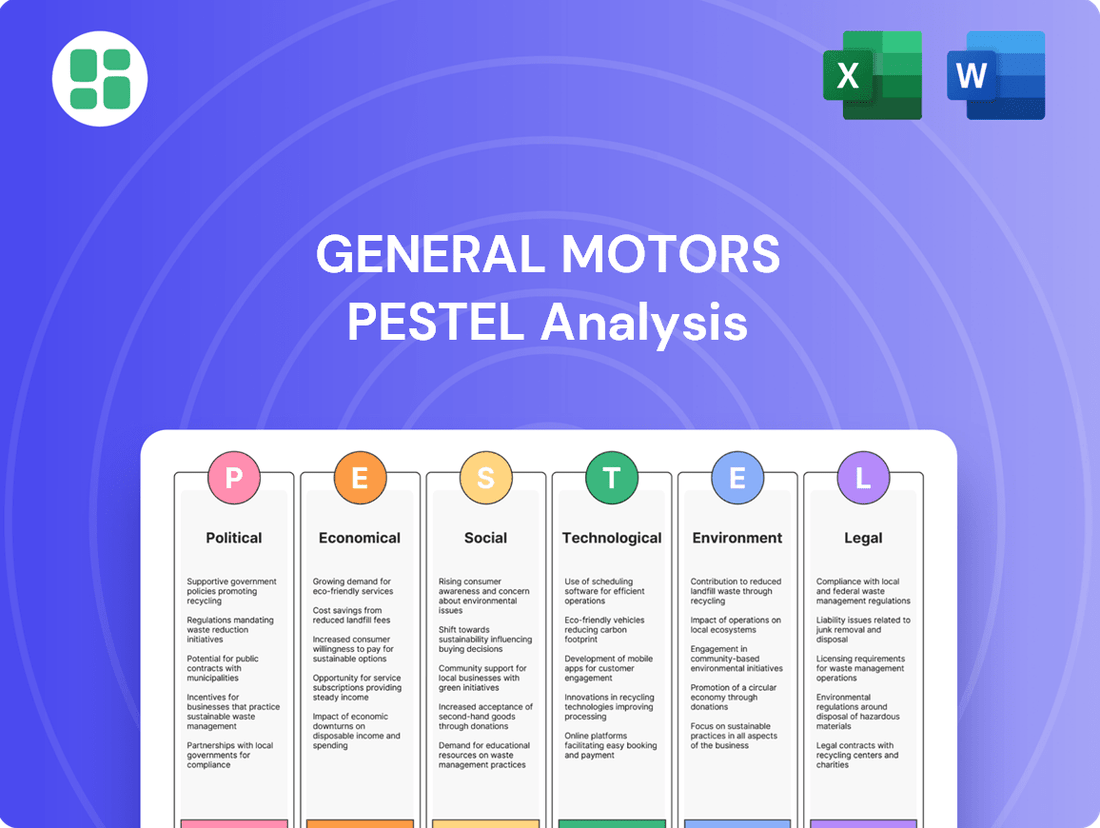
General Motors PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
General Motors Bundle
General Motors operates within a dynamic global landscape, facing evolving political regulations, economic shifts, and rapid technological advancements. Understanding these external forces is crucial for strategic planning and forecasting future success. Our comprehensive PESTLE analysis dives deep into these factors, offering actionable intelligence to navigate the automotive industry. Download the full version to gain a competitive edge and make informed decisions.
Political factors
Government regulations, especially concerning emissions and electric vehicles (EVs), are a major force shaping General Motors' (GM) direction. The Biden administration's ambitious target of 67% of new vehicles being electric by 2032 directly fuels GM's significant investments in its EV lineup and charging infrastructure.
However, potential policy shifts create market uncertainty. For instance, reports suggest a future Trump administration might reconsider federal EV charging subsidies and tax credits, which could impact consumer demand and GM's EV sales projections.
International trade policies and tariffs significantly impact General Motors' financial performance. The U.S. government's recent imposition of a 100% tariff on EVs from China and a 25% tariff on critical minerals and EV batteries directly increases production costs.
These tariffs also affect the affordability of GM's vehicles for consumers. For instance, GM projected a substantial hit to its 2025 earnings, estimated between $4 billion and $5 billion, largely due to these trade barriers, especially on vehicles sourced from South Korea, Mexico, and Canada.
Government incentives, like the federal EV tax credit, significantly influence consumer purchasing decisions and, consequently, General Motors' electric vehicle sales. For instance, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 provided a credit of up to $7,500 for eligible new EVs.
