Graphic Packaging Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Graphic Packaging Bundle
Graphic Packaging operates within a competitive landscape shaped by several key forces. Understanding the intensity of buyer power and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating this market effectively. The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis offers a comprehensive strategic breakdown of these dynamics.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Graphic Packaging’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers to Graphic Packaging Holding Company is significantly shaped by the concentration within its key raw material markets, particularly pulp and paperboard. When a small number of suppliers dominate these sectors, they possess a greater ability to dictate pricing and contractual terms, directly impacting Graphic Packaging's cost structure.
The market for recycled fiber, a crucial component for Graphic Packaging's environmentally friendly packaging solutions, has experienced notable price volatility. This fluctuation points to a degree of leverage held by suppliers in this segment. For instance, in 2024, the price of recycled corrugated containerboard saw increases driven by demand and supply dynamics, underscoring supplier influence.
To counter this supplier power, Graphic Packaging is strategically investing in its own infrastructure, including the development of a new recycled paperboard facility. This vertical integration aims to secure a more stable and cost-effective supply of essential materials, thereby reducing its reliance on external suppliers and mitigating their bargaining leverage.
The availability of substitute raw materials significantly impacts supplier bargaining power for companies like Graphic Packaging. For instance, while paperboard is a key input, the company can leverage the global recycled fibers market, which is projected to continue its growth trajectory, to source alternative materials. This diversification in sourcing options, including different types of virgin pulp from various regions, inherently lessens the leverage any single supplier might hold.
Graphic Packaging faces significant supplier bargaining power due to high switching costs. For instance, retooling specialized machinery to accommodate different material specifications or the lengthy process of qualifying new suppliers can represent substantial financial and operational hurdles. These embedded costs make it difficult for Graphic Packaging to easily shift to alternative suppliers, thereby strengthening the leverage of existing ones.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into packaging production can significantly bolster their bargaining power. This means if suppliers can start making the finished packaging themselves, they have more leverage over companies like Graphic Packaging. For Graphic Packaging, this threat is generally lower because their primary suppliers are raw material providers, such as pulp and paperboard producers. These suppliers would need substantial capital and a different skill set to enter the complex world of finished packaging manufacturing.
However, very large paper companies that are already integrated might consider this a viable strategy. For instance, a major paperboard producer could potentially leverage its existing infrastructure and market position to move into producing folding cartons or other packaging formats, directly competing with Graphic Packaging. This would shift the power dynamic, allowing them to dictate terms more forcefully.
- Supplier Forward Integration: Suppliers moving into the buyer's industry increases their bargaining power.
- Graphic Packaging's Position: Generally low concern due to suppliers being raw material producers, not finished packaging manufacturers.
- Capital & Expertise Barrier: Entering finished packaging requires significant investment and different technical knowledge.
- Potential Threat: Large, integrated paper companies are the most likely to pose this forward integration threat.
Uniqueness and Importance of Input to Product Quality
The uniqueness and importance of a supplier's input to Graphic Packaging's final product quality and differentiation significantly influence supplier power. While paperboard itself can be a commodity, specialized coatings, inks, or advanced barrier solutions crucial for sustainable packaging features often originate from more specialized and thus more powerful suppliers.
Graphic Packaging's strategic emphasis on innovative and eco-friendly packaging means that certain unique inputs are not just desirable but critical for maintaining its competitive edge. For instance, suppliers providing advanced, compostable barrier materials or specialized printing inks that meet stringent environmental regulations hold considerable leverage. In 2024, the demand for sustainable packaging solutions continued to surge, with companies like Graphic Packaging investing heavily in R&D for these materials, increasing the bargaining power of suppliers who can deliver these specialized inputs reliably and at scale.
- Specialized Coatings and Inks: Suppliers offering proprietary, high-performance coatings or eco-friendly inks that enhance product appeal and sustainability are key.
- Advanced Barrier Materials: Inputs that provide superior moisture, oxygen, or grease barriers, especially those that are compostable or recyclable, are critical for food and beverage packaging.
