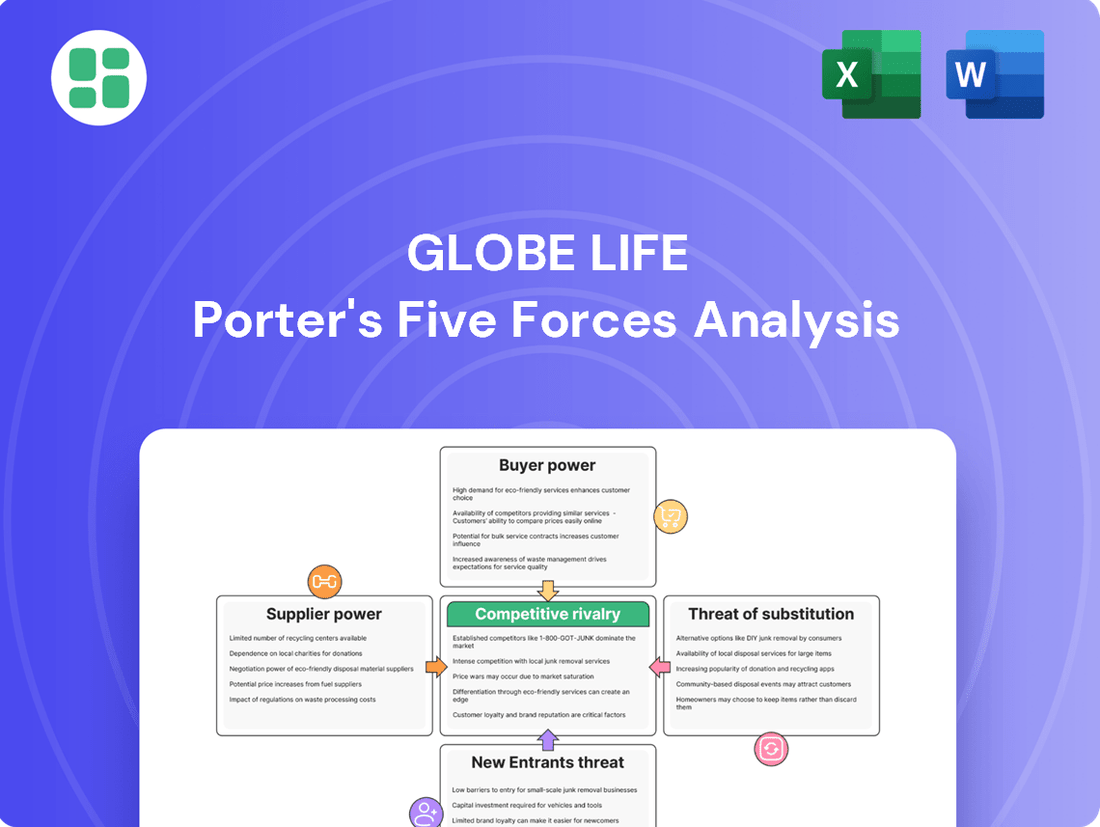
Globe Life Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Globe Life Bundle
Globe Life's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the insurance market effectively.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Globe Life’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Globe Life, like many insurance companies, utilizes reinsurers to manage its risk exposure, especially for substantial or unexpected claims. The bargaining power of reinsurers can be a considerable factor, particularly in markets with fewer players or when highly specialized reinsurance is required, potentially impacting Globe Life's ability to underwrite policies and its overall profitability. For instance, in 2023, the global reinsurance market saw continued capacity adjustments, with some segments experiencing price increases, underscoring the influence reinsurers can wield.
While reinsurers hold influence, Globe Life likely mitigates this by cultivating relationships with a diverse group of reinsurers, thereby spreading its reliance and reducing the leverage of any single reinsurer. This strategy is crucial for maintaining stable underwriting capacity and protecting its financial performance against unforeseen events.
The insurance sector's growing dependence on sophisticated technology for underwriting, claims, customer relations, and data analysis places significant leverage with technology and software providers. Globe Life's operational effectiveness and competitive standing are directly tied to these advanced systems, making reliable partnerships crucial.