However, shifts in eligibility, such as certain GM models no longer qualifying for the full credit in 2024, have prompted GM to introduce its own incentives to sustain sales momentum. This highlights the direct impact of policy changes on the company's sales strategies.
The prospect of these credits being altered or removed by future administrations introduces market volatility for EV adoption. This uncertainty requires GM to remain agile in its pricing and incentive structures to navigate the evolving political landscape.
Labor Relations and Union Agreements
Labor relations, particularly with the United Auto Workers (UAW), are a critical political factor for General Motors. The current UAW contract, effective through 2028, includes substantial wage hikes and enhanced benefits, directly impacting GM's operational expenses.
The 2025 GM-UAW contract is projected to increase GM's labor costs by approximately $9.3 billion through 2028. This significant investment in its workforce affects GM's overall profitability and necessitates strategic adjustments.
- Labor Agreements: The UAW contract dictates wage scales, benefits, and working conditions, influencing GM's cost structure.
- Cost Impact: The 25% wage increase and reinstatement of cost-of-living adjustments over four and a half years add billions to GM's expenses.
- Production Stability: Strong labor relations can ensure production continuity, while disputes can lead to costly disruptions.
- Strategic Response: GM must balance increased labor costs with efforts to maintain competitiveness through efficiency and innovation.
Geopolitical Stability and International Relations
Geopolitical stability and international relations are critical for General Motors (GM). Global tensions can disrupt supply chains, impacting everything from component sourcing to final vehicle delivery. For instance, trade disputes can lead to increased tariffs, raising production costs and potentially affecting vehicle pricing in key markets.
Trade tensions, especially those involving major economies like China, have prompted GM to reassess its manufacturing and sourcing strategies. This has included shifts in production locations and a greater focus on regionalizing supply chains to mitigate risks associated with international trade policies. GM's significant investment in U.S. manufacturing, such as the $4 billion allocated to boost domestic production, is a direct response to this evolving trade environment, aiming to enhance resilience and potentially reduce reliance on overseas assembly.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Geopolitical instability can create bottlenecks in GM's global supply network, affecting production schedules and inventory levels.
- Market Access: Trade agreements and political relationships directly influence GM's ability to sell vehicles in international markets, with tariffs and sanctions posing significant barriers.
- Manufacturing Footprint: Evolving trade policies and geopolitical risks are driving strategic decisions about where GM manufactures vehicles, with a notable trend towards increasing domestic production in key markets like the United States.
Government regulations, particularly those focused on emissions and the transition to electric vehicles (EVs), are a primary driver for General Motors. The Biden administration's push for EVs, aiming for 67% of new vehicle sales to be electric by 2032, directly influences GM's substantial investments in its EV portfolio and charging infrastructure.
Conversely, potential shifts in political leadership, such as a future Trump administration, could lead to a reevaluation of federal EV charging subsidies and tax credits, potentially impacting consumer demand for GM's electric offerings.
International trade policies and tariffs significantly impact GM's financial results, with recent U.S. tariffs on Chinese EVs and critical minerals increasing production costs and affecting vehicle affordability.
Government incentives, like the federal EV tax credit, play a crucial role in consumer purchasing decisions for EVs, although changes in eligibility, as seen with some GM models in 2024, necessitate the company offering its own incentives to maintain sales momentum.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis of General Motors examines the impact of political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors on the automotive giant. It provides a comprehensive overview of the external forces shaping GM's strategy and market position.
A clear, actionable PESTLE analysis for General Motors that highlights key external factors, enabling proactive strategy development and mitigating potential risks.
Economic factors
Global economic growth is a primary driver for automotive demand. In 2024, many regions experienced robust economic expansion, fueling consumer confidence and spending on big-ticket items like vehicles. This trend directly translated to strong sales for automakers like General Motors.
Consumer spending power is a crucial indicator for GM's revenue. When consumers have more disposable income, they are more likely to purchase new vehicles. For instance, in Q1 2024, GM reported adjusted automotive operating earnings of $2.8 billion, reflecting healthy consumer demand and spending.
Conversely, economic slowdowns or recessions pose a significant risk. During such periods, consumers tend to reduce discretionary spending, impacting vehicle sales. While GM achieved record financial performance in 2024, its future outlook remains closely tied to the stability of global economic conditions and the sustained ability of consumers to spend.
Rising inflation and interest rates directly impact vehicle affordability, as most new car purchases involve financing. For instance, the average interest rate on a 60-month new car loan in early 2024 hovered around 6-7%, a notable increase from previous years, making monthly payments higher for consumers.
