Grid Dynamics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Grid Dynamics Bundle
Grid Dynamics operates in a dynamic tech landscape where buyer power can be significant due to the availability of alternative solutions. The threat of new entrants is moderate, as establishing a strong reputation and technical expertise takes time and investment. Understanding these pressures is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Grid Dynamics’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The digital engineering field thrives on specialized expertise, especially in areas like artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and data analytics. This scarcity of highly skilled talent means that individual professionals in these niches possess considerable leverage. Consequently, companies like Grid Dynamics face increased recruitment expenses and must develop robust retention plans to secure this critical human capital.
Grid Dynamics' commitment to expanding its talent pool is evident in its headcount growth. As of June 30, 2025, the company reported 5,013 employees, a substantial increase from 3,961 employees in the second quarter of 2024. This expansion highlights their ongoing efforts to acquire and retain the specialized skills necessary to meet escalating client demands in a competitive market.
Grid Dynamics relies on proprietary software and tools from third-party vendors, including cloud platforms like Google Cloud and specialized development environments. This reliance can give these software vendors significant bargaining power, especially if their tools are critical and difficult to replace. For instance, in 2024, the global cloud computing market was valued at over $600 billion, highlighting the scale and importance of these platforms.
Grid Dynamics relies on major cloud infrastructure providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud for its scalable engineering solutions. The market's concentration, with a few dominant players, grants these providers significant bargaining power, impacting pricing and service agreements for Grid Dynamics.
In 2024, the global cloud computing market was valued at approximately $600 billion, highlighting the immense scale and influence of these providers. Grid Dynamics' strategic partnership with Google Cloud, including its expansion into Generative AI solutions, underscores the critical nature of these supplier relationships and the need to manage this supplier power effectively.
Labor Market Conditions and Wage Inflation
The tech labor market in 2024 continues to be competitive, with significant demand for specialized skills in areas like artificial intelligence and cloud computing. This tightness directly impacts companies like Grid Dynamics, as it drives up wage inflation. For instance, reports from early 2024 indicated that average salaries for AI engineers could range from $150,000 to $200,000 annually, a substantial increase over previous years.
This rising cost of talent is a key factor in the bargaining power of suppliers, which in this context are the skilled professionals Grid Dynamics hires. When demand for specific expertise outstrips supply, these professionals can command higher wages, directly increasing Grid Dynamics' operational expenses. If these increased labor costs cannot be effectively passed on to clients through service pricing, it can lead to compressed profit margins.
- Talent Scarcity: In 2024, the demand for AI and digital transformation specialists remains high, creating a scarcity of qualified candidates.
- Wage Inflation: This scarcity fuels wage inflation, with average salaries for in-demand tech roles seeing an upward trend.
- Cost Pressure: Increased labor costs directly impact Grid Dynamics' operational expenses and can pressure profit margins.
- Talent Development: Initiatives like Grid-U underscore the critical reliance on and investment in skilled personnel to mitigate these pressures.
Switching Costs for Talent
The bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by the switching costs associated with talent. For Grid Dynamics, the substantial investment in recruiting, onboarding, and training specialized engineers and consultants makes it difficult and costly to replace existing teams or shift to different talent pools. This inherent stickiness in their workforce grants employees greater leverage in negotiating compensation and work conditions.
Grid Dynamics' strategic expansion of its global delivery network, now spanning 19 countries, with a considerable portion of its workforce located outside the US, further highlights this dynamic. This distributed talent base, while offering diversification, also means that localized talent shortages or increased labor costs in specific regions can impact the company's operational flexibility and cost structure.
- High Recruitment and Training Expenses: The financial and time investment in acquiring and developing specialized IT talent creates a barrier to rapid workforce changes.
- Employee Retention and Negotiation Power: The cost of employee turnover strengthens the bargaining position of existing skilled professionals.
- Global Talent Pool Management: Managing a dispersed workforce across 19 countries presents both opportunities and challenges in controlling labor costs and ensuring consistent skill availability.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Grid Dynamics is primarily concentrated in the highly skilled talent it employs and the critical third-party software and cloud platforms it utilizes. The scarcity of specialized digital engineering expertise, particularly in AI and cloud computing, grants these professionals significant leverage, driving up wage inflation. For instance, in 2024, demand for AI specialists led to average salaries for AI engineers ranging from $150,000 to $200,000 annually, increasing operational costs for Grid Dynamics.