- Sustainable Material Innovations: Suppliers at the forefront of developing new, sustainable paperboard alternatives or additives give them significant bargaining power.
- Regulatory Compliance: Providers of materials that meet evolving global environmental and safety regulations are indispensable, increasing their influence.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Graphic Packaging is moderate, influenced by the concentration of raw material producers and the availability of substitutes. While some suppliers of specialized coatings and inks hold significant sway due to the unique properties they offer, the overall market for pulp and paperboard is more competitive, limiting extreme leverage.
In 2024, the cost of recycled corrugated containerboard, a key input, saw fluctuations, indicating some supplier pricing power. However, Graphic Packaging’s strategy of vertical integration, exemplified by its new recycled paperboard facility, aims to mitigate this by securing supply and reducing reliance on external sources.
The company also benefits from the growing global recycled fibers market, which provides alternative sourcing options and diversifies its supplier base. This reduces the dependence on any single supplier, thereby tempering their individual bargaining strength.
| Factor | Impact on Graphic Packaging | 2024 Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (Pulp & Paperboard) | Moderate to High | Concentration exists, but competition among major players limits extreme power. |
| Availability of Substitutes (Recycled Fiber) | High | Growing recycled fiber market offers alternatives, reducing reliance on virgin pulp. |
| Switching Costs | High | Retooling and supplier qualification are costly, favoring incumbent suppliers. |
| Importance of Input (Specialty Coatings/Inks) | High for specific inputs | Suppliers of unique, eco-friendly materials have increased leverage due to demand. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Low | Suppliers are primarily raw material producers; entering finished packaging is a significant barrier. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Graphic Packaging's position in the global packaging industry.
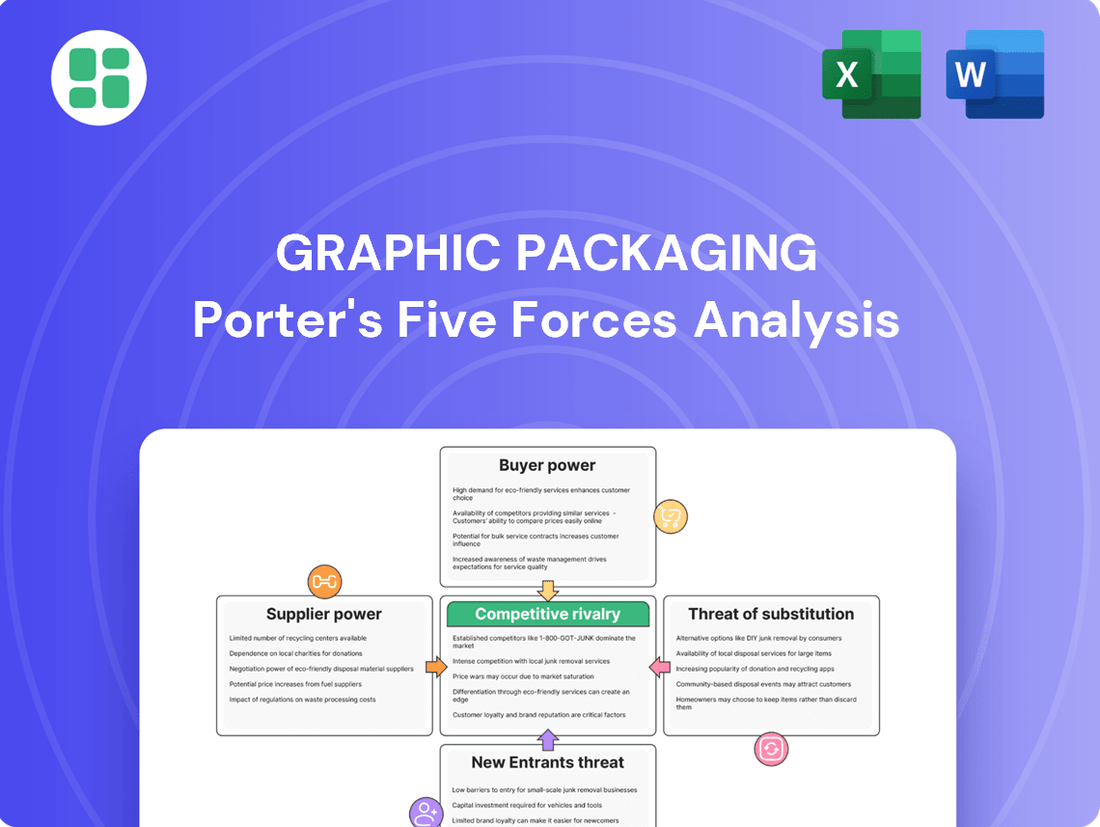
Effortlessly identify and address competitive pressures by visualizing Graphic Packaging's Porter's Five Forces with an intuitive, interactive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Graphic Packaging's customer base includes prominent players in the food, beverage, and foodservice industries. These large clients, due to their substantial purchase volumes, wield considerable influence, often negotiating for better pricing, longer payment periods, and tailored product offerings.
