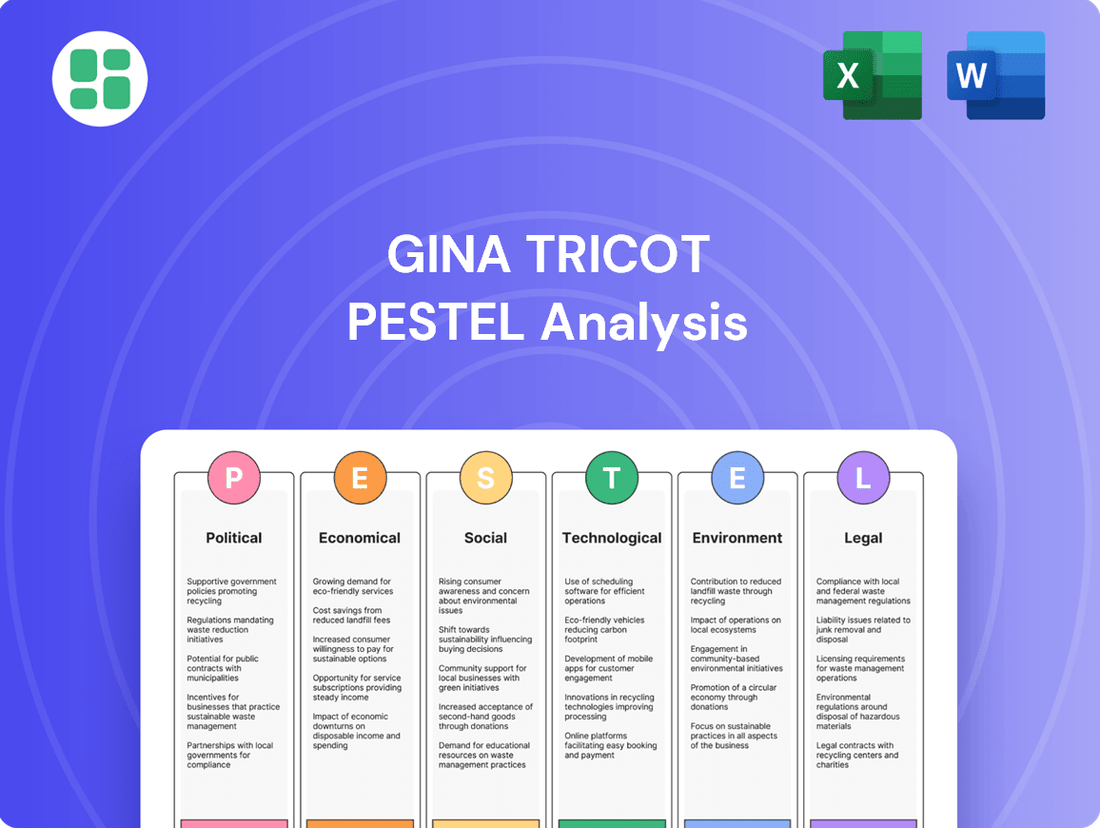
Gina Tricot PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Gina Tricot Bundle
Gina Tricot operates within a dynamic global marketplace, where political shifts, economic fluctuations, and evolving social trends significantly influence its strategy. Understanding these external forces is crucial for navigating the fashion industry's challenges and opportunities. Our comprehensive PESTLE analysis delves into these critical factors, offering actionable intelligence to inform your business decisions.
From navigating complex international regulations to capitalizing on emerging consumer preferences, this analysis provides a clear roadmap. Gain a competitive edge by understanding the full external landscape shaping Gina Tricot's future. Download our in-depth PESTLE analysis now and unlock the insights you need to thrive.
Political factors
The stability of the Swedish government and its retail-focused policies are crucial for Gina Tricot. For instance, Sweden's commitment to free trade agreements, as evidenced by its participation in the EU single market, generally supports stable import and export conditions. However, any shifts in government or policy, such as potential changes to VAT rates or consumer protection laws, could directly affect Gina Tricot's operating costs and market strategies.
Gina Tricot's operations are heavily influenced by international trade agreements and tariffs, especially concerning its European Union base and key sourcing regions. For instance, the EU's trade policies, including its agreements with countries like Bangladesh and Vietnam, directly impact the cost of imported apparel. In 2024, the EU continued to negotiate and adapt its trade relationships, with ongoing discussions around sustainability and ethical sourcing potentially leading to new regulatory frameworks that could affect import costs.
The imposition or removal of tariffs can significantly alter Gina Tricot's cost of goods sold. For example, a sudden tariff on textiles from a major Asian supplier could increase production expenses, forcing the company to either absorb the cost, impacting profit margins, or pass it on to consumers through higher prices. This dynamic necessitates careful monitoring of global trade policy shifts to maintain competitive pricing and supply chain resilience.
