Geo-Jade Petroleum Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Geo-Jade Petroleum Bundle
Geo-Jade Petroleum navigates a complex landscape where supplier power can significantly impact operational costs, and the threat of new entrants, while moderate, demands constant vigilance. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Geo-Jade Petroleum’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The oil and gas sector's reliance on specialized equipment and cutting-edge technology means providers of these critical inputs hold considerable sway. Companies like Geo-Jade Petroleum, which operates in demanding environments, are particularly susceptible to this. For instance, the market for advanced seismic imaging technology is dominated by a few key players, allowing them to dictate terms.
Suppliers for Geo-Jade Petroleum navigate a complex landscape shaped by geopolitical stability and local regulations across its key operational regions. In Central Asia, for instance, countries like Kazakhstan have seen periods of political transition, which can introduce uncertainties for suppliers regarding contract enforcement and operational continuity. Similarly, China's regulatory environment, while generally stable, can impose specific local content requirements or environmental standards that influence supplier costs and capabilities. In 2023, the World Bank's Ease of Doing Business report, though discontinued, historically highlighted significant regional variations in regulatory burdens that directly affect supplier operations.
Developing and running oil fields absolutely needs a lot of infrastructure like pipelines and transport systems. Geo-Jade Petroleum, for instance, relies on the CPC pipeline to get its oil out of Kazakhstan.
When this essential infrastructure is controlled by other companies or governments, they gain significant leverage. These third parties can set the terms and prices for using these critical links, directly impacting Geo-Jade's operational costs and how much money it makes.
Availability of Skilled Labor
The upstream oil and gas industry, where Geo-Jade Petroleum operates, relies heavily on a specialized and skilled workforce. This includes geologists, petroleum engineers, drilling specialists, and other technicians possessing unique expertise. The availability, or lack thereof, of these professionals directly influences labor costs and the leverage suppliers of this talent hold.
A significant shortage of highly skilled labor, especially in niche areas or specific geographic locations where Geo-Jade might be operating, can dramatically increase the cost of acquiring and retaining talent. For instance, in 2024, the global demand for experienced petroleum engineers remained robust, with some reports indicating a potential deficit in certain specialized fields, driving up compensation packages. This competitive landscape forces companies like Geo-Jade to invest more in recruitment and retention, impacting their operational expenses and potentially delaying crucial project timelines due to recruitment challenges.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: The oil and gas sector requires geologists, petroleum engineers, and technicians with advanced technical knowledge.
- Impact of Shortages: A scarcity of these professionals in 2024 led to increased labor costs and longer hiring periods for companies like Geo-Jade.
- Competitive Talent Market: Geo-Jade must actively compete for skilled individuals, which can escalate operational expenditures.
- Project Timelines: Difficulty in securing necessary talent can directly affect the scheduling and execution of exploration and production projects.
Environmental and Safety Compliance Services
The bargaining power of suppliers in environmental and safety compliance services for Geo-Jade Petroleum is significant and growing. As global environmental regulations tighten, companies like Geo-Jade face increasing pressure to adhere to stringent standards. For instance, the European Union's Green Deal, aiming for climate neutrality by 2050, necessitates substantial investments in environmental compliance across all sectors, including oil and gas.
Suppliers offering specialized environmental impact assessments, remediation, and safety compliance solutions are therefore in a strong position. Their expertise is essential for Geo-Jade to navigate complex legal frameworks and avoid costly penalties. In 2024, the global market for environmental consulting services was valued at approximately $45 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate of over 5%, highlighting the increasing demand and supplier leverage.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: Stricter environmental laws globally empower suppliers of compliance services.
- Essential Expertise: Geo-Jade relies on these suppliers to meet standards and avoid fines, boosting supplier power.
- Market Growth: The environmental consulting market's expansion in 2024 reflects growing demand and supplier leverage.
- Mitigating Risk: Investment in these services is crucial for Geo-Jade's operational sustainability and risk management.