The bargaining power of these major customers is further magnified if a significant percentage of Graphic Packaging's overall income is derived from a limited number of these key accounts. For instance, in 2023, Graphic Packaging reported that its largest customer accounted for approximately 10% of its net sales, highlighting the importance of managing these relationships effectively.
Customer switching costs for Graphic Packaging are significant. Integrating new packaging designs into existing production lines and supply chains requires substantial time and investment. For instance, a food and beverage company might need to recalibrate machinery, re-test product safety, and update regulatory documentation, all of which represent considerable hurdles.
Customers, especially in the fast-moving consumer goods industry, are very focused on price and are always looking for ways to save money. This means they put a lot of pressure on Graphic Packaging to keep its prices competitive, a trend that's even stronger when the economy is tough and people are looking for good value.
This intense price sensitivity directly impacts Graphic Packaging. For instance, in 2023, the company reported that declines in price, volume, and product mix led to a notable impact on its net sales and EBITDA, highlighting how crucial pricing is for their financial performance.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers backward integrating into packaging production is generally low for Graphic Packaging's diverse client base. Most clients, particularly those in the food and beverage or consumer packaged goods sectors, lack the specialized machinery, substantial capital, and technical know-how required for effective packaging manufacturing, which falls outside their core competencies.
While the barrier to entry for packaging production is high, very large multinational corporations with significant purchasing power and extensive supply chains might explore limited in-house packaging solutions for specific, high-volume product lines. This is often driven by a desire for greater control over quality, cost, or supply chain resilience.
For instance, in 2024, major players in the consumer staples market, such as Procter & Gamble or Nestlé, might evaluate the feasibility of producing certain packaging components internally if the scale of their operations justifies the investment. However, the complexity and capital intensity of modern, sustainable packaging solutions typically make outsourcing to specialists like Graphic Packaging more economically viable and strategically sound.
The bargaining power of customers is further mitigated by Graphic Packaging's ability to offer a wide range of innovative and sustainable packaging solutions, which many clients would find difficult and costly to replicate independently.
Availability of Substitute Packaging for Customers
Customers can choose from a range of packaging materials, including plastics, glass, and metal, which can dilute the bargaining power of paperboard manufacturers. This availability of alternatives gives buyers more leverage to negotiate prices or switch suppliers if they are not satisfied with the offerings of paperboard companies.
However, the growing emphasis on sustainability is shifting this dynamic. As consumers increasingly favor eco-friendly options, paperboard's recyclability and biodegradability make it a more attractive choice. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 68% of consumers are willing to pay more for products with sustainable packaging, directly impacting the perceived value of paperboard versus other materials.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Growing demand for sustainable packaging favors paperboard.
- Reduced Leverage of Non-Paper Substitutes: Environmentally conscious customers are less likely to switch away from paper-based solutions.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: This trend can diminish the bargaining power of customers who previously relied on non-paper packaging alternatives.