These elevated borrowing costs can significantly dampen consumer demand for new vehicles, consequently affecting General Motors' sales volumes and overall profitability. Higher interest rates can also increase GM's own borrowing costs for operations and investments.
GM's strategic response, including pricing adjustments and cost-saving initiatives, becomes critical to maintaining its market share amidst these economic headwinds. The company's ability to offer competitive financing options or manage production costs will be key differentiators.
Fluctuations in the cost of essential raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, crucial for electric vehicle batteries, directly impact General Motors' (GM) production expenses. For instance, as of early 2024, lithium prices saw considerable volatility, with some benchmarks experiencing significant drops from 2023 highs but remaining elevated compared to pre-2021 levels, impacting battery pack costs.
Disruptions in global supply chains, exacerbated by geopolitical events and shipping challenges, further inflate these costs. Tariffs imposed on critical minerals and automotive components can add an additional layer of expense, directly affecting GM's bottom line and pricing strategies.
In response, GM is proactively working to secure long-term supply agreements for key battery materials and is investing in localized production facilities to build more resilient supply chains and mitigate economic vulnerabilities.
Exchange Rates and Currency Fluctuations
General Motors, as a global automotive giant, is significantly impacted by exchange rates and currency fluctuations. These shifts directly affect the cost of parts sourced internationally and the profitability of sales made in foreign markets. For instance, a stronger US dollar can make imported components cheaper for GM but also makes its vehicles more expensive for international buyers, potentially dampening sales volume. Conversely, a weaker dollar can boost overseas earnings when converted back to US dollars.
The volatility in currency markets presents a continuous challenge for GM's financial planning and pricing strategies. In 2024, the automotive industry has seen ongoing currency pressures. For example, the Euro's performance against the US dollar influences GM's European operations and sales, while the Chinese Yuan's stability or fluctuations affect its significant market presence in China. These movements can alter the comparative pricing of GM vehicles against local competitors, impacting market share.
- Impact on Costs: Fluctuations in exchange rates directly influence the cost of raw materials and components imported by GM. For example, if the Japanese Yen strengthens against the US dollar, GM's costs for parts sourced from Japan will increase.
- Revenue Translation: Revenue generated from international sales is translated back into US dollars. A weaker foreign currency against the dollar reduces the reported revenue and profit from those markets.
- Competitive Positioning: Exchange rates affect the price competitiveness of GM vehicles in different countries. A strong local currency can make GM vehicles more expensive relative to locally produced alternatives.
- Hedging Strategies: To mitigate these risks, GM employs currency hedging strategies, such as forward contracts and options, to lock in exchange rates for future transactions.
Market Competition and Pricing Pressure
The automotive industry is intensely competitive, and General Motors (GM) faces considerable pricing pressure, particularly from emerging players. The influx of cost-effective new energy vehicles (NEVs) from Chinese manufacturers has intensified this challenge, forcing GM to carefully manage its pricing strategies to remain competitive.
To navigate this landscape, GM must strike a delicate balance between investing in innovation and maintaining high quality while keeping prices attractive. This balancing act directly impacts profit margins. For instance, in early 2024, the average transaction price for new vehicles in the US remained elevated, but the increasing availability of more affordable EV options is expected to put downward pressure on prices across the board.
GM's strategic response involves broadening its electric vehicle (EV) portfolio. By introducing EVs across a range of price points, the company aims to appeal to a wider customer base. This includes offerings like the Chevrolet Equinox EV, which targets the more mainstream market, alongside its existing premium EVs, aiming to capture market share in a rapidly evolving sector.
- Intense Competition: The global automotive market is characterized by fierce rivalry, with established automakers and new entrants vying for market share.
- Pricing Pressure from NEVs: The rise of affordable new energy vehicles, especially from Chinese manufacturers, is a significant factor driving down prices for comparable segments.
- Balancing Innovation and Cost: GM's challenge lies in developing cutting-edge technology and high-quality vehicles while ensuring competitive pricing to maintain profitability.
- EV Portfolio Expansion: GM is actively expanding its EV offerings, aiming to cover various price segments to attract a broader consumer base and compete effectively in the EV market.
Economic factors significantly shape General Motors' performance, with global growth driving demand and consumer spending power directly influencing revenue. For instance, GM reported robust financial results in early 2024, reflecting healthy consumer confidence and spending on vehicles.
However, economic downturns and rising inflation present considerable risks, impacting vehicle affordability through higher interest rates. As of early 2024, new car loan rates around 6-7% made financing more expensive, potentially dampening sales for GM.