Furthermore, reliance on major cloud providers like Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure, which dominated a global market valued at over $600 billion in 2024, gives these vendors substantial influence over pricing and service terms. The high switching costs associated with replacing proprietary software or retraining teams further solidify supplier power, impacting Grid Dynamics' flexibility and profitability.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Power | Impact on Grid Dynamics | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skilled Talent (Employees) | Scarcity of AI/Cloud expertise, high demand | Increased wage inflation, higher recruitment/retention costs | AI Engineer salaries: $150k-$200k annually |
| Cloud Infrastructure Providers | Market concentration, critical service provision | Influence on pricing, service level agreements | Global Cloud Market Value: >$600 billion |
| Proprietary Software Vendors | Criticality of tools, high switching costs | Potential for increased licensing fees, limited vendor choice | N/A (Specific vendor data not publicly available) |
What is included in the product
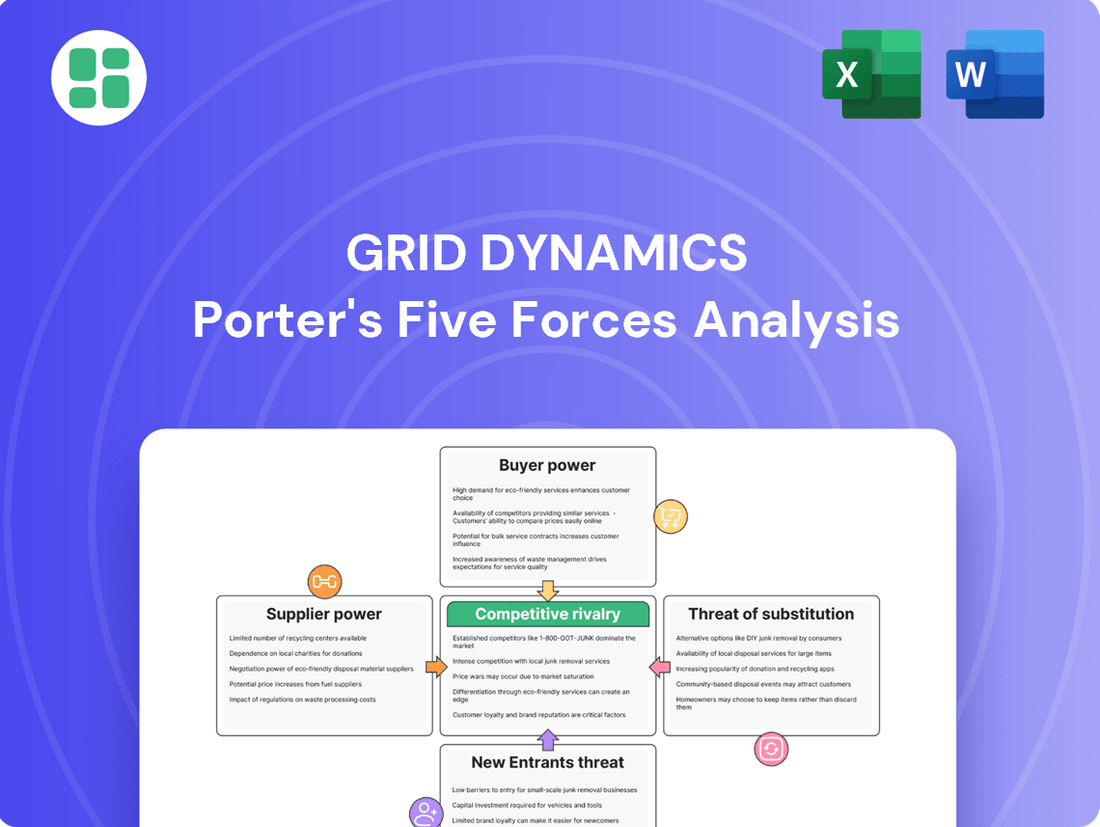
Grid Dynamics' Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity of the IT services industry, examining threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the impact of substitute services.
Instantly identify and quantify competitive threats with a dynamic framework, enabling proactive strategy development and risk mitigation.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer concentration risk is a significant factor for Grid Dynamics. The company serves large enterprises, meaning a substantial portion of its income can be tied to a few major clients. This dependency can give these key customers substantial bargaining power.