Graphic Packaging's customer concentration, with its largest client representing about 10% of net sales in 2023, grants significant leverage, especially concerning pricing and customized solutions. High switching costs, due to the complexity of integrating new packaging, also limit customer power. However, the increasing consumer demand for sustainable packaging, with 68% of consumers in a 2024 survey willing to pay more for eco-friendly options, strengthens paperboard's position and can dilute the bargaining power of customers seeking alternatives.
| Customer Factor | Impact on Graphic Packaging | 2023/2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for major clients | Largest customer ~10% of net sales (2023) |
| Switching Costs | Significant barriers for customers | Machinery recalibration, safety testing, regulatory updates |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure for competitive pricing | Price declines impacted 2023 net sales and EBITDA |
| Availability of Substitutes | Dilutes paperboard power | Plastics, glass, metal packaging exist |
| Sustainability Trend | Favors paperboard, reduces substitute power | 68% consumers willing to pay more for sustainable packaging (2024) |
What You See Is What You Get
Graphic Packaging Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Graphic Packaging Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. You're viewing the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or placeholder content. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use, providing comprehensive insights into Graphic Packaging's strategic landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The paper packaging sector sees significant competition, featuring major global entities such as International Paper, Smurfit Kappa, WestRock, and Mondi Group, alongside a multitude of smaller, regional competitors. This diverse landscape means Graphic Packaging faces rivals that range from fully integrated paper producers to specialized packaging converters.
The paper packaging market is seeing consistent growth, fueled by a strong push for eco-friendly options and the booming e-commerce sector. This expanding market generally helps to ease competition, as there’s enough room for everyone to thrive. For instance, the global paper and paperboard packaging market was valued at approximately $250 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow steadily.
Graphic Packaging actively differentiates itself through innovative and sustainable packaging. They focus on creating products like folding cartons and food containers that are environmentally responsible, a key factor in today's market. For instance, their commitment to replacing plastic with paperboard addresses growing consumer and regulatory demand for eco-friendly options.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, stemming from substantial investments in fixed assets like paper mills and specialized converting plants, make it difficult for companies to leave the market. This reluctance to exit can fuel intense rivalry, as firms may continue operating and competing aggressively even when market conditions are unfavorable. For instance, Graphic Packaging's reported 2023 capital expenditures were approximately $690 million, highlighting the significant asset base within the industry.
These substantial fixed costs mean that companies often prefer to continue production, even at lower margins, rather than incur losses from shutting down operations or selling assets at a discount. This dynamic can lead to price wars and a general intensification of competition across the board. Graphic Packaging's announcement in late 2023 regarding the closure of a recycled paperboard manufacturing facility demonstrates strategic capacity adjustments, but the overall industry structure still presents significant hurdles for complete exits.
- Significant Fixed Assets: Industries with high capital intensity, such as paper manufacturing, have substantial investments in specialized machinery and production facilities.
- Reluctance to Exit: High exit barriers discourage companies from leaving the market, even during economic downturns, leading to prolonged competitive pressure.
- Capacity Adjustments: Firms like Graphic Packaging may undertake strategic closures of specific facilities, but the overall industry’s asset base remains a key factor in competitive dynamics.
Cost Structure and Price Competition
The graphic packaging industry is inherently cost-intensive, with significant expenditures tied to essential raw materials such as pulp, recycled fiber, and energy. These input costs are subject to considerable volatility, directly impacting the industry's price dynamics. When these costs rise, companies often face pressure to pass them on, leading to heightened price competition, especially if there's overcapacity in specific market segments.
Graphic Packaging, for instance, has publicly acknowledged experiencing an increase in input cost inflation. In response to these inflationary pressures, the company has strategically implemented price increases to safeguard its profit margins and maintain financial stability. This proactive approach is crucial for navigating the competitive landscape where cost management is paramount.