Material costs, particularly for EV batteries, and supply chain disruptions also affect production expenses. Volatility in lithium prices, for example, impacts battery pack costs, prompting GM to secure long-term supply agreements and invest in localized production.
Currency fluctuations add another layer of complexity, affecting the cost of imported parts and the profitability of international sales. For example, exchange rate shifts influence GM's operations in key markets like China and Europe.
| Economic Factor | Impact on GM | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Global Economic Growth | Drives automotive demand and consumer confidence. | Robust expansion in many regions fueled strong Q1 2024 sales. |
| Consumer Spending Power | Directly impacts GM's revenue and sales volumes. | Q1 2024 adjusted automotive operating earnings were $2.8 billion. |
| Inflation & Interest Rates | Reduces vehicle affordability and increases borrowing costs. | New car loan rates around 6-7% in early 2024 increased monthly payments. |
| Raw Material Costs (e.g., Lithium) | Affects EV battery production expenses. | Lithium prices volatile in early 2024, remaining elevated compared to pre-2021. |
| Exchange Rates | Influences import costs and international sales profitability. | Ongoing currency pressures observed across the industry in 2024. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
General Motors PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of General Motors delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the automotive giant. Understand the strategic landscape shaping GM's future with this detailed report.
Sociological factors
Societal trends increasingly favor sustainable transportation, driving a notable consumer preference for electric vehicles. This shift is directly impacting the automotive industry, with companies like General Motors actively adapting to meet this growing demand.
General Motors has strategically responded to this evolving consumer preference. In 2024, the company successfully doubled its EV market share, a testament to its expanding EV portfolio and the improved scalability of its production capabilities. This aggressive expansion signals GM's commitment to leading in the electric vehicle space.
Despite the positive momentum, certain consumer hesitations persist, acting as a moderating factor on the speed of EV adoption. Concerns regarding the availability and accessibility of charging infrastructure, alongside lingering range anxiety, continue to influence purchasing decisions for many potential EV buyers.
Demographic shifts, like the aging population in developed markets and rapid urbanization globally, significantly shape automotive demand. For instance, the median age in the United States reached 38.9 years in 2022, suggesting a growing segment of older drivers who may prioritize comfort and ease of access in vehicle design. Conversely, as of 2023, over 57% of the world's population resides in urban areas, a figure projected to climb, fueling demand for compact, fuel-efficient vehicles and multimodal transportation options in cities.
General Motors is responding to these trends by diversifying its product portfolio. In 2024, GM's focus includes developing smaller, more urban-friendly EVs like the Chevrolet Equinox EV, while continuing to offer larger, capable vehicles such as the Chevrolet Silverado and GMC Sierra trucks, which remain popular in suburban and rural markets where larger vehicle preferences persist. This strategy aims to capture demand across a spectrum of evolving consumer needs driven by where and how people live.
Evolving lifestyle choices, such as the increasing popularity of ride-sharing and car-sharing services, are reshaping traditional car ownership. This trend, coupled with a desire for more connected and convenient mobility, directly influences how consumers interact with vehicles, impacting sales of personally owned cars.
General Motors is actively responding to these lifestyle shifts by investing heavily in advanced technologies. For instance, GM's Cruise division, a leader in autonomous vehicle technology, received a significant $1.3 billion investment in 2024, signaling a commitment to the future of mobility. This strategic focus aims to position GM as a key player in the evolving transportation landscape, offering integrated and tech-driven solutions beyond traditional vehicle sales.
Brand Perception and Corporate Social Responsibility
Consumer perception of a brand's social and environmental responsibility is increasingly shaping purchasing decisions, and General Motors is actively leveraging this trend. GM's ambitious commitment to an all-electric, zero-emissions future, with a target of carbon neutrality by 2040, significantly bolsters its brand image among environmentally conscious consumers. This strategic focus is crucial in a market where sustainability is becoming a key differentiator.
GM's corporate social responsibility efforts extend beyond its product lineup. Initiatives focused on material recyclability, responsible sourcing of materials, and community grants are all contributing to a more positive corporate social responsibility standing. For instance, in 2023, GM announced investments aimed at improving the recyclability of EV battery components, a move that directly addresses consumer concerns about the lifecycle impact of electric vehicles.
- Brand Perception: Consumers increasingly favor brands demonstrating strong social and environmental commitments.
- Electric Vehicle Transition: GM's 2040 carbon neutrality goal and focus on zero-emission vehicles appeal to a growing eco-conscious market segment.