Gina Tricot operates within Sweden and other European countries, where labor laws are generally quite strict. These regulations cover critical areas such as minimum wage, maximum working hours, paid leave, and employee benefits. For instance, Sweden's employment protection legislation is robust, offering significant security to employees. This directly impacts Gina Tricot's operational costs, particularly in areas like staffing levels and compensation packages.
Compliance with these labor laws is not just a legal necessity but also crucial for maintaining a positive employer brand. Failure to adhere to regulations concerning working conditions or employee rights can lead to substantial fines and damage Gina Tricot's reputation, affecting its ability to attract and retain talent. In 2024, for example, many European nations continued to see discussions and potential adjustments to regulations around gig economy workers and flexible employment, which could influence retail staffing models.
The retail sector, including fashion, often experiences fluctuations in demand, requiring flexible workforce planning. However, strict labor laws can make it challenging to adjust staffing levels quickly in response to seasonal peaks or downturns. Gina Tricot must continuously adapt its human resource strategies to ensure compliance while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in its store operations and distribution centers.
Taxation policies
Gina Tricot's profitability is directly influenced by corporate tax rates and value-added tax (VAT) or sales taxes in its operating regions. For instance, Sweden, its primary market, has a corporate tax rate of 20.6% as of 2024. Changes in these tax structures, such as potential VAT increases or shifts in corporate tax burdens, can necessitate adjustments to pricing strategies and impact overall financial performance.
Navigating these tax landscapes is crucial for effective financial planning. For example, if a key market like Germany were to increase its standard VAT rate from the current 19%, Gina Tricot would need to evaluate how to absorb or pass on this cost to maintain its competitive edge. Such policy shifts directly affect the company's bottom line and its capacity for reinvestment.
Key taxation considerations for Gina Tricot include:
- Corporate Tax Rates: Fluctuations in the 20.6% Swedish corporate tax rate and similar rates in other operational countries directly affect net profit.
- VAT and Sales Taxes: Changes in VAT rates, such as the 25% standard rate in Denmark or the 21% in the Netherlands, impact consumer prices and the company's revenue.
- International Tax Agreements: Evolving tax treaties and transfer pricing regulations between countries where Gina Tricot operates can influence its global tax liability and operational costs.
- Potential Tax Reforms: Anticipating future tax policy changes, like potential digital services taxes or environmental levies, is vital for long-term financial strategy.
Consumer protection and advertising regulations
Consumer protection and advertising regulations significantly shape Gina Tricot's operations, especially given its direct-to-consumer sales model. Laws around consumer rights, product safety, and truthful advertising are paramount for building and maintaining customer trust. In 2024, for instance, the EU continued to strengthen consumer protection directives, impacting online retailers by requiring clearer information on product origins and return policies. Non-compliance can lead to substantial fines and damage brand reputation.
Gina Tricot must navigate a complex web of regulations designed to safeguard consumers. This includes adhering to advertising standards that prohibit misleading claims about product quality, materials, or pricing. For example, in the UK, the Advertising Standards Authority (ASA) actively polices marketing, and a fashion retailer found to be making unsubstantiated claims could face significant penalties and reputational damage. Staying abreast of evolving legislation, such as those concerning data privacy in marketing communications, is crucial for avoiding legal entanglements and ensuring continued customer confidence.
Key regulatory considerations for Gina Tricot include:
- Consumer Rights: Ensuring clear policies on returns, refunds, and product guarantees, especially for online purchases.
- Product Safety: Complying with regulations regarding the materials used in apparel, such as restrictions on certain dyes or chemicals.
- Advertising Standards: Maintaining transparency and accuracy in all marketing materials and online product descriptions to avoid misleading consumers.
- Data Privacy: Adhering to regulations like GDPR for the collection and use of customer data in marketing efforts.
Political stability in Gina Tricot's operating regions, particularly Sweden and the EU, is a key factor. Government policies on trade, consumer protection, and labor laws directly influence operational costs and market strategies. For instance, Sweden's corporate tax rate of 20.6% in 2024 impacts net profit, and any changes to VAT rates across its markets, like Germany's 19% standard VAT, necessitate strategic pricing adjustments.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis for Gina Tricot examines the impact of Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors on its business operations and strategic planning.
It provides a comprehensive overview of the external landscape, highlighting potential challenges and opportunities to inform decision-making.
A concise PESTLE analysis for Gina Tricot, presented in clear, simple language, acts as a pain point reliever by making complex external factors easily understandable for all stakeholders during strategic discussions.