- Raw Material Volatility: Pulp and recycled fiber prices can fluctuate significantly, impacting production costs.
- Energy Costs: Energy is a major input, and its price swings directly influence profitability.
- Overcapacity Impact: Excess production capacity in certain areas intensifies price wars among competitors.
- Price Adjustments: Companies like Graphic Packaging use price increases to offset rising input costs and protect margins.
The competitive rivalry within the paper packaging industry is intense, driven by a large number of global and regional players. This crowded market means Graphic Packaging constantly contends with rivals of varying scales and integration levels. The ongoing growth in demand, particularly for sustainable and e-commerce-friendly packaging, helps to temper some of this rivalry, as the expanding market can accommodate more participants.
However, significant investments in fixed assets, such as paper mills, create high exit barriers. Companies are often reluctant to leave the market, even during downturns, which can prolong competitive pressure and lead to aggressive pricing strategies. For example, Graphic Packaging's substantial capital expenditures, reported around $690 million in 2023, illustrate the industry's asset-heavy nature.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (Approx. USD Billions) | Key Product Focus |
|---|---|---|
| International Paper | 20.4 | Pulp, paper, packaging |
| Smurfit Kappa | 12.4 | Paper-based packaging solutions |
| WestRock | 9.3 | Paper and packaging solutions |
| Mondi Group | 8.8 | Sustainable packaging and paper |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Graphic Packaging's paper-based products, such as plastics, glass, and metal, hinges on their price-performance balance. While paper gains traction for its eco-friendly profile, other materials might excel in specific areas like barrier protection, robustness, or sheer cost efficiency for certain uses. For instance, in 2024, the global flexible packaging market, which includes plastics, was valued at over $250 billion, showcasing the scale of these alternatives.
Customer propensity to substitute is significantly influenced by growing environmental consciousness and regulatory pressures against single-use plastics. For instance, in 2024, many regions saw increased legislation targeting plastic packaging, pushing consumers and businesses toward more sustainable materials like paperboard. This shift directly impacts the demand for Graphic Packaging's products, making paper-based solutions more attractive.
Many consumers and brands are actively seeking eco-friendly alternatives, which reduces the attractiveness of plastic and other non-paper options and boosts demand for paperboard. Surveys in early 2024 indicated that over 60% of consumers consider sustainability when making purchasing decisions, a figure that continues to rise. This heightened awareness makes it harder for non-paper substitutes to retain market share.
The market for alternative packaging materials is experiencing rapid innovation, with advancements in bioplastics, compostable options, and plant-based solutions derived from sugarcane or hemp. These emerging materials, while currently niche, represent a potential long-term threat if they can achieve cost-competitiveness and comparable performance at a larger scale. Graphic Packaging itself is actively participating in this shift by replacing traditional plastic packaging with its paperboard alternatives.
Switching Costs for Buyers to Substitute
Switching costs for buyers considering alternative packaging materials can be substantial. These costs often involve significant investments in re-designing packaging to accommodate new materials, retooling existing filling and packaging lines, and making necessary adjustments to supply chains. For instance, a food manufacturer might need to invest in new sealing equipment if they switch from paperboard to flexible plastic films. These upfront expenses act as a considerable barrier, slowing down the adoption of substitutes and allowing companies like Graphic Packaging to maintain market share while they innovate.
The regulatory environment, particularly the global push for enhanced sustainability and circular economy principles, is increasingly influencing these switching costs. As governments mandate or incentivize the use of recyclable, compostable, or biodegradable packaging, the perceived cost and complexity of adopting substitutes can decrease. For example, the EU's Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation, with its focus on increasing recycled content and reducing single-use plastics, encourages a shift away from traditional materials, potentially lowering the barrier for buyers to explore alternatives to paper-based packaging.
- Significant Re-design and Retooling: Companies switching from paper packaging may face costs associated with new printing plates, die-cutters, and specialized filling machinery, impacting their operational efficiency and capital expenditure.