In the second quarter of 2025, Grid Dynamics reported that its top five clients represented 37.5% of its total revenue. This level of concentration means these clients can exert considerable influence during negotiations regarding pricing, the scope of projects they commission, and the service level agreements (SLAs) that govern the relationship.
Grid Dynamics, like many digital engineering firms, faces a market brimming with alternatives. Customers can choose from a wide array of service providers, including large, established global consultancies and smaller, highly specialized niche players. This abundance of choice directly translates into increased customer bargaining power, as clients can easily shift their business if they find better pricing or superior service elsewhere.
The competitive intensity in the digital engineering sector means customers have significant leverage. For instance, in 2024, the global IT services market was valued at over $1.3 trillion, with digital transformation services representing a substantial and growing segment. This vast market size indicates a healthy supply of providers, empowering customers to negotiate terms more effectively and demand higher quality service delivery.
The bargaining power of customers in the context of Grid Dynamics' project scale and complexity is considerable. Clients undertaking large, intricate digital transformation projects, which often represent multi-year, high-value engagements, typically have the leverage to negotiate detailed contracts. These contracts frequently include stringent performance metrics and specific deliverables, allowing customers to exert significant influence over the terms and conditions of the projects.
Grid Dynamics' success in securing substantial deals across diverse sectors such as automotive, financial services, and consumer packaged goods (CPG) underscores its involvement in projects with significant scope. For instance, in 2023, Grid Dynamics reported revenue growth of 18.4%, reaching $720.4 million, indicating the scale of its operations and the size of the projects it undertakes. This scale often translates into greater customer power, as the investment is substantial, leading clients to demand high standards and favorable terms to ensure project success and return on investment.
Price Sensitivity of Large Enterprises
Large enterprise clients, particularly those within the Fortune 1000, often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is especially true for services that can be viewed as standardized or where cost optimization is a primary objective in their procurement strategies.
This heightened price sensitivity directly translates into more rigorous negotiation tactics from these major clients, potentially impacting Grid Dynamics' profitability. For instance, Grid Dynamics reported a non-GAAP gross margin of 34.7% in Q2 2025, highlighting the delicate balance required between offering competitive pricing and ensuring sustained financial health.
- Fortune 1000 clients often prioritize cost-efficiency.
- This can lead to intense price negotiations.
- Grid Dynamics' Q2 2025 non-GAAP gross margin was 34.7%.
- Balancing price competitiveness with profitability is crucial.
Customer Switching Costs
Customer switching costs in the digital engineering sector, while present, are often manageable for clients. These can include expenses related to knowledge transfer, system integration, and potential downtime during a transition. However, for clients seeking superior value or more innovative solutions, these costs might not be a significant deterrent. For instance, a company looking to leverage cutting-edge AI capabilities might find the cost of switching from a legacy provider to a firm like Grid Dynamics, which heavily invests in AI research and development, to be a worthwhile investment.
Grid Dynamics actively works to minimize the impact of switching costs by fostering strong client relationships and demonstrating tangible value. Their focus on creating competitive advantages and enhancing customer experiences through tailored solutions and continuous innovation aims to make clients less inclined to explore alternatives. In 2024, a significant portion of Grid Dynamics' client retention strategy revolved around proactive engagement and demonstrating ROI, with many clients reporting satisfaction with the ease of integration and the speed of value realization from new projects.
- Low Switching Costs: Clients may incur costs like knowledge transfer and integration efforts when changing digital engineering providers.
- Value-Driven Decisions: Clients are often willing to absorb switching costs if they perceive better value or innovation from a competitor.
- Grid Dynamics' Mitigation Strategy: The company focuses on building competitive advantages and enhancing customer experience to retain clients.
- Client Retention Focus (2024): Grid Dynamics emphasized proactive engagement and demonstrating return on investment to maintain client loyalty.