Economic factors
Consumer spending in Sweden, a key market for Gina Tricot, showed resilience through 2024, with retail sales volumes increasing by 2.5% year-over-year as of Q3 2024. This trend is supported by a moderate rise in real disposable income, which grew by an estimated 1.8% in the same period, indicating consumers have funds for discretionary purchases like fashion.
However, the economic outlook for the Nordic region in late 2024 and into 2025 suggests a potential moderation in growth. Inflationary pressures, though easing, may still impact purchasing power, leading to more cautious consumer behavior and a potential shift towards value-oriented fashion choices. Gina Tricot's ability to adapt its product offerings and pricing strategies will be crucial.
Rising inflation in 2024 and continuing into 2025 directly impacts Gina Tricot's operational expenses. For instance, the Eurozone's inflation rate, while moderating from its 2022 peaks, remained a concern throughout 2024, with projections for 2025 suggesting continued, albeit slower, price increases for essential inputs. This translates to higher costs for raw materials like cotton and synthetic fibers, as well as increased expenses in manufacturing and logistics.
Consequently, Gina Tricot faces pressure on its cost of goods sold. If the company cannot fully absorb these rising input costs or pass them on to consumers through price adjustments without significantly impacting sales volume, its profit margins could shrink. For example, a 5% increase in raw material costs, if only partially recovered through a 2% price hike, would directly reduce profitability.
Therefore, vigilant monitoring of inflation trends, particularly in key sourcing and operating regions, is paramount. This allows Gina Tricot to refine its procurement strategies, negotiate better terms with suppliers, and implement dynamic pricing models to mitigate the erosive effects of inflation on its bottom line.
Fluctuations in exchange rates significantly impact Gina Tricot's cost of goods and international revenue. For instance, a weakening Swedish Krona against the US Dollar or Euro, common in late 2023 and early 2024, would increase the cost of sourcing materials and finished goods from countries like China or Bangladesh. Conversely, a stronger Krona could make imports cheaper but reduce the value of sales made in foreign currencies.
In 2024, the Swedish Krona experienced volatility, trading around 10.50 SEK to the EUR for much of the year, a level that generally increases import costs for Swedish retailers. This means Gina Tricot likely faced higher expenses for inventory sourced in Euros. Hedging strategies are crucial for companies like Gina Tricot to stabilize these costs and maintain predictable profit margins amidst currency swings.
Economic growth and recession risks
The economic growth outlook significantly impacts Gina Tricot's performance. Robust economic expansion typically fuels consumer confidence, leading to increased discretionary spending on fashion. Conversely, a slowdown or recessionary environment poses a direct threat, potentially reducing demand for Gina Tricot's products as consumers prioritize essential goods. For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth to be 3.2% in 2024, a slight slowdown from 2023, with risks tilted to the downside, which could affect consumer spending in key European markets where Gina Tricot operates.
Navigating these economic uncertainties requires Gina Tricot to be agile. A weakening economy necessitates a re-evaluation of sales forecasts and a careful management of operational costs. The company must be prepared to adjust inventory levels and marketing strategies to align with potentially lower consumer spending.
- Global economic growth forecast for 2024: 3.2% (IMF projection).
- Potential impact of inflation on consumer purchasing power for fashion items.
- Varied economic performance across Gina Tricot's key European markets.
- Importance of flexible forecasting and cost management in response to economic shifts.
Interest rates and credit availability
Changes in interest rates significantly influence Gina Tricot's operational costs and expansion strategies. For instance, if the European Central Bank (ECB) maintains its key interest rates, as it did through much of 2023 and into early 2024, it can make borrowing for new store openings or technology upgrades more manageable. Conversely, a sharp increase in rates, such as those seen in some global markets during 2022-2023, would directly elevate the cost of capital, potentially hindering ambitious growth plans.
The ease with which Gina Tricot can access credit is equally crucial. Robust credit availability allows the company to secure necessary funding for inventory purchases, seasonal stocking, and day-to-day operations. In 2024, the banking sector's lending practices, influenced by regulatory environments and economic sentiment, will determine how readily firms like Gina Tricot can secure lines of credit or term loans to support their business model.
- Interest Rate Impact: Higher borrowing costs directly reduce profitability by increasing financial expenses on loans for expansion or inventory.
- Credit Availability: Access to flexible credit lines is vital for managing working capital and seizing opportunities for growth in a dynamic retail market.
- Economic Context (2024): Continued moderate interest rate environments, as seen in some major European economies, can support affordability for capital investments.
- Financing Growth: The company's ability to secure favorable credit terms directly correlates with its capacity to invest in new markets or enhance its digital infrastructure.