- Supply Chain Adjustments: Integrating new packaging materials can require changes in warehousing, transportation, and inventory management, adding complexity and potential disruption.
- Regulatory Incentives for Sustainability: Initiatives promoting recycled content and recyclability can reduce the financial and operational burden for businesses adopting alternative, more sustainable packaging solutions.
Regulatory and Environmental Drivers
Stricter government regulations, like bans on single-use plastics and mandates for increased recyclable content, are significantly pushing both businesses and consumers toward paper-based packaging alternatives. This trend directly reduces the appeal and viability of many traditional substitutes for Graphic Packaging's products.
For instance, by early 2024, many regions had implemented or were planning to implement bans on specific plastic items, directly benefiting paper-based packaging. This regulatory push is a powerful force that effectively lowers the threat of substitutes for Graphic Packaging's core business, as the alternatives are becoming less attractive and more restricted.
- Regulatory Pressure: Bans on single-use plastics and mandates for recycled content are increasing globally.
- Consumer Shift: Growing environmental awareness drives demand for sustainable packaging solutions.
- Market Advantage: Paper-based packaging benefits from these trends, diminishing the threat from plastic and other materials.
The threat of substitutes for Graphic Packaging's paper-based products remains moderate, largely due to ongoing innovations in alternative materials and evolving consumer preferences. While paper benefits from its sustainability image, substitutes like advanced plastics, bioplastics, and even reusable packaging systems present a persistent challenge.
In 2024, the global market for sustainable packaging, including paperboard and emerging bio-based materials, continued to grow, indicating a strong demand for eco-friendly options. However, the cost-competitiveness and performance parity of these substitutes are still developing. For example, while bioplastics are gaining traction, their production costs can be higher than traditional plastics, influencing their widespread adoption.
Switching costs for businesses can still be a barrier to adopting substitutes, especially for high-volume product lines. However, increasing regulatory pressure and consumer demand for sustainable packaging are gradually reducing these barriers. For instance, by early 2024, several major consumer goods companies had committed to increasing their use of recycled content and reducing plastic, which indirectly lowers the switching cost for paper-based alternatives.
| Substitute Material | Key Advantages | Key Disadvantages | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastics (including bioplastics) | Barrier properties, durability, cost-effectiveness for certain applications | Environmental concerns (non-biodegradability), potential regulatory restrictions | Global flexible packaging market valued over $250 billion; bioplastics market growing but still a fraction of total |
| Glass | Premium feel, inertness, excellent barrier properties | Weight, fragility, higher transportation costs | Niche applications, particularly in beverages and premium food |
| Metal (Aluminum, Steel) | Excellent barrier properties, recyclability, durability | Higher cost, potential for corrosion, limited design flexibility | Dominant in beverage cans and some food packaging; high recycling rates |
Entrants Threaten
The paper packaging industry demands significant upfront investment, creating a formidable barrier for newcomers. Establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, acquiring specialized machinery, and integrating complex production processes like pulp and paperboard mills require hundreds of millions of dollars. This capital intensity naturally deters potential entrants who may lack the necessary financial backing.
Graphic Packaging's own operational scale underscores this. For instance, the company's substantial investments in facilities, such as its Waco, Georgia plant, which underwent a significant expansion in 2022 costing approximately $100 million, illustrate the ongoing capital commitment necessary to compete effectively in this sector.
Established players in the graphic packaging industry, like Graphic Packaging, leverage substantial economies of scale. This means they can buy raw materials in bulk, operate highly efficient, large-scale manufacturing facilities, and manage distribution networks more cost-effectively. For instance, in 2023, Graphic Packaging reported net sales of $7.7 billion, demonstrating the sheer volume of their operations that underpins these cost advantages.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in matching these economies of scale. Without the established volume, they cannot negotiate favorable pricing on raw materials or spread fixed manufacturing costs over as many units. This initial cost disadvantage makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on price with industry veterans who have honed their processes and built extensive supply chains over years, often benefiting from an experience curve effect that further lowers costs with each unit produced.