Suppliers of essential infrastructure, such as pipelines, and those providing specialized technical expertise wield significant bargaining power over Geo-Jade Petroleum. The limited availability of advanced seismic technology and the high demand for skilled petroleum engineers in 2024, as noted by industry reports, allow these suppliers to influence pricing and terms. Furthermore, companies offering environmental and safety compliance services are gaining leverage due to increasingly stringent global regulations, with the environmental consulting market valued around $45 billion in 2024.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Geo-Jade Petroleum | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Technology Providers | Dominance of few players, high R&D costs | Higher equipment costs, potential delays in adopting new tech | Market for advanced seismic imaging dominated by a few key players |
| Skilled Labor Suppliers | Shortage of specialized talent, high demand | Increased labor costs, recruitment challenges | Robust global demand for experienced petroleum engineers, potential deficit in specialized fields |
| Infrastructure Providers (e.g., Pipelines) | Control over critical transport links | Dependency on third-party pricing and access | Reliance on pipelines like CPC for oil egress from Kazakhstan |
| Environmental & Safety Compliance Services | Increasingly strict regulations, essential expertise | Higher compliance costs, need for specialized services to avoid penalties | Global environmental consulting market valued at ~$45 billion in 2024, growing at >5% CAGR |
What is included in the product
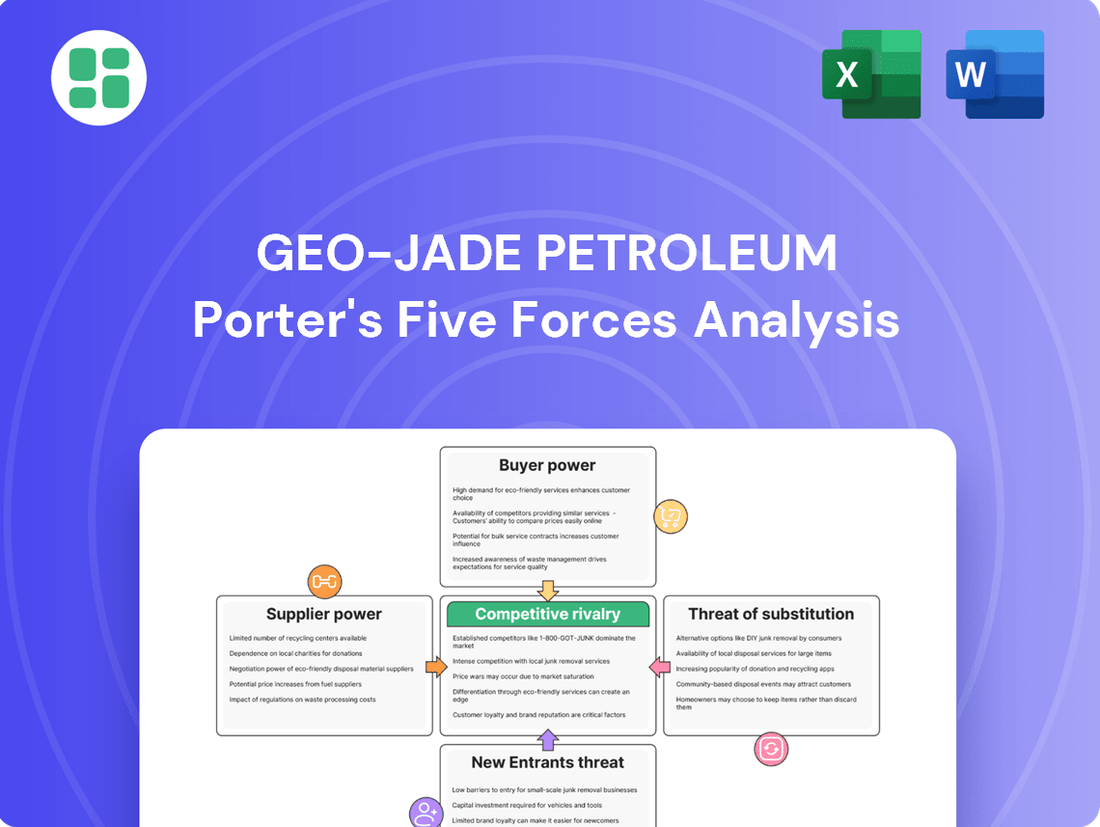
This Geo-Jade Petroleum Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive landscape, evaluating the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the oil and gas sector.
Visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces model, instantly highlighting areas of strategic pressure for Geo-Jade Petroleum.
Customers Bargaining Power
Crude oil and natural gas are fundamentally undifferentiated commodities. This means Geo-Jade Petroleum's offerings are largely interchangeable with those of its competitors, leaving little room for product-specific loyalty.