Consumer spending in Sweden, a key market for Gina Tricot, showed resilience through 2024, with retail sales volumes increasing by 2.5% year-over-year as of Q3 2024. This trend is supported by a moderate rise in real disposable income, which grew by an estimated 1.8% in the same period, indicating consumers have funds for discretionary purchases like fashion. However, the economic outlook for the Nordic region in late 2024 and into 2025 suggests a potential moderation in growth, with inflation potentially impacting purchasing power and leading to more cautious consumer behavior. Rising inflation in 2024 and continuing into 2025 directly impacts Gina Tricot's operational expenses, translating to higher costs for raw materials and logistics, potentially shrinking profit margins if not managed effectively.
Fluctuations in exchange rates significantly impact Gina Tricot's cost of goods and international revenue. For instance, the Swedish Krona experienced volatility in 2024, trading around 10.50 SEK to the EUR for much of the year, which generally increases import costs for Swedish retailers. This means Gina Tricot likely faced higher expenses for inventory sourced in Euros, making hedging strategies crucial to stabilize costs and maintain predictable profit margins amidst currency swings.
The economic growth outlook significantly impacts Gina Tricot's performance, with the IMF projecting global growth at 3.2% in 2024, a slight slowdown that could affect consumer spending in key European markets. Changes in interest rates also influence operational costs and expansion strategies; for example, the European Central Bank's key interest rates, which remained moderate through early 2024, can make borrowing for new ventures more manageable, while credit availability is vital for managing working capital.
| Economic Factor | 2024 Data/Projection | Impact on Gina Tricot |
|---|---|---|
| Swedish Retail Sales Volume | +2.5% (YoY, Q3 2024) | Positive indicator for demand, but future moderation expected. |
| Real Disposable Income (Sweden) | +1.8% (Est. 2024) | Supports discretionary spending, but inflation may erode purchasing power. |
| Global Economic Growth | 3.2% (IMF Projection 2024) | Slight slowdown may impact consumer confidence in key markets. |
| EUR/SEK Exchange Rate | ~10.50 (2024 Average) | Increases import costs for Euro-denominated goods. |
| Inflation (Eurozone) | Easing but persistent concern in 2024/2025 | Raises raw material, manufacturing, and logistics costs. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Gina Tricot PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive Gina Tricot PESTLE analysis delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the company's operations. You'll gain valuable insights into the strategic landscape affecting Gina Tricot's business decisions and future growth.
Sociological factors
Gina Tricot, a fashion retailer, is deeply influenced by the fast-paced nature of style. Consumer tastes can change quickly, and there's a noticeable increase in demand for clothing that is both sustainable and produced ethically. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that 65% of Gen Z consumers consider sustainability when making fashion purchases, a significant shift from previous years.
Gina Tricot's core customer base, primarily women, is experiencing significant demographic shifts. In 2024, the median age of women in key European markets continues to rise, impacting preferences for styles and fits. For instance, in Sweden, where Gina Tricot has a strong presence, the proportion of women aged 45-64 has grown, suggesting a need for more mature-oriented collections alongside their established younger demographic.
Changes in income levels also play a crucial role. While economic uncertainty in 2024 might lead some consumers to seek more value-oriented purchases, a segment of the target market may still have disposable income for fashion. Gina Tricot's strategy must balance affordability with perceived quality and trend relevance to capture these varying income brackets effectively.
Lifestyle choices are evolving too, with a growing emphasis on sustainability and comfort. By 2025, consumer demand for ethically sourced materials and versatile clothing that transitions from casual to more dressed-up occasions is expected to intensify. Gina Tricot's ability to adapt its product development and marketing to reflect these evolving lifestyle preferences will be critical for maintaining market relevance and customer loyalty.
Evolving lifestyles are significantly reshaping how consumers approach clothing. The rise of remote work, for instance, has led to a greater demand for comfortable, versatile pieces that can transition from home to casual outings. A 2024 survey indicated that 60% of consumers now prioritize comfort in their clothing purchases, a notable shift from pre-pandemic trends.
Gina Tricot needs to align its product offerings with these changing priorities. This means developing collections that blend style with the practicality required for a more hybrid daily routine. Think elevated loungewear and adaptable separates that cater to both relaxed home environments and less formal professional settings.
The blurring of lines between traditional workwear and casual attire presents a prime opportunity for brands like Gina Tricot. By offering stylish, yet comfortable, options that bridge this gap, the company can capture a significant segment of the market. For example, the demand for smart casual wear, which saw a 15% increase in online searches in late 2024, highlights this trend.