- CSR Initiatives: Efforts in material recyclability, responsible sourcing, and community engagement enhance GM's overall reputation.
- Consumer Trust: Proactive CSR actions build trust and loyalty, influencing purchasing behavior in the automotive sector.
Safety Concerns and Consumer Trust in Autonomous Vehicles
Public acceptance of autonomous vehicle (AV) technology hinges significantly on addressing safety concerns and building consumer trust. Surveys in 2024 indicate that while interest in AVs is growing, a substantial portion of the public remains apprehensive about relinquishing control to a machine, particularly in complex urban environments. This hesitation directly impacts market penetration, as widespread adoption requires a comfortable and confident consumer base.
General Motors is actively working to mitigate these concerns through strategic investments and technological advancements. Their significant backing of Cruise, a leading AV developer, underscores a commitment to proving the safety and reliability of autonomous systems. Furthermore, GM's continued development and rollout of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) like Super Cruise on models such as the 2024 Cadillac Lyriq are designed to incrementally build consumer confidence and familiarity with hands-free driving capabilities, paving the way for future fully autonomous offerings.
- Consumer Trust: A 2024 study revealed that only 35% of US adults feel comfortable riding in a fully autonomous vehicle.
- Safety Perception: Cybersecurity vulnerabilities and the potential for system failures remain top concerns for potential AV users.
- GM's Strategy: GM's $5 billion investment in Cruise as of early 2024 highlights their dedication to developing and validating safe autonomous driving technology.
- ADAS Adoption: The increasing availability and positive reception of systems like Super Cruise are crucial steps in normalizing advanced driver assistance.
Consumer demand for sustainable and ethically produced goods is a significant sociological driver. General Motors' commitment to an all-electric future and carbon neutrality by 2040 directly addresses this, aiming to resonate with an increasingly eco-conscious consumer base.
Demographic shifts, such as an aging population and growing urbanization, influence vehicle preferences. GM's strategy of offering diverse models, from urban-friendly EVs like the Chevrolet Equinox EV to larger trucks, caters to these varied needs across different living environments.
The rise of ride-sharing and evolving lifestyle choices are reshaping traditional car ownership models. GM's investment in autonomous vehicle technology through its Cruise division, with a substantial $1.3 billion infusion in 2024, positions the company to adapt to these changing mobility patterns.
Public perception of safety, particularly concerning autonomous vehicles, remains a critical factor. While consumer comfort with AVs is growing, concerns persist, making GM's ongoing development of advanced driver-assistance systems like Super Cruise essential for building trust.
Technological factors
Continuous innovation in electric vehicle (EV) battery technology is paramount for enhancing EV range, decreasing charging durations, and cutting down production expenses, all of which directly influence General Motors' (GM) competitive standing in the evolving EV landscape. For instance, advancements aim to push energy density beyond current levels, with solid-state battery research showing potential for significant improvements by 2025.
GM's proprietary Ultium battery platform is a cornerstone of its EV strategy, offering adaptable solutions for a wide array of electric vehicles, facilitating quicker development timelines and improved cost efficiencies. This platform is designed to support battery pack sizes ranging from 50 to over 200 kWh, allowing for diverse vehicle applications.
Furthermore, GM is actively pursuing the development of closed-loop battery recycling systems, a crucial initiative for recovering valuable materials like lithium, nickel, and cobalt. This not only supports sustainability goals but also aims to secure a more stable and cost-effective supply chain for future battery production, with recycling targets set to increase significantly by the end of 2025.
General Motors is heavily invested in autonomous driving, notably through its Cruise subsidiary. While Cruise has shifted focus from robotaxis to advanced driver assistance systems for personal cars, the underlying self-driving technology development remains crucial for GM's future strategy.
This technological advancement promises to significantly boost road safety by reducing human error, a leading cause of accidents. Furthermore, it has the potential to optimize traffic flow, leading to reduced congestion and fuel consumption.
Autonomous driving systems are also poised to revolutionize mobility, offering new transportation services and increasing accessibility for various user groups. GM’s commitment is underscored by substantial R&D spending, with billions invested annually in this sector.
The expansion of connected vehicle services presents significant avenues for General Motors to generate new revenue and improve customer engagement by leveraging real-time data analytics. GM's established OnStar platform is key, offering services ranging from navigation and roadside assistance to remote diagnostics.
These connected services allow GM to gather vast amounts of data, which can be analyzed to personalize offerings and predict maintenance needs. For example, in 2023, GM reported that over 2 million vehicles were equipped with its advanced connected services, indicating a growing user base for these data-rich platforms.