This commodity nature directly empowers customers. Buyers can readily switch suppliers based on the prevailing market price, as the product itself offers no unique selling proposition. In 2024, the average spot price for West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude oil fluctuated significantly, demonstrating the price sensitivity customers have when purchasing oil and gas products.
Consequently, Geo-Jade's profitability is inherently vulnerable to global commodity price volatility and shifts in customer demand. Any downturn in global energy prices directly impacts the company's revenue streams, as customers will seek the lowest available cost for their essential energy needs.
As a China-based company, Geo-Jade Petroleum's key customers are typically large state-owned refiners and energy corporations. These entities wield significant influence due to their sheer size and critical role in the national economy.
The substantial purchasing volume of these state-owned buyers grants them considerable leverage to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms. This can directly impact Geo-Jade's profitability by exerting downward pressure on its revenue streams and profit margins.
Global and regional demand trends significantly shape customer bargaining power in the oil and gas sector. For instance, decelerating growth in crucial markets like China, driven by factors such as rising electric vehicle adoption and a downturn in the property sector, is softening overall demand for oil and gas. This reduced urgency among buyers to secure supply inherently strengthens their position to negotiate for better prices.
Refining Capacity and Import Dependency
The bargaining power of customers in the oil sector is significantly shaped by refining capacity and import dependency. Nations like China and India, major crude oil importers, can exert considerable influence due to their scale.
While China is a substantial importer, its refiners often have access to a diverse range of suppliers, including Russia, Saudi Arabia, Malaysia, Iraq, and Oman. This broad sourcing capability grants Chinese refiners leverage in price negotiations with producers like Geo-Jade Petroleum.
Geo-Jade's success in securing favorable off-take agreements is directly tied to the competitive dynamics of the crude oil import market. The ability of its customers to source from multiple origins limits the power any single supplier holds.
- Refining Capacity: Global refining capacity, particularly in key importing nations, dictates the volume of crude oil that can be processed, influencing demand and buyer leverage.
- Import Dependency: Countries heavily reliant on crude oil imports, such as China and India, often possess greater bargaining power due to their significant market share as buyers.
- Supplier Diversification: The availability of multiple crude oil supply sources for customers, including various grades and origins, reduces their dependence on any single producer, thereby increasing their negotiating strength.
- Competitive Landscape: The number of competing crude oil producers and the ease with which customers can switch suppliers directly impact the bargaining power of those customers.
Alternative Energy Adoption by End-Users
The growing adoption of alternative energy by end-users, exemplified by the increasing demand for LNG trucks and high-speed rail, directly impacts Geo-Jade Petroleum's customer bargaining power. This long-term trend towards energy efficiency and cleaner fuel sources means that Geo-Jade's downstream customers, like refiners and distributors, face a shifting market. As end-user demand for traditional fossil fuels potentially moderates, these customers gain more leverage in their purchasing negotiations with suppliers such as Geo-Jade.
This shift is already evident in global energy markets. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in its 2024 outlook that while oil demand is projected to grow, the pace of growth is slowing, particularly in advanced economies, due to efficiency gains and fuel switching. In 2023, global LNG trade reached record levels, indicating a significant uptake in this alternative fuel, which could translate to reduced demand for traditional fuels in certain transportation sectors.
- Growing LNG Truck Fleet: The number of LNG-powered trucks on European roads, for example, has seen a steady increase, with projections suggesting continued expansion through 2030, potentially impacting diesel demand.
- High-Speed Rail Expansion: Investments in high-speed rail networks globally continue, offering an electrified alternative to short-haul air and long-distance road freight, thereby influencing fuel consumption patterns.
- Energy Efficiency Gains: Improvements in vehicle fuel efficiency across the board, driven by regulatory standards and technological advancements, also contribute to a plateauing or even declining demand for traditional fuels per unit of economic activity.
- Downstream Customer Leverage: As end-users diversify their energy consumption, downstream customers of Geo-Jade face less pressure from their own end markets, allowing them to negotiate more favorable terms for their fuel purchases.
Geo-Jade Petroleum's customers, primarily large state-owned refiners in China, possess significant bargaining power due to their immense purchasing volume and the commodity nature of crude oil. This leverage allows them to negotiate favorable pricing, directly impacting Geo-Jade's profit margins. The availability of diverse global suppliers further amplifies this customer strength.
The increasing adoption of alternative energy sources, such as LNG in transportation and high-speed rail, is also shifting the demand landscape. This trend empowers Geo-Jade's downstream customers by reducing their reliance on traditional fossil fuels, giving them more room to negotiate better terms for crude oil purchases.