Cultural attitudes and ethical consumption
Cultural attitudes are increasingly prioritizing sustainability and ethical practices, directly impacting consumer choices in the fashion industry. Consumers are more aware than ever of the environmental and social footprint of their purchases, driving demand for transparency in supply chains and fair labor conditions. This shift means brands like Gina Tricot must actively demonstrate their commitment to responsible sourcing and production to resonate with their target audience.
Ethical consumption is no longer a niche concern but a significant market driver. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of consumers consider a brand's sustainability efforts when making purchasing decisions. Gina Tricot, to maintain brand loyalty and attract environmentally and socially conscious customers, needs to clearly communicate its efforts in these areas, moving beyond mere compliance to genuine commitment.
- Growing consumer demand for sustainable fashion: A 2024 survey found that 65% of shoppers are willing to pay more for sustainable clothing.
- Emphasis on ethical labor: Reports from 2024 highlighted increased scrutiny on garment worker wages and conditions, with consumers expecting brands to ensure fair treatment.
- Transparency in the supply chain: Consumers are actively seeking information about where and how their clothes are made, pushing for greater traceability from brands.
- Brand reputation and loyalty: Companies demonstrating strong ethical and sustainable practices in 2024 reported higher customer retention rates compared to those lagging.
Social media influence and digital communities
Social media platforms and online fashion communities are pivotal in shaping trends and consumer perceptions for Gina Tricot. The company's engagement on channels like Instagram and TikTok directly impacts brand visibility and customer interaction.
In 2024, fashion brands are allocating significant portions of their marketing budgets to social media. For instance, a significant percentage of marketing spend is directed towards influencer collaborations and paid social campaigns, with some reports indicating over 50% of fashion marketing budgets are now focused on digital channels, a trend expected to continue into 2025.
- Influencer Marketing Growth: The global influencer marketing market reached an estimated $21.1 billion in 2023, with fashion being a dominant sector, and projections show continued double-digit growth through 2025.
- User-Generated Content Impact: Online communities foster user-generated content, which significantly boosts brand trust. A study from 2024 found that 70% of consumers are more likely to trust a brand when they see positive reviews and content from other users.
- Trend Acceleration: Digital communities can accelerate fashion trend cycles. Trends that might have taken seasons to emerge are now often visible and adopted within weeks due to the rapid dissemination of information on platforms like TikTok and Pinterest.
- Direct-to-Consumer Engagement: Gina Tricot's ability to interact directly with customers via social media allows for real-time feedback and personalized marketing, enhancing customer loyalty and driving sales.
Sociological factors significantly shape Gina Tricot's market landscape, driven by evolving consumer values and demographics. The increasing demand for sustainable and ethically produced clothing is a paramount concern, with a 2024 survey indicating that 65% of shoppers are willing to pay more for sustainable fashion. This trend is amplified by a growing emphasis on transparency in supply chains and fair labor practices, as highlighted by reports in 2024 scrutinizing garment worker wages and conditions.
Technological factors
Gina Tricot’s online presence is built on sophisticated e-commerce technology, ensuring a smooth journey for customers from initial browsing to final purchase. In 2024, the fashion e-commerce market saw continued growth, with global online retail sales projected to reach over $6.3 trillion, highlighting the importance of a strong digital foundation.
The company’s success hinges on ongoing advancements in website features, mobile application enhancements, and data-driven personalized digital marketing strategies. These efforts are vital for attracting and keeping customers in an increasingly competitive online landscape. For instance, in 2024, personalized product recommendations driven by AI were shown to increase conversion rates by up to 15% for leading fashion retailers.
Investing in and maintaining a robust e-commerce infrastructure is not just beneficial but essential for Gina Tricot's sustained growth and market competitiveness. This includes ensuring site speed, security, and scalability to handle increasing traffic and transactions, especially during peak sales periods.
Gina Tricot's adoption of supply chain digitalization and automation, focusing on areas like inventory management and logistics, is crucial for enhancing efficiency and cutting operational expenses. By integrating technologies such as RFID for real-time tracking and AI for precise demand forecasting, the company can respond more rapidly to fast-changing fashion cycles.
These technological advancements directly impact Gina Tricot's ability to optimize stock levels, minimizing overstock and reducing waste. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that fashion retailers leveraging AI in demand forecasting saw an average reduction in stockouts by 15% and a decrease in excess inventory by 10%, directly translating to improved profitability and sustainability.
Gina Tricot leverages data analytics and AI to forecast fashion trends and understand consumer behavior, aiming to reduce unsold inventory. By analyzing social media buzz and sales figures, the company can make more informed design and purchasing choices. For instance, a report in early 2024 highlighted how fashion retailers using AI saw a potential reduction in stockouts by up to 15% and a decrease in overstock by 10% compared to those not employing such technologies.