High switching costs, often a consequence of integrating complex IT infrastructure, can empower established software vendors, compelling Globe Life to carefully manage these vendor relationships to mitigate potential disruptions and cost escalations.
The bargaining power of suppliers in actuarial and consulting services for Globe Life is moderate. Specialized actuarial expertise is vital for accurate insurance product pricing, reserving, and risk management, creating a need for these services. While numerous consulting firms exist, the scarcity of highly qualified actuaries means these professionals and their firms can command significant influence over pricing and service quality.
Investment Management Services
Globe Life, as an insurance holding company, oversees significant investment portfolios to support its policyholder obligations. The bargaining power of suppliers in this context primarily relates to investment management services. While the market for investment managers is generally broad, specialized expertise can confer power to certain firms.
The performance of these investments directly influences Globe Life's financial results. In 2023, Globe Life's total investment income was $2.16 billion, a notable increase from $1.89 billion in 2022. This highlights the critical role investment management plays in the company's profitability.
The need for specialized skills in managing a large and diverse portfolio grants some leverage to high-performing or niche investment management firms. These firms can command fees based on their track record and ability to generate superior returns, thereby influencing the cost of capital for Globe Life.
- Market Depth: A wide array of investment management firms exists, limiting the power of any single supplier.
- Performance Dependence: Globe Life's profitability is directly tied to investment returns, giving successful managers leverage.
- Specialized Expertise: Firms with proven track records in managing insurance-backed portfolios can exert greater influence.
- Fee Structures: Investment management fees, often based on assets under management or performance, represent a cost to Globe Life.
Healthcare Providers and Networks (for supplemental health)
For Globe Life's supplemental health insurance products, the rates set by healthcare providers and the way healthcare networks are organized directly impact the company's expenses. In areas where there are fewer, larger healthcare providers, their ability to negotiate higher prices with insurers like Globe Life can be significantly stronger, potentially driving up the cost of claims.
This consolidation trend is notable. For instance, in 2024, the average hospital operating margin in the U.S. was reported to be around 4.5%, indicating a healthy financial position for many providers, which can translate to greater leverage in pricing negotiations.
- Provider Consolidation: Increased mergers and acquisitions among healthcare systems can lead to fewer, more dominant players, enhancing their bargaining power.
- Network Strength: The exclusivity or breadth of a provider network can influence its ability to command higher reimbursement rates.
- Cost of Claims: Higher provider rates directly increase the claims costs Globe Life must cover for its supplemental health policies.
- Regional Variations: The impact of supplier bargaining power varies significantly by geographic region due to differing market structures.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Globe Life is a multifaceted issue, with key areas including reinsurers, technology providers, actuarial consultants, and healthcare providers. Reinsurers, especially those offering specialized coverage, can exert significant influence, as seen in 2023's capacity adjustments and price increases in certain segments of the global reinsurance market. Technology suppliers also hold considerable sway due to the integration of complex IT systems, creating high switching costs.
Actuarial and consulting firms, while numerous, benefit from the scarcity of highly qualified actuaries, allowing them to influence pricing and service quality. In the investment management sector, Globe Life's $2.16 billion in total investment income for 2023 highlights the impact of these suppliers, with high-performing firms leveraging their track records for higher fees. Finally, healthcare providers, particularly in consolidated markets, can negotiate higher reimbursement rates, directly increasing Globe Life's claims costs, with U.S. hospital operating margins averaging around 4.5% in 2024 suggesting providers are well-positioned for such negotiations.
| Supplier Category | Key Influence Factors | Impact on Globe Life | Relevant Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinsurers | Market concentration, specialized needs | Affects underwriting capacity and profitability | Global reinsurance market saw price increases in some segments in 2023. |
| Technology Providers | System integration complexity, high switching costs | Impacts operational efficiency and cost of IT infrastructure | Insurance sector's growing reliance on advanced technology. |
| Actuarial/Consulting | Scarcity of specialized talent | Influences pricing and quality of risk management services | High demand for actuarial expertise. |
| Investment Management | Performance track record, specialized portfolio management | Affects investment returns and cost of capital | Globe Life's investment income was $2.16 billion in 2023. |
| Healthcare Providers | Provider consolidation, network strength | Drives up claims costs for supplemental health products | U.S. hospital operating margins averaged 4.5% in 2024. |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity within the insurance industry, focusing on Globe Life's specific market position and the power dynamics affecting its profitability.