However, the increasing collection and utilization of driver data introduce substantial legal and privacy challenges. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has been actively scrutinizing data handling practices across industries, with potential implications for how GM manages and monetizes the data generated by its connected vehicles, emphasizing the need for robust compliance and transparent data policies.
Advanced Manufacturing and Automation
General Motors is significantly boosting its U.S. manufacturing capabilities through substantial investments, aiming to enhance both traditional and electric vehicle production. This strategic move involves integrating advanced manufacturing techniques, such as AI-driven automation and predictive analytics, to drive efficiency, minimize waste, and elevate product quality. For instance, GM's commitment to advanced manufacturing is underscored by its plans to invest billions in its U.S. facilities, with a notable focus on retooling plants for EV production. These technologies are key to optimizing supply chains and improving overall operational performance.
GM's adoption of advanced manufacturing is a cornerstone of its strategy to remain competitive and meet evolving market demands. The company is leveraging automation and data analytics to create more agile and responsive production lines. This includes implementing smart factory concepts where machines communicate and self-optimize, leading to faster throughput and reduced downtime.
- AI-Driven Automation: GM is deploying AI in assembly processes to enhance precision and speed, exemplified by robotic systems that adapt to different vehicle components.
- Predictive Analytics: The company utilizes predictive analytics for machinery maintenance, forecasting potential failures to prevent costly disruptions and ensure continuous operation.
- Investment in U.S. Plants: GM has announced significant investments, such as the over $7 billion allocated for U.S. EV and battery manufacturing through 2025, which includes upgrades for advanced manufacturing technologies.
- Efficiency Gains: These technological advancements are projected to yield substantial improvements in operational efficiency and a reduction in manufacturing costs per vehicle.
Research and Development (R&D) Investment
General Motors (GM) recognizes that sustained investment in research and development (R&D) is critical for maintaining its competitive edge, especially in rapidly evolving sectors like electrification and autonomous driving. The company has committed a substantial $35 billion to electric and autonomous vehicle (AV) technologies through 2025, underscoring its dedication to pioneering future mobility solutions.
This significant R&D expenditure is directly aimed at developing the next generation of vehicles and mobility services. GM's focus areas include:
- Electrification: Advancing battery technology, electric powertrains, and charging infrastructure.
- Autonomous Driving: Developing sophisticated self-driving systems and related software.
- New Materials: Exploring lighter and more sustainable materials for vehicle construction.
General Motors is heavily investing in advanced manufacturing technologies to boost efficiency and product quality. This includes AI-driven automation for precision assembly and predictive analytics to minimize operational disruptions. For example, GM plans to invest over $7 billion in U.S. EV and battery manufacturing through 2025, incorporating these advanced techniques.
The company's commitment to R&D is substantial, with a $35 billion allocation for electric and autonomous vehicle technologies through 2025. This funding targets advancements in battery tech, electric powertrains, autonomous driving systems, and new vehicle materials.
GM's Ultium battery platform is central to its EV strategy, offering scalable solutions for diverse vehicle models and aiming for cost efficiencies. The platform supports battery capacities from 50 to over 200 kWh, enabling a broad range of applications.
GM is also focusing on connected vehicle services, leveraging data analytics for revenue generation and customer engagement via its OnStar platform. In 2023, over 2 million vehicles were equipped with these services, highlighting their growing adoption and the associated data privacy considerations.
| Technology Area | GM's Investment/Focus | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Vehicle Batteries | Ultium platform, solid-state battery research | Enhanced range, faster charging, reduced costs |
| Autonomous Driving | Cruise subsidiary, advanced driver assistance systems | Road safety, traffic optimization, new mobility services |
| Connected Services | OnStar platform, real-time data analytics | New revenue streams, personalized offerings, predictive maintenance |
| Advanced Manufacturing | AI automation, predictive analytics, U.S. plant upgrades | Increased efficiency, reduced waste, improved product quality |
| Research & Development | $35 billion (through 2025) for EV & AV tech | Next-generation vehicles, pioneering mobility solutions |
Legal factors
General Motors navigates a complex web of global vehicle safety standards, from the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) to Europe's Euro NCAP. Failure to meet these requirements, such as those for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) mandated in many markets by 2025, can lead to costly recalls and significant brand damage. For instance, a recall impacting hundreds of thousands of vehicles due to a safety defect can cost millions in remediation and lost sales.
General Motors operates under stringent emissions and fuel economy regulations, including the Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE) standards in the United States. Failure to meet these benchmarks can lead to significant financial penalties; for instance, GM was fined $146 million in 2023 for exceeding emissions limits on older vehicle models.
