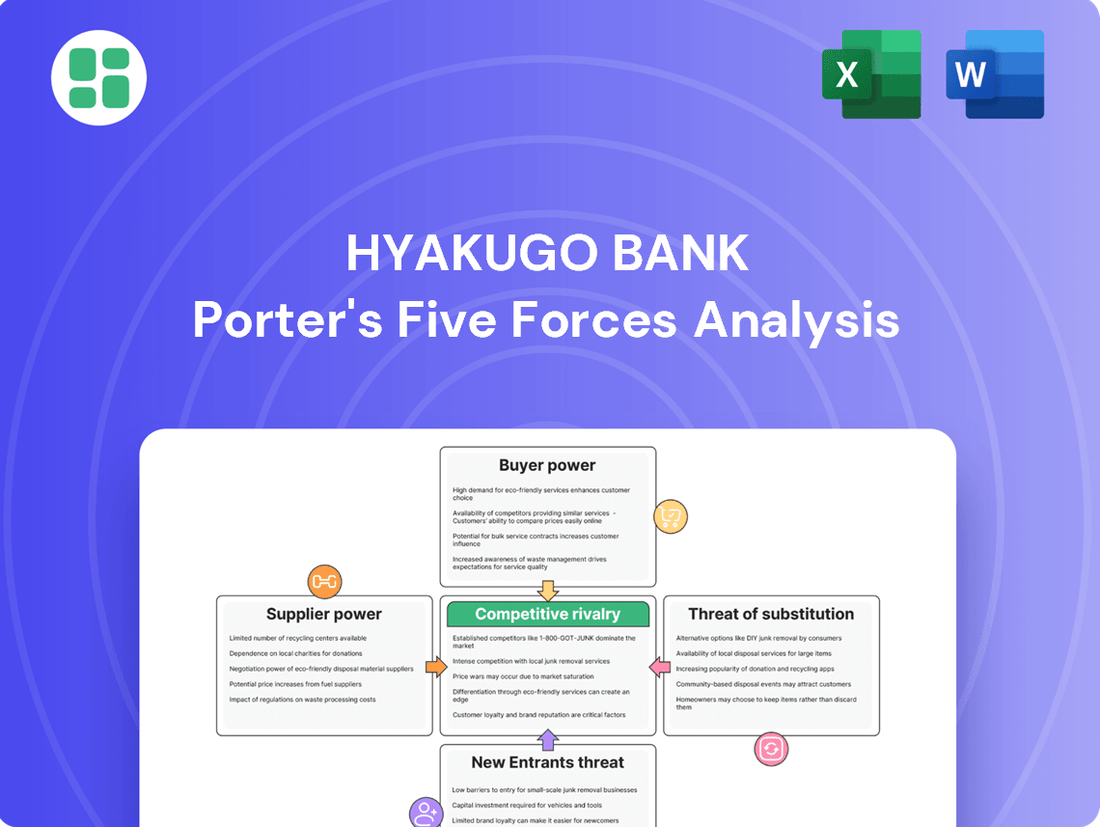
Hyakugo Bank navigates a landscape shaped by intense rivalry, evolving customer expectations, and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp the bank's strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hyakugo Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hyakugo Bank's reliance on technology providers for its core banking systems and digital services significantly influences its operational efficiency and competitive edge. The bargaining power of these suppliers is amplified when their offerings are specialized, such as advanced AI-driven fraud detection or robust cloud infrastructure, making switching costs high for the bank.
In 2024, the global FinTech market, a key area for Hyakugo Bank's technology needs, was projected to reach over $1.5 trillion, indicating a substantial and competitive landscape where key providers can exert considerable influence. If a critical system provider, like those offering core banking software, experiences a significant price increase or service disruption, it could directly impact Hyakugo Bank's ability to offer seamless customer experiences and maintain its market position.