The bargaining power of customers for Grid Dynamics is substantial, driven by client concentration, the availability of numerous alternatives in the digital engineering market, and the inherent leverage large enterprises hold. This power allows clients to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, directly influencing Grid Dynamics' profitability, as evidenced by their Q2 2025 non-GAAP gross margin of 34.7%.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Grid Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Top five clients represented 37.5% of revenue in Q2 2025. | Grants significant negotiation leverage to key clients. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Vast IT services market with many providers. | Empowers customers to switch for better pricing or service. |
| Price Sensitivity | Large enterprises, especially Fortune 1000, focus on cost optimization. | Leads to intense price negotiations, pressuring margins. |
| Switching Costs | Manageable costs for clients seeking superior value. | Clients may switch despite costs if better value is perceived. |
Full Version Awaits
Grid Dynamics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Grid Dynamics Porter's Five Forces Analysis, giving you a clear understanding of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase. You can confidently expect the same in-depth insights and actionable strategies to be available for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The digital engineering services market is intensely competitive, characterized by a vast number of global and regional players. This fragmentation means companies like Grid Dynamics are constantly navigating a crowded landscape, vying for the attention and business of major clients, particularly Fortune 1000 companies.
Large, established IT services firms and agile, specialized digital consultancies alike are all competing for market share. This broad spectrum of competitors, from giants to niche providers, naturally escalates the rivalry as everyone seeks to capture the same opportunities.
The competitive pressure is further amplified by key players, such as DXC Technology and Wipro, actively shifting their focus towards artificial intelligence (AI)-centric services. This strategic pivot by major competitors signals a trend and necessitates that other firms, including Grid Dynamics, also innovate and adapt to remain competitive in this evolving digital arena.
Grid Dynamics carves out its niche by specializing in enterprise AI, cloud migration, and data analytics, primarily targeting Fortune 1000 clients in retail, finance, and technology. This focus on high-demand, complex solutions sets it apart, though many rivals also tout similar capabilities, intensifying the need for demonstrable value. Grid Dynamics emphasizes its eight years of experience and established leadership in enterprise AI as a key differentiator in this competitive landscape.
The digital transformation and AI market is a hotbed of activity, with rapid growth attracting new companies and spurring existing ones to broaden their services. This expansion, while creating ample opportunities, also fuels intense competition as businesses vie for greater market share.
For instance, Grid Dynamics demonstrated this dynamic by reporting a robust 21.7% year-over-year revenue increase in the second quarter of 2025. This impressive growth was largely attributed to their strategic focus on AI integration and successful acquisitions, highlighting how companies are leveraging these trends to outpace rivals.
Acquisitions and Market Consolidation
The IT services industry, including companies like Grid Dynamics, is characterized by significant competitive rivalry fueled by ongoing mergers and acquisitions. This consolidation trend allows firms to rapidly expand their service offerings, client portfolios, and global presence, thereby intensifying competition.
Grid Dynamics actively participated in this consolidation in 2024, strategically acquiring JUXT and Mobile Computing. These moves were aimed at bolstering its expertise in crucial sectors like financial services and manufacturing, positioning it to compete more effectively against larger, established players.
- Increased Scale: Acquisitions create larger entities with greater resources, potentially leading to more aggressive pricing and service innovation.
- Capability Expansion: Companies buy others to gain new technologies or expertise, narrowing the competitive advantage of those who don't consolidate.
- Market Share Growth: Mergers and acquisitions directly increase a company's market share, making it harder for smaller competitors to gain traction.
- Intensified Rivalry: The emergence of more powerful, consolidated competitors naturally escalates the intensity of rivalry across the industry.
Talent Pool Competition
Competition for top digital engineering and consulting talent is intense, directly impacting operational costs and strategic advantage. Companies must offer compelling compensation packages, comprehensive benefits, and clear pathways for career advancement to secure skilled professionals.
Grid Dynamics' commitment to talent acquisition is evident in its headcount growth, a strategic imperative to meet increasing market demand for its services. This focus on building a robust talent pipeline is crucial for maintaining its competitive edge in the digital transformation landscape.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: In 2024, the demand for specialized tech talent continued to drive up recruitment and retention costs across the industry.
- Employee Retention: Offering competitive salaries and benefits is paramount; for instance, tech salaries in major hubs saw an average increase of 8-12% in 2024.
- Grid Dynamics' Growth: Grid Dynamics reported a significant increase in its global workforce in 2024, reflecting its aggressive strategy to onboard skilled engineers and consultants.
- Skills Gap: The ongoing shortage of experienced digital engineers means companies like Grid Dynamics must invest heavily in training and development to bridge critical skills gaps.
Competitive rivalry in the digital engineering sector is fierce, with numerous global and regional players vying for market share. This intense competition is further fueled by major companies like DXC Technology and Wipro pivoting towards AI-centric services, pushing others, including Grid Dynamics, to innovate rapidly.