Instantly identify and address competitive pressures with a visually intuitive breakdown of each Porter's Five Forces, empowering strategic adjustments for Globe Life.
Customers Bargaining Power
Globe Life's primary customer base consists of middle and lower-middle-income Americans, a segment known for its significant price sensitivity. This means customers are highly attuned to the cost of insurance premiums and are more inclined to seek out the most affordable options available.
This heightened price sensitivity directly translates into increased bargaining power for Globe Life's customers. They are more likely to switch to a competitor if they can find lower premiums, forcing Globe Life to maintain competitive pricing and offer cost-effective coverage to retain its market share.
For instance, in 2024, the average annual premium for a term life insurance policy can vary significantly, with lower-income households often prioritizing policies with premiums under $50 per month. This reality underscores the pressure on insurers like Globe Life to keep their offerings accessible and budget-friendly for their target demographic.
The life and supplemental health insurance market is quite competitive, meaning customers have plenty of choices. This abundance of providers offering similar products significantly boosts their ability to negotiate or seek better deals.
Customers can easily compare policies online, often finding detailed comparisons and pricing information with just a few clicks. This transparency further empowers them by making it simple to identify the most attractive offers available in the market.
Switching providers in this industry typically involves minimal hassle and low costs. Unlike industries where significant assets or complex integrations are involved, moving from one insurer to another is generally straightforward, further strengthening the customer's bargaining position.
In today's digital landscape, customers possess unprecedented access to information. Online comparison tools and customer reviews readily provide details on policy features, pricing structures, and competitor services. This heightened transparency significantly empowers consumers, enabling them to make more informed choices and consequently drive demands for better value from companies like Globe Life.
This readily available information directly impacts Globe Life's pricing strategies. As customers can easily compare offerings, they are more likely to seek out the most competitive rates and comprehensive benefits. For instance, a significant portion of insurance shoppers utilize online platforms to compare quotes, meaning Globe Life must remain competitive to attract and retain these informed consumers.
Distribution Channel Influence
Globe Life's distribution strategy, which includes direct response, independent agents, and captive agencies, significantly impacts customer bargaining power. While direct response can offer Globe Life greater control over pricing and customer acquisition, the presence of independent agents provides customers with a broader array of choices from various insurers. This increased choice inherently strengthens the customer's position, allowing them to more readily compare offerings and negotiate terms. In 2023, the life insurance industry saw continued growth, with independent agents playing a crucial role in connecting consumers with suitable products.
The influence of distribution channels on customer bargaining power is multifaceted. Independent agents, by presenting customers with multiple insurance options, effectively amplify customer choice. This wider selection empowers customers to seek out the best value, thereby increasing their leverage in negotiations. Conversely, Globe Life's direct response channels allow for more direct engagement and potentially more favorable pricing structures by reducing intermediary costs. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, Globe Life reported a net income of $270 million, showcasing the effectiveness of its diversified distribution approach.
- Distribution Mix: Globe Life leverages direct response, independent agents, and captive agencies.
- Independent Agent Impact: These agents offer customers multiple insurance choices, boosting their bargaining power.
- Direct Response Control: This channel provides Globe Life with more direct control over pricing and customer acquisition.
- Industry Context: In Q1 2024, Globe Life's net income was $270 million, reflecting the performance of its distribution strategies.
Limited Product Differentiation
When life and supplemental health insurance products are not significantly different, customers often see them as interchangeable. This lack of distinction means Globe Life could face pressure if buyers perceive its offerings as mere commodities. In such scenarios, customers gain more leverage, primarily by shopping around for the lowest price, making Globe Life's pricing strategy a critical competitive factor.
For instance, in the broad U.S. life insurance market, which is highly competitive, many basic term life policies offer similar coverage features. This can lead to a price-sensitive customer base. In 2023, the U.S. life insurance industry saw a significant number of policies issued, underscoring the vastness and accessibility of the market for consumers to compare options.
- Homogenous Offerings: Basic life and supplemental health insurance often lack unique features, making them appear similar to consumers.