Suppliers of financial data and market intelligence, such as Bloomberg and Refinitiv, wield significant bargaining power over Hyakugo Bank. This information is critical for the bank's daily operations, risk assessment, and the development of new financial products. For instance, Bloomberg Terminal subscriptions, a key data service, cost tens of thousands of dollars annually per user, making it a substantial operational expense.
The specialized nature and proprietary algorithms behind these data services create high switching costs for Hyakugo Bank. If the bank were to change its primary data provider, it would likely face considerable disruption in its analytical processes and potentially a loss of historical data continuity, impacting its ability to make informed decisions.
The availability of skilled human capital, especially in critical fields like IT, data analytics, and specialized consulting, significantly impacts supplier power. When there's a scarcity of these specialized professionals within the Japanese financial sector, it directly translates to higher recruitment and retention expenses for institutions like Hyakugo Bank.
Regulatory Bodies and Compliance Services
Regulatory bodies, such as the Financial Services Agency (FSA) and the Bank of Japan (BOJ), act as powerful influencers on banks like Hyakugo Bank, even if they aren't traditional suppliers. Their mandates for compliance, including stringent anti-money laundering (AML) and data privacy rules, directly impact operational costs and strategic direction. For instance, in 2024, Japanese banks continued to invest heavily in digital transformation and cybersecurity to meet these evolving regulatory expectations, with compliance costs representing a significant portion of IT budgets.
The bargaining power of these regulatory entities is substantial. Hyakugo Bank must allocate resources to adapt to new policies and maintain compliance, which can involve significant investments in technology and specialized personnel. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and reputational damage, underscoring the leverage these bodies hold over the banking sector.
- Regulatory Influence: FSA and BOJ set compliance standards impacting bank operations.
- Investment Demands: Adherence to AML and data privacy rules requires ongoing financial commitment.
- Operational Impact: Evolving regulations necessitate adjustments in technology and staffing.
- Risk Mitigation: Compliance spending is crucial to avoid penalties and protect reputation.
Infrastructure and Utility Providers
Infrastructure and utility providers, such as those managing electricity, telecommunications, and data centers, hold significant bargaining power. Hyakugo Bank, like any financial institution, relies heavily on these essential services for its daily operations and digital infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, the cost of energy for commercial businesses in Japan saw fluctuations, directly impacting operational expenses for entities like Hyakugo Bank. Any disruption or substantial price increase from these critical suppliers can directly affect the bank's operational stability and overall cost structure.
The necessity of these services means that switching providers can be complex and costly, further solidifying the suppliers' leverage. Consider the telecommunications sector; reliable and high-speed internet is non-negotiable for banking transactions and customer service. In 2023, Japan's average broadband download speed was reported to be around 170 Mbps, highlighting the critical reliance on these networks. Therefore, Hyakugo Bank faces a situation where these providers can exert considerable influence.
- Essential Services: Electricity, internet, and data hosting are fundamental to Hyakugo Bank's functioning.
- High Switching Costs: Migrating critical infrastructure to new providers is often expensive and time-consuming.
- Operational Dependence: Disruptions from these suppliers can halt banking operations, impacting revenue and customer trust.
- Market Concentration: In some regions or for specific services, the number of reliable providers may be limited, increasing supplier power.
Hyakugo Bank's bargaining power with its suppliers is significantly influenced by the concentration of providers and the specialized nature of their offerings. For critical technology and data services, where few providers dominate, their ability to dictate terms increases, especially given the high costs associated with switching. In 2024, the continued consolidation within the FinTech and data analytics sectors meant that specialized providers could command premium pricing, impacting Hyakugo Bank's operational budget.