Grid Dynamics addresses this by specializing in enterprise AI, cloud migration, and data analytics for Fortune 1000 clients, differentiating itself through its eight years of enterprise AI leadership. The market's rapid growth attracts new entrants and encourages existing firms to expand services, intensifying the competition for opportunities.
Grid Dynamics reported a 21.7% year-over-year revenue increase in Q2 2025, driven by AI integration and acquisitions, demonstrating a successful strategy amidst this competitive landscape. Industry consolidation through mergers and acquisitions, like Grid Dynamics' 2024 acquisitions of JUXT and Mobile Computing, creates larger entities with greater resources, expanding capabilities and market share, thus escalating overall rivalry.
The competition for top digital talent is a significant factor, driving up recruitment and retention costs. In 2024, tech salaries saw an average increase of 8-12%, and Grid Dynamics expanded its global workforce to meet demand, underscoring the critical need for investment in talent acquisition and development to bridge skills gaps.
| Metric | 2024 Impact | Implication for Grid Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| Talent Acquisition Costs | Increased significantly due to high demand for specialized tech skills. | Higher operational expenses; need for competitive compensation packages. |
| Tech Salary Growth | Average increase of 8-12% in major hubs. | Increased pressure to offer attractive remuneration to attract and retain talent. |
| Workforce Expansion | Grid Dynamics reported significant global workforce growth. | Indicates aggressive strategy to meet client demand and scale operations. |
| Skills Gap | Ongoing shortage of experienced digital engineers. | Necessitates investment in training and development to build internal capabilities. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large enterprises, particularly those in the Fortune 1000, often possess substantial in-house IT departments. These internal teams can develop digital transformation and AI solutions, directly substituting for external providers like Grid Dynamics. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of large enterprises planned to increase their internal IT spending on AI development, highlighting this competitive threat.
The decision for a company to build versus buy often hinges on a careful cost-benefit analysis. Developing solutions internally can offer greater control and customization, especially for highly sensitive or strategic projects. However, it also requires significant upfront investment in talent, infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance, which might exceed the cost of outsourcing to a specialist like Grid Dynamics.
For many digital transformation needs, clients can turn to off-the-shelf software and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms. These solutions often provide faster implementation and a lower upfront investment than bespoke engineering, particularly for common business processes.
While Grid Dynamics offers expertise in integrating these pre-built solutions, the availability of robust SaaS alternatives, such as Salesforce for CRM or Workday for HR, presents a direct threat. For instance, the CRM market alone was valued at over $60 billion in 2024, highlighting the significant adoption of such platforms.
The rise of freelance platforms and the gig economy presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional digital engineering firms like Grid Dynamics. For smaller, more modular projects or to fill specific skill gaps, clients can easily tap into a vast pool of individual contractors or small, specialized teams. This offers a flexible and often more cost-effective alternative to engaging a full-service digital engineering company, allowing businesses to scale resources up or down as needed without long-term commitments.
While the gig economy offers agility, its viability as a complete substitute for complex, large-scale digital transformations remains limited. The coordination, integration, and long-term strategic oversight required for major initiatives are typically better handled by established firms with dedicated project management and end-to-end solution capabilities. For instance, in 2024, the global freelance platform market was valued at over $3.7 billion, demonstrating its growing influence, yet major enterprise digital transformation projects often involve budgets in the tens or hundreds of millions, requiring a level of managed service that gig platforms alone may struggle to consistently provide.
Generic Business Consulting Firms Expanding Tech Offerings
Traditional management consulting firms are increasingly broadening their digital and technology consulting services. This expansion directly encroaches on Grid Dynamics' core competencies, presenting a significant threat of substitutes.
These established firms often leverage existing relationships with large clients, including Fortune 1000 companies, allowing them to offer a more comprehensive suite of services. This integrated approach can position them as a viable alternative to specialized digital engineering providers like Grid Dynamics.
For instance, in 2024, major consulting players like Accenture and Deloitte reported substantial growth in their technology consulting segments, with Accenture's Technology segment revenue reaching approximately $25.5 billion for fiscal year 2024. This highlights the competitive pressure from these diversified service providers.
- Broadened Service Portfolios: Generalist consulting firms now offer digital transformation, cloud migration, AI, and data analytics, services previously dominated by specialists.
- Existing Client Relationships: Fortune 1000 companies often turn to their long-standing management consultants for digital needs, bypassing niche providers.