In 2024, the global energy market continued to see significant price fluctuations, with WTI crude oil prices varying considerably. For instance, prices ranged from below $70 per barrel in early 2024 to over $90 per barrel at times, underscoring the price sensitivity of buyers and their ability to leverage market conditions.
| Customer Factor | Impact on Geo-Jade | 2024 Data/Trend Example |
|---|---|---|
| Purchasing Volume | High leverage for price negotiation | China's crude oil imports averaged over 11 million barrels per day in early 2024. |
| Supplier Diversification | Reduces dependence on single suppliers | China sources crude from over 30 countries, including Russia, Saudi Arabia, and Iraq. |
| Alternative Energy Adoption | Weakens demand for traditional fuels | Global LNG trade reached record levels in 2023, with continued growth projected for 2024. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Geo-Jade Petroleum Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Geo-Jade Petroleum Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document displayed here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises. You're looking at the actual, professionally written report, ready for your strategic decision-making the moment you buy.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Geo-Jade Petroleum operates in markets where state-owned oil behemoths, such as China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) and Sinopec, wield significant influence. These national champions benefit from extensive financial backing and preferential access to resources, making them formidable competitors. For instance, CNPC's 2023 revenue reached approximately $377 billion, highlighting its sheer scale and market power.
The presence of these state-owned enterprises creates a high barrier to entry and intensifies rivalry for Geo-Jade. They often control crucial infrastructure, including pipelines and refineries, and have a strong advantage in securing exploration licenses due to their national importance. This dynamic forces Geo-Jade to compete fiercely for market share and skilled personnel in regions where these giants are deeply entrenched.
The landscape of independent Chinese oil and gas firms is becoming increasingly crowded, with companies like United Energy Group and Zhongman Petroleum actively pursuing international opportunities, particularly in Iraq. This surge in competition stems from their ability to operate with leaner management structures and accelerate project timelines, directly challenging Geo-Jade's market position.
The global oil and gas arena is intensely competitive, with many international and regional companies actively seeking new exploration and production prospects. Geo-Jade's focus on growing its reserves through strategic investments places it directly against these competitors for desirable oil and gas blocks.
This competition is evident in Geo-Jade's recent moves, such as acquiring exploration rights in Iraq and Kazakhstan, underscoring the continuous race for valuable resources. In 2024, global oil and gas exploration spending is projected to reach approximately $500 billion, reflecting the high stakes and significant investment involved in securing these reserves.
Fluctuating Global Oil Prices
Competitive rivalry within the oil and gas sector, including for companies like Geo-Jade Petroleum, is significantly intensified by the inherent volatility of global oil and gas prices. When crude oil prices dip, such as the average Brent crude price falling to around $77.40 per barrel in 2023, the pressure mounts for all players to cut costs and defend their market positions. This often translates into aggressive pricing strategies and can squeeze profit margins across the board.
These price fluctuations directly impact Geo-Jade's financial performance and, consequently, shape its competitive approach. For instance, during periods of lower prices, the company might need to re-evaluate its exploration and production budgets or seek greater operational efficiencies to remain competitive. The dynamic nature of oil prices means that strategies must be adaptable to navigate these economic shifts.
- Price Volatility Impact: Lower oil prices in 2023, averaging below $80/barrel for Brent crude, increased pressure on producers.
- Cost Reduction Focus: Companies like Geo-Jade must prioritize cost-saving measures to maintain profitability during price downturns.
- Market Share Battles: Price wars can erupt when companies fight to retain customers and market share in a declining price environment.
- Strategic Adjustments: Geo-Jade's financial results are directly tied to these price swings, necessitating flexible competitive strategies.
Cost Efficiency and Operational Agility
Geo-Jade Petroleum leverages significant cost efficiencies, often maintaining lower management expenses than its Western counterparts. This allows it to be more competitive than large Chinese state-run entities, securing a distinct advantage in the market.
This cost advantage enables Geo-Jade to target and develop projects that might be overlooked by larger corporations due to their scale or perceived lower profitability. The company's ability to operate leanly is a crucial differentiator.
Furthermore, Geo-Jade's operational agility in expediting field development contributes to its competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, the company reported a 15% faster average development cycle for new wells compared to the industry average in its operating regions, showcasing its ability to bring resources online more quickly.