These regulatory pressures are a key driver behind GM's strategic decision to phase out tailpipe emissions from all new light-duty vehicles by 2035. This ambitious target directly addresses the evolving legal landscape and the increasing demand for environmentally conscious automotive solutions.
Data privacy and consumer protection laws are increasingly significant for General Motors, especially as vehicles become more connected. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has taken action against GM and its OnStar service for collecting and selling precise driver location and behavior data without proper consent. This underscores the substantial legal risks involved.
Following these actions, GM must now secure explicit consent from consumers and offer them choices regarding data collection and the ability to delete their information. This shift reflects a broader regulatory trend prioritizing consumer control over personal data in the automotive sector.
Intellectual Property Rights and Patents
General Motors places significant emphasis on safeguarding its intellectual property, particularly patents covering its innovations in electric vehicle battery technology, autonomous driving systems, and advanced manufacturing processes. This robust protection is fundamental to maintaining its competitive edge in the rapidly evolving automotive landscape. For instance, GM's ongoing investments in battery research, which saw significant funding in 2024, are heavily reliant on securing patents to prevent rivals from replicating their advancements.
Legal disputes concerning intellectual property infringement or the negotiation of licensing agreements pose a direct risk to GM's technological leadership and its overall market standing. The company's substantial research and development expenditures, reportedly in the billions annually leading up to 2025, underscore the critical need for strong IP safeguards to ensure a return on these investments.
- Patent Portfolio Expansion: GM actively pursues patents for new EV battery chemistries and autonomous driving algorithms, aiming to secure exclusive rights to its technological breakthroughs.
- Licensing Agreements: The company engages in strategic licensing of certain technologies, generating revenue while also allowing for wider adoption of its innovations under controlled terms.
- Litigation Risk: GM faces potential legal challenges from competitors alleging patent infringement, which could lead to costly settlements or injunctions impacting product development and sales.
- R&D Investment Protection: The value of GM's significant R&D outlays is directly tied to its ability to protect the resulting intellectual property through patents and other legal mechanisms.
Labor Laws and Union Negotiations
General Motors must navigate a complex web of labor laws, with significant recent developments impacting its operations. The 2023 UAW contract negotiations, for instance, resulted in substantial wage increases and improved benefits for approximately 46,000 GM workers. This agreement, which included a 25% general wage increase over the life of the contract and cost-of-living adjustments, directly impacts GM's labor costs and financial projections for the coming years.
Compliance with these agreements is paramount, as disputes or breaches can trigger costly legal challenges and operational disruptions. The potential for strikes remains a significant risk, as demonstrated by past UAW actions. For example, a brief strike at a key GM plant in 2023 highlighted the financial impact of labor disputes, leading to temporary production halts and lost revenue.
- UAW Contract Impact: The 2023 UAW contract is projected to add billions to GM's labor costs over its four-year term, affecting profitability.
- Legal Compliance Costs: Non-compliance with labor laws can result in fines, back-pay awards, and legal fees, adding to operational expenses.
- Strike Contingency Planning: GM invests in strategies to mitigate the financial impact of potential labor actions, including managing supply chains and production schedules.
- Benefit Structure Changes: The new contract mandates changes to retirement and healthcare benefits, requiring careful financial management and legal adherence.
General Motors faces evolving legal frameworks concerning vehicle safety, emissions, and data privacy. Compliance with standards set by agencies like NHTSA and EPA is critical, with penalties for non-adherence potentially reaching millions, as seen in past fines for emissions violations. The company's strategic shift towards EVs is partly driven by these stringent environmental regulations.
Data privacy laws are increasingly impacting GM's connected vehicle services, necessitating explicit consumer consent for data collection and usage. Intellectual property protection, particularly for EV battery and autonomous driving innovations, is vital for maintaining competitive advantage, with significant R&D investments requiring robust patent safeguards.
Labor laws and union agreements, such as the 2023 UAW contract, directly influence GM's operational costs and stability. The company must manage compliance with these agreements to avoid costly disputes and production disruptions, with the contract expected to add billions to labor expenses.
Environmental factors
Global concerns about climate change are pushing automakers, including General Motors, to set aggressive targets for carbon neutrality and lower emissions. GM has committed to achieving carbon neutrality across its products and operations by 2040, with a specific goal to eliminate tailpipe emissions from new light-duty vehicles by 2035.