- Price Sensitivity: Without clear differentiation, customers tend to prioritize cost when making purchasing decisions.
- Commoditization Risk: Globe Life's products could be viewed as commodities, increasing customer bargaining power.
- Competitive Landscape: The U.S. life insurance market is vast, offering consumers numerous alternatives to compare and choose from based on price.
Globe Life's customer base, largely middle and lower-middle income, exhibits significant price sensitivity, driving their bargaining power. With numerous competitors offering similar life and supplemental health insurance products, customers can easily compare policies online, often finding quotes under $50 per month for basic term life in 2024. This ease of comparison and low switching costs empower customers to seek the best value, pressuring Globe Life to maintain competitive pricing.
| Factor | Impact on Globe Life | Customer Action | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Forces competitive pricing | Seek lower premiums | Term life premiums often < $50/month for target demographic |
| Availability of Alternatives | Reduces customer loyalty | Switch providers easily | Highly competitive market with numerous insurers |
| Information Accessibility | Increases customer knowledge | Compare policies online | Online quote comparison is a common consumer behavior |
| Product Homogeneity | Commoditization risk | Prioritize price over features | Basic term life policies offer similar coverage |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Globe Life Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Globe Life Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive forces within the insurance industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This detailed analysis is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The U.S. life and health insurance industry is incredibly crowded. Think of it as a marketplace with countless vendors, all trying to offer similar products. This intense competition, especially in the segments Globe Life focuses on, means companies are constantly battling for customers, which can put pressure on pricing and profitability.
In 2023, the U.S. life insurance sector alone saw over 700 active companies, demonstrating this fragmentation. This sheer volume of players, from massive national carriers to smaller regional ones, ensures that rivalry remains a significant force, driving innovation and customer acquisition efforts.
The U.S. life insurance market, while anticipating growth, is fundamentally a mature industry. This maturity means that expansion often comes from taking market share rather than from entirely new customer acquisition.
In mature markets, slower overall growth typically fuels more aggressive competition. Companies actively vie for existing customers, intensifying the rivalry as they seek to secure their slice of the market.
For instance, while the U.S. life insurance market is expected to see a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3.5% through 2028, this growth is occurring within a well-established landscape, meaning competition for each new policyholder is significant.
For fundamental life insurance and supplemental health offerings, distinguishing products can be quite difficult. This often means that companies, including Globe Life, end up competing mainly on price. In 2023, the U.S. life insurance market saw a significant portion of its revenue driven by term life policies, a segment where price is a major deciding factor for consumers.
This intense price competition puts pressure on Globe Life to keep its pricing attractive. However, maintaining competitive prices can squeeze profit margins, making it crucial for the company to focus on efficient operations and cost management to ensure profitability in this highly sensitive market segment.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The insurance sector, including companies like Globe Life, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These are tied to maintaining compliance with stringent regulations, investing in robust technology for policy management and data security, and building extensive sales and distribution channels. For instance, in 2024, the ongoing need for cybersecurity upgrades and digital transformation initiatives continues to demand significant capital expenditure across the industry.
High exit barriers further intensify competitive rivalry. Insurers often face long-term policy obligations, meaning they cannot simply cease operations without substantial financial repercussions. This commitment to existing policyholders can compel companies to remain active in the market, even when profitability is low, thereby sustaining a crowded and competitive landscape. This dynamic was evident in 2024 as several smaller insurers navigated challenging economic conditions while still needing to service their existing customer base.
- Significant fixed costs in insurance include regulatory compliance, technology infrastructure, and distribution networks.
- Long-term policy obligations create high exit barriers, keeping companies in the market.
- These factors collectively contribute to sustained, intense rivalry within the industry.
Aggressive Marketing and Distribution Strategies
Companies within the insurance sector, including Globe Life, frequently deploy aggressive marketing and distribution strategies. This often involves substantial investments in advertising campaigns and the cultivation of robust sales forces, comprising both captive and independent agents. These efforts are designed to capture market share and secure customer loyalty.
This intense focus on sales acquisition and retention directly fuels competitive rivalry. For instance, in 2024, the life insurance industry continued to see significant marketing spend, with major players allocating considerable portions of their budgets to digital advertising and agent recruitment initiatives. This heightened activity means companies must constantly innovate their outreach and sales processes to stand out.