Newcomers to the graphic packaging industry face significant hurdles in securing access to established distribution channels. Existing players have cultivated deep-rooted relationships with major consumer product companies, often holding preferred supplier status. This makes it exceedingly difficult for new entrants to gain traction and effectively penetrate the market, as they lack these critical established connections.
Brand Loyalty and Differentiation
While packaging might appear to be a simple commodity, established consumer brands heavily depend on their existing packaging suppliers for unwavering quality, cutting-edge innovation, and dependable supply chains. This reliance fosters significant brand loyalty.
Graphic Packaging's strategic emphasis on developing innovative and sustainable packaging solutions actively cultivates differentiation and strengthens customer loyalty. These factors act as a considerable hurdle for potential new entrants seeking to penetrate the market.
- Brand Loyalty: Major brands often have long-standing relationships with packaging providers, built on trust and consistent performance.
- Innovation as a Differentiator: Graphic Packaging's investment in new materials and designs, such as their sustainable paperboard solutions, sets them apart.
- Supply Chain Reliability: Ensuring a consistent and timely supply of packaging is critical for large-scale manufacturing, making it difficult for newcomers to match established reliability.
- Customer Retention: In 2023, Graphic Packaging reported strong customer retention rates, indicating the effectiveness of their differentiation strategies in warding off new competition.
Regulatory Hurdles and Environmental Compliance
The packaging industry, including graphic packaging, is increasingly shaped by evolving environmental regulations. These rules focus heavily on sustainability, recyclability, and the responsible sourcing of materials. For instance, the European Union’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) aims for ambitious targets, including 100% reusable or recyclable packaging by 2030, presenting a significant compliance challenge.
New entrants into the graphic packaging market face substantial barriers in meeting these complex and stringent compliance requirements. Navigating these regulations can be both costly and time-consuming, demanding significant investment in research, development, and operational adjustments to ensure adherence. Companies must invest in new materials, production processes, and waste management systems to meet standards like those set by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation’s New Plastics Economy Global Commitment.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating diverse and changing environmental laws across different regions requires specialized expertise and resources.
- Compliance Costs: Investing in sustainable materials, eco-friendly production methods, and waste reduction strategies can significantly increase initial operating expenses for new players.
- Market Access: Failure to meet regulatory standards can restrict market access, particularly in regions with strict environmental mandates, impacting a new entrant's ability to scale.
- Innovation Demands: Compliance often necessitates innovation in packaging design and materials, a challenge for newcomers lacking established R&D capabilities.
The threat of new entrants in the graphic packaging sector is considerably low due to high capital requirements and established economies of scale. New companies must invest heavily in advanced manufacturing and navigate complex supply chains, often requiring hundreds of millions of dollars. Graphic Packaging’s 2022 expansion in Waco, Georgia, costing around $100 million, highlights this capital intensity.
Established players like Graphic Packaging benefit from significant cost advantages derived from their vast operational scale, evidenced by their $7.7 billion in net sales in 2023. This scale allows for bulk purchasing and efficient cost management, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price without matching this volume.
Brand loyalty and innovation further deter new entrants. Major brands rely on established suppliers for consistent quality and innovative solutions, such as Graphic Packaging’s sustainable paperboard offerings. This deep-seated trust, coupled with regulatory compliance demands, creates substantial barriers for those seeking to enter the market.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | High upfront investment for facilities and machinery. | Requires hundreds of millions of dollars to establish competitive operations. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale production and purchasing. | Graphic Packaging's $7.7 billion in 2023 sales demonstrates scale benefits. |
| Brand Loyalty & Differentiation | Established relationships and innovative offerings. | Graphic Packaging's sustainable solutions foster customer retention. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting stringent environmental standards. | EU's PPWR targets for 2030 necessitate significant investment in compliance. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Graphic Packaging Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the company's SEC filings, annual reports, and investor presentations. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports and data from reputable financial information providers to capture the full competitive landscape.