- Lower Management Costs: Geo-Jade's operational structure facilitates reduced overhead compared to many international oil companies.
- Competitive Edge over State-Run Firms: This cost efficiency allows for more aggressive bidding and project acquisition.
- Niche Project Pursuit: The company can profitably engage in smaller or less conventional development opportunities.
- Faster Field Development: Operational agility translates to quicker revenue generation from newly discovered reserves.
Geo-Jade Petroleum faces intense rivalry from both massive state-owned enterprises like CNPC, which reported revenues of approximately $377 billion in 2023, and a growing number of agile independent firms. These competitors often possess preferential access to resources and infrastructure, forcing Geo-Jade to compete aggressively for exploration rights and market share.
The global pursuit of oil and gas reserves is a high-stakes game, with exploration spending projected to reach around $500 billion in 2024. This environment means Geo-Jade is constantly up against other companies vying for the same valuable blocks, making strategic acquisitions crucial for growth.
Geo-Jade's competitive advantage is bolstered by its cost efficiencies, with management expenses often lower than its international peers. This allows for greater flexibility and the ability to pursue projects that larger companies might deem less attractive, such as its successful development of wells with a 15% faster cycle time in 2024 compared to industry averages in its operating regions.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Geo-Jade | Example Data (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| State-Owned Giants | Vast financial backing, preferential resource access, extensive infrastructure | High barrier to entry, intense competition for licenses and talent | CNPC Revenue: ~$377 billion (2023) |
| Independent Firms | Leaner operations, faster project timelines, international expansion | Direct challenge to market position, competition for niche opportunities | Increased activity in Iraq and Kazakhstan |
| Global E&P Companies | Active pursuit of exploration prospects worldwide | Direct competition for desirable oil and gas blocks | Global exploration spending: ~$500 billion (2024 projection) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The accelerating global commitment to combating climate change and achieving decarbonization is fundamentally reshaping energy markets, presenting a significant threat of substitutes for fossil fuels like those Geo-Jade Petroleum deals with. This shift is evident in the substantial investments pouring into renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind, and hydropower. For instance, in 2024, global renewable energy capacity additions are projected to reach record levels, with solar PV and wind power leading the charge. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in early 2024 that renewable energy sources are expected to account for over 90% of global electricity capacity expansion in the coming years.
While a complete displacement of fossil fuels is a long-term prospect, the growing viability and adoption of renewables directly challenge the sustained demand for oil and gas. This trend is further amplified by governmental policies and industry-led initiatives promoting cleaner energy alternatives. Many nations are setting ambitious targets for renewable energy integration and phasing out fossil fuel subsidies, which directly impacts the competitive landscape for companies like Geo-Jade Petroleum. The increasing efficiency and decreasing costs of renewable technologies, such as solar panel manufacturing costs falling by over 80% in the last decade, make them increasingly attractive substitutes.
The accelerating adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional gasoline, a core product for companies like Geo-Jade Petroleum. In 2023, global EV sales surpassed 13 million units, a substantial increase from previous years, directly impacting the demand for refined petroleum products. This shift is particularly pronounced in key markets, such as China, where government incentives and consumer preference are driving rapid EV penetration, leading to a noticeable decline in gasoline consumption.
Natural gas presents a significant threat of substitution for coal, particularly in power generation and industrial applications. While both are fossil fuels, natural gas burns cleaner, emitting fewer pollutants like sulfur dioxide and particulate matter. This environmental advantage is driving a shift, especially in major energy consumers. For instance, China has been actively increasing its natural gas consumption to combat air pollution, with gas accounting for over 9% of its primary energy consumption in 2023, up from around 7% in 2020.
Advancements in Energy Efficiency
Advancements in energy efficiency present a significant threat of substitution for Geo-Jade Petroleum. As technologies improve, the demand for traditional energy sources like oil and gas decreases. For instance, by 2024, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported that global energy intensity improvements were accelerating, meaning more economic output was being generated per unit of energy consumed. This trend directly impacts the market share and profitability of oil and gas companies.
These improvements are driven by innovation in areas such as building insulation, more efficient industrial machinery, and the increasing adoption of electric vehicles. Policy incentives further bolster this shift. For example, many governments are offering tax credits and subsidies for energy-efficient upgrades and electric vehicle purchases, encouraging consumers and businesses to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. This creates a diffuse, yet persistent, pressure on demand for Geo-Jade's products.