The bank's reliance on essential infrastructure like telecommunications and energy also presents a challenge. In 2024, fluctuations in global energy prices and ongoing investments in Japan's digital infrastructure meant that utility and telecom providers had considerable leverage. For instance, the cost of high-speed data connectivity, crucial for real-time transactions, remained a significant expenditure for Hyakugo Bank, with limited viable alternatives for premium service.
| Supplier Category | Key Dependencies for Hyakugo Bank | Supplier Bargaining Power Factors (2024) | Impact on Hyakugo Bank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers (Core Banking, AI, Cloud) | System uptime, fraud detection, digital service delivery | High specialization, high switching costs, market concentration | Increased costs for upgrades, potential service disruptions |
| Data & Market Intelligence Providers (e.g., Bloomberg) | Risk assessment, trading decisions, product development | Proprietary algorithms, high subscription costs, data continuity | Significant operational expense, reliance on specific analytics |
| Infrastructure & Utilities (Telecom, Energy) | Transaction processing, customer access, data center operations | Essential services, high infrastructure investment, limited alternatives | Volatile operational costs, vulnerability to service interruptions |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Hyakugo Bank, this analysis dissects the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the presence of substitutes, providing a strategic overview of its competitive environment.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive dashboard, allowing Hyakugo Bank to pinpoint and address key market threats effectively.
Customers Bargaining Power
For fundamental banking needs such as savings accounts or basic personal loans, customers generally encounter minimal barriers to switching. This ease of transition is amplified by the proliferation of digital banking solutions and online comparison tools, allowing individuals in Mie Prefecture to readily explore alternatives to Hyakugo Bank.
Customers today are significantly more informed. By mid-2024, a substantial portion of consumers, particularly younger demographics, actively utilize online resources to research financial products, comparing everything from interest rates to service fees. This heightened financial literacy, coupled with the widespread availability of digital comparison tools, directly translates into stronger bargaining power.
This increased access to information allows customers to easily identify and switch to competitors offering superior terms or more tailored solutions. For instance, in 2024, online banking platforms saw a surge in new account openings driven by customers seeking better yields, demonstrating a clear willingness to leverage their knowledge to secure more favorable financial arrangements.
Hyakugo Bank faces significant customer bargaining power due to the widespread availability of banking options in Japan. Customers can choose from established megabanks, numerous other regional banks, and increasingly, digital-only banks, all competing for their business. This broad selection means customers can easily switch providers if they find better rates or services elsewhere, putting pressure on Hyakugo Bank to remain competitive.
Price Sensitivity in a Low-Interest Environment
In Japan's persistent low-interest-rate environment, customers exhibit significant price sensitivity, especially when considering loans and investment products. This heightened awareness of rates and fees directly translates into increased bargaining power.
This sensitivity allows customers to readily compare offerings and switch to institutions providing more attractive terms or lower fees. For instance, in 2024, with the Bank of Japan maintaining an ultra-loose monetary policy, many retail customers actively sought out the best deposit rates, even for small amounts, putting pressure on banks to offer competitive pricing.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers are highly attuned to interest rates and fees in a low-rate environment.
- Negotiating Power: This sensitivity empowers customers to negotiate better terms or switch providers.
- Competitive Landscape: Banks face pressure to offer competitive pricing to retain and attract customers.
- Impact on Fees: Even small fees can be a deciding factor for customers when interest income is minimal.
Demand for Specialized and Digital Services
Corporate clients and younger demographics are increasingly seeking out specialized financial solutions and digital-first experiences. This trend amplifies their bargaining power, as they can more easily switch to providers offering tailored services.
For instance, the demand for advanced investment products and efficient foreign exchange services is growing. Hyakugo Bank's capacity to deliver these specialized offerings, alongside a robust smartphone banking platform, directly impacts customer retention. In 2024, digital banking adoption continued its upward trajectory, with a significant portion of transactions occurring through mobile channels, underscoring the importance of these digital capabilities.
- Growing Demand for Digital Channels: A substantial percentage of banking customers, particularly younger demographics, prefer digital interactions for most of their banking needs.
- Specialized Service Expectations: Corporate clients and sophisticated individual investors expect a range of specialized financial services, from complex wealth management to streamlined international payments.