In-store technology and omnichannel integration
Gina Tricot's investment in in-store technology is crucial for a modern retail environment. Interactive displays and self-checkout options can significantly elevate the customer journey, making shopping more engaging and efficient. For instance, by mid-2024, retailers globally are seeing a significant uplift in customer satisfaction scores, often by 15-20%, when implementing advanced in-store tech solutions.
The seamless integration of online and offline channels, creating a true omnichannel experience, is paramount. This allows customers to browse online, try in-store, and purchase through their preferred method, fostering greater loyalty. Studies from 2024 indicate that companies with strong omnichannel strategies report a 10% higher annual revenue growth compared to those without.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Interactive technology in stores can boost engagement and convenience.
- Omnichannel Imperative: Seamless transitions between online and physical touchpoints are key for customer retention.
- Data-Driven Insights: Technology adoption allows for better understanding of customer behavior across all channels.
New textile technologies and sustainable materials
Advances in textile technology are opening doors for Gina Tricot to innovate. The development of sustainable materials, such as fabrics made from recycled plastic bottles or bio-based fibers like Tencel Lyocell, offers a way to improve product quality while aligning with environmental targets. For instance, the global sustainable fashion market was valued at approximately $6.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong consumer demand for eco-friendly options.
Embracing these new materials is key for Gina Tricot to reduce its environmental impact and attract consumers who prioritize sustainability. Brands that adopt these innovations can enhance their appeal in a market where eco-consciousness is increasingly influencing purchasing decisions. By investing in research and development for these materials, Gina Tricot can stay ahead of the curve.
- Recycled Polyester: Often derived from post-consumer plastic waste, reducing landfill burden.
- Organic Cotton: Grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, lowering water pollution.
- Tencel Lyocell: Produced from sustainably sourced wood pulp using a closed-loop process, minimizing chemical waste.
- Innovative Bio-materials: Emerging options like mushroom leather or algae-based textiles offer novel sustainable alternatives.
Gina Tricot's technological strategy centers on a robust e-commerce platform and data analytics to drive personalized customer experiences and efficient operations. The fashion e-commerce sector saw continued expansion in 2024, with global online retail sales expected to surpass $6.3 trillion, underscoring the necessity of advanced digital capabilities.
AI-driven personalization, like tailored product recommendations, is crucial for boosting conversion rates, which in 2024, saw increases of up to 15% for leading fashion retailers. Furthermore, digitalization of the supply chain, including AI for demand forecasting, aims to reduce stockouts by an average of 15% and excess inventory by 10%, as reported in 2024 studies.
In-store technology, such as interactive displays, is enhancing customer satisfaction, with mid-2024 data showing improvements of 15-20% for retailers adopting these solutions. The integration of online and offline channels into an omnichannel experience is also vital, with companies demonstrating strong omnichannel strategies reporting 10% higher annual revenue growth in 2024.
| Technology Area | Impact on Gina Tricot | 2024/2025 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| E-commerce Platform | Customer experience, sales conversion | Global online retail sales > $6.3 trillion |
| AI Personalization | Customer engagement, conversion rates | Up to 15% conversion rate increase |
| Supply Chain Digitalization | Efficiency, inventory management | 15% reduction in stockouts, 10% less excess inventory |
| In-Store Technology | Customer satisfaction, engagement | 15-20% uplift in customer satisfaction |
| Omnichannel Strategy | Customer loyalty, revenue growth | 10% higher annual revenue growth |
Legal factors
Gina Tricot, with its significant online presence and customer data collection, must adhere to stringent data privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Failure to comply can result in substantial financial penalties; for instance, the GDPR allows for fines up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover, whichever is higher. Maintaining customer trust and legal compliance hinges on secure data management, clear privacy statements, and robust consent processes.
Gina Tricot’s brand name and distinctive designs are protected by trademarks, crucial for maintaining its market position in the highly competitive fashion sector. These legal safeguards are vital to prevent counterfeiting and unauthorized replication of their collections, thereby preserving brand value and customer trust.
Gina Tricot must navigate a complex web of product safety and labeling regulations across its operating markets, especially concerning apparel. These rules dictate acceptable chemical content, flammability standards, and the necessity for precise material composition labeling to inform consumers. For instance, the EU's REACH regulation (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) significantly impacts textile imports, requiring rigorous testing for hazardous substances.
Failure to comply can result in severe consequences, including costly product recalls and significant legal liabilities. In 2024, fashion retailers globally faced increased scrutiny, with reports indicating a rise in regulatory actions related to non-compliant chemical substances in textiles, underscoring the importance of robust compliance strategies for companies like Gina Tricot.