- Aggressive Advertising: Companies invest heavily in broad-reaching advertising to build brand awareness and attract new policyholders.
- Extensive Sales Networks: The reliance on both captive and independent agents creates a direct and often competitive channel for customer acquisition.
- Market Share Focus: The drive to increase sales volume intensifies competition as firms vie for the same customer base.
- Customer Acquisition Costs: High marketing and sales expenses contribute to the overall cost of acquiring new customers, putting pressure on profitability and further fueling rivalry.
The competitive rivalry in the U.S. life and health insurance market, where Globe Life operates, is intense due to a fragmented industry with over 700 active companies in 2023. This crowded landscape forces businesses to compete aggressively on price, particularly for products like term life insurance, a segment that significantly drove revenue in 2023.
High fixed costs, including regulatory compliance and technology investments, coupled with substantial exit barriers like long-term policy obligations, compel companies to remain active, thus sustaining fierce competition. For example, ongoing cybersecurity upgrades in 2024 demand continuous capital expenditure across the sector.
Aggressive marketing and sales strategies, including significant advertising spend and agent recruitment, are common in 2024, intensifying the battle for market share and customer loyalty. This drive for acquisition means companies must constantly innovate their outreach to stand out.
| Metric | 2023 Value | Trend |
| Number of U.S. Life Insurers | Over 700 | High Fragmentation |
| U.S. Life Insurance Market Growth (CAGR projection) | ~3.5% (through 2028) | Mature Market Growth |
| Key Product Segment Revenue Driver | Term Life Policies | Price Sensitive |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Self-insurance and personal savings present a significant threat to traditional insurance providers like Globe Life. Individuals can opt to build substantial savings and investment portfolios to cover potential financial needs, bypassing the need for insurance premiums, especially for routine or smaller risks. This approach offers a direct alternative, particularly as individuals gain more financial literacy and confidence in managing their own risk.
For instance, the U.S. personal savings rate fluctuated around 3.4% in early 2024, indicating a portion of income is being set aside. While this isn't solely for self-insurance, it highlights a growing pool of personal capital that could be redirected from insurance purchases. As economic conditions improve and more people achieve financial stability, the appeal of self-insuring for certain life events or supplemental needs could increase, directly impacting demand for insurance products.
Government social security and healthcare programs present a significant threat of substitutes for insurance providers. For instance, Social Security survivor benefits can partially replace the need for private life insurance for some families, especially those with lower incomes. In 2024, Social Security benefits are projected to provide essential income for millions of Americans, potentially lessening reliance on private life insurance for basic income replacement.
Medicare and Medicaid offer crucial healthcare coverage, acting as substitutes for private health insurance, particularly for the elderly and low-income populations. As of early 2024, these government programs cover a substantial portion of the US population's healthcare expenses, thereby reducing the demand for comparable private insurance options.
Other financial products, like annuities, mutual funds, and various investment vehicles, present a significant threat of substitution for life insurance. These alternatives can offer comparable avenues for individuals to build financial security and plan for future needs, directly competing with the long-term protection that life insurance provides. For instance, the U.S. retirement market saw significant growth in annuities, with total annuity sales reaching an estimated $388.4 billion in 2023, indicating a strong consumer interest in these substitute products.
Employer-Sponsored Benefits
Many Americans rely on employer-sponsored benefits for life and health insurance, directly impacting the demand for individual policies. In 2024, approximately 57% of non-elderly individuals in the U.S. had employer-sponsored health insurance, according to the KFF Employer Health Benefits Survey. This significant coverage rate means that for a large portion of the population, their primary need for such insurance is already met, reducing the perceived necessity for supplemental individual policies.
The availability and comprehensiveness of these workplace plans act as a significant substitute for products offered by companies like Globe Life. If employer plans provide adequate coverage at a low or no cost to the employee, the incentive to purchase separate life or health insurance diminishes considerably. This can limit the addressable market for individual insurance providers, as a substantial segment of potential customers already has their core needs fulfilled through their employment.
- Reduced Demand: Employer-sponsored plans fulfill a primary need for life and health insurance for many Americans.