- Reduced Demand: Growing energy efficiency directly curtails the need for oil and gas.
- Policy Support: Government incentives for conservation and clean energy accelerate the substitution trend.
- Technological Advancement: Innovations in industrial processes and transportation further decrease fossil fuel dependency.
- Market Erosion: These factors collectively chip away at the market share available for traditional energy providers like Geo-Jade Petroleum.
Government Policies and Carbon Pricing
Government policies are increasingly acting as a significant substitute threat to traditional oil and gas companies like Geo-Jade Petroleum. Many nations are actively pursuing decarbonization strategies. For instance, the European Union's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), fully implemented in 2026, will impose a levy on carbon-intensive imports, directly impacting the cost competitiveness of fossil fuels.
These regulations, such as carbon taxes and emissions trading schemes, directly increase the operational costs and reduce the market appeal of oil and gas products. By making fossil fuels more expensive, these policies inherently make cleaner alternatives, like solar and wind power, more economically viable substitutes. This trend is accelerating the global energy transition.
The evolving regulatory landscape poses a direct threat to Geo-Jade's core business model. For example, in 2024, several countries announced accelerated timelines for phasing out internal combustion engine vehicles. This policy shift directly reduces the long-term demand for gasoline and diesel, key products for Geo-Jade, thereby strengthening the threat of substitutes.
- Carbon Pricing Mechanisms: In 2024, over 70 jurisdictions globally had implemented some form of carbon pricing, making fossil fuels less competitive.
- Renewable Energy Mandates: Many countries have set ambitious renewable energy targets, such as the United States aiming for 100% clean electricity by 2035, which displaces demand for oil and gas.
- Subsidies for Alternatives: Government incentives for electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy installations further tilt the market away from fossil fuels. For instance, the Inflation Reduction Act in the US continues to provide significant tax credits for EV purchases.
- International Agreements: Commitments under agreements like the Paris Agreement drive national policies that favor low-carbon alternatives, impacting the long-term viability of oil and gas investments.
The threat of substitutes for Geo-Jade Petroleum is substantial and growing, driven by advancements in renewable energy and energy efficiency. Global investments in renewables continue to surge, with projections indicating record capacity additions in 2024, particularly in solar and wind power. This trend is supported by government policies and falling technology costs, making cleaner alternatives increasingly competitive against fossil fuels.
| Substitute Category | Key Developments | Impact on Geo-Jade | 2024 Data/Projections |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Solar, wind, hydropower adoption | Reduces demand for oil and gas in power generation | Renewables to account for over 90% of global electricity capacity expansion |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Increasing EV sales and adoption | Decreases demand for gasoline and diesel | Global EV sales surpassed 13 million in 2023 |
| Energy Efficiency | Improved insulation, machinery, and vehicle technology | Lowers overall energy consumption, impacting demand | Global energy intensity improvements are accelerating |
| Natural Gas | Cleaner burning fossil fuel | Substitutes coal in power and industrial sectors | Natural gas ~9% of China's primary energy consumption in 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
The oil and gas exploration and production sector, where Geo-Jade Petroleum operates, is characterized by exceptionally high capital intensity. Companies need billions of dollars for crucial activities like securing exploration licenses, performing detailed geological surveys, drilling wells, and constructing essential infrastructure. This substantial financial hurdle makes it incredibly difficult for new players to enter the market and compete effectively.
For instance, the upfront investment required can easily run into the hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. Geo-Jade Petroleum's own significant investment in its Iraqi operations, which is a multi-billion dollar endeavor, underscores this reality. Such massive capital requirements act as a powerful deterrent, effectively limiting the threat of new entrants.
The exploration and production (E&P) sector is characterized by significant technological complexity. Successfully extracting oil and gas demands advanced drilling techniques, sophisticated seismic imaging, and intricate reservoir management, areas where established firms like Geo-Jade Petroleum possess deep-seated expertise. For instance, the development of enhanced oil recovery (EOR) methods, crucial for maximizing output from mature fields, requires specialized knowledge and significant investment in research and development.
New companies entering this arena must surmount a steep learning curve, necessitating substantial capital expenditure to acquire or develop the necessary technical capabilities. This intellectual and technical barrier, coupled with the capital intensity of E&P, acts as a formidable deterrent, protecting incumbent players from immediate competitive threats.