- Competitive Pricing and Bundling: These larger firms can bundle digital services with their traditional offerings, potentially creating more attractive packages for clients.
- Market Share Erosion: The expanding capabilities of these substitutes pose a risk of market share erosion for specialized firms if they cannot differentiate effectively.
Automation Tools and Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
The increasing prevalence of sophisticated automation tools and low-code/no-code platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional engineering services. These technologies empower businesses to develop applications and automate processes with less reliance on specialized coding expertise. For instance, the low-code development platform market was valued at approximately $21.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $100 billion by 2030, indicating a rapid expansion that directly impacts the demand for custom development.
While Grid Dynamics leverages these advancements, their broader adoption by clients can lead to a reduction in the need for bespoke engineering solutions for specific functionalities. This shift could diminish the demand for Grid Dynamics' core custom development services over the long term. For example, Gartner predicts that by 2024, 70% of new applications developed by organizations will use low-code or no-code technologies, a substantial increase from previous years.
- Market Growth: The global low-code development platform market is experiencing rapid growth, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 25% in the coming years.
- Client Adoption: Increased client self-sufficiency through these platforms can reduce their outsourcing needs for standard development tasks.
- Service Shift: Grid Dynamics may need to adapt its service offerings to focus on more complex, strategic, and integration-heavy aspects of digital transformation rather than routine development.
- Competitive Landscape: The accessibility of these tools broadens the competitive landscape, potentially bringing in new players or enabling in-house development teams to handle tasks previously outsourced.
The threat of substitutes for digital engineering firms like Grid Dynamics is multifaceted, encompassing internal IT capabilities, off-the-shelf software, the gig economy, traditional consulting firms, and low-code/no-code platforms. For instance, in 2024, over 60% of large enterprises planned to boost their internal AI development spending, directly substituting for external services. Similarly, the CRM market, valued at over $60 billion in 2024, shows how widely adopted SaaS solutions can replace custom-built systems.
Traditional management consultancies are also expanding their digital offerings. Accenture's Technology segment alone generated approximately $25.5 billion in fiscal year 2024, demonstrating their significant presence in areas that were once the domain of specialized firms. Furthermore, the low-code development platform market, projected to reach $100 billion by 2030, signifies a growing trend where clients can build applications more independently, reducing the need for traditional engineering.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Grid Dynamics | 2024 Market Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal IT Departments | Customization, Control, Cost Savings | Reduced outsourcing demand for AI/Digital Transformation | 60%+ of large enterprises increased internal IT spending on AI |
| SaaS Platforms | Faster Implementation, Lower Upfront Cost | Replaces need for bespoke solutions in common areas (e.g., CRM) | CRM market valued over $60 billion |
| Gig Economy/Freelancers | Flexibility, Cost-Effectiveness for smaller tasks | Competition for modular projects and specific skill gaps | Global freelance platform market over $3.7 billion |
| Traditional Consulting Firms | Broad Service Portfolios, Existing Client Relationships | Direct competition for digital transformation projects | Accenture's Technology segment revenue ~$25.5 billion |
| Low-Code/No-Code Platforms | Empowers self-service development, reduces need for coding expertise | Diminishes demand for custom development services | Low-code market projected to reach $100 billion by 2030 |
Entrants Threaten
Building a global digital engineering firm capable of serving major enterprises demands significant capital. This includes investing heavily in attracting and retaining top-tier engineering talent, providing ongoing specialized training, and establishing a robust international presence with offices in key markets. For instance, Grid Dynamics' expansion into 19 countries highlights the scale of investment needed to achieve global reach in this sector.
Attracting and retaining highly specialized engineers, data scientists, and AI experts is a significant challenge for any company in the tech sector, including Grid Dynamics. This intense competition for top talent acts as a barrier to entry for new players.
New entrants find it particularly difficult to quickly assemble a credible and experienced team, especially when competing against established firms with strong employer brands and compensation packages. This struggle to build a robust talent pool directly impacts their ability to innovate and deliver services effectively.
Grid Dynamics' consistent growth in headcount, reaching 5,013 employees by the second quarter of 2025, underscores the continuous demand for skilled professionals and the company's ongoing efforts to secure this critical resource.
Fortune 1000 enterprises often prioritize established providers with strong brand reputations and proven track records, making it challenging for new entrants to gain traction. Grid Dynamics benefits from its established credibility and existing client relationships, which are crucial for securing large-scale engagements. The company's continued success in winning new clients and expanding partnerships in 2024 underscores this advantage.