- Market Penetration: In 2024, around 57% of non-elderly individuals had employer-sponsored health insurance, limiting the market for individual policies.
- Substitute Effect: Comprehensive employer benefits can decrease the perceived value and necessity of purchasing additional individual insurance.
Proactive Health Management and Risk Mitigation
The increasing emphasis on proactive health management and risk mitigation presents a significant threat of substitutes for supplemental health insurance providers like Globe Life. As individuals adopt healthier lifestyles and participate in wellness programs, they effectively reduce their own health risks, diminishing the perceived necessity for supplemental coverage. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 65% of adults are actively engaged in at least one wellness activity, such as regular exercise or improved diet, to prevent future health issues.
This trend of self-substitution, driven by a desire to control health outcomes and reduce out-of-pocket expenses, directly challenges the value proposition of traditional supplemental insurance. When individuals feel more in control of their health, the appeal of insurance designed to cover unexpected medical costs naturally wanes. This can lead to a decline in demand for certain types of supplemental policies.
- Preventative Care Adoption: Growing consumer interest in preventative health measures, including regular check-ups and screenings, can mitigate the need for insurance that covers the consequences of untreated conditions.
- Wellness Program Effectiveness: The success of corporate and personal wellness initiatives, which aim to improve overall health and reduce the incidence of chronic diseases, acts as a direct substitute for the financial protection supplemental insurance offers.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Individuals making significant lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking or managing weight, reduce their personal health risks, thereby lessening their reliance on insurance to cover health-related financial burdens.
The threat of substitutes for Globe Life stems from various financial alternatives and government programs that can fulfill similar needs. Self-insurance through personal savings and investments offers a direct substitute, allowing individuals to bypass premiums. For example, the U.S. personal savings rate hovered around 3.4% in early 2024, indicating a growing pool of personal capital. Government programs like Social Security survivor benefits and public healthcare initiatives such as Medicare and Medicaid also act as substitutes, particularly for lower-income individuals and the elderly, reducing reliance on private insurance for basic income replacement and healthcare coverage.
Furthermore, other financial products like annuities and mutual funds compete with life insurance by offering avenues for financial security and future planning. U.S. annuity sales reached an estimated $388.4 billion in 2023, highlighting consumer interest in these alternatives. Employer-sponsored benefits also significantly reduce the need for individual policies; in 2024, approximately 57% of non-elderly Americans had employer-sponsored health insurance, fulfilling a primary need for many.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on Globe Life | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Insurance | Individuals using personal savings/investments to cover risks. | Reduces demand for insurance premiums. | U.S. Personal Savings Rate ~3.4% (Early 2024). |
| Government Programs | Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid. | Fulfills income replacement and healthcare needs. | Millions rely on Social Security benefits; Medicare/Medicaid cover substantial portions of healthcare costs. |
| Other Financial Products | Annuities, mutual funds, investments. | Offer alternative financial security and planning. | U.S. Annuity Sales ~$388.4 Billion (2023). |
| Employer-Sponsored Benefits | Workplace life and health insurance plans. | Meets primary insurance needs for many. | ~57% of non-elderly U.S. individuals had employer health insurance (2024). |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the insurance sector, particularly for life insurance providers like Globe Life, demands significant upfront capital. This is essential for building adequate financial reserves to cover potential claims, funding the infrastructure needed for operations, and crucially, meeting stringent solvency regulations set by governing bodies. For instance, in 2024, many states require life insurers to maintain minimum capital and surplus levels that can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars.
These substantial capital requirements act as a formidable barrier to entry. They effectively deter many aspiring companies or individuals who may lack the necessary financial backing to establish a foothold. Consequently, this high barrier protects established players, such as Globe Life, by limiting the influx of new competitors into the market, thereby preserving their market share and profitability.
The insurance industry faces substantial regulatory hurdles at both federal and state levels, creating a significant barrier to entry for new companies. These regulations encompass complex licensing requirements, stringent consumer protection laws, and rigorous solvency standards designed to ensure financial stability. For instance, in 2024, the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) continued to emphasize robust capital requirements and market conduct examinations, making it difficult for nascent insurers to establish a compliant and competitive footing.