- Impact on Switching Costs: Banks that fail to meet these demands face higher customer churn as clients can readily find alternative providers offering superior digital and specialized solutions.
- Hyakugo Bank's Digital Investment: Hyakugo Bank's continued investment in its digital infrastructure and specialized product development is crucial to mitigating customer bargaining power.
Customers possess substantial bargaining power due to the ease of switching between financial institutions in Japan, particularly in the current low-interest-rate environment. This allows them to readily compare offerings and move to providers with better terms, putting pressure on Hyakugo Bank to maintain competitive pricing and services.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Hyakugo Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Low Switching Costs | Customers face minimal barriers to opening new accounts or transferring funds, especially with digital banking options. | Increases the threat of customer churn if competitors offer superior rates or services. |
| Price Sensitivity | In a low-rate environment, customers are highly sensitive to even small differences in interest rates and fees. | Drives customers to seek out the best available yields on deposits and the lowest costs for loans. |
| Informed Customer Base | Widespread access to online comparison tools and financial information empowers customers. | Customers can easily identify and switch to banks offering more favorable terms or specialized products. |
Same Document Delivered
Hyakugo Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Hyakugo Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive overview of its competitive landscape. You'll gain detailed insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Hyakugo Bank contends with formidable competition from Japan's megabanks, including MUFG, SMFG, and Mizuho. These national giants possess vast financial resources, extensive branch networks, and a wider array of financial products, enabling them to undercut competitors on pricing and invest heavily in cutting-edge technology. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, the combined net profits of these three megabanks exceeded ¥2.5 trillion, showcasing their significant market power.
Hyakugo Bank faces significant competition from other regional banks within Mie Prefecture and its surrounding areas. These rivals vie for local deposits and loan opportunities, often leveraging deep-rooted community relationships and tailored service packages to attract customers.
For instance, in 2024, the Japanese regional banking sector saw continued consolidation and strategic realignments as institutions adapted to evolving market dynamics and regulatory landscapes. Many regional banks, like Hyakugo, are emphasizing digital transformation and enhanced customer service to differentiate themselves in this crowded field.
The banking landscape is rapidly evolving with the emergence of digital-only banks and numerous fintech companies. These agile players are introducing innovative, often more affordable, and highly convenient services like seamless online payments, streamlined digital lending processes, and accessible robo-advisory platforms. For instance, in 2024, the global fintech market was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion, highlighting the significant disruption these companies bring to traditional banking models.
Low-Interest Rate Environment Pressure
Japan's prolonged period of low interest rates has significantly squeezed banks' net interest margins. This financial pressure compels institutions like Hyakugo Bank to vie more intensely for lending opportunities and diversify income streams through fees and commissions, thereby intensifying competitive rivalry within the sector.
The Bank of Japan's commitment to maintaining an ultra-loose monetary policy, with the policy-rate remaining negative or near zero throughout much of the 2010s and into the 2020s, exemplifies this environment. For instance, as of early 2024, the benchmark interest rate remained at -0.1%, a stark indicator of the sustained low-rate landscape.
- Compressed Margins: Persistent low interest rates directly reduce the difference between what banks earn on loans and what they pay on deposits.
- Aggressive Competition for Loans: With narrower margins, banks must increase loan volumes to maintain profitability, leading to fiercer competition for borrowers.
- Shift to Fee-Based Income: Banks are increasingly reliant on non-interest income, such as wealth management, transaction fees, and advisory services, to offset margin compression.
- Heightened Rivalry: The combined effect of margin pressure and the pursuit of alternative revenues intensifies the competitive landscape among financial institutions.
Focus on Niche Markets and Consulting Services
Hyakugo Bank and its regional peers are actively sidestepping direct price wars by concentrating on specialized niche markets and offering value-added consulting. This strategy aims to build deeper relationships with local businesses by providing tailored solutions and actively contributing to regional economic growth. For instance, many Japanese regional banks reported increased engagement in business succession support and regional revitalization projects throughout 2023 and early 2024.