Employment law compliance
Gina Tricot must ensure strict compliance with employment laws across all its operations and its extensive supply chain. This includes upholding fair wage standards, ensuring safe and healthy working conditions, and implementing robust anti-discrimination policies. For instance, in 2024, Sweden, where Gina Tricot is headquartered, continues to enforce stringent labor protections, with minimum wage discussions and worker safety regulations being key areas of focus for the government and labor unions.
Adherence to these regulations is not merely a legal obligation but a crucial element for maintaining a positive brand reputation. Consumers are increasingly conscious of ethical labor practices, and any perceived violations can lead to significant backlash. In 2025, reports indicate a growing consumer demand for transparency in supply chains, with a particular emphasis on fair treatment of garment workers, a trend that directly impacts fashion retailers like Gina Tricot.
- Fair Wages: Ensuring all employees and supply chain workers receive wages that meet or exceed legal minimums and living wage benchmarks.
- Working Conditions: Maintaining safe, healthy, and non-discriminatory workplaces, free from harassment and excessive working hours.
- Supply Chain Scrutiny: Implementing rigorous auditing processes to verify compliance with labor laws and ethical standards by all suppliers.
- Health and Safety: Prioritizing worker well-being through comprehensive health and safety protocols, including regular risk assessments and training.
Environmental regulations and compliance
Gina Tricot operates within a framework of environmental regulations, impacting its textile production and supply chain. These laws cover areas like waste management, the use of chemicals in fabrics, and carbon emissions. For instance, the EU's Strategy for Sustainable and Circular Textiles, actively being implemented in 2024-2025, places stringent demands on material sourcing and end-of-life product management.
Adherence to these environmental standards is not merely about avoiding fines; it's a critical component of corporate citizenship and brand reputation. Non-compliance could lead to significant penalties, disrupting operations and damaging customer trust. Gina Tricot's commitment to sustainability, often reflected in its sourcing and production choices, directly addresses these legal obligations.
Key regulatory considerations for Gina Tricot include:
- Textile Waste Management: Regulations focusing on reducing textile waste and promoting recycling, such as extended producer responsibility schemes emerging in various European markets.
- Chemical Restrictions: Compliance with directives like REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) concerning hazardous substances used in textile manufacturing.
- Carbon Footprint Reporting: Increasing requirements for businesses to measure, report, and reduce their carbon emissions, aligning with national and international climate goals.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Laws and voluntary industry standards encouraging the use of more sustainable materials and ethical production practices throughout the supply chain.
Gina Tricot must navigate intellectual property laws, safeguarding its brand and designs from infringement. This includes trademark protection for its name and logos, and copyright for its unique creative works, preventing competitors from unfairly benefiting from its investments in brand building and design innovation.
Environmental factors
Gina Tricot faces escalating demands for sustainability from both consumers and regulatory bodies, influencing every stage of its value chain. Consumers are actively seeking out brands demonstrating genuine environmental responsibility, with a 2024 survey indicating that over 60% of shoppers consider a brand's sustainability efforts when making purchasing decisions. This growing preference directly pressures Gina Tricot to adopt more eco-friendly sourcing, production, and waste management practices.
Simultaneously, governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations to curb the fashion industry's environmental impact. For instance, upcoming EU legislation in 2025 will introduce extended producer responsibility schemes for textiles, requiring companies like Gina Tricot to manage the end-of-life of their products. Navigating these evolving legal landscapes necessitates a proactive integration of sustainable principles into Gina Tricot's overarching business strategy to ensure compliance and maintain market relevance.
Gina Tricot's reliance on natural resources, particularly cotton and water, exposes it to the risks of scarcity and price fluctuations. For instance, cotton, a key material, is highly water-intensive, with estimates suggesting it can take over 2,700 liters of water to produce a single cotton t-shirt.
The fashion industry's significant environmental footprint, including its substantial water consumption and reliance on petroleum-based synthetics, means companies like Gina Tricot must actively seek more sustainable material alternatives. This includes exploring recycled fibers and innovative bio-based materials to reduce dependency on virgin resources and mitigate environmental impact.
Responsible sourcing practices are paramount for ensuring supply chain stability and managing environmental risks. By prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate strong environmental stewardship and ethical labor practices, Gina Tricot can build a more resilient and reputable brand, especially as consumer awareness of sustainability continues to grow.
Gina Tricot faces growing pressure to manage textile waste, a byproduct of its fast-fashion model. The push for circular economy principles necessitates addressing waste from production to disposal. This includes exploring innovative textile recycling technologies, as the global textile recycling rate remains low, with estimates suggesting only around 15% of clothing is recycled annually.