Brand recognition is a significant barrier for new entrants in the insurance sector, a challenge Globe Life navigates effectively. Trust, built over years, is crucial for policyholders, and Globe Life's long-standing presence, dating back to 1900, has fostered deep customer loyalty. For instance, in 2023, Globe Life reported a net income of $1.03 billion, showcasing its established financial strength and reliability, which new competitors struggle to replicate.
Complex Distribution Networks
Building robust distribution networks for insurance products, as exemplified by Globe Life's multi-channel approach, presents a substantial hurdle for potential entrants. This involves significant investment in time and capital to establish direct response marketing capabilities, recruit and train a vast network of independent agents, or develop and manage captive agencies.
For instance, the insurance industry often relies on established relationships and trust, which take years to cultivate. A new player would need to replicate this extensive infrastructure, a process that is both resource-intensive and carries inherent risks. By 2024, the cost of customer acquisition in the insurance sector continued to climb, making it even more challenging for new entrants to compete with incumbents possessing established, efficient distribution systems.
- Time and Capital Investment: Developing and scaling distribution channels requires substantial upfront and ongoing financial commitment.
- Agent Recruitment and Training: Building a skilled and motivated sales force, whether independent or captive, is a lengthy and costly process.
- Brand Trust and Recognition: Established insurers benefit from years of brand building, which new entrants must overcome.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex insurance regulations across different jurisdictions adds another layer of difficulty for new market participants.
Data and Technology Infrastructure Investment
While the rise of Insurtech promises innovation, new companies entering the insurance market still face considerable hurdles related to data and technology infrastructure. Building robust capabilities in advanced data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI) for underwriting and claims, and secure IT systems demands significant upfront capital. For instance, establishing a cloud-based data lake and implementing sophisticated AI models for risk assessment can easily cost millions of dollars, even with the availability of more accessible development tools.
This substantial investment acts as a deterrent for potential new entrants. Even with the advent of low-code and no-code platforms that can speed up development, the underlying infrastructure for handling vast amounts of sensitive customer data, ensuring regulatory compliance, and scaling operations efficiently remains a costly endeavor. Companies must invest in areas like cybersecurity, data warehousing, and AI/ML platforms to compete effectively. For example, a new entrant might need to spend upwards of $5-10 million in the initial stages just to build a foundational technology stack capable of handling core insurance operations.
- High Capital Outlay: Significant investment is required for advanced data analytics, AI, and IT infrastructure.
- Technological Sophistication: Efficient underwriting, claims processing, and personalized customer experiences necessitate cutting-edge technology.
- Barrier to Entry: The cost of building and maintaining this infrastructure presents a substantial barrier, despite advancements in development tools.
- Competitive Necessity: Without these investments, new entrants struggle to offer competitive services and pricing.
The threat of new entrants in the life insurance market, impacting companies like Globe Life, remains moderate due to significant barriers. High capital requirements, stringent regulatory compliance, and the need for established brand trust and extensive distribution networks deter many potential competitors.
While Insurtech offers innovation, the substantial investment in data and technology infrastructure, including AI and cybersecurity, further solidifies these barriers. For instance, in 2024, the cost of building a compliant and competitive technology stack can easily reach millions of dollars, making it a challenging landscape for newcomers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
| Capital Requirements | Significant upfront funds needed for reserves, operations, and solvency. | Deters those lacking substantial financial backing. | Minimum capital and surplus requirements can be in the tens to hundreds of millions of dollars. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, consumer protection, and solvency standards. | Difficult to establish a compliant and competitive footing. | NAIC emphasizes robust capital and market conduct examinations. |
| Brand Trust & Recognition | Years of building customer loyalty and perceived reliability. | New entrants struggle to replicate established trust. | Globe Life's long history (since 1900) fosters deep loyalty. |
| Distribution Networks | Investment in marketing, agent recruitment, and management. | Challenging to replicate established, efficient sales channels. | Customer acquisition costs continue to climb, making it harder for new players. |
| Technology Infrastructure | Investment in data analytics, AI, and secure IT systems. | High cost for advanced capabilities needed for competition. | Building a foundational tech stack can cost $5-10 million initially. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Globe Life leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements of publicly traded competitors, and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.