This focus on problem-solving consulting and community engagement fosters a rivalry centered on service excellence and impact rather than solely on interest rates or fees. Banks are differentiating themselves by becoming indispensable partners to local enterprises, thereby strengthening their competitive position within their operating areas.
Key initiatives observed in 2024 include:
- Development of specialized lending products for emerging local industries.
- Expansion of advisory services for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) facing digital transformation challenges.
- Increased participation in public-private partnerships for regional development projects.
- Enhanced digital platforms offering business analytics and market insights to clients.
Competitive rivalry at Hyakugo Bank is intense, driven by powerful national megabanks, numerous regional competitors, and disruptive fintech firms. The persistent low-interest-rate environment in Japan, with rates hovering near zero as of early 2024, compresses profit margins, forcing banks to aggressively pursue lending and alternative revenue streams. This environment fuels a rivalry focused on service differentiation, specialized offerings, and deep community engagement, rather than just price competition.
| Competitor Type | Key Strengths | Impact on Hyakugo Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Megabanks (e.g., MUFG, SMFG, Mizuho) | Vast financial resources, extensive networks, broad product range, significant tech investment. Fiscal year 2023 net profits exceeded ¥2.5 trillion combined. | Ability to offer lower pricing, greater product innovation, and wider reach. |
| Regional Banks | Deep community ties, tailored local services, agility in niche markets. | Direct competition for local deposits and loans, leveraging established relationships. |
| Fintech & Digital Banks | Innovative, often lower-cost digital services (payments, lending, robo-advisory). Global fintech market projected over $1.1 trillion in 2024. | Disrupting traditional models with convenience and efficiency, attracting digitally-savvy customers. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing prevalence of digital payment platforms and e-wallets, often provided by tech companies rather than traditional banks, presents a significant threat of substitution for Hyakugo Bank. These alternatives, including QR code payment systems, offer convenience and can bypass traditional banking infrastructure for many transactions.
Japan's ambitious goal of reaching 40% cashless payments by 2025 underscores this shift, highlighting a growing consumer preference for digital methods. This trend directly impacts the volume of transactions that might otherwise be processed through Hyakugo Bank's services.
Alternative lending platforms like peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding offer individuals and businesses ways to secure financing outside of traditional banks, acting as substitutes for conventional loans. These platforms can be particularly disruptive for smaller loan amounts, as they often provide quicker access to capital and potentially more favorable terms for certain borrowers.
The P2P lending market has seen significant growth. For instance, by the end of 2023, the global P2P lending market size was estimated to be around $130 billion, with projections indicating continued expansion. This demonstrates a tangible shift in how some financing needs are being met, directly impacting traditional banking services.
Direct investment platforms and robo-advisors present a significant threat of substitution for traditional bank investment services. These digital alternatives, like Charles Schwab and Betterment, often boast lower expense ratios and commission-free trading, attracting a growing segment of self-directed investors. For instance, by the end of 2023, assets under management for robo-advisors in the US alone were projected to reach over $2 trillion, highlighting their increasing appeal and competitive pressure on incumbent institutions.
Embedded Finance Solutions
Embedded finance, where financial services are integrated into non-financial platforms, presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional banks like Hyakugo Bank. For instance, e-commerce giants now offer point-of-sale financing or integrated payment solutions, allowing consumers to complete transactions and secure credit without ever engaging with a bank directly.
This trend bypasses traditional banking channels, offering convenience and often a more streamlined user experience. By 2024, the embedded finance market is projected to reach substantial figures, indicating a growing consumer preference for these integrated solutions. For example, some reports suggest the global embedded finance market could exceed $7 trillion by 2030, with significant growth already observed in the preceding years.
- Convenience: Customers can access financial services at the point of need within their existing digital journeys.
- Reduced Friction: Embedded finance eliminates the need for separate applications and lengthy onboarding processes typically associated with banks.