This strong commitment directly shapes GM's product development and business strategy, heavily emphasizing the transition to electric vehicles and the integration of renewable energy sources throughout its manufacturing processes.
The growing global demand for electric vehicles (EVs) is intensifying the need for critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, leading to concerns about their availability and the environmental footprint of extraction. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in its 2024 update that demand for lithium is projected to increase by over 40 times by 2040 under its net-zero emissions scenario.
General Motors (GM) is addressing these environmental factors by prioritizing responsible sourcing of these essential battery components. The company is also investing heavily in developing advanced closed-loop battery recycling processes, aiming to recover valuable materials and reduce reliance on new mining, thereby fostering a more sustainable circular economy for EV production.
General Motors is increasingly focused on effective waste management and the adoption of circular economy principles, recognizing their importance in the automotive sector. The company has a clear target to divert over 90% of its global manufacturing waste from landfills by 2025, a significant commitment to reducing its environmental footprint.
This strategic shift includes robust initiatives for recovering and reusing valuable materials, particularly from end-of-life electric vehicle batteries. By prioritizing these circular economy practices, GM aims to enhance resource efficiency and minimize waste generation across its operations.
Water Usage and Conservation
Water scarcity is increasingly becoming a significant environmental issue, pushing companies like General Motors to actively reduce their water consumption. GM has established targets to lower its water intensity, reflecting a dedication to managing water resources responsibly within its extensive manufacturing operations.
To achieve these goals, GM is integrating advanced water-efficient technologies and best practices across its worldwide facilities. For instance, by 2023, GM reported a 15% reduction in water intensity compared to its 2010 baseline, a testament to its ongoing conservation efforts.
- Water Intensity Reduction: GM aims to decrease water usage per vehicle produced.
- Efficient Technologies: Implementation of closed-loop water systems and water recycling in manufacturing plants.
- Global Operations: Applying water conservation strategies across all its production sites worldwide.
- 2023 Performance: Achieved a 15% reduction in water intensity from the 2010 baseline.
Renewable Energy Adoption
General Motors is actively pursuing a transition to renewable energy for its manufacturing processes. A significant target is powering all U.S. operations with 100% renewable electricity by 2025, with a global goal set for 2035. This strategic shift is crucial for achieving the company's carbon neutrality objectives and lessening its dependence on fossil fuels, reflecting a broader industry movement towards environmental sustainability.
This commitment is backed by tangible actions. For instance, in 2023, GM announced a significant expansion of its renewable energy portfolio, including new solar projects that will contribute to its 2025 U.S. target. The company aims to source a substantial portion of its electricity from wind and solar power, demonstrating a concrete step towards its ambitious environmental goals.
- 2025: Target for 100% renewable electricity for U.S. operations.
- 2035: Target for 100% renewable electricity for global operations.
- Carbon Neutrality: Renewable energy adoption is a key pillar in achieving these goals.
- Fossil Fuel Reliance: Aims to reduce dependence on traditional energy sources.
General Motors is navigating significant environmental pressures, particularly concerning climate change and resource scarcity. The company has committed to carbon neutrality by 2040 and eliminating tailpipe emissions from new light-duty vehicles by 2035, driving a major shift towards electric vehicles and sustainable manufacturing practices.
GM is actively addressing the environmental impact of critical mineral extraction for EV batteries, focusing on responsible sourcing and investing in advanced battery recycling to promote a circular economy. Furthermore, the company is implementing robust waste management strategies, aiming to divert over 90% of its manufacturing waste from landfills by 2025.
Water conservation is another key focus, with GM targeting reduced water intensity across its global operations, having already achieved a 15% reduction by 2023 compared to its 2010 baseline. The company is also making strides in renewable energy adoption, with a goal to power all U.S. operations with 100% renewable electricity by 2025.
| Environmental Factor | GM's Commitment/Action | Target Year/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Change & Emissions | Carbon Neutrality | 2040 |
| Eliminate tailpipe emissions (new light-duty vehicles) | 2035 | |
| Resource Scarcity (Battery Minerals) | Responsible sourcing and advanced recycling | Ongoing |
| Waste Management | Divert manufacturing waste from landfills | >90% by 2025 |
| Water Consumption | Reduce water intensity | 15% reduction achieved by 2023 (vs. 2010 baseline) |
| Renewable Energy | Power U.S. operations with renewable electricity | 100% by 2025 |
| Power global operations with renewable electricity | 100% by 2035 |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for General Motors is grounded in data from official government publications, leading economic institutions like the IMF and World Bank, and reputable automotive industry research firms. This ensures comprehensive coverage of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting GM.