Proprietary Methodologies and Accelerators
Grid Dynamics' development of proprietary methodologies and accelerators for digital transformation, cloud migration, and AI implementation presents a significant barrier to new entrants. These intellectual assets, honed through extensive project experience, streamline service delivery and enhance the value proposition for clients, making it challenging for newcomers to match the efficiency and effectiveness of established players. For instance, Grid Dynamics has specifically developed proprietary accelerators to expedite its service offerings, giving it a distinct edge.
These unique frameworks and tools are not easily replicated, requiring substantial investment in research, development, and practical application to build. This deep well of accumulated knowledge and specialized tooling creates a moat around Grid Dynamics’ business, deterring potential competitors who lack similar operational efficiencies and proven track records. The ability to deliver complex projects faster and with greater certainty of outcome, thanks to these proprietary assets, is a key differentiator.
The threat of new entrants is therefore moderated by the significant upfront investment and time required to develop comparable proprietary methodologies and accelerators. New firms would need to invest heavily in building their own intellectual property and service delivery frameworks to compete effectively. This would involve not only technical expertise but also a sustained commitment to innovation and client engagement to build a comparable library of accelerators.
- Proprietary Accelerators: Grid Dynamics has developed specific accelerators for its digital transformation and AI services.
- Streamlined Delivery: These proprietary tools enable faster and more efficient project execution.
- Competitive Advantage: The unique nature of these intellectual assets creates a significant barrier for new entrants.
- Reduced Threat: The high cost and time to replicate these methodologies limit the immediate threat of new competitors.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
Grid Dynamics operates in sectors like finance and healthcare, which are heavily regulated. New companies entering these spaces must navigate intricate compliance standards and robust security measures. This significantly raises the barrier to entry, demanding substantial investment in time and resources to achieve the necessary certifications and build compliant infrastructure.
The finance sector, a key area for Grid Dynamics, saw its contribution to the company's revenue grow, becoming its second-largest vertical by Q2 2025. This growth highlights the attractiveness of the financial industry but also underscores the deep integration and established trust required to compete effectively. For potential new entrants, meeting the stringent regulatory demands of such a critical sector presents a formidable challenge, impacting their ability to gain traction and market share.
- High Compliance Costs: New entrants must invest heavily in legal, technical, and operational resources to meet industry-specific regulations.
- Extended Time-to-Market: Obtaining necessary licenses and certifications can be a lengthy process, delaying product or service launches.
- Established Player Advantage: Existing firms like Grid Dynamics have already incurred these costs and possess the expertise to manage ongoing compliance.
- Reputational Risk: Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties and damage a new entrant's reputation, which is crucial in regulated industries.
The threat of new entrants for a digital engineering firm like Grid Dynamics is significantly mitigated by high capital requirements for talent acquisition and global infrastructure. Establishing a strong brand and securing large enterprise clients, as Grid Dynamics has done, also presents a substantial hurdle for newcomers. Furthermore, the development of proprietary accelerators and methodologies requires considerable investment in R&D, creating a competitive moat.
The intense competition for highly skilled engineers, with firms like Grid Dynamics actively expanding their workforce, makes it difficult for new entrants to quickly build a credible team. For example, Grid Dynamics' headcount reached 5,013 by Q2 2025, illustrating the scale of talent needed. Established players also benefit from existing client relationships and proven track records, making it challenging for new firms to gain initial trust and secure large projects.
Grid Dynamics' proprietary accelerators and methodologies, built over years of experience, streamline service delivery and provide a distinct competitive edge. Replicating these intellectual assets requires substantial R&D investment, deterring new entrants. The company's focus on complex digital transformation and AI solutions further raises the bar for competitors. In 2024, Grid Dynamics continued to enhance these offerings, solidifying its market position.
Operating in regulated sectors like finance, where Grid Dynamics saw its revenue contribution grow significantly by Q2 2025, imposes strict compliance and security standards. New entrants must invest heavily in meeting these requirements, which can be time-consuming and costly. This regulatory landscape, coupled with the need for established trust and a strong reputation, makes market entry particularly challenging.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Grid Dynamics Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including comprehensive industry reports from leading market research firms, detailed financial statements and investor presentations from key market players, and up-to-date regulatory filings to capture all relevant competitive dynamics.