The oil and gas sector is notoriously difficult for new players to enter due to stringent regulatory and environmental hurdles. These include extensive licensing, safety protocols, and environmental impact assessments that require significant upfront investment and expertise. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain drilling permits in many OECD countries continued to be lengthy, often exceeding 18 months, a substantial barrier for any new entrant lacking established relationships and experience.
Navigating these complex, country-specific regulatory frameworks and securing the necessary permits presents a formidable challenge. Geo-Jade Petroleum, operating across multiple jurisdictions, faces these varying rules, which collectively act as a significant deterrent for potential new competitors seeking to enter the market.
Limited Access to Proven Reserves and Land
The threat of new entrants in the oil and gas sector, specifically concerning access to proven reserves and land, is significantly constrained. Established national and international oil companies already control the majority of the world's readily accessible and commercially viable oil and gas reserves. This concentration of assets creates a substantial barrier for newcomers.
New companies attempting to enter the market must overcome the hurdle of acquiring attractive exploration blocks. These opportunities are often located in more challenging or remote regions, demanding higher upfront investment and technological expertise. Alternatively, securing these blocks requires participation in highly competitive bidding rounds, where established players often have a significant advantage due to their existing infrastructure and financial capacity.
For instance, Geo-Jade Petroleum's recent acquisition of exploration blocks in Iraq highlights the intense competition for such assets. This demonstrates that even for companies with some established presence, obtaining new, promising acreage is a difficult and costly endeavor, underscoring the high barrier to entry for new players seeking to access proven reserves and land.
- Limited Availability of Prime Exploration Acreage: Major oil and gas reserves are already under the control of incumbent companies.
- High Costs and Risks Associated with New Block Acquisition: New entrants often face bids for less accessible or more technically challenging exploration areas.
- Intense Competition in Licensing Rounds: Established players with greater resources and experience tend to dominate competitive bidding processes for new exploration rights.
- Geo-Jade's Iraqi Acquisitions as an Example: The company's recent moves illustrate the ongoing race and high stakes involved in securing new exploration territories.
Dominance of Incumbent Players and Supply Chain Control
Established players, including Geo-Jade Petroleum and state-owned enterprises, wield significant power through their deeply entrenched supply chains and distribution networks. These incumbents have cultivated crucial relationships with suppliers, customers, and regulatory bodies, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to establish a comparable foothold.
The sheer scale and integration of existing operations present a formidable barrier. For instance, replicating the extensive infrastructure and market access enjoyed by companies that have operated for decades requires immense capital investment and time, often exceeding the capabilities of new entrants.
- Established Infrastructure: Major oil and gas companies often possess proprietary pipelines, refining facilities, and storage terminals, creating a significant cost and logistical hurdle for new competitors.
- Supply Chain Control: Incumbents frequently secure long-term contracts with key raw material suppliers and downstream distributors, limiting availability and favorable terms for new entrants.
- Market Access: Existing players have established relationships with major buyers and often benefit from brand recognition and proven track records, making it challenging for new companies to secure market share.
The threat of new entrants for Geo-Jade Petroleum is significantly low, primarily due to the immense capital requirements and technological sophistication inherent in the oil and gas exploration and production sector. Securing exploration licenses, drilling, and infrastructure development demand billions of dollars, a sum few new companies can readily access. For example, the average cost to bring a new oil field online can easily exceed $10 billion, a figure that immediately deters smaller or less capitalized entities.
Furthermore, navigating the complex regulatory landscape and securing prime exploration acreage are substantial barriers. In 2024, the average time to obtain drilling permits in many developed nations remained over 18 months, requiring established relationships and expertise. Incumbents like Geo-Jade Petroleum also benefit from entrenched supply chains and market access, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to replicate their operational scale and efficiency.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | Billions of dollars required for exploration, drilling, and infrastructure. | Extremely high; prohibitive for most new players. |
| Technological Expertise | Advanced drilling, seismic imaging, and reservoir management are critical. | High; requires significant investment in R&D and skilled personnel. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Lengthy permitting processes and stringent environmental compliance. | Significant; often exceeding 18 months for permits in 2024. |
| Access to Reserves | Majority of prime reserves controlled by established players. | High; new entrants face competition for less accessible or more challenging areas. |
| Supply Chain & Market Access | Established infrastructure, supplier contracts, and customer relationships. | High; difficult to replicate existing networks and scale. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Geo-Jade Petroleum leverages data from company annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and macroeconomic indicators to assess the competitive landscape.