- Data Integration: Non-financial platforms can leverage customer data to offer more tailored financial products.
- Market Growth: The rapid expansion of embedded finance signifies a direct challenge to traditional banking models.
Non-Bank Financial Service Providers
Non-bank financial service providers present a significant threat of substitution for Hyakugo Bank. These entities, including credit unions and specialized leasing companies, increasingly offer competitive alternatives for core banking services. For instance, credit unions in Japan saw their total assets reach approximately ¥47.5 trillion as of March 2023, indicating a substantial market presence and capacity to absorb banking customers.
These substitutes often cater to specific market segments with tailored products, potentially eroding Hyakugo Bank's market share. Credit guarantee companies, for example, provide crucial financing support that can bypass traditional bank lending, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises. In 2022, Japanese credit guarantee corporations provided guarantees totaling ¥10.8 trillion, facilitating access to capital for businesses that might otherwise rely on bank loans.
The growing digital landscape also empowers fintech companies and other non-traditional players to offer payment, lending, and investment services. This diversification of financial service providers means customers have more choices, intensifying competitive pressure on established banks like Hyakugo Bank. The ease of access and specialized offerings from these substitutes can draw customers away from conventional banking relationships.
- Credit Unions' Asset Growth: Japanese credit unions' total assets reached around ¥47.5 trillion by March 2023, demonstrating their growing financial clout.
- Credit Guarantee Support: In 2022, credit guarantee corporations in Japan issued guarantees worth ¥10.8 trillion, supporting business financing.
- Diversified Financial Services: Non-bank entities offer specialized products in areas like consumer credit and asset financing, directly competing with traditional banking services.
The threat of substitutes for Hyakugo Bank is substantial, stemming from digital payment platforms, alternative lending, and direct investment services. These alternatives offer convenience and often lower costs, directly challenging traditional banking models.
Japan's push towards cashless transactions by 2025, aiming for 40%, signifies a clear shift in consumer behavior. This trend is further amplified by the growth of fintech and embedded finance solutions, which integrate financial services into non-banking platforms.
For instance, by the end of 2023, global P2P lending market size was around $130 billion, and US robo-advisor assets under management were projected to exceed $2 trillion. These figures highlight the significant inroads made by substitutes in core banking functions.
| Substitute Category | Example | Market Indicator (approximate, as of late 2023/early 2024) | Impact on Hyakugo Bank |
| Digital Payments | E-wallets, QR code systems | Japan targeting 40% cashless by 2025 | Reduced transaction volume through traditional channels |
| Alternative Lending | P2P lending, Crowdfunding | Global P2P lending market ~$130 billion (end 2023) | Loss of loan origination and interest income |
| Investment Platforms | Robo-advisors, Direct trading platforms | US Robo-advisor AUM > $2 trillion (projected end 2023) | Reduced asset management fees and brokerage revenue |
| Embedded Finance | Point-of-sale financing by e-commerce | Global embedded finance market projected > $7 trillion by 2030 | Disintermediation of banking services in customer journeys |
Entrants Threaten
The Japanese banking sector presents high regulatory barriers, a significant threat to new entrants. Obtaining the necessary licenses, meeting stringent capital requirements, and establishing robust compliance infrastructure demand substantial investment and expertise. For instance, as of early 2024, the Bank of Japan continues to emphasize rigorous capital adequacy ratios and operational resilience for all financial institutions, making entry into traditional banking services exceptionally challenging.
Establishing a new bank, like Hyakugo Bank, demands substantial capital. Think about the costs for physical branches, cutting-edge technology, and maintaining enough cash on hand to operate smoothly. These significant upfront investments act as a strong deterrent, effectively limiting the number of new players who can realistically enter the market.
Established brand loyalty and trust present a significant barrier for new entrants looking to challenge incumbent banks like Hyakugo Bank. Hyakugo Bank, with its long history, has cultivated deep trust and recognition within its operating regions, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, as of early 2024, many regional banks in Japan, similar to Hyakugo Bank's operational scope, reported high customer retention rates, often exceeding 90% for core banking services, demonstrating the power of established relationships.