Implementing effective waste management and textile recycling is no longer optional but a strategic imperative. By promoting garment longevity and investing in recycling infrastructure, Gina Tricot can reduce its environmental footprint. This move is crucial as consumer awareness regarding fashion's environmental impact, particularly landfill contributions, continues to rise, influencing purchasing decisions and brand loyalty.
Carbon footprint and energy consumption
Gina Tricot's carbon footprint, spanning its manufacturing, logistics, and retail activities, is increasingly a focal point amidst growing climate change awareness. The fashion industry, in particular, is being pressed to adopt more sustainable practices.
The company is facing pressure to reduce its overall energy consumption, actively transition towards renewable energy sources, and optimize its transportation networks to significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions. This shift is crucial for aligning with global sustainability goals and consumer expectations.
Measuring and transparently reporting on carbon emissions is rapidly becoming a standard expectation for businesses. For instance, many fashion retailers are now disclosing their Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions, with Scope 3, which includes supply chain impacts, often being the largest component. Gina Tricot will likely need to provide similar disclosures to remain competitive and compliant.
- Manufacturing Emissions: A significant portion of Gina Tricot's carbon footprint originates from the production of its garments, including energy used in factories and the emissions associated with raw material processing.
- Logistics and Transportation: The global nature of fashion supply chains means that shipping finished goods from manufacturers to distribution centers and then to retail stores contributes substantially to the company's carbon output.
- Energy Consumption in Retail: Energy used for lighting, heating, and cooling in physical stores also adds to the environmental impact.
- Renewable Energy Transition: Industry trends show a growing commitment to powering operations with renewable energy. For example, many apparel brands are setting targets to source 100% renewable electricity for their own operations by 2030.
Ethical sourcing and supply chain transparency
Ensuring ethical and environmentally responsible practices throughout Gina Tricot's global supply chain, from raw material sourcing to the final manufacturing stages, represents a significant environmental consideration. This involves scrutinizing the impact of every step, aiming to minimize ecological footprints.
Growing consumer awareness and the persistent advocacy of Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) are driving a strong demand for greater transparency concerning both the environmental impact and labor conditions within fashion supply chains. For instance, in 2024, reports highlighted that over 60% of fashion consumers consider sustainability when making purchasing decisions.
Building a traceable and demonstrably sustainable supply chain is therefore not just a matter of compliance but is paramount for safeguarding Gina Tricot's brand reputation and effectively managing potential risks. By 2025, fashion brands are expected to face increased regulatory scrutiny on supply chain due diligence, making proactive measures essential.
- Consumer Demand: A significant majority of consumers, exceeding 60% in 2024 surveys, now prioritize sustainability in their fashion choices, pushing brands towards greater ethical sourcing.
- NGO Pressure: Advocacy groups continue to exert pressure on fashion retailers, demanding enhanced transparency regarding environmental impact and labor standards in their production processes.
- Regulatory Landscape: Anticipate stricter regulations by 2025, requiring fashion companies to implement robust due diligence across their entire supply chains to ensure ethical and sustainable practices.
- Brand Reputation: A transparent and ethical supply chain is crucial for maintaining consumer trust and a positive brand image, directly impacting sales and market standing.
Gina Tricot must navigate increasing consumer and regulatory demands for sustainability, impacting its entire value chain. Consumer preferences are shifting, with over 60% of shoppers in 2024 considering sustainability, pressuring Gina Tricot towards eco-friendly practices in sourcing, production, and waste management.
Upcoming EU legislation in 2025, focusing on extended producer responsibility for textiles, will require Gina Tricot to manage product end-of-life, necessitating a proactive integration of sustainable principles to ensure compliance and market relevance.
The company’s reliance on water-intensive materials like cotton, where a single t-shirt can require over 2,700 liters of water, highlights the vulnerability to resource scarcity and price volatility.
Addressing textile waste is critical, with global recycling rates around 15% annually; Gina Tricot needs to explore innovative recycling technologies and promote garment longevity to reduce its environmental footprint.
Gina Tricot faces pressure to reduce its carbon footprint, with manufacturing, logistics, and retail activities contributing significantly. The industry trend towards renewable energy, with many brands targeting 100% renewable electricity by 2030, indicates a necessary shift for Gina Tricot.
Transparency in supply chains is paramount, driven by consumer demand (over 60% in 2024 considering sustainability) and NGO advocacy, with stricter regulatory scrutiny expected by 2025.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE analysis for Gina Tricot is meticulously crafted using data from reputable sources like the Swedish government's statistical agency (SCB), the European Union's economic and environmental agencies, and leading market research firms specializing in the fashion retail sector. We also incorporate insights from reputable news outlets and industry-specific publications to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the macro-environmental factors impacting the business.