Technological Investment and Digital Transformation Pace
While financial technology, or fintech, has lowered some barriers to entry in the banking sector, new players still require substantial investment in cutting-edge technology to effectively challenge established institutions. Incumbent banks, including regional players like Hyakugo Bank, are channeling significant capital into widespread digitalization to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
This technological arms race means that even with fintech innovations, the cost of entry remains high. For instance, in 2024, the global fintech market was valued at approximately $300 billion, with a significant portion of that investment going into advanced digital infrastructure and cybersecurity. New entrants must match or exceed these investments to gain traction.
- High Capital Outlay: Competing requires massive investment in cloud computing, AI-driven analytics, and robust digital platforms, often in the tens or hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Digital Transformation Costs: Upgrading legacy systems and implementing new digital strategies for incumbent banks like Hyakugo Bank represent substantial ongoing expenses, setting a high bar for newcomers.
- Talent Acquisition: Securing skilled personnel in areas like data science, cybersecurity, and AI is crucial and costly, further increasing the investment needed for new entrants.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting stringent financial regulations necessitates significant technological and operational investment, a hurdle that all new entrants must clear.
Access to Funding and Distribution Networks
New entrants, especially fintech startups, often face significant hurdles in accessing the stable, low-cost funding that traditional banks like Hyakugo Bank leverage through their deposit bases. For instance, in 2024, the average cost of funds for established Japanese banks remained considerably lower than the interest rates new digital-only players might need to offer to attract initial capital. This disparity in funding costs creates an immediate competitive disadvantage.
Furthermore, replicating the extensive physical branch networks and established customer relationships of regional banks presents a substantial barrier. Hyakugo Bank, with its deep roots in its operating regions, benefits from a tangible local presence that fosters trust and accessibility, something purely digital competitors find arduous and costly to match quickly.
- Funding Access: New entrants struggle to match the low-cost deposit funding of established banks.
- Distribution Networks: Replicating physical branch presence and customer relationships is a significant challenge.
- Cost of Capital: Fintechs may face higher initial capital costs compared to incumbent banks.
- Local Trust: Regional banks benefit from established local trust and physical accessibility.
The threat of new entrants for Hyakugo Bank remains low due to substantial regulatory hurdles and high capital requirements. Obtaining banking licenses in Japan involves stringent checks and significant financial commitments, as emphasized by the Bank of Japan's ongoing focus on capital adequacy in early 2024. These barriers effectively deter most potential newcomers from entering the traditional banking space.
Established trust and brand loyalty also act as significant deterrents. Hyakugo Bank, like many regional Japanese banks, benefits from high customer retention rates, often exceeding 90% for core services as of early 2024, making it difficult for new players to gain market share.
While fintech has lowered some barriers, the need for substantial investment in advanced technology, comparable to the ongoing digitalization efforts of incumbents like Hyakugo Bank, keeps the cost of entry high. New entrants must also contend with the challenge of accessing low-cost funding, a significant advantage held by established banks with robust deposit bases.
| Barrier | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data (as of early 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | High cost and complexity | Bank of Japan's emphasis on capital adequacy ratios |
| Capital Requirements | Significant upfront investment | Costs for technology, branches, and liquidity |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Difficulty in customer acquisition | Regional banks' customer retention rates >90% |
| Technological Investment | Need to match incumbent digitalization | Global fintech market investment in advanced infrastructure |
| Funding Access | Higher cost of capital compared to deposits | Disparity in funding costs between established banks and new players |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Hyakugo Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of verified data sources, including the bank's official annual reports, financial disclosures, and regulatory filings with the Financial Services Agency. We also incorporate insights from industry publications, market research reports, and economic data from reputable sources like the Bank of Japan to provide a comprehensive competitive landscape.